Sensing Performance Investigations on Two-Photon Fluorescent Probes for Detecting β-Amyloid in Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Computational Details
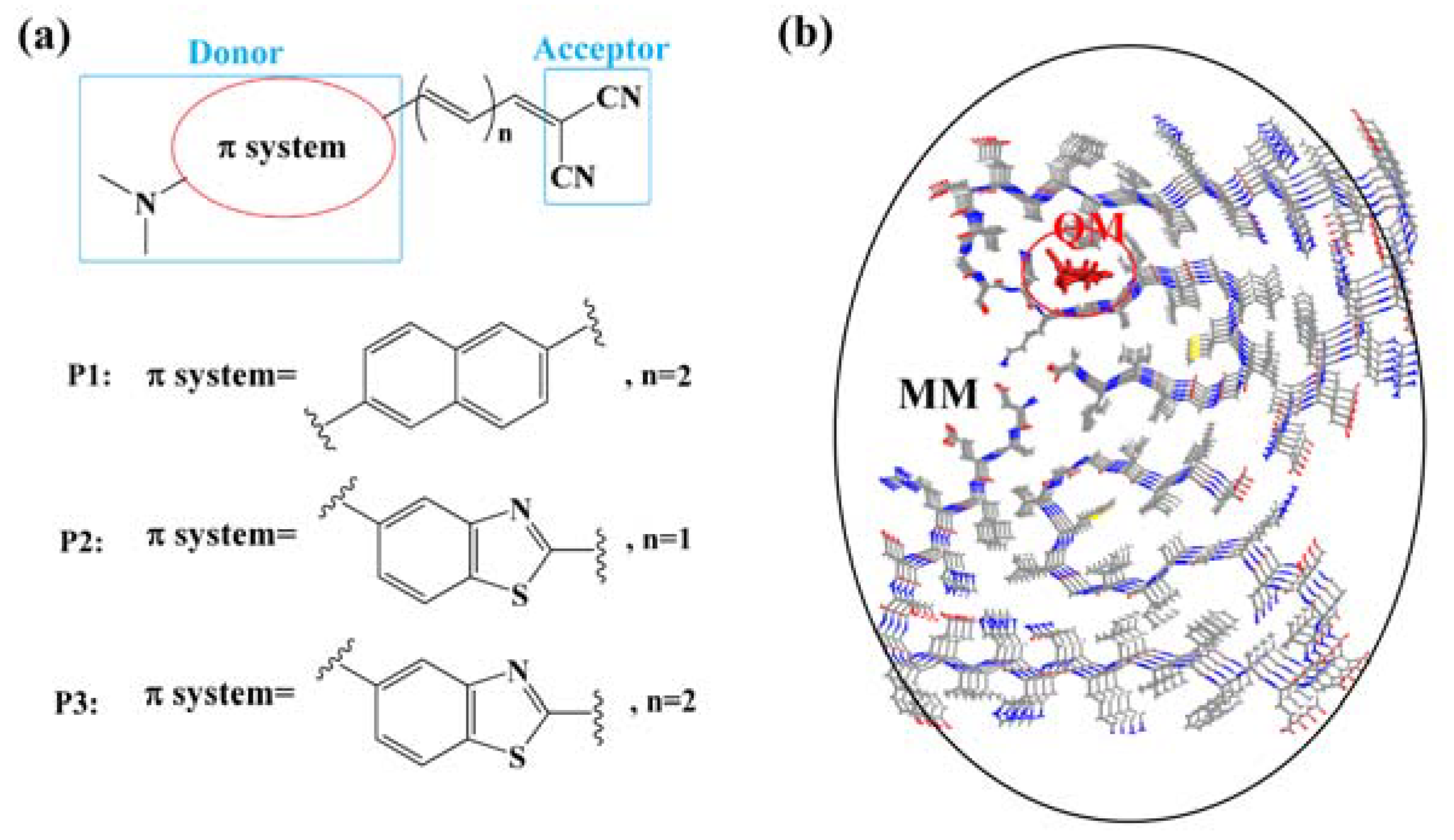
2.1. Molecular Docking
2.2. Property Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
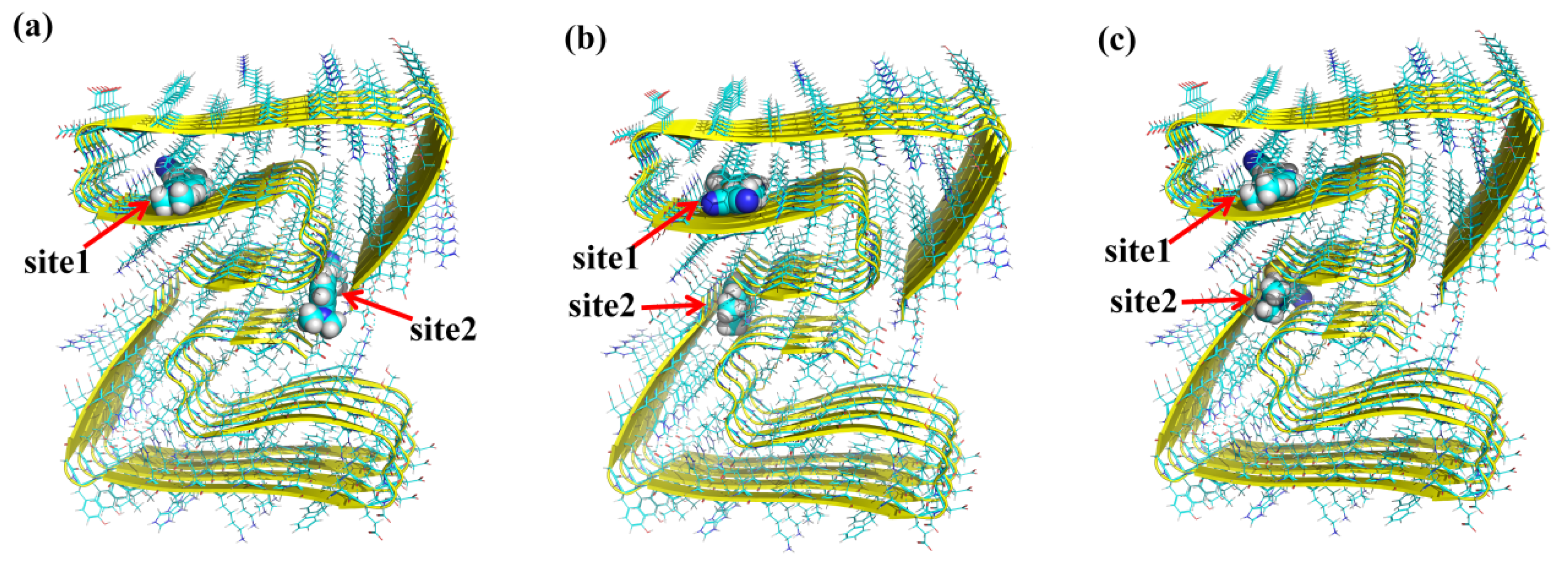
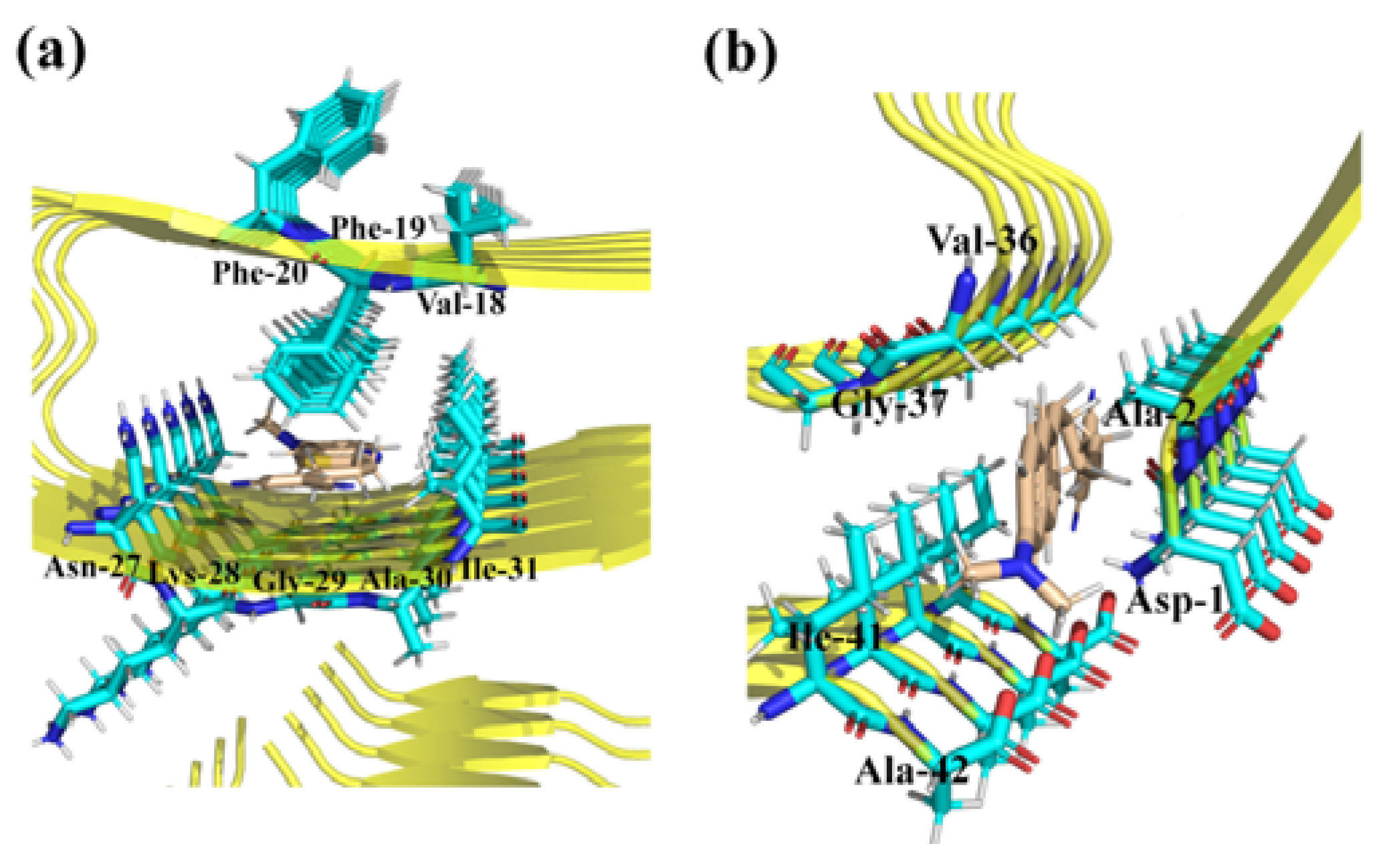
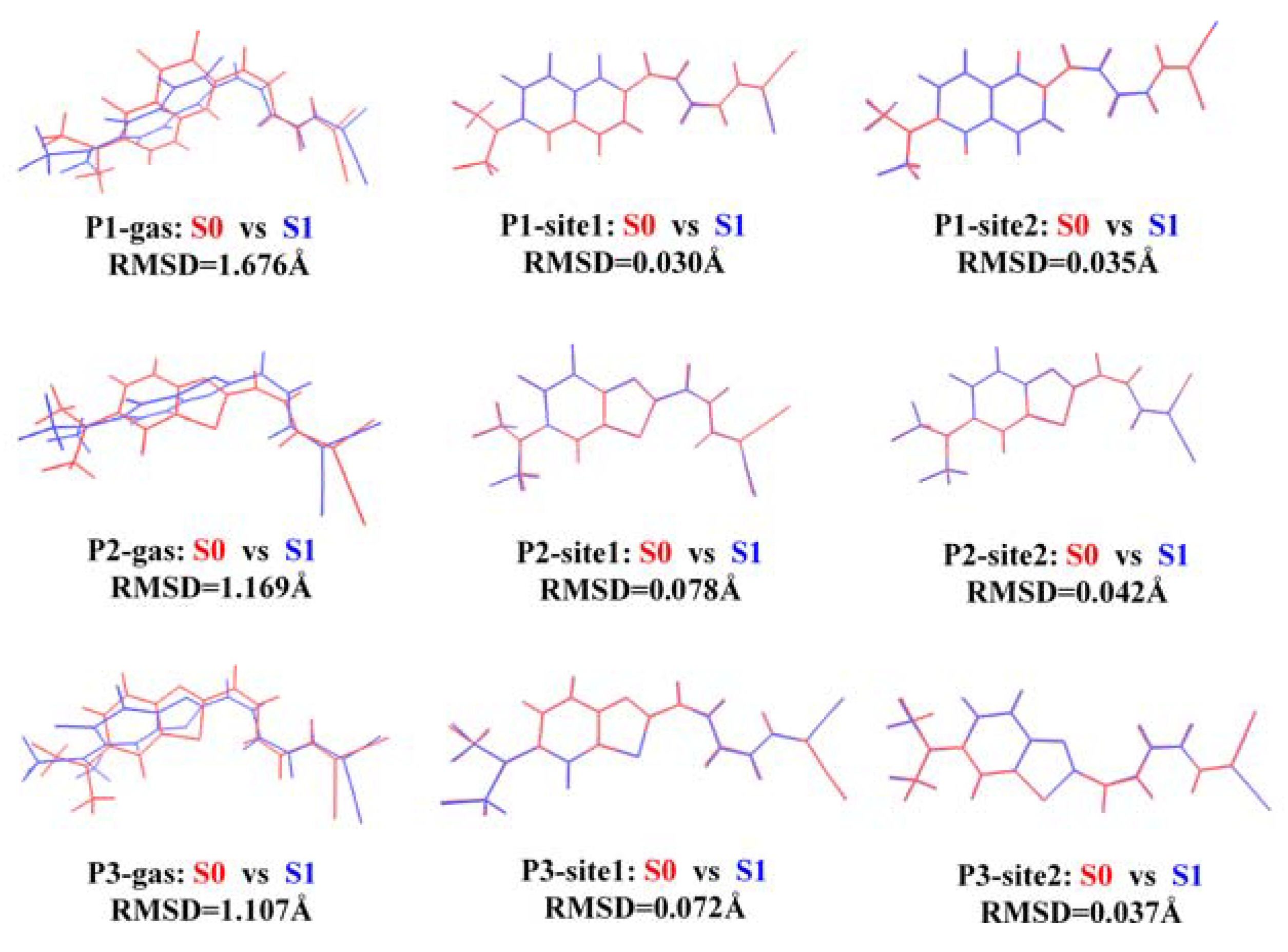
3.1. Binding Sites for the Probes with β-Amyloid
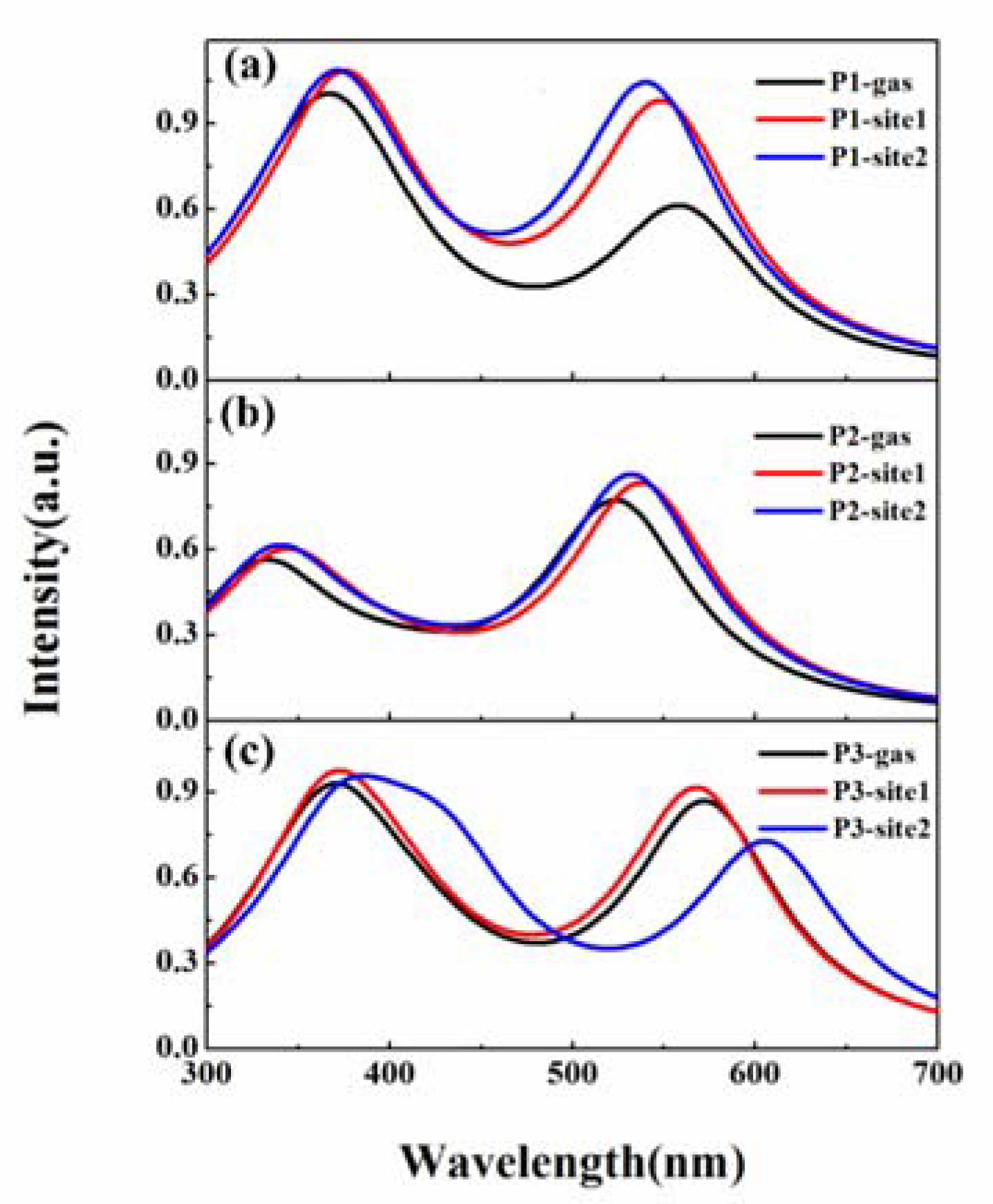
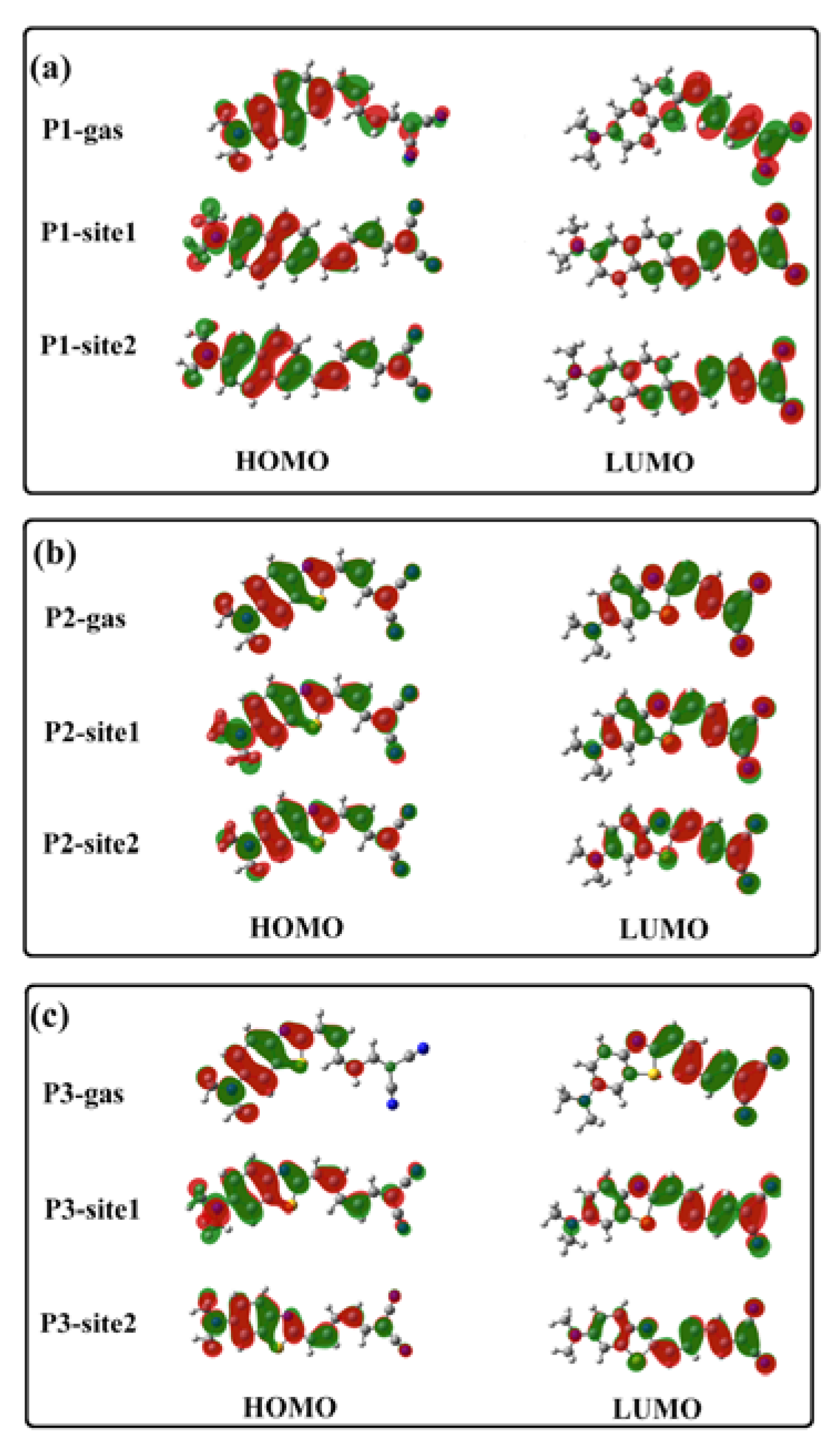
3.2. β-Amyloid-Specific OPA Properties
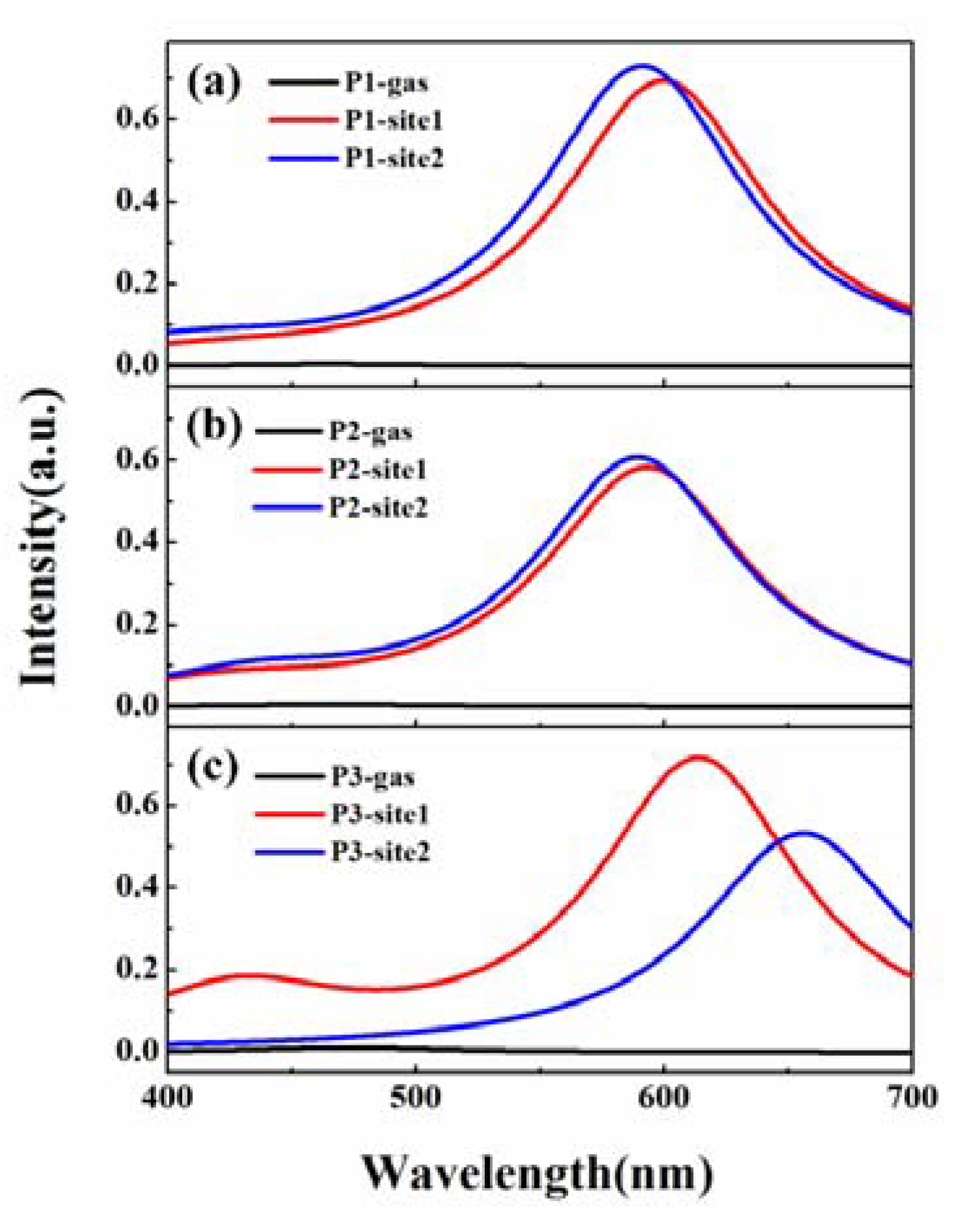
3.3. β-Amyloid-Specific OPE Properties
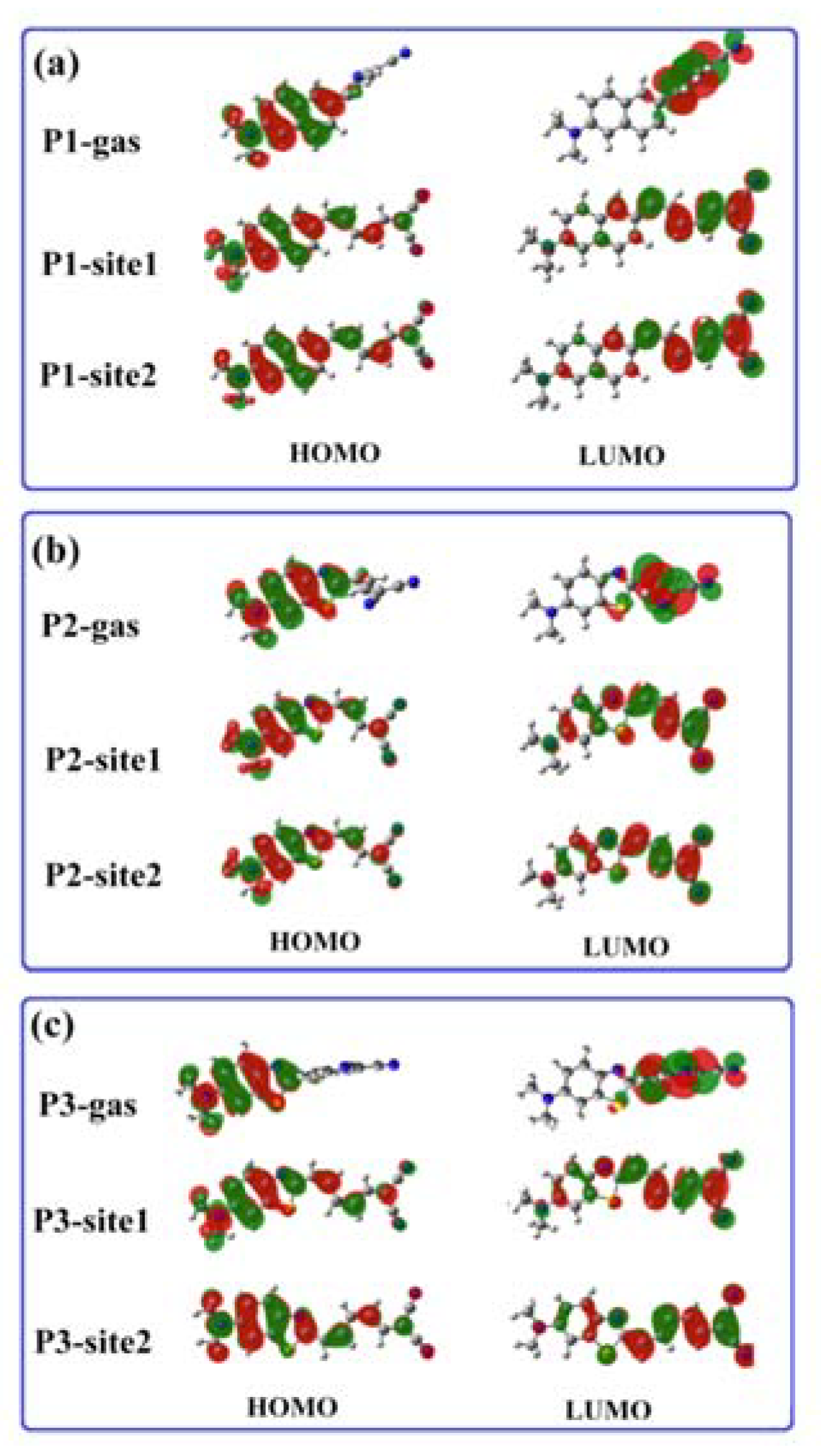
3.4. β-Amyloid-Specific TPA Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bateman, R.J.; Xiong, C.; Benzinger, T.L.; Fagan, A.M.; Goate, A.; Fox, N.C.; Marcus, D.S.; Cairns, N.J.; Xie, X.; Blazey, T.M. Clinical and biomarker changes in dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, Y. Cognitive reserve in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.L.; Ma, B.Y.; McElheny, D.; Parthasarathy, S.; Long, F.; Hoshi, M.; Nussinov, R.; Ishii, Y. Aβ (1–42) fibril structure illuminates self-recognition and replication of amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colvin, M.T.; Silvers, R.; Ni, Q.Z.; Can, T.V.; Sergeyev, I.; Rosay, M.; Donovan, K.J.; Michael, B.; Wall, J.; Linse, S. Atomic resolution structure of monomorphic Aβ42 amyloid fibrils. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 9663–9674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesne, S.E.; Sherman, M.A.; Grant, M.; Kuskowski, M.; Schneider, J.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Ashe, K.H. Brain amyloid-β oligomers in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2013, 136, 1383–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, R.Q.; Gillberg, P.-G.; Bergfors, A.; Marutle, A.; Nordberg, A. Amyloid tracers detect multiple binding sites in Alzheimer’s disease brain tissue. Brain 2013, 136, 2217–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, H.-W.; Wong, M.S. Versatile fluorescent probes for near-infrared imaging of amyloid-β species in Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Y.W.; Cho, S.W.; Jung, J.; Huh, Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D.; Ahn, K.H. Frontiers in probing Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers with fluorescent small molecules. ACS Cent. Sci. 2019, 5, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Saji, H. Recent advances in molecular imaging probes for β-amyloid plaques. Med. Chem. Comm. 2015, 6, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staderini, M.; Martín, M.A.; Bolognesi, M.L.; Menéndez, J.C. Imaging of β-amyloid plaques by near infrared fluorescent tracers: A new frontier for chemical neuroscience. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Ono, M.; Matsumura, K.; Yoshimura, M.; Kimura, H.; Saji, H. Molecular imaging of β-amyloid plaques with near-infrared boron dipyrromethane (BODIPY)-based fluorescent probes. Mol. Imaging 2013, 12, 7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.R.; Kang, D.E.; Kim, H.M.; Cho, B.R. Two-photon fluorescent probes for metal ions in live tissues. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 53, 1794–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M.; Cho, B.R. Two-photon fluorescent probes for metal ions. Chem.-Asian J. 2011, 6, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Leng, J.C.; Hu, W. Theoretical design of a two-photon fluorescent probe for nitric oxide with enhanced emission induced by photoninduced electron transfer. Sensors 2018, 18, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, C.H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, H.J.; Baik, S.H.; Song, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Mook-Jung, I.; Kim, H.M. A two-photon fluorescent probe for amyloid-β plaques in living mice. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 1303–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhu, B.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Z. In vivo detection of cerebral amyloid fibrils with smart dicynomethylene-4H-pyran-based fluorescence probe. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4781–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, L.F.; Li, Y.K.; Chen, S.B.; Yan, J.W.; Zhang, L. In vivo near-infrared fluorescence imaging of amyloid-β plaques with a dicyanoisophorone-based probe. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 961, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Watanabe, H.; Kimura, H.; Saji, H. BODIPY-based molecular probe for imaging of cerebral β-amyloid plaques. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2012, 3, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Tian, Y.L.; Zhang, C.; Tian, X.Y.; Ross, A.W.; Moir, R.D.; Sun, H.B.; Tanzi, R.E.; Moore, A.; Ran, C.Z. Near-infrared fluorescence molecular imaging of amyloid beta species and monitoring therapy in animal models of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9734–9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, C.H.; Sarkar, A.R.; Baik, S.H.; Jung, T.S.; Kim, J.J.; Kang, H.; Mook-Jung, I.; Kim, H.M. A quadrupolar two-photon fluorescent probe for in vivo imaging of amyloid-β plaques. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 4600–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Wang, K.; Zhou, K.X.; Guo, W.T.; Dai, B.; Liang, Y.; Dai, J.P.; Cui, M.C. Novel D–A–D based near-infrared probes for the detection of β-amyloid and tau fibrils in Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 8717–8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albota, M.; Beljonne, D.; Brédas, J.-L.; Ehrlich, J.E.; Fu, J.-Y.; Heikal, A.A.; Hess, S.E.; Kogej, T.; Levin, M.D.; Marder, S.R. Design of organic molecules with large two-photon absorption cross sections. Science 1998, 281, 1653–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugan, N.A.; Kongsted, J.; Rinkevicius, Z.; Ågren, H. Breakdown of the first hyperpolarizability/bond-length alternation parameter relationship. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16453–16458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, M.; Hayashi, S.; Kimura, H.; Kawashima, H.; Nakayama, M.; Saji, H. Push–pull benzothiazole derivatives as probes for detecting β-amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s brains. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 7002–7007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.C.; Ono, M.; Watanabe, H.; Kimura, H.; Liu, B.L.; Saji, H. Smart near-infrared fluorescence probes with donor–acceptor structure for in vivo detection of β-amyloid deposits. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3388–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.L.; Cui, M.C.; Zhao, L.; Tu, P.Y.; Zhou, K.X.; Dai, J.P.; Liu, B.L. Highly sensitive near-infrared fluorophores for in vivo detection of amyloid-β plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 6972–6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Ono, M.; Ariyoshi, T.; Katayanagi, R.; Saji, H. Novel benzothiazole derivatives as fluorescent probes for detection of β-amyloid and α-synuclein aggregates. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 1656–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, Revision B.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gremer, L.; Schölzel, D.; Schenk, C.; Reinartz, E.; Labahn, J.; Ravelli, R.B.; Tusche, M.; Lopez-Iglesias, C.; Hoyer, W.; Heise, H. Fibril structure of amyloid-β (1–42) by cryo–electron microscopy. Science 2017, 358, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Autodock4 and autodocktools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Goodsell, D.S.; Halliday, R.S.; Huey, R.; Hart, W.E.; Belew, R.K.; Olson, A.J. Automated docking using a lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J. Comput. Chem. 1998, 19, 1639–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, L.W.; Sameera, W.; Ramozzi, R.; Page, A.J.; Hatanaka, M.; Petrova, G.P.; Harris, T.V.; Li, X.; Ke, Z.; Liu, F. The ONIOM method and its applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 5678–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chung, L.W.; Mizuno, H.; Miyawaki, A.; Morokuma, K. A theoretical study on the nature of on-and off-states of reversibly photoswitching fluorescent protein dronpa: Absorption, emission, protonation, and raman. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 114, 1114–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, A. Molecular Electronic Structure Program. Available online: http://daltonprogram.org (accessed on 10 November 2013).
- Cances, E.; Mennucci, B.; Tomasi, J. A new integral equation formalism for the polarizable continuum model: Theoretical background and applications to isotropic and anisotropic dielectrics. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 107, 3032–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, G.L.; Murugan, N.A.; Ågren, H. Mechanistic insight into the binding profile of DCVJ and α-synuclein fibril revealed by multiscale simulations. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 10, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Ding, H.J.; Song, X.N.; Wang, C.K. Responsive mechanism of 2-(2′-hydroxyphenyl) benzoxazole-based two-photon fluorescent probes for zinc and hydroxide ions. Chin. Phys. B 2015, 24, 023301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Ono, M.; Saji, H. In vivo fluorescence imaging of β-amyloid plaques with push-pull dimethylaminothiophene derivatives. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 17124–17127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F.W. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Hu, W. Energy donor effect on the sensing performance for a series of FRET-based two-photon fluorescent Hg2+ probes. Materials 2017, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macak, P.; Luo, Y.; Norman, P.; Ågren, H. Electronic and vibronic contributions to two-photon absorption of molecules with multi-branched structures. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 113, 7055–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Norman, P.; Macak, P.; Ågren, H. Solvent-induced two-photon absorption of a push−pull molecule. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 4718–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Moon, H.; Baik, S.H.; Singha, S.; Jun, Y.W.; Wang, T.; Kim, K.H.; Park, B.S.; Jung, J.; Mook Jung, I. Two-photon absorbing dyes with minimal autofluorescence in tissue imaging: Application to in vivo imaging of amyloid-β plaques with a negligible background signal. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6781–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Site | P1 | P2 | P3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site1 | Site2 | Site1 | Site2 | Site1 | Site2 | |
| Binding energy | −12.54 | −8.09 | −10.54 | −6.98 | −11.66 | −7.89 |
| Inhibition constant | 0.645 | 118 | 18.86 | 767 | 2.86 | 166 |
| Intermolecular Energy | −13.73 | −9.28 | −11.43 | −7.87 | −12.85 | −9.08 |
| Internal Energy | −0.46 | −0.43 | −0.44 | −0.44 | −0.56 | −0.56 |
| Torsional Energy | 1.19 | 1.19 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 1.19 | 1.19 |
| Unbound Energy | −0.46 | −0.43 | −0.44 | −0.44 | −0.56 | −0.56 |
| Site | P1 | P2 | P3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas | Site1 | Site2 | Gas | Site1 | Site2 | Gas | Site1 | Site2 | |
| λOPA | 560 | 549 | 541 | 524 | 538 | 533 | 573 | 568 | 606 |
| δOPA | 0.55 | 0.90 | 0.96 | 0.73 | 0.79 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.85 | 0.66 |
| Transition Nature | H-L 98% | H-L 98% | H-L 98% | H-L 98% | H-L 98% | H-L 98% | H-L 98% | H-L 98% | H-L 98% |
| μ | 3.17 | 4.03 | 4.14 | 3.56 | 3.75 | 3.80 | 3.91 | 3.99 | 3.63 |
| Site | λTPA | σTPA | Sxx | Syy | Szz | Sxy | Sxz | Syz |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1-gas | 1119 | 411 | 757.9 | 2.8 | 0.8 | 15.8 | 10.6 | 2.3 |
| P1-site1 | 1206 | 1099 | 1335.2 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 43.6 | 7.5 | 0.2 |
| P1-site2 | 1183 | 1088 | 1303.1 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 33.9 | 15.0 | 0.6 |
| P2-gas | 1048 | 166 | 449.1 | 3.9 | 1.1 | 30.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| P2-site1 | 1129 | 338 | 690.9 | 5.6 | 1.6 | 40.4 | 1.5 | 0.8 |
| P2-site2 | 1140 | 366 | 726.0 | 4.0 | 1.4 | 36.0 | 4.2 | 0.3 |
| P3-gas | 1080 | 344 | 664.4 | 10.2 | 0.9 | 34.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| P3-site1 | 1224 | 894 | 1222.0 | 3.3 | 1.5 | 23.4 | 9.6 | 0.6 |
| P3-site2 | 1281 | 934 | 1308.8 | 2.8 | 1.4 | 33.6 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Luan, N.; Li, K.; Leng, J.; Hu, W. Sensing Performance Investigations on Two-Photon Fluorescent Probes for Detecting β-Amyloid in Alzheimer’s Disease. Sensors 2020, 20, 1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061760
Zhang Y, Luan N, Li K, Leng J, Hu W. Sensing Performance Investigations on Two-Photon Fluorescent Probes for Detecting β-Amyloid in Alzheimer’s Disease. Sensors. 2020; 20(6):1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061760
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yujin, Ni Luan, Kan Li, Jiancai Leng, and Wei Hu. 2020. "Sensing Performance Investigations on Two-Photon Fluorescent Probes for Detecting β-Amyloid in Alzheimer’s Disease" Sensors 20, no. 6: 1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061760
APA StyleZhang, Y., Luan, N., Li, K., Leng, J., & Hu, W. (2020). Sensing Performance Investigations on Two-Photon Fluorescent Probes for Detecting β-Amyloid in Alzheimer’s Disease. Sensors, 20(6), 1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061760






