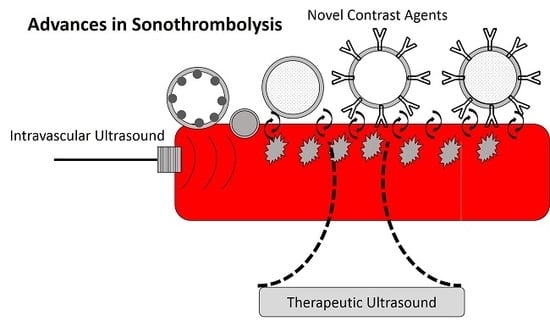
Advances in Sonothrombolysis Techniques Using Piezoelectric Transducers
Abstract
1. Background
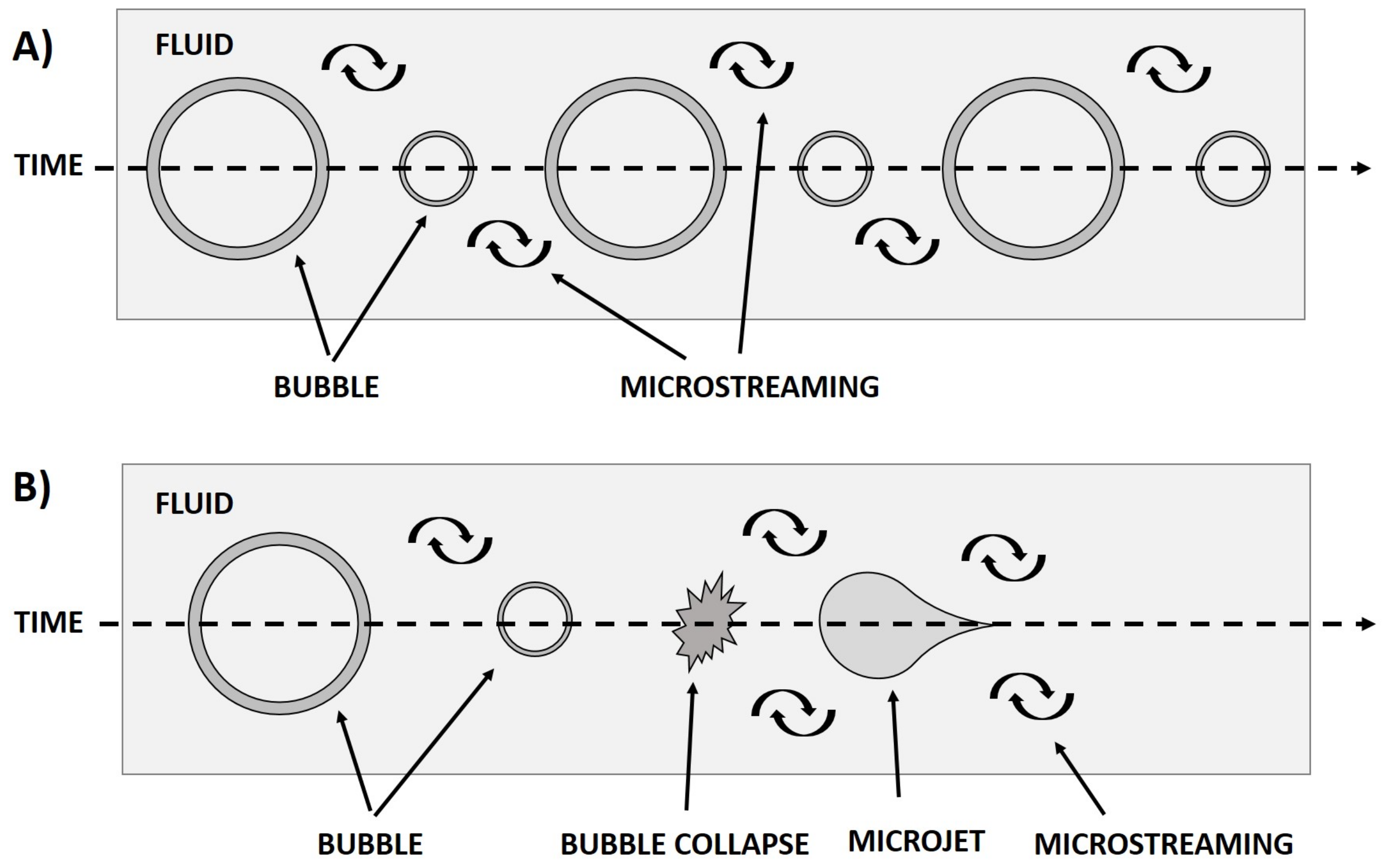
1.1. Mechanisms
1.2. Clinical Trials of Sonothrombolysis Techniques
1.3. Purpose
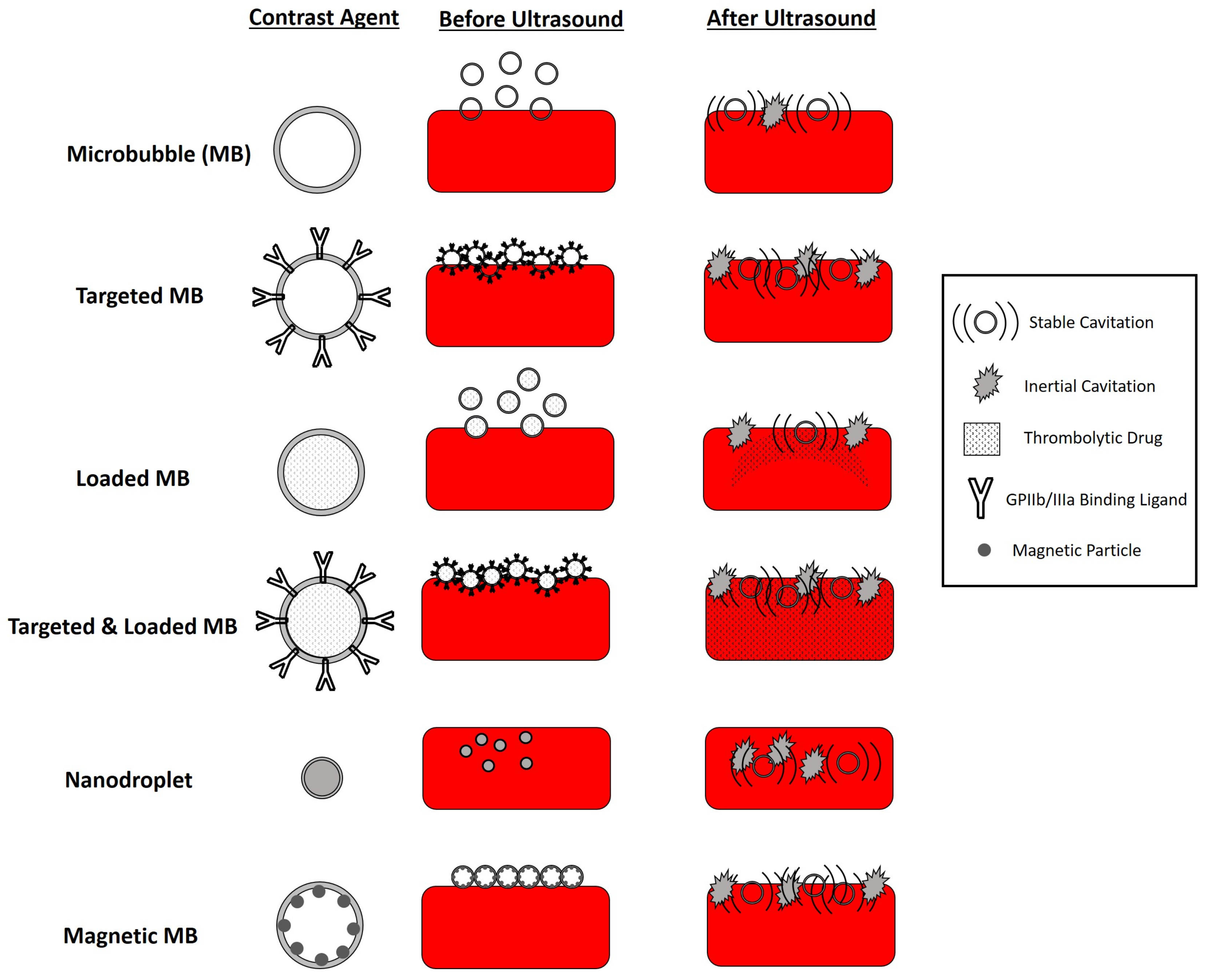
2. Novel Contrast Agents for Sonothrombolysis
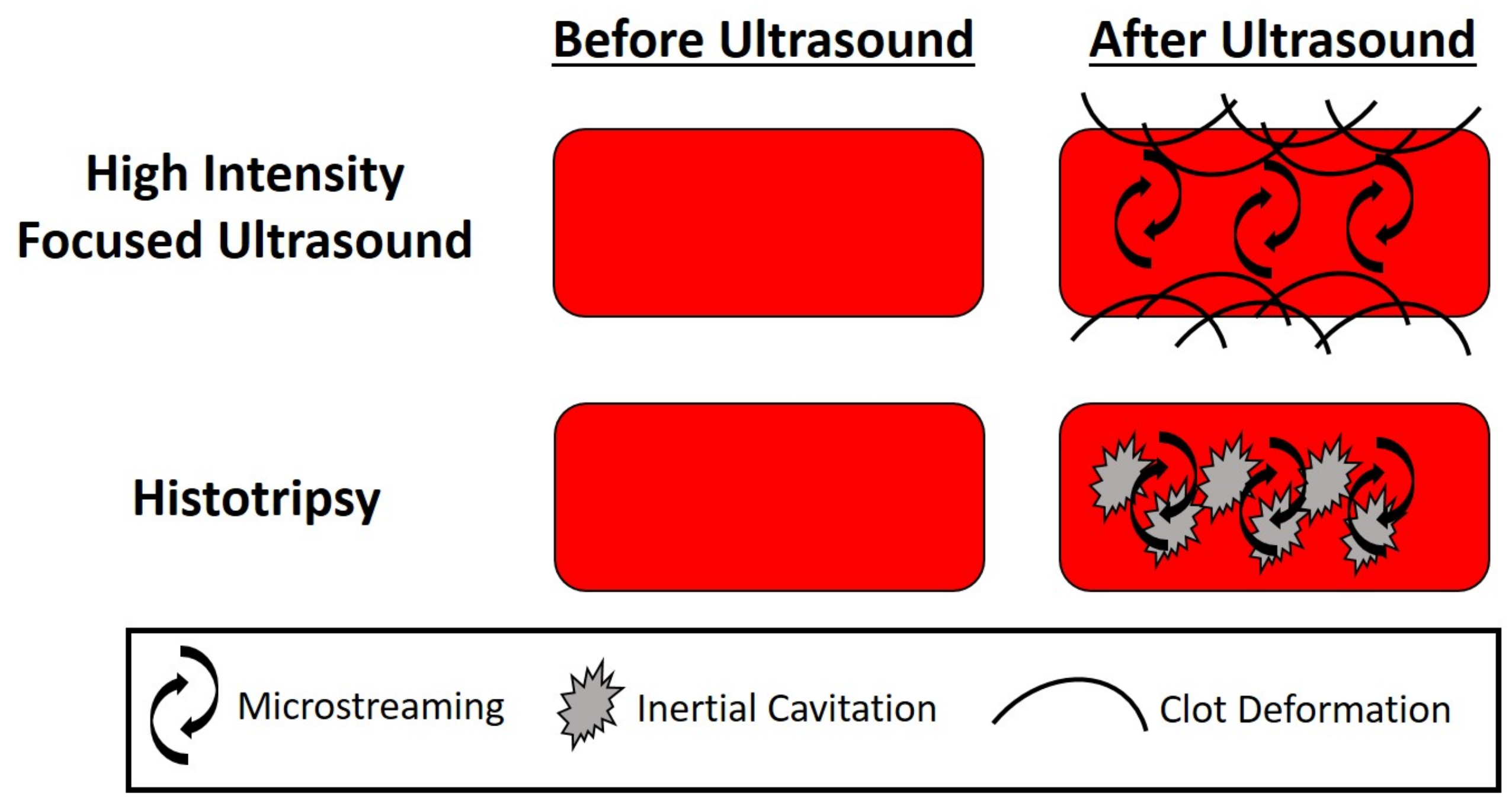
3. Therapeutic Ultrasound
4. Intravascular Sonothrombolysis
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heit, J.A.; Silverstein, M.D.; Mohr, D.N.; Petterson, T.M.; Lohse, C.M.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Melton, L.J. The epidemiology of venous thromboembolism in the community. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 86, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heit, J.A. The epidemiology of venous thromboembolism in the community. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uflacker, R. Interventional Therapy for Pulmonary Embolism. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2001, 12, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikesalingam, A.; Young, E.L.; Hinchliffe, R.J.; Loftus, I.M.; Thompson, M.M.; Holt, P.J.E. Review A Systematic Review of Percutaneous Mechanical Thrombectomy in the Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2011, 41, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.T.; Gould, M.K.; Louie, J.D.; Rosenberg, J.K.; Sze, D.Y.; Hofmann, L.V. Catheter-directed Therapy for the Treatment of Massive Pulmonary Embolism: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Modern Techniques. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 20, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, M.C.; Saver, J.L.; Gobin, Y.P.; Jahan, R.; Duckwiler, G.R.; Vinuela, F.; Kidwell, C.S.; Frazee, J.; Starkman, S. Beyond Tissue Plasminogen Activator: Mechanical Intervention in Acute Stroke. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2003, 41, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Investigators, T.P.P.S.T. Safety and Effectiveness of a New Generation of Mechanical Devices for Clot Removal in Intracranial Large Vessel Occlusive Disease. Stroke 2009, 40, 2761–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Warlow, C.P.; Counsell, C. Systematic review of evidence on thrombolytic therapy for acute ischaemic stroke. Lancet 1997, 350, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, J.P.; Hacke, W. Treatment of acute ischemic stroke part I: Recanalization strategies. Circulation 2002, 106, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, L.D.; Stolz, E.; Canhão, P.; Ferro, J.M. Systemic Thrombolysis for Cerebral Venous and Dural Sinus Thrombosis: A Systematic Review. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 37, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubiera, M.; Ribo, M.; Delgado-mederos, R.; Santamarina, E.; Delgado, P.; Montaner, J.; Alvarez-Sabín, J.; Molina, C.A. Tandem Internal Carotid Artery/Middle Cerebral An Independent Predictor of Poor Outcome After Systemic Thrombolysis. Stroke 2006, 37, 2301–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, C.; John, G.; Konstantinides, S.; Combescure, C.; Sanchez, O.; Lankeit, M.; Meyer, G.; Perrier, A. Systemic thrombolytic therapy for acute pulmonary embolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, C.; Hynynen, K.; Goertz, D. In vitro and in vivo high intensity focused ultrasound thrombolysis. Investig. Radiol. 2012, 47, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauer, C.G.; Burge, R.; Tang, D.B.; Bass, B.G.; Gomez, E.R.; Alving, B.M. Effect of Ultrasound on Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator-Induced Thrombolysis. Circulation 1992, 86, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedelmann, M.; Brandt, C.; Schneider, F.; Eicke, B.M.; Kempski, O.; Krummenauer, F.; Dieterich, M. Ultrasound-induced blood clot dissolution without a thrombolytic drug is more effective with lower frequencies. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2005, 20, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, C.K.; Vaidya, S.S.; Datta, S.; Coussios, C.C.; Shaw, G.J. Ultrasound-enhanced tissue plasminogen activator thrombolysis in an in vitro porcine clot model. Thromb. Res. 2008, 121, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everbach, E.C.; Francis, C.W. Cavitational mechanisms in ultrasound-accelerated thrombolysis at 1 MHz. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2000, 26, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinc, A.; Francis, C.W.; Trudnowski, J.L.; Carstensen, E.L. Characterization of ultrasound potentiated fibrinolysis in vitro. Blood 1993, 81, 2636–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Miller, R.M.; Lin, K.W.; Levin, A.M.; Owens, G.E.; Gurm, H.S.; Cain, C.A.; Xu, Z. Real-time feedback of histotripsy thrombolysis using bubble-induced color doppler. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 1386–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acconcia, C.; Leung, B.; Hynynen, K.; Goertz, D. Investigating the interaction between acoustically stimulated microbubbles and fibrin clots. Aip Conf. Proc. 2012, 1503, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Everbach, E.C.; Gao, S.; Drvol, L.K.; Shi, W.T.; Vignon, F.; Powers, J.E.; Lof, J.; Porter, T.R. Effects of Attenuation and Thrombus Age on the Success of Ultrasound and Microbubble-Mediated Thrombus Dissolution. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2011, 37, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chuang, Y.H.; Cheng, P.O.; Chen, S.C.; Ruan, J.L.; Li, P.C. Effects of ultrasound-induced inertial cavitation on enzymatic thrombolysis. Ultrason. Imaging 2010, 32, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, K.B.; Gruber, M.J.; Holland, C.K. Shaken and Stirred: Mechanisms of Ultrasound-Enhanced Thrombolysis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, K.E.; Ivancevich, N.M.; Haworth, K.J.; Caudell Stamper, D.N.; Vela, D.C.; Sutton, J.T.; Pyne-Geithman, G.J.; Holland, C.K. Ultrasound-Enhanced rt-PA Thrombolysis in an ex vivo Porcine Carotid Artery Model. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2011, 37, 1240–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, T.R.; Kricsfeld, D.; Lof, J.; Everbach, E.C.; Xie, F. Effectiveness of transcranial and transthoracic ultrasound and microbubbles in dissolving intravascular thrombi. J. Ultrasound Med. 2001, 20, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokop, A.F.; Soltani, A.; Roy, R.A. Cavitational Mechanisms in Ultrasound-Accelerated Fibrinolysis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2007, 33, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culp, W.C.; Erdem, E.; Roberson, P.K.; Husain, M.M. Microbubble Potentiated Ultrasound as a Method of Stroke Therapy in a Pig Model: Preliminary Findings. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2003, 14, 1433–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cintas, P.; Nguyen, F.; Boneu, B.; Larrue, V. Enhancement of enzymatic fibrinolysis with 2-MHz ultrasound and microbubbles. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 2, 1163–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Hunter, F.; Hancock, H.; Kapoor, A.; Stone, M.J.; Wood, B.J.; Xie, J.; Dreher, M.R.; Frenkel, V. In Vitro Investigations Into Enhancement of tPA Bioavailability in Whole Blood Clots Using Pulsed–High Intensity Focused Ultrasound Exposures. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, C.W.; Blinc, A.; Lee, S.; Cox, C. Ultrasound accelerates transport of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator into clots. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1995, 21, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devcic-Kuhar, B.; Pfaffenberger, S.; Gherardini, L.; Mayer, C.; Gröschl, M.; Kaun, C.; Benes, E.; Tschachler, E.; Huber, K.; Maurer, G.; et al. Ultrasound affects distribution of plasminogen and tissue-type plasminogen activator in whole blood clots in vitro. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 92, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sutton, J.T.; Ivancevich, N.M.; Perrin, S.R.; Vela, D.C.; Holland, C.K. Clot Retraction Affects the Extent of Ultrasound-Enhanced Thrombolysis in an Ex Vivo Porcine Thrombosis Model. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2013, 39, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Zhou, Y. Effect of pulse repetition frequency of high-intensity focused ultrasound on in vitro thrombolysis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 35, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, N.; Damianou, C. In Vitro Evaluation of Focused Ultrasound-Enhanced TNK-Tissue Plasminogen Activator-Mediated Thrombolysis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 1864–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, N.; Yiallouras, C.; Damianou, C. The Enhancing Effect of Focused Ultrasound on TNK-Tissue Plasminogen Activator-Induced Thrombolysis Using an In Vitro Circulating Flow Model. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 2891–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajek, D.; Burgess, A.; Huang, Y.; Hynynen, K. High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Sonothrombolysis: The Use of Perfluorocarbon Droplets to Achieve Clot Lysis at Reduced Acoustic Power. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2014, 40, 2151–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saletes, I.; Gilles, B.; Auboiroux, V.; Bendridi, N.; Salomir, R.; Béra, J.C. In Vitro Demonstration of Focused Ultrasound Thrombolysis Using Bifrequency Excitation. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Owens, G.E.; Cain, C.A.; Gurm, H.S.; Macoskey, J.; Xu, Z. Histotripsy Thrombolysis on Retracted Clots. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 1903–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, A.D.; Cain, C.A.; Duryea, A.P.; Yuan, L.; Gurm, H.S.; Xu, Z. Noninvasive Thrombolysis Using Pulsed Ultrasound Cavitation Therapy—Histotripsy. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2009, 35, 1982–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zong, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, R.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Han, S.; Wan, M. Dependence of pulsed focused ultrasound induced thrombolysis on duty cycle and cavitation bubble size distribution. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 22, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, C.W.; Onundarson, P.T.; Carstensen, E.L.; Blinc, A.; Meltzer, R.S.; Schwarz, K.; Marder, V.J. Enhancement of fibrinolysis in vitro by ultrasound. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 2063–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakharov, D.V.; Hekkenberg, R.T.; Rijken, D.C. Acceleration of Fibrinolysis by High-frequency Ultrasound. Thromb. Res. 2000, 100, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collis, J.; Manasseh, R.; Liovic, P.; Tho, P.; Ooi, A.; Petkovic-Duran, K.; Zhu, Y. Cavitation microstreaming and stress fields created by microbubbles. Ultrasonics 2010, 50, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hölscher, T.; Raman, R.; Fisher, D.J.; Ahadi, G.; Zadicario, E.; Voie, A. Effects of varying duty cycle and pulse width on high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) -induced transcranial thrombolysis. J. Ther. Ultrasound 2013, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.B.; Qin, H.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.B.; Liu, Y.M.; Jia, X.D.; Shi, N. Platelet-targeted microbubbles inhibit re-occlusion after thrombolysis with transcutaneous ultrasound and microbubbles. Ultrasonics 2011, 51, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, G.J.; Meunier, J.M.; Lindsell, C.J.; Holland, C.K. Tissue Plasminogen Activator Concentration Dependence of 120 kHz Ultrasound-Enhanced Thrombolysis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2008, 34, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kashyap, A.; Blinc, A.; Marder, V.J.; Penney, D.P.; Francis, C.W. Acceleration of fibrinolysis by ultrasound in a rabbit ear model of small vessel injury. Thromb. Res. 1994, 76, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatar, M.; Stroick, M.; Griebe, M.; Alonso, A.; Hennerici, M.G.; Daffertshofer, M. Brain temperature during 340-kHz pulsed ultrasound insonation: A safety study for sonothrombolysis. Stroke 2006, 37, 1883–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatar, M.; Stroick, M.; Griebe, M.; Alonso, A.; Kreisel, S.; Kern, R.; Hennerici, M.; Meairs, S. Effect of Combined Ultrasound and Microbubbles Treatment in an Experimental Model of Cerebral Ischemia. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2008, 34, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culp, W.C.; Flores, R.; Brown, A.T.; Lowery, J.D.; Roberson, P.K.; Hennings, L.J.; Woods, S.D.; Hatton, J.H.; Culp, B.C.; Skinner, R.D.; et al. Successful microbubble sonothrombolysis without tissue-type plasminogen activator in a rabbit model of acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2011, 42, 2280–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchoux, G.; Shivashankar, R.; Abruzzo, T.A.; Holland, C.K. In silico study of low-frequency transcranial ultrasound fields in acute ischemic stroke patients. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2014, 40, 1154–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shaw, G.J.; Bavani, N.; Dhamija, A.; Lindsell, C.J. Effect of mild hypothermia on the thrombolytic efficacy of 120 kHz ultrasound enhanced thrombolysis in an in-vitro human clot model. Thromb. Res. 2006, 117, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daffertshofer, M.; Gass, A.; Ringleb, P.; Sitzer, M.; Sliwka, U.; Els, T.; Sedlaczek, O.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Hennerici, M.G. Transcranial low-frequency ultrasound-mediated thrombolysis in brain ischemia: Increased risk of hemorrhage with combined ultrasound and tissue plasminogen activator—Results of a phase II clinical trial. Stroke 2005, 36, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, A.V.; Demchuk, A.M.; Burgin, W.S.; Robinson, D.J.; Grotta, J.C. Ultrasound-Enhanced Thrombolysis for Acute Ischemic Stroke: Phase I. Findings of the CLOTBUST Trial. J. Neuroimaging 2004, 14, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, A.V.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Köhrmann, M.; Katsanos, A.H.; Soinne, L.; Barreto, A.D.; Rothlisberger, T.; Sharma, V.K.; Mikulik, R.; Muir, K.W.; et al. Endovascular equipoise shift in a phase III randomized clinical trial of sonothrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2019, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, C.A.; Ribo, M.; Rubiera, M.; Montaner, J.; Santamarina, E.; Delgado-Mederos, R.; Arenillas, J.F.; Huertas, R.; Purroy, F.; Delgado, P.; et al. Microbubble administration accelerates clot lysis during continuous 2-MHz ultrasound monitoring in stroke patients treated with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. Stroke 2006, 37, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perren, F.; Loulidi, J.; Poglia, D.; Landis, T.; Sztajzel, R. Microbubble potentiated transcranial duplex ultrasound enhances IV thrombolysis in acute stroke. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2008, 25, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribo, M.; Molina, C.A.; Alvarez, B.; Rubiera, M.; Alvarez-Sabin, J.; Matas, M. Intra-arterial administration of microbubbles and continuous 2-MHz ultrasound insonation to enhance intra-arterial thrombolysis. J. Neuroimaging 2008, 20, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chait, J.; Aurshina, A.; Marks, N.; Hingorani, A.; Ascher, E. Comparison of Ultrasound-Accelerated Versus Multi-Hole Infusion Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis for the Treatment of Acute Limb Ischemia. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2019, 53, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelberger, R.P.; Fahrni, J.; Willenberg, T.; Baumann, F.; Spirk, D.; Diehm, N.; Do, D.; Baumgartner, I.; Kucher, N. Fixed low-dose ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis followed by routine stenting of residual stenosis for acute ilio-femoral deep-vein thrombosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 111, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelberger, R.P.; Kucher, N. Ultrasound-assisted thrombolysis for acute pulmonary embolism: A systematic review. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tichelaar, V.Y.I.G.; Brodin, E.E.; Vik, A.; Isaksen, T.; Skjeldestad, F.E.; Kumar, S.; Trasti, N.C.; Singh, K.; Hansen, J.B. A Retrospective Comparison of Ultrasound-Assisted Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis and Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis Alone for Treatment of Proximal Deep Vein Thrombosis. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 39, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Piazza, G.; Hohlfelder, B.; Jaff, M.R.; Ouriel, K.; Engelhardt, T.C.; Sterling, K.M.; Jones, N.J.; Gurley, J.C.; Bhatheja, R.; Kennedy, R.J.; et al. A Prospective, Single-Arm, Multicenter Trial of Ultrasound-Facilitated, Catheter-Directed, Low-Dose Fibrinolysis for Acute Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism: The SEATTLE II Study. JACC: Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 8, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Shi, W.; Chen, L.; Gu, J. A systematic review of ultrasound-accelerated catheter-directed thrombolysis in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2018, 45, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.J.; Luo, H. Ultrasound thrombolysis. Ultrasonics 2008, 48, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiessling, F.; Fokong, S.; Koczera, P.; Lederle, W.; Lammers, T. Ultrasound Microbubbles for Molecular Diagnosis, Therapy, and Theranostics. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auboire, L.; Sennoga, C.; Hyvelin, J.M.; Ossant, F.; Escoffre, J.M.; Tranquart, F.; Bouakaz, A. Microbubbles combined with ultrasound therapy in ischemic stroke: A systematic review of in-vivo preclinical studies. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, K.E.; Holland, C.K. Ultrasound-assisted thrombolysis for stroke therapy: Better thrombus break-up with bubbles. Stroke 2010, 41, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Owens, C.A. Ultrasound-enhanced thrombolysis: EKOS endo wave infusion catheter system. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2008, 25, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, S.; Sheehan, J.; Medel, R.; Wintermark, M.; Eames, M.; Snell, J.; Kassell, N.F.; Elias, W.J. Potential intracranial applications of magnetic resonance–guided focused ultrasound surgery. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 118, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsivgoulis, G.; Alexandrov, A. Ultrasound-enhanced thrombolysis: From bedside to bench. Stroke 2008, 39, 1404–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Meairs, S.; Alonso, A.; Hennerici, M.G. Progress in sonothrombolysis for the treatment of stroke. Stroke 2012, 43, 1706–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meairs, S.; Culp, W. Microbubbles for thrombolysis of acute ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2009, 27, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doomernik, D.E.; Schrijver, A.M.; Zeebregts, C.J.; de Vries, J.P.P.M.; Reijnen, M.M.P.J. Advancements in Catheter-Directed Ultrasound-Accelerated Thrombolysis. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2011, 18, 418–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, B.; Yan, F.; Tranquart, F.; Allémann, E. Microbubbles and ultrasound-mediated thrombolysis: A review of recent in vitro studies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2012, 22, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balucani, C.; Alexandrov, A.V. Ultrasound- and microspheres-enhanced thrombolysis for stroke treatment: State of the art. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2010, 12, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertz, D.E. An overview of the influence of therapeutic ultrasound exposures on the vasculature: High intensity ultrasound and microbubble-mediated bioeffects. Int. J. Hyperth. 2015, 31, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daffertshofer, M.; Fatar, M. Therapeutic ultrasound in ischemic stroke treatment: Experimental evidence. Eur. J. Ultrasound 2002, 16, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpaz, D. Ultrasound enhancement of thrombolytic therapy: Observations and mechanisms. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2000, 3, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atar, S.; Luo, H.; Birnbaum, Y.; Hansmann, D.; Ph, D.; Siegel, R.J. The Use of Transducer-Tipped Ultrasound Catheter for Recanalization of Thrombotic Arterial Occlusions. Echocardiography 2001, 18, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atar, S.; Luo, H.; Nagai, T.; Siegel, R.J. Ultrasonic thrombolysis: catheter-delivered and transcutaneous applications. Eur. J. Ultrasound 1999, 9, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.B.; Liu, Y.M.; Wang, M.; Qin, H.; Wang, C.B.; Liu, J.; Yu, X.J.; Zang, W.J. Thrombolysis effect of a novel targeted microbubble with low-frequency ultrasound in vivo. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 100, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.C.; Ruan, J.L.; Cheng, P.W.; Chuang, Y.H.; Li, P.C. In vitro evaluation of ultrasound-assisted thrombolysis using targeted ultrasound contrast agents. Proc. IEEE Ultrason. Symp. 2008, 246, 1659–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, A.; Dempfle, C.E.; Della Martina, A.; Stroick, M.; Fatar, M.; Zohsel, K.; Allémann, E.; Hennerici, M.G.; Meairs, S. In vivo clot lysis of human thrombus with intravenous abciximab immunobubbles and ultrasound. Thromb. Res. 2009, 124, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, K.; Kamiya, A.; Miyazaki, T.; Koga, A.; Inatomi, A.; Harada-shiba, M. Surface Modification with Lactadherin Augments the Attachment of Sonazoid Microbubbles to Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagisawa, K.; Nishioka, T.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; Takase, B.; Ishihara, M.; Kurita, A.; Yoshimoto, N.; Nishida, Y.; Iida, K.; et al. Thrombus-targeted perfluorocarbon-containing liposomal bubbles for enhancement of ultrasonic thrombolysis: in vitro and in vivo study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, G.J.; Meunier, J.M.; Huang, S.L.; Lindsell, C.J.; McPherson, D.D.; Holland, C.K. Ultrasound-enhanced thrombolysis with tPA-loaded echogenic liposomes. Thromb. Res. 2009, 124, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, S.T.; Moody, M.; Smulevitz, B.; Kim, H.; Kee, P.; Huang, S.; Holland, C.K.; McPherson, D.D. Ultrasound-enhanced thrombolytic effect of tissue plasminogen activator-loaded echogenic liposomes in an in vivo rabbit aorta thrombus model-brief report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 1357–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.W.; Jing, B.B.; Li, Y.X.; Liao, Y.R.; Kang, X.N.; Zang, W.J.; Wang, B. The Preparation of a New Self-Made Microbubble-Loading Urokinase and Its Thrombolysis Combined with Low-Frequency Ultrasound In Vitro. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2011, 37, 1828–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandadai, M.A.; Meunier, J.M.; Hart, K.; Holland, C.K.; Shaw, G.J. Plasmin-Loaded Echogenic Liposomes for Ultrasound-Mediated Thrombolysis. Trans. Stroke Res. 2015, 6, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, H.; Bader, K.B.; Huang, S.; Peng, T.; Huang, S.; McPherson, D.D.; Holland, C.K. In vitro thrombolytic efficacy of echogenic liposomes loaded with tissue plasminogen activator and octafluoropropane gas. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 517–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhar, H.; Kleven, R.T.; Peng, T.; Palaniappan, A.; Karani, K.B.; Huang, S.; McPherson, D.D.; Holland, C.K. In vitro characterization of sonothrombolysis and echocontrast agents to treat ischemic stroke. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.; Liu, P.; Gao, Y.H.; Tan, K.B.; Zhou, L.N.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.W.; Gao, Y.J. Construction of thrombus-targeted microbubbles carrying tissue plasminogen activator and their in vitro thrombolysis efficacy: A primary research. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2010, 30, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Zhou, L.; Liu, P.; He, Y.; Tan, K.; Chen, Q.; Gao, Y.; Gao, Y. In vivo thrombolysis with targeted microbubbles loading tissue plasminogen activator in a rabbit femoral artery thrombus model. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2014, 38, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Guan, L.; Mu, Y. Combined low-frequency ultrasound and urokinase-containing microbubbles in treatment of femoral artery thrombosis in a rabbit model. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüßler, J.; Strehlow, B.; Becker, A.; Schubert, R.; Schümmelfeder, J.; Nimsky, C.; Bakowsky, U. Nanoscaled ultrasound contrast agents for enhanced sonothrombolysis. Colloids Surf. Biointerfaces 2018, 172, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, D.; Du, X.; Han, M.; Zong, Y.; Wan, M. Reduced clot debris size in sonothrombolysis assisted with phase-change nanodroplets. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 54, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victor, M.d.S.; Carugo, D.; Barnsley, L.C.; Owen, J.; Coussios, C.C.; Stride, E. Magnetic targeting to enhance microbubble delivery in an occluded microarterial bifurcation. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 7451–7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victor, A.D.S.; Barnsley, L.C.; Carugo, D.; Owen, J.; Coussios, C.C.; Stride, E. Sonothrombolysis With Magnetically Targeted Microbubbles. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Kim, H.; Wu, H.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, X. Sonothrombolysis with magnetic microbubbles under a rotational magnetic field. Ultrasonics 2019, 98, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynynen, K. MRI-guided focused ultrasound treatments. Ultrasonics 2010, 50, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.y.; Liu, Y. Therapeutic Ultrasound: Its Application in Drug Delivery. Med. Res. Rev. 2002, 22, 204–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, M.J.; Frenkel, V.; Dromi, S.; Thomas, P.; Lewis, R.P.; Li, K.C.P.; Horne, M.; Wood, B.J. Pulsed-high intensity focused ultrasound enhanced tPA mediated thrombolysis in a novel in vivo clot model, a pilot study. Thromb. Res. 2007, 121, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahadi, G.; Welch, C.S.; Grimm, M.J.; Fisher, D.J.; Zadicario, E.; Ernström, K.; Voie, A.H.; Hölscher, T. Transcranial sonothrombolysis using high-intensity focused ultrasound: Impact of increasing output power on clot fragmentation. J. Ther. Ultrasound 2013, 1, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, A.; Huang, Y.; Waspe, A.C.; Ganguly, M.; Goertz, D.E.; Hynynen, K. High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) for dissolution of clots in a rabbit model of embolic stroke. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hölscher, T.; Fisher, D.; Raman, R. Noninvasive Transcranial Clot Lysis Using High Intensity Focused Ultrasound. J. Neurol. Neurophysiol. 2011, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holscher, T.; Ahadi, G.; Fisher, D.; Zadicario, E.; Voie, A. MR-guided focused ultrasound for acute stroke a rabbit model. Stroke 2013, 44, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, D.; Guo, S.; Lin, W.; Jiang, X.; Jing, Y. Thrombolysis using multi-frequency high intensity focused ultrasound at MHz range: An in vitro study. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 7403–7418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, D.; Jin, Z.; Jiang, X.; Dayton, P.A.; Jing, Y. Microbubble mediated dual-frequency high intensity focused ultrasound thrombolysis: An in vitro study. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, D.; Govind, B.; Gu, J.; Dayton, P.A.; Jing, Y. Dynamic assessment of dual-frequency microbubble-mediated sonothrombolysis in vitro. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 084702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, A.D.; Owens, G.; Gurm, H.S.; Ives, K.; Myers, D.D.; Xu, Z. Noninvasive treatment of deep venous thrombosis using pulsed ultrasound cavitation therapy (histotripsy) in a porcine model. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 22, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, L.; Vlaisavljevich, E.; Owens, G.E.; Gurm, H.S.; Charles, A.; Xu, Z.; Arbor, A.; Diseases, C.; Arbor, A.; et al. Non-invasive Thromboysis using Microtripsy: A Parameter Study. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 2015, 62, 2092–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Macoskey, J.J.; Ives, K.; Owens, G.E.; Gurm, H.S.; Shi, J.; Pizzuto, M.; Cain, C.A.; Xu, Z. Non-Invasive Thrombolysis Using Microtripsy in a Porcine Deep Vein Thrombosis Model. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 1378–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, A.; Lundt, J.; Deng, Z.; Macoskey, J.; Gurm, H.; Owens, G.; Zhang, X.; Hall, T.L.; Xu, Z. Integrated Histotripsy and Bubble Coalescence Transducer for Thrombolysis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 2697–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelberger, R.P.; Schroeder, V.; Nagler, M.; Prince, R.; Periard, D.; Hayoz, D.; Kucher, N. Enhanced Thrombolysis by Ultrasound-Assisted Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis and Microbubbles in an In Vitro Model of Iliofemoral Deep Vein Thrombosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lindsey, B.D.; Chang, W.Y.; Dai, X.; Stavas, J.M.; Dayton, P.A.; Jiang, X. Intravascular forward-looking ultrasound transducers for microbubble-mediated sonothrombolysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggs, P.; Francis, C.W.; Bartos, S.; Penney, D. Ultrasound enhancement of rabbit femoral artery thrombolysis.pdf. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1997, 5, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, M.; Hekkenberg, R.T.; Barrett-Bergshoeff, M.; Rijken, D.C. The effect of 40 kHz ultrasound on tissue plasminogen activator-induced clot lysis in three in vitro models. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2004, 30, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Steffen, W.; Cercek, B.; Arunasalam, S.; Maurer, G.; Siegel, R.J. Enhancement ultrasound of thrombolysis by external ultrasound. Am. Heart J. 1993, 125, 1564–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härdig, B.M.; Carlson, J.; Roijer, A. Changes in clot lysis levels of reteplase and streptokinase following continuous wave ultrasound exposure, at ultrasound intensities following attenuation from the skull bone. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2008, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelmann, M.; Eicke, B.M.; Lierke, E.G.; Heimann, A.; Kempski, O.; Hopf, H.C. Low-frequency ultrasound induces nonenzymatic thrombolysis in vitro. J. Ultrasound Med. 2002, 21, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Contrast Agent | Ref. | Transducer | Cent. Freq. | Intensity (W/cm2) | Duty Cycle (%) | PRF | MI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targeted MBs | [45,82,83,84,86] | Therapeutic US Device (Dongjian Company, Wuhan, China); V302 Panametrics-NDT (Olympus Corp., Tokyo, Japan); P4-2, Philips HDI 5000 (Philips, Amsterdam, The Netherlands); Timi3 Systems (Timi3 Systems, Santa Clara, CA, USA); Custom prototype 10 PZT disks (Fuji Ceramics, Tokyo, Japan) | 27 kHz–2 MHz | 1.4–1.2 | 5–50 | 25–150 Hz | 1.2–3.2 |
| Loaded MBs | [87,88,89,90,91,92] | Custom H160 single element transducer (Sonic Concepts, Inc., Woodburn, WA, USA); Therapeutic US Device (Dongjian Company, Peijing, China); 8L-RS, Vivid i (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee, WI, USA) | 120 kHz–5.7 MHz | 0.5–2.79 | 50–100 | 1.7–5 kHz | - |
| Targeted and Loaded MBs | [93,94,95] | CSY-2 (Puji, Chongqing, China); LA240 (Yum Mylab 90, Yum Mylab, Italy) | 1.6–2.8 MHz | 1.8 | 95 | - | 1.4 |
| Magnetic MBs | [99,100] | Custom single element transducer (Sonic Concepts, Inc., Woodburn, WA, USA); Custom prototype 6 PZT-5A thin plates | 500–620 kHz | - | 1.6–10 | 0.2 Hz | - |
| Therapeutic Ultrasound Technique | Ref. | Transducer | Center Freq. | Power (W) | Duty Cycle (%) | PRF | PNP (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Intensity Focused Ultrasound | [33,44,104,105,106,107,108,109,110] | ExAblate 4000 High Intensity Focused Ultrasound headsystem (InSightec, Inc, Tirat Carmel, Israel); H-102 (Sonic Concepts, Bothell, WA, USA); Custom transducer (Blatek, Inc., State College, PA, USA) | 220 kHz–1.51 MHz | 0–550 | 2.5–50 | 1–1000 Hz | 1.2–3.2 |
| Histotripsy & Microtripsy | [38,39,40,111,112,113,114] | Spherical focused transducer, 18-element therapy transducer (Imasonic, Besancon, France) | 1–1.2 MHz | - | 0.1–18 | 5–1000 Hz | 2–35 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goel, L.; Jiang, X. Advances in Sonothrombolysis Techniques Using Piezoelectric Transducers. Sensors 2020, 20, 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051288
Goel L, Jiang X. Advances in Sonothrombolysis Techniques Using Piezoelectric Transducers. Sensors. 2020; 20(5):1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051288
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoel, Leela, and Xiaoning Jiang. 2020. "Advances in Sonothrombolysis Techniques Using Piezoelectric Transducers" Sensors 20, no. 5: 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051288
APA StyleGoel, L., & Jiang, X. (2020). Advances in Sonothrombolysis Techniques Using Piezoelectric Transducers. Sensors, 20(5), 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051288