Ultrastable Offset-Locking Continuous Wave Laser to a Frequency Comb with a Compound Control Method for Precision Interferometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
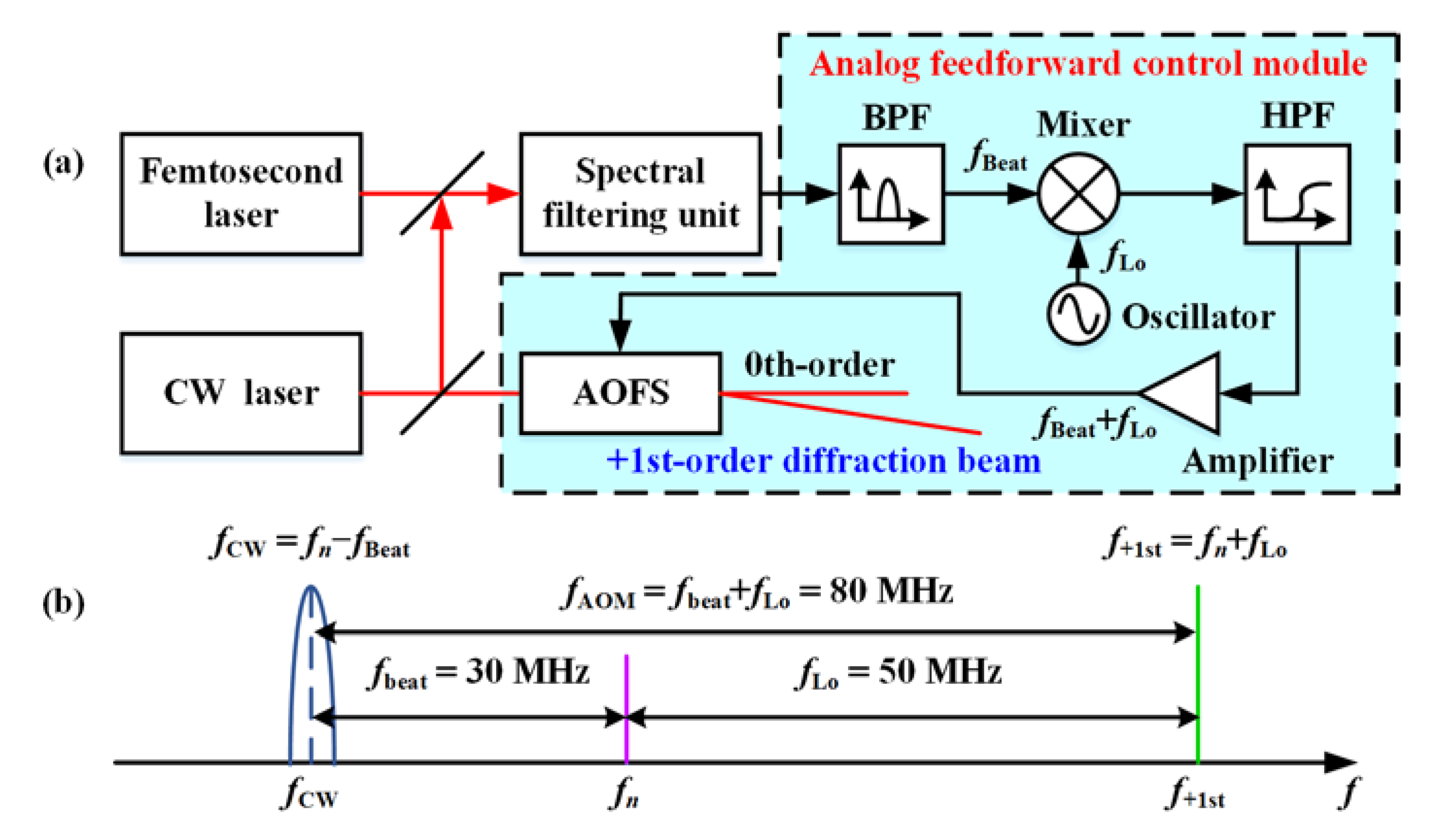
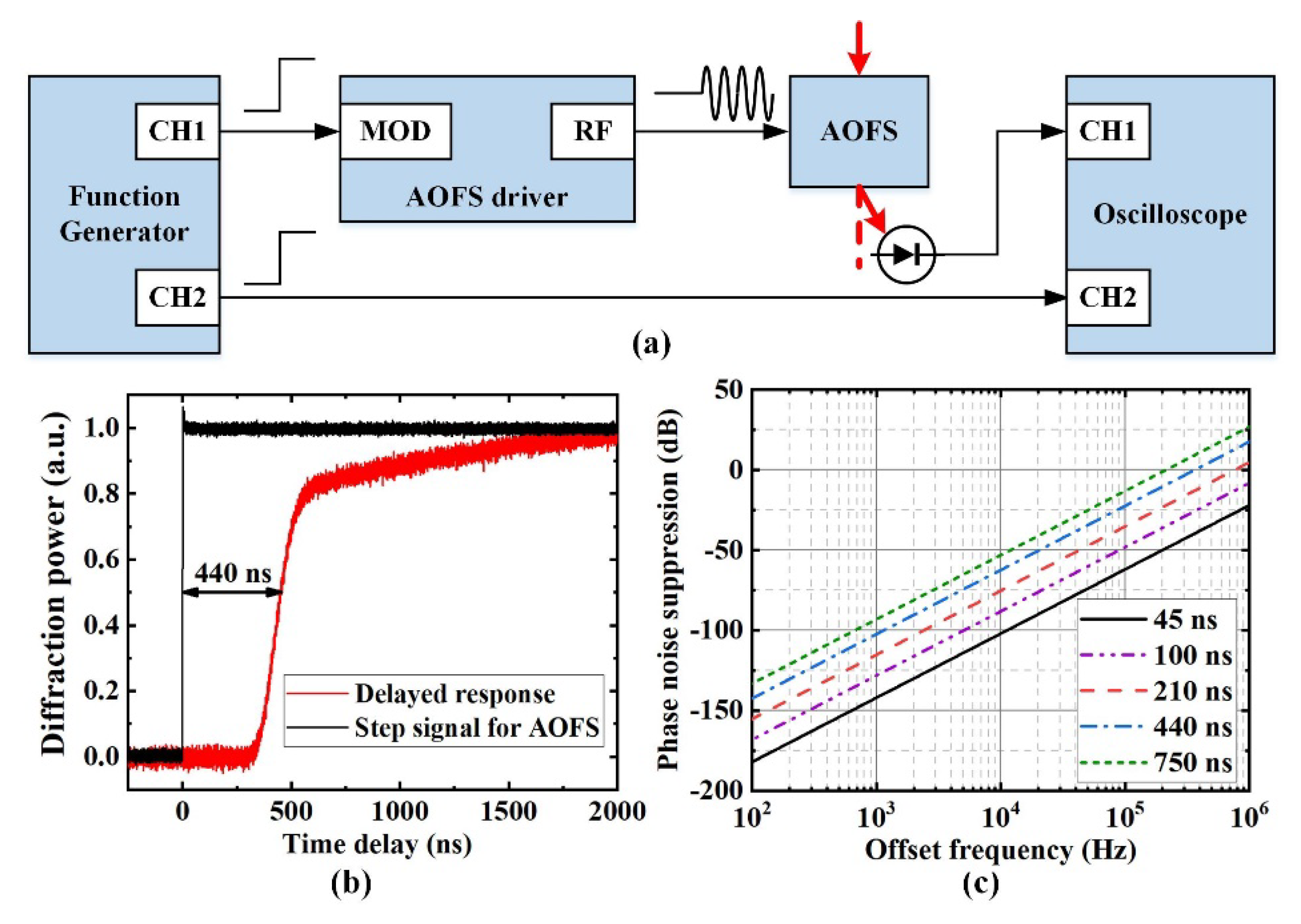
2. AOFS Based Analog Feedforward Control Principle and Its Limitation
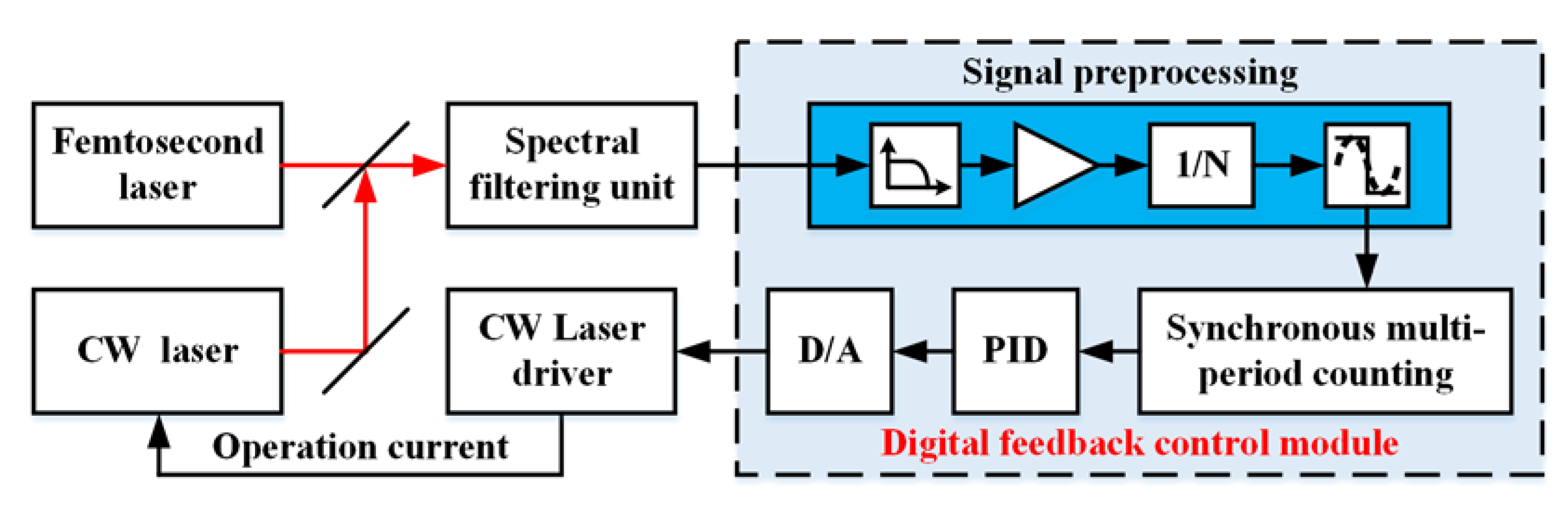
3. Digital Feedback Control for Extended Frequency Locking Range
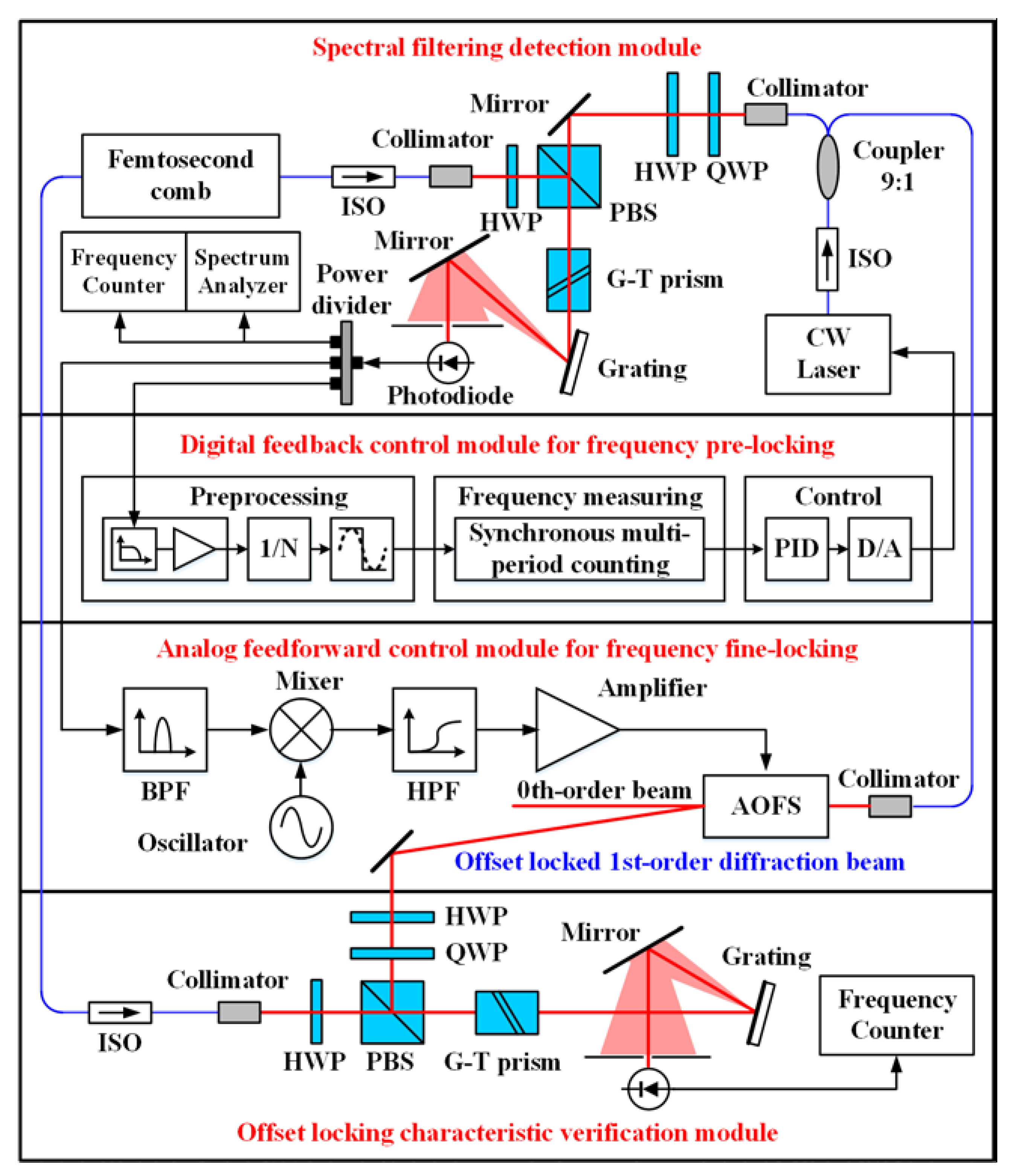
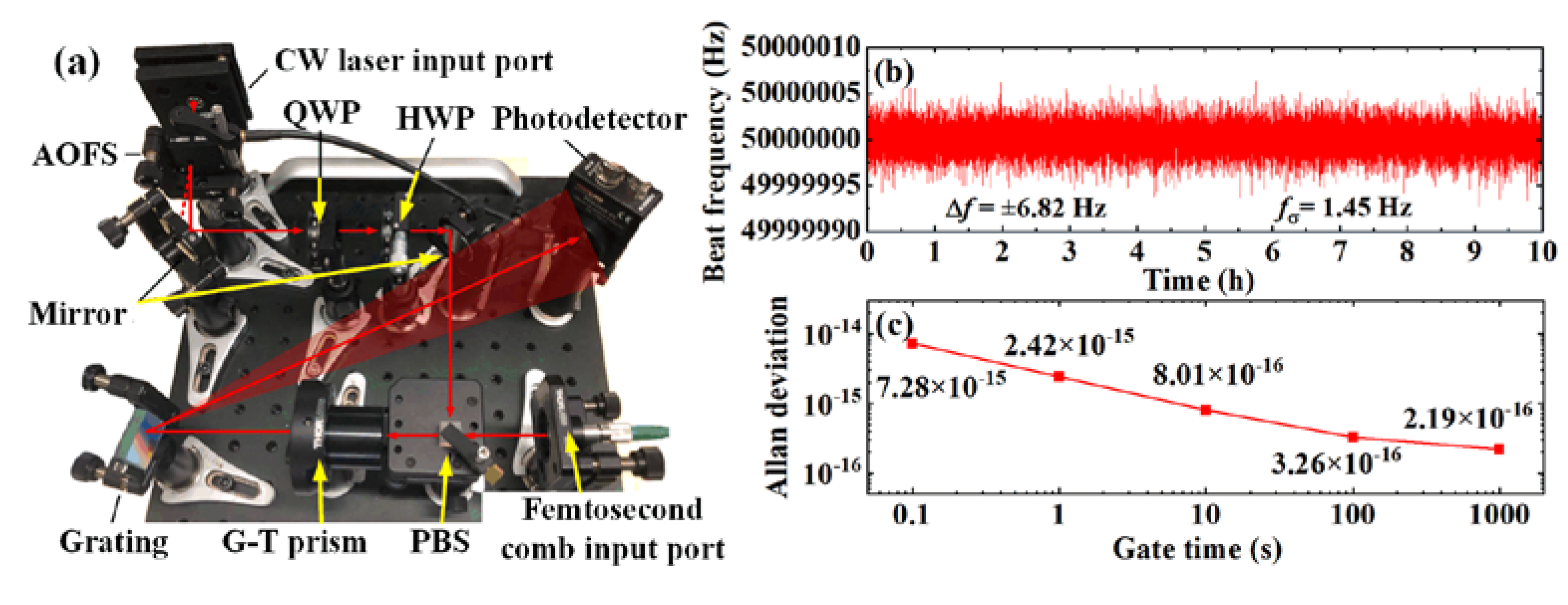
4. Experimental Setup
5. Experimental Results and Discussion
5.1. Detection of the Beat Signal with the Optimized Signal-To-Noise Ratio
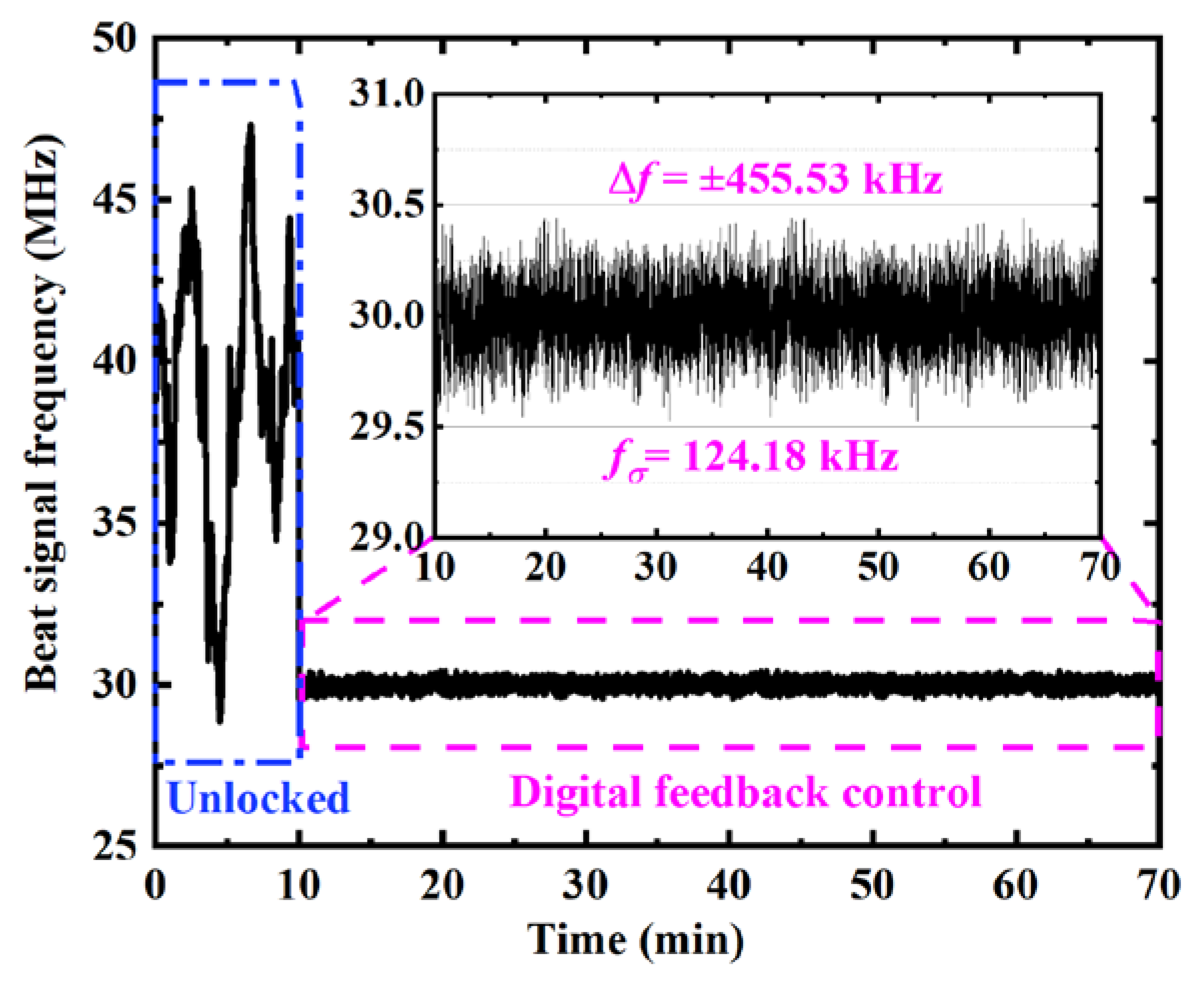
5.2. Individual Performance of the Digital Feedback and Analog Feedforward Control Modules
5.3. The Verification of Offset Locking Characteristic
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abernathy, M.R.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. Observation of gravitational waves from a binary black hole merger. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 166, 061102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Cho, K.S.; Lee, E.K.; Lee, S.J.; Chae, J.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, D.H.; Kwon, J.Y.; Amaratunga, G.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Full-colour quantum dot displays fabricated by transfer printing. Nat. Photonics 2011, 5, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, B.; Maximov, I.; Montelius, L. Nanoimprint lithography at the 6 in. wafer scale. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2000, 6, 3557–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomsadze, B.; Cundiff, S.T. Frequency combs enable rapid and high-resolution multidimensional coherent spectroscopy. Science 2017, 357, 1389–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, I.; Newbury, N.; Swann, W. Dual-comb spectroscopy. Optica 2016, 3, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millo, J.; Abgrall, M.; Lours, M.; English, E.M.L.; Jiang, H.; Guéna, J.; Clairon, A.; Tobar, M.E.; Bize, S.; Le Coq, Y.; et al. Ultralow noise microwave generation with fiber-based optical frequency comb and application to atomic fountain clock. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 141105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udem, T.; Holzwarth, R.; Hänsch, T.W. Optical frequency metrology. Nature 2002, 416, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, I.; Swann, W.C.; Nenadovic, L.; Newbury, N.R. Rapid and precise absolute distance measurements at long range. Nat. Photonics 2009, 3, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhler, N.; Salvade, Y.; Leveque, S.; Dandliker, R.; Holzwarth, R. Frequency-comb-referenced two-wavelength source for absolute distance measurement. Opt. Lett. 2006, 31, 3101–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, J.D.; Hall, J.L.; Ye, J. Continuously tunable, precise, single frequency optical signal generator. Opt. Express 2002, 10, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkler, E.; Rohde, F.; Telle, H.R. Robust interferometric frequency lock between cw lasers and optical frequency combs. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 555–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beverini, N.; Prevedelli, M.; Sorrentino, F.; Nyushkov, B.; Ruffini, A. An analog + digital phase-frequency detector for phase locking of a diode laser to an optical frequency comb. Quantum Electron. 2004, 34, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quraishi, Q.; Griebel, M.; Ostmann, T.K.; Bratschitsch, R. Generation of phase-locked and tunable continuous-wave radiation in the terahertz regime. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 3231–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, A.A.; Gatti, D.; Jiang, J.; Mohr, C.; Mefford, W.; Gianfrani, L.; Fermann, M.; Hartl, I.; Marangoni, M. Coherent phase lock of a 9 μm quantum cascade laser to a 2 μm thulium optical frequency comb. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 4083–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koke, S.; Grebing, C.; Frei, H.; Anderson, A.; Assion, A.; Steinmeyer, G. Direct frequency comb synthesis with arbitrary offset and shot-noise-limited phase noise. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, T.; Gatti, D.; Gambetta, A.; Coluccelli, N.; Galzerano, G.; Laporta, P.; Marangoni, M. Wide-bandwidth phase lock between a CW laser and a frequency comb based on a feed-forward configuration. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 2592–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, D.; Sala, T.; Gambetta, A.; Coluccelli, N.; Conti, G.N.; Galzerano, G.; Laporta, P.; Marangoni, M. Analysis of the feed-forward method for the referencing of a CW laser to a frequency comb. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 24880–24885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Ou, P.; Yin, F.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, K. Linewidth reduction by feedforward locking a laser diode to a femtosecond comb line. IEEE Photonics J. 2016, 8, 1503407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, J.; Holzwarth, R.; Udem, T.; Hänsch, T.W. Measuring the frequency of light with mode-locked lasers. Opt. Commun. 1999, 172, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschênes, J.; Genest, J. Chirped pulse heterodyne for optimal beat note detection between a frequency comb and a continuous wave laser. Opt. Express. 2015, 23, 9295–9312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telle, H.R.; Steinmeyer, G.; Dunlop, A.E.; Stenger, J.; Sutter, D.H.; Keller, U. Carrier-envelope offset phase control: A novel concept for absolute optical frequency measurement and ultrashort pulse generation. Appl. Phys. B 1999, 69, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.J.; Diels, J.C. Stabilization of femtosecond lasers for optical frequency metrology and direct optical to radio frequency synthesis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 3288–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, K.R.; Diddams, S.A.; Oates, C.W.; Curtis, E.A.; Rafac, R.J.; Itano, W.M.; Bergquist, J.C.; Fox, R.W.; Lee, W.D.; Wells, J.S.; et al. Direct comparison of two cold-atom-based optical frequency standards by using a femtosecond-laser comb. Opt. Lett. 2001, 26, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, F.; Cossel, K.C.; Thorpe, M.J.; Hartl, I.; Fermann, M.E.; Ye, J. Phase-stabilized, 1.5 W frequency comb at 2.8–4.8 microm. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 1330–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbury, N.R.; Swann, W.C. Low-noise fiber-laser frequency combs. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2007, 24, 1756–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, F.; Fortier, T.M.; Kirchner, M.S.; Taylor, J.A.; Thorpe, M.J.; Lemke, N.; Ludlow, A.D.; Jiang, Y.; Diddams, S.A. Ultralow phase noise microwave generation with an Er: Fiber-based optical frequency divider. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 3260–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruehl, A.; Martin, M.J.; Cossel, K.C.; Chen, L.; McKay, H.; Thomas, B.; Benko, C.; Dong, L.; Dudley, J.M.; Fermann, M.E.; et al. Ultrabroadband coherent supercontinuum frequency comb. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 84, 011806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, E.; Giorgetta, F.R.; Nicholson, J.W.; Swann, W.C.; Coddington, I.; Newbury, N.R. Highperformance, vibration-immune, fiber-laser frequency comb. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xu, X.; Nguyen, T.G.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; Moss, D.J. RF photonics: An optical microcombs’ perspective. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. 2018, 24, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Eliyahu, D.; Ilchenko, V.S.; Savchenkov, A.A.; Matsko, A.B.; Seidel, D.; Maleki, L. High spectral purity Kerr frequency comb radio frequency photonic oscillator. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelkens, G.; Liu, L.; Liang, D.; Jones, R.; Fang, A.; Koch, B.; Bowers, J. III-V/silicon photonics for on-chip and intra-chip optical interconnects. Laser Photonics Rev. 2010, 4, 751–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Reference | Reported SNR (dB) | Reported RBW (kHz) | Equivalent SNR (dB) for RBW = 100 kHz |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telle, 1999 [21] | 16 | 100 | 16 |
| Jones, 2001 [22] | 35 | 2 | 18 |
| Vogel, 2001 [23] | 25 | 100 | 25 |
| Adler, 2009 [24] | 40 | 10 | 30 |
| Newbury, 2007 [25] | 47 | 3 | 31.8 |
| Quinlan, 2011 [26] | 30 | 300 | 34.8 |
| Ruehl, 2011 [27] | 38 | 100 | 38 |
| Baumann, 2009 [28] | 65 | 0.3 | 39.8 |
| This work | 41 | 100 | 41 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, R.; Lv, H.; Luo, J.; Hu, P.; Yang, H.; Fu, H.; Tan, J. Ultrastable Offset-Locking Continuous Wave Laser to a Frequency Comb with a Compound Control Method for Precision Interferometry. Sensors 2020, 20, 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051248
Yang R, Lv H, Luo J, Hu P, Yang H, Fu H, Tan J. Ultrastable Offset-Locking Continuous Wave Laser to a Frequency Comb with a Compound Control Method for Precision Interferometry. Sensors. 2020; 20(5):1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051248
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Ruitao, Haisu Lv, Jing Luo, Pengcheng Hu, Hongxing Yang, Haijin Fu, and Jiubin Tan. 2020. "Ultrastable Offset-Locking Continuous Wave Laser to a Frequency Comb with a Compound Control Method for Precision Interferometry" Sensors 20, no. 5: 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051248
APA StyleYang, R., Lv, H., Luo, J., Hu, P., Yang, H., Fu, H., & Tan, J. (2020). Ultrastable Offset-Locking Continuous Wave Laser to a Frequency Comb with a Compound Control Method for Precision Interferometry. Sensors, 20(5), 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051248









