Abstract
The knowledge of the acoustic impedance of a material allows for the calculation of its acoustic absorption. Impedance can also be linked to structural and physical proprieties of materials. However, while the impedance of pavement samples in laboratory conditions can usually be measured with high accuracy using devices such as the impedance tube, complete in-situ evaluation results are less accurate than the laboratory results and is so time consuming that a full scale implementation of in-situ evaluations is practically impossible. Such a system could provide information on the homogeneity and the correct laying of an installation, which is proven to be directly linked to its acoustic emission properties. The present work studies the development of a measurement instrument which can be fastened through holding elements to a moving laboratory (i.e., a vehicle). This device overcomes the issues that afflict traditional in-situ measurements, such as the impossibility to perform a continuous spatial characterization of a given pavement in order to yield a direct evaluation of the surface’s quality. The instrumentation has been uncoupled from the vehicle’s frame with a system including a Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) controller, studied to maintain the system at a fixed distance from the ground and to reduce damping. The stabilization of this device and the measurement system itself are evaluated and compared to the traditional one.
Keywords:
p-u sensor; p-p sensor; noise; Adrienne; stabilization; damping; acoustic impedance; road surfaces 1. Introduction
Transport infrastructures continue to be a source of noise, representing a serious issue in modern society. Among the sources that should be monitored according to European Environmental Noise Directive (END) [1], roads are the one that reach most citizens, and even if the noise produced is not the most disturbing, they contribute the most to the overall noise exposure. According to the 2017 END’s review [2], nearly 100 million European citizens are exposed to road traffic Lden higher than 55 dB(A) and among them 32 million are exposed to Lden higher than 65 dB(A). Many studies show that prolonged exposure to noise can induce cardiovascular disease [3,4], alterations in blood pressure [5,6], respiratory diseases [7], hypertension [8], learning impairment [9,10], annoyance [11,12], and sleep disturbance [13,14,15].
In order to avoid the aforementioned health issues, the END set the instruments in mandatory action plans for big infrastructures and urban agglomerations [16]. More detailed noise maps are mandatory for roads with traffic flows greater than 3 million vehicles per year and mitigation should be applied when limits’ exceedances emerge. In the last decades, economic efforts have been spent in mitigation actions for road traffic noise, with rigid barriers used as an optimal choice. However, it has been proven that this solution suffers from several problems, such as diffraction at the edges, reflection of sound energy in the opposite direction, and complaints of citizens due to the reduction of fields of view, natural light, and air flow [17].
Thus, researchers are recently looking for innovative and possibly “green” solutions, such as live and integrated monitoring systems [18,19], sustainable metamaterial absorbers [20,21], sonic crystals noise barriers made of recycled materials [22], electric cars, and car sharing [23].
The overall noise produced by a vehicle is given by the sum of propulsion, tire-pavement interaction, and aerodynamic contribution, depending on the vehicle speed. As electric vehicles become more widespread, the contribution of engines to overall noise is decreasing; however, it is only relevant at low speeds. Noise produced by tire–road interaction is the responsible for most of the noise emitted by roads and is a complex phenomenon resulting from the combination of aerodynamic and vibro-dynamic phenomena [24,25]. The former is related to compression of the air trapped within the tread of the rolling tire [26] (known as air pumping) and cause noise at frequencies higher than 1 kHz. In addition, pipe and Helmholtz resonances due to the coupling of a vibrating mass of air within the tread acting as a cavity contribute to the aerodynamic noise. Vibro-dynamic noise covers frequencies lower than 1 kHz and is due to tire vibrations caused by the impact of the tire against irregularities of the road surface and by non-linear effects, such as the stick-and-slip and stick-and-snap mechanisms [25].
The knowledge of noise generation mechanisms is vital for improving mitigation actions [27] applied to the two main actors in the phenomenon: Tires have been optimized [28], and mostly, low noise pavements have recently spread, some of which have even been developed with recycled materials [29,30]. Since tire/road noise depends on structural parameters of road surfaces [31], the European Union has recently prescribed acoustic tests of newly laid surfaces [32] by means of the Close Proximity Index (CPX) method [33] during the first three months from laying date. Therefore, knowing the acoustic performance of a pavement plays an extremely important role [34,35].
Even after the laying, monitoring a pavement over time is important to keep track of the ageing effect, which dramatically reduces the acoustic performance of surfaces. Traffic and weather cause voids in the surface to clog with detritus, increasing noise emitted even by 5 dB [36,37].
CPX measurements are generally performed to evaluate the acoustic emission properties of a pavement, while other measurement methods are needed for a wider evaluation of the acoustic properties. In order to assess the effects of noise on the receptors, for example, other factors are involved besides the emission, such as acoustic propagation, which in turn depends on the absorption coefficient of the road surface. The evaluation of the absorption coefficient is also an important parameter related to the state of the installation. For this reason, being able to measure the absorption yields a broader characterization of the pavement. In fact, the surface texture and volumetric of the friction course of a pavement are the main parameters influencing rolling noise, also related to absorption coefficient [35,36,37,38,39].
Different methods are generally used to evaluate the acoustic properties of a pavement, in order to derive information about their use in practical applications: From the CPX method [40], that also evaluates the emission properties, to the absorption measurement performed with an impedance tube using standing wave ratio (ISO 10534-1) [41] in-lab or on-site (ISO 13472-2) [42], and the extended surface method, usually called “Adrienne method” (ISO 13472-1) [43,44]. A recent study [45,46] showed that Adrienne method achieves good estimates for pavement’s characteristics, whereas the impedance tube scores the best accuracy in-lab, at the expense of time consumption, and the on-site Kundt tube can give an acceptable estimate of porosity.
Models of surface impedance of the materials currently present in the literature (e.g., Allard and Atalla [47]) are based on parameters related to the geometric properties of the interconnected porous structure and therefore to the effective structure of the medium. The sound absorption is often used as a proxy of the impedance, however, knowledge on the impedance represents a more complete information and allows a better characterization of surfaces from an acoustical point of view. Thus, in the last decade, several authors explored the possibility of measuring the surface impedance, defined as the ratio between the local pressure p and particle velocity u. This measurement is usually carried out by using a pressure-velocity (p-u) probe. The convenience of using a p-u probe is twofold: On one hand, it provides a local and simultaneous measure of both pressure and particle speed, while on the other hand it allows a direct measure of the impedance. A direct measurement of velocity is not possible with other known methods, such as the p-p sensors (pressure – pressure) reported below but can be achieved indirectly. In this way, the two quantities are related to the same incident and reflected field, with consequently simpler and error-free calculations. The Adrienne method, for example, requires evaluating a direct field that requires subsequent subtraction from the measured one, but is clearly not stable over time. Another important advantage of using the p-u probe to measure the impedance/absorption coefficient is the broadband "figure of eight" directivity of the particle velocity sensor, which significantly restricts background noise and allows the sensor to be used in-situ.
Most of the studies used the probe in laboratory conditions [48,49], while, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, only few approaches have tried in-situ road surface impedance measurement [50,51,52]. Nevertheless, Tijs and de Bree’s concept [53] can be considered a precursor of the present work, as it uses a small source attached to the bumper and close to the road surface and a p-u probe, operating in near field conditions and using a spherical wave.
The methodology reported in the paper uses a p-u sensor that measures the sound intensity by means of a pressure transducer combined with a particle velocity transducer, instead of the more common p-p sensor combining two pressure microphones and then applying a finite-difference approximation to the pressure gradient. Random errors can be overcome by repeating the measurement, while bias errors can occur for multiple causes, such as phase mismatch between the two measurement channels, errors in the scanning procedure, errors due to airflow, influence of the pressure equalization vents of the microphones, non-stationary external sources, reflections from the operator as they move around the source, influence of the environment on the sound power output of the source, and the absorption of the source itself [54]. These reasons contribute to the choice of the p-u probe over a p-p one. Furthermore, background noise from sources outside the measurement surface can increase phase mismatch in p-p sensors, but not in p-u ones [55]. On the contrary, strongly reactive sound fields can increase p-u phase mismatch and have no influence with the p-p ones. Another advantage of p-u probes over p-p ones is their reduced size; however, p-u sensors are not easily calibrated.
In the framework of the NEREiDE LIFE project, a new measurement system based on a pressure-velocity (p-u) probe has been implemented on a mobile laboratory. The present paper describes an instrument mounted on a mobile laboratory able to measure the absorption coefficient of a pavement in a continuous way. A mobile laboratory allows in-situ measurements of long road sections for a more precise assessment of the quality of asphalt pavements, which can vary along the installation [56]. It also allows to make measurements in safe conditions and without necessarily closing the road to traffic.
After addressing the choice of the sensor used, this work tries to solve the primary issue regarding these measurements, which is the stabilization of the instrumentation respect to the road surface. The new approach has been derived from the Adrienne method and can measure the acoustic absorption in a contactless way, thus resulting in a wider frequency bandwidth and a larger studied portion of the road surface. A proper device, consisting of an actuator driven by a laser distance sensor, has been developed for stabilizing and damping the measuring system. This task is extremely important for maintaining the stability and correctness of the impedance evaluation and reducing the measuring errors. Its effects have been simulated and measured in order to validate its functioning.
2. Life NEREIDE Project
The present work is part of the LIFE15 ENV/IT/000268 NEREiDE project, which aims improve porous asphalt pavements and low noise surfaces made of recycled asphalts and tires. A warm mixture was produced at a high temperature giving birth to pavements that improve:
- safety in urban areas by better draining;
- the reduction of waste materials and virgin materials;
- acoustical performances and a significant reduction of noise emitted;
- asphalt laying procedure, thus reducing air pollution emissions.
Crumb rubber from scrap tires were used in order to improve the road surfaces from elastics, soundproofing and toughening characteristics points of view, while recycled asphalts were used to reduce virgin aggregates and bitumen. The project characterizes raw materials searching for the best that fit the manufacturing processes of crumb rubber in order to modify the vulcanized recycled rubber and to make it suitable for incorporation in the bitumen. The last was the binder and matrix of the new composite material, with structural and waterproofing functions that should avoid the leaching of chemicals. Laboratory tests had already selected the correct composition, grading curve and the structural characteristics, the percentage of crumb rubber, and the methods to realize them.
The new pavements had been laid in two urban areas in Tuscany and one of the major tasks of the project was the evaluation of their effectiveness. Different approaches are currently used to test their effectiveness; from surface characteristics, to acoustical properties, and surveys submitted to the exposed population. The effectiveness was evaluated through a comparison of the surface acoustical properties prior and after the laying, but also by comparing the results with measurements over standard porous asphalt. This led to another objective, which is not less important than the main one: To improve the reliability of the results by suggesting a new evaluation technique for the performances of new pavements. The method should work on-site using techniques also applicable in urban context. Then, the effectiveness of new asphalts was monitored, also considering the subjective response to noise ante and post-opera. Roadside noise measurements were used to validate outputs from a noise model in order to assign noise levels to nearby residents who were also interviewed with questionnaires that compared their response [57].
Both Close Proximity Index and statistical pass-by (SPB) methods [58] were used to measure the noise produced by tires rolling on new and reference pavements. Unfortunately, standard SPB is applicable under environmental conditions that are almost never realized in the urban context. Therefore, an urban statistical pass by method was developed adding a monitoring station placed roadside at a known distance, in addition to traffic counters. In this way, the SPB has been modified to be used in urban areas by reducing the confounding factors. The method for deriving pass by values in urban contexts can define the index of vehicles noisiness on the specific pavement and place, thus allowing a comparison of efficiency of new pavements in terms of noise at roadside.
The project also aimed at the development of a new on-site acoustical absorption measuring system built on a mobile laboratory. For this purpose, a car was equipped with several instruments in order to perform moving and static measures. A preliminary data analysis was set up and described in the present paper. The system was used to monitor acoustic properties of new surfaces realized on experimental sites and was able to give real time results and a fine spatial acoustic characterization of the road surface. The results were linked to the microscopic and macroscopic properties of the asphalt, with parameters such as porosity and tortuosity, but also to macroscopic discontinuities or structural problems. They also provide an evaluation of the current state of a whole pavement stretch, thus giving useful information on the homogeneity of results along the whole installation. This allows for the evaluation of the goodness of the mixture and its laying. In the rest of the paper, a description of the measurement’s methodology will be carried out, focusing on the difficulties regarding the stabilization of the system over a moving vehicle.
3. Methodology
Measuring the absorption coefficient with a moving vehicle is best achieved using a contactless method. The system used in this work is the sum of the following parts, each separately tested and calibrated both in controlled conditions and on the actual mobile laboratory:
(1) p-u probe, also known as intensity probes: A sensor measuring the local value of acoustic pressure (p) and particle velocity (u). With these two parameters, the probe can easily evaluate the acoustic impedance;
(2) inertial damper: An electro mechanic actuator driven by a laser distance measure between the car and the pavement surface. This tool is needed to maintain constant the distance between the probe and the asphalt and to reduce vibrations from the moving vehicle;
(3) acoustic emitter: The sound emitted by the source is measured by the probe after being reflected by the pavement;
(4) A pc and an acquisition board acting as instrumentation control system.
The p-u probe can simultaneously and directly detect local pressure and particle velocity. It consists of a miniaturized pre-amplified microphone for pressure measurements and hot wires for the particle velocity evaluation [59]. This instrument is sensitive to specific velocity direction. As reported in Figure 1, the velocity sensor measures the perpendicular component respect to the pavement. An older method for measuring the particle’s velocity consisted of using two matched microphones and calculating the pressure difference, but problems in low pressure variation occurred when considering the microphones dimension and the spacing between them. The introduction of a technique based on a hot wire overcome this issue and the particle velocity could then be evaluated with a wire whose electric resistance changes with the temperature, and hence with the speed of the flow of the air that flows over the wire. The velocity u was then evaluated with Equation (1) [60].
where E is the voltage difference at the two ends of the wire resistance, a, b, and n are three constants evaluated during calibration. The voltage across the resistance is given by Equation (2) [61].
where Ro is the value of the resistance at the temperature To and the resistance variation is given by Equation (3), where is thermal resistance coefficient and T the temperature of the hot wire.
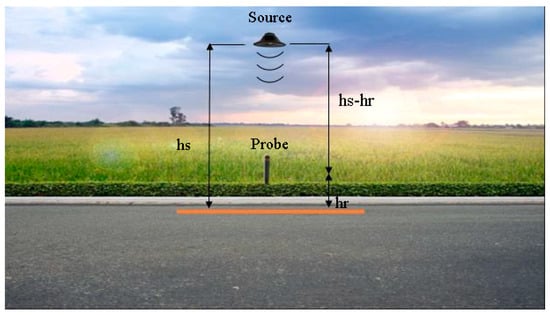
Figure 1.
Set-up of the measurement system.
The model used in this work considers a monopole source placed over the ground at hs and a receiver with height hr from the ground, as shown in Figure 1. The receiver acquires both p and u [62]. An innovative stabilization system is used to reduce the variation of the height of the source and the receiver, and it will be described in the next chapter.
The acoustic impedance was calculated with Equation (4) starting from the ratio of the complex pressure to complex velocity amplitudes measured by the probe.
The pressure and velocity values were calculated with Equations (5) considering a spherical wave of radius r:
A is the wave amplitude, is the air density, c is the speed of sound, is the angular frequency, is the acoustic wave number, λ is the wavelength.
The absorption coefficient α is defined as , where is the reflection coefficient defined in Equation 6 as the ratio of the reflected power Pr and incident power Pi.
R is the sound pressure reflection factor. p is the sum of the direct and reflected pressure wave. Similarly, u is the sum of direct and reflected velocity wave. However, since they are vectors, the negative sign must be taken into account. The impedance can then be reported in Equation (7).
where for simplicity and According to Equation (7), the explicit time dependency disappears and becomes in in the following. From the previous equation, R can be obtained Equations (8) and (9).
In order to know which parameter mostly affects the absorption coefficient, according to the theory of propagation of uncertainty, the propagation error for a multivariable function is derived for each component from the partial derivative of the function itself. Thus, the sensitivity of α respect to or can be calculated with Equations (10).
4. Results
4.1. Instrumentation Height
Since it derives from the Adrienne method, the new method is dependent on the height from the plane. Considering that the height of the vehicle from the road surface changes due to its acceleration and to superficial irregularities of the surface, the very first part of the analysis are in-lab simulations aimed to optimize receiver’s position from the ground, which is the one leading to the smallest error in the calculation of the absorption coefficient. The results are compared with the Adrienne ones.
In these calculations, the ideal source and receiver were used and the variation of receiver to source height brought by the running vehicle were considered.
The sensitivity of α respect to the variation of or were studied in the Adrienne method with Equations (11).
From Equations (11), is possible to derive Equations (12), which shows that the ratio of the sensitivities of the absorption coefficients is equal to the ratio of and . Therefore, the sensitivity to variation of height of receiver is higher in module than that respect to the variation of the height of source.
In the new method with a p-u probe as receiver, the sensitivities ratio is different and changes with frequency, pavement impedance, receiver, and source height. The sensitiveness of the absorption coefficient values obtained using the Adrienne method is far greater than the new method proposed. The absorption coefficient sensitivity to the variation of the height of the probe also results higher in the Adrienne method than in the new one.
The height of the probe corresponding to the lowest error is at 0.16 m from the pavement for the new method, while for Adrienne the height of the microphone is 0.25 m, as suggested by the standard. However, the error for the Adrienne method is higher than the new method around ±0.05 to the minimum of both curves.
The main features of Adrienne and the new method are summarized in Table 1. The new method offers a wider frequency band width and is less sensitive to variations of the receiver’s height, which makes it more appropriate for a running vehicle.

Table 1.
Comparison of in-situ measurement methods.
4.2. Damping System
The mobile laboratory moves while acquiring data, therefore the height of the measurement instrument from the road pavement changes, as stated previously. The absorption measurement system was fastened to the frame of the vehicle and hence it suffered the same oscillations, shown in Figure 2. Figure 3 shows the vertical displacement of the rear of the vehicle, measured using an accelerometer and a laser distance meter. The accelerometer displacement was obtained through a double integration, which increased low frequency noise. On the contrary, the laser worked well over the whole band, but above a certain frequency the measurement was mainly influenced by the road texture (around 20 Hz). Red and blue curves in Figure 3 are similar within the range 2–20 Hz. Therefore, the spectrum of the searched displacement corresponds to the measurement performed with the laser up to that maximum identified frequency, while the following signal is attributable to the influence of road texture.
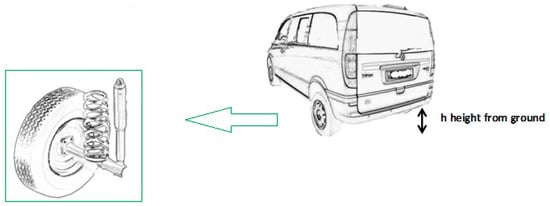
Figure 2.
Example of vehicle where is installed the absorption measurement system, with a focus on the shock absorber.
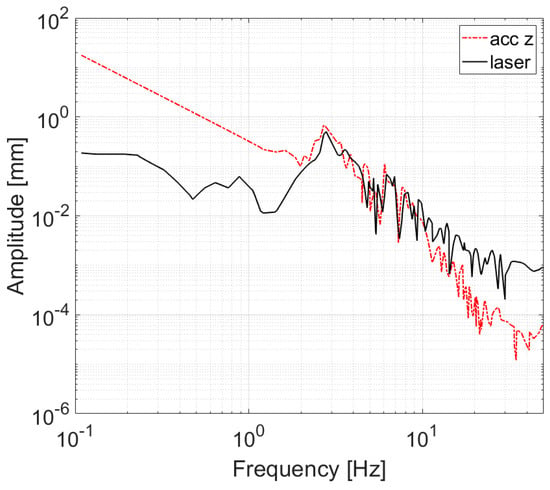
Figure 3.
Example of vehicle vertical displacement spectrum while moving.
In order to reduce the influence of height variations on the measurement, the measurement instrumentation must be uncoupled from the vehicle frame, using a system capable of keeping a constant distance h from the pavement. The characteristics of this active damping system are hereby described.
As shown in Figure 4, an active controller on the distance h has been developed using a Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) controller with the following characteristics:
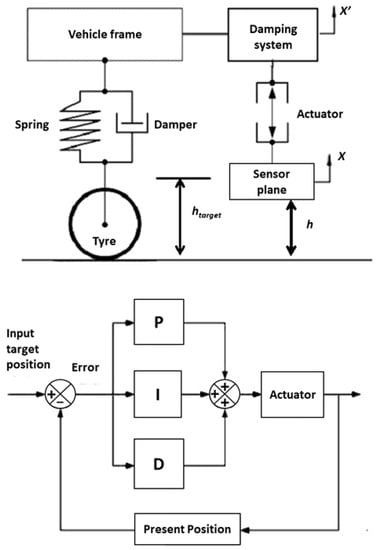
Figure 4.
Damping system model and Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) controller of the height of the absorption measurement system.
- Maximum allowable displacement xmax: 100 mm;
- Damping system with 1 degree of freedom placed along vertical axis;
- Typical vehicle frame displacement (x’): ±20 mm;
- Displacement stabilization range (error = htarget -h): 2 mm ÷ 5 mm;
- Working frequency: 0 Hz ÷ 30 Hz;
- Actuator load: 3 kg payload (loudspeaker, sensors, windscreen, laser distance sensor) plus damping system frame.
The Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) controller acts on the error e equal to the difference of the target position and the current position h of the measurement system with respect to the pavement. The target position is defined as the almost fixed height of the system. Furthermore, it takes into account the error e itself through a proportional relation, its integral I and its derivative D. The error can be expressed with Equation (13).
The function f used to drive the actuator in order to stabilize the measurement system is defined in Equation (14).
where , are constants to be calculated in accordance to the actuator system response and the acceptance error. In the present work, the accepted error was considered equal or less than 5 mm, corresponding to an absorption error due to the vehicle oscillation of around 0.01.
A simulation of the process is reported in Figure 5. The control was made through the PID controller which acts on a linear slide actuator that keeps the sensor at a fixed height h from the pavement. The actuator linear speed used in the simulation is 20 mm/s, while the road profile is taken from the on-field measurement, described below.
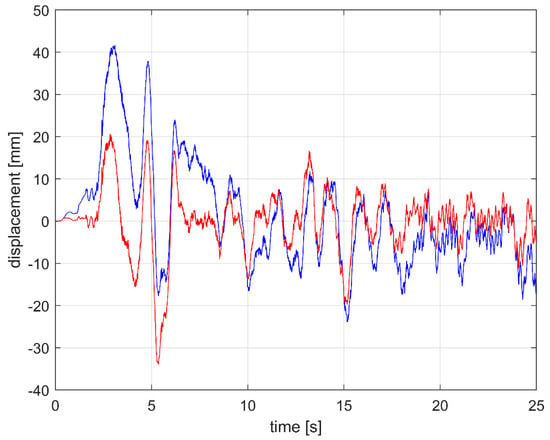
Figure 5.
Displacement simulation of the sensor plate stabilized by a PID controller (red); acquired vehicle frame vibration used as input of the PID controller (blue).
A field test was carried out on a stretch of pavement in good condition, running on the same stretch with the stabilizer device off and on. The measurements were repeated several times at a speed of 30 km/h. Although it is not easy to repeat the exact condition of each run, the results showed good repeatability. Measurements with or without stabilizer are not contemporary because only one laser displacement sensor was available for measurements. Consequently, the two measurements do not correspond to the same exact profiles; however, it can be argued that the two profiles share the same mean properties since they derive from measurements of the same road surface.
Figure 6 shows the displacements measured. The bold lines represent a 1-second smoothing for improving the visibility of the average stabilization effect. The maximum excursion using the stabilizer is approximately 0.021 m at 30 km/h. The order of magnitude of the average displacement from the expected equilibrium position in standard operating conditions are reported in Table 2.
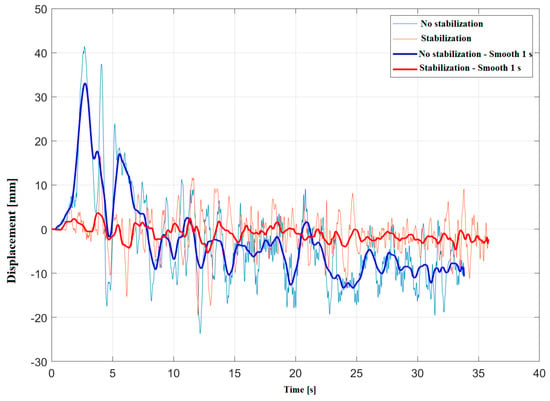
Figure 6.
Displacement measured in-situ with stabilization (red) and without stabilization (blue), with smoothing (bold lines) and without smoothing (thin lines).

Table 2.
RMS (Root mean square) of the average displacement measured at 30 km/h.
In order to evaluate how using the stabilizer affects the absorption measurement, an idealized case where the only effective variable was the position of the sensor/speaker group relative to the surface investigated was taken into account. Thus, considering a perfectly homogeneous surface, which has the same spectral trend for the reflection coefficient at each point. Furthermore, a high directionality of the sensor is assumed, so that the area actually investigated can be considered constant.
The subsequent calculations were carried out considering a hypothetical pavement with absorption from almost zero to almost one along the whole frequency range, a vehicle in motion at 30 km/h and the displacement trends with respect to an equilibrium position of 0.16 m from the pavement, as in Figure 5, both for the stabilized and non-stabilized system.
In order to simplify the application of Equation (7), it was assumed that the system remains stable, i.e., at a constant distance from the pavement, within the single measurement made by the laser distance meter. Since the instrument works at a frequency of 64 Hz, the measurements were carried out every 15.6 ms, enough time to resolve rather low signal frequencies. For example, up to about five cycles can be measured at 315 Hz.
A measurement of the p and v signals was simulated in successive windows of 15.6 ms length, calculating for each the signal Zr,i as the ratio of the respective spectra (i is the sections index). In order to do so, Equation (7) was used by imposing R, which was identical for each repetition, and the values of d1,i and d2,i related to the section. Using the calculated impedances but imposing a fixed distance of 0.16 m, the reflection coefficients Ri, representing an estimate of the error made in the absence of stabilization or with an imperfect one, were obtained. Calculating the relative error for each section becomes simple, since the actual value that R must assume is known.
Figure 7 shows a well-defined relationship between the measured absorption value and the error related to it, which is certainly influenced in absolute terms by the displacements with respect to the equilibrium.
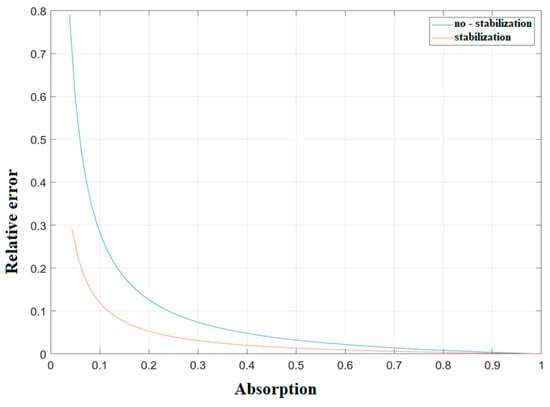
Figure 7.
Simulated relative error vs the sound absorption value.
5. Discussions and Conclusions
The present paper reported a new measurement system for the acoustic absorption of a pavement developed inside the LIFE15 ENV/IT/000268 NEREiDE project. The new method is derived from the Adrienne one (ISO 13472-1), but the sensor used is a p-u probe mounted on a vehicle moving over the road surface. With this important changes, it is now possible to measure acoustic absorption coefficient on-site, in a contactless way along all the site. Furthermore, it has been shown that the resulting frequency bandwidth is wider.
The correct set-up of the instrumentation has been studied, with particular emphasis on the height of the instrumentation above the ground. It has been shown that the ideal height, at which the lowest measurement error is achieved, is 0.16 m, slightly different from the 0.25 m used in the Adrienne method.
The present paper mainly reported the solution applied to overcome the greater difficulty for this kind of measurements, i.e., the stabilization and damping of the system, required in a vehicle in motion. The instrumentation has been uncoupled from the vehicle’s frame with a system studied to maintain constant the distance from the ground. As reported, a PID (Proportional Integral Derivative) controller was used to act on the error given by the difference of the target position and the real position of the measurement system with respect to the pavement. The test performed showed good results for keeping the instrumentation at a fixed height within an order of magnitude of 1 cm, which should be enough to achieve good accuracy in the evaluation of the absorption coefficient. For completeness, the extent of the influence is currently under study. The laboratory tests showed an excellent behavior of the stabilizer in dynamic conditions, perfectly within what was initially expected. Field measurements necessarily suffer from a greater uncertainty, which however allows to the use of the system within good margins for acoustic characterizations. In particular, the implemented possibility of obtaining the distance data from the system itself is rather useful, although it has not yet been tested. In the future, the authors expect to use the data for a possible real time correction to the calculations of the parameters that may depend on the distance.
This study improves on the work of Tijs and de Bree [53] by introducing a stabilization, but also allows the measurements at lower frequency by using a set-up similar to the Adrienne method. The required higher distance from probe to surface is safer for the instrumentation but also indirectly leads to a greater surface under study. However, this set-up implies a bigger source-pavement distance that allows a better approximation of the loudspeaker as point source on both the high and low frequencies. In addition, the methodology presented can be also considered as an improvement of the Adrienne method itself because it goes beyond the need to subtract the signals over time, resulting mathematically easier to operate and analyze.
At present, the system is designed to work at low speeds, within 30 km/h. Placed in the wake of the vehicle, the effect of the wind on the sensor is negligible, also because the sensor is equipped with a special windproof cap that gives it additional protection. In addition, the sensor is located inside an amplification horn, with the axis perpendicular to the ground, where a small windproof layer placed on the entrance and exit significantly reduces the disturbing effects generated by wind turbulence. In addition to this, the source power is sufficient to make other noise sources per se negligible. In particular, the speed sensor is highly directional, and its direction of measure is perpendicular to the road surface, thus further reducing the rolling noise produced by the wheel. Specific laboratory tests, not reported in this article, have shown effective independence of the probe measurement from sources placed outside the axis and of power comparable to the tire/road emission at the speeds investigated. While the calibration of a microphone can be performed with a suitable calibrator, no standard speed references to rely on exists for speed probes. For this purpose, the authors’ actual efforts and future developments will investigate the development of a calibration system. This phase needs to measure the acoustic impedance, which is given by the ratio between the velocity values of the particles and pressure measured at the same point. The calibration measurement will be performed inside an anechoic chamber or inside a stationary wave tube (Kundt tube) [63]. Another method could be to perform a comparative measure with the Adrienne method, estimating the absorption coefficient of a material from its surface acoustic impedance.
Finally, the authors do not exclude the study of the new presented methodology also using a suitable p-p sensor, which can still be a reliable, fast, and convenient tool for on-site measurements.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.L., G.L.; methodology, F.B.; software, F.B., F.L.C.; validation, G.L., F.F.; formal analysis, F.B., F.LC., P.G.; investigation, F.B., F.L.; resources, G.L., F.L.; data curation, F.L., P.G.; writing—original draft preparation, L.F.; writing—review and editing, L.F., F.B., P.G., F.L.C.; supervision, G.L., F.F.; project administration, F.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors thank the Tuscany Region for research grants financed for 50% with the resources of the POR FSE 2014-2020, falling within the scope of Giovanisì (www.giovanisi.it), the project of the Tuscany Region for the autonomy of young people.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Sandra Hill and Alessandro Del Pizzo for providing linguistic help and for their proof reading of the article. The authors also thank the LIFE15 ENV/IT/000268 NEREiDE project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Directive (European Commission) Directive 2002/49/EC of the European parliament and the Council of 25 June 2002 relating to the assessment and management of environmental noise. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2002, 189, 2002.
- European Commission. Report from the Commission to the European Parliament and the Council on the Implementation of the Environmental Noise Directive in Accordance with Article 11 of Directive 2002/49/EC. COM/2017/015; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Héritier, H.; Vienneau, D.; Foraster, M.; Eze, I.C.; Schaffner, E.; Thiesse, L.; Brink, M. Transportation noise exposure and cardiovascular mortality: A nationwide cohort study from Switzerland. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vienneau, D.; Schindler, C.; Perez, L.; Probst-Hensch, N.; Röösli, M. The relationship between transportation noise exposure and ischemic heart disease: A meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2015, 138, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dratva, J.; Phuleria, H.C.; Foraster, M.; Gaspoz, J.M.; Keidel, D.; Künzli, N.; Liu, L.J.S.; Pons, M.; Zemp, E.; Gerbase, M.W.; et al. Transportation noise and blood pressure in a population-based sample of adults. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 120, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babisch, W.; Swart, W.; Houthuijs, D.; Selander, J.; Bluhm, G.; Pershagen, G.; Dimakopoulou, K.; Haralabidis, A.S.; Katsouyanni, K.; Davou, E.; et al. Exposure modifiers of the relationships of transportation noise with high blood pressure and noise annoyance. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 3788–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recio, A.; Linares, C.; Banegas, J.R.; Díaz, J. Road traffic noise effects on cardiovascular, respiratory, and metabolic health: An integrative model of biological mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2016, 146, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kempen, E.; Babisch, W. The quantitative relationship between road traffic noise and hypertension: A meta-analysis. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lercher, P.; Evans, G.W.; Meis, M. Ambient noise and cognitive processes among primary schoolchildren. Environ. Behav. 2003, 35, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minichilli, F.; Gorini, F.; Ascari, E.; Bianchi, F.; Coi, A.; Fredianelli, L.; Licitra, G.; Manzoli, F.; Mezzasalma, L.; Cori, L. Annoyance judgment and measurements of environmental noise: A focus on Italian secondary schools. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, C.; Schnaiter, D.; Bose-O’Reilly, S. Combined Effects of Aircraft, Rail, and Road Traffic Noise on Total Noise Annoyance—A Cross-Sectional Study in Innsbruck. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basner, M.; Babisch, W.; Davis, A.; Brink, M.; Clark, C.; Janssen, S.; Stansfeld, S. Auditory and non-auditory effects of noise on health. Lancet 2014, 383, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiesler, C.M.; Birk, M.; Thiering, E.; Kohlböck, G.; Koletzko, S.; Bauer, C.P.; Berdel, D.; von Berg, A.; Babisch, W.; Heinrich, J. Exposure to road traffic noise and children’s behavioural problems and sleep disturbance: Results from the GINIplus and LISAplus studies. Environ. Res. 2013, 123, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onakpoya, I.J.; O’Sullivan, J.; Thompson, M.J.; Heneghan, C.J. The effect of wind turbine noise on sleep and quality of life: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Environ. Int. 2015, 82, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.; Kim, M.; Jang, C.; Choung, T.; Sim, K.A.; Seo, D.; Chang, S. The Public Health Impact of Road-Traffic Noise in a Highly-Populated City, Republic of Korea: Annoyance and Sleep Disturbance. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, G.; Ascari, E.; Fredianelli, L. Prioritizing process in action plans: A review of approaches. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2017, 3, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Park, T.; Chang, S.; Kim, I. Reduction Effects of Shaped Noise Barrier for Reflected Sound. J. Civil Environ. Eng. 2015, 5, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, M.; Wang, T.; Ho, H.; Kwok, C.; Lu, K.; Abbas, S. Towards a smart city: Development and application of an improved integrated environmental monitoring system. Sustainability 2018, 10, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merenda, F.G.; Praticò, R.; Fedele, R.; Carotenuto, F.G. Della Corte. A Real-time decision platform for the management of structures and infrastructures. Electronics 2019, 8, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, P.; Guattari, C.; Asdrubali, F.; de Lieto Vollaro, R.; Monti, A.; Ramaccia, D.; Bilotti, F.; Toscano, A. Sustainable acoustic metasurfaces for sound control. Sustainability 2016, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danihelová, A.; Němec, M.; Gergeľ, T.; Gejdoš, M.; Gordanová, J.; Sčensný, P. Usage of Recycled Technical Textiles as Thermal Insulation and an Acoustic Absorber. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredianelli, L.; Del Pizzo, A.; Licitra, G. Recent developments in sonic crystals as barriers for road traffic noise mitigation. Environments 2019, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Ko, J.; Park, Y. Factors affecting electric vehicle sharing program participants’ attitudes about car ownership and program participation. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2015, 36, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijpers, A.; Van Blokland, G. Tyre/road noise models in the last two decades: A critical evaluation. In Proceedings of INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference; No. 2, 2494-2499; Institute of Noise Control Engineering: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg, U.; Ejsmont, J. Tyre/Road Noise Reference Book; INFORMEX: Kisa, Sweden, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, P.A.; Phillips, S.M.; Watts, G.R. The Localisation, Quantification and Propagation of Noise from a Rolling Tyre; TRL Limited: Berkshire, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ögren, M.; Molnár, P.; Barregard, L. Road traffic noise abatement scenarios in Gothenburg 2015–2035. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regulation (European commission) No 1222/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 November 2009 on the labelling of tyres with respect to fuel efficiency and other essential parameters. Off. J. Eur. Union 2009, 342, 59.
- Kleizienė, R.; Šernas, O.; Vaitkus, A.; Simanavičienė, R. Asphalt Pavement Acoustic Performance Model. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berengier, M.C.; Stinson, M.R.; Daigle, G.A.; Hamet, J.F. Porous road pavements: Acoustical characterization and propagation effects. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1997, 101, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losa, M.; Leandri, P.; Licitra, G. Mixture design optimization of low-noise pavements. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2013, 2372, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbarino, E.; Quintero, R.R.; Donatello, S.; Wolf, O. Revision of green public procurement criteria for road design, construction and maintenance. In Procurement Practice Guidance Document; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. 11819-2:2017 Acoustics—Measurement of the Influence of Road Surfaces on Traffic Noise—Part 2: The Close-Proximity Method; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Praticò, F.G. On the dependence of acoustic performance on pavement characteristics. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2014, 29, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biligiri, K.P. Effect of pavement materials’ damping properties on tyre/road noise characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, G.; Moro, A.; Teti, L.; Del Pizzo, A.; Bianco, F. Modelling of acoustic ageing of rubberized pavements. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 146, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, G.; Cerchiai, M.; Teti, L.; Ascari, E.; Fredianelli, L. Durability and variability of the acoustical performance of rubberized road surfaces. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 94, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praticò, F.G.; Vaiana, R. A study on the relationship between mean texture depth and mean profile depth of asphalt pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 101, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praticò, F.G. Roads and loudness: A more comprehensive approach. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2001, 2, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, G.; Teti, L.; Cerchiai, M.; Bianco, F. The influence of tyres on the use of the CPX method for evaluating the effectiveness of a noise mitigation action based on low-noise road surfaces. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 55, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. EN ISO 10534-1, Determination of Sound Absorption Coefficient and Impedance in Impedance Tubes Part 1: Method Using Standing Wave Ratio; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. 13472-1, Acoustics—Measurement of Sound Absorption Properties of Road Surfaces In Situ—Part 2: Spot Method for Reflective Surfaces; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. 13472-1, Acoustics—Measurement of Sound Absorption Properties of Road Surfaces In Situ Part 1: Extended Surface Method; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, P.A.; Watts, G.R. A novel approach to the acoustic characterisation of porous road surfaces. Appl. Acoust. 2003, 64, 1171–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praticò, F.G.; Fedele, R.; Vizzari, D. Significance and reliability of absorption spectra of quiet pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 140, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praticò, F.G.; Vizzari, D.; Fedele, R. Estimating the resistivity and tortuosity of a road pavement using an inverse problem approach. In Proceedings of the ICSV24 24th International Congress on Sound and Vibration, London, UK, 23–27 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Allard, J.; Atalla, N. Propagation of Sound in Porous Media: Modelling Sound Absorbing Materials 2e; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Jacobsen, F. Measurement of absorption with a p-u sound intensity probe in an impedance tube. Acoust. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 118, 2117–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanoye, R.; Vermeir, G.; Lauriks, W.; Kruse, R.; Mellert, V. Measuring the free field acoustic impedance and absorption coefficient of sound absorbing materials with a combined particle velocity-pressure sensor. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 2826–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basten, T.G.; de Bree, H.E. Full bandwidth calibration procedure for acoustic probes containing a pressure and particle velocity sensor. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 127, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, E.; Lenzi, A.; Paul, S. A review of the in situ impedance and sound absorption measurement techniques. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2015, 101, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; van Keulen, W.; Tijs, E.; van de Ven, M.; Molenaar, A. Sound absorption measurement of road surface with in situ technology. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 88, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijs, E.; de Bree, H.E. An in situ method to measure the acoustic absorption of roads whilst driving. In Proceedings of the German Annual Conference on Acoustics, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 23–26 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, F. An overview of the sources of error in sound power determination using the intensity technique. Appl. Acoust. 1997, 50, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, F.; de Bree, H.E. A comparison of two different sound intensity measurement principles. J. Acoust. Soc. America 2005, 118, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pizzo, A.; Teti, L.; Moro, A.; Bianco, F.; Fredianelli, L.; Licitra, G. Influence of texture on tyre road noise spectra in rubberized pavements. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 159, 107080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Castro, F.; Iarossi, S.; De Luca, M.; Bernardini, M.; Brambilla, G.; Licitra, G. Life NEREiDE project: Preliminary evaluation of road traffic noise after new pavement laying. In INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings; Institute of Noise Control Engineering: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Volume 259, pp. 5494–5501. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. 11819-1 Acoustics—Measurement of the Influence of Road Surfaces on Traffic Noise—Part 1: Statistical Pass-By Method; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- De Bree, H.E. The Microflown: An acoustic particle velocity sensor. Acoust. Aust. 2003, 31, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, T.W. Modelling the response of a hot-wire anemometer. Appl. Math. Model. 1986, 10, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bree, H.E.; Leussink, P.; Korthorst, T.; Jansen, H.; Lammerink, T.S.; Elwenspoek, M. The μ-flown: A novel device for measuring acoustic flows. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1996, 54, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yntema, D.R.; Druyvesteyn, W.F.; Elwenspoek, M. A four particle velocity sensor device. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocker, M.J.; Hanson, D.; Li, Z.; Karjatkar, R.; Vissamraju, K.S. Measurement of acoustical and mechanical properties of porous road surfaces and tire and road noise. Transp. Res. Rec. 2004, 1891, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).