Low-Cost Sensors for Urban Noise Monitoring Networks—A Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
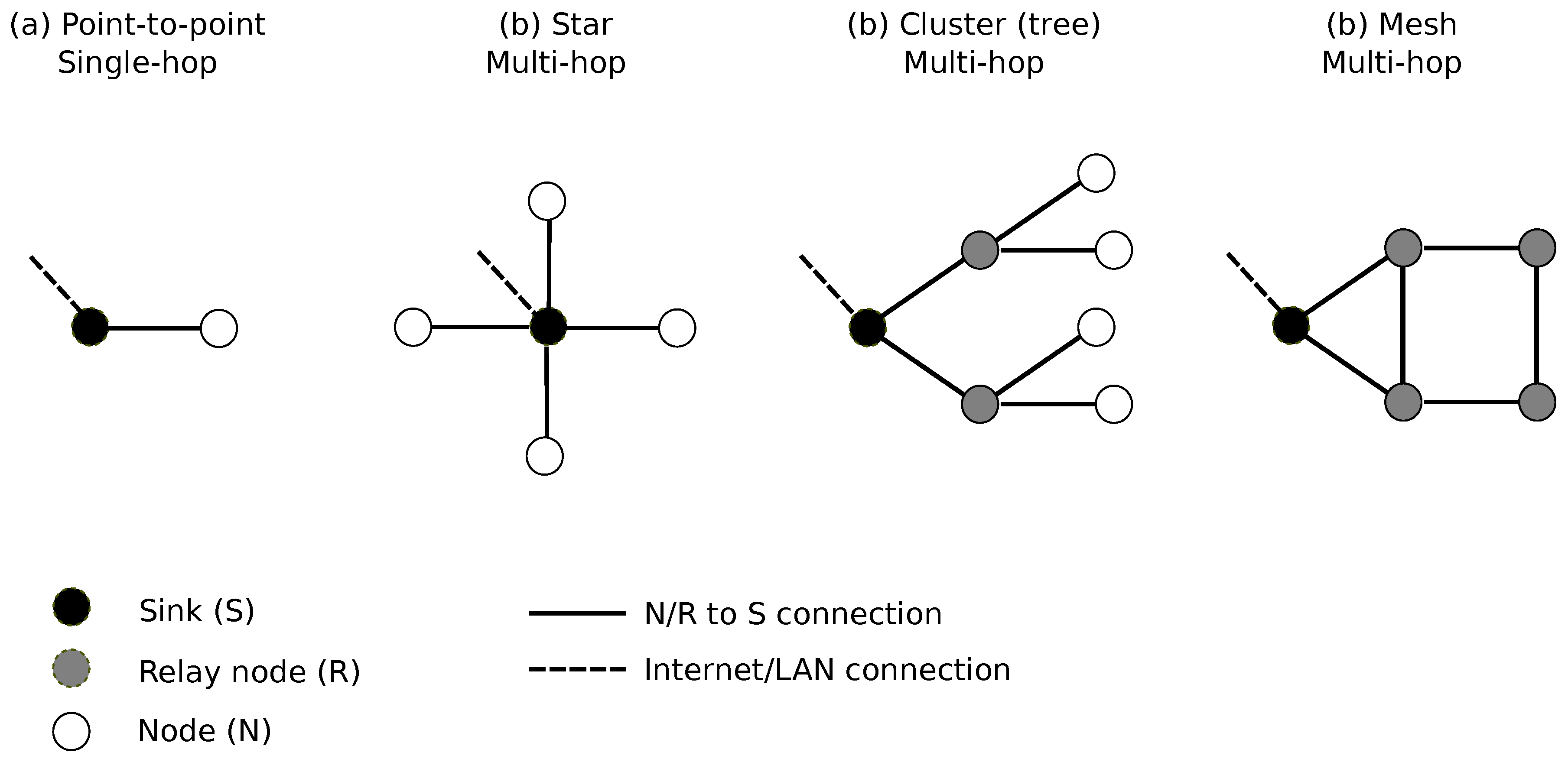
2.1. Sensor Networks: Definitions
- The network can be made up of several sinks. In this case, a group of identified nodes transmit the produced data to a specific sink. All sinks then transmit data to the servers. Another possible option is to consider that a node can choose the sink according to particular constraints, such as availability, proximity, sink load...
- The transmission of data from one node to the sink can be relayed using one or more nodes. The node then acts simultaneously as a sensor and a relay. This defines a multi-hop sensor network, as opposed to single-hop sensor network. The management of data transmission from the nodes to a given sink is then governed by relatively complex routing protocols that depend on the selected topology, such as point-to-point, star or mesh topologies.
- The nodes and the sinks may be mobile. The network is then defined mobile sensor network, as opposed to a static network. The term ’mobile’ must be considered in two ways: (1) continuously ’mobile’: a node moves continuously over time (like a sensor installed on a vehicle); (2) occasionally: a node is moved from one static position to another static position, for a long measurement time, in which case the network is always considered as a static network.
- Data transmission from a node to a sink can be performed in wired or wireless mode. In the latter case, the network is defined as a wireless acoustic sensor network (WASN). Nowadays, the wireless transmission mode is almost the main part of sensor networks for environmental monitoring. Data transmission from a sink to the server can also be carried out using one of these two transmission modes. Nodes and sinks may also simultaneously include several wireless transmission protocols, where some protocols get involved in the case of failure of the main protocol.
- The type of power supply of the nodes can also give rise to several variants: via a public or private power grid, by exchangeable battery, power supply by rechargeable battery from an external renewable energy source (solar, wind).
- Several families of nodes can also be considered, each with its own technical characteristics (measurement characteristics, processing power, power supply mode...). In this case, we are talking about a heterogeneous sensor network, to be opposed to a homogeneous network.
2.2. Low-Cost Noise Sensors: Literature Review
2.3. Synthesis
2.3.1. General Considerations
2.3.2. Sensor Platform
2.3.3. Data Transmission Protocol
2.3.4. Microphones
2.3.5. Frequency Weighting
2.3.6. Frequency Equalization
2.3.7. Calibration
2.3.8. Noise Indicators
2.3.9. Meteorological and Outdoor Conditions Effects
3. Noise Sensor Design for Low-Cost Networks
3.1. Expected Characteristics of Noise Sensors
3.1.1. Acoustic Measurement Accuracy
3.1.2. Acoustic Indicators
3.2. Sensor Platform and Components
3.2.1. Wired Sensor Platform
3.2.2. Wireless Sensor Platform
3.2.3. Microphone and ADC
3.2.4. Noise Floor Enhancement
3.2.5. Mass Storage
3.2.6. Data Transmission Protocol
3.2.7. Additional Sensors
3.3. Sensor Life
3.4. Power Resources
3.5. Acoustic Calibration
3.6. Additional Challenges
3.6.1. Detecting Network Defaults
3.6.2. Temporal Sparse Sampling Strategies
3.6.3. Optimizing Sensor Locations and Network Deployment
(1) Spatial Representativeness and Interpolation
(2) Best Sensor Location
3.6.4. Considering Hybrid Networks
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACI | Acoustic complexity index |
| ADC | Analog-to-digital converter |
| AOP | Acoustic overload point |
| ASIC | Application specific integrated circuit |
| CPU | Central processing unit |
| ECM | Electret condenser microphone |
| EIN | Equivalent input noise |
| GSM | Global system for mobile communications |
| FFT | Fast Fourier transformation |
| FGPA | Floating-point-gate-array |
| HD | Hard disk |
| I2S | Integrated interchip sound |
| IT | Information technology |
| IoT | Internet of things |
| LAN | Local area network |
| MCU | Microcontroller unit |
| MEMS | Micro-electrical-mechanical systems |
| NPL | National Physical Laboratory |
| NSN | Noise sensors networks |
| OS | Operating system |
| PC | Personal computer |
| PCB | Printed circuit board |
| PDM | Pulse density modulated |
| PLC | Power-line communication |
| POC | Proof-of-concept |
| POE | Power over Ethernet |
| PSR | Power supply rejection |
| PSRR | Power supply rejection ratio |
| RF | Radio-frequency |
| R-Pi | Raspberry Pi |
| SD | Secure digital |
| SIM | Subscriber identity module |
| SN | Sensors networks |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| SSD | Solid-state drive |
| TFSD | Time and frequency second derivative |
| THD | Total harmonic distortion |
| USB | Universal serial bus |
| Wi-Fi | Wireless fidelity |
| WASN | Wireless acoustic sensor network |
References
- WHO Regional Office for Europe. Environmental Noise Guidelines for the European Region; World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, P.; Palou, J. Directive 2002/49/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 June 2002 relating to the assessment and management of environmental noise—Declaration by the Commission in the Conciliation Committee on the Directive relating to the assessment and management of environmental noise. Annex I OJ 2002, 189, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, J.; Marquis-Favre, C.; Dubois, D.; Pierrette, M. Road Traffic in Urban Areas: A Perceptual and Cognitive Typology of Pass-By Noises. Acta Acustica Acustica 2012, 98, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gille, L.A.; Marquis-Favre, C.; Klein, A. Noise Annoyance Due To Urban Road Traffic with Powered-Two-Wheelers: Quiet Periods, Order and Number of Vehicles. Acta Acustica Acustica 2016, 102, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumond, P.; Can, A.; Mallet, V.; De Coensel, B.; Ribeiro, C.; Botteldooren, D.; Lavandier, C. Kriging-based spatial interpolation from measurements for sound level mapping in urban areas. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 5, 2847–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mietlicki, F.; Mietlicki, C.; Sineau, M. An Innovative Approach for long term environmental noise measurement: RUMEUR Network in the Paris Region. In Proceedings of the 10th European Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering, Maastricht, The Netherlands, 31 May–3 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- International Electrotechnical Commission Electroacoustics—Sound Level Meters—Part 1: Specifications (IEC 61672-1). 2013. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/5708 (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Hart, J.K.; Martinez, K. Environmental Sensor Networks: A revolution in the earth system science? Earth Sci. Rev. 2006, 78, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrenetxea, G.; Ingelrest, F.; Schaefer, G.; Vetterli, M. Wireless Sensor Networks for Environmental Monitoring: The SensorScope Experience. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Zurich Seminar on Communications, Zurich, Switzerland, 12–14 March 2008; pp. 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, B.; Rehmani, M.H. Applications of wireless sensor networks for urban areas: A survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2016, 60, 192–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, F.; Dauwe, S.; Cuong, N.T.; Cariolaro, D.; Touhafi, A.; Dhoedt, B.; Botteldooren, D.; Steenhaut, K. Towards an Environmental Measurement Cloud: Delivering Pollution Awareness to the Public. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2014, 10, 541360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.; Geraghty, D.; Humphreys, I.; Farrell, S. Assessing Environmental Impact of Transport Noise with Wireless Sensor Networks. Transp. Res. Rec. 2008, 2058, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.C.; Galatioto, F. Novel wireless pervasive sensor network to improve the understanding of noise in street canyons. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, G.; Dong, R.; Wang, H. Traffic noise monitoring and simulation research in Xiamen City based on the Environmental Internet of Things. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2013, 20, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manvell, D.; Ballarin Marcos, L.; Stapelfeldt, H.; Sanz, R. Sadmam – Combining measurements and calculations to map noise in Madrid. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering, Prague, Czech Republic, 22–26 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, E.; King, E.A. Smartphone-based noise mapping: Integrating sound level meter app data into the strategic noise mapping process. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellucci, P.; Peruzzi, L.; Zambon, G. LIFE DYNAMAP project: The case study of Rome. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 117 Pt B, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, R.; Mallet, V.; Issarny, V. Assimilation of mobile phone measurements for noise mapping of a neighborhood. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 144, 1279–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benocci, R.; Confalonieri, C.; Roman, H.E.; Angelini, F.; Zambon, G. Accuracy of the Dynamic Acoustic Map in a Large City Generated by Fixed Monitoring Units. Sensors 2020, 20, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Van Renterghem, T.; De Coensel, B.; Botteldooren, D. Dynamic noise mapping: A map-based interpolation between noise measurements with high temporal resolution. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 101, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botteldooren, D.; De Coensel, B.; Oldoni, D.; Renterghem, T.; Dauwe, S. Sound monitoring networks new style. In Proceedings of the Acoustics, Gold Coast, Australia, 2–4 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Botteldooren, D.; Van renterghem, T.; Oldoni, D.; Samuel, D.; Dekoninck, L.; Thomas, P.; Wei, W.; Boes, M.; De Coensel, B.; De Baets, B.; et al. The internet of sound observatories. Proc. Mtgs. Acoust. 2013, 19, 040140. [Google Scholar]
- Oldoni, D.; De Coensel, B.; Boes, M.; Rademaker, M.; De Baets, B.; Van Renterghem, T.; Botteldooren, D. A computational model of auditory attention for use in soundscape research. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, J.; Bello, J.P. Unsupervised feature learning for urban sound classification. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 19–24 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Socoró, J.C.; Alías, F.; Alsina-Pagès, R.M. An Anomalous Noise Events Detector for Dynamic Road Traffic Noise Mapping in Real-Life Urban and Suburban Environments. Sensors 2017, 17, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gontier, F.; Lagrange, M.; Aumond, P.; Can, A.; Lavandier, C. An Efficient Audio Coding Scheme for Quantitative and Qualitative Large Scale Acoustic Monitoring Using the Sensor Grid Approach. Sensors 2017, 17, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offenhuber, D.; Auinger, S.; Seitinger, S.; Muijs, R. Los Angeles noise array—Planning and design lessons from a noise sensing network. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloaguen, J.R.; Can, A.; Lagrange, M.; Petiot, J.F. Road traffic sound level estimation from realistic urban sound mixtures by Non-negative Matrix Factorization. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 143, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, J.P.; Silva, C.; Nov, O.; Dubois, R.L.; Arora, A.; Salamon, J.; Mydlarz, C.; Doraiswamy, H. SONYC: A System for Monitoring, Analyzing, and Mitigating Urban Noise Pollution. Commun. ACM 2019, 62, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M.M.; Shouraki, S.B.; Iranmehr, E.; Linares-Barranco, B. Sound Source Localization in Wide-range Outdoor Environment Using Distributed Sensor Network. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Cao, Q.; Huang, C.; Wang, L.; Abdelzaher, T.F.; Stankovic, J.A.; Ward, M. Design, Implementation, and Evaluation of EnviroMic: A Storage-centric Audio Sensor Network. ACM Trans. Sen. Netw. 2009, 5, 22:1–22:35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.S.; Ewers, R.M.; Jones, N.S.; Orme, C.D.L.; Picinali, L. Robust, real—time and autonomous monitoring of ecosystems with an open, low-cost, networked device. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 2383–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Pfersich, S.; Eldridge, A.; Zhou, J.; Tian, D.; Leung, V.C.M. Wireless acoustic sensor networks and edge computing for rapid acoustic monitoring. IEEE J. Autom. Sin. 2019, 6, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauwe, S.; Van Renterghem, T.; Botteldooren, D.; Dhoedt, B. Multiagent-Based Data Fusion in Environmental Monitoring Networks. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2012, 8, 324935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mydlarz, C.; Sharma, M.; Lockerman, Y.; Steers, B.; Silva, C.; Bello, J.P. The Life of a New York City Noise Sensor Network. Sensors 2019, 19, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, S.; Ostermaier, B.; Adelmann, R. On the Use of Sensor Nodes and Mobile Phones for the Assessment of Noise Pollution Levels in Urban Environments. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Networked Sensing Systems, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 17–19 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Alsina-Pagès, R.M.; Hernandez-Jayo, U.; Alías, F.; Angulo, I. Design of a Mobile Low-Cost Sensor Network Using Urban Buses for Real-Time Ubiquitous Noise Monitoring. Sensors 2016, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risojević, V.; Rozman, R.; Pilipović, R.; Češnovar, R.; Bulić, P. Accurate Indoor Sound Level Measurement on a Low-Power and Low-Cost Wireless Sensor Node. Sensors 2018, 18, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alías, F.; Alsina-Pagès, R.M. Review of Wireless Acoustic Sensor Networks for Environmental Noise Monitoring in Smart Cities. J. Sens. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, M.J.; Scanaill, C.N. Sensor Network Topologies and Design Considerations. In Sensor Technologies: Healthcare, Wellness, and Environmental Applications; McGrath, M.J., Scanaill, C.N., Eds.; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 79–95. [Google Scholar]
- Guillaume, G.; Can, A.; Petit, G.; Fortin, N.; Palominos, S.; Gauvreau, B.; Bocher, E.; Picaut, J. Noise mapping based on participative measurements. Noise Mapp. 2016, 3, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, S.; Ostermaier, B.; Vitaletti, A. First Experiences Using Wireless Sensor Networks for Noise Pollution Monitoring. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Real-World Wireless Sensor Networks, Glasgow, Scotland, 1 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Santini, S.; Vitaletti, A. Wireless sensor networks for environmental noise monitoring. Fachgespräch Sensornetzwerke 2007, 3, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Filipponi, L.; Santini, S.; Vitaletti, A. Data Collection in Wireless Sensor Networks for Noise Pollution Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems, Santorini Island, Greece, 11–14 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Barham, R.; Goldsmith, M. Performance of a new MEMS measurement microphone and its potential application. In Proceedings of the Institute of Acoustics, Spring Conference, Reading, UK, 10–11 April 2008; pp. 370–377. [Google Scholar]
- Barham, R.; Goldsmith, M.; Chan, M.; Simmons, D. Development and performance of a multi-point distributed environmental noise measurement system using MEMS microphones. In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference and Exhibition on Noise Control, Euronoise 2009, Edinburgh, Scotland, UK, 26–28 October 2009; pp. 1039–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Barham, R.; Chan, M.; Cand, M. Practical experience in noise mapping with a MEMS microphone based distributed noise measurement system. INTER-NOISE NOISE-CON Congr. Conf. Proc. 2010, 2010, 4725–4733. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, B.; Barham, R.; Sheridan, S.; Sotirakopoulos, K. Exploring the ’big acoustic data’ generated by an acoustic sensor network deployed at a crossrail construction site. In Proceedings of the 24th International Congress on Sound and Vibration (ICSV24), London, UK, 23–27 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hakala, I.; Kivelä, I.; Ihalainen, J.; Luomala, J.; Gao, C. Design of Low-Cost Noise Measurement Sensor Network: Sensor Function Design. In Proceedings of the 2010 First International Conference on Sensor Device Technologies and Applications, Venice/Mestre, Italy, 18–25 July 2010; pp. 172–179. [Google Scholar]
- Hakala, I.; Tikkakoski, M.; Kivelä, I. Wireless Sensor Network in Environmental Monitoring—Case Foxhouse. In Proceedings of the 2008 Second International Conference on Sensor Technologies and Applications (sensorcomm 2008), Cap Esterel, France, 25–31 August 2008; pp. 202–208. [Google Scholar]
- Kivelä, I.; Gao, C.; Luomala, J.; Ihalainen, J.; Hakala, I. Design of Networked Low-Cost Wireless Noise Measurement Sensors. Int. J. Sens. Transducers 2011, 10, 171–190. [Google Scholar]
- Kivelä, I.; Gao, C.; Luomala, J.; Hakala, I. Design of noise measurement sensor network: Networking and communication part. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Sensor Technologies and Applications, Nice/Saint Laurent du Var, France, 21–27 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kivelä, I.; Hakala, I. Area-based environmental noise measurements with a wireless sensor network. In Proceedings of the 10th European Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering, Maastricht, The Netherlands, 31 May–3 June 2015; pp. 218–220. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, W.M.; Jarvis, S.A. Energy harvesting noise pollution sensing WSN mote: Survey of capabilities and limitations. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Wireless Sensor (ICWISE), Kuching, Sarawak, Malaysia, 2–4 December 2013; pp. 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Polastre, J.; Szewczyk, R.; Culler, D. Telos: Enabling ultra-low power wireless research. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 25–27 April 2005; pp. 364–369. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, W.M.; Jarvis, S.A. On the design of an energy-harvesting noise-sensing WSN mote. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2014, 2014, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariscal-Ramirez, J.A.; Fernandez-Prieto, J.A.; Gadeo-Martos, M.A.; Canada-Bago, J. Knowledge-based wireless sensors using sound pressure level for noise pollution monitoring. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications, Córdoba, Spain, 22–24 November 2011; pp. 1032–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Mariscal-Ramirez, J.A.; Fernandez-Prieto, J.A.; Canada-Bago, J.; Gadeo-Martos, M.A. A New Algorithm to Monitor Noise Pollution Adapted to Resource-constrained Devices. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2015, 74, 9175–9189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Garcia, J.; Felici-Castell, S.; Perez-Solano, J.J.; Cobos, M.; Navarro, J.M. Low-Cost Alternatives for Urban Noise Nuisance Monitoring Using Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Garcia, J.; Pérez-Solano, J.J.; Cobos-Serrano, M.; Navarro-Camba, E.A.; Felici-Castell, S.; Soriano-Asensi, A.; Montes-Suay, F. Spatial Statistical Analysis of Urban Noise Data from a WASN Gathered by an IoT System: Application to a Small City. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega-Linares, J.E.; Navarro Ruiz, J.M. On the Application of the Raspberry Pi as an Advanced Acoustic Sensor Network for Noise Monitoring. Electronics 2016, 5, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mydlarz, C.; Salamon, J.; Bello, J.P. The implementation of low-cost urban acoustic monitoring devices. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 117, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckens, C.; Porter, C.; Rink, T. Wireless Sensor Networks for Long-Term Monitoring of Urban Noise. Sensors 2018, 18, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartalucci, C.; Borchi, F.; Carfagni, M.; Furferi, R.; Governi, L.; Lapini, A.; Volpe, Y.; Curcuruto, S.; Mazzocchi, E.; Marsico, G.; et al. LIFE MONZA: Project description and actions’ updating. Noise Mapp. 2018, 5, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartalucci, C.; Borchi, F.; Carfagni, M.; Furferi, R.; Governi, L.; Silvaggio, R.; Curcuruto, S.; Nencini, L. Design of a prototype of a smart noise monitoring system. In Proceedings of the 24th International Congress on Sound and Vibration (ICSV24), London, UK, 23–27 July 2017; pp. 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Silvaggio, R.; Curcuruto, S.; Bellomini, R.; Luzzi, S.; Borchi, F.; Bartalucci, C. Noise Low Emission Zone implementation in urban planning: results of monitoring activities in pilot area of LIFE MONZA project. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Congress on Acoustics (ICA), Aachen, Germany, 8–13 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ardouin, J.; Charpentier, L.; Lagrange, M.; Gontier, F.; Fortin, N.; Écotière, D.; Picaut, J.; Mietlicki, F. An innovative low cost sensors for urban sound monitoring. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 2018, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–29 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- López, J.M.; Alonso, J.; Asensio, C.; Pavón, I.; Gascó, L.; de Arcas, G. A Digital Signal Processor Based Acoustic Sensor for Outdoor Noise Monitoring in Smart Cities. Sensors 2020, 20, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Yu, D. Digital Environmental Noise Monitoring System Based on B/S Architecture and Floating-Point DSP. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Tianjin, China, 17–19 October 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Blythe, P.; Neasham, J.; Sharif, B.; Watson, P.; Bell, M.C.; Edwards, S.; Suresh, V.; Wagner, J.; Bryan, H. An environmental sensor system for pervasively monitoring road networks. In Proceedings of the IET Road Transport Information and Control Conference and the ITS United Kingdom Members’ Conference (RTIC 2008), Manchester, UK, 20–22 May 2008; p. 91. [Google Scholar]
- Farrés, J.C. Barcelona noise monitoring network. In Proceedings of the 10th European Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering, Maastricht, The Netherlands, 1–3 June 2015; pp. 2315–2320. [Google Scholar]
- Sevillano, X.; Socoró, J.C.; Alías, F.; Bellucci, P.; Peruzzi, L.; Radaelli, S.; Coppi, P.; Nencini, L.; Cerniglia, A.; Bisceglie, A.; et al. DYNAMAP – Development of low cost sensors networks for real time noise mapping. Noise Mapp. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renterghem, T.V.; Thomas, P.; Dominguez, F.; Dauwe, S.; Touhafi, A.; Dhoedt, B.; Botteldooren, D. On the ability of consumer electronics microphones for environmental noise monitoring. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widder, J. Basic Principles of MEMS Microphones. 2014. Available online: https://www.edn.com/basic-principles-of-mems-microphones/ (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- STMicroelectronics. AN4427—Application Note—Gasket Design for Optimal Acoustic Performance in MEMS Microphones. Available online: https://www.st.com/content/ccc/resource/technical/document/application_note/e9/86/75/b2/8e/fd/48/69/DM00103201.pdf/files/DM00103201.pdf/jcr:content/translations/en.DM00103201.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2019).
- Nencini, L.; Bellucci, P.; Peruzzi, L. Identification of failure markers in noise measurement low cost devices. In Proceedings of the 45th International Congress and Exposition of Noise Control Engineering, Inter-Noise, Hamburg, Germany, 21–24 August 2016; pp. 6362–6369. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, M.A.; Shah, I.A.; Lee, D.G.; Hur, S. Design Approaches of MEMS Microphones for Enhanced Performance. J. Sens. 2019, 2019, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbi, J.; Marusic, S.; Rao, A.S.; Law, Y.W.; Palaniswami, M. A pilot study of urban noise monitoring architecture using wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), Mysore, India, 22–25 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Jin, H.; Guo, L.; Wu, S.; Gu, T. Audio-on-demand over wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 20th International Workshop on Quality of Service, Coimbra, Portugal, 4–5 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bartalucci, C.; Borchi, F.; Carfagni, M.; Furferi, R.; Governi, L.; Lapini, A.; Bellomini, R.; Luzzi, S.; Nencini, L. The smart noise monitoring system implemented in the frame of the Life MONZA project. In Proceedings of the 11th European Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 27–31 May 2018; pp. 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Broas, M.; Raami, J.; Mattila, T.T.; Paulasto-Kröckel, M. Reliability assessment of a MEMS microphone under mixed flowing gas environment and shock impact loading. Microelectron. Reliab. 2014, 54, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumond, P.; Can, A.; De Coensel, B.; Ribeiro, C.; Botteldooren, D.; Lavandier, C. Modeling soundscape pleasantness using perceptual assessments and acoustic measurements along paths in urban context. Acta Acustica Acustica 2017, 103, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspberry Pi 4 Specs and Benchmarks. Available online: https://magpi.raspberrypi.org/articles/raspberry-pi-4-specs-benchmarks (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- Lewis, J. Analog and Digital MEMS Microphone Design Considerations. 2013. Available online: https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/technical-articles/Analog-and-Digital-MEMS-Microphone-Design-Considerations-MS-2472.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- Bluetooth Technology Website. Available online: https://www.bluetooth.com/ (accessed on 28 February 2020).
- Wi-Fi Alliance. Available online: https://www.wi-fi.org/ (accessed on 28 February 2020).
- Zigbee Alliance. Available online: https://zigbeealliance.org/ (accessed on 28 February 2020).
- LoRa Alliance. Available online: https://lora-alliance.org/ (accessed on 28 February 2020).
- Sigfox—The Global Communications Service Provider for the Internet of Things (IoT). Available online: https://www.sigfox.com/en (accessed on 28 February 2020).
- Guide: Lifetime Cost of Ownership for Class 1 Sound Level Meters. Available online: https://blog.bksv.com/guide-lifetime-cost-of-ownership-for-class-1-sound-level-meters (accessed on 28 February 2020).
- Jordan, D.C.; Kurtz, S.R. Photovoltaic Degradation Rates-an Analytical Review: Photovoltaic degradation rates. Prog. Photovoltaics Res. Appl. 2013, 21, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaine, F.; Lebental, B.; Rivano, H. In Situ Calibration Algorithms for Environmental Sensor Networks: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 5968–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrés, J.C.; Novas, J.C. Issues and challenges to improve the Barcelona Noise Monitoring Network. In Proceedings of the 11th European Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 27–31 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dauwe, S.; Oldoni, D.; Baets, B.D.; Renterghem, T.V.; Botteldooren, D.; Dhoedt, B. Multi-criteria anomaly detection in urban noise sensor networks. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laso, P.M.; Brosset, D.; Puentes, J. Analysis of quality measurements to categorize anomalies in sensor systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 Computing Conference, London, UK, 18–20 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed, W.; Elhoseny, M.; Sabbeh, S.; Riad, A. Self-maintenance model for Wireless Sensor Networks. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 70, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Wan, S.; Umer, T. Distributed Fault Detection for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Support Vector Regression. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2018, 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, A.; Aumond, P.; De Coensel, B.; Ribeiro, C.; Botteldooren, D.; Lavandier, C. Probabilistic Modelling of the Temporal Variability of Urban Sound Levels. Acta Acustica Acustica 2018, 104, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrigón Morillas, J.M.; Gómez Escobar, V.; Méndez Sierra, J.A.; Vílchez Gómez, R.; Trujillo Carmona, J. An environmental noise study in the city of Cáceres, Spain. Appl. Acoust. 2002, 63, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, A.; Dekoninck, L.; Botteldooren, D. Measurement network for urban noise assessment: Comparison of mobile measurements and spatial interpolation approaches. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 83, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozalo, G.R.; Morillas, J.M.B.; Escobar, V.G.; Vilchez-Gómez, R.; Sierra, J.A.M.; Rio, F.J.C.D.; Gajardo, C.P. Study of the Categorisation Method Using Long-term Measurements. Arch. Acoust. 2013, 38, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Luo, T.; Behm, H.; Coppack, T. Spatiotemporal variability of soundscapes in a multiple functional urban area. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2013, 115, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, F.; Li, Y.; Johnson, S.; Johnson, J.; Varughese, S.; Copes, R.; Liu, F.; Wu, H.J.; Hou, R.; Chen, H. Temporal and spatial variability of traffic-related noise in the City of Toronto, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Pan, Z.; Yang, H.; Hou, G.; Wei, W. Optimizing stations location for urban noise continuous intelligent monitoring. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 127, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, S.; Seto, E.; Northcross, A.; Quinn, N.W.T.; Convertino, M.; Jones, R.L.; Maier, H.R.; Schlink, U.; Steinle, S.; Vieno, M.; et al. Integrating modelling and smart sensors for environmental and human health. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2015, 74, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahzadeh, S.; Navimipour, N.J. Deployment strategies in the wireless sensor network: A comprehensive review. Comput. Commun. 2016, 91–92, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketshabetswe, L.K.; Zungeru, A.M.; Mangwala, M.; Chuma, J.M.; Sigweni, B. Communication protocols for wireless sensor networks: A survey and comparison. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picaut, J.; Fortin, N.; Bocher, E.; Petit, G.; Aumond, P.; Guillaume, G. An open-science crowdsourcing approach for producing community noise maps using smartphones. Build. Environ. 2019, 148, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.; King, E.A.; Curn, J.; Cahill, V.; Bustamante, F.; Rice, H.J. Environmental noise mapping using measurements in transit. In Proceedings of the ISMA 2010, Leuven, Belgium, 20–22 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Di Francesco, M.; Das, S.K.; Anastasi, G. Data Collection in Wireless Sensor Networks with Mobile Elements: A Survey. ACM Trans. Sen. Netw. 2011, 8, 7:1–7:31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, A.; Dekoninck, L.; Rademaker, M.; Van Renterghem, T.; De Baets, B.; Botteldooren, D. Noise measurements as proxies for traffic parameters in monitoring networks. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 410–411, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, A.; Rademaker, M.; Van Renterghem, T.; Mishra, V.; Van Poppel, M.; Touhafi, A.; Theunis, J.; De Baets, B.; Botteldooren, D. Correlation analysis of noise and ultrafine particle counts in a street canyon. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, Z.; Kheirbek, I.; Clougherty, J.E.; Ito, K.; Matte, T.; Markowitz, S.; Eisl, H. Noise, air pollutants and traffic: Continuous measurement and correlation at a high-traffic location in New York City. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S. Spatio-temporal covariation of urban particle number concentration and ambient noise. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5518–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Ketzel, M.; Kakosimos, K.; Sørensen, M.; Jensen, S.S. Road traffic air and noise pollution exposure assessment—A review of tools and techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalles, G.; Kamel, Y.; Anderson, I.; Lee, M.; Neil, C.; Henry, M.; Cappiello, S.; Mydlarz, C.; Baglione, M.; Roginska, A. A Low-Cost High-Quality MEMS Ambisonic Microphone. Audio Eng. Soc. 2017, 143, 9857. [Google Scholar]
| Reference | Node Plateform | MCU | N-2-S | Mic. | ADC | Power | Pre-Processing | Cost | Goal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barham and Goldsmith [45] (2008) | FPGA | GSM | a-M | B (15d) | A-w, C-w, Tc | 100 EUR | Op-WSN | ||
| Santini et al. [42] (2008) | Tmote | 16-bits | 802.15.4 | ECM | 12-bit (8 kHz) | AA-B | POC | ||
| McDonald et al. [12] (2008) | Triton | 32-bits | 802.11b | ECM | 16-bit (49 kHz) | A-w | 130 GBP | Op-WSN | |
| Hakala et al. [49] (2010) | CiNet | 8-bits | 802.15.4 | ECM | 10-bit (33 kHz) | AA-B (ds) | A-w, G, Cal | Op-WSN | |
| Tan and Jarvis [54] (2013) | TelosB | 16-bits | 802.15.4 | ECM | 12-bit (33 kHz) | B/S | POC | ||
| Tan and Jarvis [56] (2014) | TelosB | 16-bits | 802.15.4 | a-M | 12-bit (33 kHz) | B/S | POC | ||
| Segura-Garcia et al. [59] (2015) | Tmote | 16-bits | 802.15.4 | ECM | 12-bit (8/20 kHz) | B (78d) | Cal | 41.45 EUR | POC |
| Segura-Garcia et al. [59] (2015) | R-Pi | 32-bits | 802.11 | ECM | 16-bit (22.05 kHz) | LR20-B (39h) | Cal | Op-WSN | |
| Noriega-Linares and Navarro Ruiz [61] (2016) | R-Pi | 32-bits | wired LAN | ECM | W | Cal, Eq, 1/3 | 121 USD | POC | |
| Alsina-Pagès et al. [37] (2016) | NXP chip | 32-bits | Wi-Fi/GSM | ECM | 12-bit (nc) | B | Design only | ||
| Mydlarz et al. [62] (2017) | mini-PC | 32-bits | Wi-Fi | a-M | 16-bit (44.1 kHz) | W | Eq | 100 USD | POC |
| Risojević et al. [38] (2018) | STM32F0 series | 32-bits | ZigBee | a-M | B (7d) | A-w, G, Cal | 41.45 EUR | Op-WSN | |
| Peckens et al. [63] (2018) | Teensy USB | 32-bits | XBee | ECM | 16-bit (20 kHz) | B (7d) | A-w, G, Cal | 135 USD | POC |
| Ardouin et al. [67] (2018) | STM32L4 series | 32-bits | 802.15.4 | d-M | 16-bit (32 kHz) | B/S | A-w, 1/3, enc | POC | |
| Ardouin et al. [67] (2018) | R-Pi | 32-bits | 802.15.4 | d-M | 16-bit (32 kHz) | W | A-w, 1/3, enc | POC | |
| Silvaggio et al. [66] (2019) | mini-PC | GSM | d-M | B/S,W | A-w, 1/3 | Op-WSN | |||
| Silvaggio et al. [66] (2019) | MCU | GSM | ECM | B/S,W | A-w, 1/3 | Op-WSN | |||
| Mydlarz et al. [62] (2019) | R-Pi | 32-bits | Wi-Fi/POE | d-M | 16-bit (48 kHz) | W | A-w, C-w, 1/3 | 80 EUR | Op-WSN |
| López et al. [68] (2020) | DSP Board | 32-bits | radio (868 MHz) | ECM | 24-bit (108 kHz) | B | Z-w, A-w, C-w, 1/3, 1/1 | Op-WSN |
| Reference | F-Range | Dynamic | L-Range | Residual Noise | Outputs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barham and Goldsmith [45] (2008) | 20–20k Hz | 70 dB | 30–100 dB | 25 dB | L, L (10 mn) |
| Santini et al. [42] (2008) | L | ||||
| McDonald et al. [12] (2008) | L | ||||
| Hakala et al. [49] (2010) | <16.5 kHz | 30–90 dB | L, L | ||
| Tan and Jarvis [54] (2013) | <5 kHz * | 93 dB * | 60 dB * | ||
| Tan and Jarvis [56] (2014) | 100 dB * | 50–60 dB * | Peak | ||
| Segura-Garcia et al. [59] (2015) | <20 kHz | 96 dB | Psychoacoustic metrics | ||
| Noriega-Linares and Navarro Ruiz [61] (2016) | 125–8k Hz * (1/3) | L, L (N=10,50,90), 1/3 | |||
| Alsina-Pagès et al. [37] (2016) | |||||
| Sevillano et al. [72] (2016) | 35–115 dB | L, audio | |||
| Piper et al. [48] (2017) | L | ||||
| Mydlarz et al. [62] (2019, 2017) | 20–20k Hz | 88.1 dBA | 29.9 dBA * | Audio (10 s) | |
| Risojević et al. [38] (2018) | up to 16 kHz * | 72 dB | 50–100 dB * | L | |
| Peckens et al. [63] (2018) | <10 kHz * | 50 dB * | 50 dB * | L (10 mn each 1 hour) | |
| Ardouin et al. [67] (2018) | 20–16k Hz | 35–105 dBA | L, L, 1/3 | ||
| Silvaggio et al. [66] (2019) | 20–20k Hz | 70 dB | 30(40)–100(110) dB | 30–35 dBA | L, 1/3 |
| Mydlarz et al. [62] (2019) | 32–100 dBA | L, L, 1/3, audio (10s) | |||
| López et al. [68] (2020) | up to 8 kHz | 39.1–120.1 dB | L, L, Peak, Max, Min, L (N=1,5,10,50,90,95,99), 1/3, 1/1 |
| Property | Minimal Target | Optimal Target |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement range | 30–105 dB(A) | 30–105 dB(A) |
| Frequency range | 100–12k Hz | 100–16k Hz |
| Integrated sound level | L | L |
| L | ||
| Spectrum | None | 1/3 octave bands |
| Measurement frequency | Continuous | |
| Pre-processing | A-weighting | (A, Z)-weighting |
| Calibration | Calibration | |
| 1/3 octave bands analysis | ||
| Frequency equalization | ||
| Other indicators | Source recognition | |
| Noise event detection | ||
| Additional sensors | Temperature | Temperature |
| Hygrometry | Hygrometry | |
| Price | 50 EUR | 150 EUR |
| Protocol | Bluetooth [85] | Bluetooth LE [85] | Wi-Fi [86] | Wi-Fi [86] | Zigbee and 6LoWPAN [87] | LoRaWAN [88] | Sigfox [89] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specification | 802.15.1 | 802.15.1 | 802.11g | 802.11n | 802.15.4 | LoRa Alliance | Sigfox |
| Frequency | 2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz 5 GHz | 868 MHz (EU) 915 MHz (US) 2.4 GHz | Sub-GHz ISM band 868 MHz in EU | Sub-GHz ISM band 868 MHz in EU |
| Range indoor (m) | 30 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 30 | >100 | >100 |
| Range max (m) | 100 | 50 | 75 | 125 | 1500 | >10,000 | >10,000 |
| Data speed max | 3 Mbit/s | 1 Mbit/s | 54 Mbit/s | 540 Mbit/s | 250 kbit/s | 11 kbit/s | 100 bit/s |
| Data speed typ. | 2.1 Mbit/s | 270 kbit/s | 25 Mbit/s | 200 Mbit/s | 150 kbit/s | 300–11k bit/s | 100 bit/s |
| Peak current | 150 mA | 20 mA | 150 mA | 150 mA | 50 mA | 25 mA | 25 mA |
| Sleep current | 5 mA | 1 A | 100 A | 100 A | 5 A | 4 A | 4 A |
| Battery life | Month | Year | Day | Day | Month/Year | Years | Years |
| Network topologies | Star | Star | Star | Star, Tree, Mesh | Star | Star | |
| Applications | Headsets Computer peripherals | Mobile phones Sport trackers eHealth devices Wireless sensors | PC (networking) WLAN | Same as 802.11g with improved performances Outdoor LAN | Smart home Wireless sensor networks Smart metering | Smart building Smart city | Smart building Smart city |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Picaut, J.; Can, A.; Fortin, N.; Ardouin, J.; Lagrange, M. Low-Cost Sensors for Urban Noise Monitoring Networks—A Literature Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082256
Picaut J, Can A, Fortin N, Ardouin J, Lagrange M. Low-Cost Sensors for Urban Noise Monitoring Networks—A Literature Review. Sensors. 2020; 20(8):2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082256
Chicago/Turabian StylePicaut, Judicaël, Arnaud Can, Nicolas Fortin, Jeremy Ardouin, and Mathieu Lagrange. 2020. "Low-Cost Sensors for Urban Noise Monitoring Networks—A Literature Review" Sensors 20, no. 8: 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082256
APA StylePicaut, J., Can, A., Fortin, N., Ardouin, J., & Lagrange, M. (2020). Low-Cost Sensors for Urban Noise Monitoring Networks—A Literature Review. Sensors, 20(8), 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20082256





