FRET-Based Aptasensor for the Selective and Sensitive Detection of Lysozyme
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Aptasensor
2.3. Preparation of Functionalized Flow Cell
2.4. Aptasensor Immobilization and Single-Molecule Imaging
2.5. Single-Molecule Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
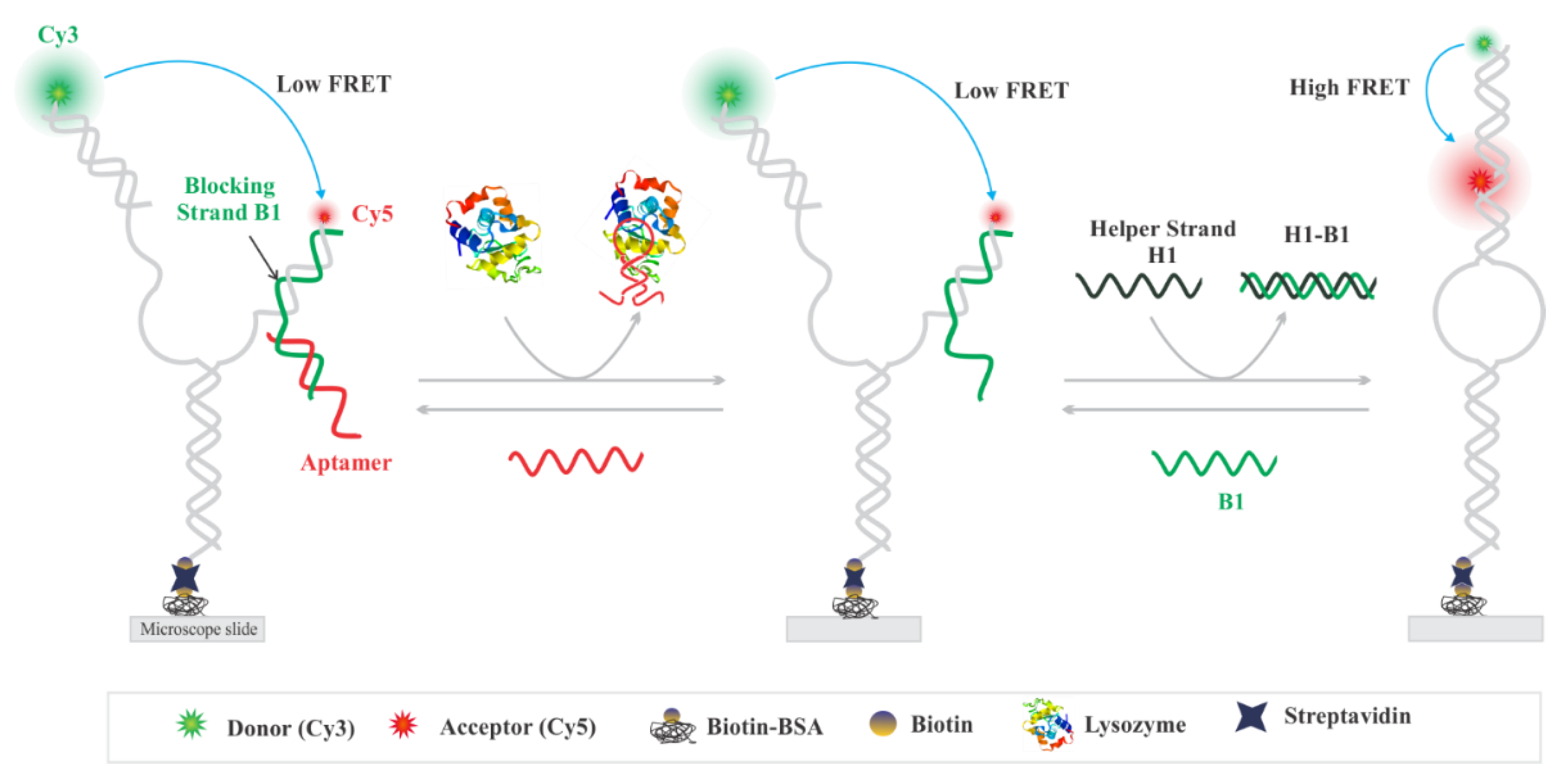
3.1. Experimental Design
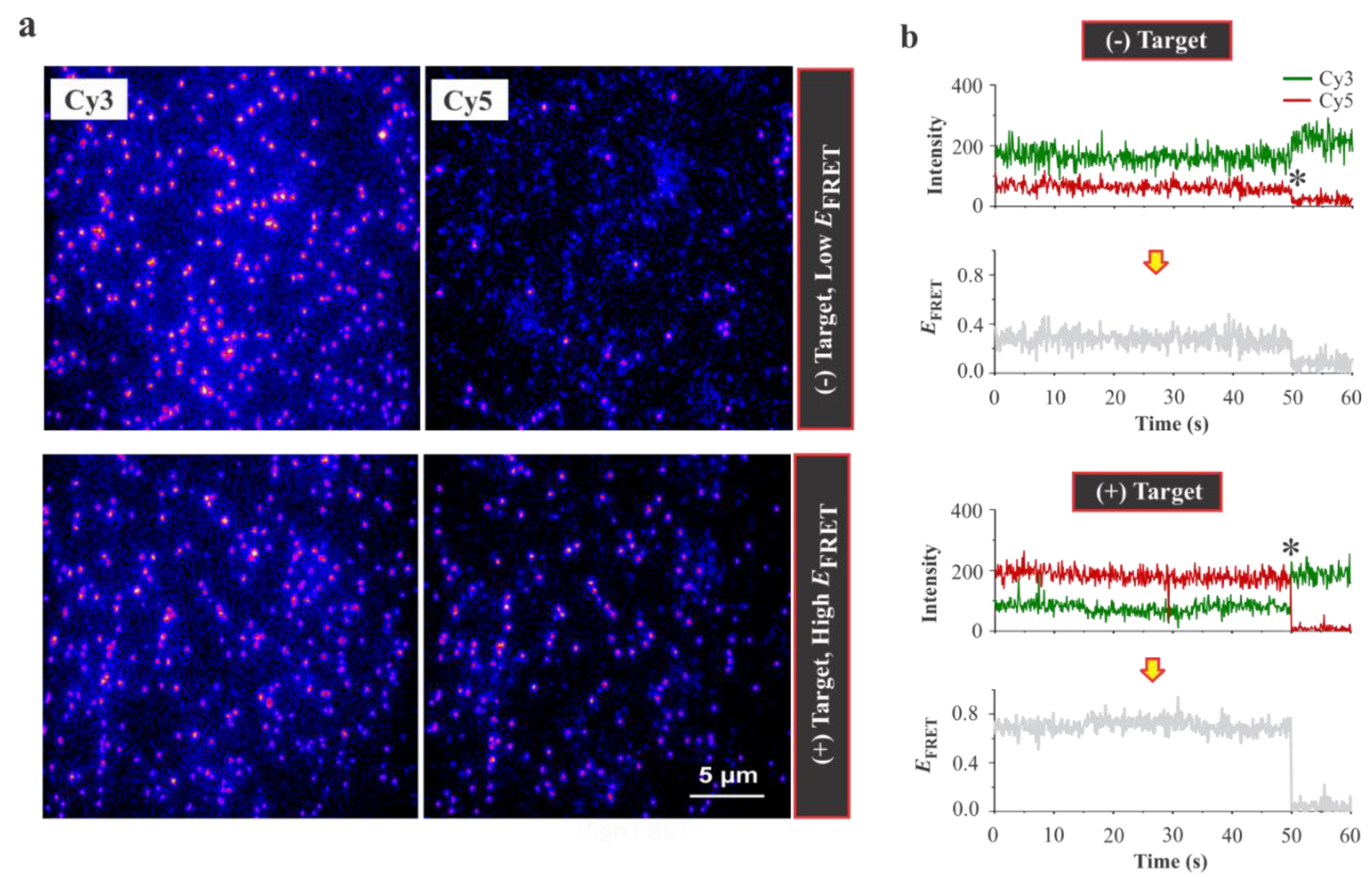
3.2. Single-Molecule Analysis of Aptasensor
3.3. Design Feasibility Assessment
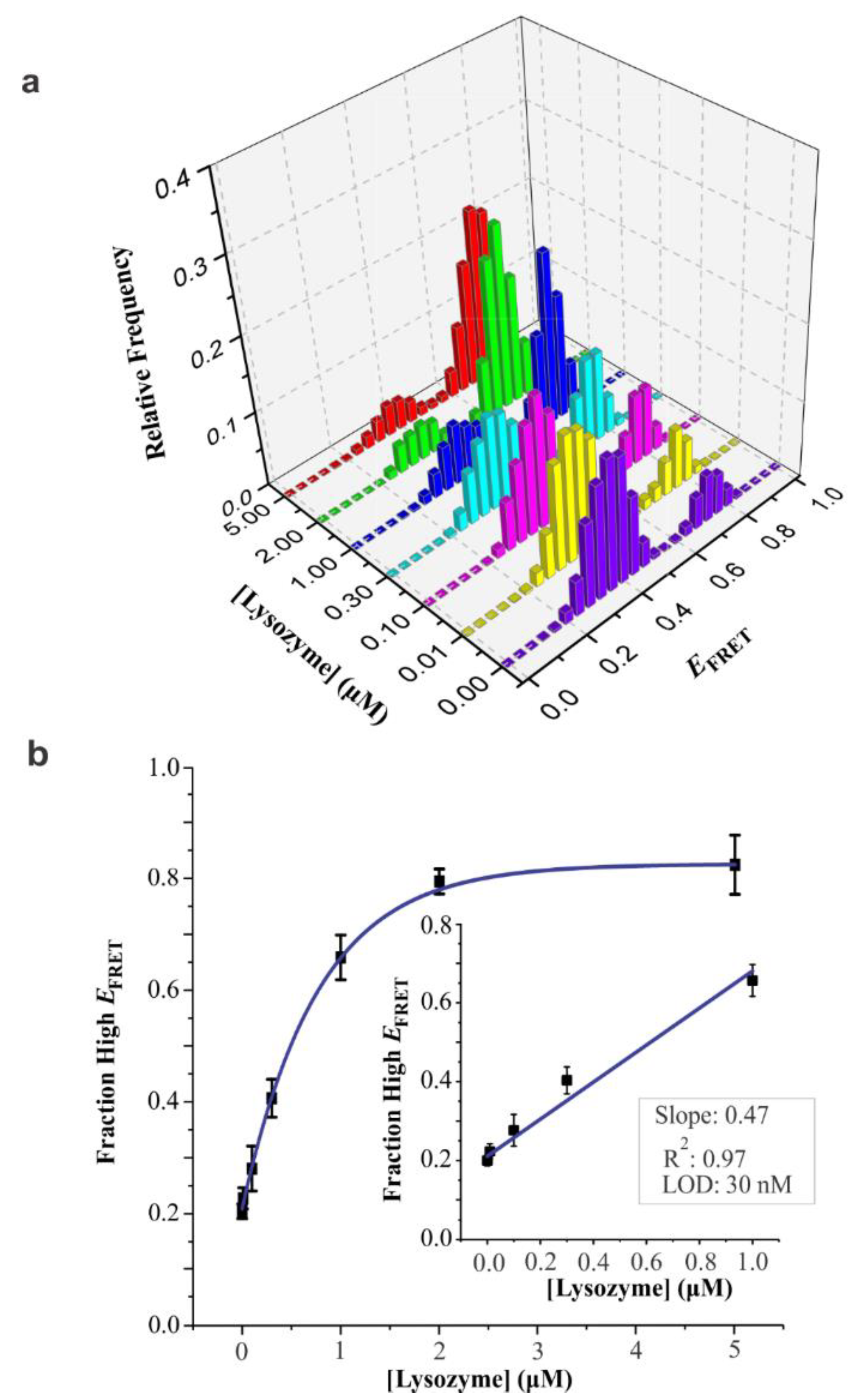
3.4. Analytical Sensitivity
3.5. Selectivity of Lysozyme Aptasensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vasilescu, A.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Boukherroub, R.; Szunerits, S. Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Sensing of Lysozyme. Chemosensors 2016, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamei, H.R.; Rezaei, B.; Ensafi, A.A. An ultrasensitive electrochemical anti-lysozyme aptasensor with biorecognition surface based on aptamer/amino-rGO/ionic liquid/amino-mesosilica nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 181, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragland, S.A.; Criss, A.K. From bacterial killing to immune modulation: Recent insights into the functions of lysozyme. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.I.; Maddaus, A.G.; Song, E. A Low-Cost Inkjet-Printed Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for the Selective Detection of Lysozyme. Biosensors 2018, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xia, N.; Li, T.; Bai, Y.; Chen, X. Aptasensor for visual and fluorometric determination of lysozyme based on the inner filter effect of gold nanoparticles on CdTe quantum dots. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 2917–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Tuo, S.; Jiang, F.; Niu, X.; Pan, F.; Wang, H. Lysozyme Aptamer-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for the Purification of Lysozyme from Chicken Egg White. Foods 2019, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pushkaran, A.C.; Nataraj, N.; Nair, N.; Götz, F.; Biswas, R.; Mohan, C.G. Understanding the Structure–Function Relationship of Lysozyme Resistance in Staphylococcus aureusby Peptidoglycan O-Acetylation Using Molecular Docking, Dynamics, and Lysis Assay. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Dowarha, D.; Katte, R.; Chou, R.-H.; Filipek, A.; Yu, C. Lysozyme as the anti-proliferative agent to block the interaction between S100A6 and the RAGE V domain. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahanta, S.; Paul, S.; Srivastava, A.; Pastor, A.; Kundu, B.; Chaudhuri, T.K. Stable self-assembled nanostructured hen egg white lysozyme exhibits strong anti-proliferative activity against breast cancer cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 130, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, B.G.; Malmquist, J. Quantitative Immunochemical Determination of Lysozyme (Muramidase) in Serum and Urine. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1971, 27, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, H.; Sato, S.; Matsuda, R.; Sugiura, Y.; Kawaguchi, H.; Niimi, T.; Yoshida, S.; Morishita, M. Serum lysozyme levels and clinical features of sarcoidosis. Lung 1999, 177, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieco, M.H.; Reddy, M.M.; Kothari, H.B.; Lange, M.; Buimovici-Klein, E.; William, D. Elevated β2-microglobulin and lysozyme levels in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1984, 32, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, C.; Vizoso, F.; Alonso, L.; Rodríguez, J.C.; González, L.O.; Fernández, M.; Lamelas, M.L.; Sánchez, L.M.; García-Muñiz, J.L.; Baltasar, A.; et al. Expression and prognostic significance of lysozyme in male breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2002, 4, R16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polimeni, M.; Valente, E.; Aldieri, E.; Khadjavi, A.; Giribaldi, G.; Prato, M. Human lysozyme as a potential diagnostic marker in malaria: A mechanistic study of haemozoin-induced monocyte degranulation. Malar. J. 2012, 11, P80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmfors, L.; Boman, A.; Civitelli, L.; Nath, S.; Sandin, L.; Janefjord, C.; McCann, H.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Halliday, G.; et al. Protective properties of lysozyme on β-amyloid pathology: Implications for Alzheimer disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 83, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandin, L.; Nath, S.; Armstrong, A.; Janefjord, C.; McCann, H.; Halliday, G.M.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Brorsson, A.-C.; Kagedal, K. The Role of Lysozyme in Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Dement 2015, 11, P477–P478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, O.P.; Batra, P.; Ali, Z.; Anupurba, S.; Das, B.K. Cerebrospinal fluid lysozyme level for the diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis in children. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2003, 49, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pruzanski, W.; Saito, S.; Ogryzlo, M.A. The significance of lysozyme (muramidase) in rheumatoid arthritis. i. levels in serum and synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheum. 1970, 13, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torsteinsdóttir, I.; Håkansson, L.; Hällgren, R.; Gudbjörnsson, B.; Arvidson, N.-G.; Venge, P. Serum lysozyme: A potential marker of monocyte/macrophage activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 1999, 38, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falchuk, K.R.; Perrotto, J.L.; Isselbacher, K.J. Serum Lysozyme in Crohn’s Disease. A Useful Index of Disease Activity. Gastroenterology 1975, 69, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daeschel, M.A.; Musafija-Jeknic, T.; Wu, Y.; Bizzarri, D.; Villa, A. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Analysis of Lysozyme in Wine. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2002, 53, 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Carstens, C.; Deckwart, M.; Webber-Witt, M.; Schäfer, V.; Eichhorn, L.; Brockow, K.; Fischer, M.; Christmann, M.; Paschke-Kratzin, A. Evaluation of the Efficiency of Enological Procedures on Lysozyme Depletion in Wine by an Indirect ELISA Method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6247–6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerkaert, B.; Mestdagh, F.; De Meulenaer, B. Detection of hen’s egg white lysozyme in food: Comparison between a sensitive HPLC and a commercial ELISA method. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, Q.; Tang, G.; Liu, S.; Xu, S.; Zhang, X. A facile electrochemical aptasensor for lysozyme detection based on target-induced turn-off of photosensitization. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Aguayo, D.; Del Valle, M. Label-Free Aptasensor for Lysozyme Detection Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Sensors 2018, 18, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Gan, S.; Xu, Q.; Qiu, X.; Gao, P.; Huang, S. A three-way junction aptasensor for lysozyme detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 39, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Chu, X. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence aptasensor for lysozyme based on copolymer nanospheres encapsulated black phosphorus quantum dots. Talanta 2019, 199, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Zhuo, K.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, G.; Wang, J. Fluorescent probe based on carbon dots/silica/molecularly imprinted polymer for lysozyme detection and cell imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 5799–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Qin, G.; Lan, Y.; Wei, Y.; Dong, C. A turn-on phosphorescence aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of lysozyme in humoral samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 289, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, T.; Qiang, H.; Chen, Z. Core-shell Cu@Au nanoparticles-based colorimetric aptasensor for the determination of lysozyme. Talanta 2017, 163, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Yu, C.-J.; Cheng, T.-L.; Tseng, W.-L. Colorimetric Detection of Lysozyme Based on Electrostatic Interaction with Human Serum Albumin-Modified Gold Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2008, 24, 3654–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilescu, A.; Gáspár, S.; Gheorghiu, M.; David, S.; Dinca, V.; Peteu, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Boukherroub, R.; Szunerits, S. Surface Plasmon Resonance based sensing of lysozyme in serum on Micrococcus lysodeikticus-modified graphene oxide surfaces. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihai, I.; Vezeanu, A.; Polonschii, C.; Albu, C.; Radu, G.-L.; Vasilescu, A. Label-free detection of lysozyme in wines using an aptamer based biosensor and SPR detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 206, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.K.H.; Ge, B.; Yu, H.-Z. Aptamer-Based Biosensors for Label-Free Voltammetric Detection of Lysozyme. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 5158–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, R.B.; Periasamy, A. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) microscopy imaging of live cell protein localizations. J. Cell Boil. 2003, 160, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimse, S.B.; Sonawane, M.D.; Song, K.-S.; Kim, T. Biomarker detection technologies and future directions. Analyst 2016, 141, 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Bruno, J.G.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, T.K. Aptamers in the Therapeutics and Diagnostics Pipelines. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4016–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Bhirde, A.A.; Morgan, N.Y.; Eden, H.S.; Chen, X. Electrochemical Immunosensors for Detection of Cancer Protein Biomarkers. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6546–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zu, Y. A Highlight of Recent Advances in Aptamer Technology and Its Application. Molecules 2015, 20, 11959–11980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, J.; Chen, K.; Xu, Y.; Liu, B.; Liao, J.; Zhu, L.; Hu, X.; Li, J.; Pu, Y.; et al. Selection and characterization of DNA aptamer against glucagon receptor by cell-SELEX. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J. Clinical applications of nucleic acid aptamers in cancer. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 2, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, T. Single-Molecule Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer. Methods 2001, 25, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.-Y. Single-molecule FRET for Ultrasensitive Detection of Biomolecules. NanoBioImaging 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, D.R.; Kaur, A.; Megalathan, A.; Sapkota, K.; Dhakal, S. Build Your Own Microscope: Step-By-Step Guide for Building a Prism-Based TIRF Microscope. Methods Protoc. 2018, 1, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, N.; Ouldridge, T.E.; Šulc, P.; Schaeffer, J.M.; Yurke, B.; Louis, A.A.; Doye, J.P.K.; Winfree, E. On the biophysics and kinetics of toehold-mediated DNA strand displacement. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 10641–10658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.; Ellington, A.D. Automated selection of anti-protein aptamers. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2001, 9, 2525–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Sapkota, K.; Dhakal, S. Multiplexed Nucleic Acid Sensing with Single-Molecule FRET. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megalathan, A.; Cox, B.D.; Wilkerson, P.D.; Kaur, A.; Sapkota, K.; Reiner, J.E.; Dhakal, S. Single-molecule analysis of i-motif within self-assembled DNA duplexes and nanocircles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 7199–7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, K.; Megalathan, A.; Moore, D.; Dhakal, S.; Kaur, A.; Donkoh-Moore, C. Single-Step FRET-Based Detection of Femtomoles DNA. Sensors 2019, 19, 3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for the Physics of Living Cells. smFRET Data Acquisition and Analysis Package. Available online: https://cplc.illinois.edu/software/ (accessed on 8 February 2020).
- Roy, R.; Hohng, S.; Ha, T. A Practical Guide to Single Molecule FRET. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, C.E.; Marshall, R.A.; Puglisi, J.D. An Oxygen Scavenging System for Improvement of Dye Stability in Single-Molecule Fluorescence Experiments. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 1826–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porstmann, B.; Jung, K.; Schmechta, H.; Evers, U.; Pergande, M.; Porstmann, T.; Kramm, H.-J.; Krause, H. Measurement of lysozyme in human body fluids: Comparison of various enzyme immunoassay techniques and their diagnostic application. Clin. Biochem. 1989, 22, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Ruiz, M.E.; Díaz-Díaz, E.; Cárdenas-León, M.; Argüelles-Medina, R.; Sánchez-Canales, P.; Larrea-Gallo, F.; Soria-Castro, E.; Guarner-Lans, V. Glycation does not modify bovine serum albumin (BSA)-induced reduction of rat aortic relaxation: The response to glycated and nonglycated BSA is lost in metabolic syndrome. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumori, Y.; Takeda, H.; Fujisawa, T.; Ushijima, K.; Onodera, S.; Shiomi, N. Blood glucose and insulin concentrations are reduced in humans administered sucrose with inosine or adenosine. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1946–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eleftheriadis, T.; Pissas, G.; Liakopoulos, V.; Stefanidis, I. Cytochrome c as a Potentially Clinical Useful Marker of Mitochondrial and Cellular Damage. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sapkota, K.; Dhakal, S. FRET-Based Aptasensor for the Selective and Sensitive Detection of Lysozyme. Sensors 2020, 20, 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030914
Sapkota K, Dhakal S. FRET-Based Aptasensor for the Selective and Sensitive Detection of Lysozyme. Sensors. 2020; 20(3):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030914
Chicago/Turabian StyleSapkota, Kumar, and Soma Dhakal. 2020. "FRET-Based Aptasensor for the Selective and Sensitive Detection of Lysozyme" Sensors 20, no. 3: 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030914
APA StyleSapkota, K., & Dhakal, S. (2020). FRET-Based Aptasensor for the Selective and Sensitive Detection of Lysozyme. Sensors, 20(3), 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030914





