Comparing the Use of High- to Low-Cost Black Carbon and Carbon Dioxide Sensors for Characterizing On-Road Diesel Truck Emissions
Abstract
1. Introduction
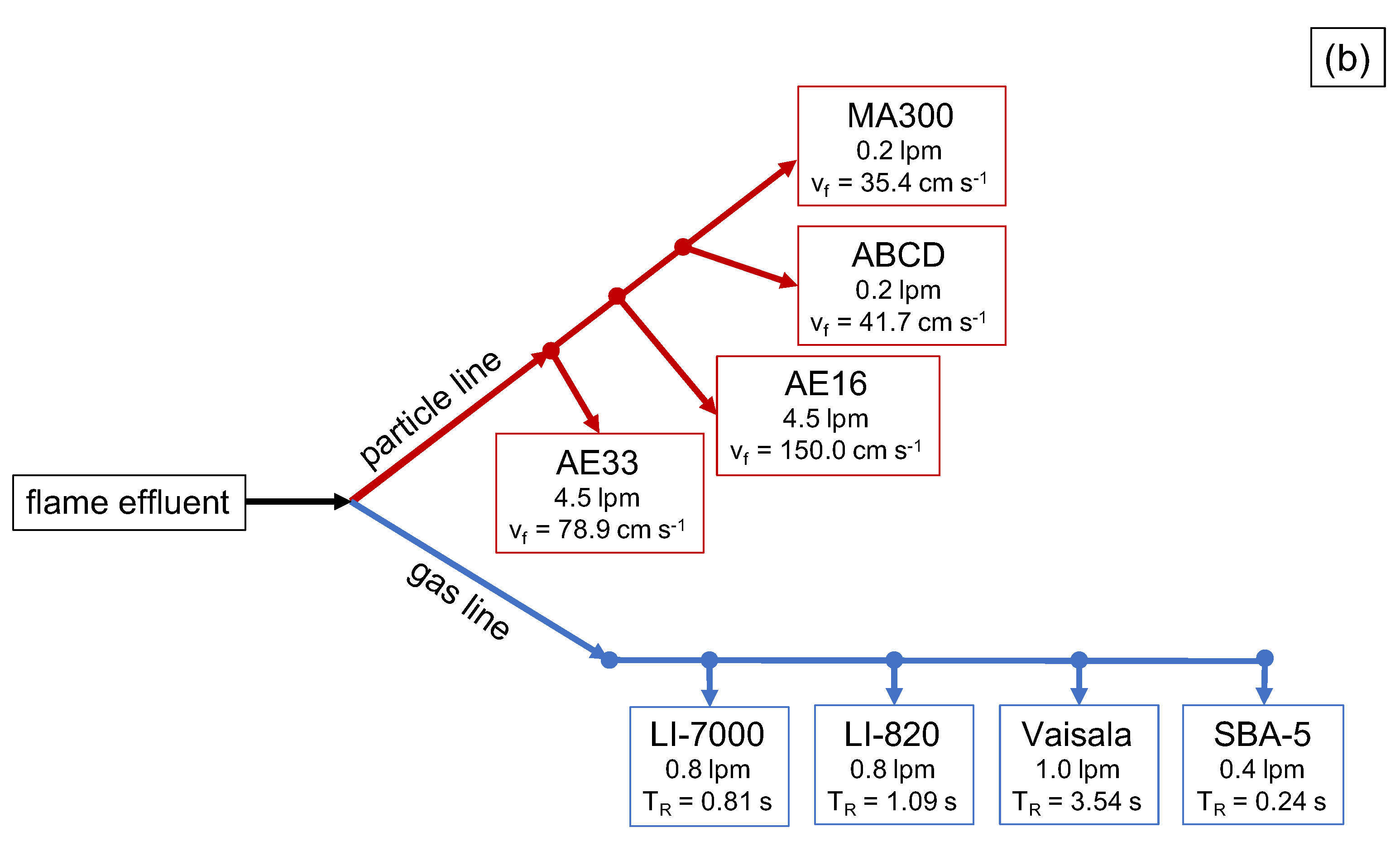
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
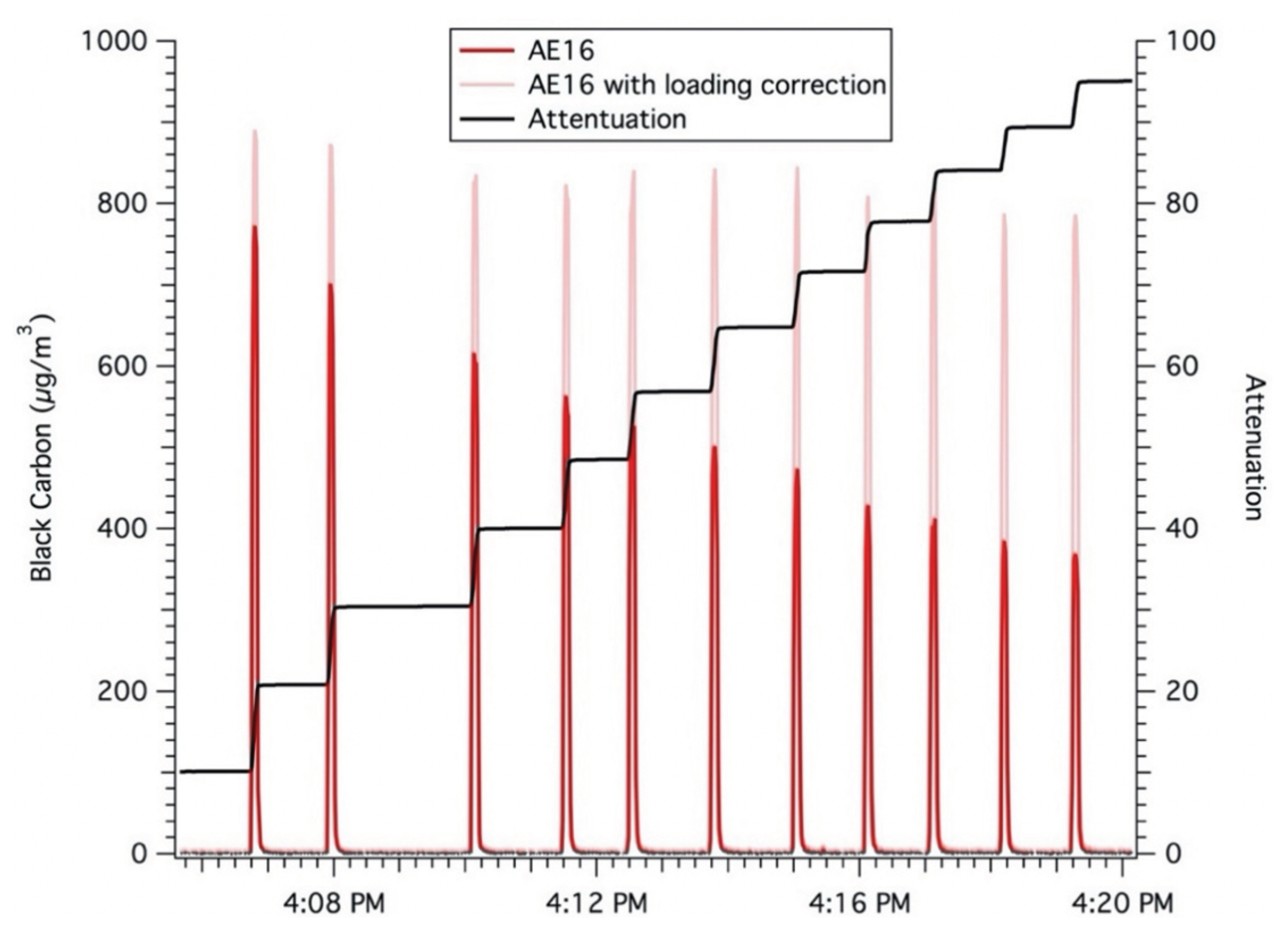
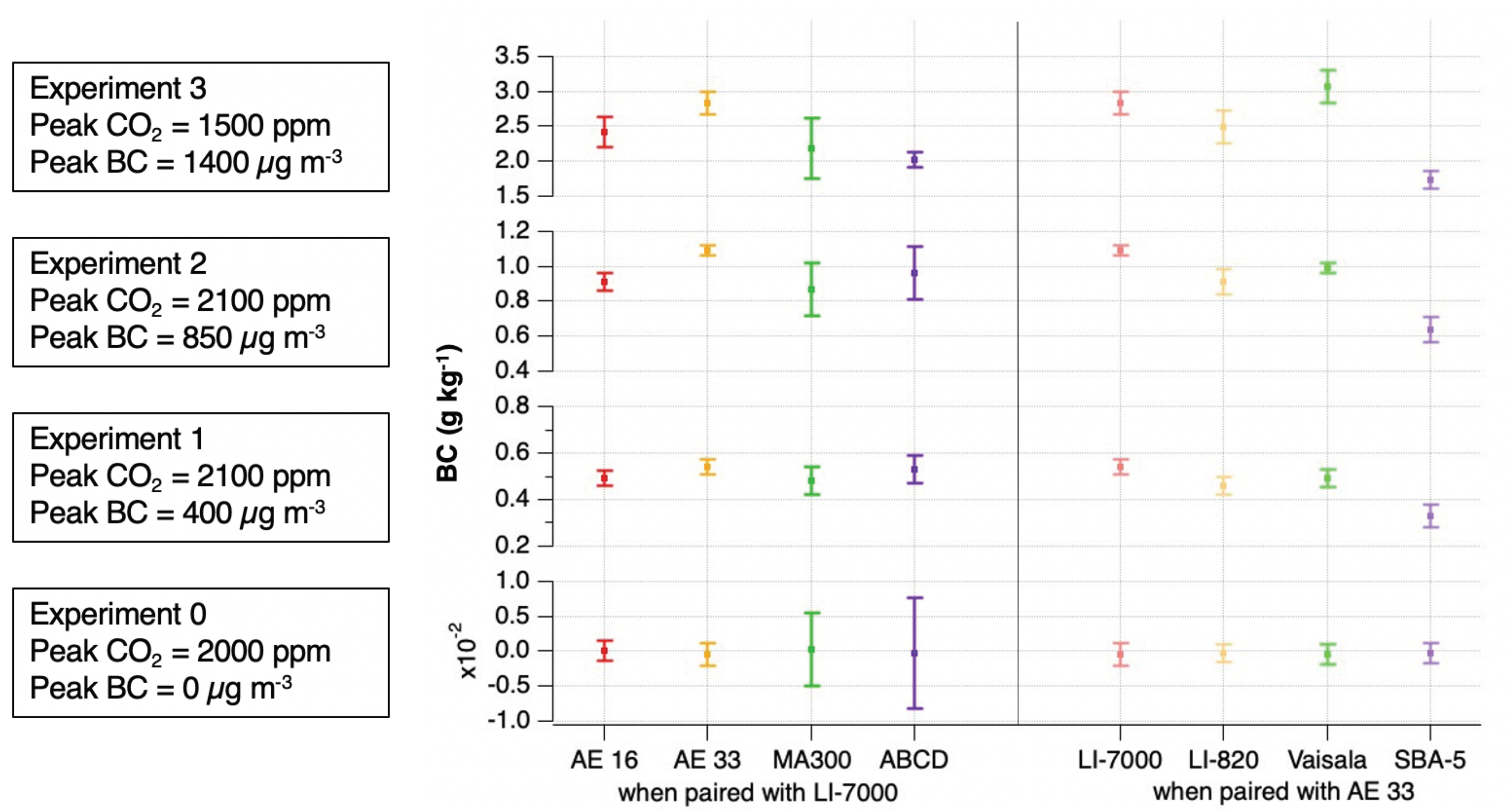
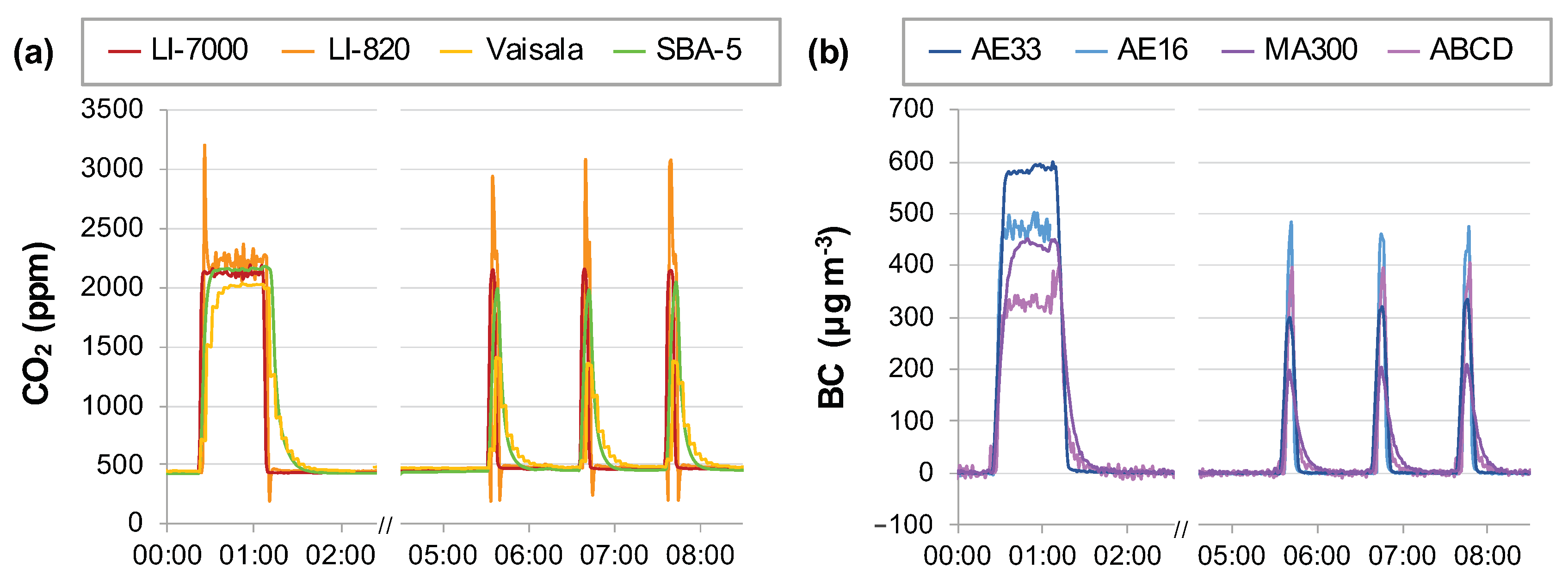
3.1. Sensor Performance in the Laboratory
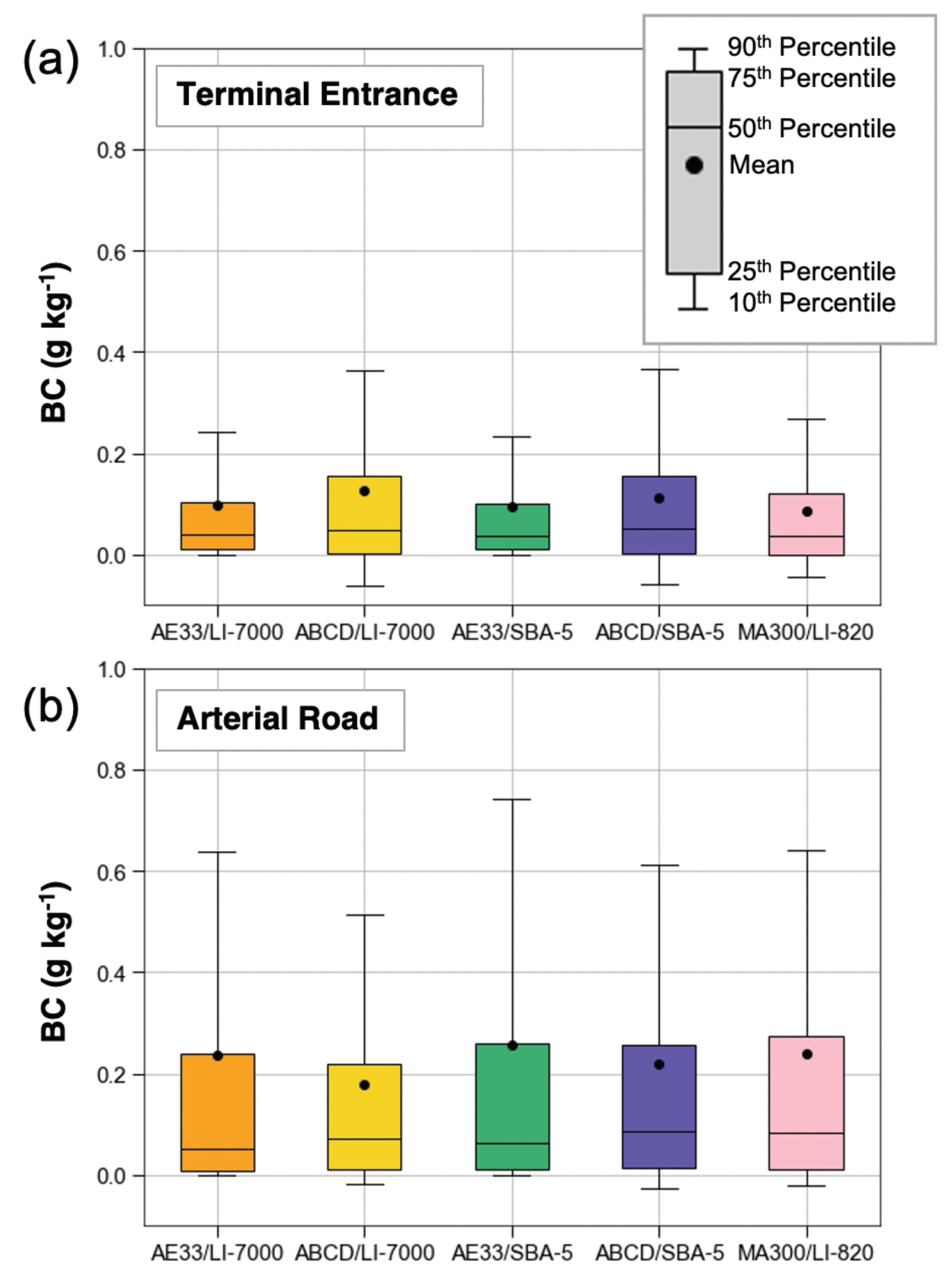
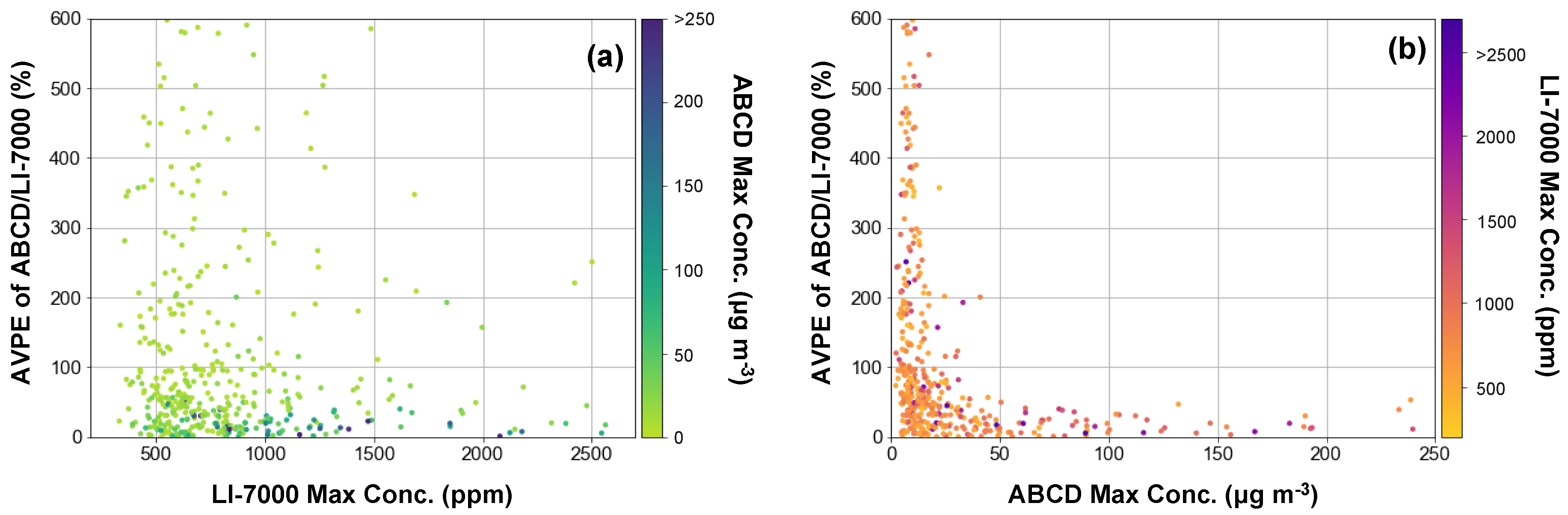
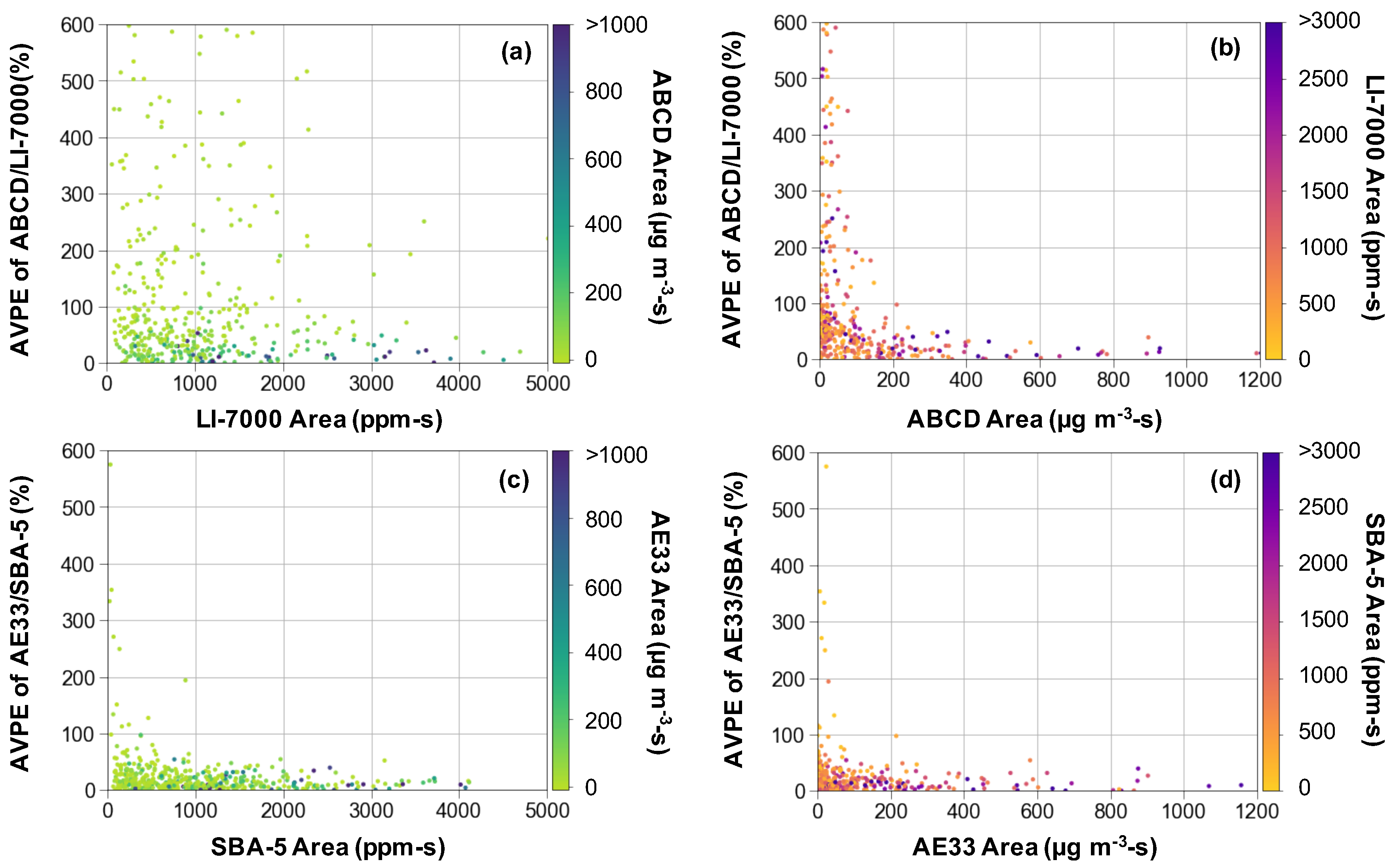
3.2. Sensor Performance in the Field
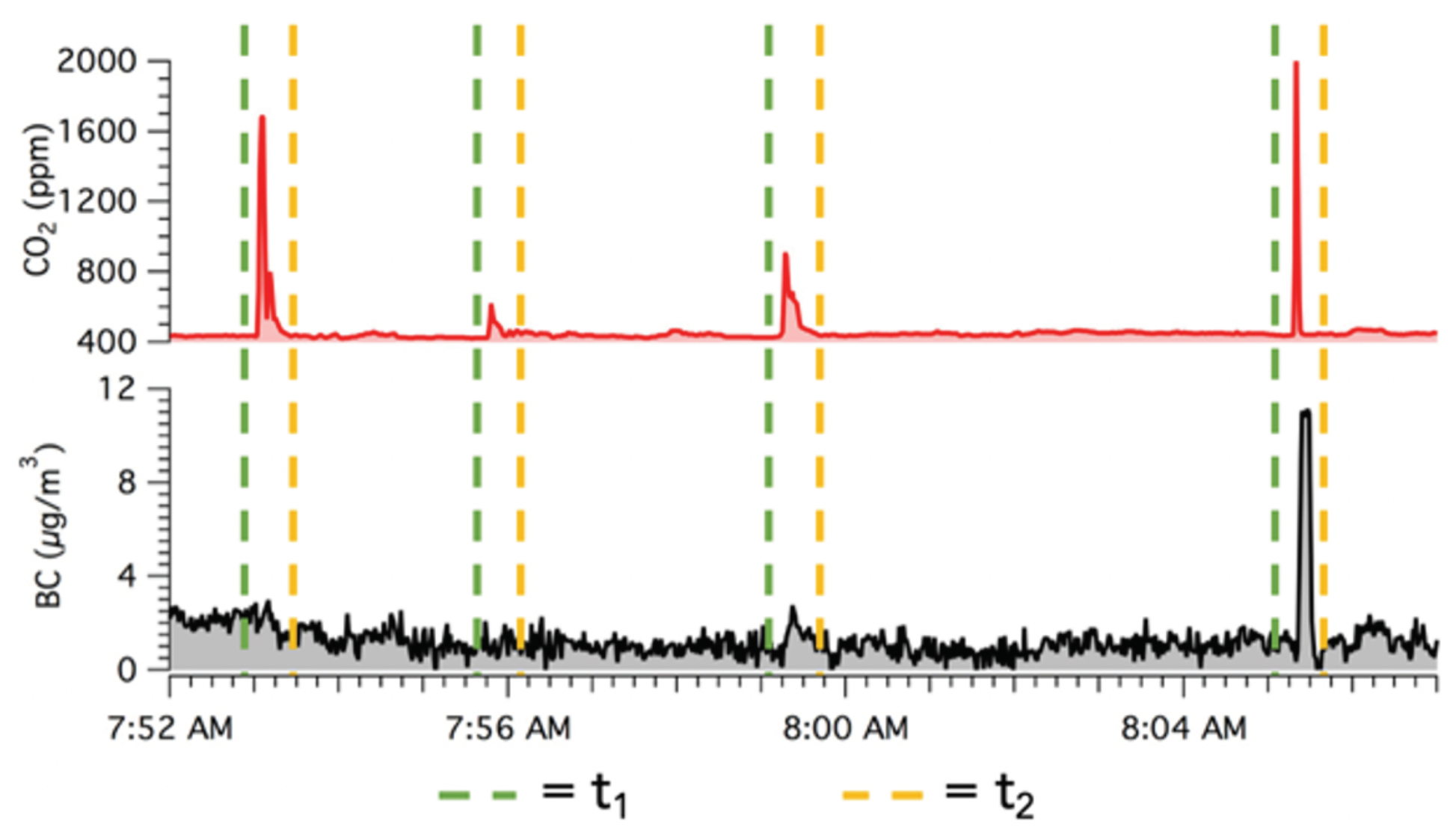
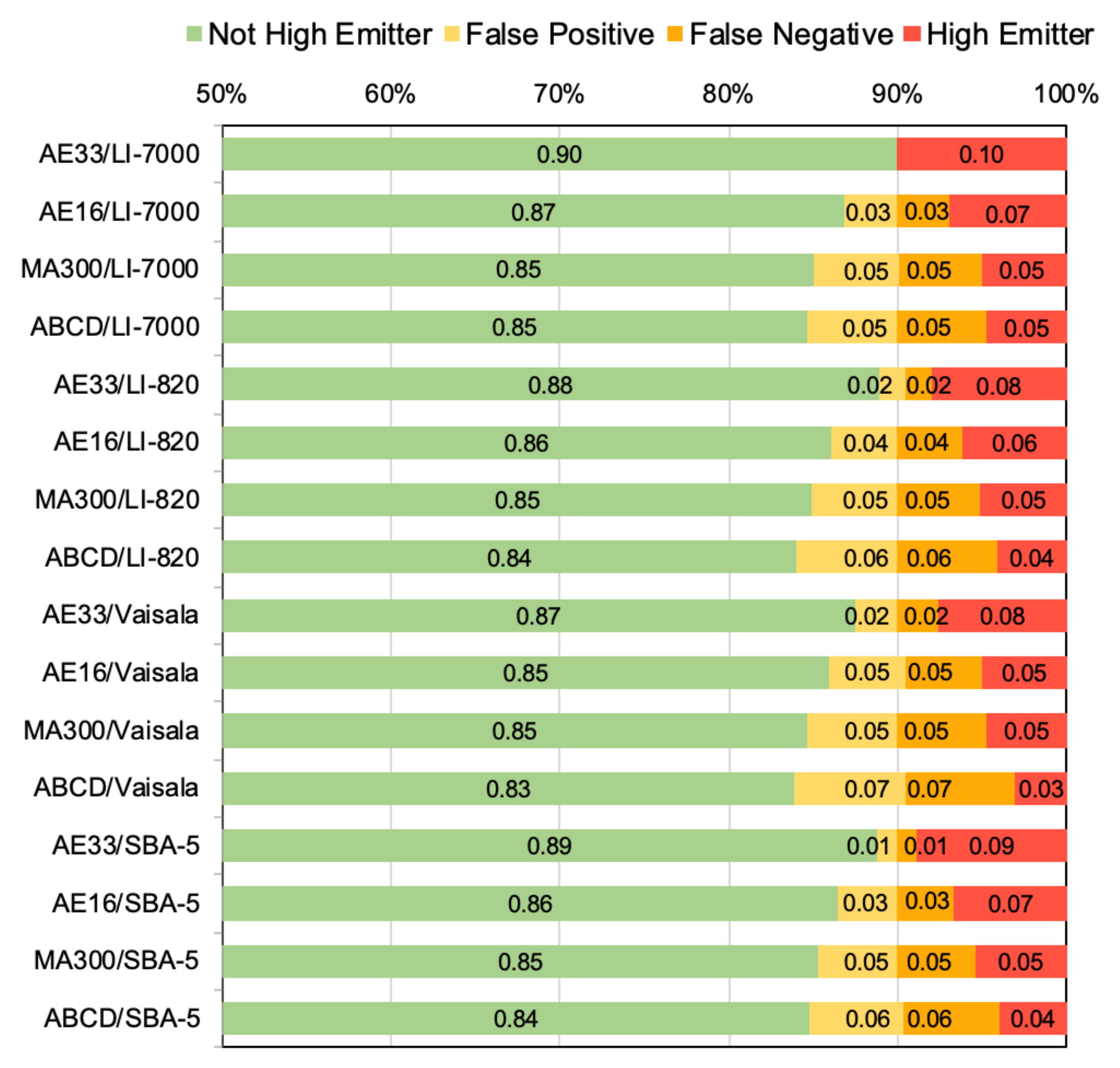
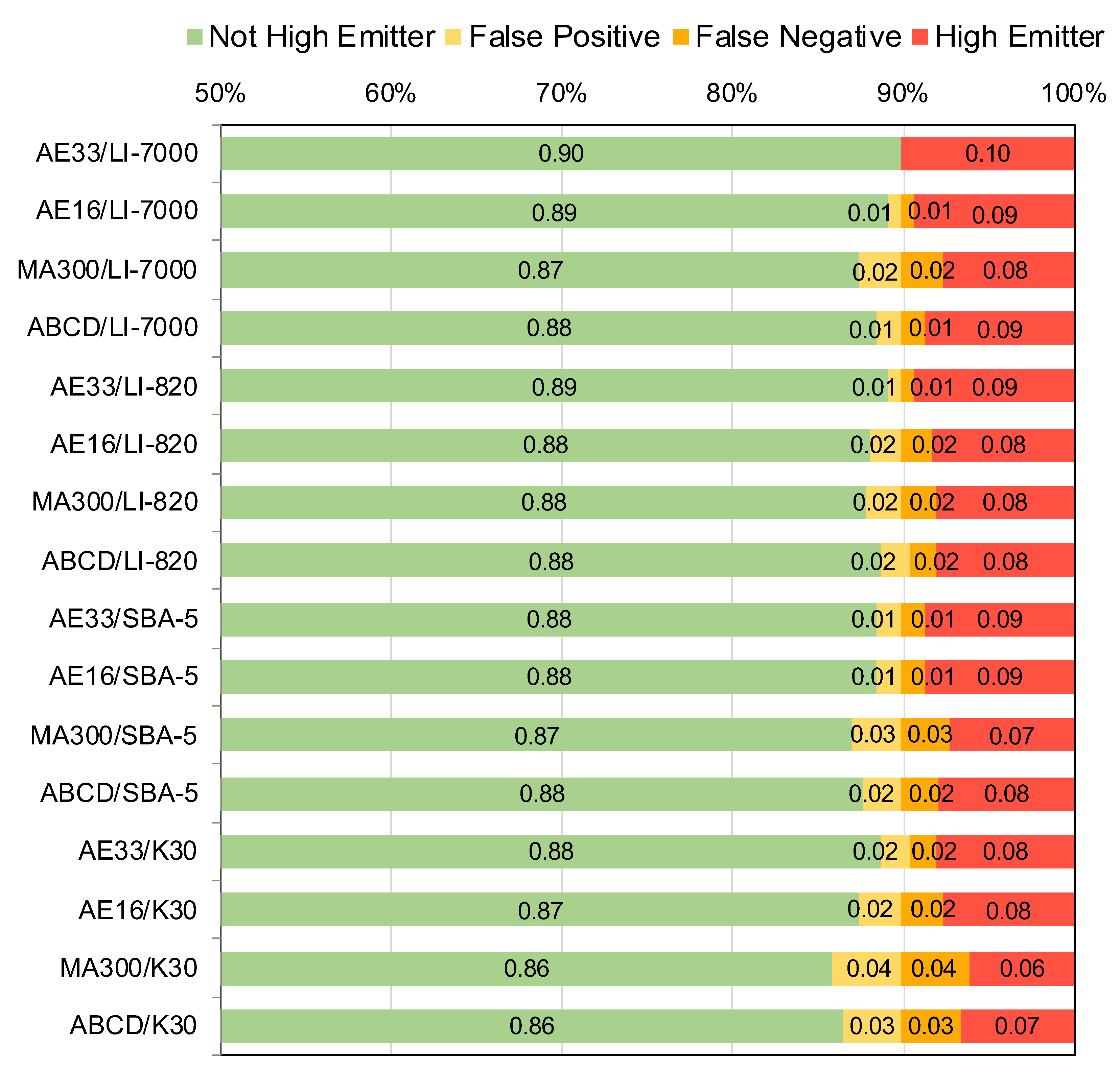
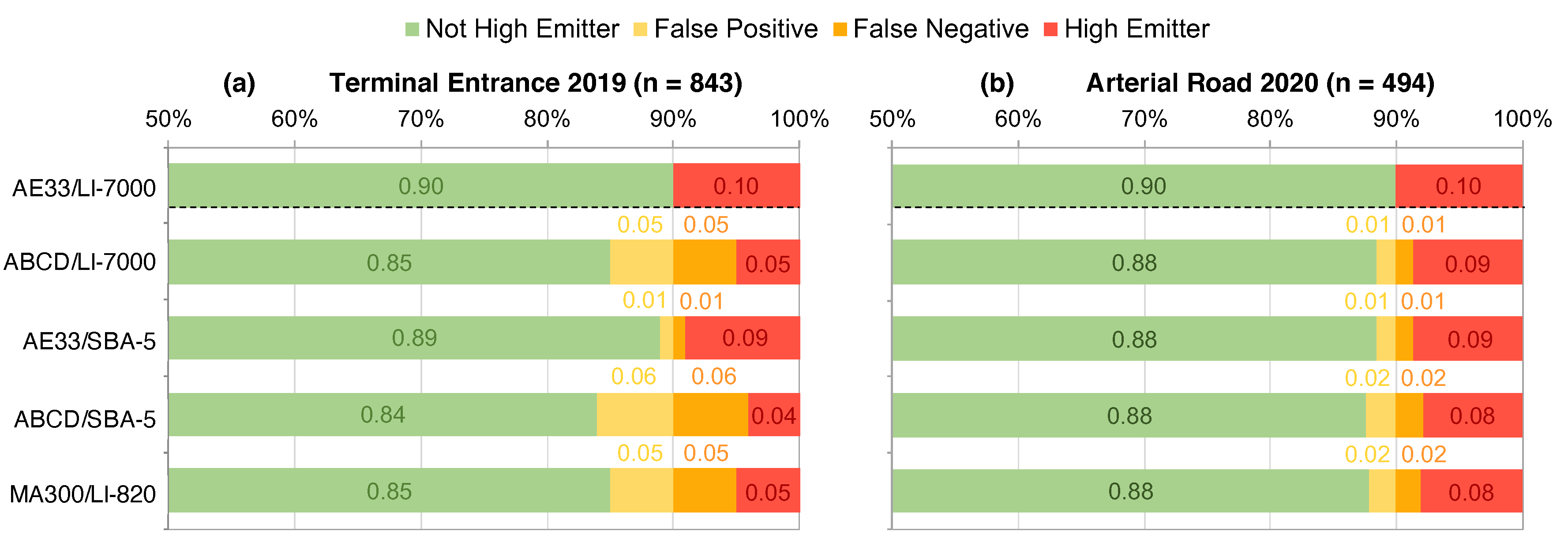
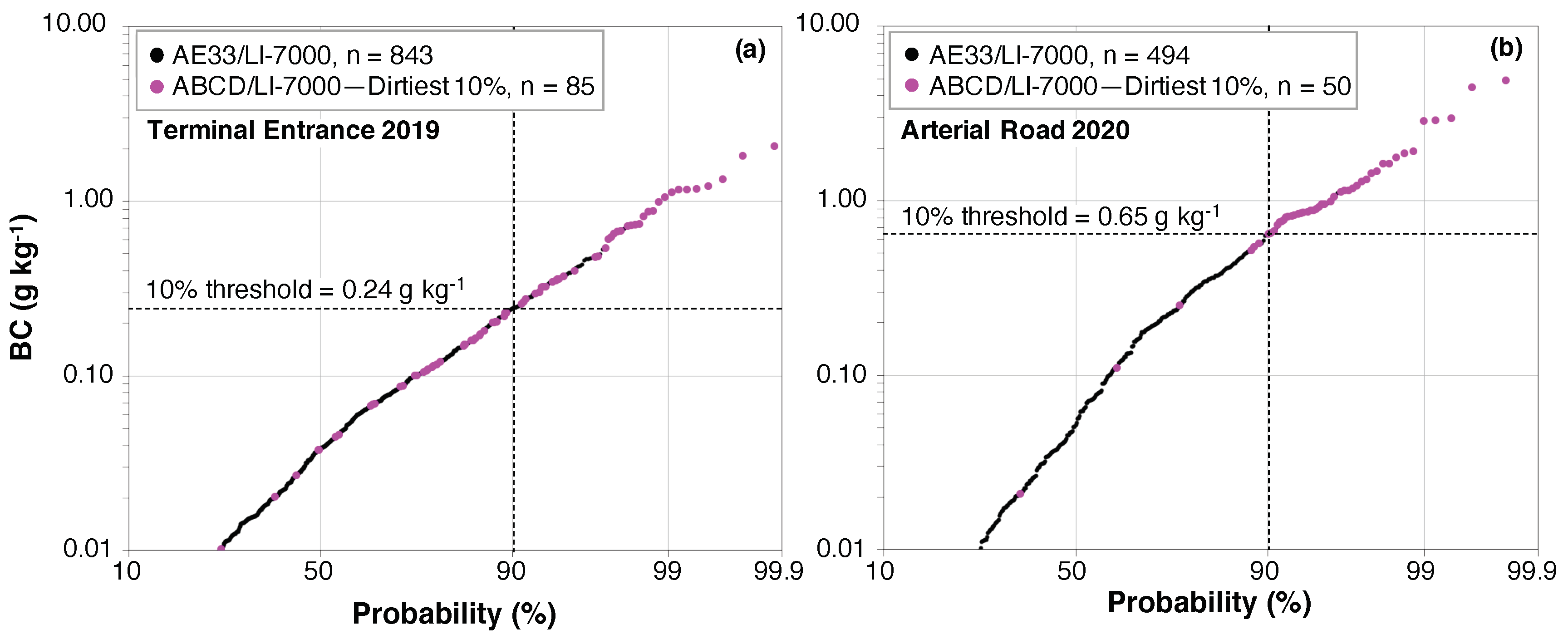
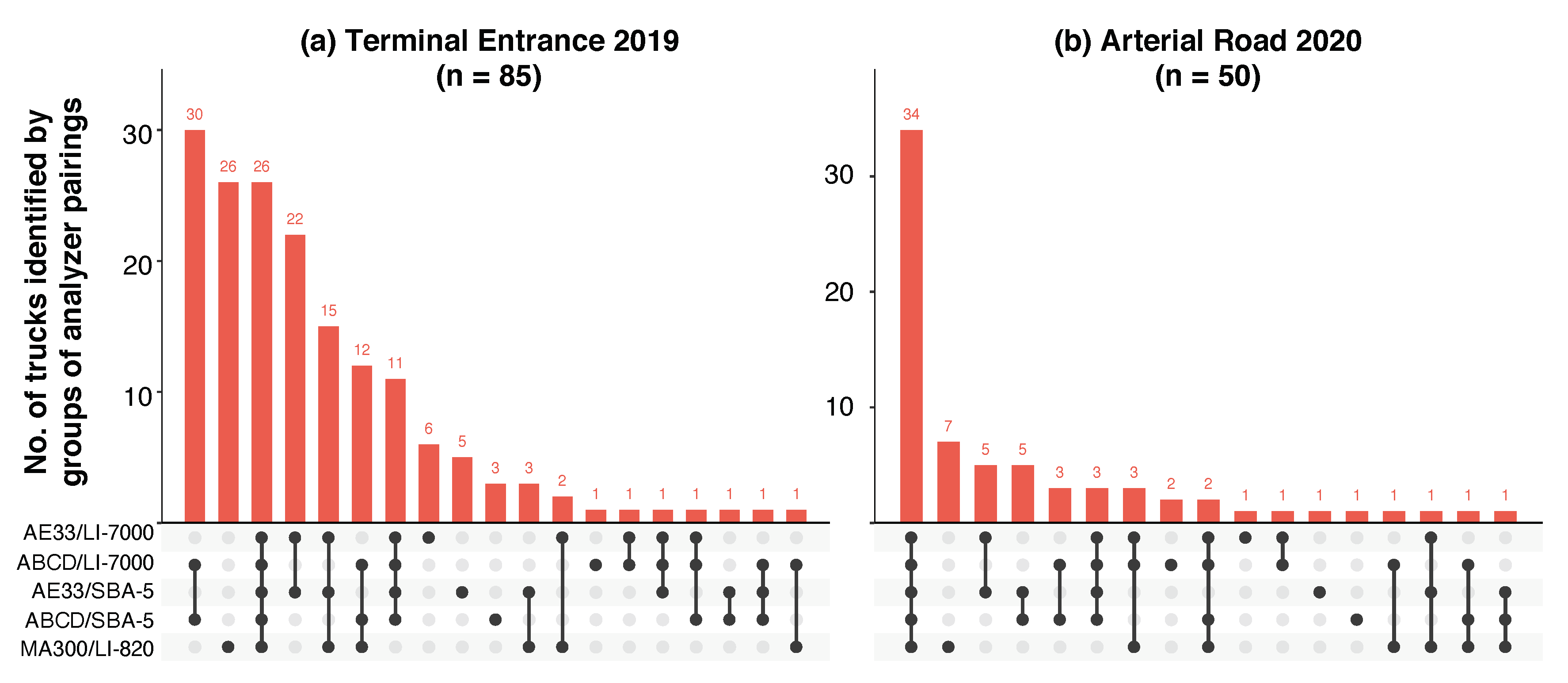
3.3. Field Performance of Sensors Identifying High Emitters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
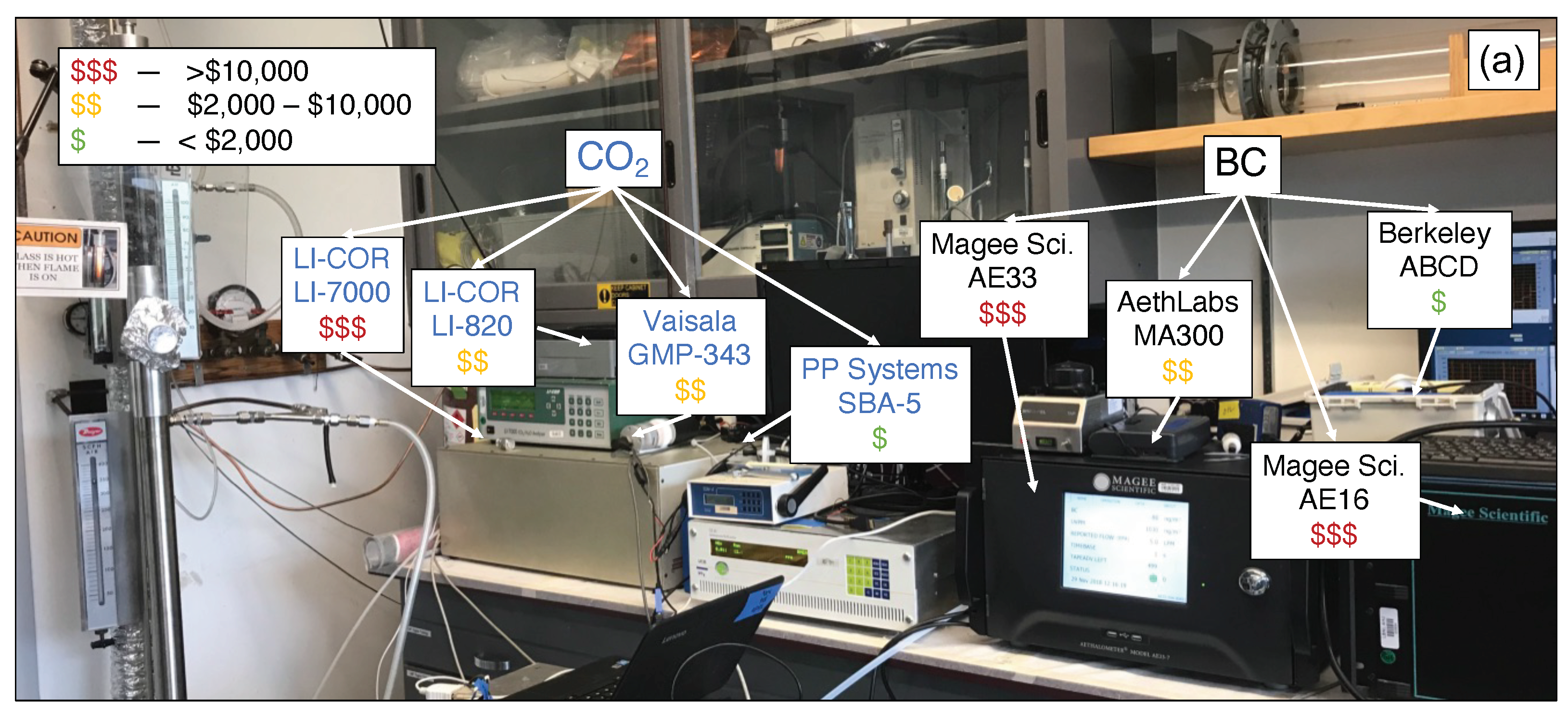


Appendix B
| Sample Statistic | Terminal Entrance 2019 | Arterial Road 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BC Emission Factors (g kg−1) | Mean (± 95% Confidence) | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.24 ± 0.04 |
| Median | 0.04 | 0.05 | |
| 90th Percentile | 0.24 | 0.65 | |
| 10th Percentile | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Absolute; Background-Subtracted Peak CO2 (ppm) | Mean | 695; 240 | 850; 400 |
| Median | 620; 180 | 720; 260 | |
| 90th Percentile | 1070; 550 | 1375; 840 | |
| 10th Percentile | 470; 55 | 515; 150 | |
| Absolute; Background-Subtracted Peak BC (µg m−3) | Mean | 3.8; 3.4 | 23.2; 18.0 |
| Median | 1.7; 1.5 | 8.8; 4.9 | |
| 90th Percentile | 6.7, 5.5 | 45.7; 35.7 | |
| 10th Percentile | 0.9; 1.3 | 3.2; 1.8 |
References
- Bond, T.C.; Streets, D.G.; Yarber, K.F.; Nelson, S.M.; Woo, J.-H.; Klimont, Z. A technology-based global inventory of black and organic carbon emissions from combustion. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, 14203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunekreef, B.; Holgate, S.T. Air pollution and health. Lancet 2002, 360, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, D. Traffic-Related Air Pollution: A Critical Review of the Literature on Emissions, Exposure, and Health Effects; Special Report 17; Health Effects Institute (HEI): Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hoek, G.; Krishnan, R.M.; Beelen, R.; Peters, A.; Ostro, B.; Brunekreef, B.; Kaufman, J.D. Long-term air pollution exposure and cardio-respiratory mortality: A review. Environ. Health Glob. Access Sci. Source 2013, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manisalidis, I.; Stavropoulou, E.; Stavropoulos, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makri, A.; Stilianakis, N.I. Vulnerability to air pollution health effects. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2008, 211, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, L.; Zhou, J. Neighborhood air quality, respiratory health, and vulnerable populations in compact and sprawled regions. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2010, 76, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajat, A.; Hsia, C.; O’Neill, M.S. Socioeconomic Disparities and Air Pollution Exposure: A Global Review. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2015, 2, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA Final Emission Standards for 2004 and Later Model Year Highway Heavy-Duty Vehicles and Engines. 2000. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPDF.cgi/P1001YS2.PDF?Dockey=P1001YS2.PDF (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Sofia, D.; Gioiella, F.; Lotrecchiano, N.; Giuliano, A. Mitigation strategies for reducing air pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 19226–19235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preble, C.V.; Dallmann, T.R.; Kreisberg, N.M.; Hering, S.V.; Harley, R.A.; Kirchstetter, T.W. Effects of Particle Filters and Selective Catalytic Reduction on Heavy-Duty Diesel Drayage Truck Emissions at the Port of Oakland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8864–8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preble, C.V.; Cados, T.E.; Harley, R.A.; Kirchstetter, T.W. In-Use Performance and Durability of Particle Filters on Heavy-Duty Diesel Trucks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11913–11921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, M.J.; Bishop, G.A. Long-Term Fuel-Specific NOx and Particle Emission Trends for In-Use Heavy-Duty Vehicles in California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6070–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallmann, T.R.; Harley, R.A.; Kirchstetter, T.W. Effects of diesel particle filter retrofits and accelerated fleet turnover on drayage truck emissions at the port of Oakland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10773–10779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, G.A.; Hottor-Raguindin, R.; Stedman, D.H.; McClintock, P.; Theobald, E.; Johnson, J.D.; Lee, D.W.; Zietsman, J.; Misra, C. On-road heavy-duty vehicle emissions monitoring system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, M.J.; Bishop, G.A. Repeat Fuel Specific Emission Measurements on Two California Heavy-Duty Truck Fleets. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4100–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Bluett, J.G.; Fisher, G.W.; Kuschel, G.I.; Stedman, D.H. On-road remote sensing of vehicle exhaust emissions in Auckland, New Zealand. Clean Air Environ. Qual. 2005, 39, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Organ, B.; Zhou, J.L.; Surawski, N.C.; Hong, G.; Chan, E.F.C.; Yam, Y.S. Emission measurement of diesel vehicles in Hong Kong through on-road remote sensing: Performance review and identification of high-emitters. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelp, M.; Gould, T.; Austin, E.; Marshall, J.D.; Yost, M.; Simpson, C.; Larson, T. Sensitivity analysis of area-wide, mobile source emission factors to high-emitter vehicles in Los Angeles. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoleni, C.; Kuhns, H.D.; Moosmüller, H.; Keislar, R.E.; Barber, P.W.; Robinson, N.F.; Watson, J.G.; Nikolic, D. On-Road vehicle particulate matter and gaseous emission distributions in las vegas, nevada, compared with other areas. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2004, 54, 711–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senate Bill No. 210. 2019. Available online: https://leginfo.legislature.ca.gov/faces/billTextClient.xhtml?bill_id=201920200SB210 (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Vojtisek-Lom, M.; Arul Raj, A.F.; Jindra, P.; Macoun, D.; Pechout, M. On-road detection of trucks with high NOx emissions from a patrol vehicle with on-board FTIR analyzer. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; (California Air Resources Board, Sacramento, CA, USA). Personal communication, 2018.
- Kumar, P.; Morawska, L.; Martani, C.; Biskos, G.; Neophytou, M.; Di Sabatino, S.; Bell, M.; Norford, L.; Britter, R. The rise of low-cost sensing for managing air pollution in cities. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castell, N.; Dauge, F.R.; Schneider, P.; Vogt, M.; Lerner, U.; Fishbain, B.; Broday, D.; Bartonova, A. Can commercial low-cost sensor platforms contribute to air quality monitoring and exposure estimates? Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caubel, J.J.; Cados, T.E.; Kirchstetter, T.W. A new black carbon sensor for dense air quality monitoring networks. Sensors 2018, 18, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Kaufman, A.; Hanley, T.; Rice, J.; Garvey, S. Evaluation of Field-Deployed Low Cost PM Sensors; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Snyder, E.G.; Watkins, T.H.; Solomon, P.A.; Thoma, E.D.; Williams, R.W.; Hagler, G.S.W.; Shelow, D.; Hindin, D.A.; Kilaru, V.J.; Preuss, P.W. The changing paradigm of air pollution monitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11369–11377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofia, D.; Giuliano, A.; Gioiella, F.; Barletta, D.; Poletto, M. Modeling of an air quality monitoring network with high space-time resolution. Comput. Aided Chem. Eng. 2018, 43, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.; Claiborn, C.; Larson, T.; Gould, T.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Gundel, L. Loading effect correction for real-time aethalometer measurements of fresh diesel soot. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2007, 57, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchstetter, T.W.; Novakov, T. Controlled generation of black carbon particles from a diffusion flame and applications in evaluating black carbon measurement methods. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1874–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban-Weiss, G.A.; Lunden, M.M.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Harley, R.A. Measurement of black carbon and particle number emission factors from individual heavy-duty trucks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Make and Model | Approximate Price ($K) | Accuracy *,^ | Precision, Sensitivity, or Noise ^ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | CO2Meter K30 | 0.2 | ±30 ppm ± 3% | ±20 ppm ± 1%, Sensitivity |
| PP Systems SBA-5 | 2 | <1% | N/A | |
| Vaisala GMP343 | 3 | ± (5 ppm + 2%) | ±3 ppm at 370 ppm, Noise | |
| LI-COR LI-820 | 4 | 3% | <1 ppm at 370 ppm, RMS Noise | |
| LI-COR LI-7000 | 12 | 1% | 12 ppb at 370 ppm, RMS Noise | |
| BC | UC Berkeley ABCD | N/A | ~25% relative to AE33 | ~9%, Precision |
| AethLabs MA300 | 10 | N/A | N/A | |
| Magee Scientific AE16 | 20 | 5% | < 0.1 μg m−3, Sensitivity | |
| Magee Scientific AE33 | 25 | N/A | N/A |
| Specified BC Sensor Paired with LI-7000 CO2 Analyzer, μ (CV) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp. | Peak BC (μg m−3) | AE33 | AE16 | MA300 | ABCD |
| 0 | 0 | −0.41 × 10−3 (381) | 0.07 × 10−3 (2213) | 0.23 × 10−3 (2216) | −0.31 × 10−3 (2519) |
| 1 | 450 | 0.54 (6.3) | 0.49 (5.3) | 0.48 (13.4) | 0.53 (10.8) |
| 2 | 850 | 1.08 (3.3) | 0.91 (6.0) | 0.86 (17.2) | 0.96 (16.6) |
| 3 | 1400 | 2.85 (4.9) | 2.39 (6.6) | 2.27 (19.9) | 2.04 (4.8) |
| Specified CO2 Sensor Paired with AE33 BC Analyzer, μ (CV) | |||||
| Exp. | Peak CO2 (ppm) | LI-7000 | LI-820 | Vaisala | SBA-5 |
| 0 | 2000 | −0.41 × 10−3 (381) | −0.36 × 10−3 (345) | −0.38 × 10−3 (374) | −0.36 × 10−3 (392) |
| 1 | 2100 | 0.54 (6.3) | 0.46 (8.7) | 0.49 (7.2) | 0.34 (7.1) |
| 2 | 2100 | 1.08 (3.3) | 0.91 (8.1) | 0.99 (3.6) | 0.64 (12.1) |
| 3 | 1500 | 2.85 (4.9) | 2.53 (7.5) | 3.11 (6.9) | 1.73 (5.9) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sugrue, R.A.; Preble, C.V.; Kirchstetter, T.W. Comparing the Use of High- to Low-Cost Black Carbon and Carbon Dioxide Sensors for Characterizing On-Road Diesel Truck Emissions. Sensors 2020, 20, 6714. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236714
Sugrue RA, Preble CV, Kirchstetter TW. Comparing the Use of High- to Low-Cost Black Carbon and Carbon Dioxide Sensors for Characterizing On-Road Diesel Truck Emissions. Sensors. 2020; 20(23):6714. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236714
Chicago/Turabian StyleSugrue, Rebecca A., Chelsea V. Preble, and Thomas W. Kirchstetter. 2020. "Comparing the Use of High- to Low-Cost Black Carbon and Carbon Dioxide Sensors for Characterizing On-Road Diesel Truck Emissions" Sensors 20, no. 23: 6714. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236714
APA StyleSugrue, R. A., Preble, C. V., & Kirchstetter, T. W. (2020). Comparing the Use of High- to Low-Cost Black Carbon and Carbon Dioxide Sensors for Characterizing On-Road Diesel Truck Emissions. Sensors, 20(23), 6714. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236714





