Novel Time-Resolved Fluorescence Immunochromatography Paper-Based Sensor with Signal Amplification Strategy for Detection of Deoxynivalenol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Reagent
2.2. Instrument
2.3. Preparation of Fluorescent Probes (Eu-IgGs)
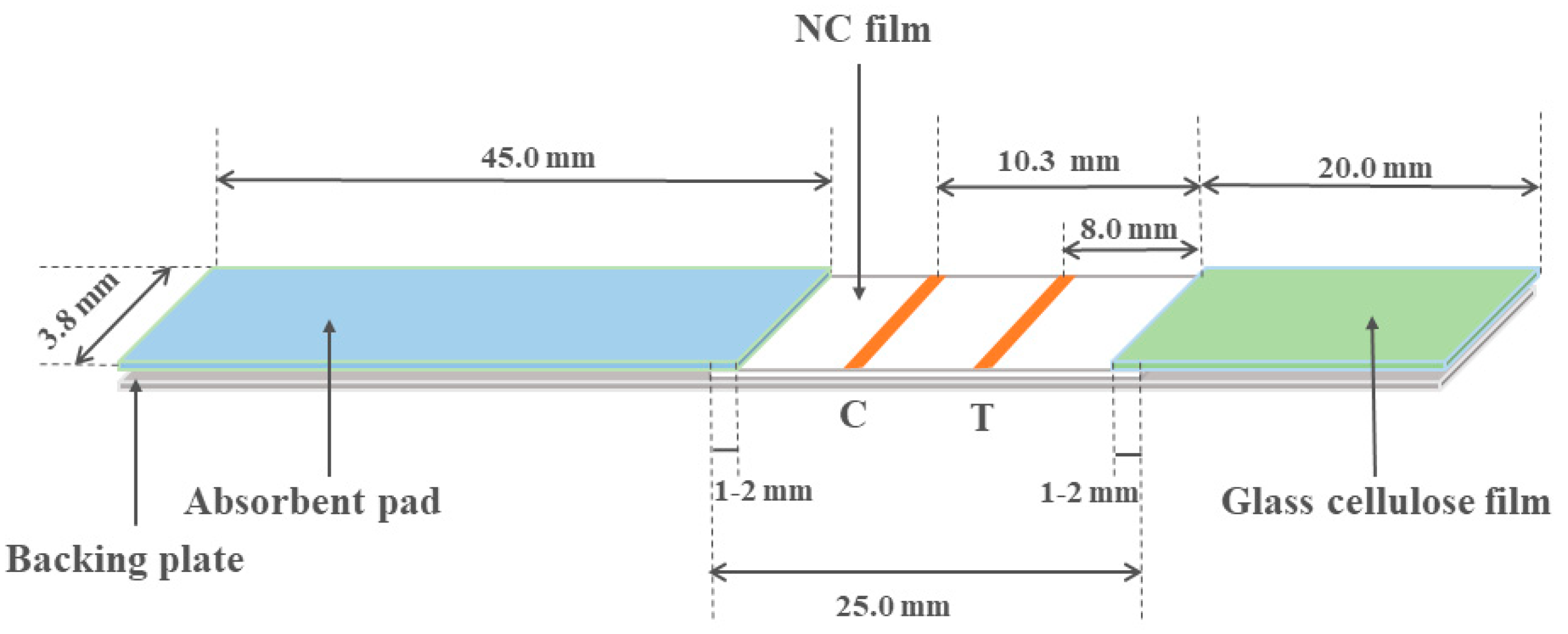
2.4. Preparation of Paper-Based Sensors
2.5. Working Method of the TRFIA Paper-Based Sensor
2.6. Sample Pretreatment Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Eu-IgGs
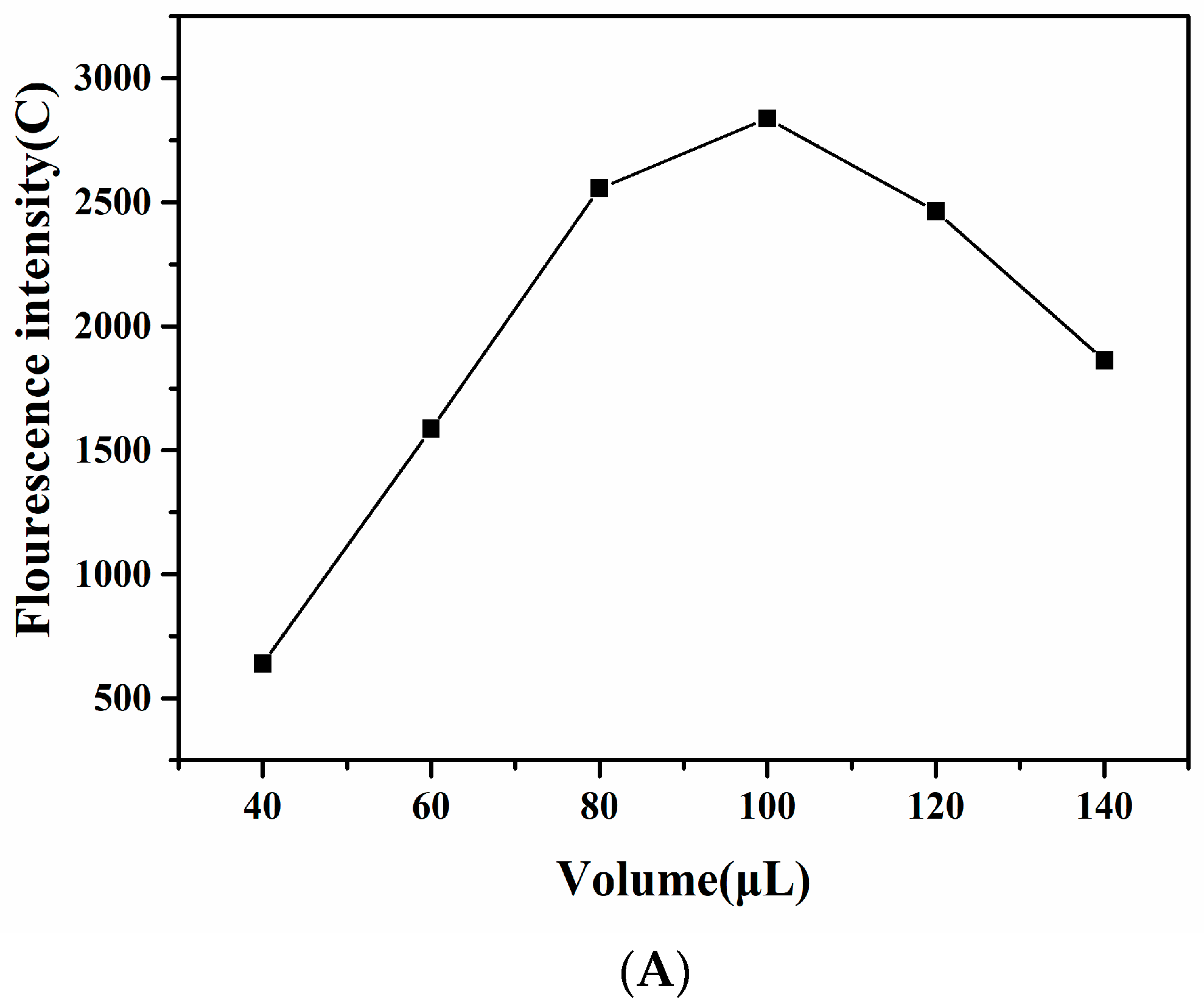
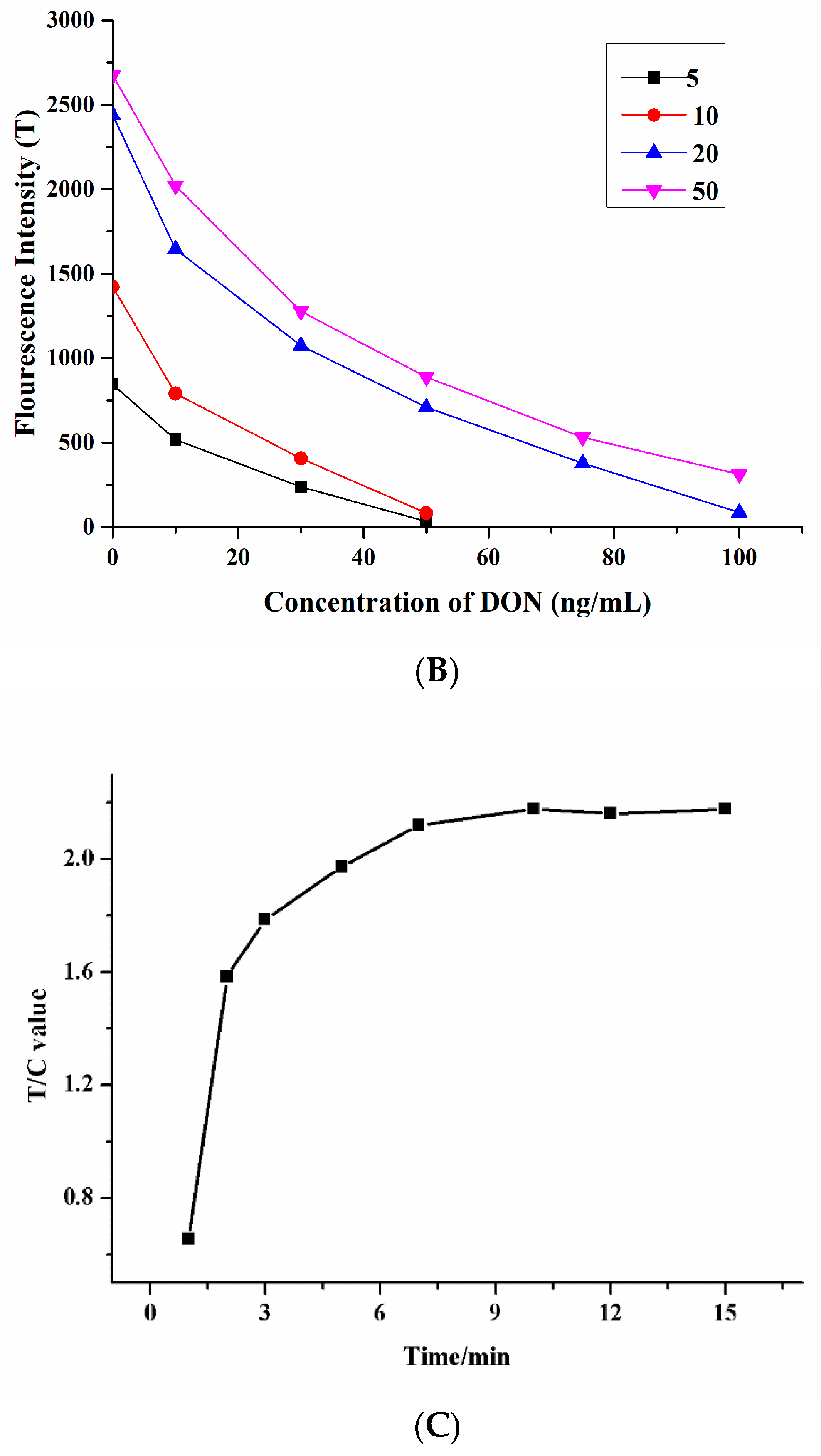
3.2. Condition Optimization of TRFIA Paper-Based Sensor
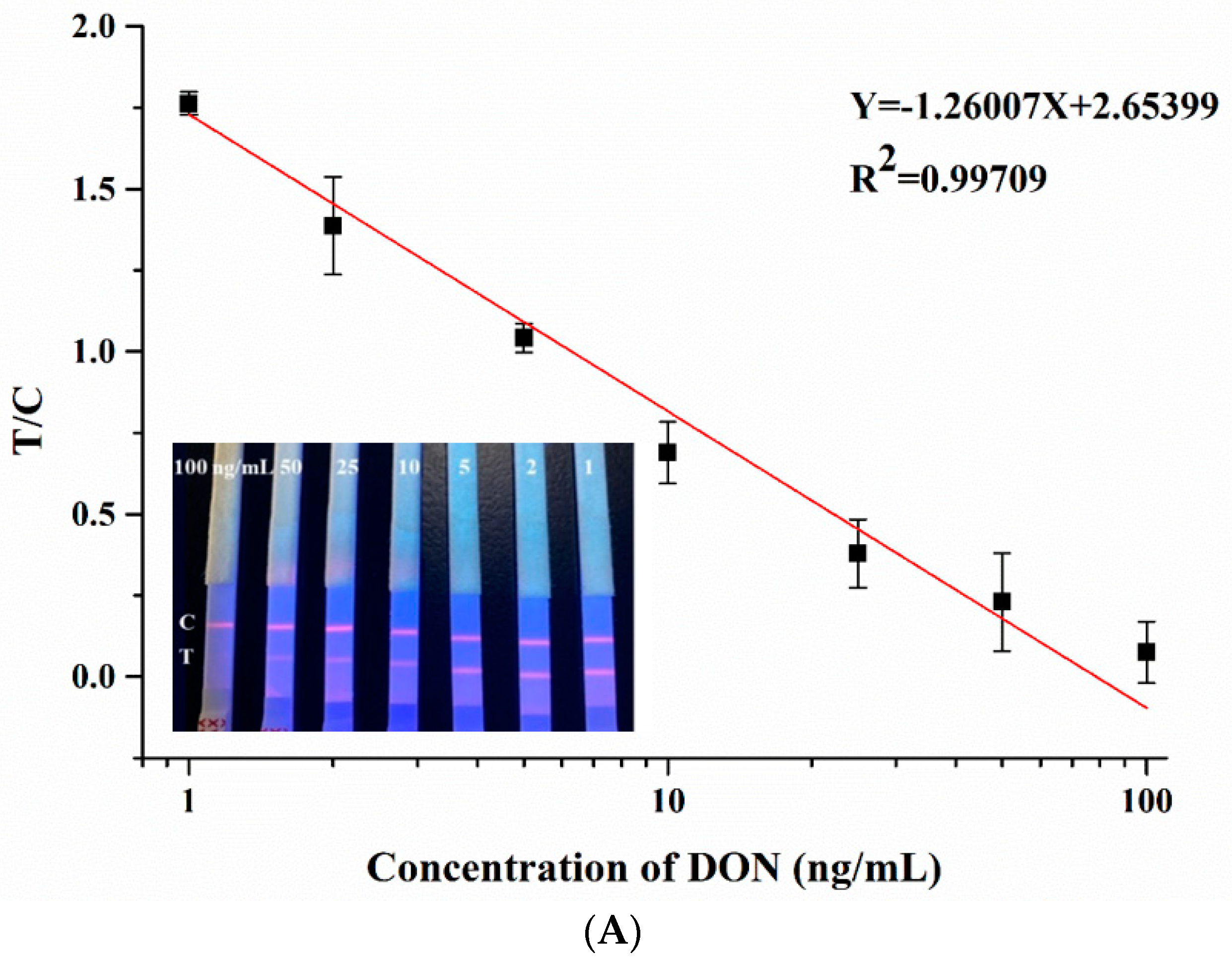
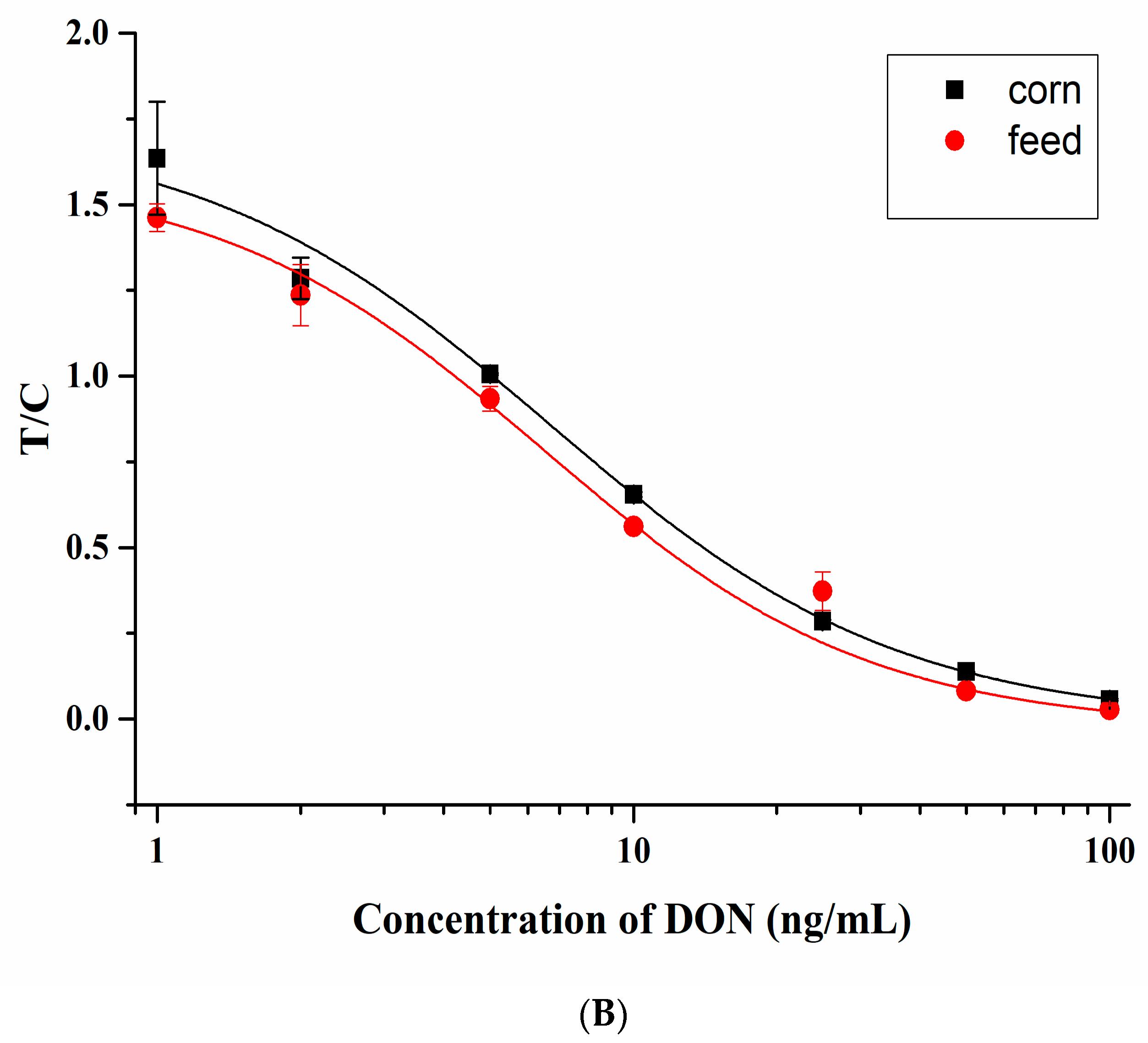
3.3. Detection of DON
3.4. Performance Test of Paper-Based Sensor
3.5. Detection of DON in Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nguyen, P.-A.; Strub, C.; Fontana, A.; Schorr-Galindo, S. Crop molds and mycotoxins: Alternative management using biocontrol. Biol. Control. 2017, 104, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Shi, X.; Zhang, H.; Yao, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, Q.; Xia, L.; Sun, X. An electrochemical immunosensor based on a combined amplification strategy with the GO-CS/CeO2-CS nanocomposite for the detection of aflatoxin M1. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Lan, L.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, F.; Ping, J. Recent progress in application of nanomaterial enabled-biosensors for ochratoxin a detection. Trac-Trend Anal. Chem. 2018, 102, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stastny, K.; Stepanova, H.; Hlavova, K.; Faldyna, M. Identification and determination of deoxynivalenol (DON) and deepoxy-deoxynivalenol (DOM-1) in pig colostrum and serum using liquid chromatography in combination with high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS (HR)). J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2019, 1126–1127, 121735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Raza, N.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Vikrant, K.; Kim, K.-H.; Bhardwaj, N. Advances in nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors for the detection of microbial toxins, pathogenic bacteria in food matrices. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; You, L.; Wu, W.; Wang, X.; Chrienova, Z.; Nepovimova, E.; Wu, Q.; Kuca, K. The neurotoxicity of trichothecenes T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol (DON): Current status and future perspectives. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Long, M. The biological detoxification of deoxynivalenol: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerome Jeyakumar, J.M.; Zhang, M.; Thiruvengadam, M. Determination of mycotoxins by HPLC, LC-ESI-MS/MS, and MALDI-TOF MS in Fusarium species-infected sugarcane. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 123, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romera, D.; Mateo, E.M.; Mateo-Castro, R.; Gomez, J.V.; Gimeno-Adelantado, J.V.; Jimenez, M. Determination of multiple mycotoxins in feedstuffs by combined use of UPLC-MS/MS and UPLC-QTOF-MS. Food Chem. 2018, 267, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pack, E.; Stewart, J.; Rhoads, M.; Knight, J.; De Vita, R.; Clark-Deener, S.; Schmale, D.G. Quantification of zearalenone and α-zearalenol in swine liver and reproductive tissues using GC-MS. Toxicon X 2020, 8, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picardo, M.; Sanchís, J.; Núñez, O.; Farré, M. Suspect screening of natural toxins in surface and drinking water by high performance liquid chromatography and high-resolution mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H. Ultrasensitive Immunosensor for Aflatoxin B1 Detection Based on Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode Modified by Ferrocene @Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 9170–9180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloth, K.; Rye-Johnsen, M.; Didier, A.; Dietrich, R.; Martlbauer, E.; Niessner, R.; Seidel, M. A regenerable immunochip for the rapid determination of 13 different antibiotics in raw milk. Analyst 2009, 134, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, R.R.G.; Santos, D.R.; Chu, V.; Azevedo, A.M.; Aires-Barros, M.R.; Conde, J.P. A point-of-use microfluidic device with integrated photodetector array for immunoassay multiplexing: Detection of a panel of mycotoxins in multiple samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, S.; Khan, I.M.; Yu, Y.; Pasha, I.; Shoaib, M.; Mohsin, A.; Mushtaq, B.S.; Akhtar, W.; Wang, Z. A ‘turnon’ aptasensor for simultaneous and time-resolved fluorometric determination of zearalenone, trichothecenes A and aflatoxin B1 using WS2 as a quencher. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, M.; Wu, N.; Zeng, K.; Du, D. Dual-label time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay as an advantageous approach for investigation of diethyl phthalate & dibutyl phthalate in surface water. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133793. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Li, X.; Fan, Y.; Yang, C.; Lv, X. Simultaneous detection of gastric cancer screening biomarkers plasma pepsinogen I/II using fluorescent immunochromatographic strip coupled with a miniature analytical device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 286, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P. Monoclonal antibody-europium conjugate-based lateral flow time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay for quantitative determination of T-2 toxin in cereals and feed. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 2822–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Xu, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, C.; Chen, A. Development and performance of a fast quantitative test strip for vomiting toxin based on time-resolved fluorescent nanometer microspheres. Food Process. 2017, 42, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Ye, J.; Xue, W.; Zheng, X.; Wang, S.; Sang, H. Applicability evaluation of time-resolved fluoro-immunoassay detection system for deoxynivalenol. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2018, 9, 3490–3496. [Google Scholar]
- Majdinasab, M.; Zareian, M.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P. Development of a new format of competitive immunochromatographic assay using secondary antibody-europium nanoparticle conjugates for ultrasensitive and quantitative determination of ochratoxin A. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Wang, D.; Zhou, A.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Poapolathep, A.; Zhang, L.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P. Rapid, On-Site, Ultrasensitive Melamine Quantitation Method for Protein Beverages Using Time-Resolved Fluorescence Detection Paper. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5671–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Jin, Z.; Zou, S.; Chen, C.; Song, Q.; Deng, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, X.; Jia, A.; Tang, Y. EuNPs-mAb fluorescent probe based immunochromatographic strip for rapid and sensitive detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Talanta 2020, 214, 120865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Song, S.; Zheng, Q.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. Ultrasensitive and eco-friendly immunoassays based monoclonal antibody for detection of deoxynivalenol in cereal and feed samples. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Ren, P.; Huang, L.; Ouyang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Kong, X.; Li, T.; Yin, Y.; Wu, Y.; He, Q. Simultaneous detection of aflatoxin B1, ochratoxin A, zearalenone and deoxynivalenol in corn and wheat using surface plasmon resonance. Food Chem. 2019, 300, 125176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, H.; Huang, Z.; Li, Y.; He, Q.; Tu, Z.; Ji, Y.; Ren, W. A peptide/maltose-binding protein fusion protein used to replace the traditional antigen for immunological detection of deoxynivalenol in food and feed. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Meng, H.; Wang, Z. One-Step Core/Multishell Quantum Dots-Based Fluoroimmunoassay for Screening of Deoxynivalenol in Maize. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 2569–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Huang, T.; Li, X.; Huang, Z. Flower-like gold nanoparticles-based immunochromatographic test strip for rapid simultaneous detection of fumonisin B1 and deoxynivalenol in Chinese traditional medicine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 177, 112895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhu, L.; Li, M.; Lei, S.; Qiu, X. Quantitative detection of Deoxynivalenol in food and feed based on nanogold immunochromatographic assay. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 242, 042017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Woo, S.Y.; Malachova, A.; Michlmayr, H.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, G.J.; Chun, H.S. Simple validated method for simultaneous determination of deoxynivalenol, nivalenol, and their 3-β-D-glucosides in baby formula and Korean rice wine via HPLC-UV with immunoaffinity cleanup. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2019, 36, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Detection Technologies | Limit of Detection (LOD) (ng/mL) | References |
|---|---|---|
| Lateral-flow immunochromatographic assay strip | 1.97–46.8 | [24] |
| Simultaneous surface plasmon resonance | 3.26 | [25] |
| Colloidal gold immunochromatographic assay | 25 | [26] |
| Direct competitive fluorescent-labeled immunosorbent assay | 5.6 | [27] |
| Flower-like gold nanoparticles-based immunochromatographic test strip | 5 | [28] |
| Immunochromatographic test card (DON-GICT) | 40 | [29] |
| HPLC-UV | 4.4 | [30] |
| Immunochromatographic assay using secondary antibody-europium nanoparticle conjugates | 0.121 | This work |
| Samples | Spiked (ng/mL) | Detected (ng/mL) | Recovery (%) | Relative Standard Deviation (RSD) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 10 | 8.81 | 88.07 | 8.23 |
| 50 | 60.61 | 121.22 | 10.49 | |
| 80 | 85.26 | 106.58 | 6.98 | |
| Feed | 10 | 10.47 | 104.67 | 8.74 |
| 50 | 53.74 | 107.49 | 8.28 | |
| 80 | 75.84 | 94.8 | 3.09 |
| Samples | LC-MS/MS (ng/mL) | Paper-Based Sensors (ng/mL) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn 1 | 65.96 | 58.16 | 88.17 |
| Corn 2 | 33.19 | 26.63 | 80.24 |
| Corn 3 | 47.03 | 55.21 | 117.40 |
| Feed 1 | 26.97 | 31.02 | 115.02 |
| Feed 2 | 80.21 | 72.87 | 90.85 |
| Feed 3 | 55.76 | 52.35 | 93.88 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, H.; An, X.; Xiang, Y.; Guan, F.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Sun, X.; Guo, Y. Novel Time-Resolved Fluorescence Immunochromatography Paper-Based Sensor with Signal Amplification Strategy for Detection of Deoxynivalenol. Sensors 2020, 20, 6577. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226577
Dong H, An X, Xiang Y, Guan F, Zhang Q, Yang Q, Sun X, Guo Y. Novel Time-Resolved Fluorescence Immunochromatography Paper-Based Sensor with Signal Amplification Strategy for Detection of Deoxynivalenol. Sensors. 2020; 20(22):6577. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226577
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Haowei, Xingshuang An, Yaodong Xiang, Fukai Guan, Qi Zhang, Qingqing Yang, Xia Sun, and Yemin Guo. 2020. "Novel Time-Resolved Fluorescence Immunochromatography Paper-Based Sensor with Signal Amplification Strategy for Detection of Deoxynivalenol" Sensors 20, no. 22: 6577. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226577
APA StyleDong, H., An, X., Xiang, Y., Guan, F., Zhang, Q., Yang, Q., Sun, X., & Guo, Y. (2020). Novel Time-Resolved Fluorescence Immunochromatography Paper-Based Sensor with Signal Amplification Strategy for Detection of Deoxynivalenol. Sensors, 20(22), 6577. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226577





