SGDAN—A Spatio-Temporal Graph Dual-Attention Neural Network for Quantified Flight Delay Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
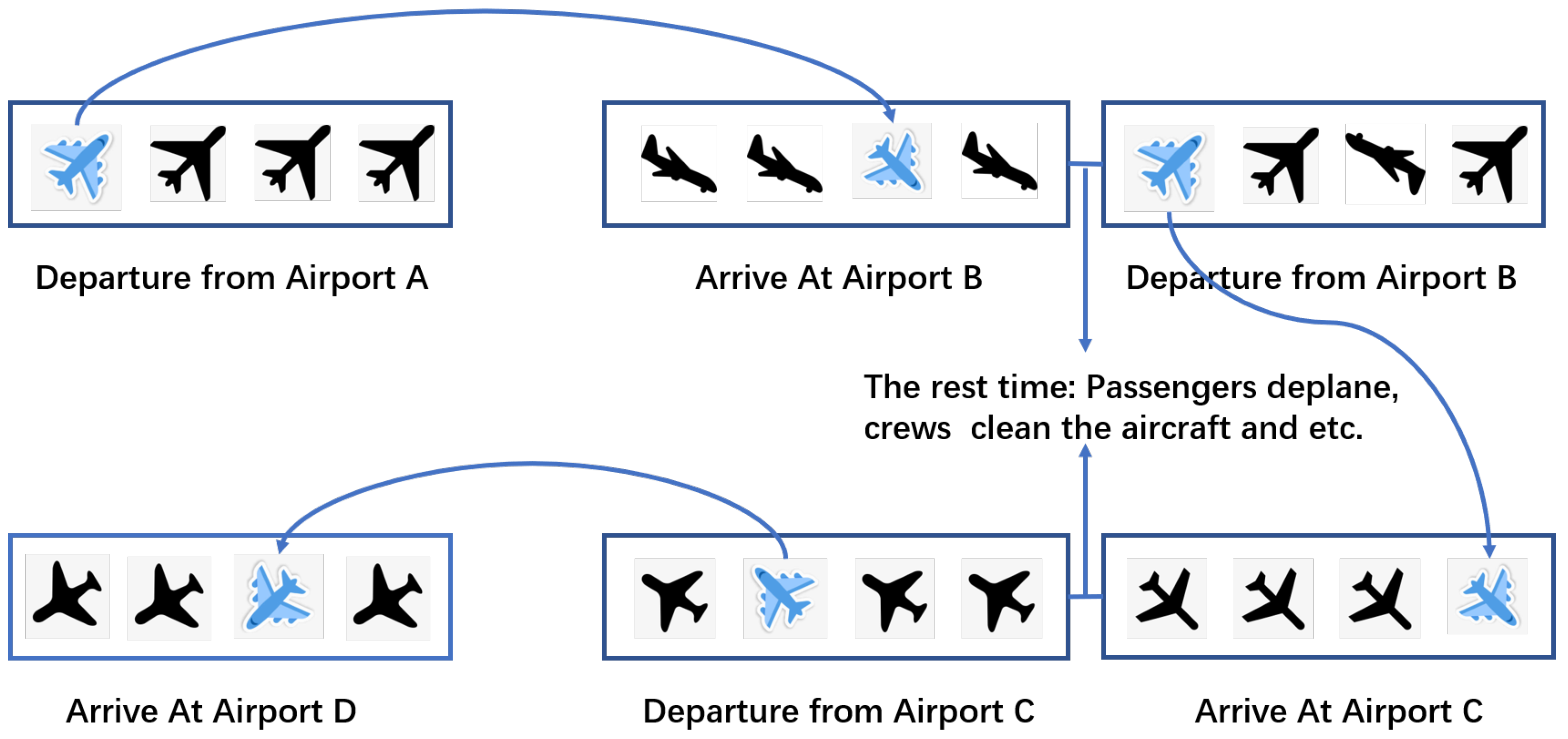
- It abstracts the complex air spatio-temporal network into graph sequences, which uses graphs to model spatial dependencies, and sequences to model temporal dependencies.
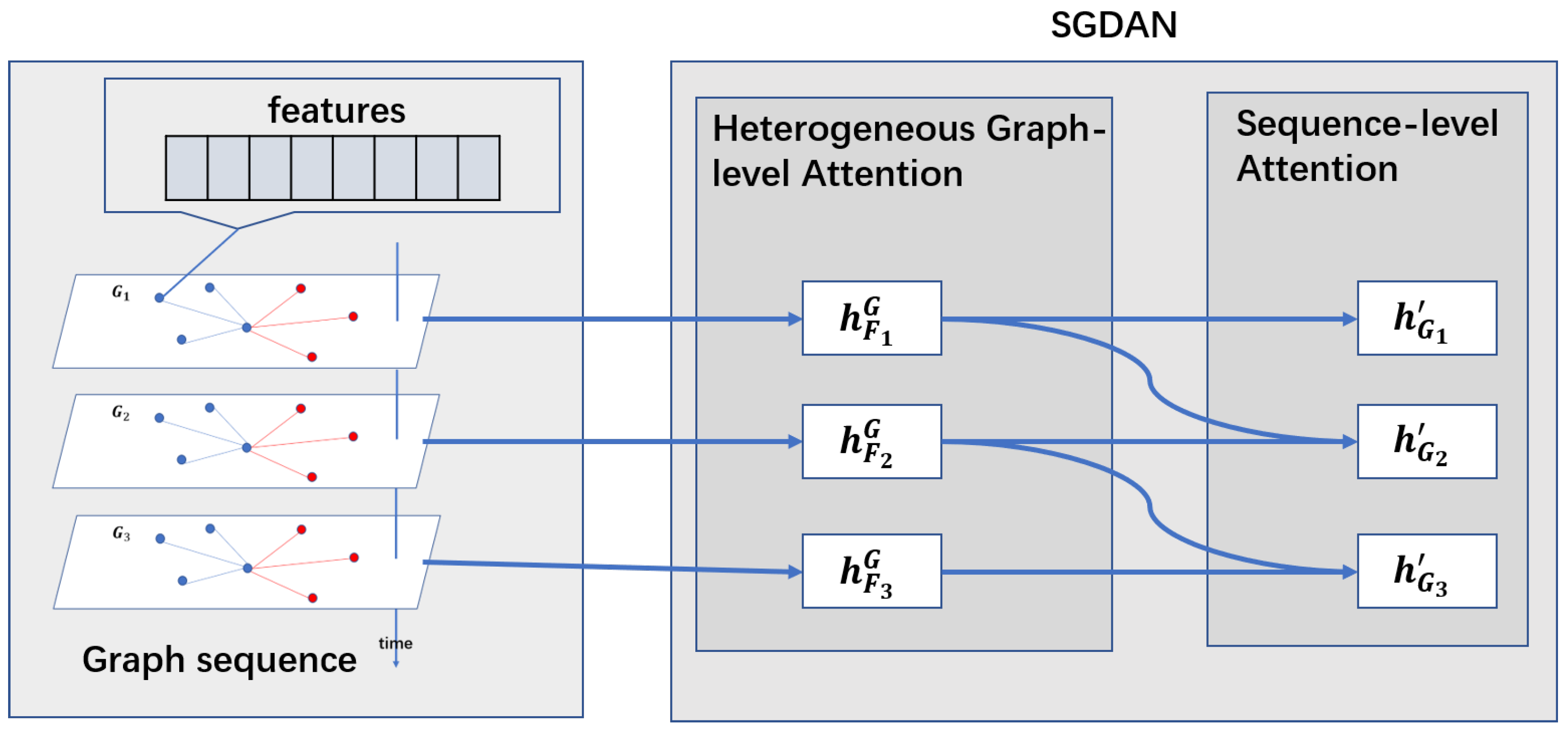
- Based on the abstraction, it proposes a novel model, SGDAN, which embeds the graphs by using heterogeneous graph attention and a soft gate to control multi-head. Through the heterogeneous graph-level attention, SGDAN embeds the impact of other flights with the same departure or arrival airports effectively. Then SGDAN uses sequences-level attention to embed the flight sequences which integrates the impact of the previous flights that share the same aircraft.
- In predicting the flight departure delay time task, SGDAN gets a better result compared with state-of-the-art models. It proves that it is feasible and effective to abstract the spatio-temporal network into graph sequences and then construct a graph neural network in spatio-temporal networks.
2. Related Work
2.1. Flight Delay Prediction
2.2. Graph Neural Networks
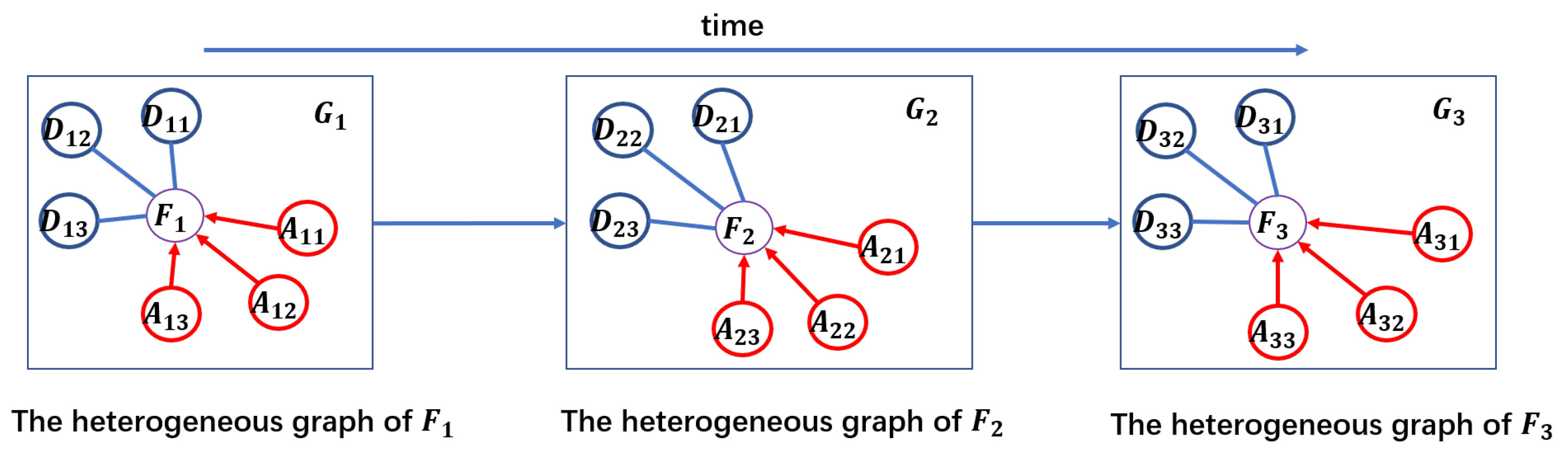
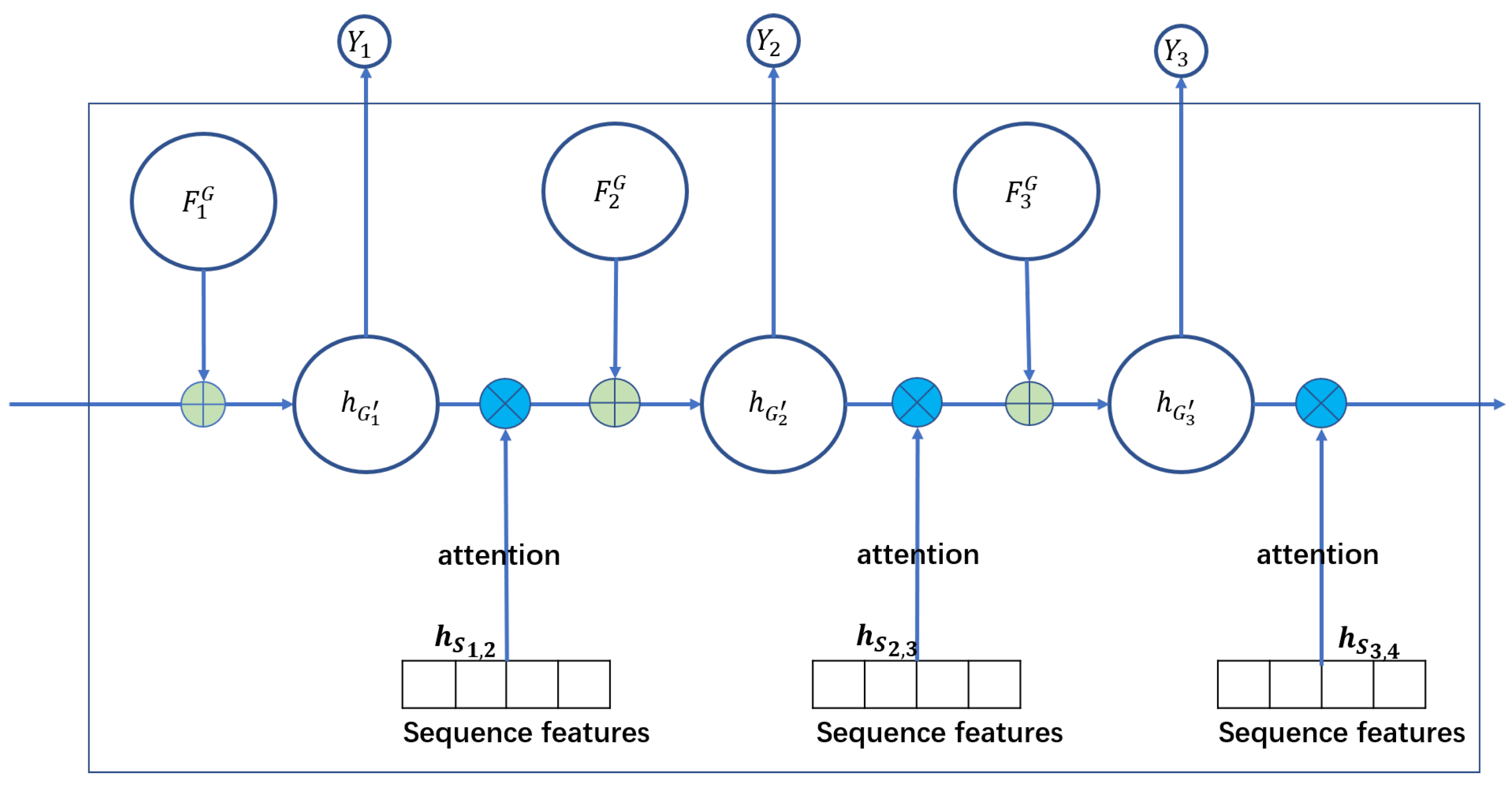
3. Model: SGDAN
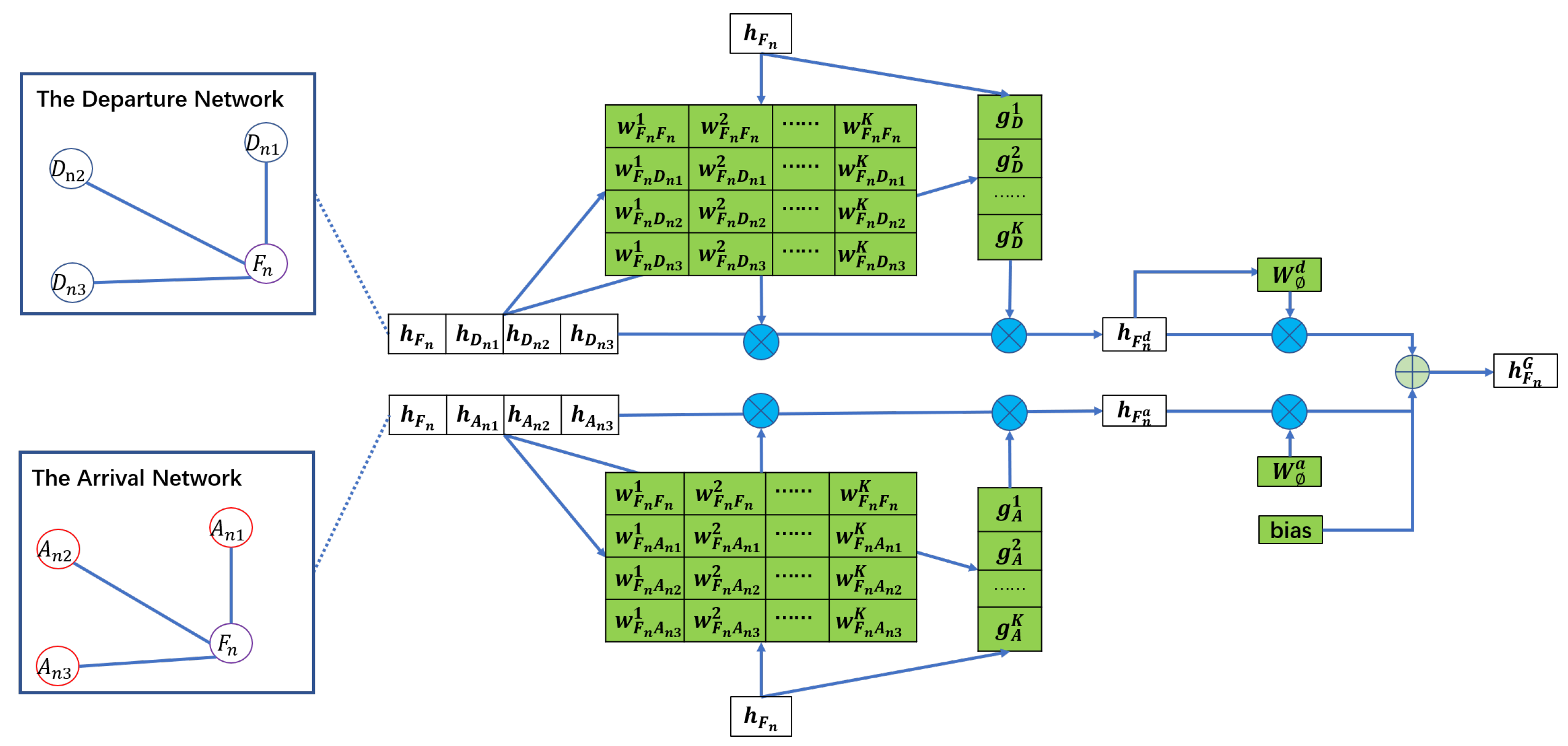
3.1. Heterogeneous Graph-Level Attention
3.1.1. Nodes Aggregating Based on Different Meta-Path
3.1.2. Different Meta-Path Aggregating
3.2. Sequence-Level Attention
4. Experiments
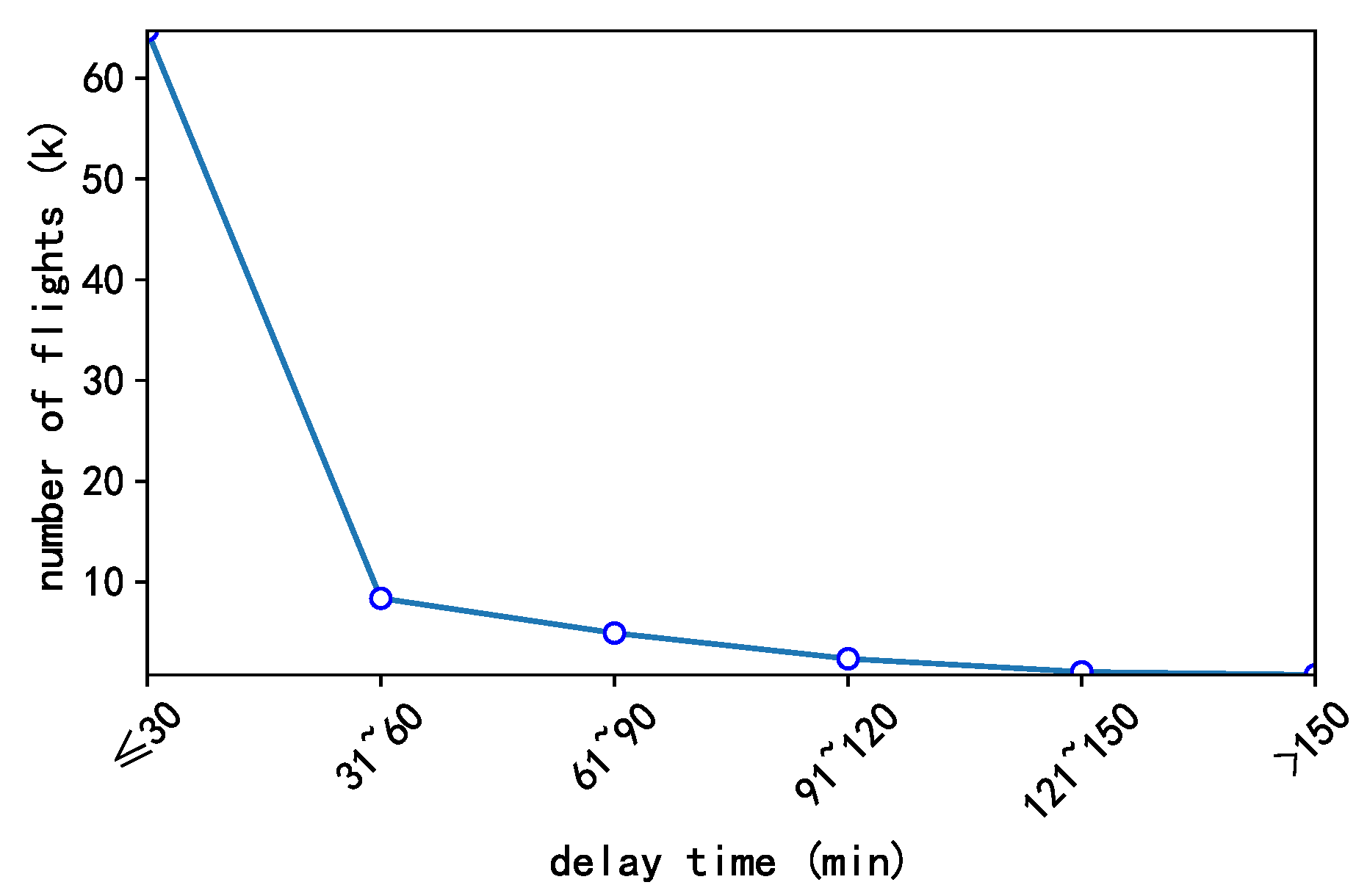
4.1. Data Set
4.1.1. Data Preprocessing
4.1.2. Features.
- weather.where and are temperature, visibility, wind speed, cloud, and weather phenomenon.
- aircraft.where and are the aircraft type and age.
- time.where and are the day of week, day of month, month and the season.
- air routes.where and are the crow-fly distance, the azimuth angle of the routes, backlog rate at the departure airport, departure rate at the departure airport, delay rate at the arrival airport and acceptance rate at the arrival airport. Among them, and are calculated from latitude and longitude of the departure airport and arrival airport, the others are calculated by the following formulas:where is the number of flights that should have departed but did not actually depart in the time window, and is the number of flights that should have departed in the time window.where is the number of flights that have departed in the time window, and is the mean of historical departures in the time window.where is the number of flights that should have arrived but did not actually arrive in the time window, and is the number of flights that should have arrived in the time window.where is the number of flights that have arrived in the time window, and is the mean of historical arrivals in the time window.
- Crow-fly distance. A crow-fly distance of flight , calculated from latitude and longitude of its departure airport and arrival airport.
- the rest time between the previous flight and the flight .
- the distance between the arrival airport of the previous flight and the departure airport of the flight .
4.2. Experimental Evaluation
4.3. Baselines
4.3.1. Binary Categories
4.3.2. Three Categories
4.3.3. Four Categories
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mueller, E.; Chatterji, G. Analysis of aircraft arrival and departure delay characteristics. In Proceedings of the AIAA’s Aircraft Technology, Integration, and Operations (ATIO) 2002 Technical Forum, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1–3 October 2002; p. 5866. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Y.; Ball, M.O.; Jank, W.S. Estimating flight departure delay distributions—A statistical approach with long-term trend and short-term pattern. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2008, 103, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.B.; Zhang, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, X.B.; Zhang, J. Delay causality network in air transport systems. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2018, 118, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wu, C.L.; Feng, T.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, S. Comparative analysis on propagation effects of flight delays: A case study of china airlines. J. Adv. Transp. 2018, 2018, 5236798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, N.; Moro, S.; Costa, C.J.; Aparício, M. Factors influencing charter flight departure delay. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2019, 100413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishna, P.; Ganesan, R.; Sherry, L. Accuracy of reinforcement learning algorithms for predicting aircraft taxi-out times: A case-study of Tampa Bay departures. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2010, 18, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adacher, L.; Flamini, M.; Romano, E. Airport ground movement problem: Minimization of delay and pollution emission. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 3830–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.; Donohue, G.; Hoffman, K.; Chen, C.H. Optimum airport capacity utilization under congestion management: A case study of New York LaGuardia airport. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2008, 31, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murça, M.C.R.; Hansman, R.J. Identification, Characterization, and Prediction of Traffic Flow Patterns in Multi-Airport Systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 20, 1683–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollo, J.J.; Balakrishnan, H. Characterization and prediction of air traffic delays. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2014, 44, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.M. The impacts of changing flight demands and throughput performance on airport delays through the Great Recession. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2016, 86, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Hansen, M. Deconstructing delay: A non-parametric approach to analyzing delay changes in single server queuing systems. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2013, 58, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wu, C.L. Enhanced delay propagation tree model with Bayesian Network for modelling flight delay propagation. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2018, 41, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Liu, B.; Tian, Y.; Wan, L. A Methodology for Predicting Aggregate Flight Departure Delays in Airports Based on Supervised Learning. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, G.; Liu, F.; Sun, J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, D. Flight Delay Prediction Based on Aviation Big Data and Machine Learning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Sun, J.; Liu, M.; Yang, J.; Gui, G. Generalized Flight Delay Prediction Method Using Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 91st Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Spring), Antwerp, Belgium, 25–28 May 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, S.; Marco, G.; Ah Chung, T.; Markus, H.; Gabriele, M. The graph neural network model. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2009, 20, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Bruna, J.; Zaremba, W.; Szlam, A.; Lecun, Y. Spectral Networks and Locally Connected Networks on Graphs. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6203. [Google Scholar]
- Henaff, M.; Bruna, J.; LeCun, Y. Deep convolutional networks on graph-structured data. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.05163. [Google Scholar]
- Hammond, D.K.; Vandergheynst, P.; Gribonval, R. Wavelets on graphs via spectral graph theory. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2011, 30, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defferrard, M.; Bresson, X.; Vandergheynst, P. Convolutional neural networks on graphs with fast localized spectral filtering. In Proceedings of the neural information processing systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; pp. 3844–3852. [Google Scholar]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-Supervised Classification with Graph Convolutional Networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.02907. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Ma, T.; Xiao, C. Fastgcn: Fast learning with graph convolutional networks via importance sampling. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.10247. [Google Scholar]
- Duvenaud, D.; Maclaurin, D.; Aguileraiparraguirre, J.; Gómezbombarelli, R.; Hirzel, T.; Aspuruguzik, A.; Adams, R.P. Convolutional Networks on Graphs for Learning Molecular Fingerprints. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Atwood, J.; Towsley, D. Diffusion-convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; pp. 1993–2001. [Google Scholar]
- Niepert, M.; Ahmed, M.O.; Kutzkov, K. Learning convolutional neural networks for graphs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 2014–2023. [Google Scholar]
- Monti, F.; Boscaini, D.; Masci, J.; Rodola, E.; Svoboda, J.; Bronstein, M.M. Geometric deep learning on graphs and manifolds using mixture model cnns. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5115–5124. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, W.L.; Ying, Z.; Leskovec, J. Inductive Representation Learning on Large Graphs. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 1024–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, R.; He, R.; Chen, K.; Eksombatchai, P.; Hamilton, W.L.; Leskovec, J. Graph Convolutional Neural Networks for Web-Scale Recommender Systems. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Veličković, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Lio, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph Attention Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, X.; Xie, J.; Hao, M.; Yeung, D.Y. GaAN: Gated Attention Networks for Learning on Large and Spatiotemporal Graphs. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.07294. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J. Semi-supervised learning on graphs with generative adversarial nets. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Torino, Italy, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 913–922. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I. NIPS 2016 Tutorial: Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1701.00160. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ji, H.; Shi, C.; Wang, B.; Cui, P.; Yu, P.; Ye, Y. Heterogeneous Graph Attention Network. In Proceedings of the World Wide Web Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 May 2019; pp. 2022–2032. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, M.; Bengio, Y.; Tang, J. GMNN: Graph Markov Neural Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.06214. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Pan, S.; Jiang, J.; Huo, H.; Long, G. DAGCN: Dual Attention Graph Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Budapest, Hungary, 14–19 July 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, W.; Cui, Z.; Yang, J. Dual-Attention Graph Convolutional Network. In Pattern Recognition; Palaiahnakote, S., Sanniti di Baja, G., Wang, L., Yan, W.Q., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 238–251. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yi, F.; Zhu, N.; Xiong, H. Spatio-Temporal Dual Graph Attention Network for Query-POI Matching. In Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Virtual Event, Xi’an, China, 25–30 July 2020; pp. 629–638. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.; Lee, C.; Bahng, H.; Tae, Y.; Jin, S.; Kim, K.; Ko, S.; Choo, J. ST-GRAT: A Novel Spatio-temporal Graph Attention Networks for Accurately Forecasting Dynamically Changing Road Speed. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, Galway, Ireland, 19–23 October 2020; pp. 1215–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Ge, J.; Ning, K. An Airport Scene Delay Prediction Method Based on LSTM. In Advanced Data Mining and Applications; Gan, G., Li, B., Li, X., Wang, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 160–169. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.J.; Choi, S.; Briceno, S.; Mavris, D. A deep learning approach to flight delay prediction. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/AIAA 35th Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), Sacramento, CA, USA, 25–29 September 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
| Variables | Description |
|---|---|
| V | A node set |
| E | An edge set |
| M | A meta-path set, include FAF and FDF |
| L | The nodes’ label set |
| A heterogeneous graph, | |
| A graph sequence. | |
| The current flight of the n-th heterogeneous graph in graph sequence | |
| The flight ’s neighbors with the same departure airport, | |
| The flight ’s neighbors with the same arrival airport, | |
| Flight i’s features, | |
| Aggregate feature of flight in the departure network | |
| Aggregate feature of flight in the arrival network | |
| Aggregate feature of flight in the whole heterogeneous graph | |
| The soft gate to control the importance of k-th head in departure network | |
| The soft gate to control the importance of k-th head in arrival network | |
| The feature of sequence and | |
| Final embedding of Flight |
| Delay Time (min) | Precision | Recall | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ≤30 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.93 |
| 31–60 | 0.83 | 0.75 | 0.79 |
| 61–90 | 0.85 | 0.72 | 0.76 |
| 91–120 | 0.83 | 0.63 | 0.72 |
| 121–150 | 0.90 | 0.40 | 0.55 |
| >150 | 0.91 | 0.45 | 0.60 |
| total accuracy | 0.89 |
| Delay Time (min) | Precision | Recall | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ≤30 | 0.97 | 0.79 | 0.87 |
| 31–60 | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.80 |
| 61–90 | 0.54 | 0.70 | 0.61 |
| 91–120 | 0.35 | 0.85 | 0.50 |
| 121–150 | 0.16 | 0.92 | 0.27 |
| >150 | 0.20 | 0.95 | 0.33 |
| total accuracy | 0.79 |
| Model | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| [41] LSTM | 0.88 |
| [42] LSTM | 0.87 |
| [5] NN | 0.73 |
| [5] SVM | 0.73 |
| [5] RF | 0.76 |
| [16] GBDT | 0.88 |
| [15] | 0.90 |
| SGDAN | 0.91 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Z.; Mei, G.; Liu, S.; Pan, L.; Bian, L.; Tang, H.; Wang, D. SGDAN—A Spatio-Temporal Graph Dual-Attention Neural Network for Quantified Flight Delay Prediction. Sensors 2020, 20, 6433. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226433
Guo Z, Mei G, Liu S, Pan L, Bian L, Tang H, Wang D. SGDAN—A Spatio-Temporal Graph Dual-Attention Neural Network for Quantified Flight Delay Prediction. Sensors. 2020; 20(22):6433. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226433
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Ziyu, Guangxu Mei, Shijun Liu, Li Pan, Lei Bian, Hongwu Tang, and Diansheng Wang. 2020. "SGDAN—A Spatio-Temporal Graph Dual-Attention Neural Network for Quantified Flight Delay Prediction" Sensors 20, no. 22: 6433. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226433
APA StyleGuo, Z., Mei, G., Liu, S., Pan, L., Bian, L., Tang, H., & Wang, D. (2020). SGDAN—A Spatio-Temporal Graph Dual-Attention Neural Network for Quantified Flight Delay Prediction. Sensors, 20(22), 6433. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226433






