Three-Dimensional Wind Measurement Based on Ultrasonic Sensor Array and Multiple Signal Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. 3D Wind Measurement
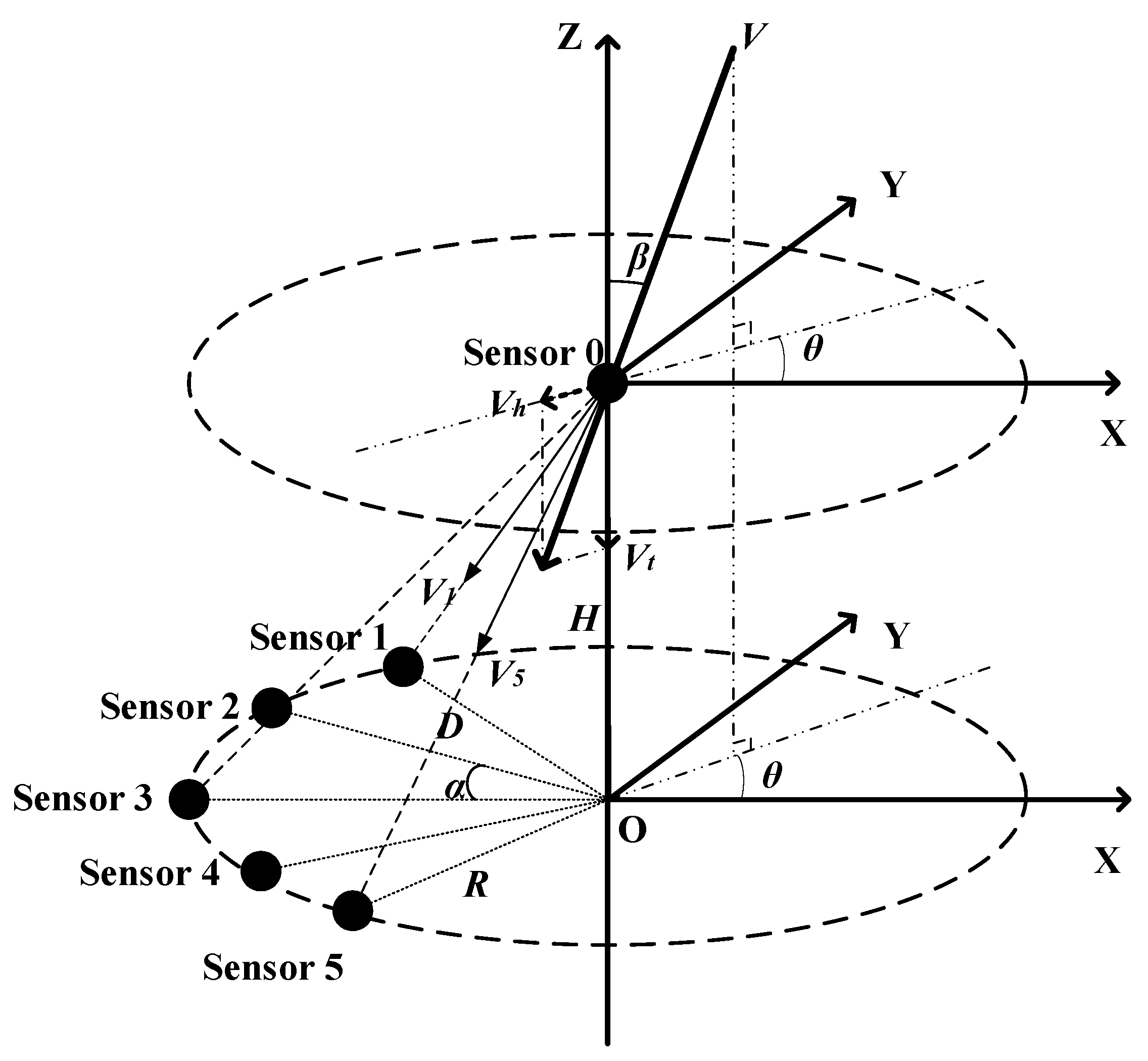
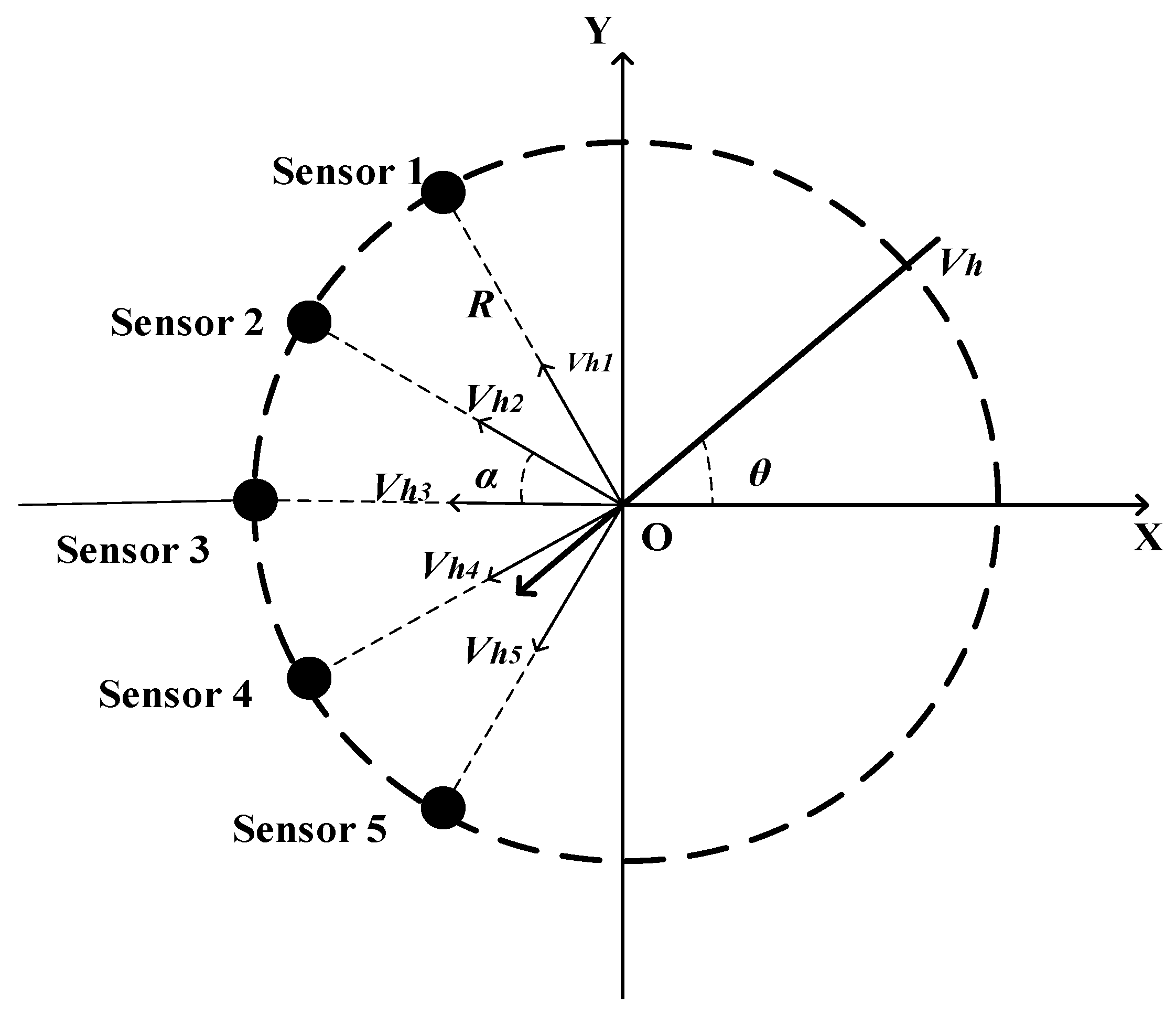
2.1. The Ultrasonic Sensor Array
2.2. Measuring Principle
2.2.1. Premise Assumptions
2.2.2. Signal Model
2.3. Wind Measurement Based on MUSIC Algorithm
3. Simulations and Results
3.1. Simulations
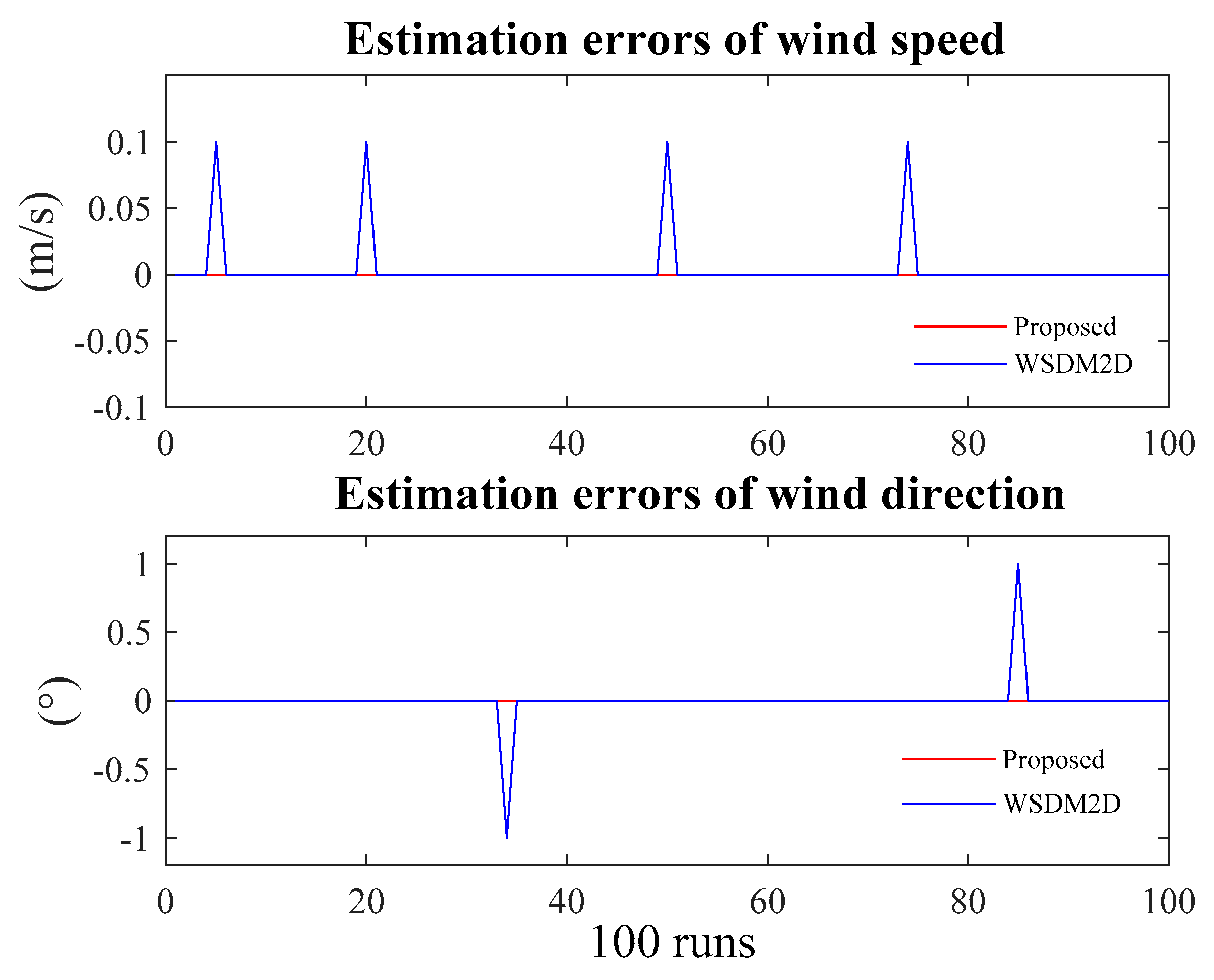
3.2. Comparison with State-Of-The-Art Method
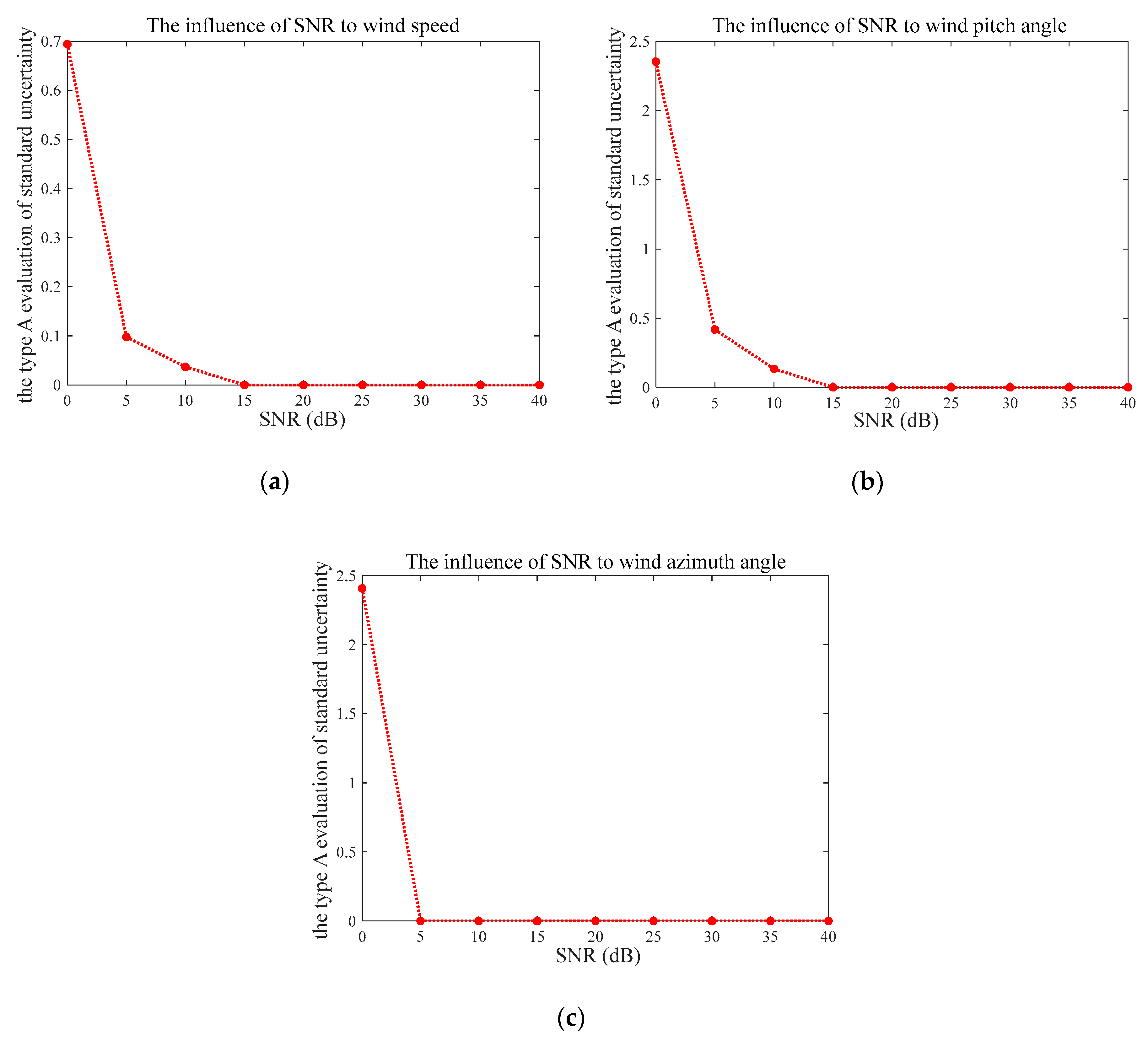
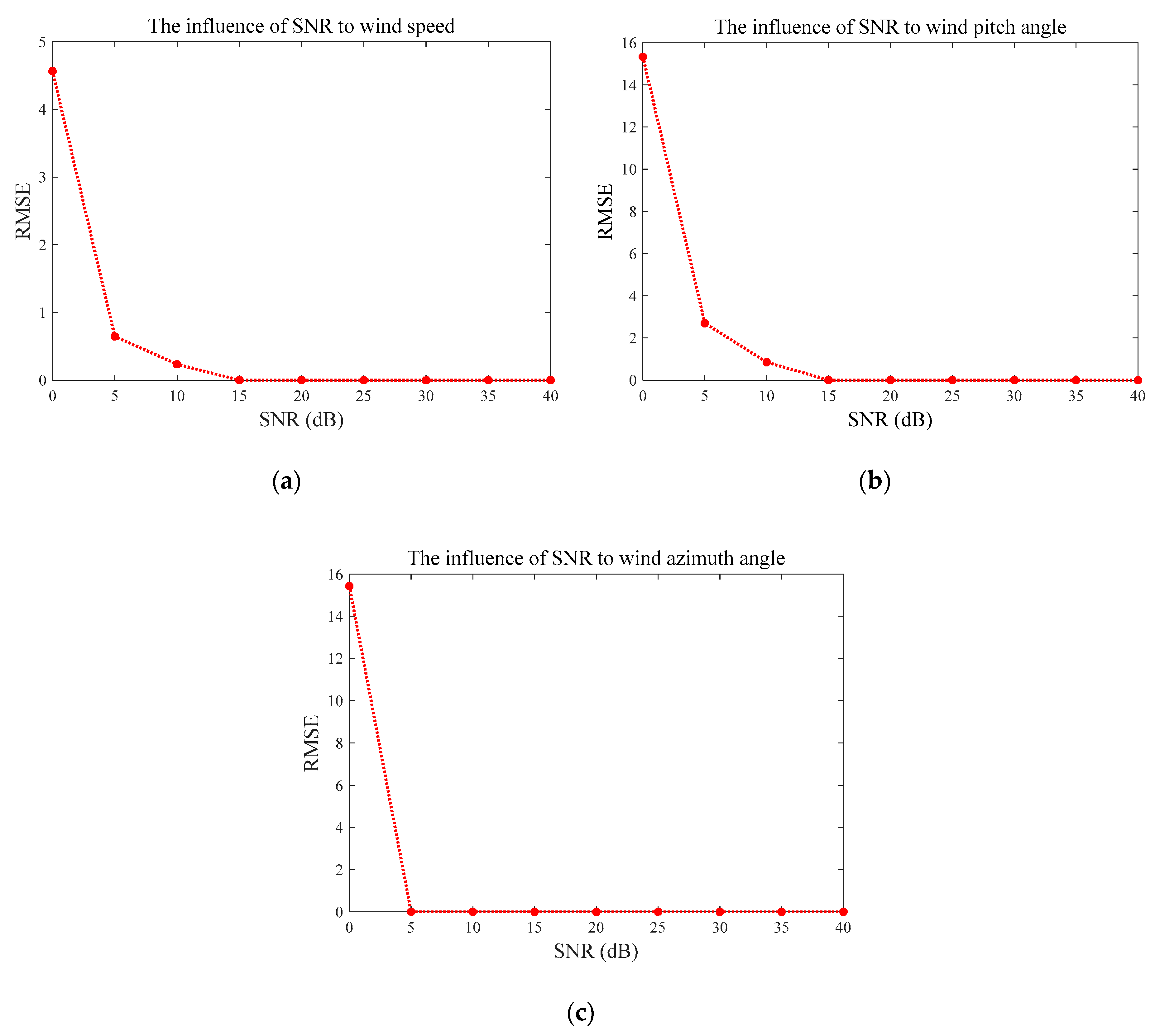
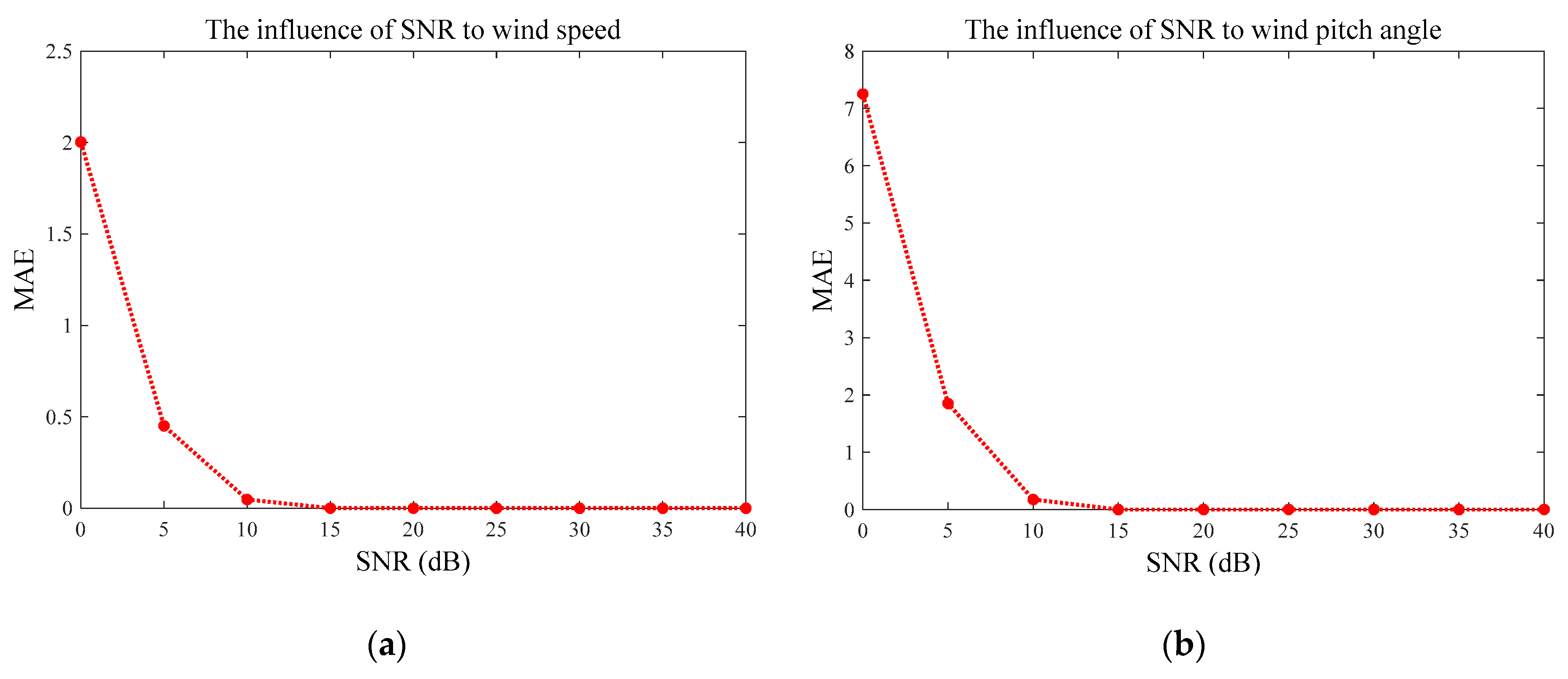
- The trends of RMSEs and MAEs are consistent, which all decrease with higher SNR.
- Accordingly, the biggest RMSE and MAE of wind speed and direction occur at SNR of 0 dB. The biggest wind speed RMSE of the proposed method is slightly bigger than that of WSDM2D, while the biggest direction RMSE is smaller.
- The speed and direction RMSEs of proposed method tend to zeros as SNR of 5 dB, outperforming the WSDM2D method, which converges to zero since SNR15 dB. Wind speed and direction MAEs of two methods have similar patterns with those of RMSEs.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pechak, O.; Mavrotas, G.; Diakoulaki, D. Investigating the role of the clean development mechanism within the global green energy market: The case of wind energy. In Proceedings of the 2010 7th International Conference on the European Energy Market, Madrid, Spain, 23–25 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, A.K.; Saha, M. Wind power: A renewable alternative source of green energy. Int. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2012, 1, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabouris, J.; Kanellos, F.D. Impacts of large-scale wind penetration on designing and operation of electric power systems. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2010, 1, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Wijayatung, P. Grid integration of wind power best practices for emerging wind markets. In Adb Sustainable Development Working Paper Series; Technical Report; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong City, Philippines, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, R.J.; Fan, X.C.; He, Y. Comprehensive evaluation index system for wind power utilization levels in wind farms in china. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ran, P.; Li, Z.; Ni, W. Thermodynamic analysis of a hybrid thermal-compressed air energy storage system for the integration of wind power. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 66, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Energy Administration. Available online: http://www.nea.gov.cn/2019-01/28/c137780779.htm (accessed on 28 January 2019).
- Cavallo, A. Controllable and affordable utility-scale electricity from intermittent wind resources and compressed air energy storage (CAES). Energy 2007, 32, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlia, T.M.I.; Saktisahdan, T.J.; Jannifar, A.; Hasan, M.H.; Matseelar, H.S.C. A review of available methods and development on energy storage technology update. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 532–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treiber, N.A.; Heinermann, J.; Kramer, O. Wind power prediction with machine learning. In Computational Sustainability; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 13–29. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, A.K.; Ramesh, L. Application of neural networks in wind power (generation) prediction. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Sustainable Power Generation and Supply, Nanjing, China, 6–7 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pichugina, Y.; Banta, R.; Brewer, A.; Choukulkar, A.; Marquis, M.; Olson, J.; Hardesty, M. Doppler lidar in the wind forecast improvement projects. In EPJ Web of Conferences. EDP Sci. 2016, 119, 10001. [Google Scholar]
- Schlipf, D.; Kapp, S.; Anger, J.; Bischoff, O.; Hofs, M.; Rettenmeier, A.; Khn, M. Prospects of optimization of energy production by lidar assisted control of wind turbines. Proc. EWEA Conf. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- René, B.; Ashim, G.; Wim, B. Assessing the severity of wind gusts with lidar. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 758. [Google Scholar]
- Hyson, P. Cup anemometer response to fluctuating wind speeds. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1972, 11, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, P.; Javier, C.; Sanz-Andrés, A. Aerodynamic analysis of cup anemometers performance: The stationary harmonic response. Sci. World. J. 2013, 2013, 197325. [Google Scholar]
- Roibas-Millan, E.; Cubas, J.; Pindado, S. Studies on cup anemometer performances carried out at IDR/UPM institute. Past and Present Research. Energies 2017, 10, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghrouche, M.; Adane, A.; Boussey, J.; Ameur, S.; Meunier, D.; Tardu, S. A miniature silicon hot wire sensor for automatic wind speed measurements. Renew. Energy 2005, 30, 1881–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Yi, Z.; Gao, S.; Qin, M.; Huang, Q.A. DRIE trenches and full-bridges for improving sensitivity of 2-d micromachined silicon thermal wind sensor. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2017, 26, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Qin, M.; Ye, Y.; Yi, Z.; Huang, Q.A. Modelling and characterization of a robust, lowpower and wide-range thermal wind sensor. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 5571–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, R.C. Ultrasonic Measurements and Technologies; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, G.M.G.; Pereira, D.S.J.D.; De Franca, J.A.; Bernadete, D.M.F.M.; Lucas, D.S.R.; Moreira, M.; Elias, P. Development of 3-d ultrasonic anemometer with nonorthogonal geometry for the determination of high-intensity winds. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 2836–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi-Bo, D.; Yi-Feng, Z.; Chun-Yu, L.; Jian, W. Study of the ultrasonic three-dimensional wind speed measurement methods based on the phase difference. In Proceedings of the 2016 Sixth International Conference on Instrumentation & Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control (IMCCC), Harbin, China, 21–23 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pindado, S.; Barrero-Gil, A.; Sanz, A. Cup anemometers’ loss of performance due to ageing processes, and its effect on annual energy production (AEP) estimates. Energies 2012, 5, 1664–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azorin-Molina, C.; Asin, J.; McVicar, T.R.; Minola, L.; Lopez-Moreno, J.I.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Chen, D. Evaluating anemometer drift: A statistical approach to correct biases in wind speed measurement. Atmos. Res. 2018, 203, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindado, S.; Cubas, J.; Sorribes-Palmer, F. The Cup Anemometer, a Fundamental Meteorological Instrument for the Wind Energy Industry. Research at the IDR/UPM Institute. Sensors 2014, 14, 21418–21452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.M.; Lu, J.Y.; Miao, J.M.; Hans, H.; Rahman, H.A.; Pan, S.S.; Norford, L. An aerodynamically efficient sphere anemometer with integrated hot-film sensors for 2-d environmental airflow monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2011 16th International Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference, Beijing, China, 5–9 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bucci, G.; Ciancetta, F.; Fiorucci, E.; Gallo, D.; Landi, C.; Luiso, M. A low-cost ultrasonic wind speed and direction measurement system. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 6–9 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Jun, Y. High accuracy time of flight measurement for ultrasonic anemometer applications. In Proceedings of the 2013 Third International Conference on Instrumentation, Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control, Shenyang, China, 21–23 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Contini, D.; Donateo, A.; Belosi, F. Accuracy of measurements of turbulent phenomena in the surface layer with an ultrasonic anemometer. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2006, 23, 785–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, V.; Windorfer, H. Comparison of pressure and ultrasound measurements in vortex flow meters. Measurement 2003, 33, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankanin, G. The vortex flowmeter: Various methods of investigating phenomena. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, R1–R16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Kim, S.; Park, S. Two-dimensional ultrasonic anemometer using the directivity angle of an ultrasonic sensor. Microelectron. J. 2008, 39, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, P.; Bhakthavatchalu, R.; Kumar, P.P. Time of flight measurement system for an ultrasonic anemometer. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Control, Instrumentation, Communication and Computational Technologies (ICCICCT), Kumaracoil, India, 16–17 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xinbo, L.; Haixin, S.; Wei, G.; Yaowu, S.; Guojun, L.; Yue, W. Wind speed and direction measurement based on arc ultrasonic sensor array signal processing algorithm. ISA Trans. 2016, 65, 437–444. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1986, 34, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung-Yen, L.; Shao-Hua, T.; Chieh-Wen, T.; Huei-Jeng, L. Influence of the vertical wind and wind direction on the power output of a small vertical-axis wind turbine installed on the rooftop of a building. Appl. Energy 2018, 209, 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ruan, H.; Wang, S. Fast direction finding technology based on music algorithm with circular array. J. Data Acquis. Process. 2011, 26, 374–378. [Google Scholar]
- Xinbo, L.; GeYan, Z.; Wei, G.; Haixin, S.; Guojun, L.; Yue, W.; Yaowu, S. A novel ultrasonic array signal processing scheme for wind measurement. ISA Trans. 2018, 81, 259–269. [Google Scholar]
- Changuel, H.; Harabi, F.; Gharsallah, A. 2-L-shape two-dimensional arrival angle estimation with a classical subspace algorithm. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2006, 66, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qi, Z.S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, B.H.; Gong, C. Performance analysis of MUSIC for conformal array. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, Shanghai, China, 21–25 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cuerva, A.; Sanz-Andrés, A.; Navarro, J. On multiple-path sonic anemometer measurement theory. Exp. Fluids 2003, 34, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandard, E.; Kouame, D.; Battault, R. Transit time ultrasonic flowmeter: Velocity profile estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 18–21 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, D.; Gomes, L.; Costa, A. Wind speed and direction measurement based on time of flight ultrasonic anemometer. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 26th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Edinburgh, UK, 19–21 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H. DOA Estimation Based on MUSIC Algorithm. Linnéuniversitetet, Kalmar Vaxjo. 16 May 2014. Available online: http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:lnu:diva-35058 (accessed on 16 January 2020).


| SNR (dB) | RMSE | MAE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Direction | Speed | Direction | |||||
| Proposed | WSD M2D | Proposed | WSDM2D | Proposed | WSDM2D | Proposed | WSDM2D | |
| 0 | 6.023 | 3.150 | 4.970 | 13.506 | 0.824 | 0.337 | 0.820 | 1.420 |
| 5 | 0 | 0.020 | 0 | 0.141 | 0 | 0.004 | 0 | 0.020 |
| 10 | 0 | 0.010 | 0 | 0.100 | 0 | 0.001 | 0 | 0.010 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, B.; Teng, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, R.; Ju, Y.; Liu, S. Three-Dimensional Wind Measurement Based on Ultrasonic Sensor Array and Multiple Signal Classification. Sensors 2020, 20, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20020523
Ma B, Teng J, Zhu H, Zhou R, Ju Y, Liu S. Three-Dimensional Wind Measurement Based on Ultrasonic Sensor Array and Multiple Signal Classification. Sensors. 2020; 20(2):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20020523
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Bian, Jing Teng, Huixian Zhu, Rong Zhou, Yun Ju, and Shi Liu. 2020. "Three-Dimensional Wind Measurement Based on Ultrasonic Sensor Array and Multiple Signal Classification" Sensors 20, no. 2: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20020523
APA StyleMa, B., Teng, J., Zhu, H., Zhou, R., Ju, Y., & Liu, S. (2020). Three-Dimensional Wind Measurement Based on Ultrasonic Sensor Array and Multiple Signal Classification. Sensors, 20(2), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20020523





