Toward Joint Acquisition-Annotation of Images with Egocentric Devices for a Lower-Cost Machine Learning Application to Apple Detection
Abstract
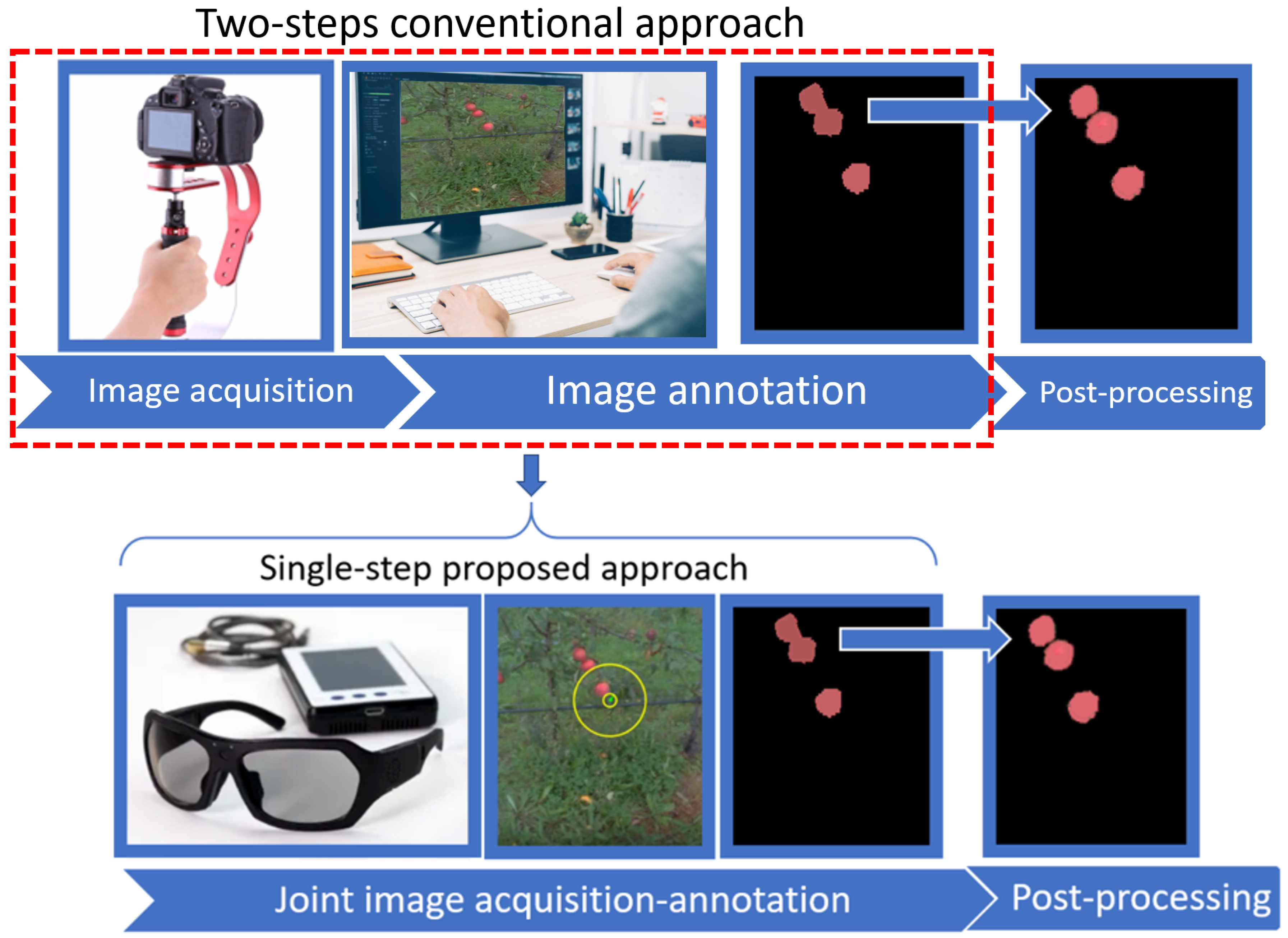
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Material and Method
3.1. Egocentric Vision Device
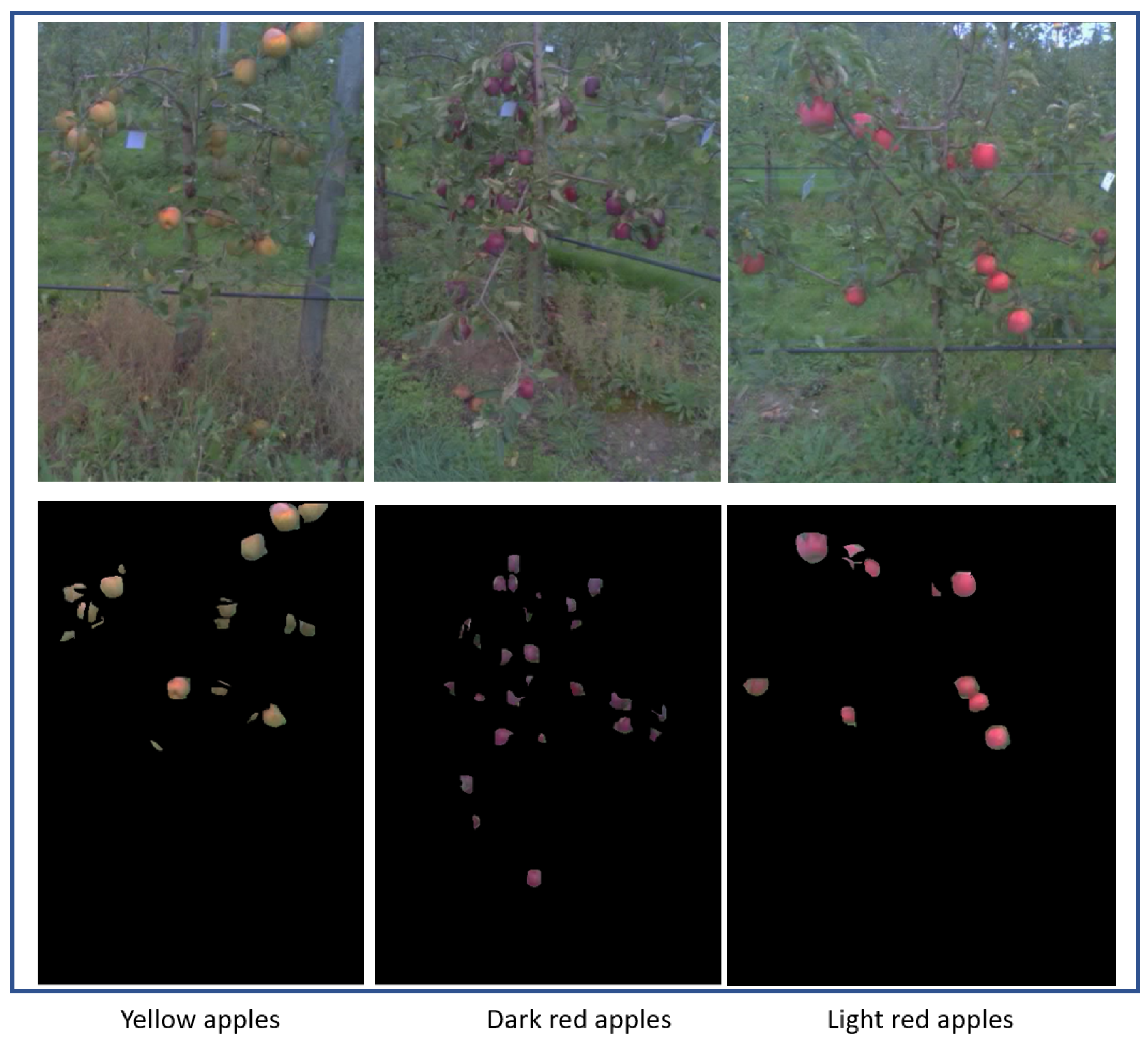
3.2. Dataset
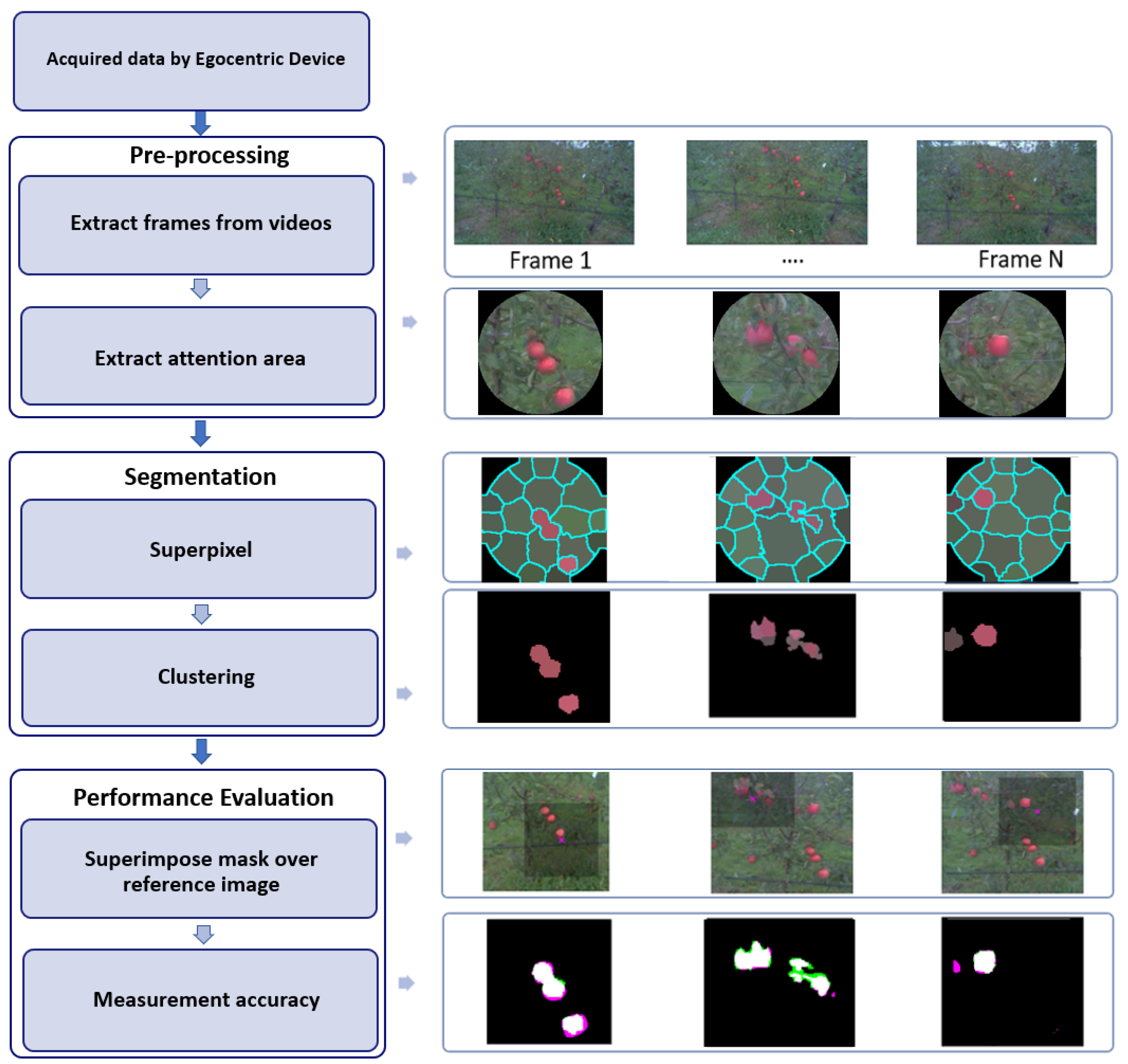
4. Image Processing Pipeline
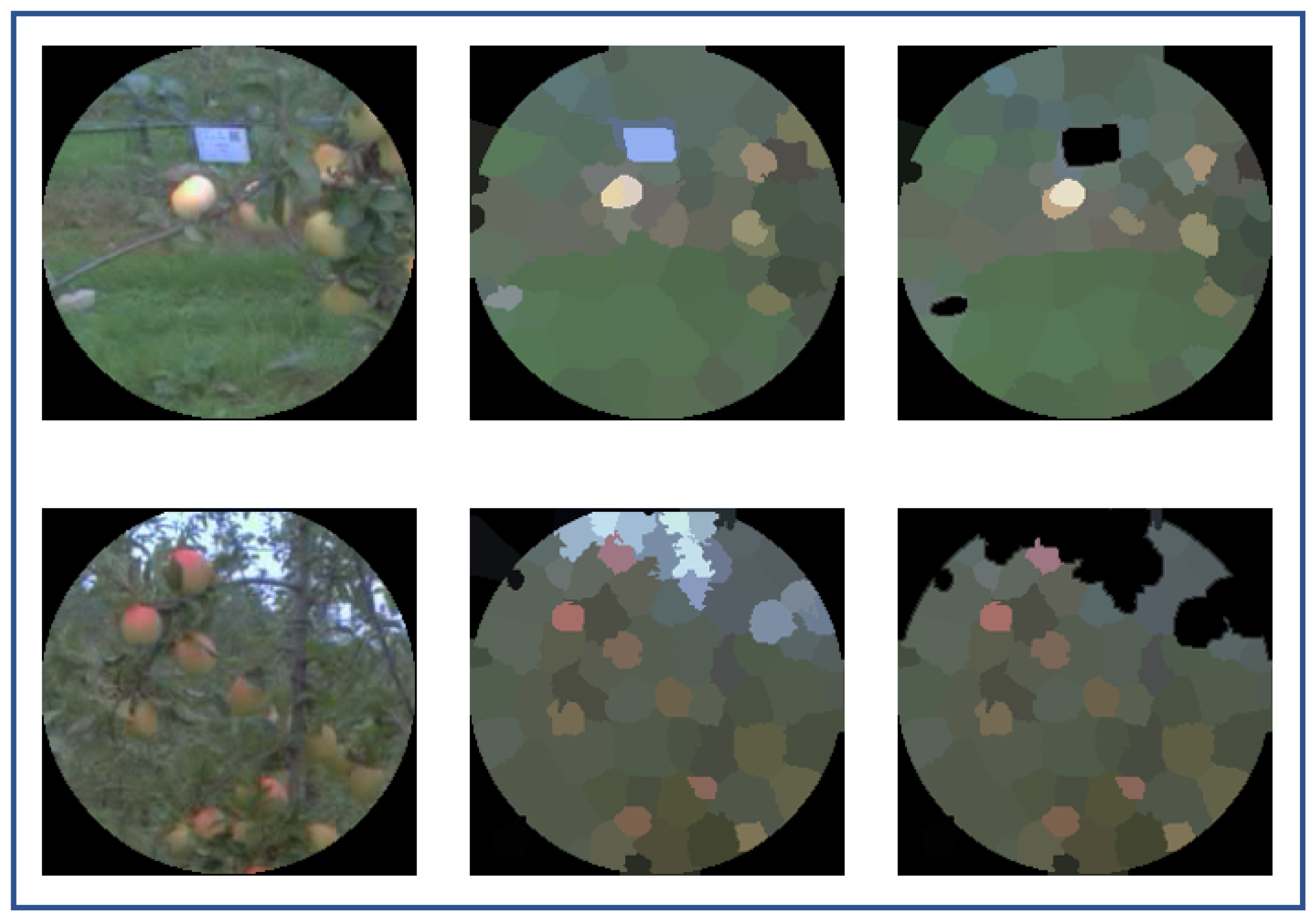
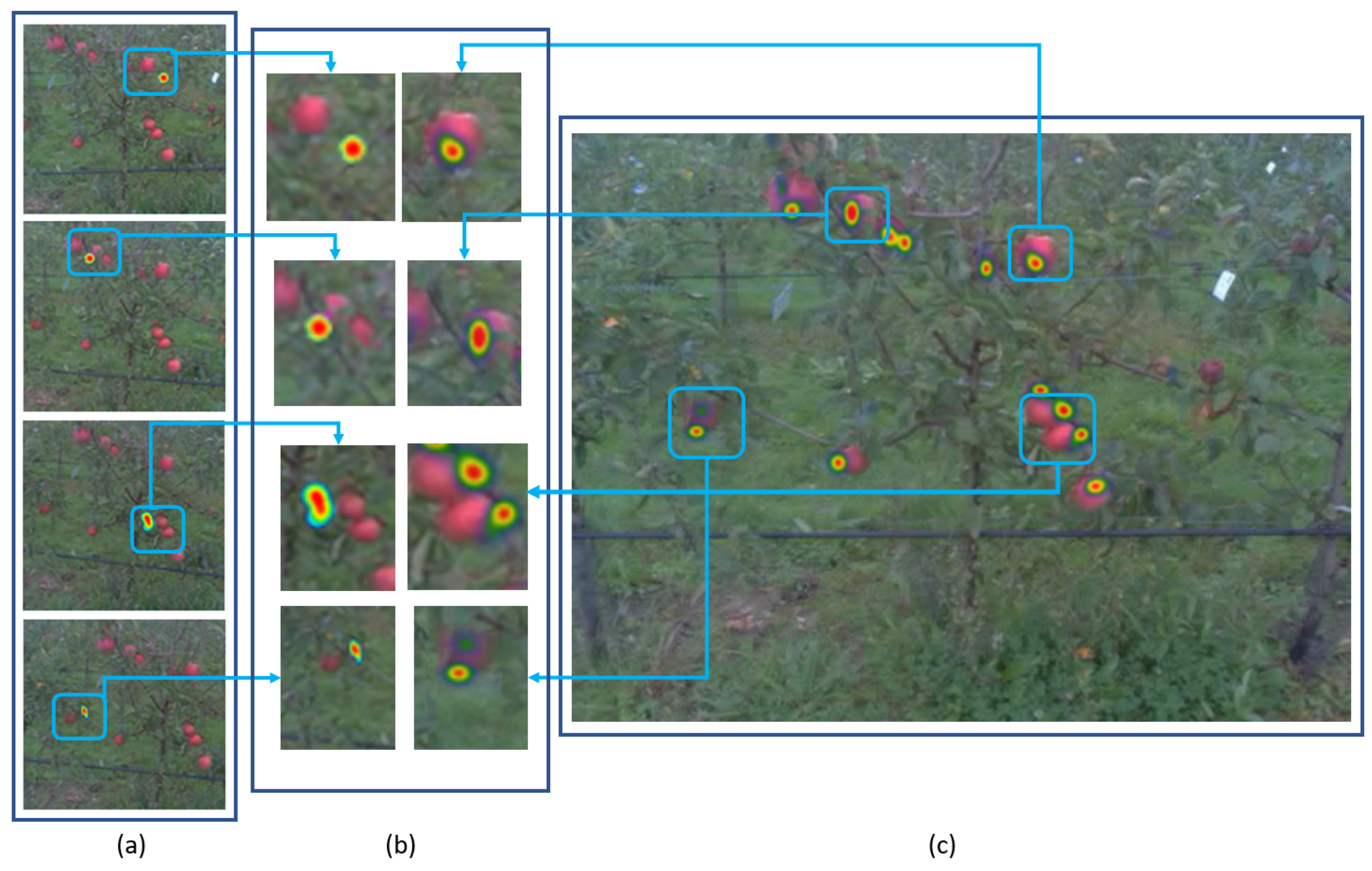
5. Strategies for Extracting Attention Area
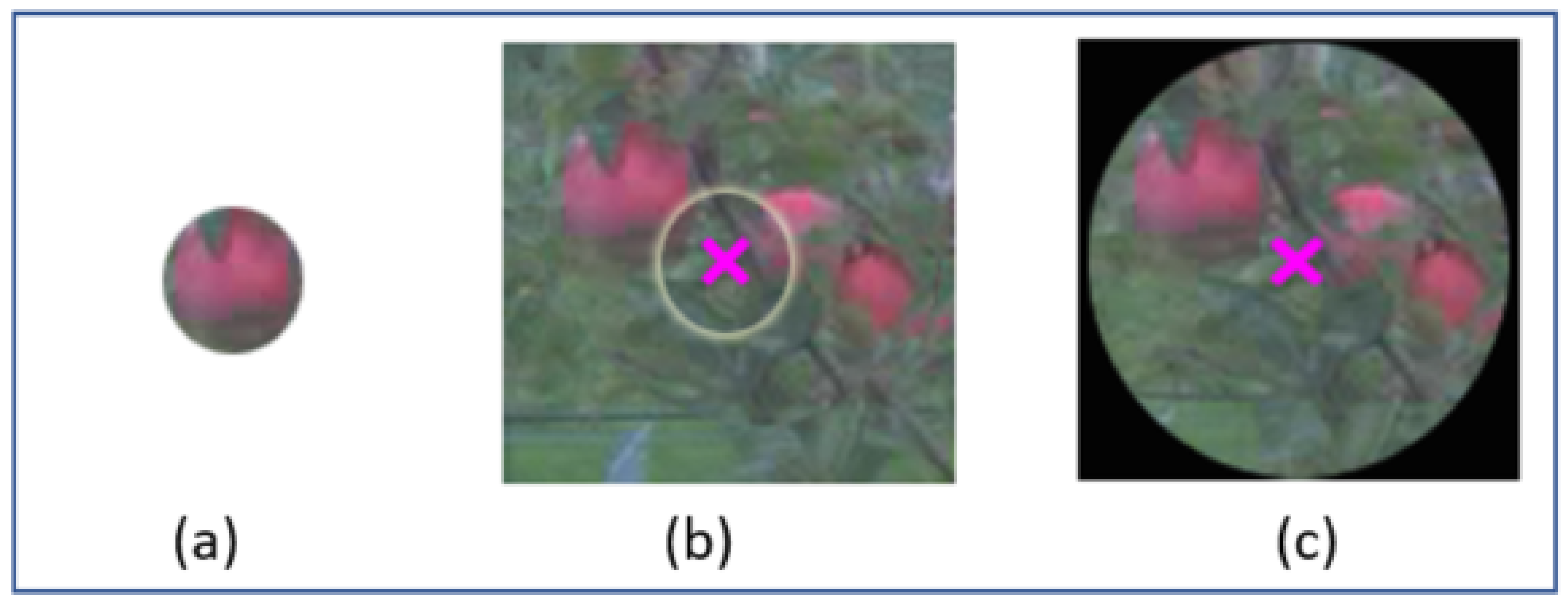
5.1. Attention Area from Eye-Tracking
5.1.1. Selection by Eye-Tracking Glasses
5.1.2. Selection by Screen-Based Eye-Tracking
5.2. Attention Area without Eye-Tracking
5.2.1. Full-Frame
5.2.2. Egocentric Prior
5.2.3. Saliency Map
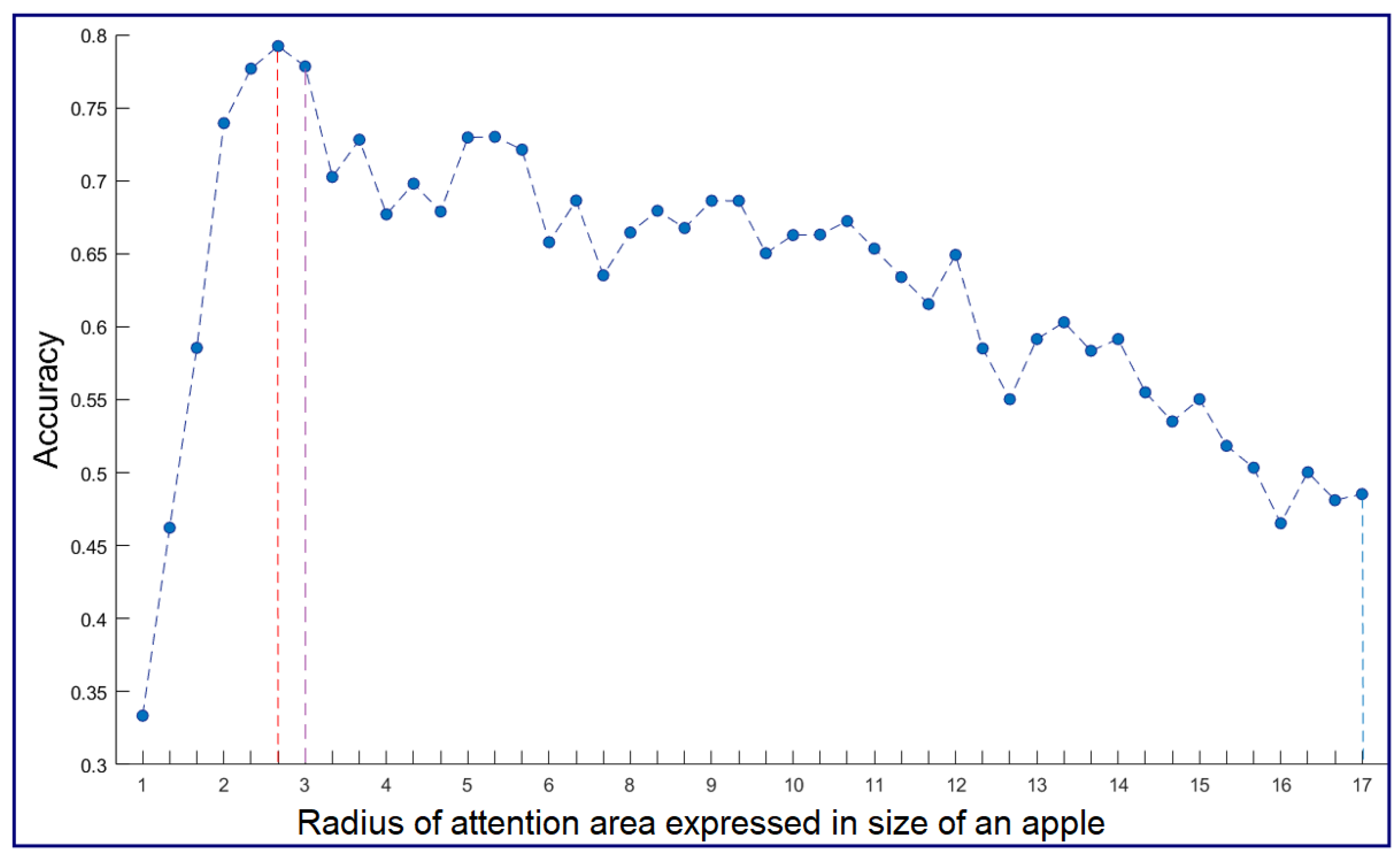
6. Results and Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamilaris, A.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F.X. Deep learning in agriculture: A survey. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 147, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, L.; Rousseau, D.; Belin, É.; Demilly, D.; Chapeau-Blondeau, F. Simulation of image acquisition in machine vision dedicated to seedling elongation to validate image processing root segmentation algorithms. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2014, 104, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrida, M.V.; Scharr, H.; Tsaftaris, S.A. ARIGAN: Synthetic arabidopsis plants using generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW 2017), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2064–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, L.; Mateus, D.; Chatelain, P.; Declara, D.; Schworm, N.; Stangl, S.; Multhoff, G.; Navab, N. Assisting the examination of large histopathological slides with adaptive forests. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 35, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuffrida, M.V.; Chen, F.; Scharr, H.; Tsaftaris, S.A. Citizen crowds and experts: Observer variability in image-based plant phenotyping. Plant Methods 2018, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, R.; Ijsselmuiden, J.; Hemming, J.; Henten, E.V. Data synthesis methods for semantic segmentation in agriculture: A Capsicum annuum dataset. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 144, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douarre, C.; Schielein, R.; Frindel, C.; Gerth, S.; Rousseau, D. Transfer learning from synthetic data applied to soil–root segmentation in X-ray tomography images. J. Imaging 2018, 4, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiei, S.; Ahmad, A.; Rasti, P.; Belin, E.; Rousseau, D. Low-cost image annotation for supervised machine learning. Application to the detection of weeds in dense culture. In British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Computer Vision Problems in Plant Phenotyping (CVPPP); BMVA Press: Newcastle, UK, 2018; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Douarre, C.; Crispim-Junior, C.F.; Gelibert, A.; Tougne, L.; Rousseau, D. Novel data augmentation strategies to boost supervised segmentation of plant disease. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 165, 104967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.; Nieto, J.; Taylor, Z.; Underwood, J.; Sukkarieh, S. Orchard fruit segmentation using multi-spectral feature learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 5314–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubbens, J.; Cieslak, M.; Prusinkiewicz, P.; Stavness, I. The use of plant models in deep learning: An application to leaf counting in rosette plants. Plant Methods 2018, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, A.; Farhadi, A.; Rehg, J.M. Understanding egocentric activities. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, A.R.; Caprani, N.; Conaire, C.Ó.; Kalnikaite, V.; Gurrin, C.; Smeaton, A.F.; O’Connor, N.E. Passively recognising human activities through lifelogging. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2011, 27, 1948–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirsiavash, H.; Ramanan, D. Detecting activities of daily living in first-person camera views. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 2847–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Grauman, K. Story-driven summarization for egocentric video. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2714–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, A.; Ren, X.; Rehg, J.M. Learning to recognize objects in egocentric activities. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 3281–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erculiani, L.; Giunchiglia, F.; Passerini, A. Continual egocentric object recognition. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 2019, arXiv:1912.05029v2. [Google Scholar]
- Davison, A.J.; Reid, I.D.; Molton, N.D.; Stasse, O. MonoSLAM: Real-time single camera SLAM. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 1052–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rituerto, A. Modeling the environment with egocentric vision systems. Electron. Lett. Comput. Vis. Image Anal. 2015, 14, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alletto, S.; Serra, G.; Calderara, S.; Cucchiara, R. Understanding social relationships in egocentric vision. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 4082–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt, A.; Morerio, P.; Regazzoni, C.S.; Rauterberg, M. The Evolution of First Person Vision Methods: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2015, 25, 744–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.Y.; Hsu, S.C.; Huang, C.L. First-person-vision-based driver assistance system. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Audio, Language and Image Processing, Shanghai, China, 7–9 July 2014; pp. 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayol, W.W.; Davison, A.J.; Tordoff, B.J.; Murray, D.W. Applying active vision and SLAM to wearables. In Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics; Dario, P., Chatila, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 15, pp. 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, S.; Benois-Pineau, J.; Mégret, R.; Dovgalecs, V.; Dartigues, J.F.; Gaëstel, Y. Human daily activities indexing in videos from wearable cameras for monitoring of patients with dementia diseases. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 August 2010; pp. 4113–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, A.R.; Hodges, S.E.; King, A.C.; Smeaton, A.F.; Berry, E.; Moulin, C.J.; Lindley, S.; Kelly, P.; Foster, C. Wearable cameras in health: The state of the art and future possibilities. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 44, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fathi, A.; Rehg, J.M. Learning to predict gaze in egocentric video. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 3216–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Kitani, K.M. Pixel-level hand detection in ego-centric videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 3570–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambach, S.; Lee, S.; Crandall, D.J.; Yu, C. Lending a hand: Detecting hands and recognizing activities in complex egocentric interactions. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; Volume 2015, pp. 1949–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Fan, H.; Kitani, K.M. Going Deeper into First-Person Activity Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 1894–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatler, B.W.; Baddeley, R.J.; Gilchrist, I.D. Visual correlates of fixation selection: Effects of scale and time. Vis. Res. 2005, 45, 643–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walber, T. Making use of eye tracking information in image collection creation and region annotation. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (MM 2012), Nara, Japan, 29 October–2 November 2012; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1405–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A.; Wang, K.; Santillan, C.; Hsiao, A.; Sirlin, C.B.; Murphy, P.M. Image Annotation by Eye Tracking: Accuracy and Precision of Centerlines of Obstructed Small-Bowel Segments Placed Using Eye Trackers. J. Digit. Imaging 2019, 32, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, E.A.; Goksel, A.K. Pictorial Pattern Recognition Applied To Fruit Harvesting. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1977, 20, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Grand, E.; Rabatel, A.G.; Pellenc, R.; Journeau, A.; Aldon, M.J. Magali: A self-propelled robot to pick apples. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. Pap. 1987, 46, 353–358. [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker, A.D.; Miles, G.E.; Mitchell, O.R.; Gaultney, L.D. Fruit Location in a Partially Occluded Image. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1987, 30, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaughter, D.C.; Harrell, R.C. Color vision in robotic fruit harvesting. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sites, P.W.; Delwiche, M.J. Computer Vision To Locate Fruit on a Tree. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1988, 31, 257–263, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabatel, G. A vision system for Magali, the fruit picking robot. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Agricultural Engineering, Paris, France, 2–5 March 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Kassay, L. Hungarian robotic apple harvester. In Proceedings of the ASAE Annual Meeting Papers, Charlotte, NC, USA, 21–24 June 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ceres, R.; Pons, J.; Jimenez, A.; Martin, J.; Calderon, L. Agribot: A Robot for Aided Fruit Harvesting. Ind. Robot. 1998, 25, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, A.R.; Ceres, R.; Pons, J.L.; Jimenez, A.R.; Ceres, R.; Pons, J.L. A survey of computer vision methods for locating fruit on trees. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2000, 43, 1911–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Damerow, L.; Sun, Y.; Blanke, M.M. Using colour features of cv. ’Gala’ apple fruits in an orchard in image processing to predict yield. Precis. Agric. 2012, 13, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Glasbey, C.A.; Horgan, G.W.; Polder, G.; Dieleman, J.A.; van der Heijden, G.W. Automatic fruit recognition and counting from multiple images. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 118, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, I.; Ge, Z.; Dayoub, F.; Upcroft, B.; Perez, T.; McCool, C. Deepfruits: A fruit detection system using deep neural networks. Sensors 2016, 16, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boogaard, F.P.; Rongen, K.S.; Kootstra, G.W. Robust node detection and tracking in fruit-vegetable crops using deep learning and multi-view imaging. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 192, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Nuske, S.; Bergerman, M.; Singh, S. Automated Crop Yield Estimation for Apple Orchards. In Experimental Robotics; Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.; Underwood, J.; Nieto, J.; Sukkarieh, S. A feature learning based approach for automated fruit yield estimation. In Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics; Mejias, L., Corke, P., Roberts, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 105, pp. 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargoti, S.; Underwood, J. Image classification with orchard metadata. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; Volume 2016, pp. 5164–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargoti, S.; Underwood, J.P. Image Segmentation for Fruit Detection and Yield Estimation in Apple Orchards. J. Field Robot. 2017, 34, 1039–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Huang, K. Semi-Supervised Learning: Background, Applications and Future Directions; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pise, N.N.; Kulkarni, P. A Survey of Semi-Supervised Learning Methods. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, Suzhou, China, 13–17 December 2008; Volume 2, pp. 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.J. Semi-Supervised Learning Literature Survey; Technical Report; University of Wisconsin-Madison Department of Computer Sciences: Madison, WI, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, P.; Kislay, A.; Plonski, P.A.; Luby, J.; Isler, V. Vision-based preharvest yield mapping for apple orchards. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 164, 104897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberger, J.; Gordon, S.; Greenspan, H. An efficient image similarity measure based on approximations of KL-divergence between two gaussian mixtures. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Nice, France, 13–16 October 2003; Volume 1, pp. 487–493. [Google Scholar]
- Blignaut, P. Fixation identification: The optimum threshold for a dispersion algorithm. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2009, 71, 881–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K. Eye movements in reading and information processing: 20 years of research. Psychol. Bull. 1998, 124, 372–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, R.J.K. What You Look at is What You Get: Eye Movement-Based Interaction Techniques. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI 90), Seattle, WA, USA, 1–5 April 1990; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, D.E. Eye Movements and Visual Cognition: Scene Perception and Reading; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 146–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, R.J.K. Eye Movement-Based Human-Computer Interaction Techniques: Toward Non-Command Interfaces. Adv. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2003, 4, 151–190. [Google Scholar]
- Salvucci, D.D.; Goldberg, J.H. Identifying Fixations and Saccades in Eye-Tracking Protocols. In Proceedings of the 2000 Symposium on Eye Tracking Research & Applications (ETRA’00), Palm Beach Gardens, FL, USA, 6–8 November 2000; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manor, B.R.; Gordon, E. Defining the temporal threshold for ocular fixation in free-viewing visuocognitive tasks. J. Neurosci. Methods 2003, 128, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchowski, A. Eye Tracking Methodology; Springer: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shic, F.; Scassellati, B.; Chawarska, K. The incomplete fixation measure. In Proceedings of the 2008 Symposium on Eye Tracking Research & Applications, Savannah, GA, USA, 26–28 March 2008; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; p. 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spakov, O.; Miniotas, D. Application of Clustering Algorithms in Eye Gaze Visualizations. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/b016/02b60a1fcb1ca06f6af0d4273a6336119bae.pdf (accessed on 21 June 2020).
- Zagoruyko, S.; Komodakis, N. Paying More Attention to Attention: Improving the Performance of Convolutional Neural Networks via Attention Transfer. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.03928. [Google Scholar]
- Safren, O.; Alchanatis, V.; Ostrovsky, V.; Levi, O. Detection of green apples in hyperspectral images of apple-tree foliage using machine vision. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 2303–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gené-Mola, J.; Vilaplana, V.; Rosell-Polo, J.R.; Morros, J.R.; Ruiz-Hidalgo, J.; Gregorio, E. KFuji RGB-DS database: Fuji apple multi-modal images for fruit detection with color, depth and range-corrected IR data. Data Brief 2019, 25, 104289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häni, N.; Roy, P.; Isler, V.; Hani, N.; Roy, P.; Isler, V. MinneApple: A Benchmark Dataset for Apple Detection and Segmentation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Chen, C. Fruit detection and segmentation for apple harvesting using visual sensor in orchards. Sensors 2019, 19, 4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jia, W.; Ruan, C.; Zhao, D.; Gu, Y.; Chen, W. The recognition of apple fruits in plastic bags based on block classification. Precis. Agric. 2018, 19, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, D.; Jia, W.; Ji, W.; Sun, Y. A Detection Method for Apple Fruits Based on Color and Shape Features. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 67923–67933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achanta, R.; Shaji, A.; Smith, K.; Lucchi, A.; Fua, P.; Süsstrunk, S. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 2274–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartigan, J.A.; Wong, M.A. Algorithm AS 136: A K-Means Clustering Algorithm. Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, A. SensoMotoric Instruments launches SMI Eye Tracking. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SensoMotoric_Instruments (accessed on 21 June 2020).
- Achanta, R.; Estrada, F.; Wils, P.; Süsstrunk, S. Salient region detection and segmentation. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); ICVS 2008; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 5008, pp. 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itti, L.; Koch, C.; Niebur, E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achanta, R.; Hemami, S.; Estrada, F.; Susstrunk, S. Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Li, W. Review on superpixel segmentation algorithms. Appl. Res. Comput. 2014, 31, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y.; Ma, X.; Soomro, N.Q. Superpixel segmentation: A benchmark. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2017, 56, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutz, D.; Hermans, A.; Leibe, B. Superpixels: An evaluation of the state-of-the-art. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2018, 166, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinshtein, A.; Stere, A.; Kutulakos, K.N.; Fleet, D.J.; Dickinson, S.J.; Siddiqi, K. Turbopixels: Fast superpixels using geometric flows. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 31, 2290–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Method (Section) | Dice | Jaccard | Good Detection | True-Negative Rate | Shift Error | Time (Second) | Time Gain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full-Frame (Section 5.2.1) | 0.24 ± 0.22 | 0.21 ± 0.16 | 0.31 ± 0.20 | 0.17 ± 0.72 | 174.11 ± 34 | 880 | 24 |
| Glasses Eye-tracker (Section 5.1) | 0.78± 0.08 | 0.64 ± 0.08 | 0.84 ± 0.16 | 0.09 ± 0.07 | 15.97 ± 11 | 1960 | 11 |
| Screen-based Eye-tracker (Section 5.1.2) | 0.85± 0.09 | 0.77 ± 0.13 | 0.88 ± 0.12 | 0.09 ± 0.13 | 2.37 ± 1.86 | 3240 | 6 |
| Egocentric Prior (Section 5.2.2) | 0.46 ± 0.36 | 0.38 ± 0.31 | 0.54 ± 0.39 | 0.28 ± 0.23 | 84.82 ± 7.25 | 1960 | 11 |
| Saliency (Section 5.2.3) | 0.27 ± 0.13 | 0.16 ± 0.08 | 0.42 ± 0.45 | 0.51 ± 0.17 | 7.21 ± 8.28 | 2358 | 9 |
| Method | Joint Acquisition Annotation | Fastest Execution Time | Best Annotation | Best Counting | Best Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full-Frame | + | + | - | - | - |
| Glasses Eye-tracker | + | - | + | + | - |
| Screen-based Eye-tracker | - | - | + | + | + |
| Egocentric Prior | + | - | - | - | - |
| Saliency | + | - | - | - | + |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samiei, S.; Rasti, P.; Richard, P.; Galopin, G.; Rousseau, D. Toward Joint Acquisition-Annotation of Images with Egocentric Devices for a Lower-Cost Machine Learning Application to Apple Detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 4173. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154173
Samiei S, Rasti P, Richard P, Galopin G, Rousseau D. Toward Joint Acquisition-Annotation of Images with Egocentric Devices for a Lower-Cost Machine Learning Application to Apple Detection. Sensors. 2020; 20(15):4173. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154173
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamiei, Salma, Pejman Rasti, Paul Richard, Gilles Galopin, and David Rousseau. 2020. "Toward Joint Acquisition-Annotation of Images with Egocentric Devices for a Lower-Cost Machine Learning Application to Apple Detection" Sensors 20, no. 15: 4173. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154173
APA StyleSamiei, S., Rasti, P., Richard, P., Galopin, G., & Rousseau, D. (2020). Toward Joint Acquisition-Annotation of Images with Egocentric Devices for a Lower-Cost Machine Learning Application to Apple Detection. Sensors, 20(15), 4173. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154173







