Application of a Glucose Dehydrogenase-Fused with Zinc Finger Protein to Label DNA Aptamers for the Electrochemical Detection of VEGF
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Investigation of Aptamer and Antibody Combination for the Sandwich Assay
2.3. Investigation of Binding Specificity of ZF-GDH Towards Its Target Sequence
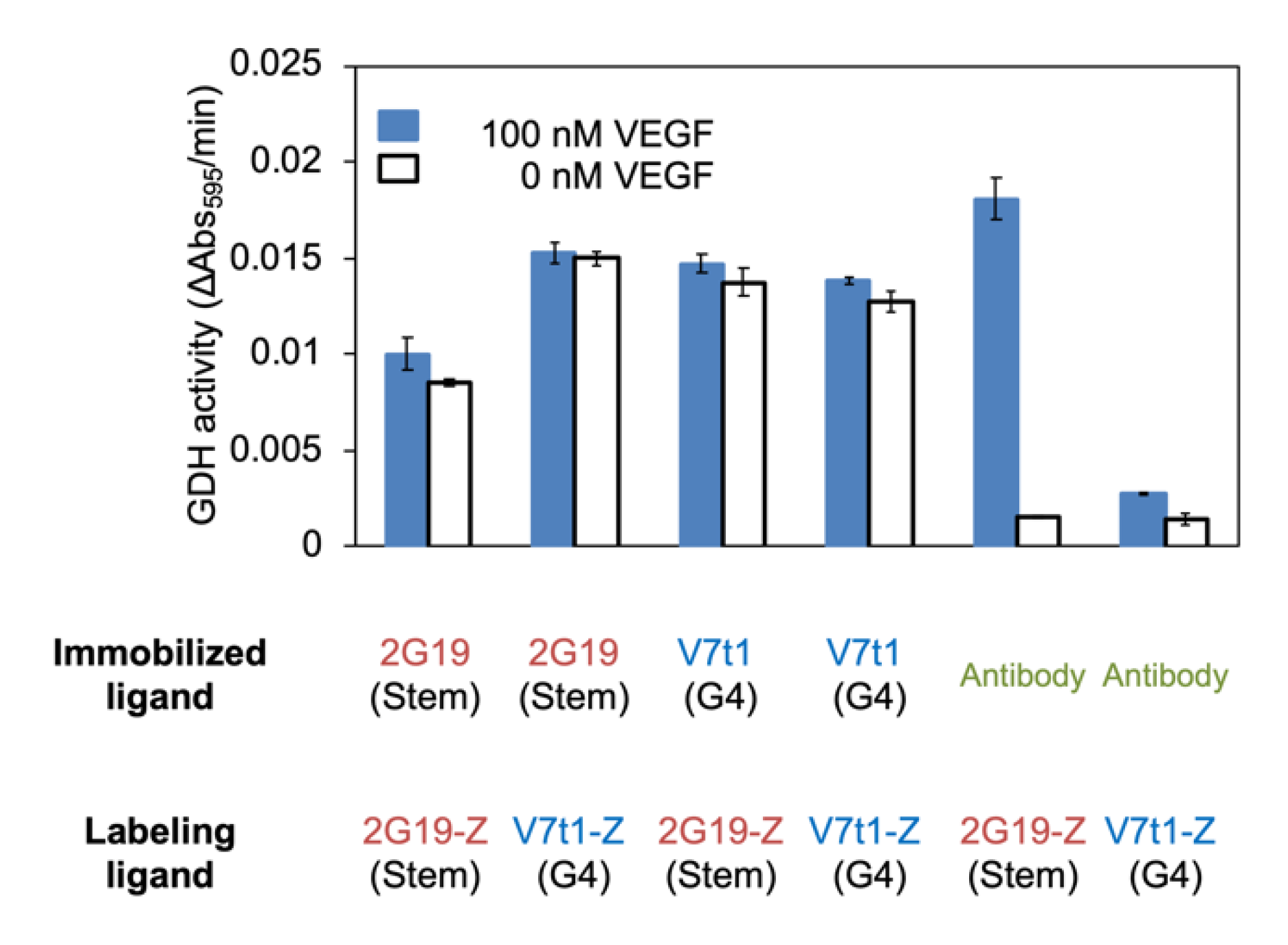
2.4. Investigation of VEGF Concentration Dependency on Plate Using Antibody and Aptamer
2.5. Preparation of Antibody-Immobilized Gold Electrode
2.6. Investigation of the Non-Specific Adsorption on a Gold Electrode
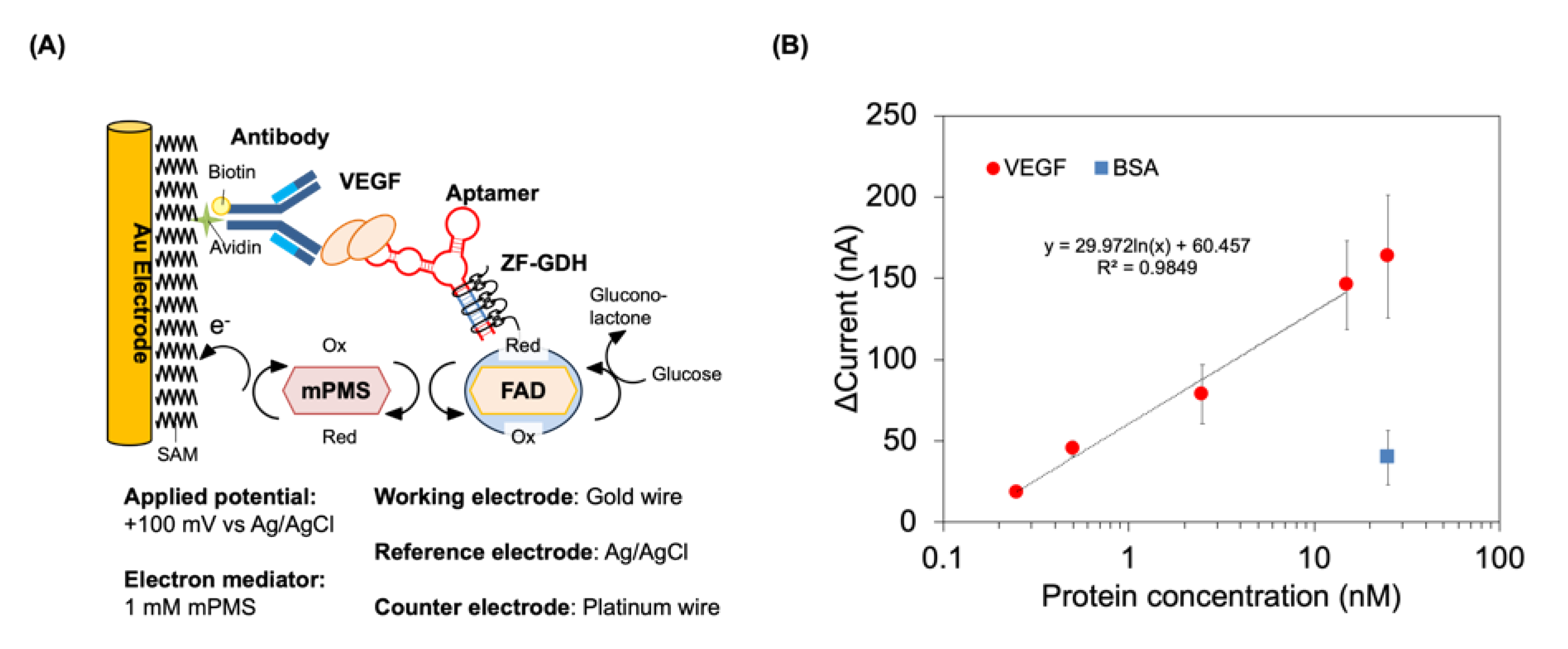
2.7. Electrochemical Detection of VEGF Using GDH-Labeled Aptamer
3. Results
3.1. GDH Labeling of VEGF-Binding Aptamer Using ZF-GDH and Characterization of the Labeled Aptamer
3.2. Construction of Electrochemical Detection System Using GDH-Labeled 2G19-Z to Detect VEGF
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikebukuro, K.; Kiyohara, C.; Sode, K. Electrochemical detection of protein using a double aptamer sandwich. Anal. Lett. 2004, 37, 2901–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalonga, A.; Pérez-Calabuig, A.M.; Villalonga, R. Electrochemical biosensors based on nucleic acid aptamers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Amphlett, G.; Blattler, W.A.; Lambert, J.M.; Zhang, W. Structural characterization of the maytansinoid–monoclonal antibody immunoconjugate, huN901–DM1, by mass spectrometry. Protein Sci. 2005, 14, 2436–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazane, S.A.; Sok, D.; Cho, E.H.; Uson, M.L.; Kuhn, P.; Schultz, P.G.; Smider, V.V. Site-specific DNA-antibody conjugates for specific and sensitive immuno-PCR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3731–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikebukuro, K.; Kiyohara, C.; Sode, K. Novel electrochemical sensor system for protein using the aptamers in sandwich manner. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 2168–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukasawa, M.; Yoshida, W.; Yamazaki, H.; Sode, K.; Ikebukuro, K. An aptamer-based bound/free separation system for protein detection. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, S.; Kojima, K.; Sode, K. Review of glucose oxidases and glucose dehydrogenases: A bird’s eye view of glucose sensing enzymes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2011, 5, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbuto, S.; Idoyaga, J.; Vila-Perello, M.; Longhi, M.P.; Breton, G.; Steinman, R.M.; Muir, T.W. Induction of innate and adaptive immunity by delivery of poly dA:dT to dendritic cells. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.I.; McFarland, J.M.; Rabuka, D.; Gartner, Z.J. A Modular approach for assembling aldehyde-tagged proteins on DNA scaffolds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 10850–10853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duckworth, B.P.; Chen, Y.; Wollack, J.W.; Sham, Y.; Mueller, J.D.; Taton, T.A.; Distefano, M.D. A universal method for the preparation of covalent protein-DNA conjugates for use in creating protein nanostructures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8819–8822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Peng, H.; Tao, J.; Li, X.F.; Chris Le, X. Quantitative synthesis of protein–DNA conjugates with 1:1 stoichiometry. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 7491–7494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, C.B.; Kodal, A.L.; Nielsen, J.S.; Schaffert, D.H.; Scavenius, C.; Okholm, A.H.; Voigt, N.V.; Enghild, J.J.; Kjems, J.; Torring, T.; et al. Template-directed covalent conjugation of DNA to native antibodies, transferrin and other metal-binding proteins. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, F.; Mie, M.; Grimm, S.; Nygren, P.-Å.; Kobatake, E. Detection of Antigens Using a Protein–DNA Chimera Developed by Enzymatic Covalent Bonding with phiX Gene A*. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5040–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovendahl, K.N.; Hayward, A.N.; Gordon, W.R. Sequence-directed covalent protein-DNA linkages in a single step using HUH-Tags. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 7030–7035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mie, M.; Niimi, T.; Mashimo, Y.; Kobatake, E. Construction of DNA-NanoLuc luciferase conjugates for DNA aptamer-based sandwich assay using Rep protein. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Murakami, Y.; Tatsumi, A.; Sumida, K.; Kezuka, A.; Fukaya, T.; Kumagai, T.; Osawa, Y.; Sode, K.; Ikebukuro, K. Enzyme linking to DNA aptamers via a zinc finger as a bridge. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 11467–11469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, S.A.; Nekludova, L.; Pabo, C.O. DNA recognition by Cys2His2 zinc finger proteins. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2000, 29, 183–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaj, T.; Gersbach, C.A.; Barbas, C.F. ZFN, TALEN, and CRISPR/Cas-based methods for genome engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urnov, F.D.; Rebar, E.J.; Holmes, M.C.; Zhang, H.S.; Gregory, P.D. Genome editing with engineered zinc finger nucleases. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stains, C.I.; Porter, J.R.; Ooi, A.T.; Segal, D.J.; Ghosh, I. DNA Sequence-Enabled Reassembly of the Green Fluorescent Protein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10782–10783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, A.T.; Stains, C.I.; Ghosh, I.; Segal, D.J. Sequence-Enabled Reassembly of β-Lactamase (SEER-LAC): A Sensitive Method for the Detection of Double-Stranded DNA. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 3620–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.; Kumagai, T.; Takahashi, C.; Kezuka, A.; Murakami, Y.; Osawa, Y.; Motoki, H.; Matsuo, T.; Horiuchi, M.; Sode, K.; et al. Detection of pathogenic bacteria by using zinc finger protein fused with firefly luciferase. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8028–8032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Tatsumi, A.; Abe, K.; Yoshida, W.; Sode, K.; Ikebukuro, K. Electrochemical detection of pathogenic bacteria by using a glucose dehydrogenase fused zinc finger protein. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 4991–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor: Basic science and clinical progress. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 581–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, H.J.; Chen, Y.-H.; Parker, L.M.; Savoie, J.; Younger, J.; Kuter, I.; Ryan, P.D.; Garber, J.E.; Chen, H.; Campos, S.M.; et al. VEGF as a marker for outcome among advanced breast cancer patients receiving anti-VEGF therapy with bevacizumab and vinorelbine chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 7871–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Li, B.; Winer, J.; Armanini, M.; Gillett, N.; Phillips, H.S.; Ferrara, N. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature 1993, 362, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girmens, J.-F.; Sahel, J.-A.; Marazova, K. Dry age-related macular degeneration: A currently unmet clinical need. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2012, 1, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.; Lee, H.-S.; Inoue, Y.; Moss, J.; Singer, L.G.; Strange, C.; Nakata, K.; Barker, A.F.; Chapman, J.T.; Brantly, M.L.; et al. MILES Trial Group Serum VEGF-D a concentration as a biomarker of lymphangioleiomyomatosis severity and treatment response: A prospective analysis of the Multicenter International Lymphangioleiomyomatosis Efficacy of Sirolimus (MILES) trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2013, 1, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-H.; Kim, Y.-K. Increased plasma VEGF levels in major depressive or manic episodes in patients with mood disorders. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 136, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanefeld, M.; Appelt, D.; Engelmann, K.; Sandner, D.; Bornstein, S.R.; Ganz, X.; Henkel, E.; Hasse, R.; Birkenfeld, A.L. Serum and plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factors in relation to quality of glucose control, biomarkers of inflammation, and diabetic nephropathy. Horm. Metab. Res. 2016, 48, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisada, R.; Yagi, T. 1-Methoxy-5-methylphenazinium methyl Sulfate. A photochemically stable electron mediator between NADH and various electron acceptors. J. Biochem. 1977, 82, 1469–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Nakajima, M.; Kojima, K.; Murakami, K.; Ferri, S.; Sode, K. Screening of Aspergillus-derived FAD-glucose dehydrogenases from fungal genome database. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 2255–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrod-Erickson, M.; Rould, M.A.; Nekludova, L.; Pabo, C.O. Zif268 protein-DNA complex refined at 1.6 Å a model system for understanding zinc finger-DNA interactions. Structure 1996, 4, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukaya, T.; Abe, K.; Savory, N.; Tsukakoshi, K.; Yoshida, W.; Ferri, S.; Sode, K.; Ikebukuro, K. Improvement of the VEGF binding ability of DNA aptamers through in silico maturation and multimerization strategy. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 212, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, Y.; Sode, K.; Ikebukuro, K. Screening and improvement of an anti-VEGF DNA aptamer. Molecules 2010, 15, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marušič, M.; Veedu, R.; Wengel, J.; Plavec, J. G-rich VEGF aptamer with locked and unlocked nucleic acid modifications exhibits a unique G-quadruplex fold. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 9524–9536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.; Choo, Y.; Klug, A. Design of polyzinc finger peptides with structured linkers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 1432–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Tatsumi, A.; Tsukakoshi, K.; Wilson, E.D.; Abe, K.; Sode, K.; Ikebukuro, K. Application of a Glucose Dehydrogenase-Fused with Zinc Finger Protein to Label DNA Aptamers for the Electrochemical Detection of VEGF. Sensors 2020, 20, 3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20143878
Lee J, Tatsumi A, Tsukakoshi K, Wilson ED, Abe K, Sode K, Ikebukuro K. Application of a Glucose Dehydrogenase-Fused with Zinc Finger Protein to Label DNA Aptamers for the Electrochemical Detection of VEGF. Sensors. 2020; 20(14):3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20143878
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jinhee, Atsuro Tatsumi, Kaori Tsukakoshi, Ellie D. Wilson, Koichi Abe, Koji Sode, and Kazunori Ikebukuro. 2020. "Application of a Glucose Dehydrogenase-Fused with Zinc Finger Protein to Label DNA Aptamers for the Electrochemical Detection of VEGF" Sensors 20, no. 14: 3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20143878
APA StyleLee, J., Tatsumi, A., Tsukakoshi, K., Wilson, E. D., Abe, K., Sode, K., & Ikebukuro, K. (2020). Application of a Glucose Dehydrogenase-Fused with Zinc Finger Protein to Label DNA Aptamers for the Electrochemical Detection of VEGF. Sensors, 20(14), 3878. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20143878





