Quick and Sensitive Detection of Water Using Galvanic-Coupled Arrays with a Submicron Gap for the Advanced Prediction of Dew Condensation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
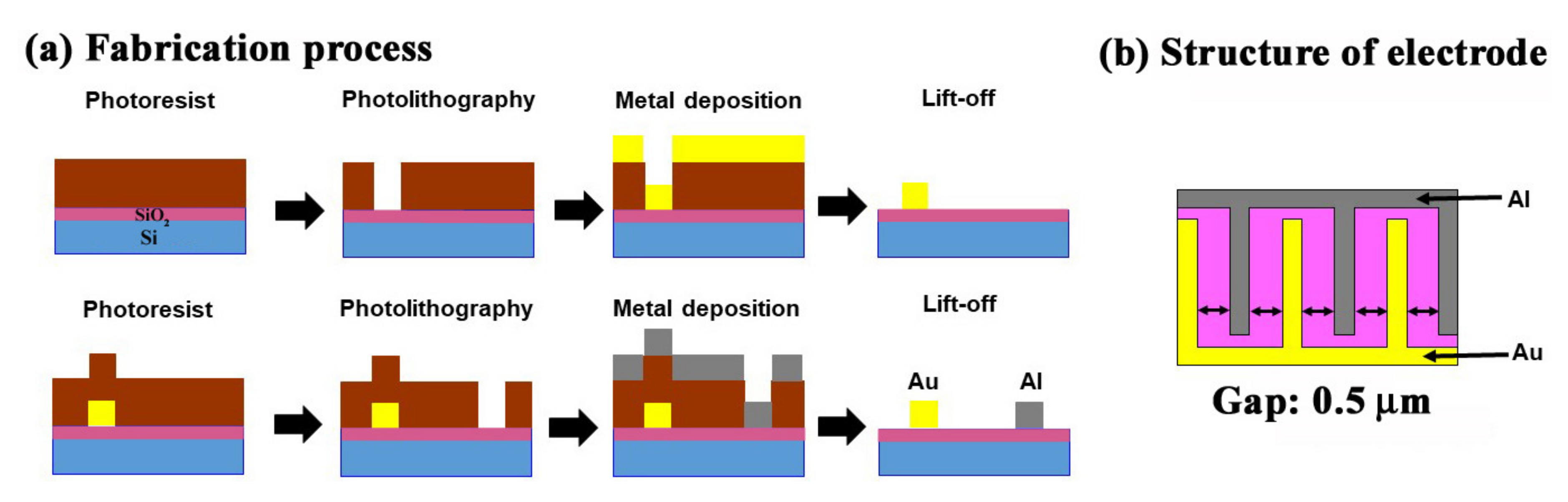
2.1. Preparation of the Sensor Chip
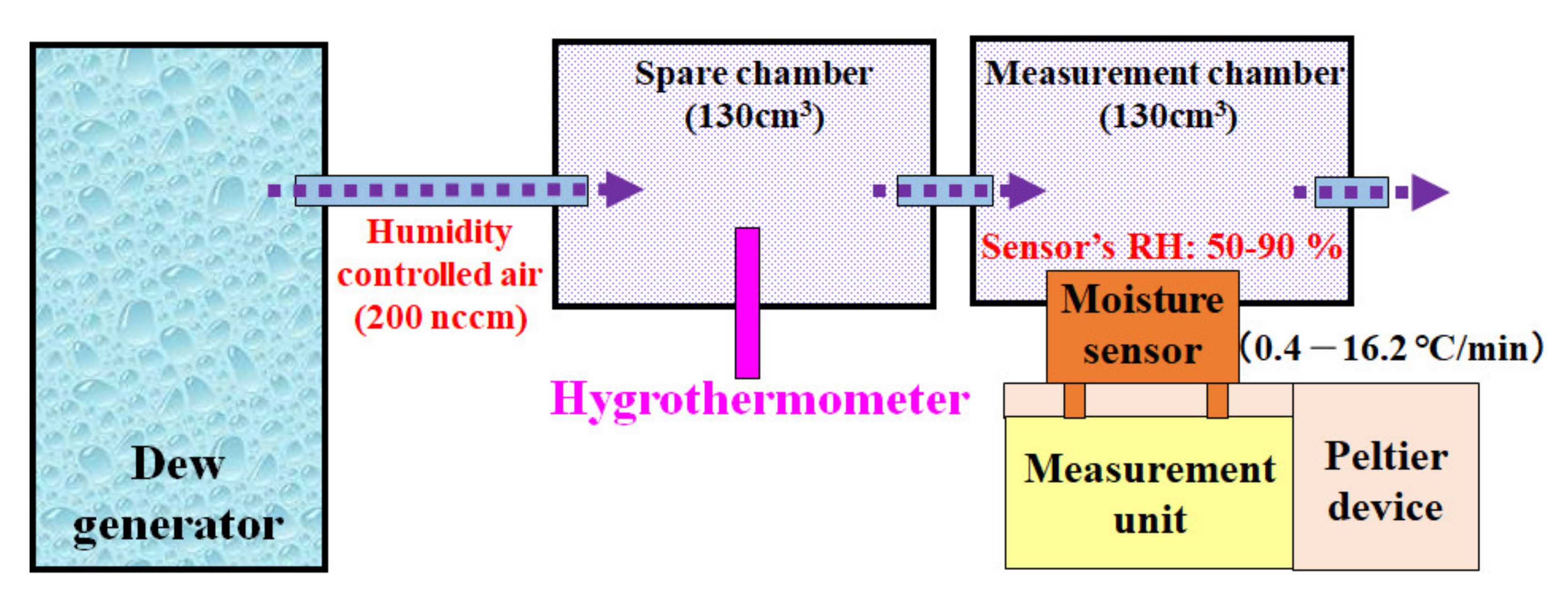
2.2. Introduction of Droplets on the Sensor’s Surface
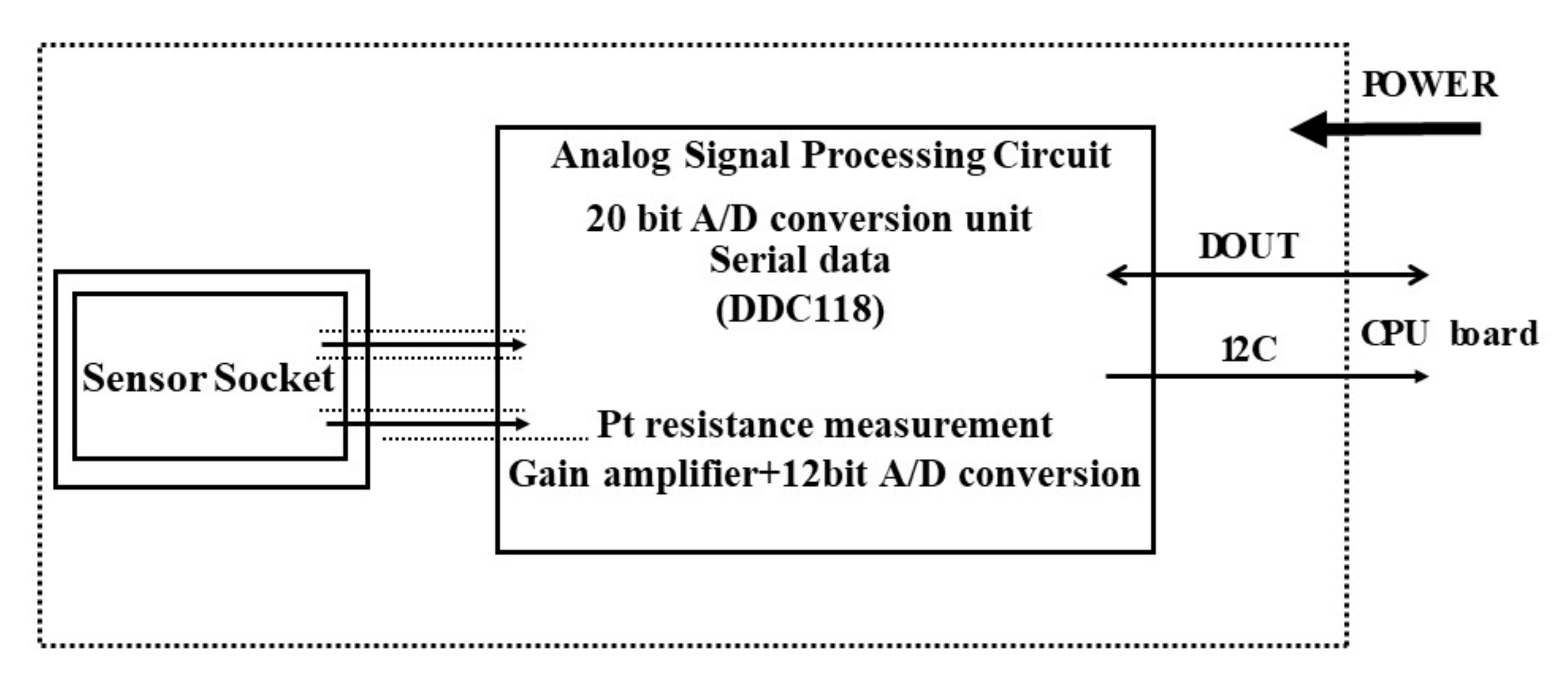
2.3. Measurement of the Sensor Output
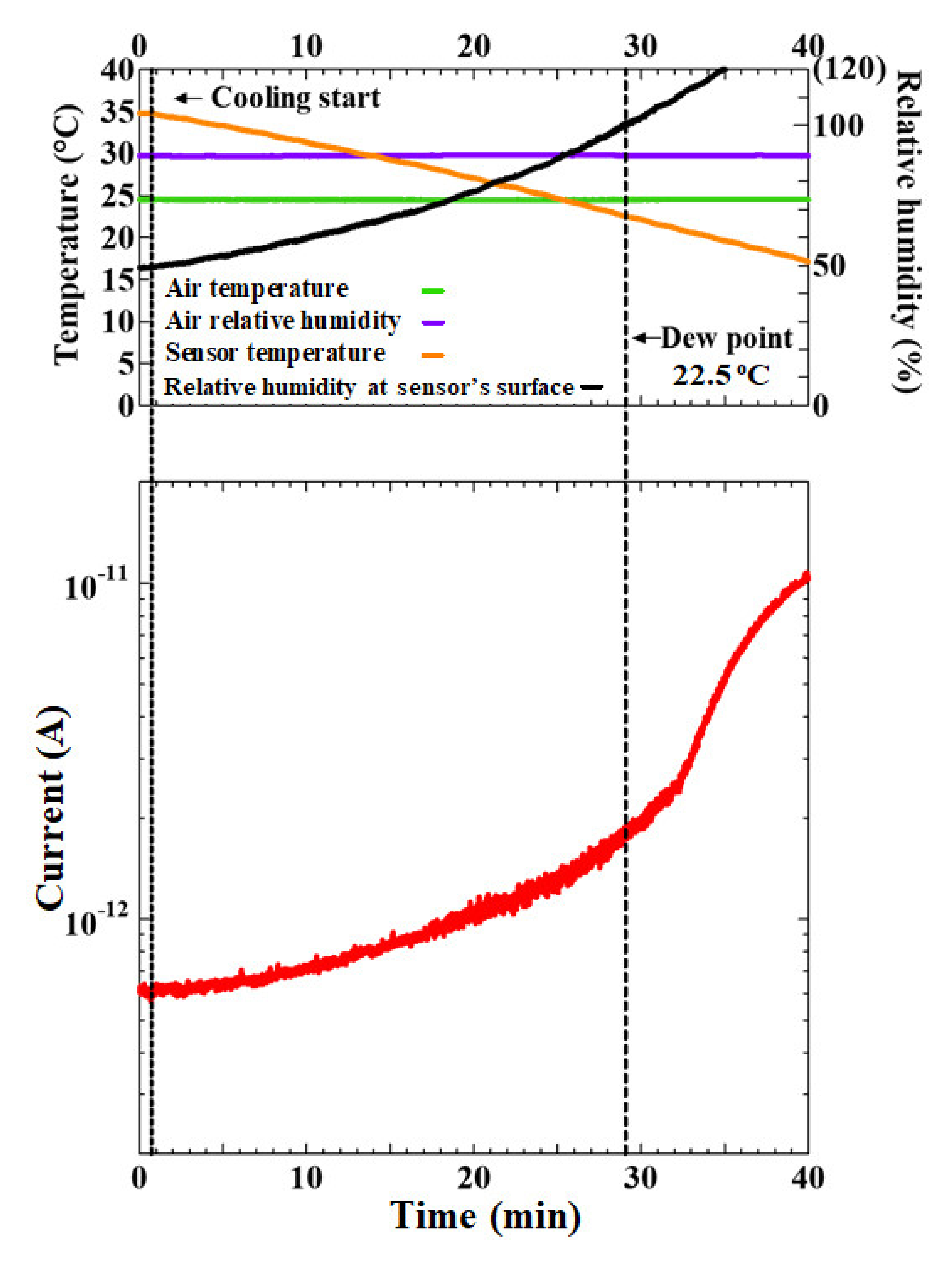
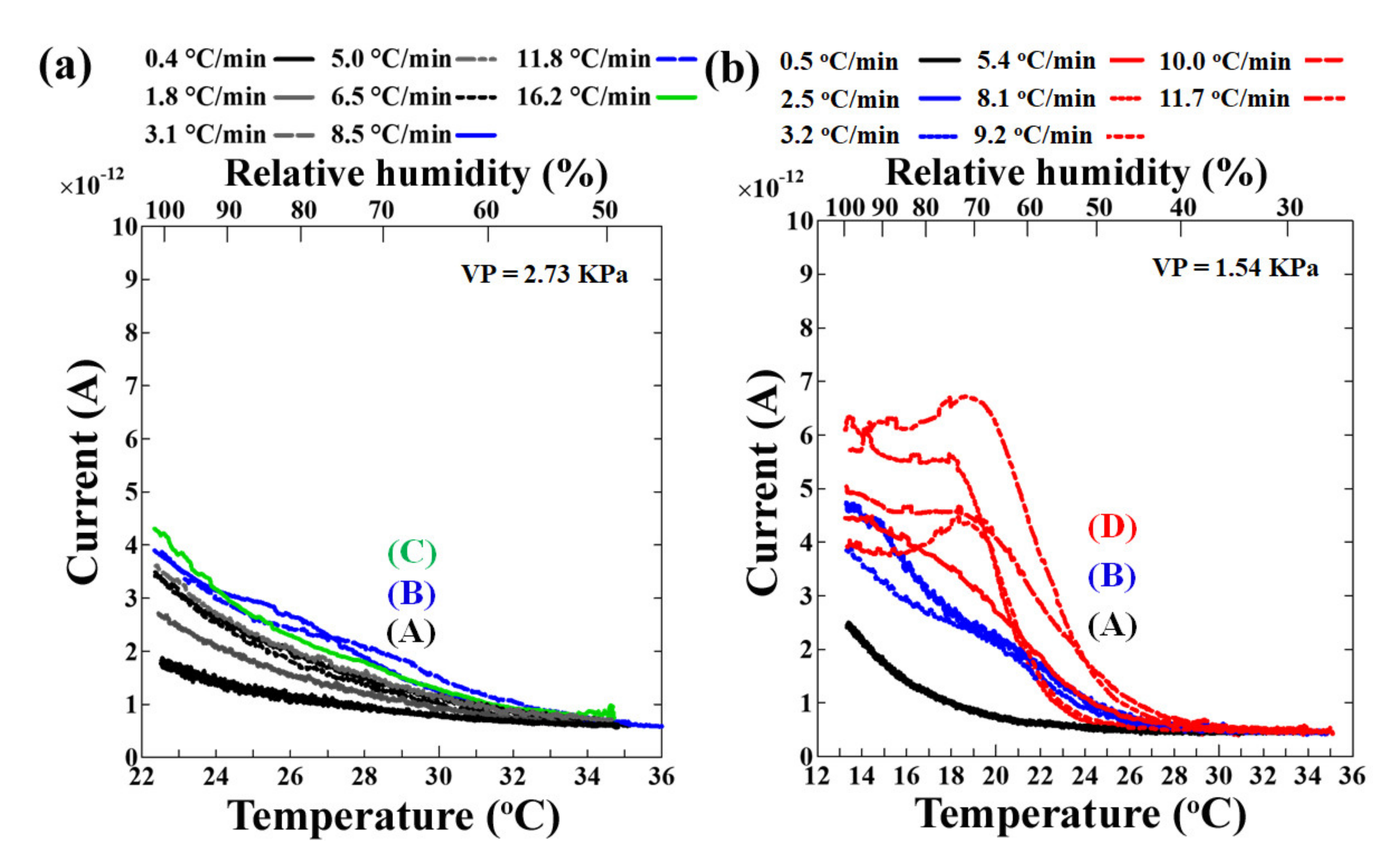
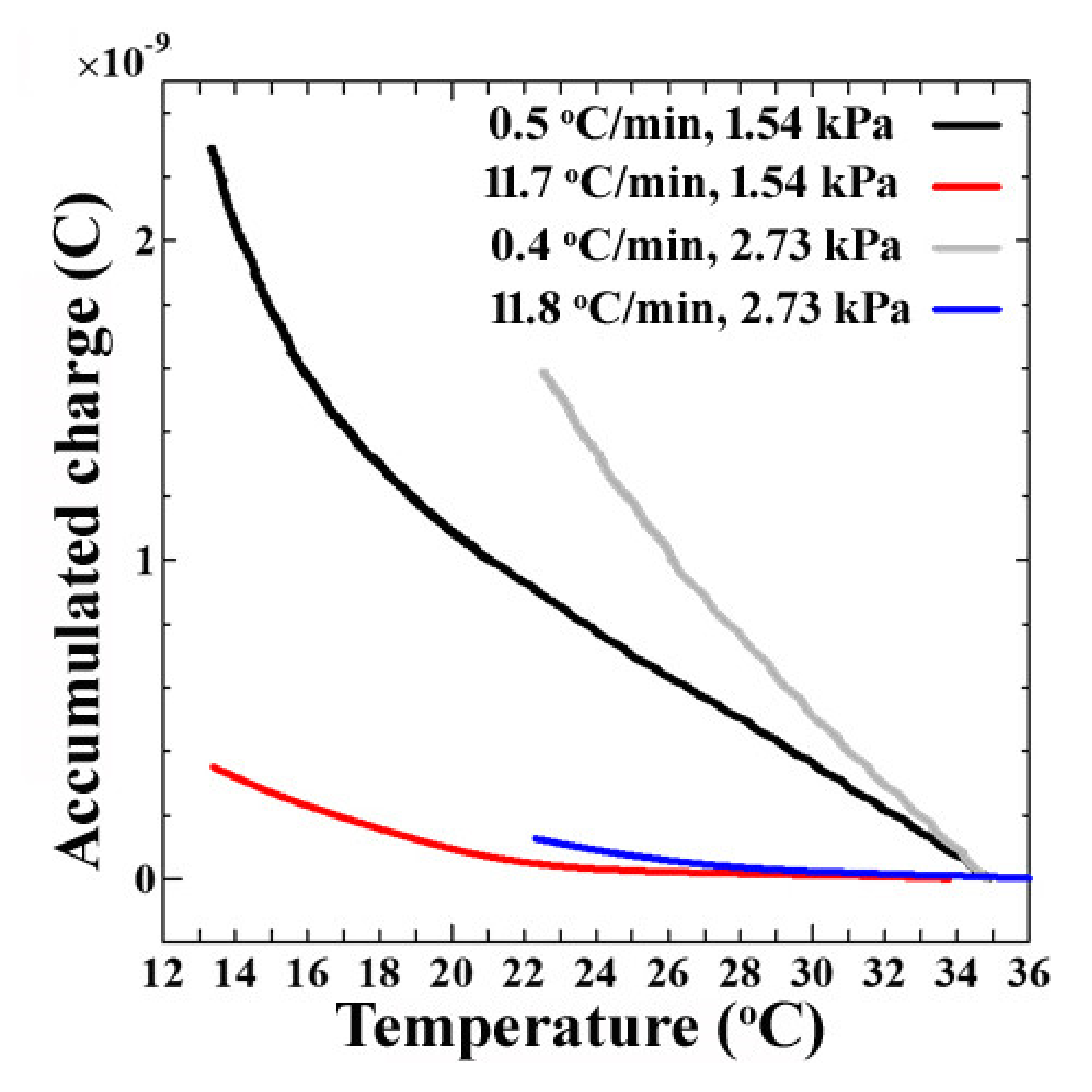
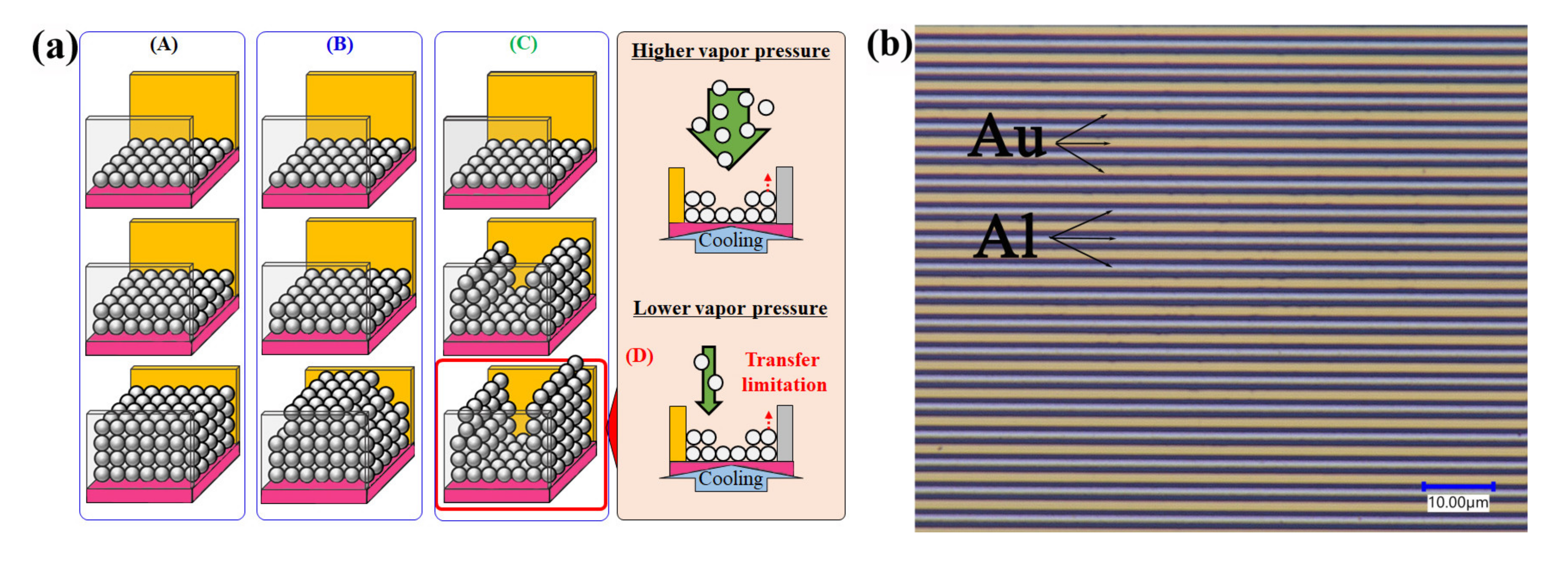
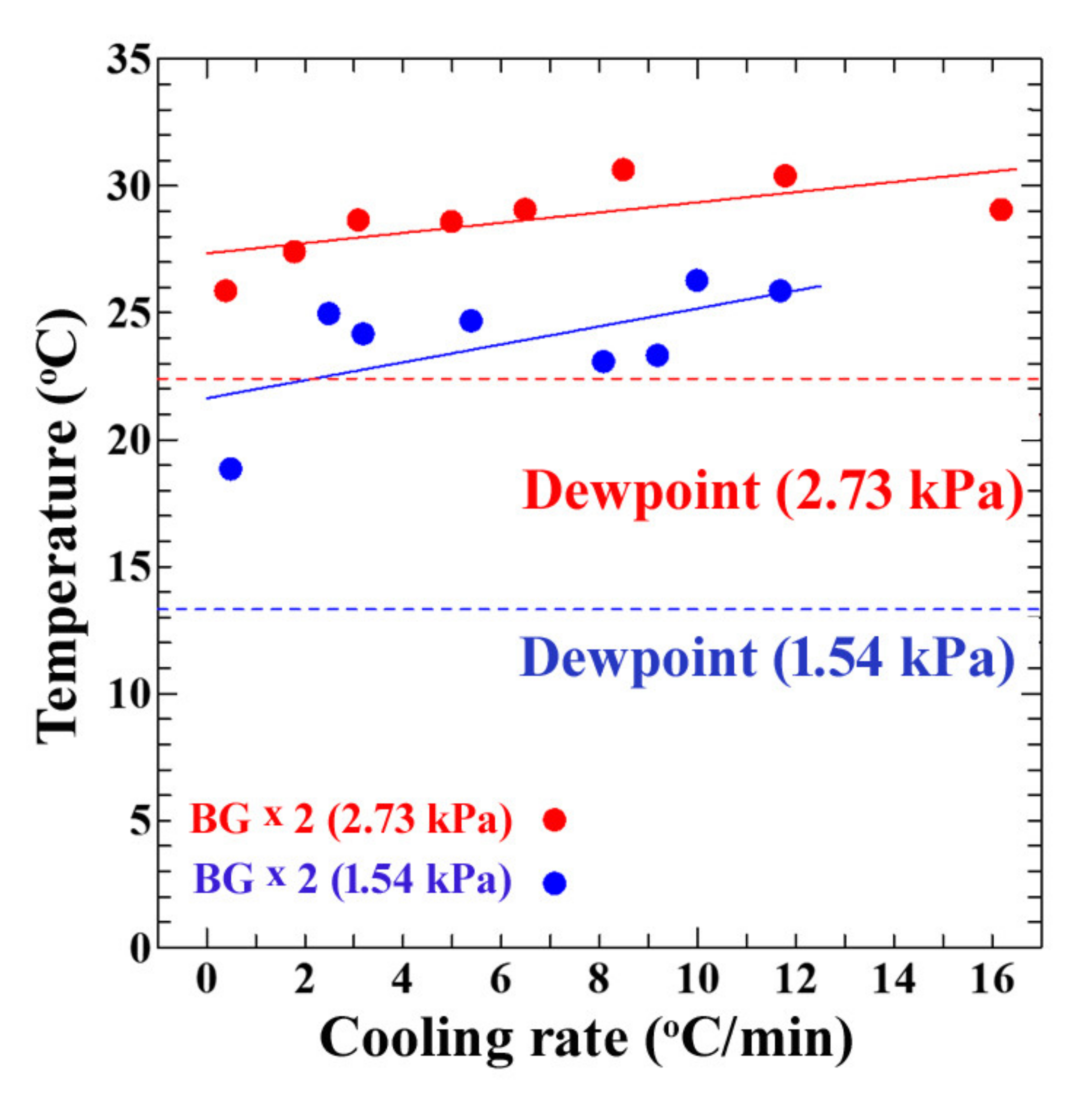
3. Results and Discussion
Dependence of the Sensor’s Output on Vapor Pressure and Cooling Rates of the Sensor’s Surface
4. Conclusions
- The moisture sensor showed high sensitivity and accuracy toward the detection of adsorbed water molecules in addition to water droplets.
- Even in a phase preceding dew condensation, the adsorption of water molecules could be detected.
- The relationship between the output response with variations of the cooling rate, initial temperature of the sensor’s surface, and water vapor pressure was clarified. The higher the cooling rate and vapor pressure, the higher the output response from the sensor.
- The response of the moisture sensor to the variation in cooling rates allowed for the prediction of prior dew condensation, which depends upon the heat capacity of the targets.
- The experimental parameters and conditions were optimized for the advanced dew/humidity detection.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tételin, A.; Pellet, C.; Laville, C.; N’Kaoua, G. Fast response humidity sensors for a medical microsystem. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 91, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lu, C. Humidity sensors: A review of materials and mechanisms. Sens. Lett. 2005, 3, 274–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, M.; Kyung, Y.; Eom, K. Capacitive humidity sensor tag smart refrigerator system using the capacitive to voltage converter (CVC). Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2011, 36, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kolpakov, S.A.; Gordon, N.T.; Mou, C.; Zhou, K. Toward a new generation of photonic humidity sensors. Sensors 2014, 14, 3986–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahani, H.; Wagiran, R.; Hamidon, M.N. Humidity sensors principle, mechanism, and fabrication technologies: A comprehensive review. Sensors 2014, 14, 7881–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavinatto, F.J.; Paschoal, C.W.A.; Arias, A.C. Printed and flexible biosensor for antioxidants using interdigitated ink-jetted electrodes and gravure-deposited active layer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-Y.; Lee, G.-B. Humidity sensors: A review. Sens. Lett. 2005, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittersma, Z.M. Recent achievements in miniaturised humidity sensors—A review of transduction techniques. Sens. Actuators B Phys. 2002, 96, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, K.M.; Gillett, N.P.; Jones, P.D.; Thorne, P.W. Attribution of observed surface humidity changes to human influence. Nature 2007, 449, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imam, S.A.; Choudhary, A.; Sachan, V.K. Design issues for wireless sensor networks and smart humidity sensors for precision agriculture: A review. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Soft Computing Techniques and Implementations (ICSCTI), Faridabad, India, 8–10 October 2015; pp. 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandana, L.S.; Sekhar, A.J.R. Weather monitoring using wireless sensor networks based on IOT. Int. J. Sci. Res. Sci. Technol. 2018, 4, 525–531. [Google Scholar]
- Yawut, C.; Kilaso, S. A wireless sensor network for weather and disaster alarm systems. Int. Conf. Inf. Electron. Eng. 2011, 6, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, J.; Peng, X.; Feng, P.; Sheng, Y.; Zhang, J. Study of humidity sensors based on nanostructured carbon films produced by physical vapor deposition. Sens. Actuators B 2013, 178, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldocchi, D.D. Assessing the eddy covariance technique for evaluating carbon dioxide exchange rates of ecosystems: Past, present and future. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetter, J.R.; Penrose, W.R.; Yao, S. Sensors, chemical sensors, electrochemical sensors, and ECS. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Liu, Y.J.; Wang, F.; He, C. Highly sensitive and fast response colorimetric humidity sensors based on graphene oxides film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 19882–19886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakita, J.; Chikyow, T. Detection of micro/nano droplet by galvanic current. ECS Trans. 2017, 75, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.L.; Kubota, Y.; Sakamoto, Y.; Kawakita, J. Micro/nano galvanic-coupled arrays for early and initial detection and prediction of dew condensation. Sens. Actuators A 2020, 303, 111838. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, R.G.; Ando, T.; Sakamoto, Y.; Kawakita, J. Enhancement of sensitivity and accuracy of micro/nano water droplets detection using galvanic-coupled arrays. Sensors 2019, 19, 4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakita, J. Condensation detection element. JP Patent 044040, 14 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chappandaa, K.N.; Shekhahb, O.; Yassinea, O.; Patolea, S.P.; Eddaoudib, M.; Salamaa, K.N. The quest for highly sensitive QCM humidity sensors: The coating of CNT/MOF composite sensing films as case study. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 257, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zenga, Y.; Hu, Z.; Liu, J.; Jiang, J.; Miao, L.; Yi, F.; et al. QCM-based humidity sensor and sensing properties employing colloidal SnO2 nanowires. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 293, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Hygrometer | Dew Sensor | Dew Point Meter | Moisture Sensor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detection of droplet (dew) | Not possible | Not possible | Possible | Possible (>0.2 μm) |
| Response time | 10 s | 10 s | about a min | <0.02 s |
| Control of sensor’s material | Limited control | Not possible | Not possible | Possible |
| Size | Palm | Palm | Desktop | Palm |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shrestha, R.G.; Kubota, Y.; Sakamoto, Y.; Kawakita, J. Quick and Sensitive Detection of Water Using Galvanic-Coupled Arrays with a Submicron Gap for the Advanced Prediction of Dew Condensation. Sensors 2020, 20, 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113314
Shrestha RG, Kubota Y, Sakamoto Y, Kawakita J. Quick and Sensitive Detection of Water Using Galvanic-Coupled Arrays with a Submicron Gap for the Advanced Prediction of Dew Condensation. Sensors. 2020; 20(11):3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113314
Chicago/Turabian StyleShrestha, Rekha Goswami, Yusuke Kubota, Yukihiro Sakamoto, and Jin Kawakita. 2020. "Quick and Sensitive Detection of Water Using Galvanic-Coupled Arrays with a Submicron Gap for the Advanced Prediction of Dew Condensation" Sensors 20, no. 11: 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113314
APA StyleShrestha, R. G., Kubota, Y., Sakamoto, Y., & Kawakita, J. (2020). Quick and Sensitive Detection of Water Using Galvanic-Coupled Arrays with a Submicron Gap for the Advanced Prediction of Dew Condensation. Sensors, 20(11), 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113314






