Surface Temperature Simulation of Lunar Dayside and Its Geological Applications: A Case in Sinus Iridum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. A Physical Temperature Model
2.2. Parameter Identification
2.2.1. Improving Is Model
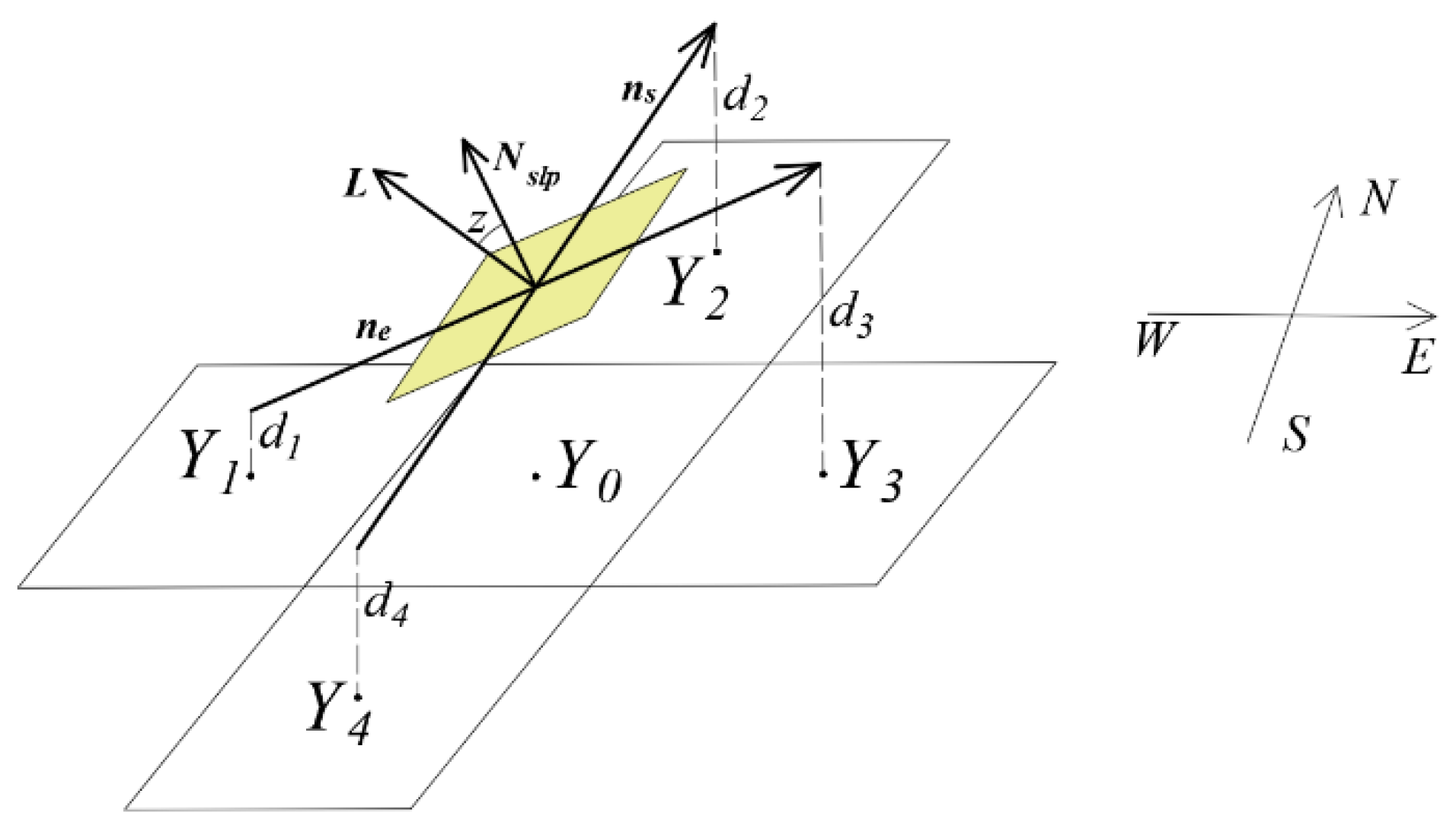
2.2.2. Acquisition of Illumination Condition
2.2.3. Diffuse Reflection Energy
2.2.4. Lunar Surface Albedo
2.2.5. Infrared Emissivity
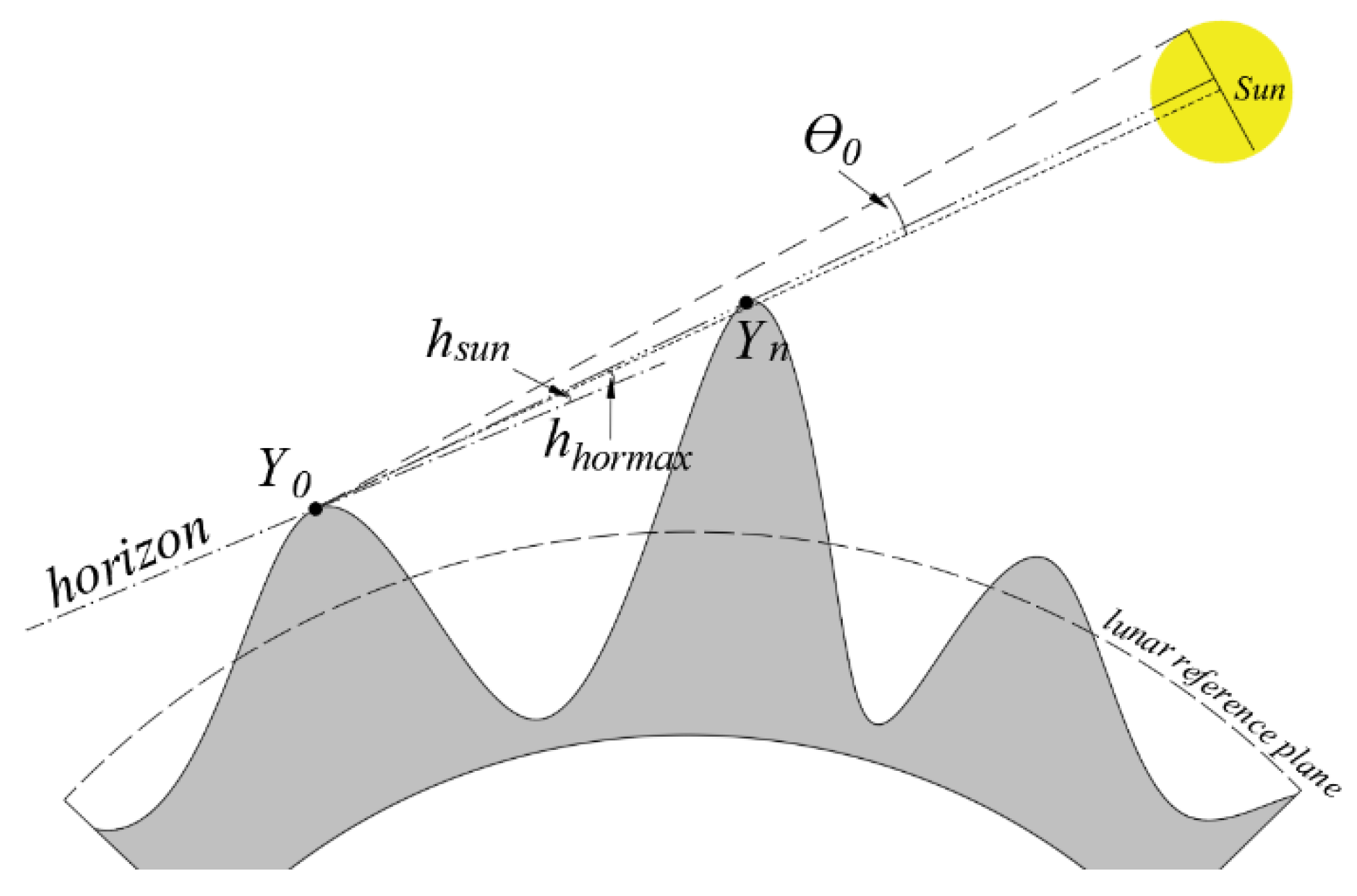
2.3. Temperature after Shading
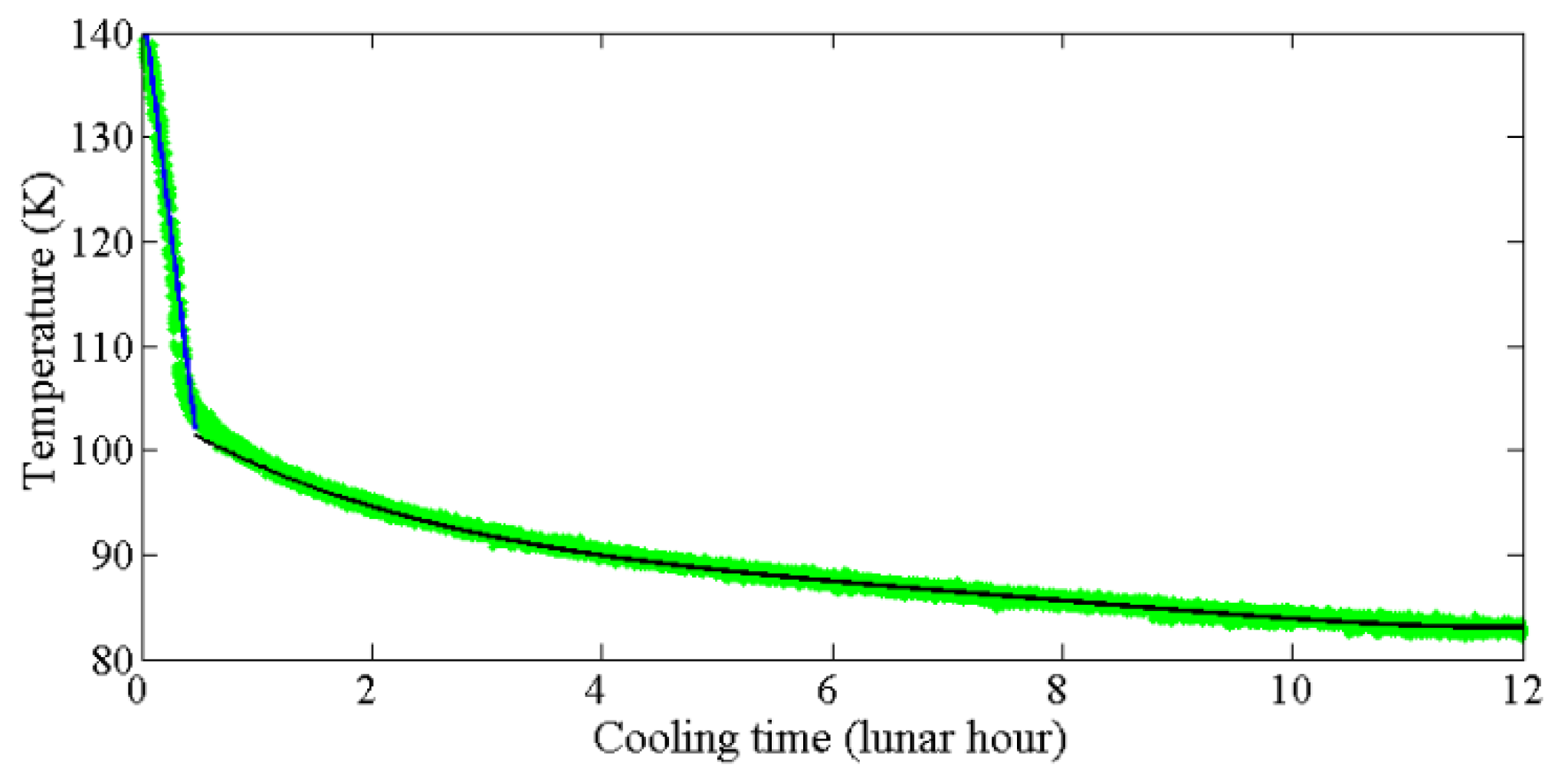
2.3.1. Apollo 15 Heat-Flow Experiment (HFE) Data versus Cooling Time
2.3.2. Global Application of Apollo 15 HFE Data
3. Data Processing and Analyzing
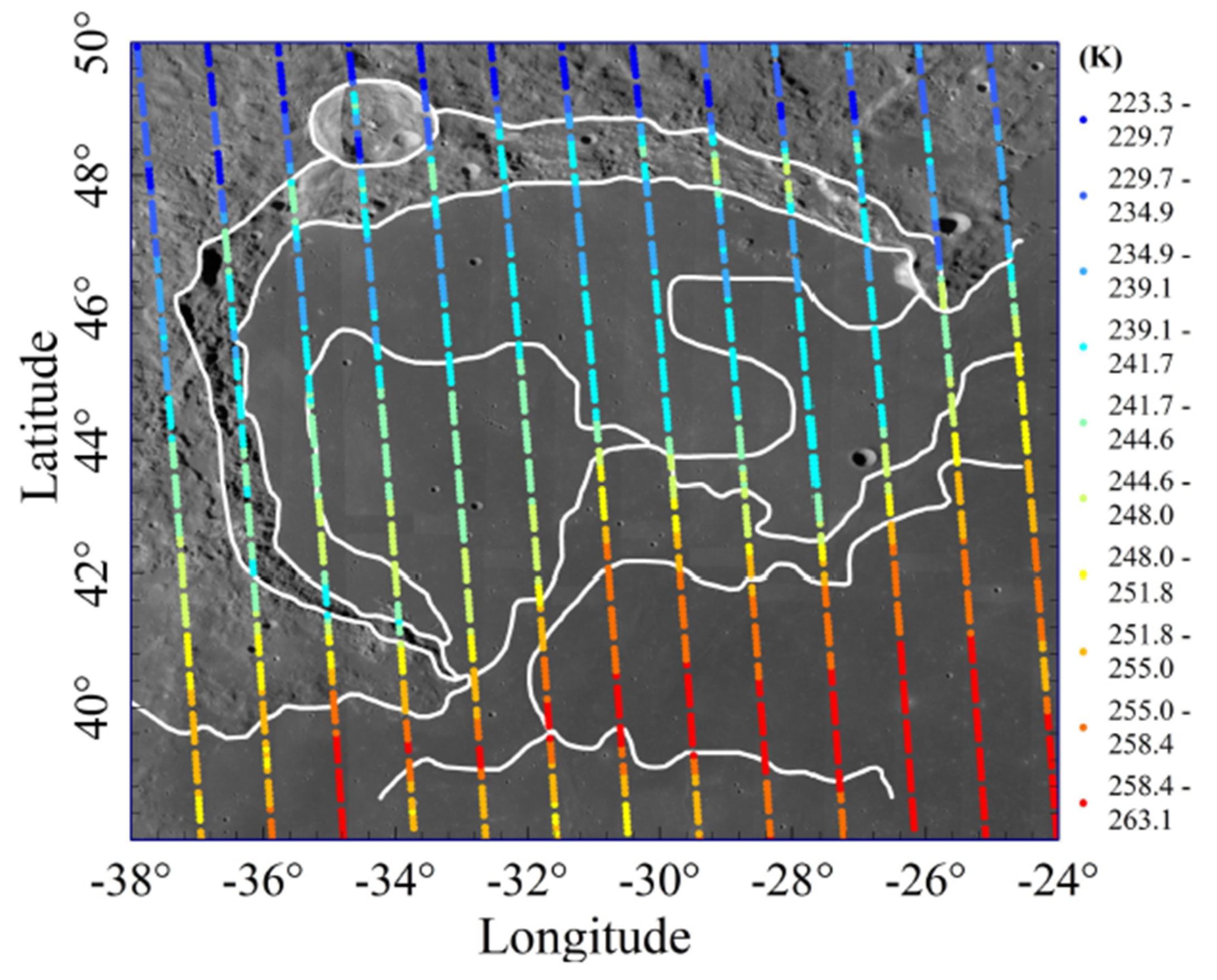
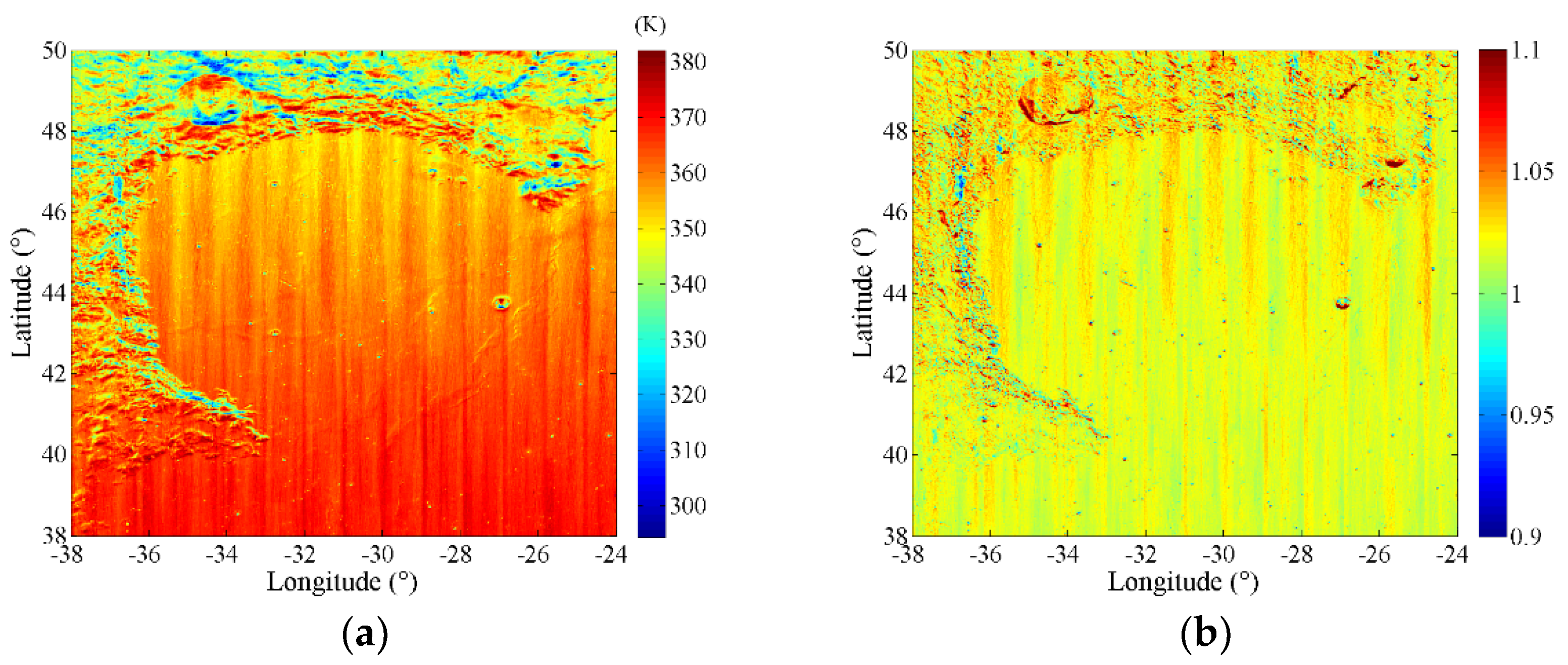
3.1. Sinus Iridum
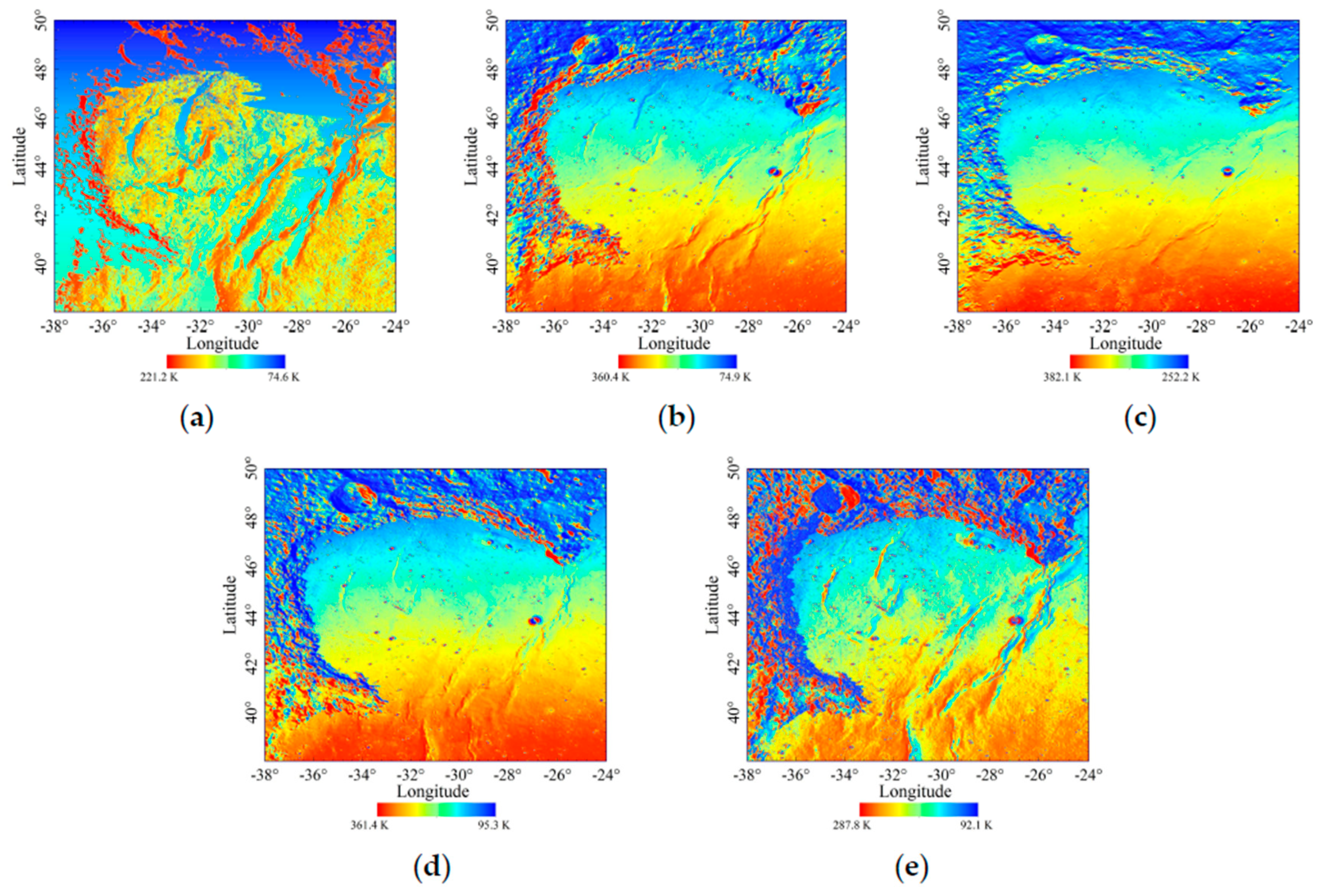
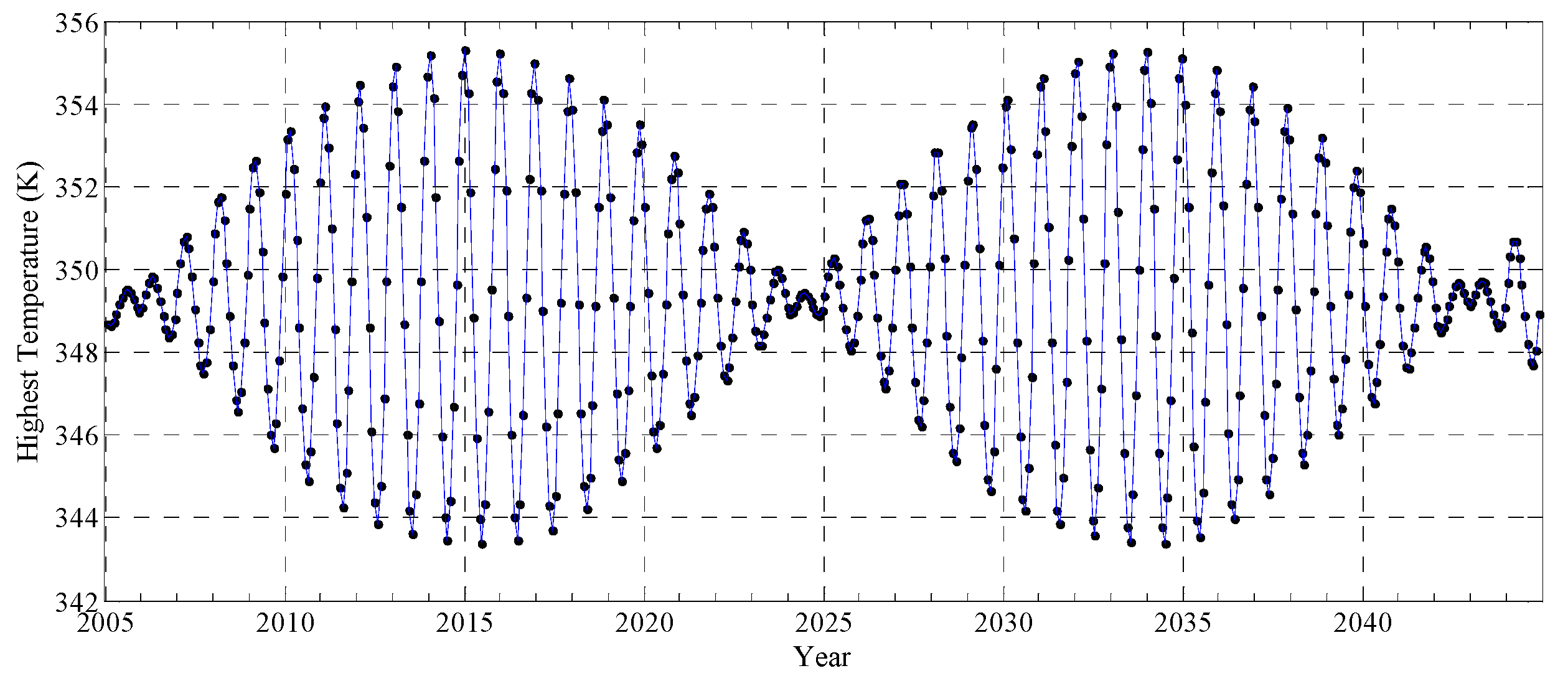
3.2. Simulation Results
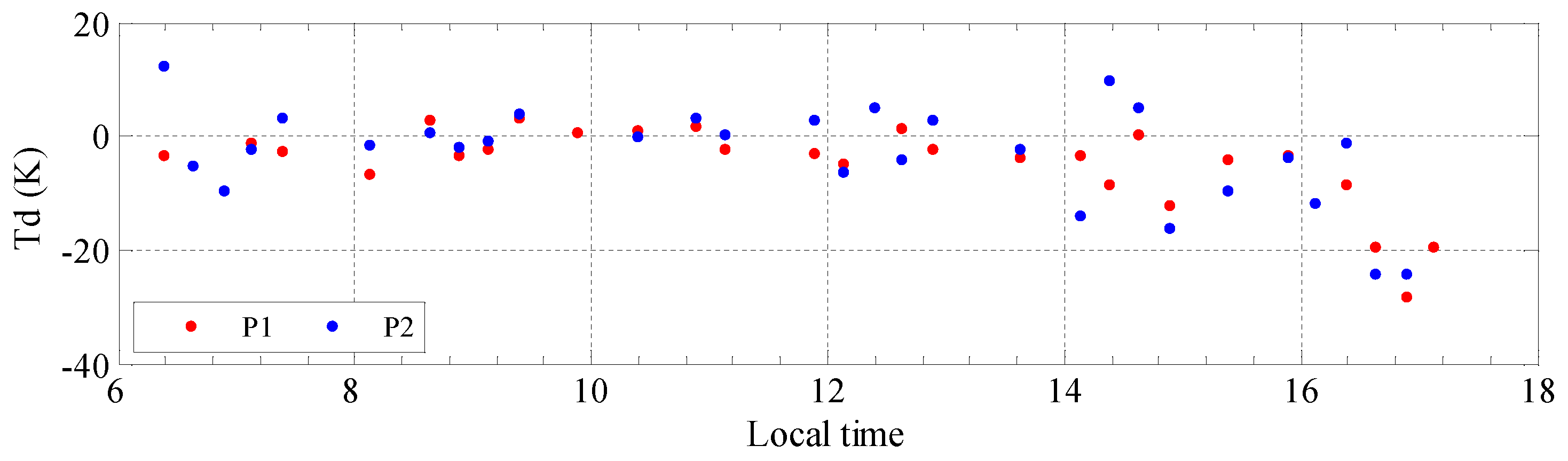
3.3. Uncertainty Analysis
4. Discussions
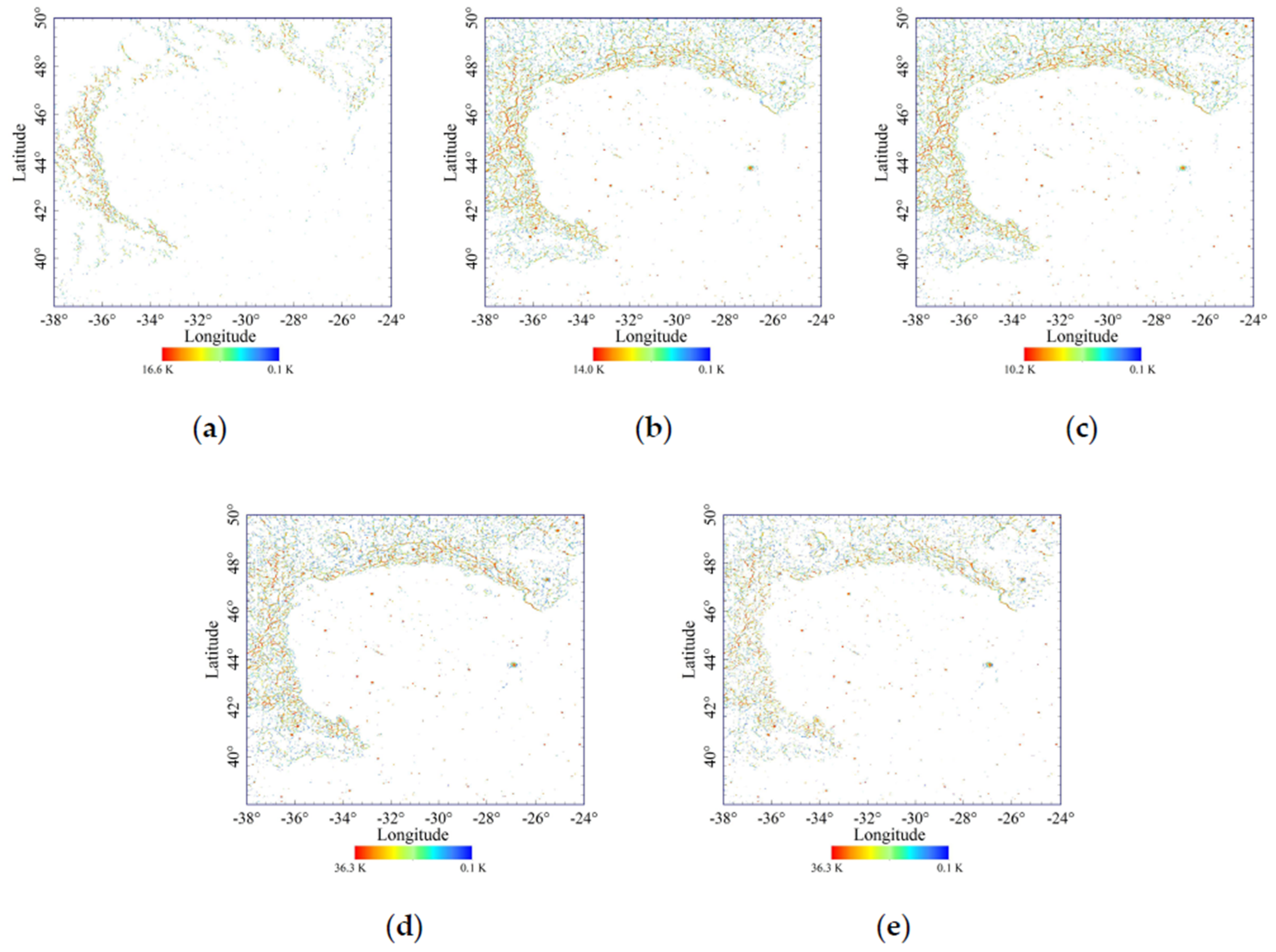
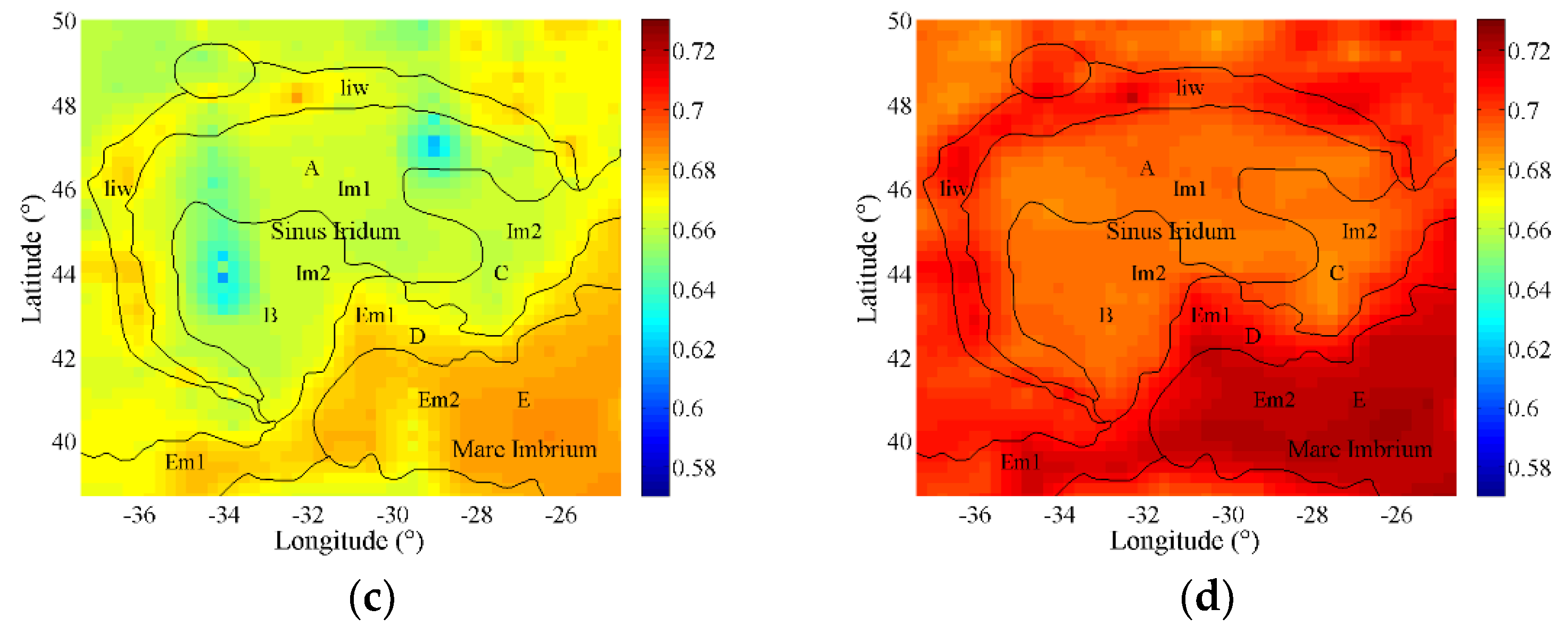
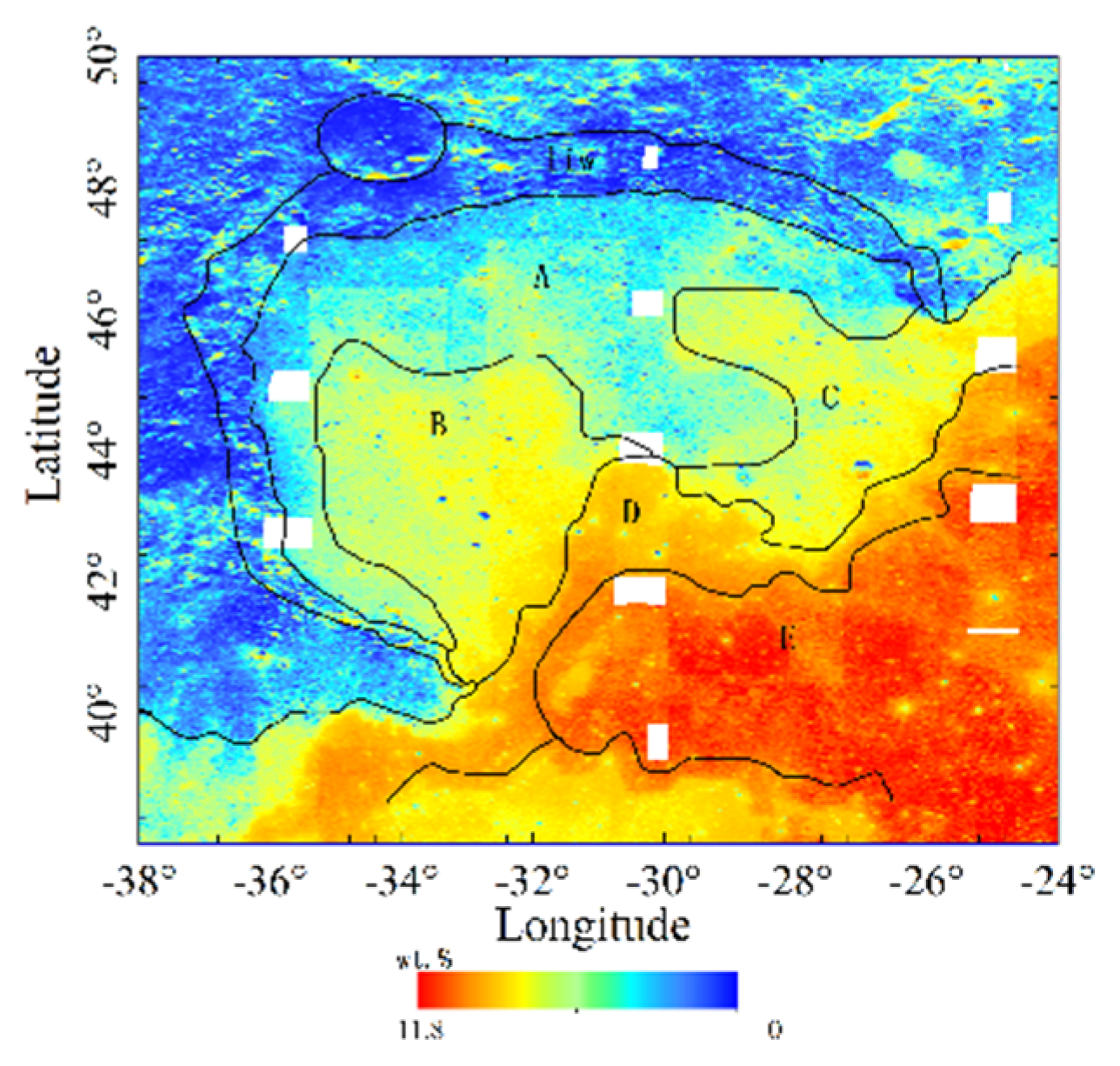
4.1. Geological Application with Remote-Sensing Data
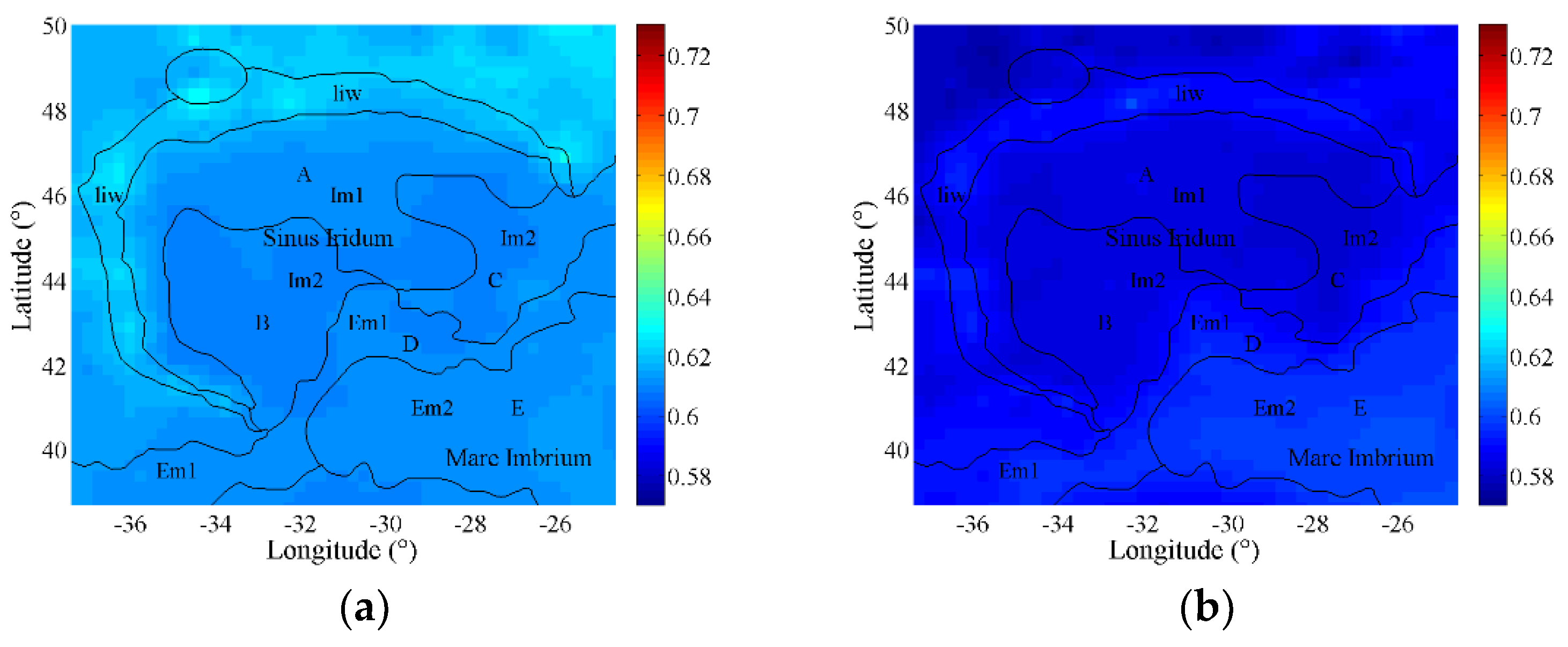
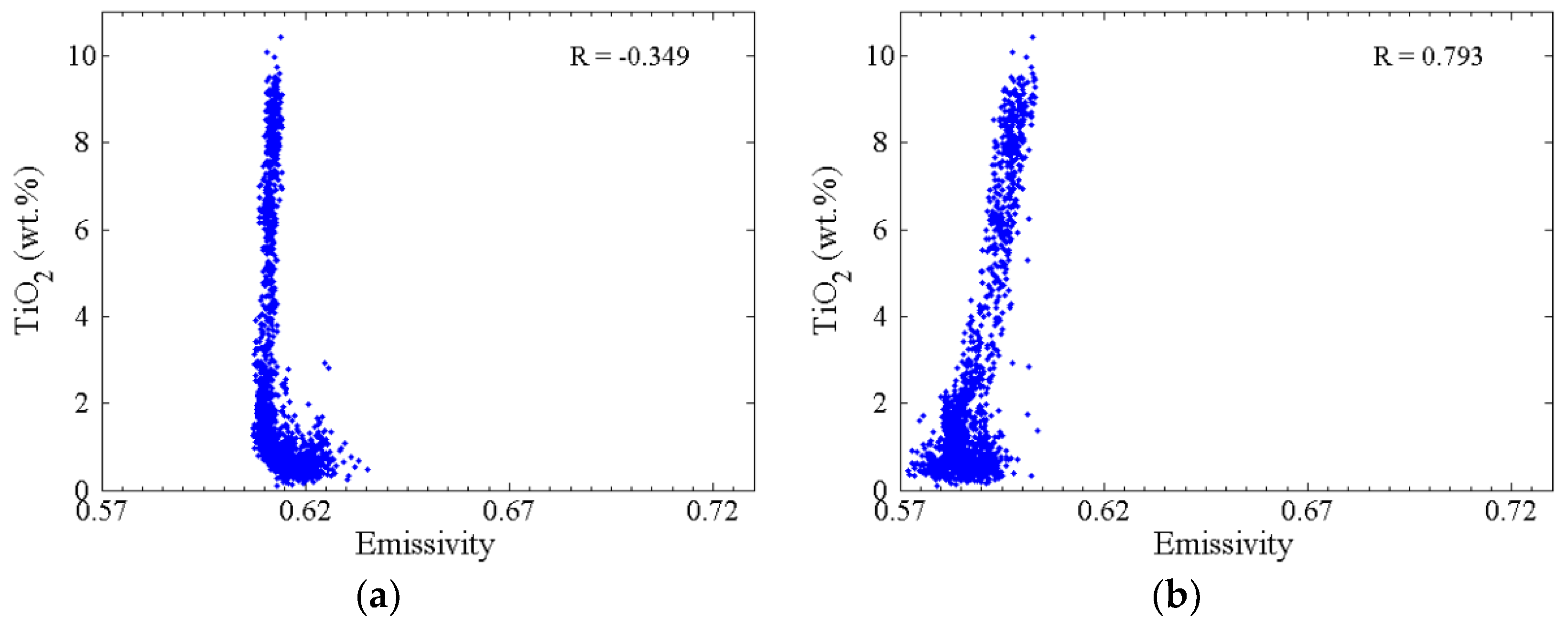
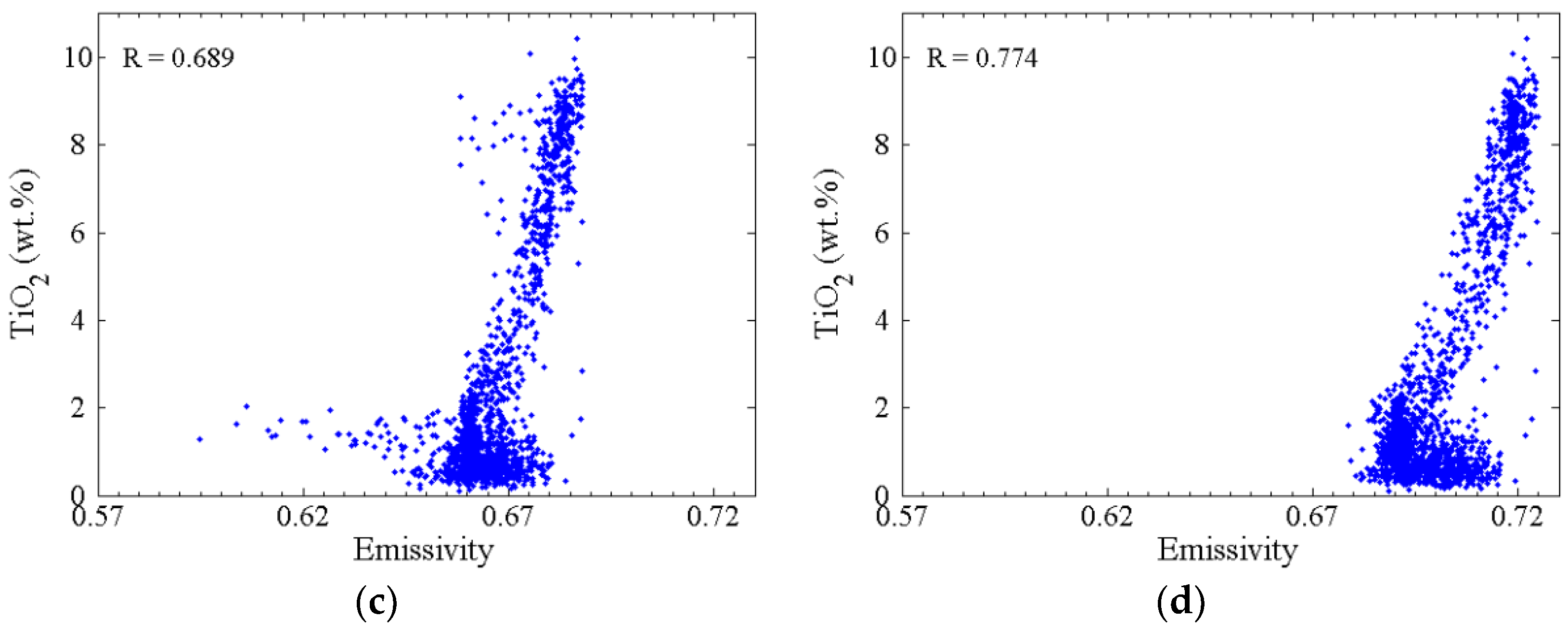
4.1.1. Estimated Spectral Emissivity Features with Chang’E-2 Microwave Radiometer (CELMS) Data
4.1.2. Estimated Spectral Emissivity Features with Diviner Thermal Infrared (TIR) Data
4.2. Useful Supplementary Information
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vasavada, A.R.; Bandfield, J.L.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Hayne, P.O.; Siegler, M.A.; Williams, J.-P.; Paige, D.A. Lunar equatorial surface temperatures and regolith properties from the Diviner Lunar Radiometer Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, E00H18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.G.; Xu, Y.; Cai, Z.C.; Chen, S.B.; Lian, Y.; Huang, H. Influence of lunar topography on simulated surface temperature. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 2131–2139. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, T.; Fa, W.Z. High frequency thermal emission from the lunar surface and near surface temperature of the Moon from Chang’E-2 microwave radiometer. Icarus 2014, 232, 34–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayne, P.O.; Bandfield, J.L.; Siegler, M.A.; Vasavada, A.R.; Ghent, R.R.; Williams, J.-P.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Aharonson, O.; Elder, C.M.; Lucey, P.G.; et al. Global Regolith Thermophysical Properties of the Moon from the Diviner Lunar Radiometer Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2017, 122, 2371–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.T.; Fa, W.Z.; Jin, Y.Q. Brightness Temperature of Lunar Surface for Calibration of Multichannel Millimeter-Wave Radiometer of Geosynchronous FY-4M. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 3055–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Cheng, A.Y. A lunar surface effective solar irradiance real-time model. Chin. J. Geophys. 2008, 51, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.P.; Zheng, Y.C.; Xu, A.A.; Tang, Z.S. Lunar Surface Temperature of Global Moon: Preparation of Database with Topographic and Albedo Effects. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 13, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.G.; Zhang, J.D.; Cai, Z.C.; Ping, J.S.; Tang, Z.S. Microwave Thermal Emission Features of Mare Orientale Revealed by CELMS Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2991–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.R.; Fa, W.Z. Thermal conductivity of surficial lunar regolith estimated from Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Diviner Radiometer data. Planet Space Sci. 2016, 124, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.-P.; Paige, D.A.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Sefton-Nash, E. The global surface temperatures of the moon as measured by the diviner lunar radiometer experiment. Icarus 2017, 283, 300–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.G.; Hu, S.; Wang, T.X.; Li, C.; Cai, Z.C.; Ping, J.S. Passive Microwave Probing Mare Basalts in Mare Imbrium Using CE-2 CELMS Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 3097–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.G.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, S.B.; Zheng, Y.C.; Shi, J.C.; Wang, T.X.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Ping, J.S.; Lu, Y. Thermophysical Features of Shallow Lunar Crust Demonstrated by Typical Copernican Craters Using CE-2 CELMS Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 2565–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.C.; Tsang, K.T.; Chan, K.L.; Zou, Y.L.; Zhang, F.; Ouyang, Z.Y. First microwave map of the Moon with Chang’E-1 data: The role of local time in global imaging. Icarus 2012, 219, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Chen, S.B.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Xiao, Y. The Sinus Iridum surface brightness temperature temporal-spatial distributions by LRO diviner data. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2017, 36, 628–635, 640. [Google Scholar]
- Paige, D.A.; Foote, M.C.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Schofield, J.T.; Calcutt, S.; Vasavada, A.R. The lunar reconnaissance orbiter diviner lunar radiometer experiment. Space Sci. Rev. 2010, 150, 125–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Jiang, J.S.; Xu, C.D.; Zhang, D.H.; Zhang, W.G. Calibration and brightness temperature algorithm of CE-1 Lunar Microwave Sounder (CELMS). Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 1392–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, E.; Nicholson, S.B. Temperature of the dark side of the Moon and of the Moon during eclipse. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1927, 39, 227–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, E.; Nicholson, S.B. Lunar radiation and temperatures. Astrophys. J. 1930, 71, 102–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langseth, M.G.; Clark, S.P.; Chute, J.L.; Keihm, S.J.; Wechsler, A.E. The Apollo 15 lunar heat-flow measurement. Moon 1972, 4, 390–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiken, G.H.; Vaniman, D.T.; French, B.M. A User’s Guide to the Moon; Cambridge Univ. Press: London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Wesselink, A.J. Heat conductivity and nature of the lunar surface material. Bull. Astron. Inst. Neth. 1948, 10, 351–363. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger, J.C. The surface temperature of the Moon. Aust. J. Phys. 1953, 6, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, W.P.; Watkins, J.R.; Calvert, T.A. Temperatures and thermophysical properties of the lunar outermost layer. Moon 1975, 13, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racca, G.D. Moon surface thermal characteristics for moon orbiting spacecraft thermal analysis. Planet. Space Sci. 1995, 43, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasavada, A.R.; Paige, D.A.; Wood, S.E. Near-surface temperatures on Mercury and the Moon and the stability of polar ice deposits. Icarus 1999, 141, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.Z.; Jiang, J.S. Simulations on the influence of lunar surface temperature profiles on CE-1 lunar microwave sounder brightness temperature. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Guo, Q. The lunar surface temperature real-time model. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 21, 928–938. [Google Scholar]
- Davidsson, B.J.R.; Rickman, H. Surface roughness and three-dimensional heat conduction in thermophysical models. Icarus 2014, 243, 58–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhl, D.; Welch, W.J.; Rea, D.G. Reradiation and thermal emission from illuminated craters on the lunar surface. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 1968, 73, 5281–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubanenko, L.; Aharonson, O. Stability of ice on the Moon with rough topography. Icarus 2017, 141, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Z.; Li, J.L.; Ping, J.S.; Hideo, H. Determination of the free lunar libration modes from ephemeris DE430. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 17, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Li, X.Y.; Wei, G.F. Numerical simulation of effective solar irradiance and temperatures at simple crater of lunar dayside (in Chinese). Sci. Sin.-Phys. Mech. Astron. 2019, 49, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.T.; Wang, X.Q.; Bi, S.S.; Wu, J.T.; Huang, S.P. Effects of solar radiation, terrestrial radiation and lunar interior heat flow on surface temperature at the nearside of the Moon: Based on numerical calculation and data analysis. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 60, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountain, F.A.; West, E.A. Thermal conductivity of particulate basalt as a function of density in simulated lunar and Martian environments. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 1970, 75, 4063–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, P. A vector-based slope and aspect generation algorithm. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1987, 53, 1109–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, K.H. A comparison of algorithms used to compute hill slope as a property of the DEM. Comput. Geosci.-UK 1998, 24, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, X. Error Analysis on Grid-Based Slope and Aspect Algorithms. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2004, 70, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.D.; Meng, Z.G.; Ping, J.S.; Li, W.X.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhao, R. Preliminary study of illumination characteristics of Aristarchus plateau using LOLA data. J. Deep Space Explor. 2017, 4, 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.D. Research on the Illumination Model of the Moon Using LOLA Data and Its Significance. Master’s Thesis, College of Geoexploration Science and Technology, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Keihm, S.J. Interpretation of the Lunar Microwave Brightness Temperature Spectrum: Feasibility of Orbital Heat Flow Mapping. Icarus 1984, 60, 568–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliason, E.; Isbell, C.; Lee, E.; Becker, T.; Gaddis, L.; McEwen, A.; Robinson, M. Mission to the Moon: The Clementine UVVIS Global Lunar Mosaic, PDS Volumes USA_NASA_PDS_CL_4001 through 4078, produced by the U.S. Geological Survey and distributed on CD media by the Planetary Data System. 1999. Available online: http://www.mapaplanet.org (accessed on 10 October 2019).
- Lawson, S.L.; Jakosky, B.M. Lunar surface thermophysical properties derived from Clementine LWIR and UVVIS images. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 27911–27932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, L.M.; Hunt, G.R.; Balsamo, S.R.; Salisbury, J.W. Midinfrared emission spectra of Apollo 14 and 15 soils and remote compositional mapping of the moon. In Proceedings of the 3rd Lunar Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 10–13 January 1972; pp. 3069–3076. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, C.H.; Agrawal, D.K.; Anastassakis, E.; Lowndes, R.P.; Tornberg, N.E. Far infrared and Raman spectroscopic investigations of lunar materials from Apollo 11, 12, 14 and 15. In Proceedings of the 3rd Lunar Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 10–13 January 1972; pp. 3077–3095. [Google Scholar]
- Bandfield, J.L.; Hayne, P.O.; Williams, J.P.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Paige, D.A. Lunar surface roughness derived from LRO Diviner radiometer observations. Icarus 2015, 248, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.E.; Zuber, M.T.; Neumann, G.A.; Mazarico, E.; Lemoine, F.G.; Head, J.W., III; Lucey, P.G.; Aharonson, O.; Robinson, M.S.; Sun, X.L.; et al. Summary of the results from the lunar orbiter laser altimeter after seven years in lunar orbit. Icarus 2017, 283, 70–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaber, G.G. Geologic Map of the Sinus Iridum Quadrangle of the Moon; 1-602(LAC-24); US Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1969.
- Hiesinger, H.; Jaumann, R.; Neukum, G.; Head, J.W., III. Ages of Mare basalts on the lunar nearside. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2000, 105, 29239–29275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.B.; Meng, Z.G.; Cui, T.F.; Lian, Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, X.Q. Geologic investigation and mapping of the Sinus Iridum quadrangle from Clementine, SELENE, and Chang’e-1 data. Sci. China Phys. Mech. 2010, 53, 2179–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Xiao, L.; Zhao, J.N.; Huang, Q.; Haruyama, J. Geological features and evolution history of Sinus Iridum, the Moon. Planet. Space Sci. 2014, 101, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Z.; Li, L.; Luo, X.X.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Pieters, C.M.; Basilesky, A.T.; Head, J.W., III. Geology, tectonism and composition of the northwest Imbrium region. Icarus 2018, 303, 67–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Z.; Wang, Z.Z. Simulations of lunar equatorial regolith temperature profile based on measurements of Diviner on lunar reconnaissance orbiter. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2232–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.T.; Paige, D.A.; Arvidson, R.E.; Grayzeck, E. Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Diviner Lunar Radiometer Experiment: Reduced Data Record and Derived Products Software Interface Specification. In Technical Report; Version 1.14; PDS Geosciences Node: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing Fundamentals and Radiometry. In Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1981; Volume 1, pp. 186–205. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.G.; Wang, H.H.; Zheng, Y.C.; Wang, Y.Z.; Miyamoto, H.; Cai, Z.C.; Ping, J.S.; Zhu, Y.Z. Several Geological Issues of Schrödinger Basin Exposed by CE-2 CELMS Data. Adv. Astron. 2019, 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagfors, T. Remote probing of the moon by infrared and microwave emissions and by radar. Radio Sci. 1970, 5, 189–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.A.; Campbell, D.B.; Margot, J.L.; Ghent, R.; Nolan, M.; Chandler, J.; Carter, L.M.; Stacy, N.J.S. Focused 70-cm wavelength radar mapping of the Moon. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 4032–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.P.; Chen, K.; Huang, Q.L.; Guo, W.; Li, Q.X.; Gui, L.Q.; Cheng, Y.B. Brightness Temperature Calculation of Lunar Crater: Interpretation of Topographic Effect on Microwave Data from Chang’E. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 4499–4510. [Google Scholar]
- Wieczorek, M.A.; Huang, S. A reanalysis of Apollo 15 and 17 Surface and Subsurface Temperature Series. In Proceedings of the 37th Lunar and Planetary Science, Houston, TX, USA, 13–17 March 2006; p. 1682. [Google Scholar]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Ping, J.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, M. Surface Temperature Simulation of Lunar Dayside and Its Geological Applications: A Case in Sinus Iridum. Sensors 2019, 19, 5545. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19245545
Zhang J, Ping J, Zeng Z, Yang Y, Li X, Wang M. Surface Temperature Simulation of Lunar Dayside and Its Geological Applications: A Case in Sinus Iridum. Sensors. 2019; 19(24):5545. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19245545
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jidong, Jinsong Ping, Zhaofa Zeng, Yongzhang Yang, Xiangyue Li, and Mingyuan Wang. 2019. "Surface Temperature Simulation of Lunar Dayside and Its Geological Applications: A Case in Sinus Iridum" Sensors 19, no. 24: 5545. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19245545
APA StyleZhang, J., Ping, J., Zeng, Z., Yang, Y., Li, X., & Wang, M. (2019). Surface Temperature Simulation of Lunar Dayside and Its Geological Applications: A Case in Sinus Iridum. Sensors, 19(24), 5545. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19245545





