Improved Models of Imaging of Skylight Polarization Through a Fisheye Lens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
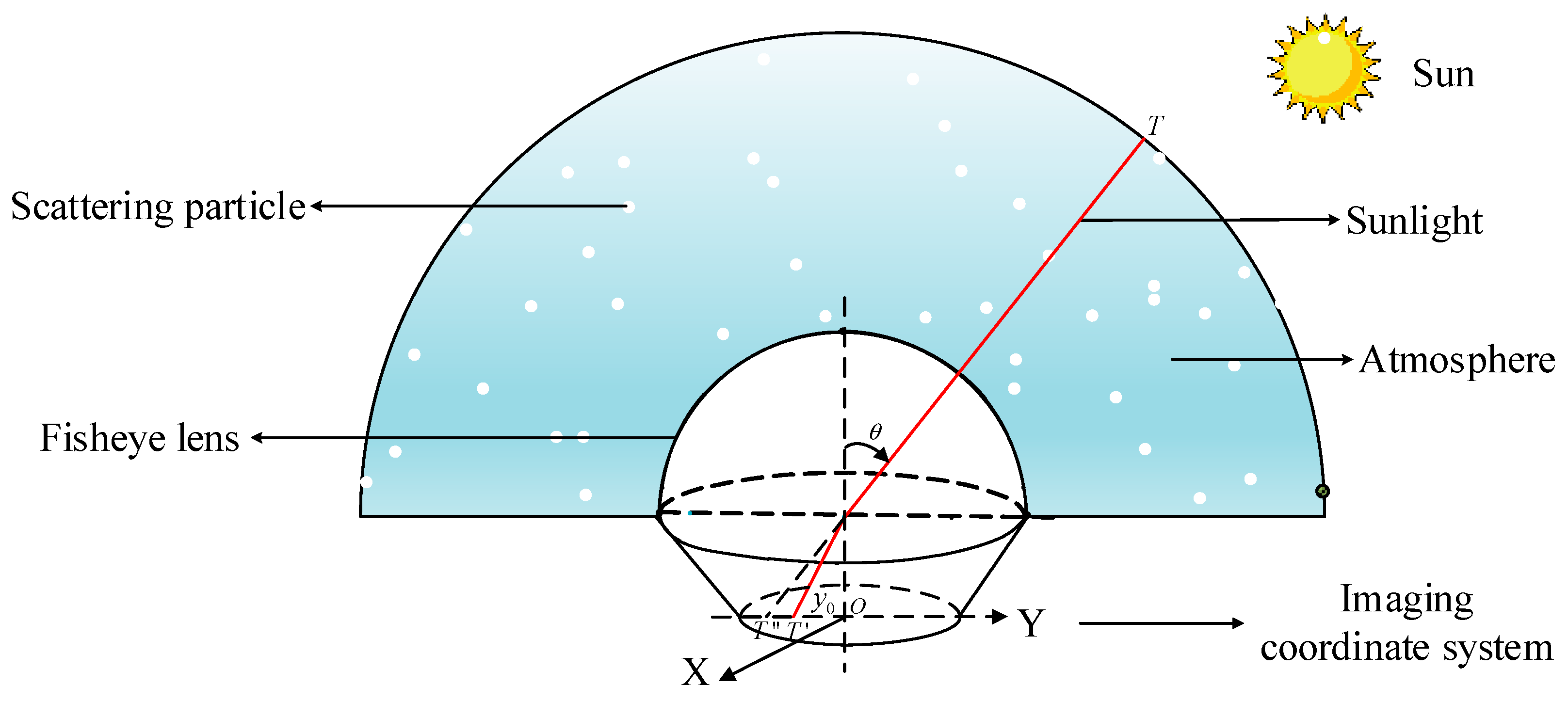
2.1. Method for Obtaining the Skylight Polarization Pattern
2.2. Rayleigh Skylight Polarization Pattern and Its Representation
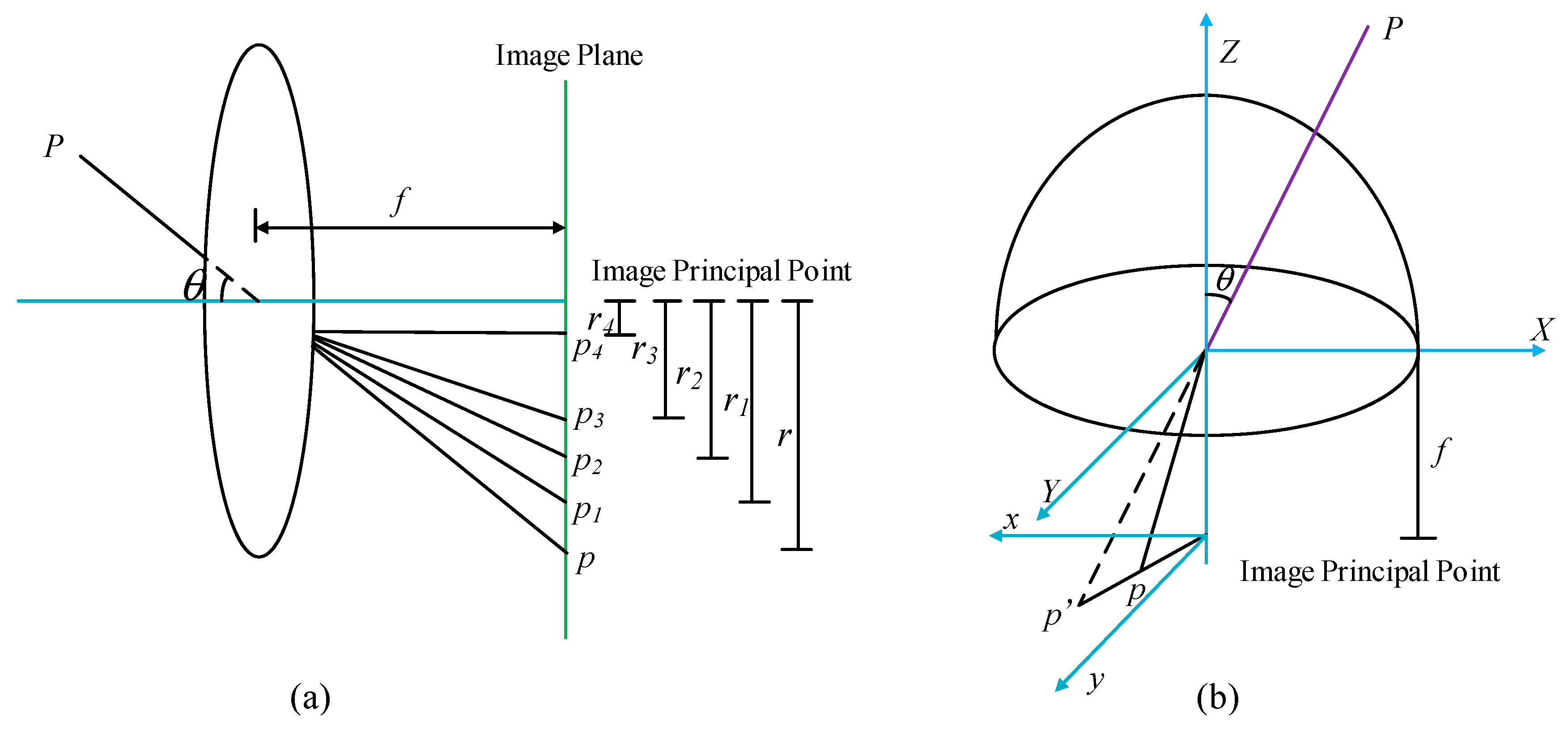
2.3. Improved Models Based on Imaging Theories of Skylight Polarization
2.3.1. Improved Model of Skylight Polarization in Equidistance Imaging Mode
2.3.2. Improved Model of Skylight Polarization in Equisolid Angle Imaging Mode
2.3.3. Improved Model of Skylight Polarization in Stereographic Imaging Mode
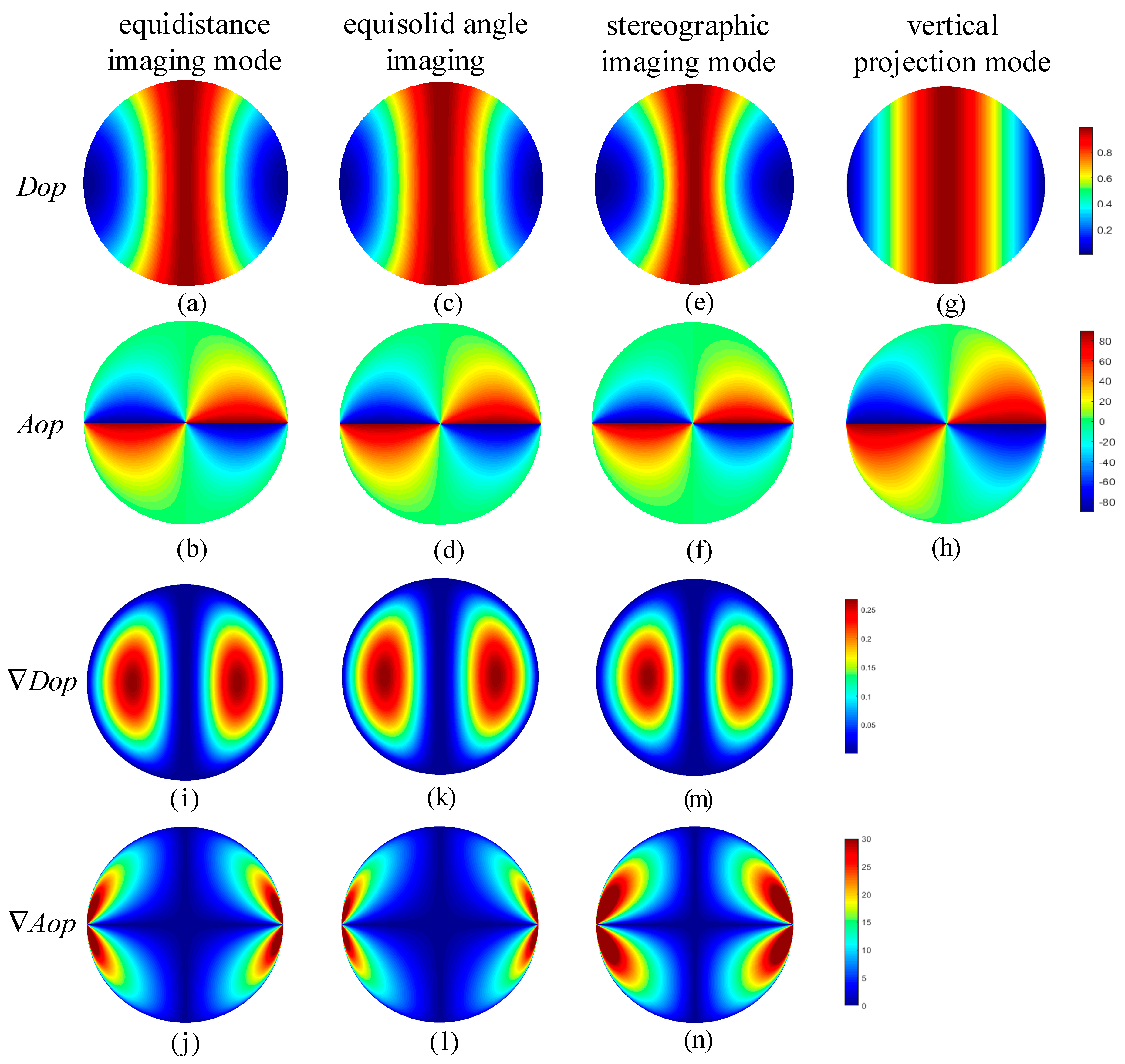
2.4. Distortion Analysis of the Improved Models of Skylight Polarization Based on Imaging Theories
3. Results and Discussion
Experiment and Result Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coulson, K.L. Polarization and Intensity of Light in the Atmosphere; A. Deepak Publishing: Hampton, VA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Fent, K. Polarized skylight orientation in the desert ant Cataglyphis. J. Comp. Physiol. 1986, 158, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacke, M.; Nilsson, D.E.; Scholtz, C.H.; Byrne, M.; Warrant, E.J. Animal behaviour: Insect orientation to polarized moonlight. Nature 2003, 424, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dacke, M.; Baird, E.; Byrne, M.; Scholtz, C.H.; Warrant, E.J. Dung beetles use the Milky Way for orientation. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powel, S.B.; Garnett, R.; Marshall, J.; Rizk, C.; Gruev, V. Bioinspired polarization vision enables underwater geolocalization. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaao6841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, T.W.; Marshall, J. Patterns and properties of polarized light in air and water. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 366, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, A.; Sabbah, S.; Erlic, C.; Shashar, N. Navigation by light polarization in clear and turbid waters. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 366, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barta, A.; Farkas, A.; Száz, D.; Egri, Á.; Barta, P.; Kovács, J.; Csák, B.; Jankovics, I.; Szabó, G.; Horváth, G. Polarization transition between sunlit and moonlit skies with possible implications for animal orientation and Viking navigation: Anomalous celestial twilight polarization at partial moon. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 5193–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossel, S.; Wehner, R. How bees analyse the polarization patterns in the sky. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 1984, 154, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrinos, D.; Kobayashi, H.; Pfeifer, R.; Maris, M.; Labhart, T. An autonomous agent navigating with a polarized light compass. Adapt. Behav. 1997, 6, 131–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiguo, F.; Jun, G.; Jingmin, W.; Wuxin, Z.; Yi, H. Investigation of atmospheric polarization measurement method imitating POL-neurons of cataglyphis. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2008, 29, 745–749. [Google Scholar]
- Usher, K.; Ridley, P.; Corke, P. A camera as a polarized light compass: Preliminary experiments. In Proceedings of the Australian Conference on Robotics and Automation, Sydney, Australia, 14–15 November 2001; pp. 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Voss, K.J. Electro-optic camera system for measurement of the underwater radiance distribution. Opt. Eng. 1989, 28, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Voss, K. Polarized radiance distribution measurement of skylight. II. Experiment and data. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 8753–8764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, G.; Barta, A.; Gal, J.; Suhai, B.; Haiman, O. Ground-based full-sky imaging polarimetry of rapidly changing skies and its use for polarimetric cloud detection. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhai, B.; Horváth, G. How well does the Rayleigh model describe the E-vector distribution of skylight in clear and cloudy conditions? A full-sky polarimetric study. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2004, 21, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pust, N.J.; Shaw, J.A. Dual-field imaging polarimeter using liquid crystal variable retarders. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 5470–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pust, N.J.; Shaw, J.A. Digital all-sky polarization imaging of partly cloudy skies. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, H190–H198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanghavi, S.; Davis, A.B.; Eldering, A. vSmartMOM: A vector matrix operator method-based radiative transfer model linearized with respect to aerosol properties. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2014, 133, 412–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.; Elias, M.; Andraud, C.; Lafait, J. Comparison between the auxiliary function method and the discrete-ordinate method for solving the radiative transfer equation for light scattering. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2003, 20, 2321–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capilla, M.T.; Talavera, C.F.; Ginestar, D.; Verdú, G. A study of the radiative transfer equation using a spherical harmonics-nodal collocation method. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2017, 189, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kotchenova, S.Y.; Vermote, E.F.; Matarrese, R.; Klemm, F.J., Jr. Validation of a vector version of the 6S radiative transfer code for atmospheric correction of satellite data. Part I Path Radiance Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 6762–6774. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, M.V.; Dennis, M.R.; Lee, R.L., Jr. Polarization singularities in the clear sky. N. J. Phys. 2004, 6, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkie, A.; Ulbricht, C.; Tobler, R.F.; Zotti, G.; Purgathofer, W. An analytical model for skylight polarization. In Proceedings of the Eurographics Workshop on Rendering Techniques, The Eurographics Association, Norköping, Sweden, 21–23 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Fan, Z.; Roberts, N.W. An analytical model for the celestial distribution of polarized light, accounting for polarization singularities, wavelength and atmospheric turbidity. J. Opt. 2016, 18, 065601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaoui, M. Polarized skylight navigation. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, B37–B46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleck, M.M. Perspective Projection: The Wrong Imaging Model; Technical report; University of Iowa: Iowa City, IA, USA, 1995; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kumler, J.J.; Bauer, M.L. Fish-eye lens designs and their relative performance. Proc. SPIE 2000, 4093, 360–369. [Google Scholar]
- Kannala, J.; Brandt, S.S. A generic camera model and calibration method for conventional, wide-angle, and fish-eye lenses. IEEE T Pattern Anal. 2006, 28, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Ding, M.; Qin, N.; Lai, X. Digital deformation model for fisheye image rectification. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 22252–22261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, I.; Andreas, A. Solar position algorithm for solar radiation applications. Sol. Energy 2004, 76, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Xuan, J.; Jia, B. Polarization patterns under different sky conditions and a navigation method based on the symmetry of the AOP map of skylight. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 28589–28603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegedüs, R.; Åkesson, S.; Horváth, G. Polarization patterns of thick clouds: Overcast skies have distribution of the angle of polarization similar to that of clear skies. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2007, 24, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomozi, I.; Horváth, G.; Wehner, R. How the clear-sky angle of polarization pattern continues underneath clouds: Full-sky measurements and implications for animal orientation. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 4, 2933–2942. [Google Scholar]









| Time | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8:30 | 29.10 | 61.62 | 43.46 | 18.16 |
| 10:00 | 46.24 | 50.05 | 30.88 | 19.17 |
| 11:05 | 55.86 | 41.22 | 26.97 | 14.25 |
| 14:28 | 47.17 | 51.16 | 28.11 | 23.05 |
| 15:38 | 34.21 | 61.66 | 40.80 | 20.86 |
| 17:00 | 17.43 | 70.06 | 53.57 | 16.49 |
| Time | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8:30 | 29.10 | 97.90 | 73.78 | 24.12 |
| 10:00 | 46.24 | 89.17 | 42.77 | 46.40 |
| 11:05 | 55.86 | 80.08 | 48.99 | 31.09 |
| 14:28 | 47.17 | 90.06 | 53.71 | 36.35 |
| 15:38 | 34.21 | 98.65 | 71.23 | 27.42 |
| 17:00 | 17.43 | 96.86 | 80.25 | 16.61 |
| Time | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8:30 | 29.10 | 55.38 | 50.42 | 43.46 | 11.92 | 6.96 |
| 10:00 | 46.24 | 44.53 | 33.25 | 30.88 | 13.65 | 2.37 |
| 11:05 | 55.86 | 35.17 | 28.13 | 26.97 | 8.20 | 1.16 |
| 14:28 | 47.17 | 44.26 | 36.46 | 28.11 | 16.15 | 8.35 |
| 15:38 | 34.21 | 58.36 | 43.72 | 40.80 | 17.56 | 2.92 |
| 17:00 | 17.43 | 68.59 | 59.28 | 53.57 | 15.02 | 5.71 |
| Time | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8:30 | 29.10 | 92.34 | 86.57 | 73.78 | 18.56 | 12.79 |
| 10:00 | 46.24 | 80.25 | 66.48 | 42.77 | 37.48 | 23.71 |
| 11:05 | 55.86 | 70.13 | 58.24 | 48.99 | 21.14 | 9.25 |
| 14:28 | 47.17 | 82.56 | 70.16 | 53.71 | 28.85 | 16.45 |
| 15:38 | 34.21 | 95.53 | 89.17 | 71.23 | 24.30 | 17.94 |
| 17:00 | 17.43 | 90.37 | 88.45 | 80.25 | 10.12 | 8.20 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, S.; Gao, J.; Wang, D.; Yang, T.; Wang, X. Improved Models of Imaging of Skylight Polarization Through a Fisheye Lens. Sensors 2019, 19, 4844. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19224844
Sun S, Gao J, Wang D, Yang T, Wang X. Improved Models of Imaging of Skylight Polarization Through a Fisheye Lens. Sensors. 2019; 19(22):4844. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19224844
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Shaobo, Jun Gao, Daqian Wang, Tian Yang, and Xin Wang. 2019. "Improved Models of Imaging of Skylight Polarization Through a Fisheye Lens" Sensors 19, no. 22: 4844. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19224844
APA StyleSun, S., Gao, J., Wang, D., Yang, T., & Wang, X. (2019). Improved Models of Imaging of Skylight Polarization Through a Fisheye Lens. Sensors, 19(22), 4844. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19224844





