A Social Virtual Reality-Based Application for the Physical and Cognitive Training of the Elderly at Home
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. A Social Application for Dual Task Training
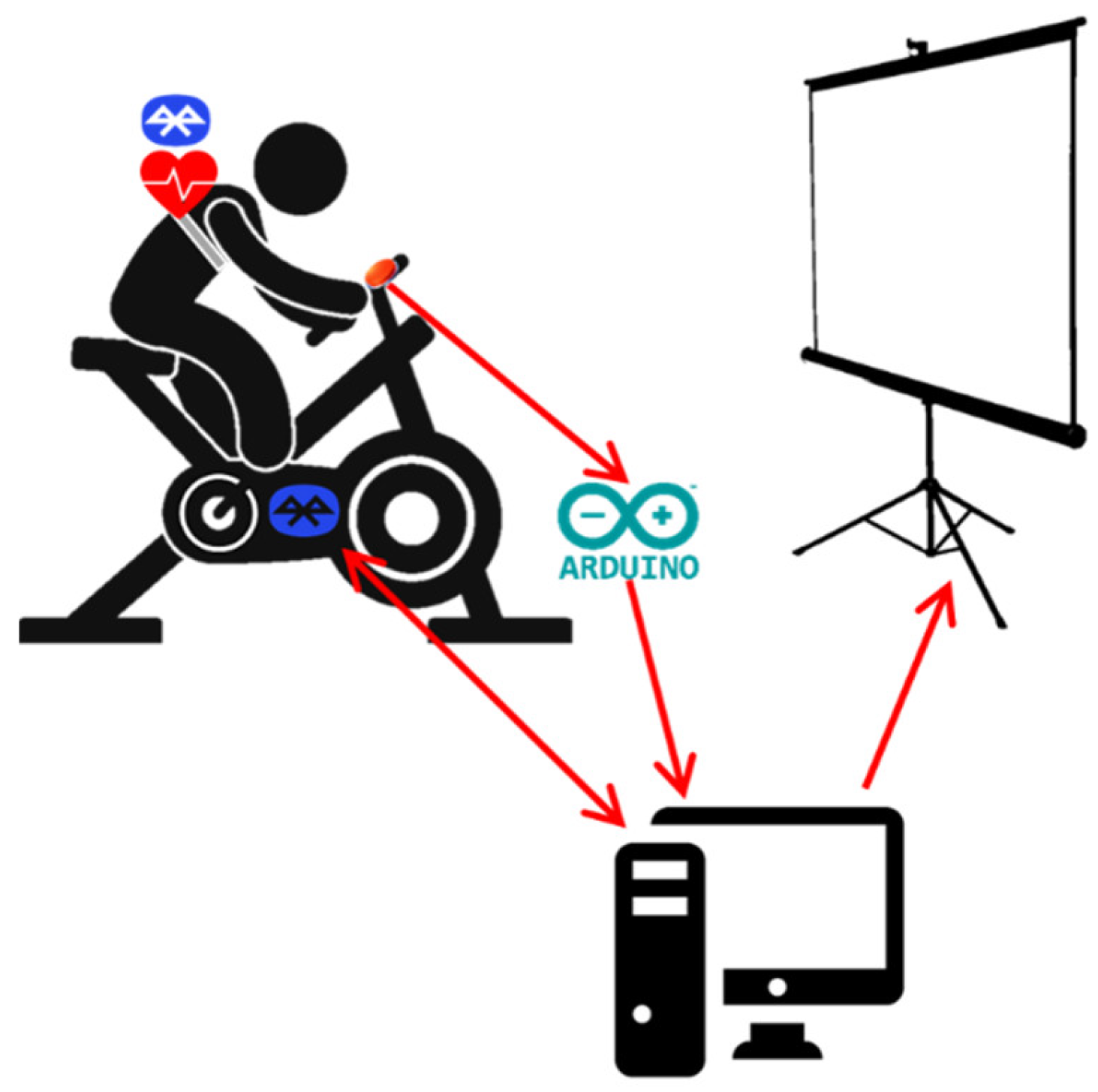
3.1. SocialBike Architecture
Application Networking
- The continuous streaming of data across the network (e.g., to communicate to others the current position and rotation of a specific player), performed by a serializing function.
- ‘Remote Procedure Calls’ (RPCs) for infrequent actions.
- The change in game objects’ ‘Custom Properties’, for very rare status updates.
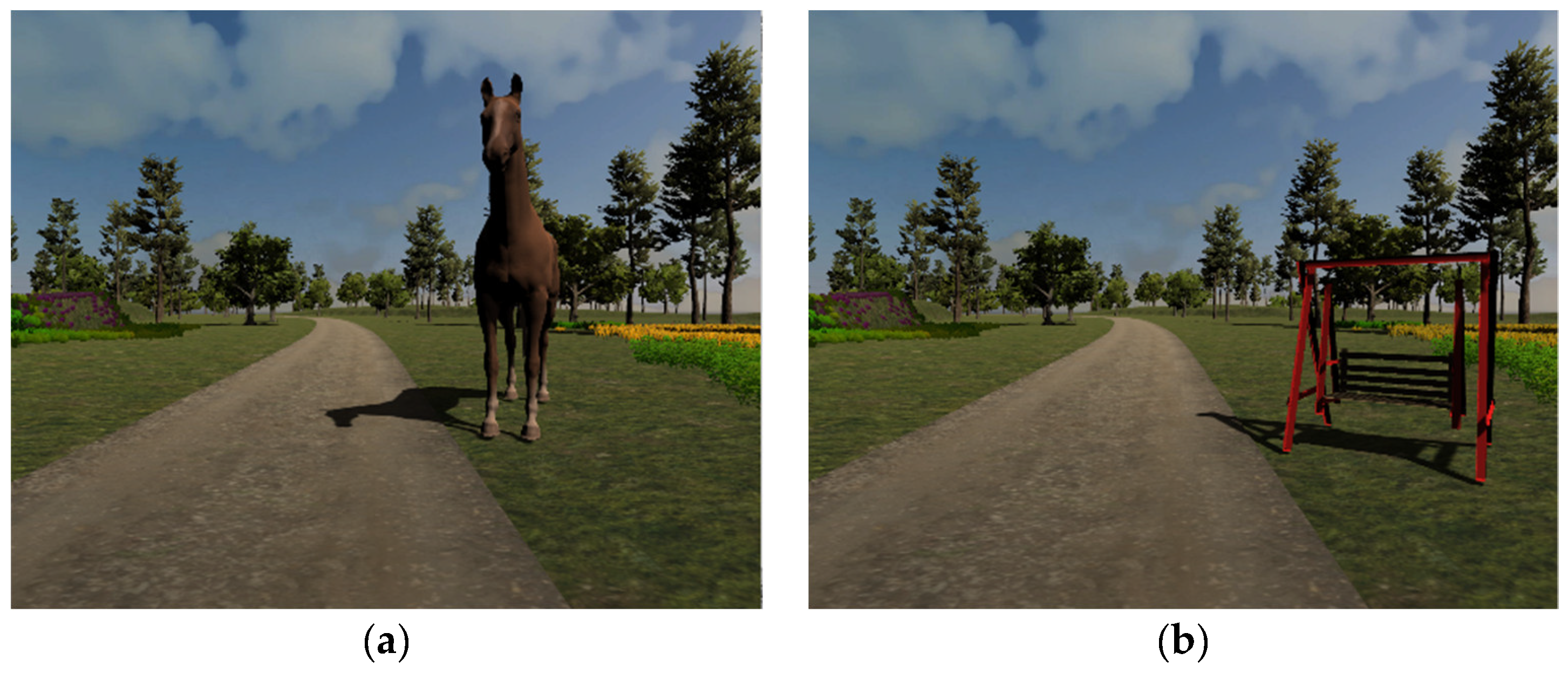
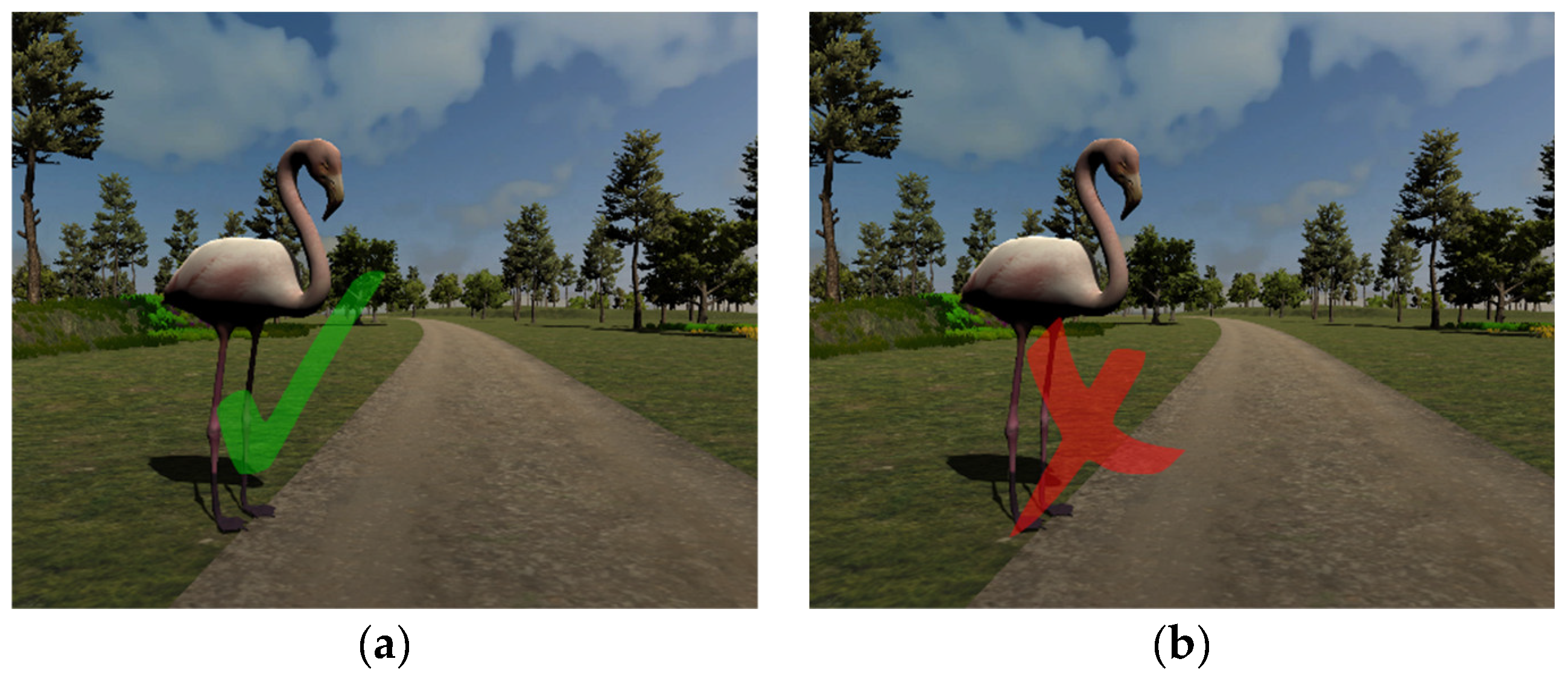
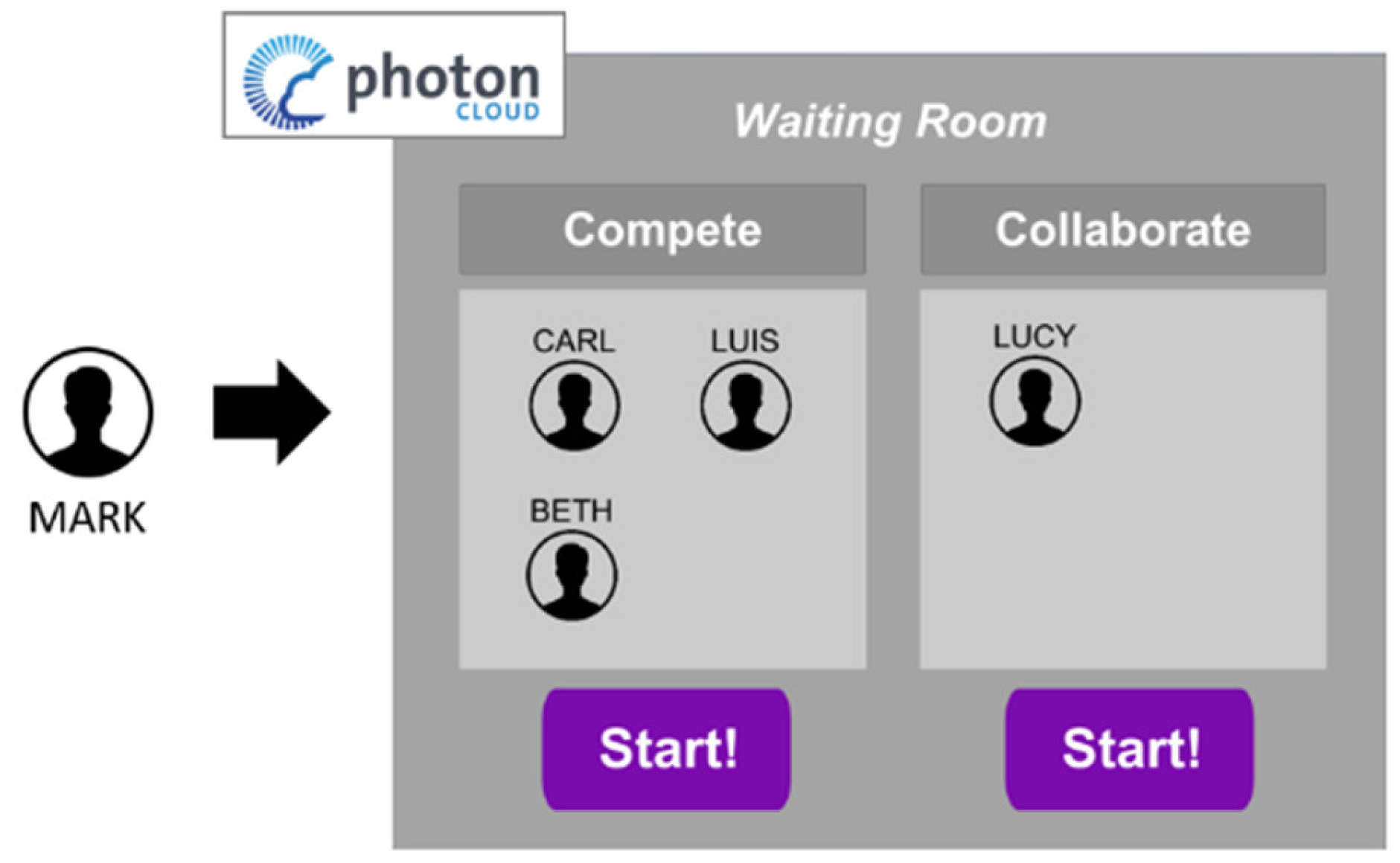
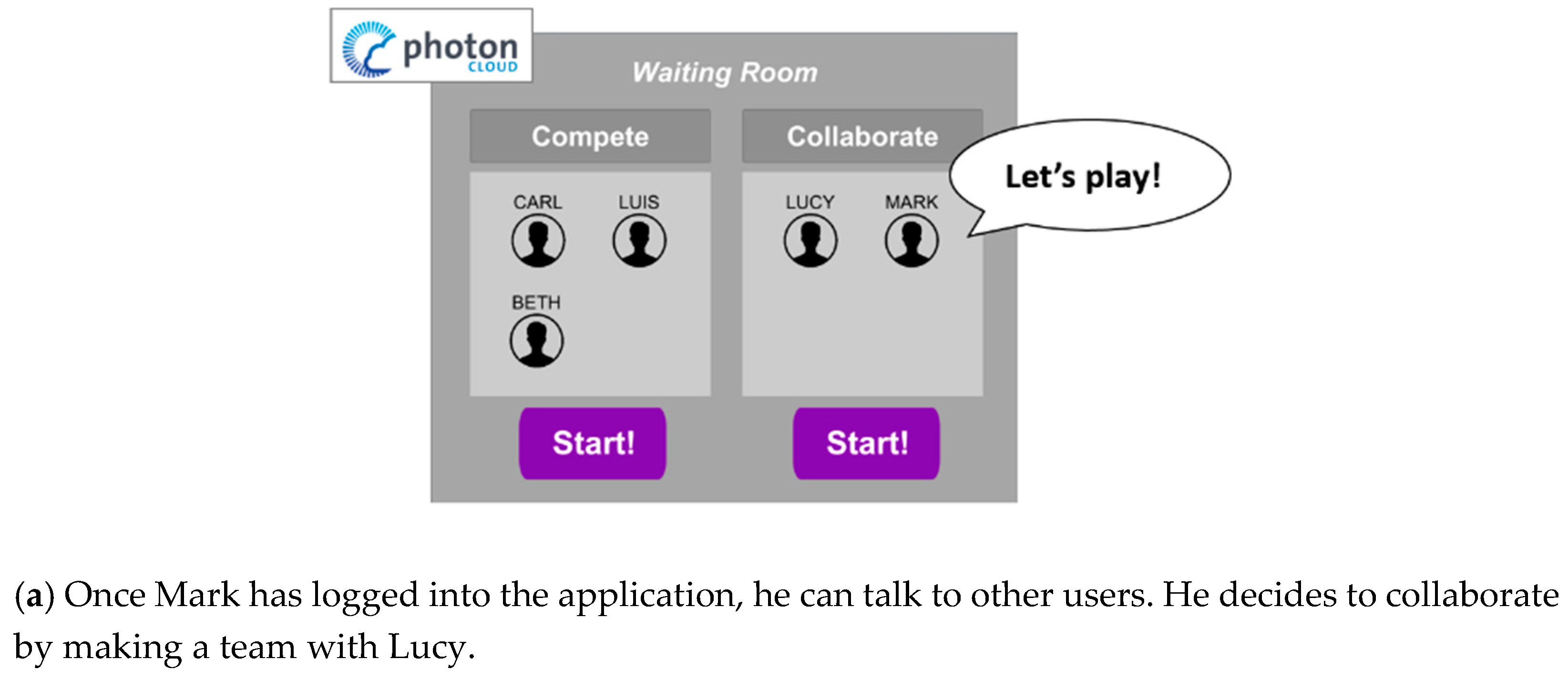
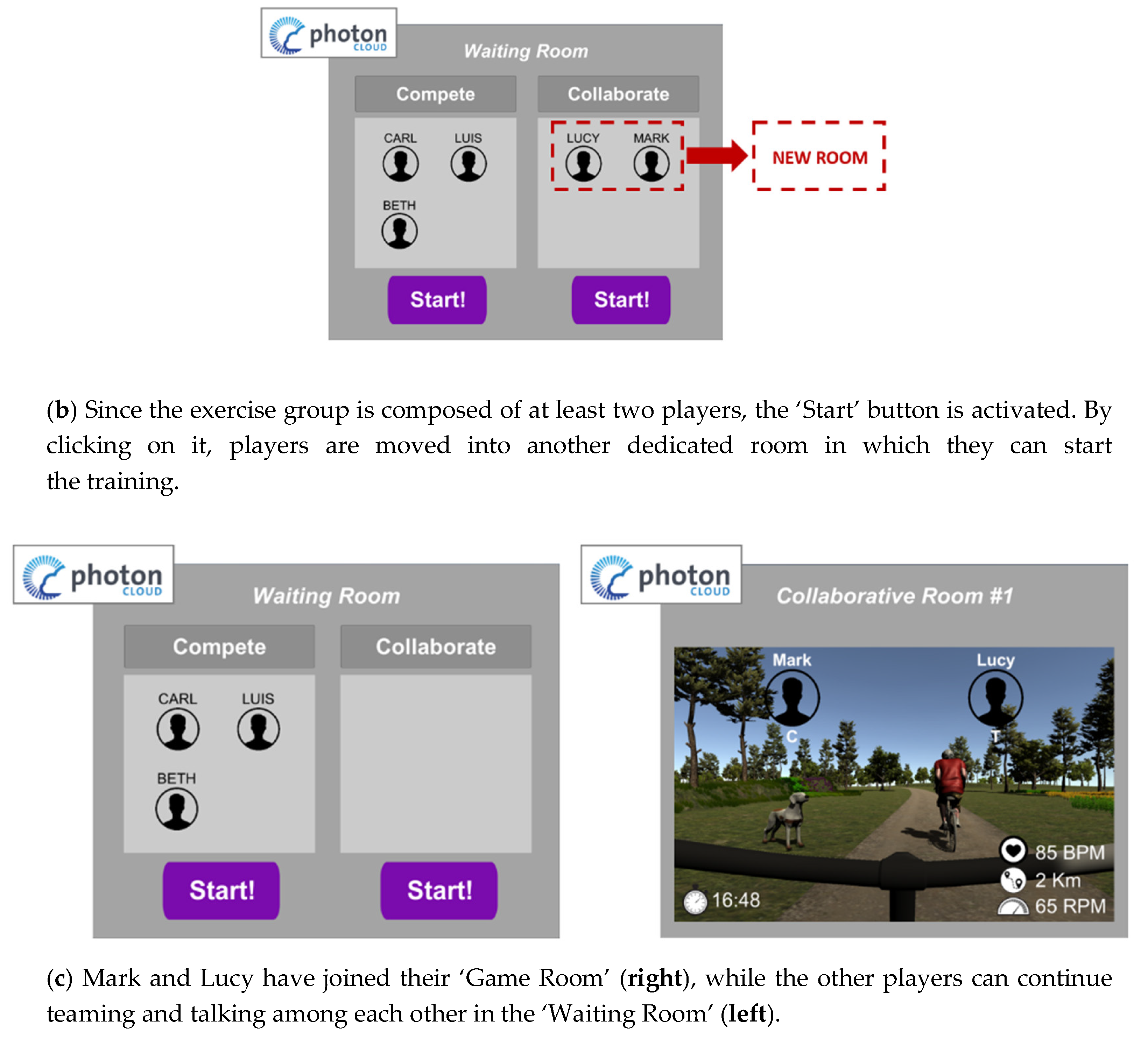
3.2. The Application Flow
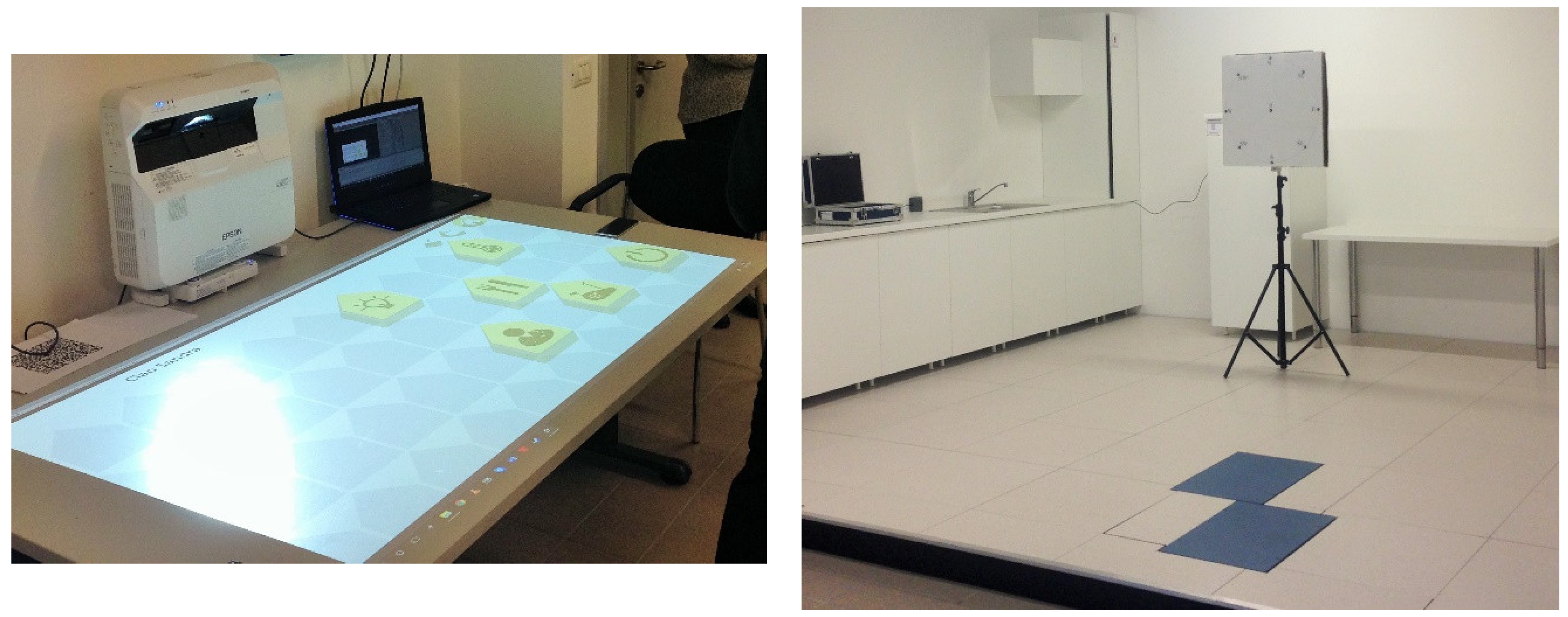
4. SocialBike in the “House of the Future”
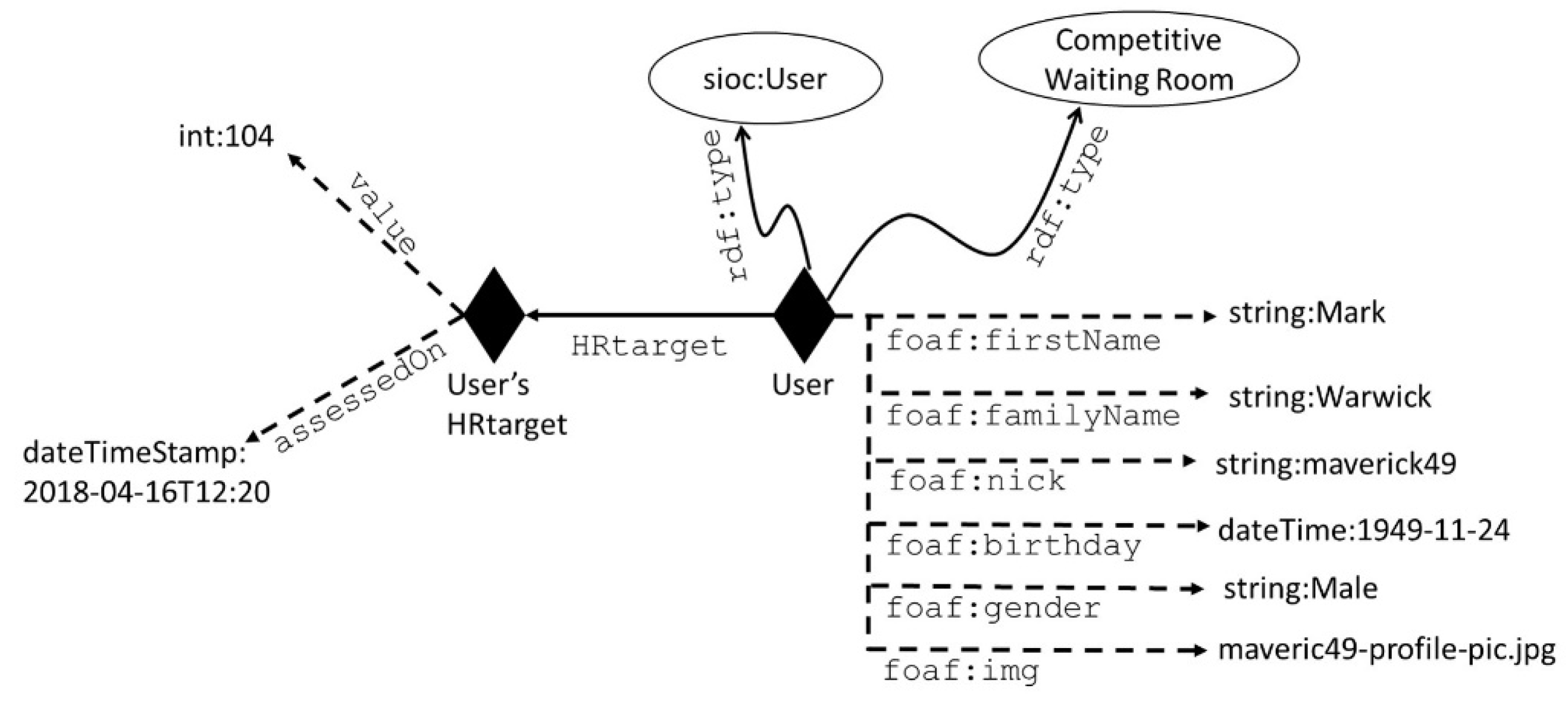
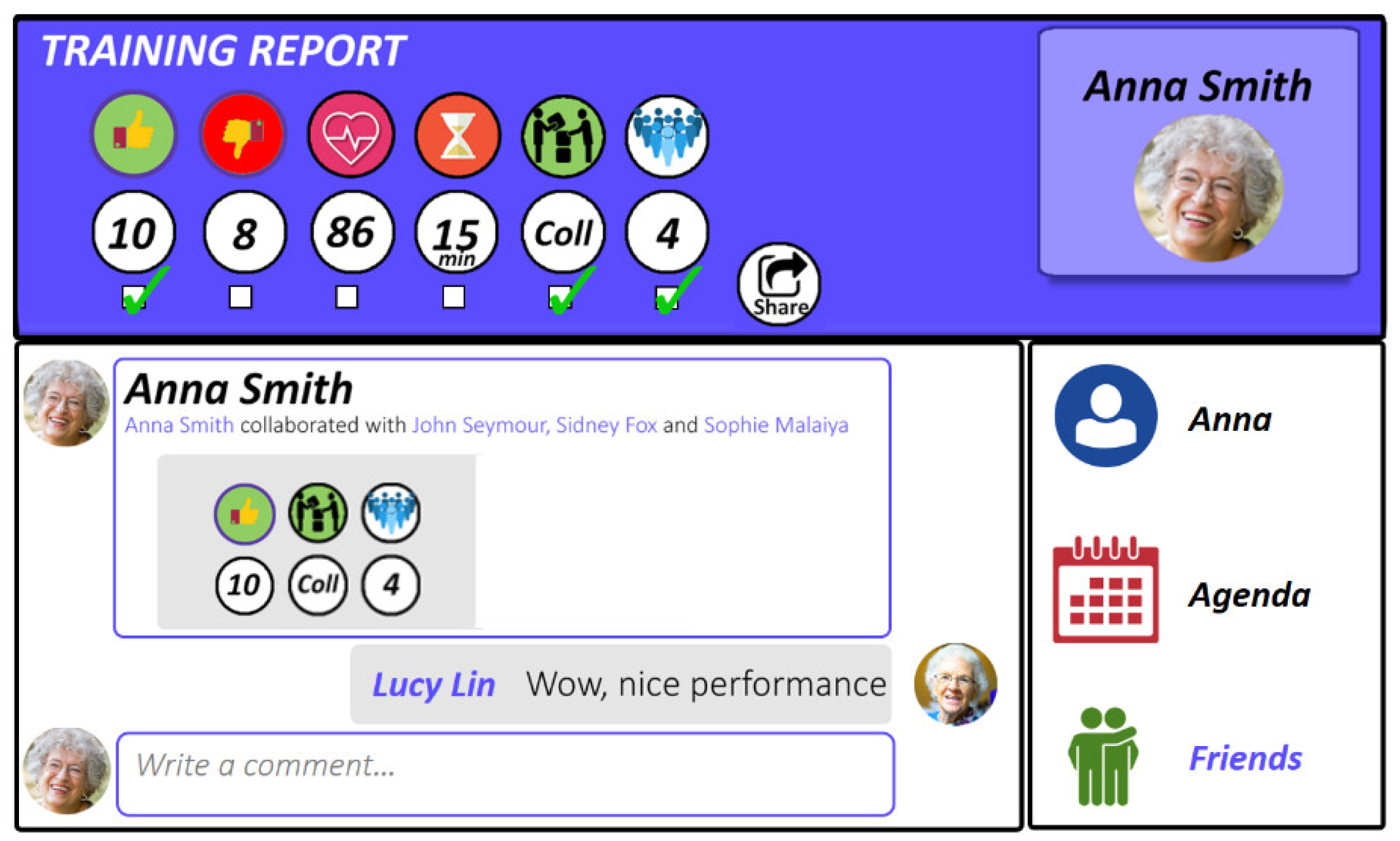
4.1. Social Media Network
4.2. User’s Monitoring and Progress
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kochhar, R.; Oates, R. Attitudes about Aging: A Global Perspective; Pew Research Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. World Report on Ageing and Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N.J. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedarko, N.S. The biology of aging and frailty. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2011, 27, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, S. Economic and social implications of aging societies. Science 2014, 346, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, S. Assessing self-maintenance: Activities of daily living, mobility, and instrumental activities of daily living. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1983, 31, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L. The state of aging and health in America 2007. Aging Health 2007, 3, 139–141. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, W.; Martinez, A.; Sanchez, W.; Estrada, H.; Castro-Sánchez, N.A.; Mujica, D. A systematic review of proposals for the social integration of elderly people using ambient intelligence and social networking sites. Cogn. Comput. 2016, 8, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.J.; Augusto, J.C.; Jakkula, V.R. Ambient intelligence: Technologies, applications, and opportunities. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2009, 5, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloret, J.; Canovas, A.; Sendra, S.; Parra, L. A smart communication architecture for ambient assisted living. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Rhuma, A.; Naqvi, S.M.; Wang, L.; Chambers, J. A posture recognition-based fall detection system for monitoring an elderly person in a smart home environment. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2012, 16, 1274–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal, B.; Al-Khatib, K. Smart home automation system for elderly, and handicapped people using XBee. Int. J. Smart Home 2015, 9, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocanu, I.; Schpor, O.-A.; Cramariuc, B.; Rusu, L. Mobile@ Old: A Smart Home Platform for Enhancing the Elderly Mobility. Adv. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2017, 17, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deen, M.J. Information and communications technologies for elderly ubiquitous healthcare in a smart home. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2015, 19, 573–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Future Homes for Future Communities (FHfFC). Available online: http://www.fhffc.it/ (accessed on 20 December 2018).
- Pizzagalli, S.; Spoladore, D.; Arlati, S.; Sacco, M.; Greci, L. HIC: An interactive and ubiquitous home controller system for the smart home. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 6th International Conference on Serious Games and Applications for Health (SeGAH), Vienna, Austria, 16–18 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gaggioli, A.; Greci, L.; Arlati, S.; Stramba-Badiale, M.; Pedroli, E.; Colombo, D.; Serino, S.; Cipresso, P.; Riva, G. Positive Bike—An Immersive Biking Experience for Combined Physical and Cognitive Training of Elderly Patients. Annu. Rev. Cyberther. Telemed. 2017, 15, 196–199. [Google Scholar]
- Collard, R.M.; Boter, H.; Schoevers, R.A.; Oude Voshaar, R.C. Prevalence of frailty in community-dwelling older persons: A systematic review. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012, 60, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobbens, R.J.; Luijkx, K.G.; Wijnen-Sponselee, M.T.; Schols, J.M. Toward a conceptual definition of frail community dwelling older people. Nurs. Outlook 2010, 58, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, A.J.; Morgan, K.; Bendall, M.J.; Dallosso, H.; Ebrahim, S.B.; Arie, T.H.; Fentem, P.H.; Bassey, E.J. Falls by elderly people at home: Prevalence and associated factors. Age Ageing 1988, 17, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speechley, M.; Tinetti, M. Falls and injuries in frail and vigorous community elderly persons. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1991, 39, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, K.S.; Lee, F.; Mackenzie, A.E.; Lee, D.T. Psychosocial consequences of falling: The perspective of older Hong Kong Chinese who had experienced recent falls. J. Adv. Nurs. 2002, 37, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, I.P.; Bulpitt, C.J. The prognosis of falls in elderly people living at home. Age Ageing 1999, 28, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, L.E.; Villareal, D.T. Physical exercise as therapy for frailty. In Frailty: Pathophysiology, Phenotype and Patient Care; 83rd Nestlé Nutrition Institute Workshop, Barcelona, March 2014; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Theou, O.; Stathokostas, L.; Roland, K.P.; Jakobi, J.M.; Patterson, C.; Vandervoort, A.A.; Jones, G.R. The effectiveness of exercise interventions for the management of frailty: A systematic review. J. Aging Res. 2011, 2011, 569194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pi, Y.; Chen, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Chan, C. Cognitive motor interference for preventing falls in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Age Ageing 2014, 44, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Lamar, M.; Bhatt, T. Effect of type of cognitive task and walking speed on cognitive-motor interference during dual-task walking. Neuroscience 2014, 260, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plummer, P.; Eskes, G.; Wallace, S.; Giuffrida, C.; Fraas, M.; Campbell, G.; Clifton, K.; Skidmore, E.R. Cognitive-motor interference during functional mobility after stroke: State of the science and implications for future research. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 2565–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plummer-D’Amato, P.; Brancato, B.; Dantowitz, M.; Birken, S.; Bonke, C.; Furey, E. Effects of gait and cognitive task difficulty on cognitive-motor interference in aging. J. Aging Res. 2012, 2012, 583894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pollina, L.; Guessous, I.; Petoud, V.; Combescure, C.; Buchs, B.; Schaller, P.; Kossovsky, M.; Gaspoz, J.M. Integrated care at home reduces unnecessary hospitalizations of community-dwelling frail older adults: A prospective controlled trial. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voukelatos, A.; Merom, D.; Sherrington, C.; Rissel, C.; Cumming, R.G.; Lord, S.R. The impact of a home-based walking programme on falls in older people: The Easy Steps randomised controlled trial. Age Ageing 2015, 44, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckinx, F.; Rolland, Y.; Reginster, J.-Y.; Ricour, C.; Petermans, J.; Bruyère, O. Burden of frailty in the elderly population: Perspectives for a public health challenge. Arch. Public Health 2015, 73, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Gale, C.R.; Westbury, L.; Cooper, C. Social isolation and loneliness as risk factors for the progression of frailty: The English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Age Ageing 2017, 47, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, H.; Ishizaki, T.; Kato, M.; Morimoto, A.; Tamate, A.; Uchiyama, Y.; Yasumura, S. How often and how far do frail elderly people need to go outdoors to maintain functional capacity? Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2010, 50, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, C.A.; Mann, K.; Wasek, S.; Arbesman, M. Systematic review of the effect of home modification and fall prevention programs on falls and the performance of community-dwelling older adults. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2012, 66, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley-Hague, H.; Boulton, E.; Hall, A.; Pfeiffer, K.; Todd, C. Older adults’ perceptions of technologies aimed at falls prevention, detection or monitoring: A systematic review. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2014, 83, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrington, C.; Michaleff, Z.A.; Fairhall, N.; Paul, S.S.; Tiedemann, A.; Whitney, J.; Cumming, R.G.; Herbert, R.D.; Close, J.C.; Lord, S.R. Exercise to prevent falls in older adults: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrington, C.; Whitney, J.C.; Lord, S.R.; Herbert, R.D.; Cumming, R.G.; Close, J.C. Effective exercise for the prevention of falls: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 2234–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, L.D.; Robertson, M.C.; Gillespie, W.J.; Sherrington, C.; Gates, S.; Clemson, L.M.; Lamb, S.E. Interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 9, CD007146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betker, A.; Szturm, T.; Moussavi, Z. Development of an interactive motivating tool for rehabilitation movements. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Shanghai, China, 17–18 January 2005; pp. 6893–6896. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, A.J.; Robertson, M.C.; La Grow, S.J.; Kerse, N.M.; Sanderson, G.F.; Jacobs, R.J.; Sharp, D.M.; Hale, L.A. Randomised controlled trial of prevention of falls in people aged ≥ 75 with severe visual impairment: The VIP trial. BMJ 2005, 331, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Diest, M.; Lamoth, C.J.; Stegenga, J.; Verkerke, G.J.; Postema, K. Exergaming for balance training of elderly: State of the art and future developments. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2013, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Crouse, J. Playing in parallel: The effects of multiplayer modes in active video game on motivation and physical exertion. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2013, 16, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorderer, P.; Hartmann, T.; Klimmt, C. Explaining the enjoyment of playing video games: The role of competition. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Entertainment Computing, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 8–10 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, A.L.; Anderson-Hanley, C.; Arciero, P.J. Virtual and live social facilitation while exergaming: Competitiveness moderates exercise intensity. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2012, 34, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiano, A.E.; Calvert, S.L. Wii tennis play for low-income African American adolescents’ energy expenditure. Cyberpsychology 2011, 5, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Kim, J.; Tenzek, K.E.; Lee, K.M. The effects of competition on intrinsic motivation in exergames and the conditional indirect effects of presence. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the International Communication Association, Singapore, 22–26 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson-Hanley, C.; Snyder, A.L.; Nimon, J.P.; Arciero, P.J. Social facilitation in virtual reality-enhanced exercise: Competitiveness moderates exercise effort of older adults. Clin. Interv. Aging 2011, 6, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, L.A.; Buckley, J.; Corballis, P.M.; Lutteroth, C.; Wuensche, B.C. Competition and cooperation with virtual players in an exergame. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2016, 2, e92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiano, A.E.; Abraham, A.A.; Calvert, S.L. Adolescent exergame play for weight loss and psychosocial improvement: A controlled physical activity intervention. Obesity 2013, 21, 598–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feltz, D.L.; Forlenza, S.T.; Winn, B.; Kerr, N.L. Cyber buddy is better than no buddy: A test of the Köhler motivation effect in exergames. Games Health Res. Dev. Clin. Appl. 2014, 3, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.; Brooks, K.A. Virtual vs. traditional exercise training in previously untrained subjects. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2013, 2, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Mrakic-Sposta, S.; Di Santo, S.G.; Franchini, F.; Arlati, S.; Zangiacomi, A.; Greci, L.; Moretti, S.; Jesuthasan, N.; Marzorati, M.; Rizzo, G.; et al. Effects of Combined Physical and Cognitive Virtual Reality-Based Training on Cognitive Impairment and Oxidative Stress in MCI Patients: A Pilot Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, C.E.; Blissmer, B.; Deschenes, M.R.; Franklin, B.A.; Lamonte, M.J.; Lee, I.M.; Nieman, D.C.; Swain, D.P. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: Guidance for prescribing exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1334–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unity 3D. Available online: https://unity3d.com/ (accessed on 20 December 2018).
- Photon Engine: Multiplayer Game Development Made Easy. Available online: https://www.photonengine.com/ (accessed on 20 December 2018).
- Chodzko-Zajko, W.J.; Proctor, D.N.; Singh, M.A.; Minson, C.T.; Nigg, C.R.; Salem, G.J.; Skinner, J.S. Exercise and physical activity for older adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 1510–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, S.; Patel, H. Health and safety implications of virtual reality: A review of empirical evidence. Appl. Ergon. 2002, 33, 251–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitzler, P.; Krotzsch, M.; Ru-dolph, S. Foundations of Semantic Web Technologies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Spoladore, D.; Sacco, M. Semantic and Dweller-Based Decision Support System for the Reconfiguration of Domestic Environments: RecAAL. Electronics 2018, 7, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mika, P. Social networks and the semantic web. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence, Beijing, China, 20–24 September 2004; pp. 285–291. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, T.R. A translation approach to portable ontology specifications. Knowl. Acquis. 1993, 5, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brickley, D.; Miller, L. FOAF Vocabulary Specification 0.91; Technical Report; ILRT: Bristol, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- The Resource Description Framework in Attributes. Available online: https://rdfa.info/ (accessed on 20 December 2018).
- Horrocks, I.; Patel-Schneider, P.F.; Boley, H.; Tabet, S.; Grosof, B.; Dean, M. SWRL: A semantic web rule language combining OWL and RuleML. W3C Memb. Submiss. 2004, 21, 79. [Google Scholar]
- GeoNames Ontology. Available online: http://www.geonames.org/ontology/documentation.html (accessed on 20 December 2018).
- Maki, B.E.; Holliday, P.J.; Topper, A.K. A prospective study of postural balance and risk of falling in an ambulatory and independent elderly population. J. Gerontol. 1994, 49, M72–M84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, P.B.; Gideon, P.; Brockman, K.G.; Fought, R.L.; Ray, W.A. Clinical and biomechanical measures of balance fall predictors in ambulatory nursing home residents. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 1996, 51, M239–M246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.A.; Bryant, A.L.; Pua, Y.; McCrory, P.; Bennell, K.; Hunt, M. Validity and reliability of the Nintendo Wii Balance Board for assessment of standing balance. Gait Posture 2010, 31, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, S.; Hao, M.L.; Tsai, M.-C.; Hafezi, M.; Azad, A.; Keramatimoezabad, F. Effectiveness of Integral Kinesiology Feedback for Fitness-Based Games. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Games, Entertainment, Media Conference (GEM), Galway, Ireland, 15–17 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, S.; Janzen, R.; Ali, M.A.; Scourboutakos, P.; Guleria, N. Integral Kinematics (Time-Integrals of Distance, Energy, etc.) and Integral Kinesiology. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Games, Entertainment, Media Conference (GEM), Toronto, ON, Canada, 22–24 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pedroli, E.; Greci, L.; Colombo, D.; Serino, S.; Cipresso, P.; Arlati, S.; Mondellini, M.; Boilini, L.; Giussani, V.; Goulene, K.; et al. Characteristics, Usability, and Users Experience of a System Combining Cognitive and Physical Therapy in a Virtual Environment: Positive Bike. Sensors 2018, 18, 2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottura, S.; Fontana, L.; Arlati, S.; Zangiacomi, A.; Redaelli, C.; Sacco, M. A virtual reality system for strengthening awareness and participation in rehabilitation for post-stroke patients. J. Multimodal User Interfaces 2015, 9, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, N.; Bailenson, J. The Proteus effect: The effect of transformed self-representation on behavior. Hum. Commun. Res. 2007, 33, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arlati, S.; Colombo, V.; Spoladore, D.; Greci, L.; Pedroli, E.; Serino, S.; Cipresso, P.; Goulene, K.; Stramba-Badiale, M.; Riva, G.; et al. A Social Virtual Reality-Based Application for the Physical and Cognitive Training of the Elderly at Home. Sensors 2019, 19, 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19020261
Arlati S, Colombo V, Spoladore D, Greci L, Pedroli E, Serino S, Cipresso P, Goulene K, Stramba-Badiale M, Riva G, et al. A Social Virtual Reality-Based Application for the Physical and Cognitive Training of the Elderly at Home. Sensors. 2019; 19(2):261. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19020261
Chicago/Turabian StyleArlati, Sara, Vera Colombo, Daniele Spoladore, Luca Greci, Elisa Pedroli, Silvia Serino, Pietro Cipresso, Karine Goulene, Marco Stramba-Badiale, Giuseppe Riva, and et al. 2019. "A Social Virtual Reality-Based Application for the Physical and Cognitive Training of the Elderly at Home" Sensors 19, no. 2: 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19020261
APA StyleArlati, S., Colombo, V., Spoladore, D., Greci, L., Pedroli, E., Serino, S., Cipresso, P., Goulene, K., Stramba-Badiale, M., Riva, G., Gaggioli, A., Ferrigno, G., & Sacco, M. (2019). A Social Virtual Reality-Based Application for the Physical and Cognitive Training of the Elderly at Home. Sensors, 19(2), 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19020261








