Al2O3-Based a-IGZO Schottky Diodes for Temperature Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design and Fabrication
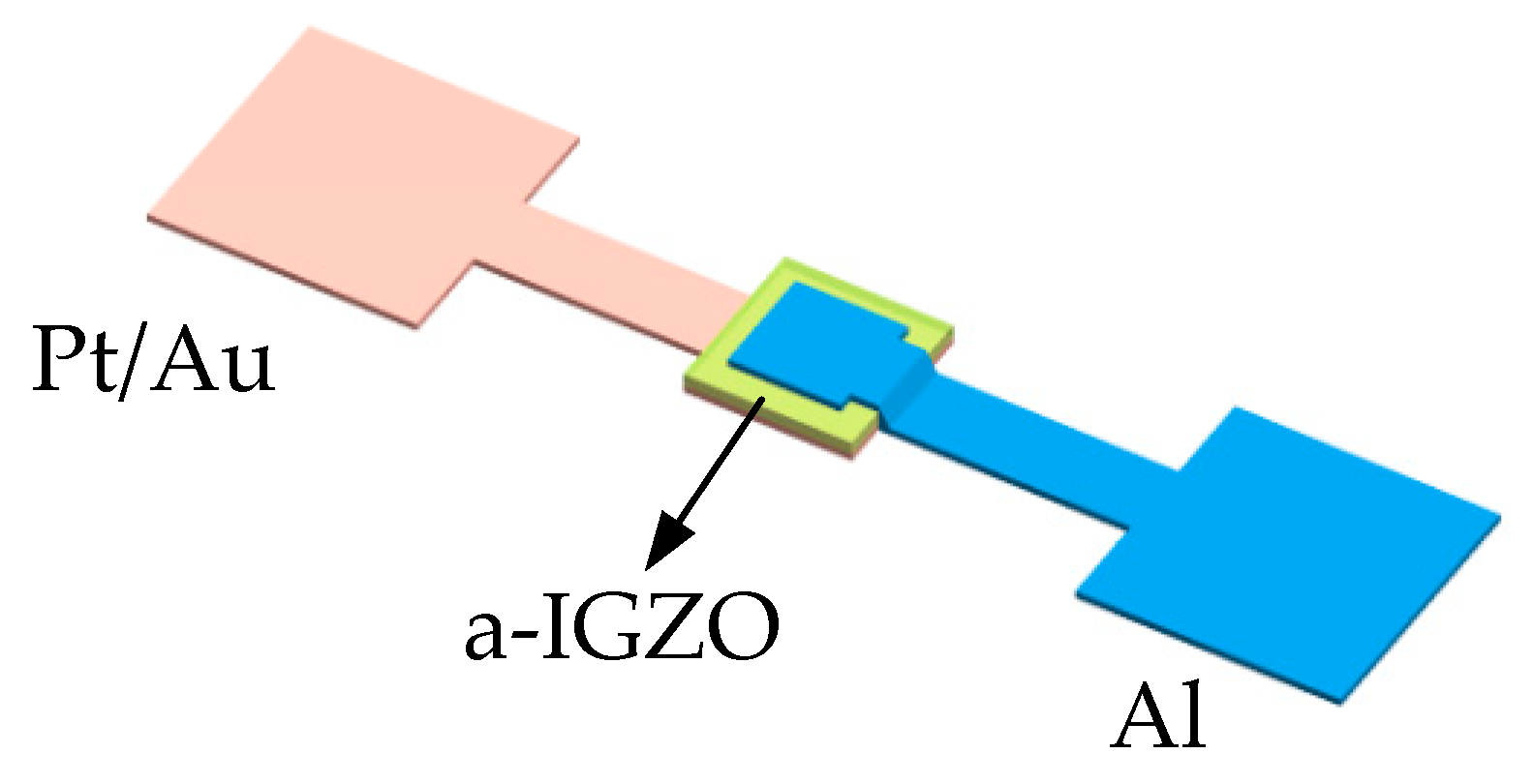
2.1. Diode Design
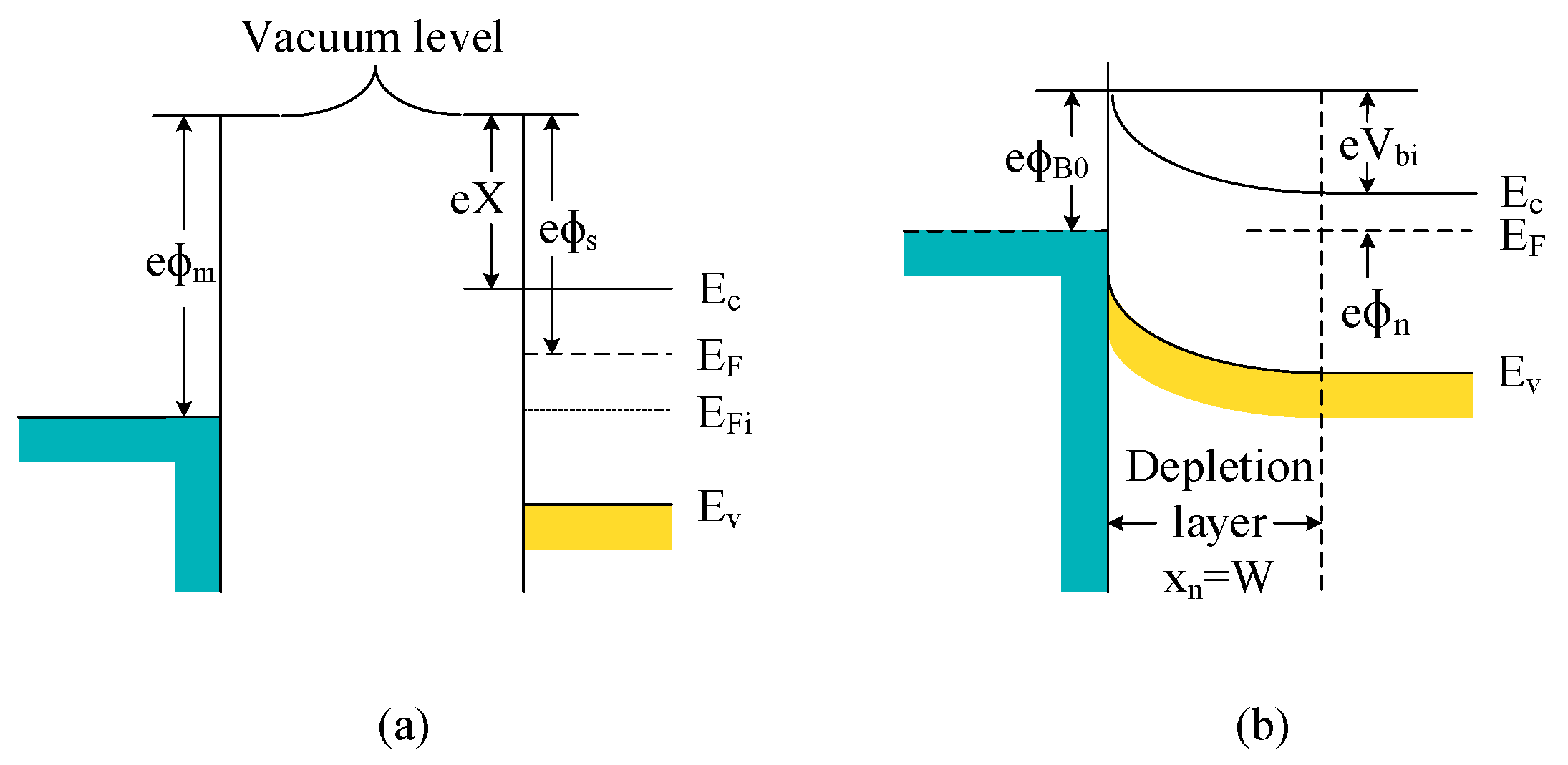
2.2. Equivalent Model of the Diode and Extracted Parameters
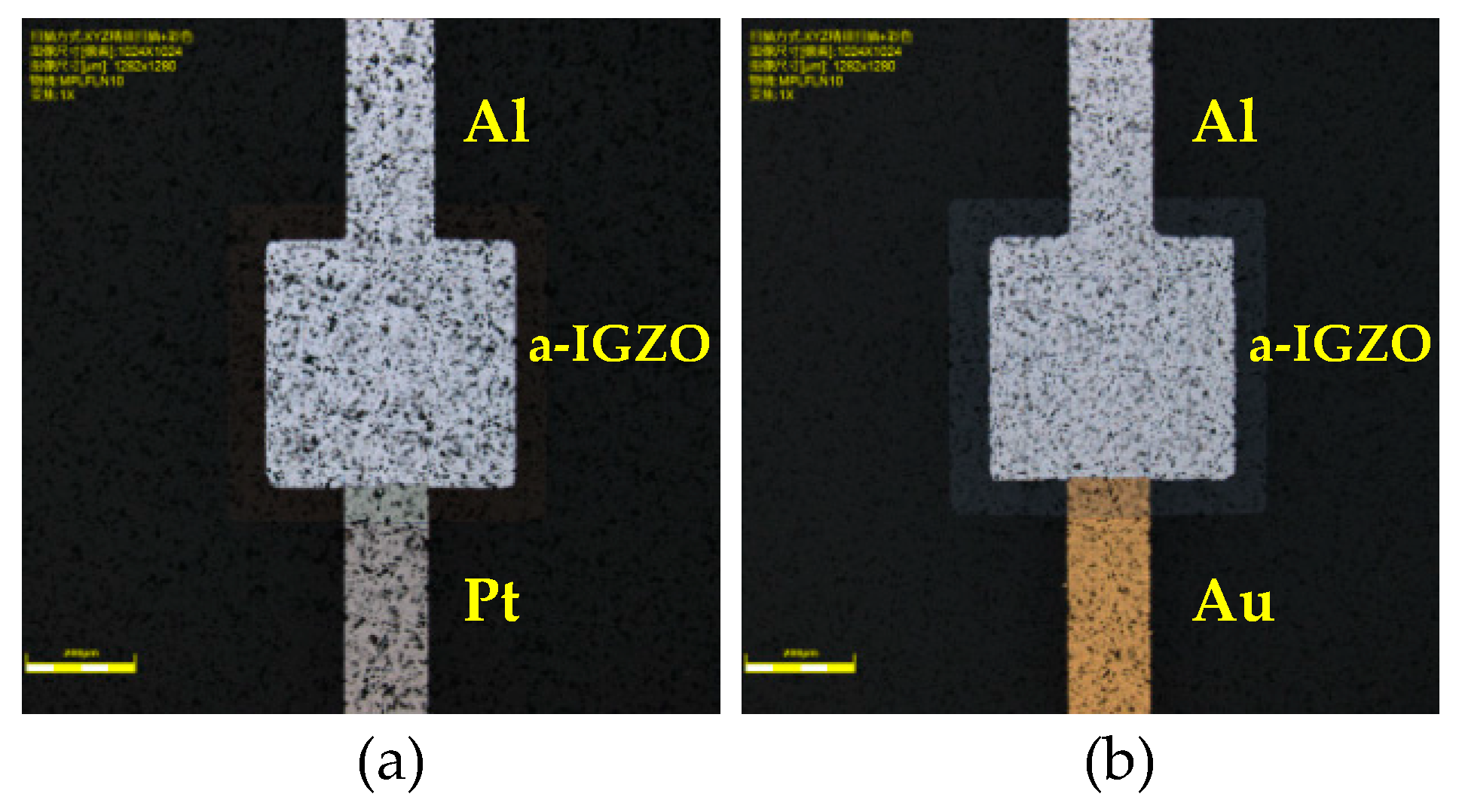
2.3. Device Fabrication
3. Results and Discussion
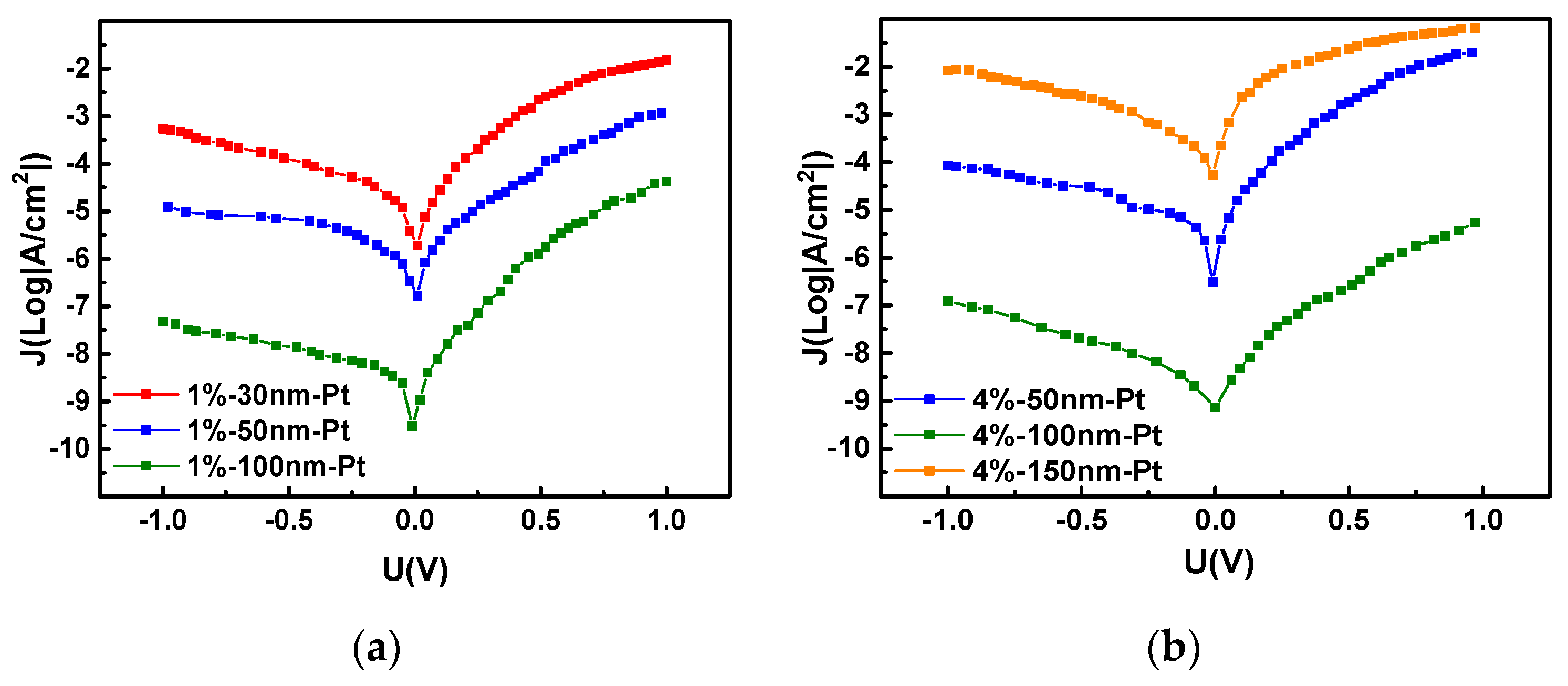
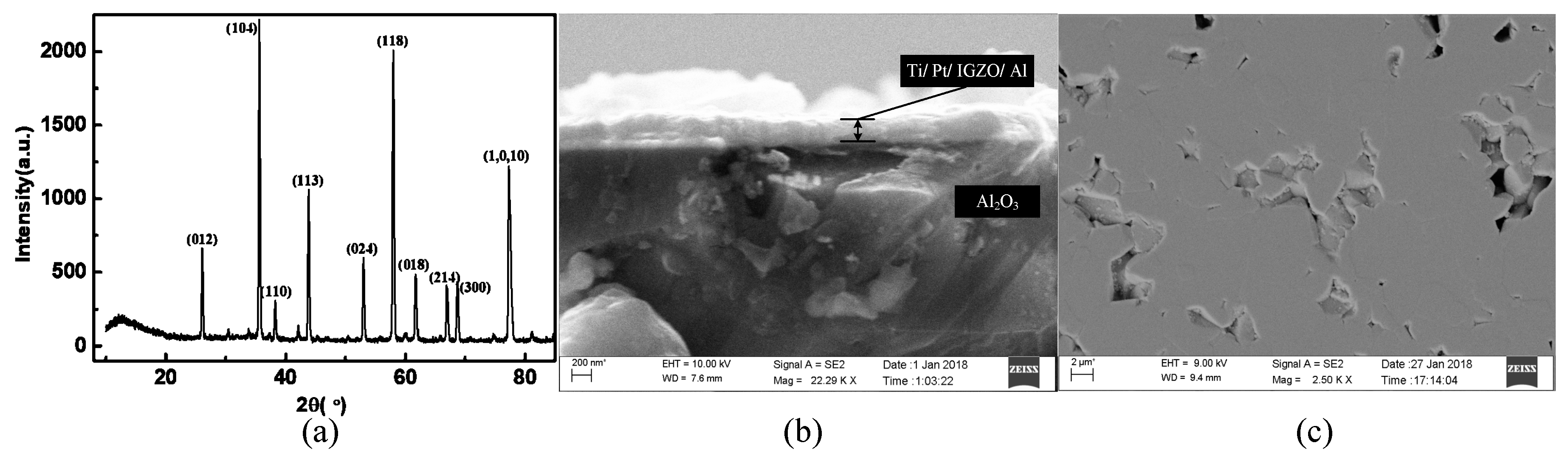
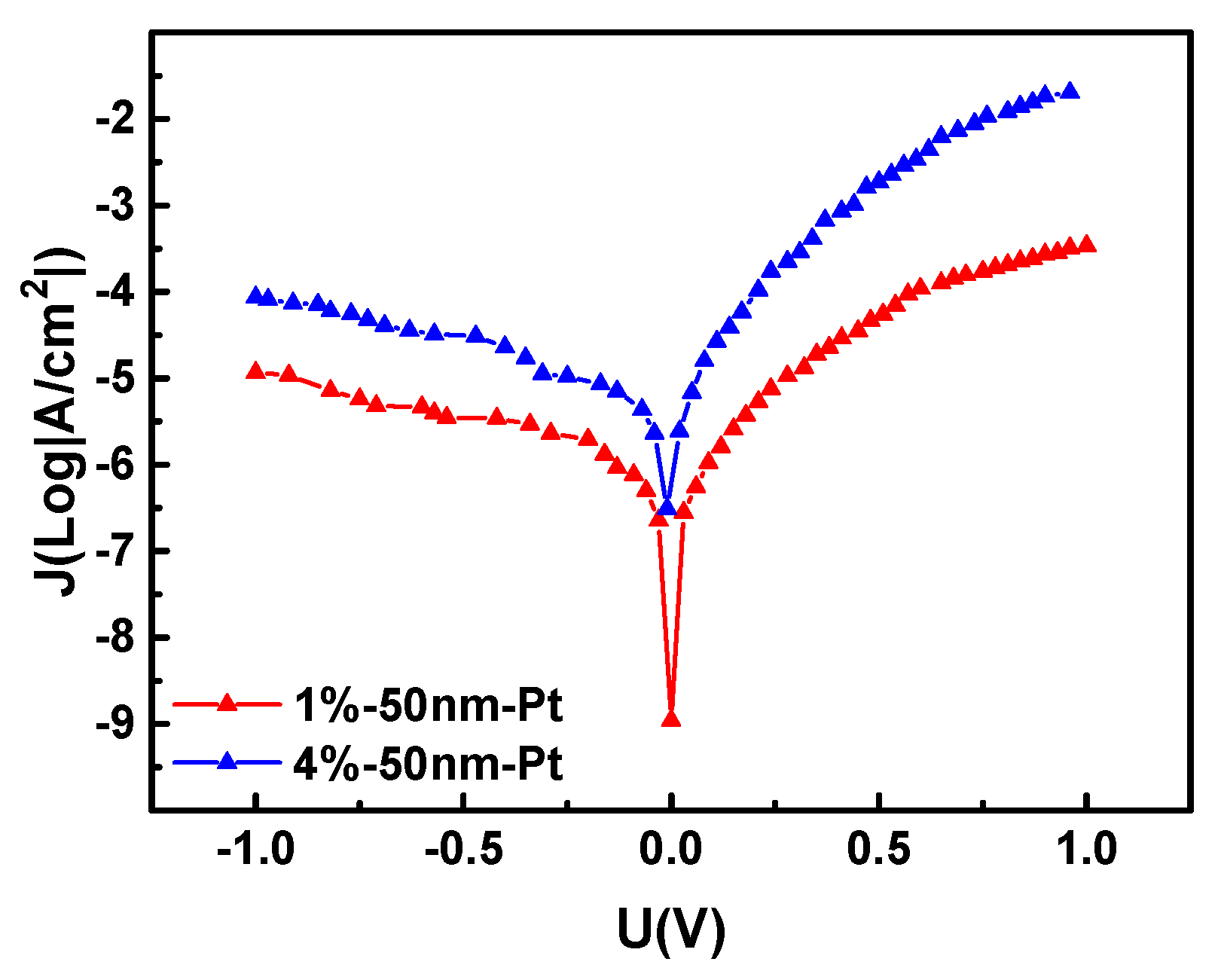
3.1. a-IGZO Schottky Diodes on Al2O3 Ceramics
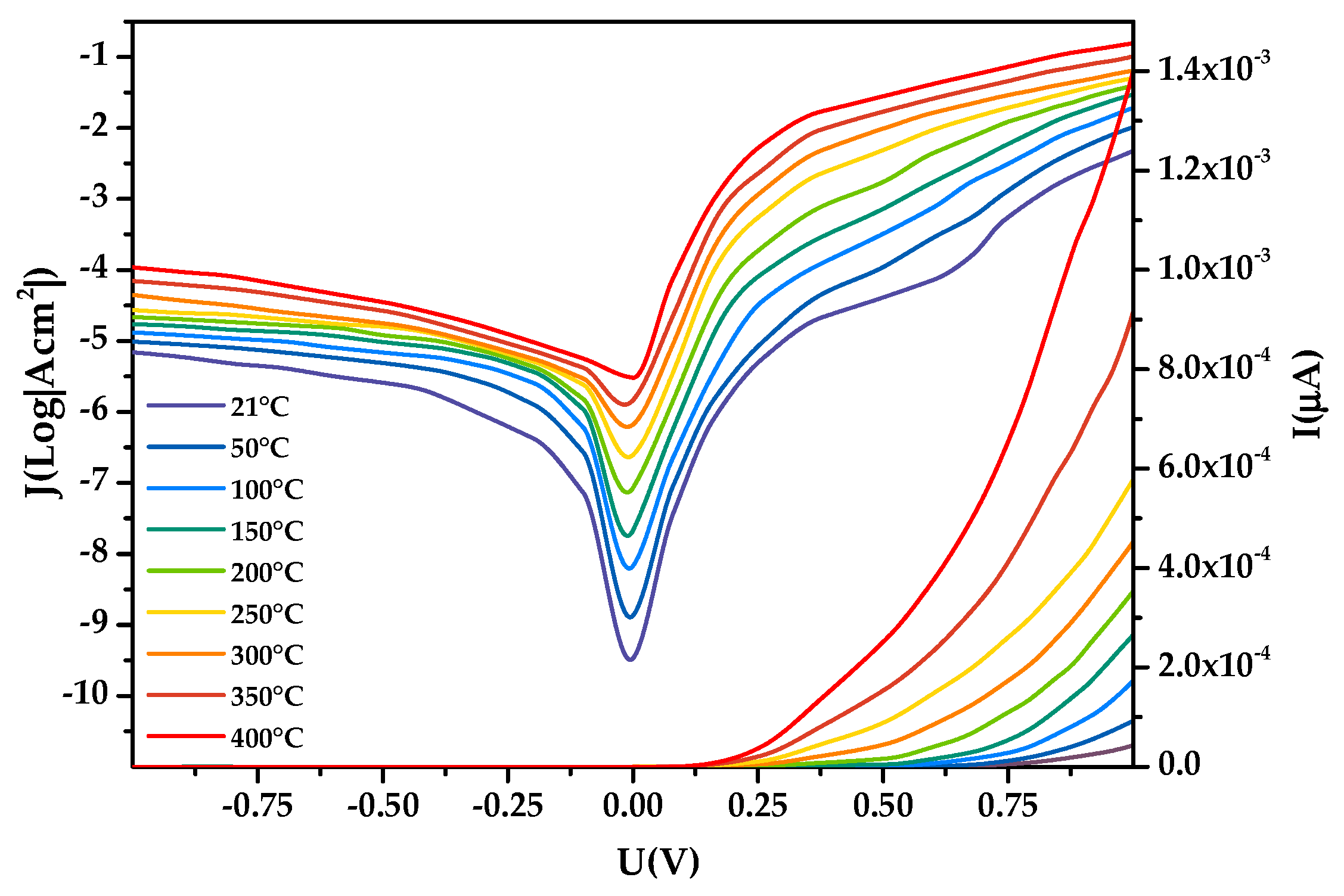
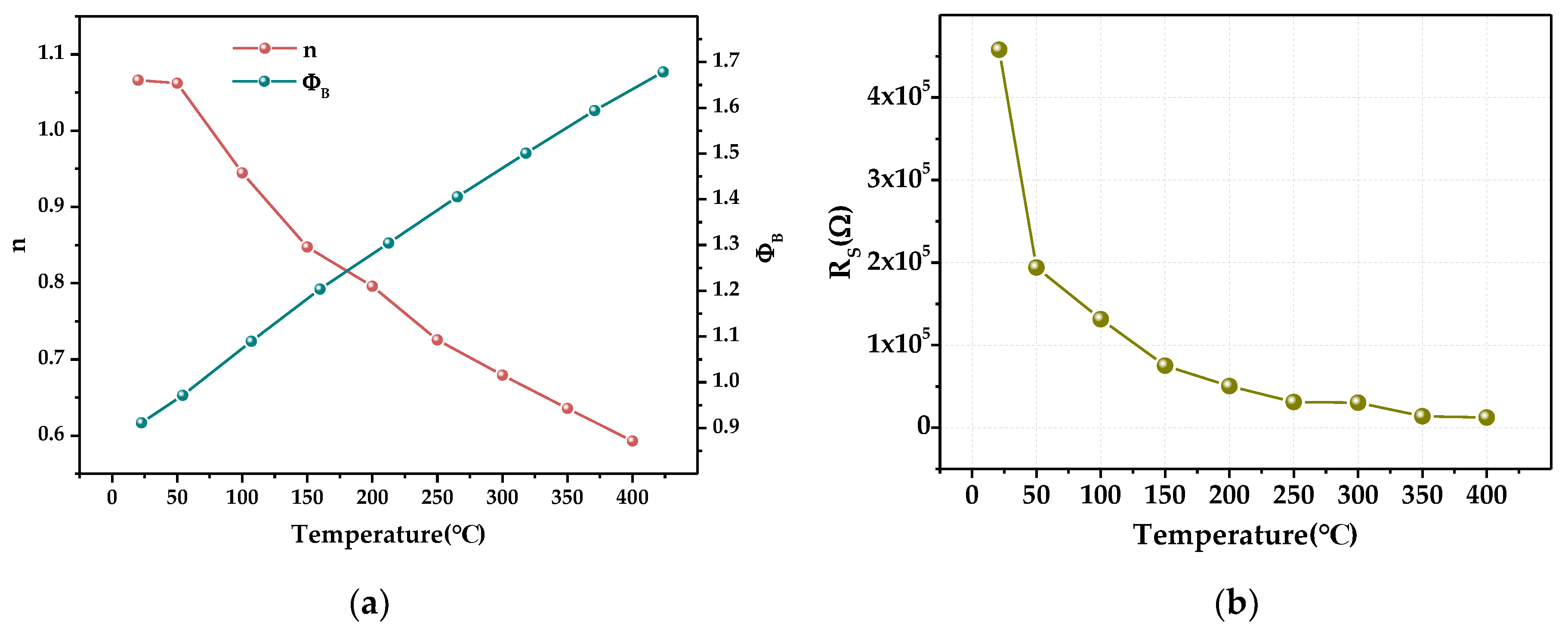
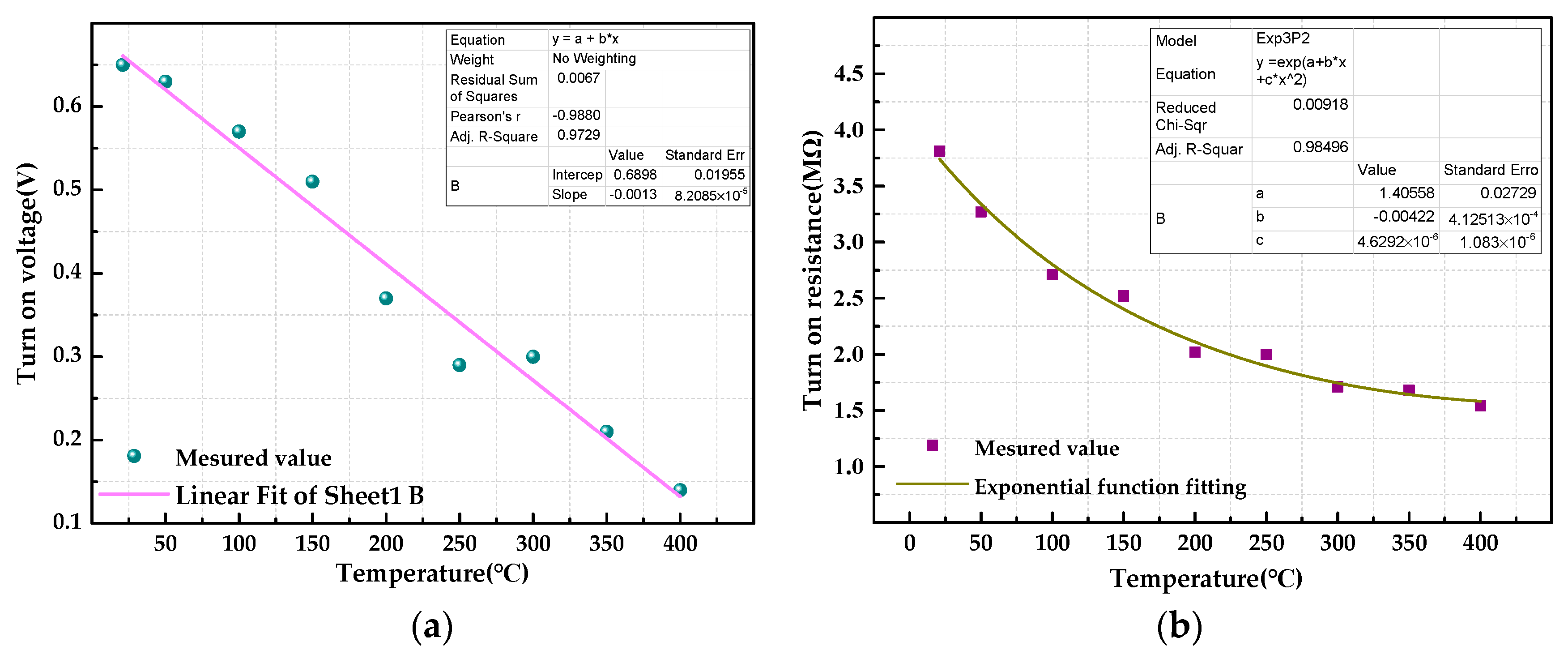
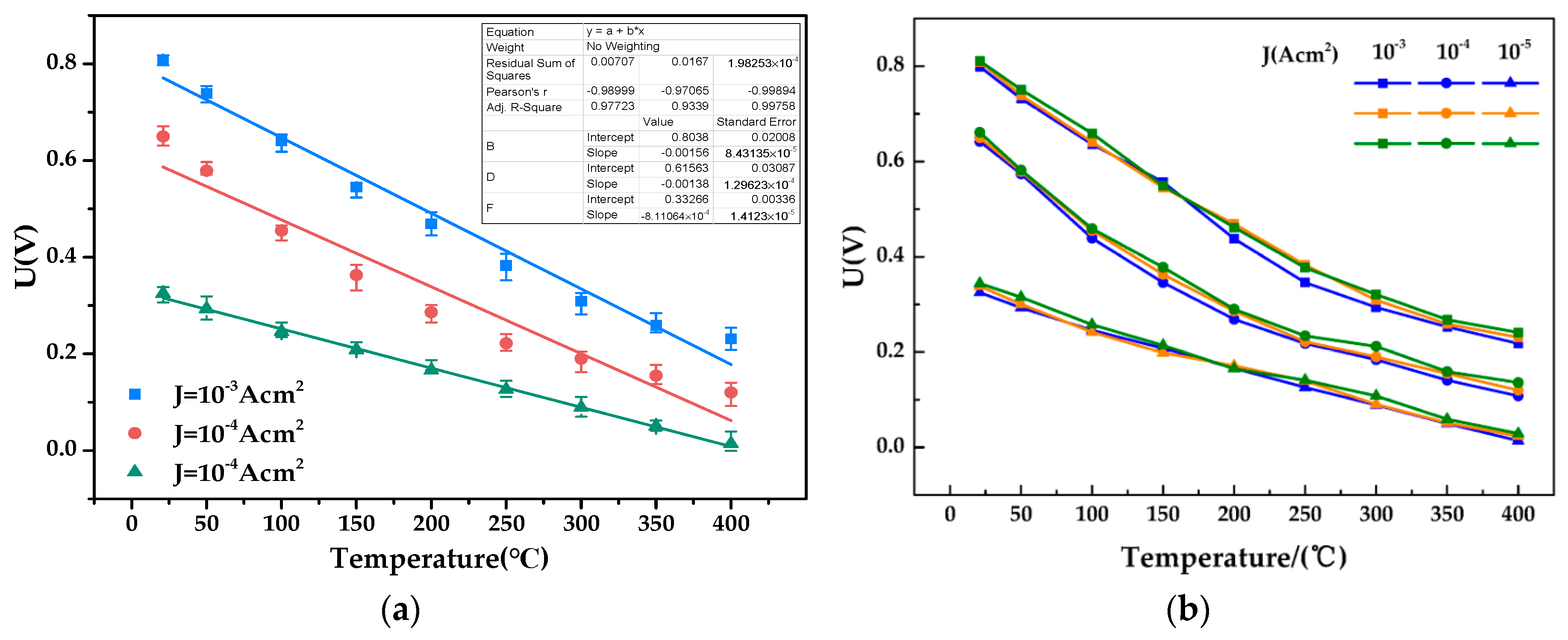
3.2. High-Temperature Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, E.N. 4H-Silicon Carbide PN Diode for Harsh Environment Temperature Sensing Applications; University of California at Berkeley: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Neudeck, P.G.; Okojie, R.S.; Chen, L.Y. High-temperature electronics—A role for wide bandgap semiconductors. Proc. IEEE 2002, 90, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Lien, W.C.; Maralani, A.; Pisano, A.P. Integrated 4H-silicon carbide diode bridge rectifier for high temperature (773 K) environment. In Proceedings of the 2014 44th European Solid State Device Research Conference (ESSDERC), Venice, Italy, 22–26 September 2014; pp. 138–141. [Google Scholar]
- Dipalo, M.; Gao, Z.; Scharpf, J.; Pietzka, C.; Alomari, M.; Medjdoub, F.; Carlin, J.F.; Grandjean, N.; Delage, S.; Kohn, E. Combining diamond electrodes with GaN heterostructures for harsh environment ISFETs. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2009, 18, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearton, S.J.; Kang, B.S.; Kim, S.; Ren, F.; Gila, B.P.; Abernathy, C.R.; Lin, J.; Chu, S.N. GaN-based diodes and transistors for chemical, gas, biological and pressure sensing. J. Phys. 2004, 16, R961–R994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, H.; Hou, M.; Jain, S.R.; Lim, J.; Senesky, D.G. Interdigitated Pt-GaN Schottky interfaces for high-temperature soot-particulate sensing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 368, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Micovic, M.; Tsen, T.; Delaney, M.; Chow, D.; Schmitz, A.; Hashimoto, P.; Wong, D.; Moon, J.S.; Hu, M.; et al. GaN HFET digital circuit technology for harsh environments. Electron. Lett. 2003, 39, 1708–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, H.; Senesky, D.G. Low-resistance gateless high electron mobility transistors using three-dimensional inverted pyramidal AlGaN/GaN surfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 492–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, O.J.; Conkle, J.R.; Birnbaum, T.J. Wireless Temperature Measurement System and Methods of Making and Using Same. U.S. Patent US8348504, 29 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nomura, K.; Ohta, H.; Ueda, K.; Kamiya, T.; Hirano, M.; Hosono, H. Thin-film transistor fabricated in single-crystalline transparent oxide semiconductor. Science 2003, 300, 1269–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Ohta, H.; Takagi, A.; Kamiya, T.; Hirano, M.; Hosono, H. Room-temperature fabrication of transparent flexible thin-film transistors using amorphous oxide semiconductors. Nature 2004, 432, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabuta, H.; Sano, M.; Abe, K.; Aiba, T.; Den, T.; Kumomi, H.; Nomura, K.; Kamiya, T.; Hosono, H. High-mobility thin-film transistor with amorphous InGaZnO4 channel fabricated by room temperature rf-magnetron sputtering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 112123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, M.; Takechi, K.; Eguchi, T.; Tokumitsu, E.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kaneko, S. Flexible high-performance amorphous InGaZnO4 thin-film transistors utilizing excimer laser annealing. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 48, 081607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, M.; Lajn, A.; Frenzel, H.; von Wenckstern, H.; Grundmann, M.; Barquinha, P.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Low-temperature processed Schottky-gated field-effect transistors based on amorphous gallium-indium-zinc-oxide thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 2007–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Nomura, K.; Kamiya, T.; Hosono, H. Diffusion-Limited a-IGZO/Pt Schottky Junction Fabricated at 200 °C on a Flexible Substrate. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2011, 32, 1695–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C. Large-scale complementary macroelectronics using hybrid integration of carbon nanotubes and IGZO thin-film transistors. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Wilson, J.; Ma, X.; Jin, J.; Song, A. Room Temperature Processed Ultrahigh-Frequency Indium-Gallium–Zinc-Oxide Schottky Diode. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2016, 37, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, E.; Barquinha, P.; Martins, R. Oxide semiconductor thin-film transistors: A review of recent advances. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2945–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Maeng, W.J.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J.S. Review of recent developments in amorphous oxide semiconductor thin-film transistor devices. Thin Solid Films 2012, 520, 1679–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasin, A.; Steudel, S.; Vanaverbeke, F.; Myny, K.; Nag, M.; Ke, T.H.; Schols, S.; Gielen, G.; Genoe, J.; Heremans, P. UHF IGZO Schottky diode. In Proceedings of the Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–13 December 2012; pp. 12.4.1–12.4.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasin, A.; Nag, M.; Bhoolokam, A.; Myny, K.; Steudel, S.; Schols, S.; Genoe, J.; Gielen, G.; Heremans, P. Gigahertz operation of a-IGZO Schottky diodes. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2013, 60, 3407–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Chen, P.H.; Chang, T.C.; Chang, K.C.; Zhang, S.D.; Tsai, T.M.; Pan, C.H.; Chen, M.C.; Su, Y.T.; Tseng, Y.T.; et al. Attaining resistive switching characteristics and selector properties by varying forming polarities in a single HfO2-based RRAM device with a vanadium electrode. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 8586–8590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, J.R.; Jung, S.Y.; Yeon, H.W.; Kwon, J.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.H.; Joo, Y.C. Effects of metal electrode on the electrical performance of amorphous In–Ga–Zn–O thin film transistor. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 51, 011401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, T.; Hosono, H. Material characteristics and applications of transparent amorphous oxide, semiconductors. NPG Asia Mater. 2010, 2, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuh, C.S.; Sze, S.M.; Liu, P.T.; Teng, L.F.; Chou, Y.T. Role of environmental and annealing conditions on the passivation-free in-Ga–Zn–O TFT. Thin Solid Films 2011, 520, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Xin, Q.; Song, A. Flexible indium-gallium-zinc-oxide Schottky diode operating beyond 2.45 GHz. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bartolomeo, A. Graphene Schottky diodes: An experimental review of the rectifying graphene/semiconductor heterojunction. Phys. Rep. Rev. Sect. Phys. Lett. 2016, 606, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, A.; Nomura, K.; Ohta, H.; Yanagi, H.; Kamiya, T.; Hirano, M.; Hosono, H. Carrier transport and electronic structure in amorphous oxide semiconductor, a-InGaZnO4. Thin Solid Films 2005, 486, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Kamiya, T.; Kikuchi, Y.; Hirano, M.; Hosono, H. Comprehensive studies on the stabilities of a-In-Ga-Zn-O based thin film transistor by constant current stress. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 3012–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.H.; Kamiya, T.; Nomura, K.; Hosono, H.; Wu, C.C. Modeling of amorphous InGaZnO4 thin film transistors and their subgap density of states. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 133503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Kamiya, T.; Ohta, H.; Hirano, M.; Hosono, H. Defect passivation and homogenization of amorphous oxide thin-film transistor by wet O2, annealing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 192107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Nakanishi, T.; Nomura, K.; Kamiya, T.; Hosono, H. Trap densities in amorphous-InGaZnO4 thin-film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 133512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoderick, E.H.; Williams, R.H. Metal-Semiconductor Contacts, 2nd ed.; Oxford Univ. Press: Oxford, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Sze, S.M.; Ng, K.K. Physics of Semiconductor Devices, 3rd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chasin, A.; Steudel, S.; Myny, K.; Nag, M.; Ke, T.H.; Schols, S.; Genoe, J.; Gielen, G.; Heremans, P. High-performance a-In-Ga-Zn-O Schottky diode with oxygen-treated metal contacts. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 113505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olziersky, A.; Barquinha, P.; Vilà, A.; Magana, C.; Fortunato, E.; Morante, J.R.; Martins, R. Role of Ga2O3–In2O3–ZnO channel composition on the electrical performance of thin-film transistors. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 131, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bartolomeo, A.; Giubileo, F.; Luongo, G.; Iemmo, L.; Martucciello, N.; Niu, G.; Fraschke, M.; Skibitzki, O.; Schroeder, T.; Lupina, G. Tunable Schottky barrier and high responsivity in graphene/Sinanotip optoelectronic device. 2D Mater. 2017, 4, 015024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tataroglu, A.; Altindal, S. The analysis of the series resistance and interface states of MIS Schottky diodes at high temperatures using I–V characteristics. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 484, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
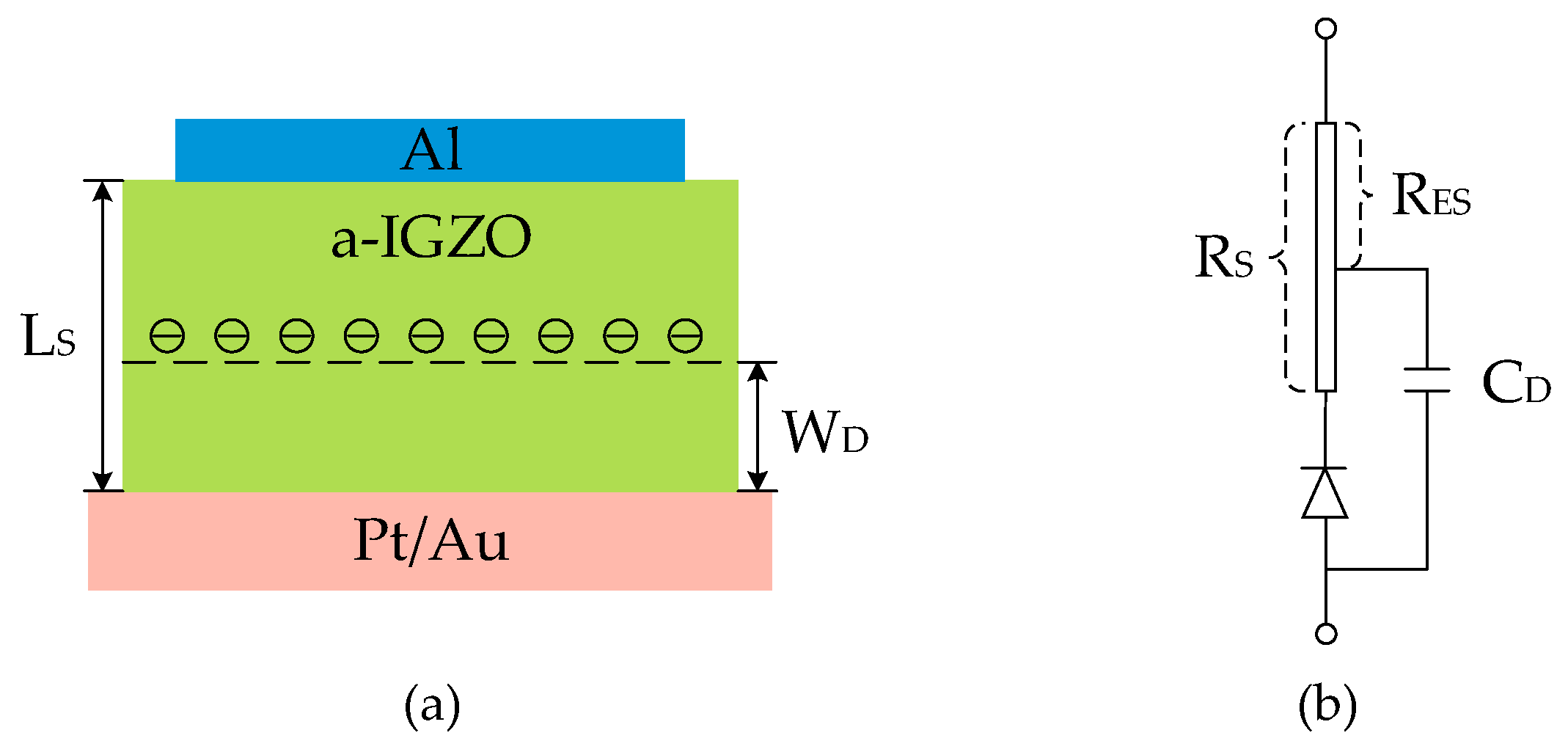


| O2: (Ar + O2) | Element | Element Mass Ratio (%) | Elemental Atomic Ratios (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1% | In | 28.33 | 36.12 |
| Ga | 17.34 | 36.42 | |
| Zn | 12.26 | 27.46 | |
| 4% | In | 12.49 | 36.03 |
| Ga | 6.93 | 32.94 | |
| Zn | 6.11 | 31.03 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Q.; Lu, F.; Tan, Q.; Zhou, T.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, W. Al2O3-Based a-IGZO Schottky Diodes for Temperature Sensing. Sensors 2019, 19, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19020224
Guo Q, Lu F, Tan Q, Zhou T, Xiong J, Zhang W. Al2O3-Based a-IGZO Schottky Diodes for Temperature Sensing. Sensors. 2019; 19(2):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19020224
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Qianqian, Fei Lu, Qiulin Tan, Tianhao Zhou, Jijun Xiong, and Wendong Zhang. 2019. "Al2O3-Based a-IGZO Schottky Diodes for Temperature Sensing" Sensors 19, no. 2: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19020224
APA StyleGuo, Q., Lu, F., Tan, Q., Zhou, T., Xiong, J., & Zhang, W. (2019). Al2O3-Based a-IGZO Schottky Diodes for Temperature Sensing. Sensors, 19(2), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19020224





