Recent Developments of High-Resolution Chemical Imaging Systems Based on Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensors (LAPSs)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Measurement System Set-Up
2.1. Sensor Construction and Sensing Materials
2.2. Modulated Light
2.3. Measurement Modes
2.3.1. Constant-Voltage Mode
2.3.2. Constant-Current Mode
2.3.3. Potential-Tracking Mode
2.3.4. Phase Mode
2.3.5. Pulse-Driven Mode
3. Spatial Resolution
3.1. Semiconductor Substrate
3.2. Property of Modulated Light
4. Temporal Resolution
4.1. Single Modulated Light Without Mechanical Movement
4.2. Multi-Frequency Modulation Light Source Array
5. Integration with Microfluidic Devices
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hafeman, D.G.; Parce, J.W.; McConnell, H.M. Light-addressable potentiometric sensor for biochemical systems. Science 1988, 240, 1182–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, H.M.; Owicki, J.C.; Parce, J.W.; Miller, D.L.; Baxter, G.T.; Wada, H.G.; Pitchford, S. The cytosensor microphysiometer: Biological applications of silicon technology. Science 1992, 257, 1906–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owicki, J.C.; Bousse, L.J.; Hafeman, D.G.; Kirk, G.L.; Olson, J.D.; Wada, H.G.; Parce, J.W. The light-addressable potentiometric sensor: Principles and biological applications. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1994, 23, 87–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafner, F. Cytosensor Microphysiometer: Technology and recent applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2000, 15, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, B.; George, M.; Gaub, H.E.; Behrends, J.C.; Parak, W.J. Spatially resolved monitoring of cellular metabolic activity with a semiconductor-based biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J. Light-addressable potentiometric sensors (LAPS): Recent trends and applications. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2007, 49, 87–128. [Google Scholar]
- Bratov, A.; Abramova, N.; Ipatov, A. Recent trends in potentiometric sensor arrays—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 678, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöning, M.J.; Poghossian, A. Bio FEDs (Field-Effect devices): State-of-the-art and new directions. Electroanalysis 2006, 18, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasov, Y.G.; Tarantov, Y.A.; Bobrov, P.V. Analytical characteristics and sensitivity mechanisms of electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor system-based chemical sensors-a critical review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 376, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöning, M.J.; Poghossian, A.; Yoshinobu, T.; Luth, H. Semiconductor-based field-effect structures for chemical sensing. Adv. Environ. Chem. Sens. Technol. 2001, 4205, 188–198. [Google Scholar]
- Poghossian, A.; Yoshinobu, T.; Simonis, A.; Ecken, H.; Luth, H.; Schöning, M.J. Penicillin detection by means of field-effect based sensors: EnFET, capacitive EIS sensor or LAPS? Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 78, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verzellesi, G.; Colalongo, L.; Passeri, D.; Margesin, B.; Rudan, M.; Soncini, G.; Ciampolini, P. Numerical analysis of ISFET and LAPS devices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1997, 44, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poghossian, A.; Ingebrandt, S.; Offenhausser, A.; Schöning, M.J. Field-effect devices for detecting cellular signals. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2009, 20, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.; Kim, J.Y.; Ahn, J.H.; Choi, J.M.; Im, M.; Choi, Y.K. Integration of field effect transistor-based biosensors with a digital microfluidic device for a lab-on-a-chip application. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poghossian, A.; Schöning, M.J. Label-free sensing of biomolecules with field-effect devices for clinical applications. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 1197–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, L.; Krause, S.; Chazalviel, J.N. Scanning photoinduced impedance microscopy using amorphous silicon photodiode structures. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 6208–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, S.; Moritz, W.; Talabani, H.; Xu, M.; Sabot, A.; Ensell, G. Scanning photo-induced impedance microscopy-resolution studies and polymer characterization. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, S.; Talabani, H.; Xu, M.; Moritz, W.; Griffiths, J. Scanning photo-induced impedance microscopy–An impedance based imaging technique. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 2143–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinobu, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J. Recent developments of chemical imaging sensor systems based on the principle of the light-addressable potentiometric sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Campos, I.; Zhang, D.W.; Krause, S. Biological imaging using light-addressable potentiometric sensors and scanning photo-induced impedance microscopy. Proc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2017, 473, 20170130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshinobu, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Werner, C.F.; Poghossian, A.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J. Light-addressable potentiometric sensors for quantitative spatial imaging of chemical species. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2017, 10, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Du, L.P.; Krause, S.; Wu, C.S.; Wang, P. Surface modification and construction of LAPS towards biosensing applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 265, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.T.; Guan, M.Y.; Huang, G.Y.; Qiu, H.M.; Chen, Z.C.; Li, G.Y.; Huang, Y. Highly sensitive covalently functionalized light-addressable potentiometric sensor for determination of biomarker. Mat. Sci. Eng. C Mater. 2016, 63, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.T.; Zhu, N.X.; Li, S.S.; Jia, H.Q.; Xue, Y.W.; Cui, L.J.; Huang, Y.; Li, G.Y. Light-addressable potentiometric sensor with gold nanoparticles enhancing enzymatic silver deposition for 1,5-anhydroglucitol determination. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 123, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Yu, B.; Isoda, H.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. Visualization of the recovery process of defects in a cultured cell layer by chemical imaging sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.W.; Wu, F.; Wang, J.; Watkinson, M.; Krause, S. Image detection of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by light-addressable potentiometric sensors (LAPS). Electrochem. Commun. 2016, 72, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Sakakita, S.; Yoshinobu, T. A novel data acquisition method for visualization of large pH changes by chemical imaging sensor. ISIJ Int. 2016, 56, 492–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, M.; Yoshinobu, T.; Iwasaki, H. Scanning-laser-beam semiconductor pH-imaging sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1994, 20, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, M.; Yoshinobu, T.; Iwasaki, H. Improvement of spatial-resolution of a laser-scanning pH-imaging sensor. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 33, L394–L397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, M.; Inoue, S.; Oishi, R.; Yoshinobu, T.; Iwasaki, H. Observation of microorganism colonies using a scanning-laser-beam pH-sensing microscope. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1995, 79, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, M.; Inoue, S.; Yoshinobu, T.; Iwasaki, H. High-resolution pH imaging sensor for microscopic observation of microorganisms. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1996, 34, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantism, S.; Takenaga, S.; Wagner, T.; Wagner, P.; Schöning, M.J. Differential imaging of the metabolism of bacteria and eukaryotic cells based on light-addressable potentiometric sensors. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 246, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.I.; Sugawara, Y.; Kanoh, S.; Yoshinobu, T.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J. Image correction method for the chemical imaging sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 144, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Nakao, M.; Yoshinobu, T.; Iwasaki, H. Chemical-imaging sensor using enzyme. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1996, 32, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Campos, I.; Wu, F.; Zhu, J.Y.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Palma, M.; Watkinson, M.; Krause, S. The effect of gold nanoparticles on the impedance of microcapsules visualized by scanning photo-induced impedance microscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 208, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinobu, T.; Harada, T.; Iwasaki, H. Application of the pH-imaging sensor to determining the diffusion coefficients of ions in electrolytic solutions. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 39, L318–L320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Ichimura, H.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. Chemical imaging of the concentration profile of ion diffusion in a microfluidic channel. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 189, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Wu, C.; Ha, D.; Wang, T.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P. A novel microphysiometer based on high sensitivity LAPS and microfluidic system for cellular metabolism study and rapid drug screening. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; Ha, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, H.X.; Wang, X.; Sun, Q.Y.; Wang, P. Design of a novel hybrid sensor with microelectrode array and LAPS for heavy metal determination using multivariate nonlinear calibration. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M.; Zeng, W.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, Y.P.; Chen, T.C. Spatial resolution and 2D chemical image of light-addressable potentiometric sensor improved by inductively coupled-plasma reactive-ion etching. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, W.; Yoshinobu, T.; Finger, F.; Krause, S.; Martin-Fernandez, M.; Schöning, M.J. High resolution LAPS using amorphous silicon as the semiconductor material. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 103, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Lin, Y.H.; Lai, C.S. Miniaturized amorphous-silicon based chemical imaging sensor system using a mini-projector as a simplified light-addressable scanning source. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M.; Liao, Y.H.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, T.C.; Lai, C.S.; Pijanowska, D.G. P-I-N amorphous silicon for thin-film light-addressable potentiometric sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinobu, T.; Schöning, M.J.; Finger, F.; Moritz, W.; Iwasaki, H. Fabrication of thin-film LAPS with amorphous silicon. Sensors 2004, 4, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.L.; Jiang, S.H.; Kunze, J.; Schmuki, P.; Krause, S. High resolution LAPS and SPIM. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 12, 758–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.L.; Krause, S.; Munoz, A.G.; Kunze, J.; Schmuki, P. Repair of thin thermally grown silicon dioxide by anodic oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 3395–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, W.; Gerhardt, I.; Roden, D.; Xu, M.; Krause, S. Photocurrent measurements for laterally resolved interface characterization. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 2000, 367, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Chang, L.B.; Lai, C.S.; Lin, R.M.; Chu, F.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Chow, L.; Jeng, M.J. GaN thin film based light addressable potentiometric sensor for pH sensing application. Appl. Phys. Express 2013, 6, 036601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M.; Chen, C.H.; Chang, L.B.; Lai, C.S. IGZO thin-film light-addressable potentiometric sensor. IEEE Electr. Device L 2016, 37, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.W.; Wu, F.; Krause, S. LAPS and SPIM imaging using ITO-coated glass as the substrate material. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8129–8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinobu, T.; Ecken, H.; Poghossian, A.; Luth, H.; Iwasaki, H.; Schöning, M.J. Alternative sensor materials for light-addressable potentiometric sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 76, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöning, M.J.; Tsarouchas, D.; Beckers, L.; Schubert, J.; Zander, W.; Kordos, P.; Luth, H. A highly long-term stable silicon-based pH sensor fabricated by pulsed laser deposition technique. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1996, 35, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, A.; Motoya, K.; Watanabe, S.; Kubo, I. Novel sensors for potassium, calcium and magnesium ions based on a silicon transducer as a light-addressable potentiometric sensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 382, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.M.; Harada, T.; Yoshinobu, T.; Iwasaki, H.; Schöning, M.J.; Luth, H. Investigation of pulsed laser-deposited Al2O3 as a high pH-sensitive layer for LAPS-based biosensing applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 71, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lue, C.E.; Lai, C.S.; Chen, H.Y.; Yang, C.M. Light addressable potentiometric sensor with fluorine-terminated hafnium oxide layer for sodium detection. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 49, 04DL05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.H.; Lu, T.F.; Wang, J.C.; Yang, J.H.; Lue, C.E.; Yang, C.M.; Li, S.S.; Lai, C.S. Effects of CF4 plasma treatment on pH and pNa sensing properties of light-addressable potentiometric sensor with a 2-nm-thick sensitive HfO2 layer grown by atomic layer deposition. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 50, 04DL06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Lu, T.F.; Wang, J.C.; Yang, C.M.; Pijanowska, D.G.; Chin, C.H.; Lue, C.E.; Lai, C.S. LAPS with nanoscaled and highly polarized HfO2 by CF4 plasma for NH4(+) detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 180, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Yang, C.M. A IGZO-based light-addressable potentiometric sensor on a PET susbtrate. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Glasgow, UK, 8–10 July 2019; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.M.; Chiang, T.W.; Yeh, Y.T.; Das, A.; Lin, Y.T.; Chen, T.C. Sensing and pH-imaging properties of niobium oxide prepared by rapid thermal annealing for electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor structure and light-addressable potentiometric sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M.; Yang, Y.C.; Chen, C.H. Thin-film light-addressable potentiometric sensor with SnOx as a photosensitive semiconductor. Vacuum 2019, 168, 108809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.L.; Watkinson, M.; Gautrot, J.; Krause, S. High-sensitivity light-addressable potentiometric sensors using silicon on sapphire functionalized with self-assembled organic monolayers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cuartero, M.; Goncales, V.R.; Gooding, J.J.; Bakker, E. Light-addressable ion sensing for real-time monitoring of extracellular potassium. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 16801–16805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaibani, P.M.; Jiang, K.R.; Haghighat, G.; Hassanpourfard, M.; Etayash, H.; Naicker, S.; Thundat, T. The detection of Escherichia coli (E. coli) with the pH sensitive hydrogel nanofiber-light addressable potentiometric sensor (NF-LAPS). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 226, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaibani, P.M.; Etayash, H.; Naicker, S.; Kaur, K.; Thundat, T. Metabolic study of cancer cells using a pH sensitive hydrogel nanofiber light addressable potentiometric sensor. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourzina, Y.; Yoshinobu, T.; Schubert, J.; Luth, H.; Iwasaki, H.; Schöning, M.J. Ion-selective light-addressable potentiometric sensor (LAPS) with chalcogenide thin film prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 80, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, H.; Zou, S.F.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Ye, X.S.; Wang, P. A novel electronic tongue combined MLAPS with stripping voltammetry for environmental detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 110, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloock, J.P.; Moreno, L.; Bratov, A.; Huachupoma, S.; Xu, J.; Wagner, T.; Yoshinobu, T.; Ermolenko, Y.; Vlasov, Y.G.; Schöning, M.J. PLD-prepared cadmium sensors based on chalcogenide glasses–ISFET, LAPS and mu ISE semiconductor structures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 118, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Molina, R.; Yoshinobu, T.; Kloock, J.P.; Biselli, M.E.; Canzoneri, M.; Schnitzler, T.; Schöning, M.J. Handheld multi-channel LAPS device as a transducer platform for possible biological and chemical multi-sensor applications. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 53, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Cai, H.; Fu, J.; Wang, P.; Yang, G. Line-scanning LAPS array for measurement of heavy metal ions with micro-lens array based on MEMS. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 129, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.; Hu, N.; Wu, C.X.; Kirsanov, D.; Legin, A.; Khaydukova, M.; Wang, P. Novel structured light-addressable potentiometric sensor array based on PVC membrane for determination of heavy metals. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 174, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermolenko, Y.; Yoshinobu, T.; Mourzina, Y.; Furuichi, K.; Levichev, S.; Vlasov, Y.; Schöning, M.J.; Iwasaki, H. Lithium sensor based on the laser scanning semiconductor transducer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 459, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinobu, T.; Schöning, M.J.; Otto, R.; Furuichi, K.; Mourizina, Y.; Ermolenko, Y.; Iwasaki, H. Portable light-addressable potentiometric sensor (LAPS) for multisensor applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 95, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourzina, Y.G.; Ermolenko, Y.E.; Yoshinobu, T.; Vlasov, Y.; Iwasaki, H.; Schöning, M.J. Anion-selective light-addressable potentiometric sensors (LAPS) for the determination of nitrate and sulphate ions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 91, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Wang, P.; Ye, X.S.; Zhang, Q.T.; Li, R.; Yan, W.M.; Zheng, X.X. A novel microphysiometer based on MLAPS for drugs screening. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 277–286. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinobu, T.; Iwasaki, H.; Ui, Y.; Furuichi, K.; Ermolenko, Y.; Mourzina, Y.; Wagner, T.; Nather, N.; Schöning, M.J. The light-addressable potentiometric sensor for multi-ion sensing and imaging. Methods 2005, 37, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermolenko, Y.E.; Yoshinobu, T.; Mourzina, Y.G.; Vlasov, Y.G.; Schöning, M.J.; Iwasaki, H. Laser-scanned silicon transducer (LSST) as a multisensor system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 103, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimura, Y.; Yokoyama, M.; Kimura, K. Comparison between silicone-rubber membranes and plasticized poly (vinyl chloride) membranes containing calix [4] arene ionophores for sodium ion-sensitive field-effect transistors in applicability to sodium assay in human-body fluids. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1994, 22, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Tsujimura, Y.; Yokoyama, M. Silicone-rubber membrane sodium-ion sensors based on calix [4] arene neutral carriers. Pure Appl. Chem. 1995, 67, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarychev-Mikhailov, S.; Legin, A.; Mortensen, J.; Levitchev, S.; Vlasov, Y. Potentiometric and theoretical studies of the carbonate sensors based on 3-bromo-4-hexyl-5-nitrotrifluoroacetophenone. Analyst 2004, 129, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazale, A.; Sant, W.; Launay, J.; Ginot, F.; Temple-Boyer, P. Study of field effect transistors for the sodium ion detection using fluoropolysiloxane-based sensitive layers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 177, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cazale, A.; Sant, W.; Ginot, F.; Launay, J.C.; Savourey, G.; Revol-Cavalier, F.; Lagarde, J.M.; Heinry, D.; Launay, J.; Temple-Boyer, P. Physiological stress monitoring using sodium ion potentiometric microsensors for sweat analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 225, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermolenko, Y.; Yoshinobu, T.; Mourzina, Y.; Levichev, S.; Furuichi, K.; Vlasov, Y.; Schöning, M.J.; Iwasaki, H. Photocurable membranes for ion-selective light-addressable potentiometric sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 85, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Kanai, Y.; Uchida, H.; Katsube, T. Integrated biosensor employing a surface photovoltage technique. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1994, 20, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, A.; Ikeda, S.; Kubo, I.; Karube, I. Biosensors based on light-addressable potentiometric sensors for urea, penicillin and glucose. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 373, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Uchida, H.; Katsube, T.; Ishimaru, Y.; Iida, T. Integration of bienzymatic disaccharide sensors for simultaneous determination of disaccharides by means of light addressable potentiometric sensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 471, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourzina, I.G.; Yoshinobu, T.; Ermolenko, Y.E.; Vlasov, Y.G.; Schöning, M.J.; Iwasaki, H. Immobilization of urease and cholinesterase on the surface of semiconductor transducer for the development of light-addressable potentiometric sensors. Microchim. Acta 2004, 144, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Siqueira, J.R.; Werner, C.F.; Backer, M.; Poghossian, A.; Zucolotto, V.; Oliveira, O.N.; Schöning, M.J. Layer-by-layer assembly of carbon nanotubes incorporated in light-addressable potentiometric sensors. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 14765–14770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, J.R., Jr.; Maki, R.M.; Paulovich, F.V.; Werner, C.F.; Poghossian, A.; de Oliveira, M.C.; Zucolotto, V.; Oliveira, O.N., Jr.; Schöning, M.J. Use of information visualization methods eliminating cross talk in multiple sensing units investigated for a light-addressable potentiometric sensor. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, K.; Yoshida, M.; Sakai, T.; Matsuzaka, A.; Wagner, T.; Kanoh, S.; Yoshinobu, T.; Schöning, M.J. Differential setup of light-addressable potentiometric sensor with an enzyme reactor in a flow channel. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 50, 04DL08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.F.; Takenaga, S.; Taki, H.; Sawada, K.; Schöning, M.J. Comparison of label-free ACh-imaging sensors based on CCD and LAPS. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 177, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Gao, C.; Feng, D.; Wu, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Xing, K.; Feng, X. Bio-initiated light addressable potentiometric sensor for unlabeled biodetection and its MEDICI simulation. Analyst 2011, 136, 4533–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, Y.F.; Gao, C.Y.; He, J.; Feng, D.F.; Xing, K.L.; Wu, M.; Liu, Y.; Cai, W.S.; Feng, X.Z. Unlabeled multi tumor marker detection system based on bioinitiated light addressable potentiometric sensor. Analyst 2012, 137, 3806–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Yin, X.B.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, S.; Song, M.; Xing, K.L. Graphene oxide modified light addressable potentiometric sensor and its application for ssDNA monitoring. Analyst 2012, 137, 5866–5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.S.; Bronder, T.; Poghossian, A.; Werner, C.F.; Backer, M.; Schöning, M.J. Label-free electrical detection of DNA with a multi-spot LAPS: First step towards light-addressable DNA chips. Phys. Status Solidi A 2014, 211, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Bronder, T.; Poghossian, A.; Werner, C.F.; Schöning, M.J. Label-free detection of DNA using a light-addressable potentiometric sensor modified with a positively charged polyelectrolyte layer. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6143–6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.S.; Poghossian, A.; Bronder, T.S.; Schöning, M.J. Sensing of double-stranded DNA molecules by their intrinsic molecular charge using the light-addressable potentiometric sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 229, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartore, M.; Adami, M.; Nicolini, C.; Bousse, L.; Mostarshed, S.; Hafeman, D. Minority-carrier diffusion length effects on light-addressable potentiometric sensor (laps) devices. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1992, 32, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.F.; Wagner, T.; Yoshinobu, T.; Keusgen, M.; Schöning, M.J. Frequency behaviour of light-addressable potentiometric sensors. Phys. Status Solidi A 2013, 210, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Miyamoto, K.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. Theoretical study and simulation of light-addressable potentiometric sensors. Phys. Status Solidi A 2014, 211, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Miyamoto, K.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. Device simulation of the light-addressable potentiometric sensor for the investigation of the spatial resolution. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.; Parak, W.J.; Gerhardt, I.; Moritz, W.; Kaesen, F.; Geiger, H.; Eisele, I.; Gaub, H.E. Investigation of the spatial resolution of the light-addressable potentiometric sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2000, 86, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parak, W.J.; George, M.; Domke, J.; Radmacher, M.; Behrends, J.C.; Denyer, M.C.; Gaub, H.E. Can the light-addressable potentiometric sensor (LAPS) detect extracellular potentials of cardiac myocytes? IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 47, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, D.E.; Levine, S.; Healy, T.W. Site-binding model of electrical double-layer at oxide-water interface. J. Chem. Soc. Farad. Trans. 1 1974, 70, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousse, L.; Meindl, J.D. Surface potential-pH characteristics in the theory of the oxide-electrolyte interface. Geochem. Processes Miner. Surf. 1986, 323, 253–264. [Google Scholar]
- Fung, C.D.; Cheung, P.W.; Ko, W.H. A generalized theory of an electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor field-effect transistor. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 1986, 33, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hal, R.E.G.; Eijkel, J.C.T.; Bergveld, P. A general model to describe the electrostatic potential at electrolyte oxide interfaces. Adv. Colloid Interfac. 1996, 69, 31–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshinobu, T.; Ecken, H.; Poghossian, A.; Simonis, A.; Iwasaki, H.; Luth, H.; Schöning, M.J. Constant-current-mode LAPS (CLAPS) for the detection of penicillin. Electroanalysis 2001, 13, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinameri, K.; Munakata, C.; Mayama, K. A scanning photon microscope for non-destructive observations of crystal defect and interface trap distributions in silicon-wafers. J. Phys. E Sci. Instrum. 1988, 21, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Wagner, T.; Yoshinobu, T.; Kanoh, S.; Schöning, M.J. Phase-mode LAPS and its application to chemical imaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 154, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.F.; Miyamoto, K.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. Lateral resolution enhancement of pulse-driven light-addressable potentiometric sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 248, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y. High-spatial resolution LAPS. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1998, 52, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parak, W.J.; Hofmann, U.G.; Gaub, H.E.; Owicki, J.C. Lateral resolution of light-addressable potentiometric sensors: An experimental and theoretical investigation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1997, 63, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.T. Theoretical analysis and design of submicron-LAPS. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 105, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenheuvel, J.C.; Vanoort, R.C.; Geerts, M.J. Diffusion length measurements of thin amorphous-silicon layers. Solid State Commun. 1989, 69, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kong, S.; Chen, F.M.; Chen, W.; Du, L.P.; Cai, W.; Huang, L.Q.; Wu, C.S.; Zhang, D.W. A bioelectronic taste sensor based on bioengineered Escherichia coli cells combined with ITO-constructed electrochemical sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1079, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zhou, B.; Wang, J.; Zhong, M.C.; Das, A.; Watkinson, M.; Hing, K.; Zhang, D.W.; Krause, S. Photoelectrochemical imaging system for the mapping of cell surface charges. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 5896–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Seki, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. Novel photoexcitation method for light-addressable potentiometric sensor with higher spatial resolution. Appl. Phys. Express 2014, 7, 067301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Seki, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. Device simulation of the light-addressable potentiometric sensor with a novel photoexcitation method for a higher spatial resolution. In Proceedings of the 28th European Conference on Solid-State Transducers (Eurosensors 2014), Brescia, Italy, 7–10 September 2014; pp. 456–459. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto, K.; Seki, K.; Guo, Y.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. Enhancement of the spatial resolution of the chemical imaging sensor by a hybrid fiber-optic illumination. In Proceedings of the 28th European Conference on Solid-State Transducers (Eurosensors 2014), Brescia, Italy, 7–10 September 2014; pp. 612–615. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto, K.; Seki, K.; Suto, T.; Werner, C.F.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. Improved spatial resolution of the chemical imaging sensor with a hybrid illumination that suppresses lateral diffusion of photocarriers. Sens. Actuators B Chem 2018, 273, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Sakakita, S.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. Application of chemical imaging sensor to in-situ pH imaging in the vicinity of a corroding metal surface. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 183, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Chen, T.C.; Lin, Y.T.; Lai, C.S.; Yang, C.M. Ultra-high scanning speed chemical image sensor based on light addressable potentiometric sensor with analog micro-mirror. In Proceedings of the SENSORS, 2013 IEEE, Baltimore, MD, USA, 3–6 November 2013; pp. 1412–1415. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Chen, T.C.; Yang, C.M.; Lai, C.S. A high-speed, flexible-scanning chemical imaging system using a light-addressable potentiometric sensor integrated with an analog micromirror. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 198, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Yang, C.M.; Chen, T.C.; Lai, C.S. Analog micromirror-LAPS for chemical imaging and zoom-in application. Vacuum 2015, 118, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Werner, C.F.; Miyamoto, K.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. Development and characterisation of a compact light-addressable potentiometric sensor (LAPS) based on the digital light processing (DLP) technology for flexible chemical imaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 170, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Werner, C.F.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. Utilising digital micro-mirror device (DMD) as scanning light source for light-addressable potentiometric sensors (LAPS). Sens. Lett. 2011, 9, 812–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Das, A.; Lai, C.S. A simple and convenient set-up of light addressable potentiometric sensors (LAPS) for chemical imaging using a commercially available projector as a light source. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 7062–7074. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto, K.; Kaneko, K.; Matsuo, A.; Wagner, T.; Kanoh, S.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. Miniaturized chemical imaging sensor system using an OLED display panel. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 170, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.F.; Wagner, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Yoshinobu, T.; Schöning, M.J. High speed and high resolution chemical imaging based on a new type of OLED-LAPS set-up. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 175, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Kuwabara, Y.; Kanoh, S.; Yoshinobu, T.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J. Chemical image scanner based on FDM-LAPS. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 137, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Itabashi, A.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. High-speed chemical imaging inside a microfluidic channel. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 194, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qintao, Z.; Ping, W.; Parak, W.J.; George, M.; Zhang, G. A novel design of multi-light LAPS based on digital compensation of frequency domain. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 73, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Werner, C.F.B.; Miyamoto, K.I.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. A high-density multi-point LAPS set-up using a VCSEL array and FPGA control. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 154, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itabashi, A.; Kosaka, N.; Miyamoto, K.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. High-speed chemical imaging system based on front-side-illuminated LAPS. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 182, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Hirayama, Y.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. Visualization of enzymatic reaction in a microfluidic channel using chemical imaging sensor. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 113, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousse, L.; Mcreynolds, R.J.; Kirk, G.; Dawes, T.; Lam, P.; Bemiss, W.R.; Farce, J.W. Micromachined multichannel systems for the measurement of cellular-metabolism. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1994, 20, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousse, L.J.; Parce, J.W.; Owicki, J.; Kercso, K. Silicon micromachining in the fabrication of biosensors using living cells. In Proceedings of the IEEE 4th Technical Digest on Solid-State Sensor and Actuator Workshop, Hilton Head Island, SC, USA, 4–7 June 1990; pp. 173–176. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto, K.I.; Sato, T.; Abe, M.; Wagner, T.; Schöning, M.J.; Yoshinobu, T. Light-addressable potentiometric sensor as a sensing element in plug-based microfluidic devices. Micromachines 2016, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.; Gu, C.; Gan, Y.; Wu, Q.; He, C.; Tu, J.; Pan, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Kong, L.; Wan, H. Microfluidic chip system integrated with light addressable potentiometric sensor (LAPS) for real-time extracellular acidification detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 301, 127004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, Q.; Lin, J.M. Microfluidic technologies in cell isolation and analysis for biomedical applications. Analyst 2017, 142, 421–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
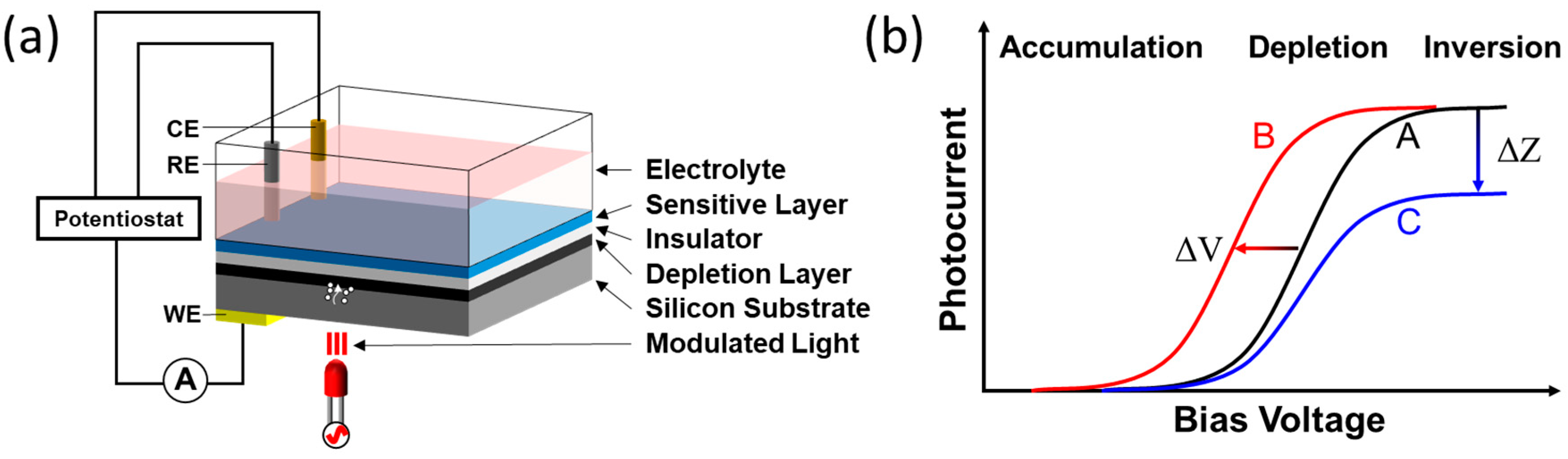


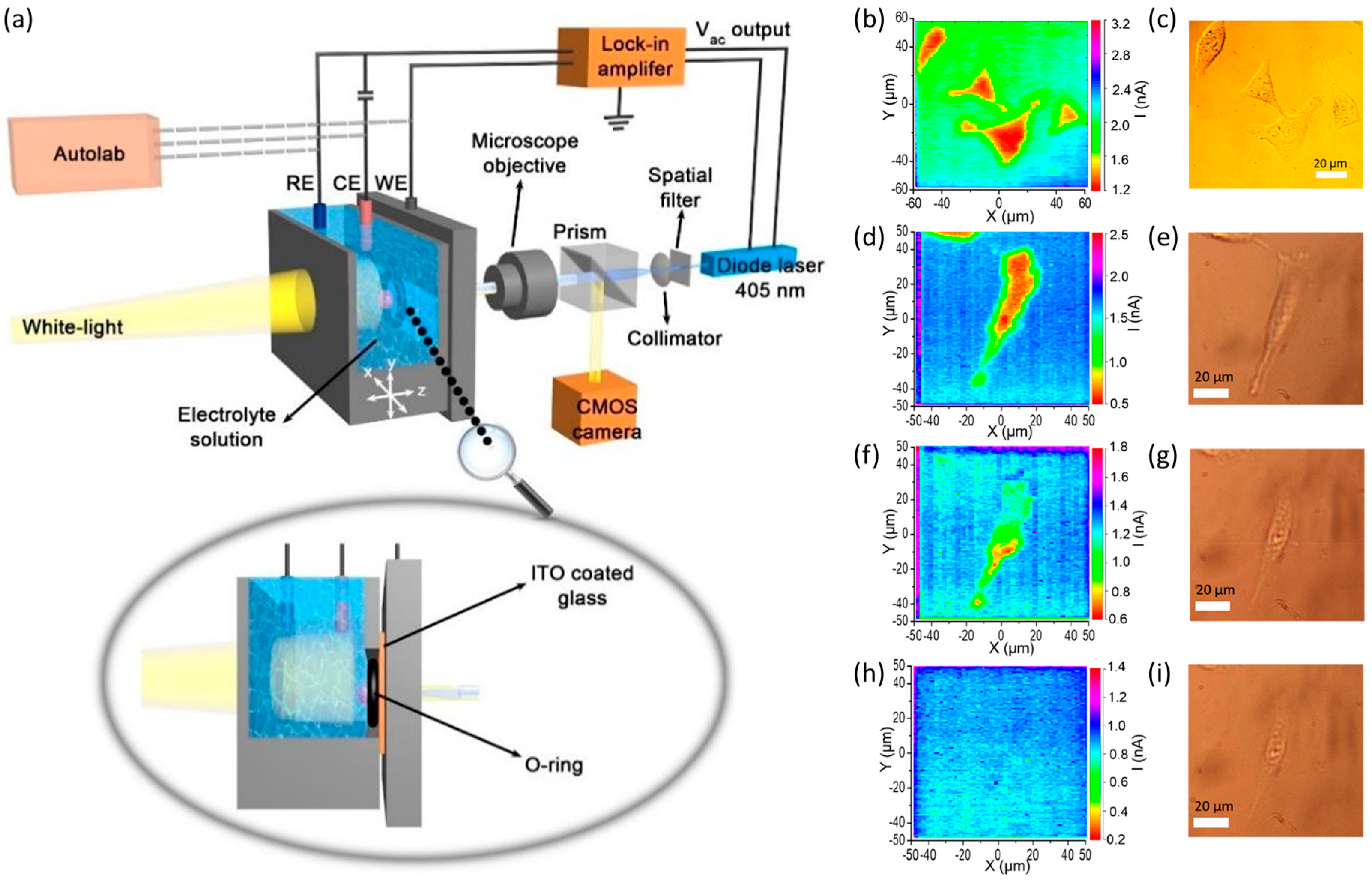




| Measurement Modes | Pros | Cons | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Constant-Voltage Mode | Rapid Measurement; Suitable for Multi-Pixel Imaging | Small Detection Range; Potential Conversion Rrrors | [28,101] |
| Constant-Current Mode | Unlimited Detection Range; Accurate Measurement | Necessary Feedback Loop; Long Measurement Time | [4,107] |
| Potential-Tracking Mode | Entire I-V Curves; Unlimited Detection Range; Relatively Accurate | Additional Curve-Fitting; Necessary Charging Time | [27] |
| Phase Mode | Good Robustness; Good Imaging Uniformity | Necessary Simultaneous Record of Photocurrent and Modulation Signal; Potential Conversion Errors | [109] |
| Pulse-Driven Mode | High Spatial Resolution; High Contrast of Line Scan | Low SNR; Long Measurement Time | [110] |
| Methods | Notes | Sensor Construction | Modulated Light Parameters 1 | Spatial Resolution | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semiconductor Substrate Properties | High Doping Concentration | Simulation Results | 50 nm SiO2/50 nm Si3N4/200 μm Si | Backside Illumination; λ = 800 nm, f = 5 kHz, P = 6 W/cm2, S = 20 μm | <30 μm | [100] |
| Short Diffusion Length Materials | Semiconductor Material: GaAs | 8 μm Pt/100 nm Anodic Oxide/8 μm Epilayer of GaAs | Frontside Illumination; λ = 780 nm, f = 10 kHz, P = 0.18 mW, S = 2.6 μm | 3.1 μm | [47] | |
| Semiconductor Material: Amorphous Si | 20~150 nm Metal Gate/50 nm Si3N4/30 nm SiO2/0.3~1.5 μm a-Si/Glass/500 nm Al/700 ZnO | Frontside Illumination; λ = 430 nm, P = 1 mW, S = 1.03 μm | <1 μm | [41] | ||
| Thinned Semiconductor Substrate | Infrared Light | 100 nm Au/Photoresist Pattern/100 nm Si3N4/50 nm SiO2/20 μm Si | Backside Illumination; λ = 830 nm, f = 1~10 kHz, S = ~1 μm | <10 μm | [31] | |
| Transparent Substrate with Thin Semiconductor Layer | Silicon on Sapphire | Photoresist Pattern/6.7 nm Anodic Oxide/0.5 μm Si/500 μm Sapphire/20 nm Cr/80 nm Au | Backside Illumination; λ = 405 nm, f = 1 kHz, P = 1 mW (Single Photon Effect) | 1.5 μm | [45,61] | |
| ITO Coated Glass; No Insulator | PMMA dot/~140 nm ITO/500 μm Glass | Backside Illumination; λ = 405 nm, f = 10 Hz, S = ~1 μm | 2.3 μm | [50,116] | ||
| Modulated Light Properties | Small Light Spot Size | Spot Size at Micron Level | 100 nm Si3N4/50 nm SiO2/300 μm Si/AuSb | Backside Illumination; λ = 633 nm, f = 1~10 kHz, P = 10 mW, S = ~1 μm | <500 μm | [28] |
| Infrared Light | Thin Silicon Substrate | 100 nm Au/Photoresist Pattern/100 nm Si3N4/50 nm SiO2/20 μm Si | Backside Illumination; λ = 830 nm, f = 1~10 kHz, S = ~1 μm | < 10 μm | [31] | |
| Auxiliary Illumination | Ring-Shaped Constant Light | 50 nm Si3N4/50 nm SiO2/200 μm Si/Au | Backside Illumination; λ = 832 nm, Modulated, P = 0.002 mW; λ = 832 nm, Constant, P = 0.1 mW | <68 μm | [119,120] | |
| Pulse-Driven Modulated Light | Charge Amplifier | 40 nm Si3N4/40 nm SiO2/200 μm Si/Au | Backside Illumination; λ = 905 nm, t = 2 μs, P = 85 mW, S = ~1.1 μm | 110 μm | [110] | |
| Two-Photon Effect | Silicon on Sapphire | Photoresist Pattern/6.7 nm Anodic Oxide/0.5 μm Si/500 μm Sapphire/20 nm Cr/80 nm Au | Backside Illumination; λ = 405 nm, f = 1 kHz, P = 1 mW (Two-Photon Effect) | 0.8 μm | [45,61] | |
| Methods | Notes | Sensor Construction | Modulated Light Parameters 1 | Temporal Resolution 2 | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Modulated Light Without Mechanical Movement | Analog Gimbal-Less Two-Axis Micromirror | Light Spot Movement by Angular Rotation | 10 nm Si3N4/3 nm SiO2/500 μm Si | Backside Illumination; λ = 658 nm, f = 5~20 kHz, S = 300 μm | R = 500 × 400 pixels, S1 = 14.5 × 10.5 mm2, S2 = 300 μm, t = 40 s; R = 10 × 8 pixels, S1 = 2.8 × 5 mm2, S2 = 300 μm, FPS = 16 | [123,124] |
| DLP-Based Digital Micromirror Device (DMD) | 480 × 320 Micromirror Array; Modulation by Digital Switch | Si3N4/SiO2/Si/Au | Backside Illumination; f = 713 Hz, S = 4.3 μm | S1 = 20.8 × 15.6 mm2, S2 = 2.6 × 2.6 mm2, t = 2 s; S1 = 5 × 5 mm2, S2 = 0.87 × 0.87 mm2, t = 5 s; S1 = 1 × 1 mm2, S2 = 0.13 × 0.13 mm2, t = 60 s | [125,126] | |
| DLP-Based Projector | \ | 20 nm HfO2/1 μm a-Si/10 nm Mo/70 nm ITO/Glass | Backside Illumination; f = 30 Hz, S = 72 μm × 72 μm | R = 160 ×25 pixels, S1 = 2.88 × 1.8 mm2, S2 = 155× 155 μm2, t = 800 s; R = 98 × 22 pixels, S1 = 1.764 × 1.188 mm2, S2 = 106× 106 μm2, t = 431.2 s; | [42] | |
| OLED Display | High Modulation Frequency | Si3N4/SiO2/Si/Al | Backside Illumination; f = 1.74 kHz, S = 200 × 200 μm | R = 96 × 64 pixels, S1 = 20.1 × 13.2 mm2, S2 = 0.4 × 0.2 mm2, t = 150 s | [129] | |
| Multi-Frequency Modulation Light Source Array (FDM) | High-Density VCSEL Array | 12 VCSEL Diodes with a Pitch of 250 μm | Ta2O5/SiO2/Si | Backside Illumination; λ = 850 nm, f = 3 kHz ~ 4.1 kHz, Step = 100 Hz, S = 500 μm | R = 12 × 22 pixels, S1 = 3 × 10 mm2, S2 = 0.5 mm × 3 mm, t = 3.6 s | [133] |
| Two-Dimensional LED Array | 7 × 5 LED Array; Illumination Line by Line | 100 nm Si3N4/50 nm SiO2/200 μm Si | Frontside Illumination; λ = 660 nm, f = 6 ~ 10 kHz, Step = 1 kHz, S = 2 mm | R = 7 × 5 pixels, S1 = 17 × 12 mm2, S2 = 2 mm × 12 mm, FPS = 70 | [134] | |
| Optical Fiber Array with Microfluidic Channel | 64 Light Beams; Flexible Measurement Layout | PDMS/Si3N4/SiO2/Si | Frontside Illumination; λ = 600 ~ 625 nm, f = 6.4 ~ 12.7 kHz, Step = 100 Hz, S = 500 μm | R = 8 × 8 pixels, S1 = 12 × 12 mm2, S2 = 0.5 mm × 0.5 mm, FPS = 100 | [131] | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, T.; Qiu, Y.; Gan, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhou, S.; Wan, H.; Wang, P. Recent Developments of High-Resolution Chemical Imaging Systems Based on Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensors (LAPSs). Sensors 2019, 19, 4294. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194294
Liang T, Qiu Y, Gan Y, Sun J, Zhou S, Wan H, Wang P. Recent Developments of High-Resolution Chemical Imaging Systems Based on Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensors (LAPSs). Sensors. 2019; 19(19):4294. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194294
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Tao, Yong Qiu, Ying Gan, Jiadi Sun, Shuqi Zhou, Hao Wan, and Ping Wang. 2019. "Recent Developments of High-Resolution Chemical Imaging Systems Based on Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensors (LAPSs)" Sensors 19, no. 19: 4294. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194294
APA StyleLiang, T., Qiu, Y., Gan, Y., Sun, J., Zhou, S., Wan, H., & Wang, P. (2019). Recent Developments of High-Resolution Chemical Imaging Systems Based on Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensors (LAPSs). Sensors, 19(19), 4294. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194294






