Target-Specific Action Classification for Automated Assessment of Human Motor Behavior from Video
Abstract
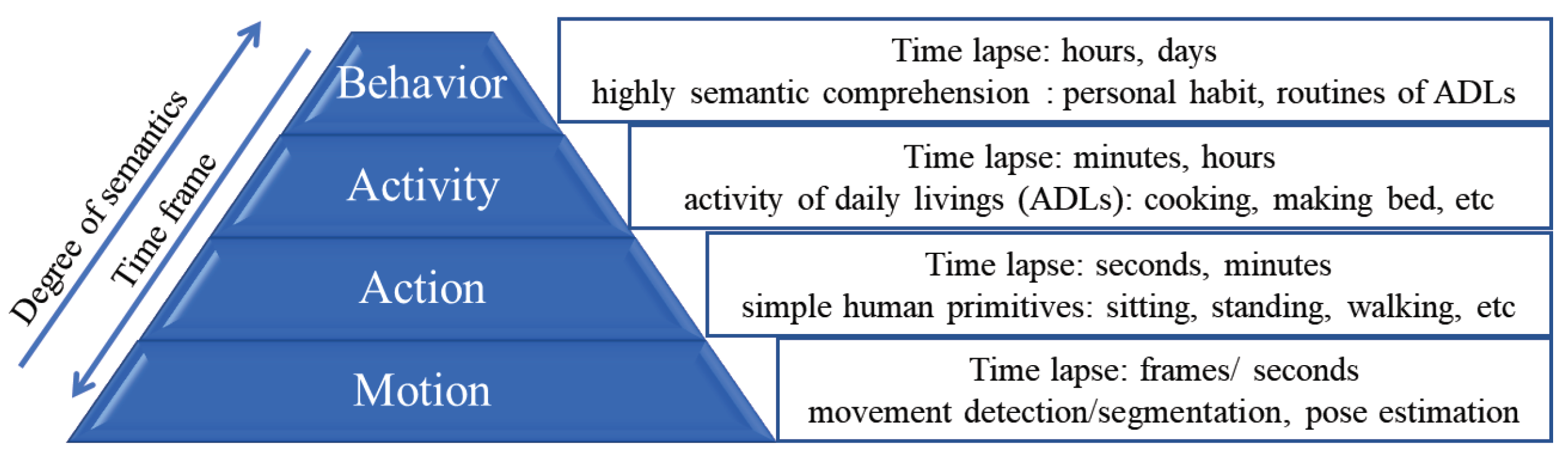
:1. Introduction
1.1. Our Contributions
1.2. Related Works
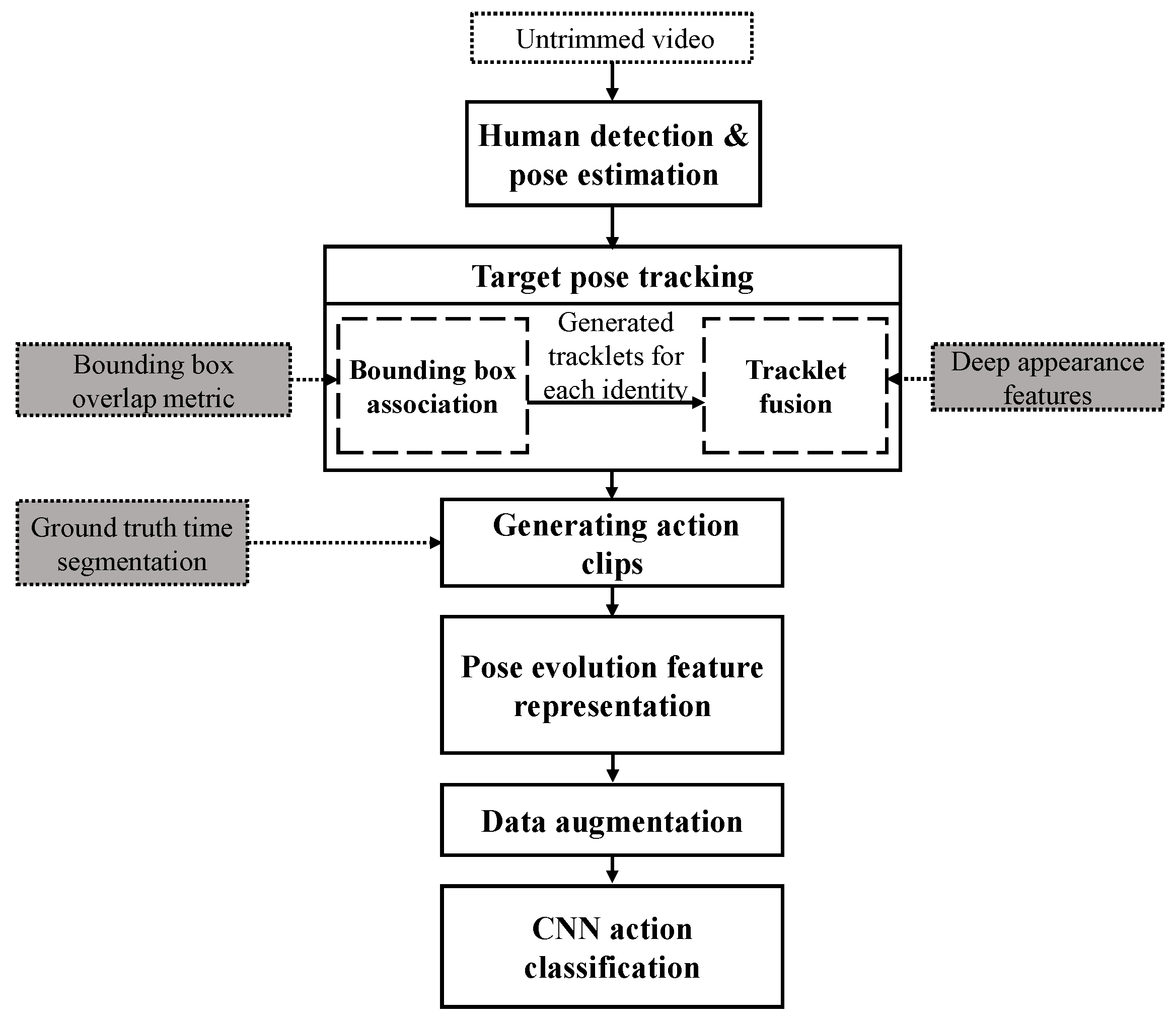
2. Target Pose Tracking
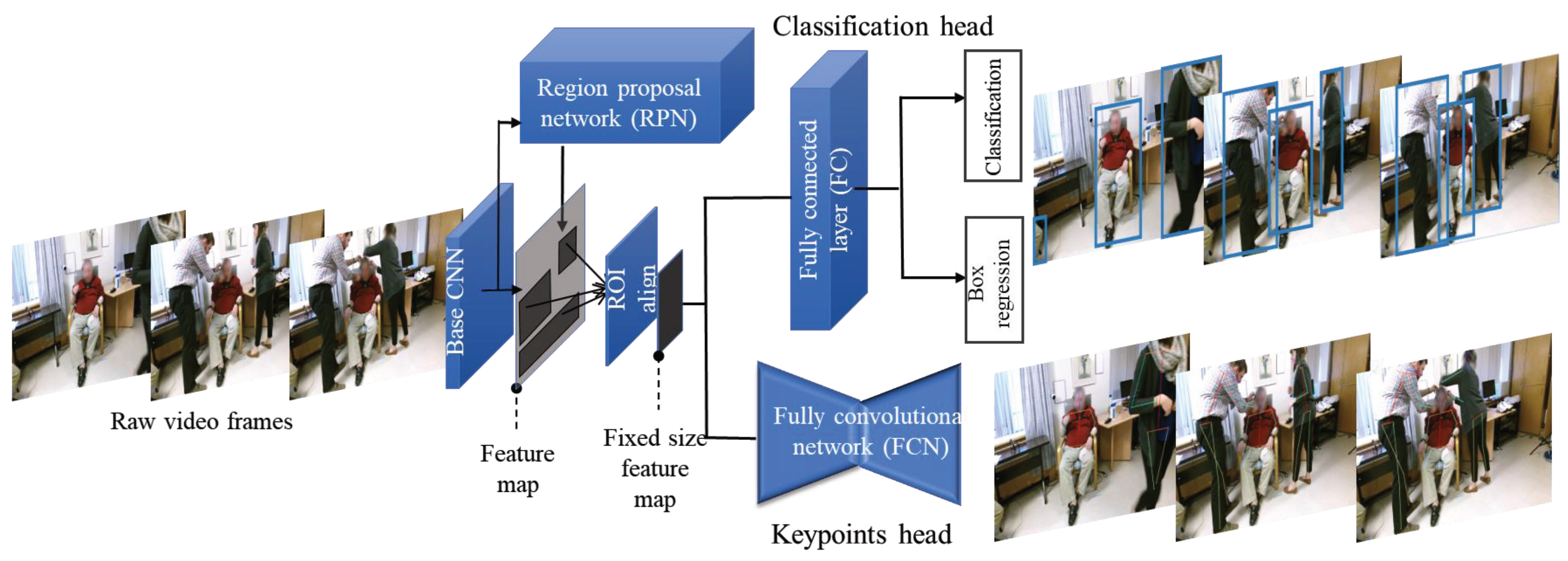
2.1. Human Pose Estimation
2.2. Cascaded Pose Tracking
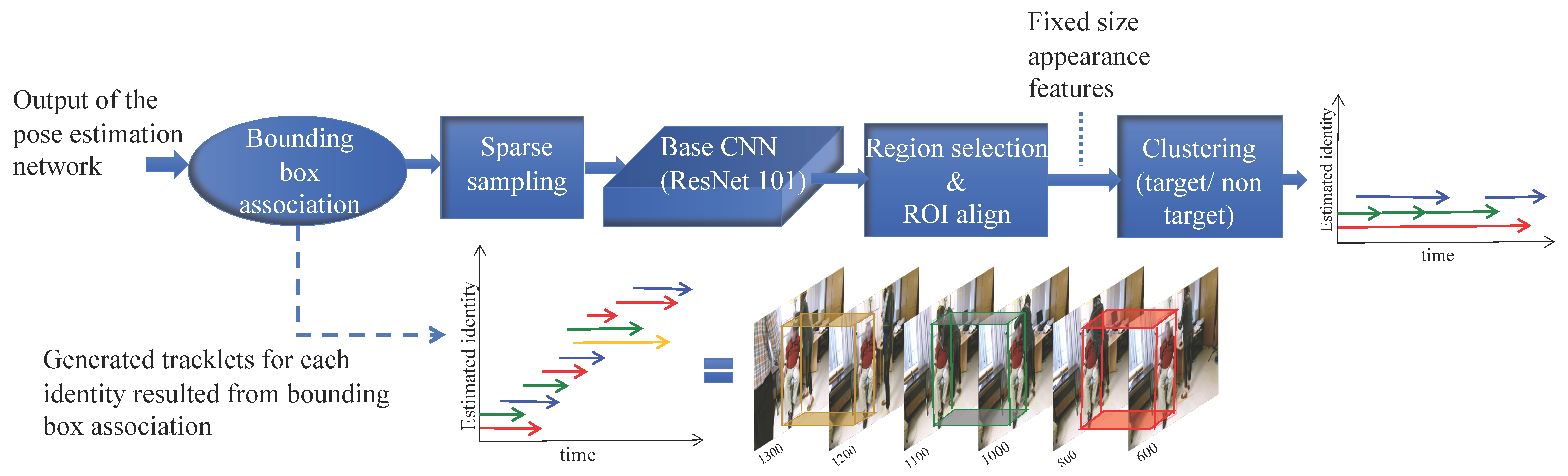
2.2.1. Short Term Tracking Based on Temporal Association
2.2.2. Long Term Tracking using Appearance based Tracklet Fusion
3. Action Classification Based on Pose Evolution Representation
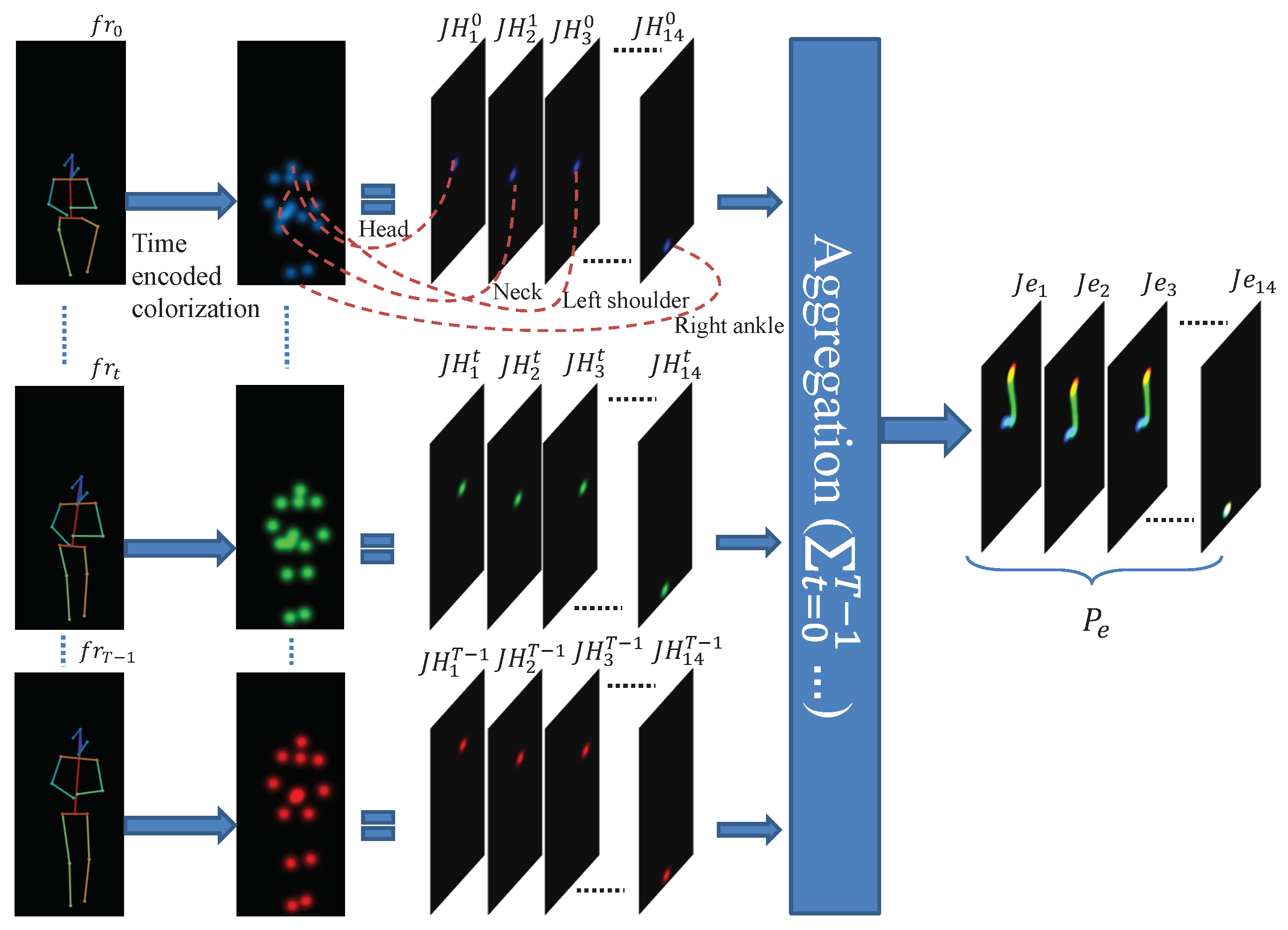
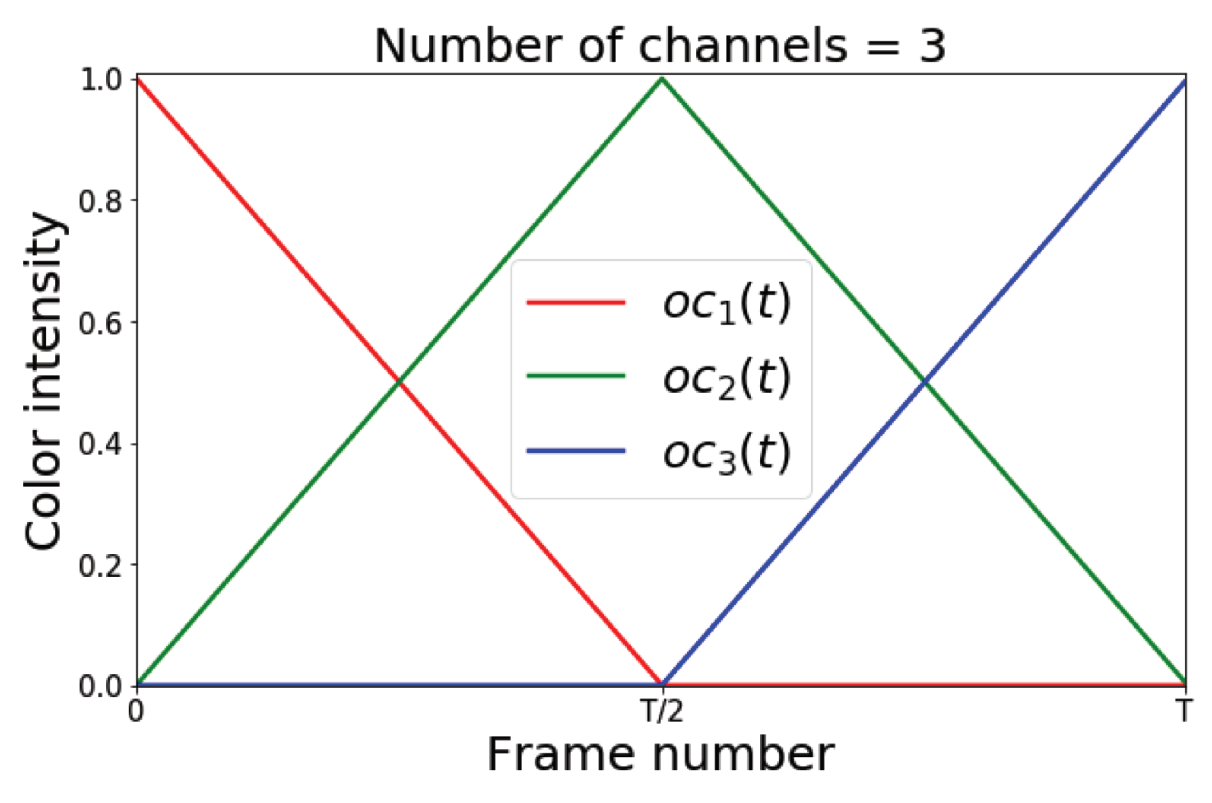
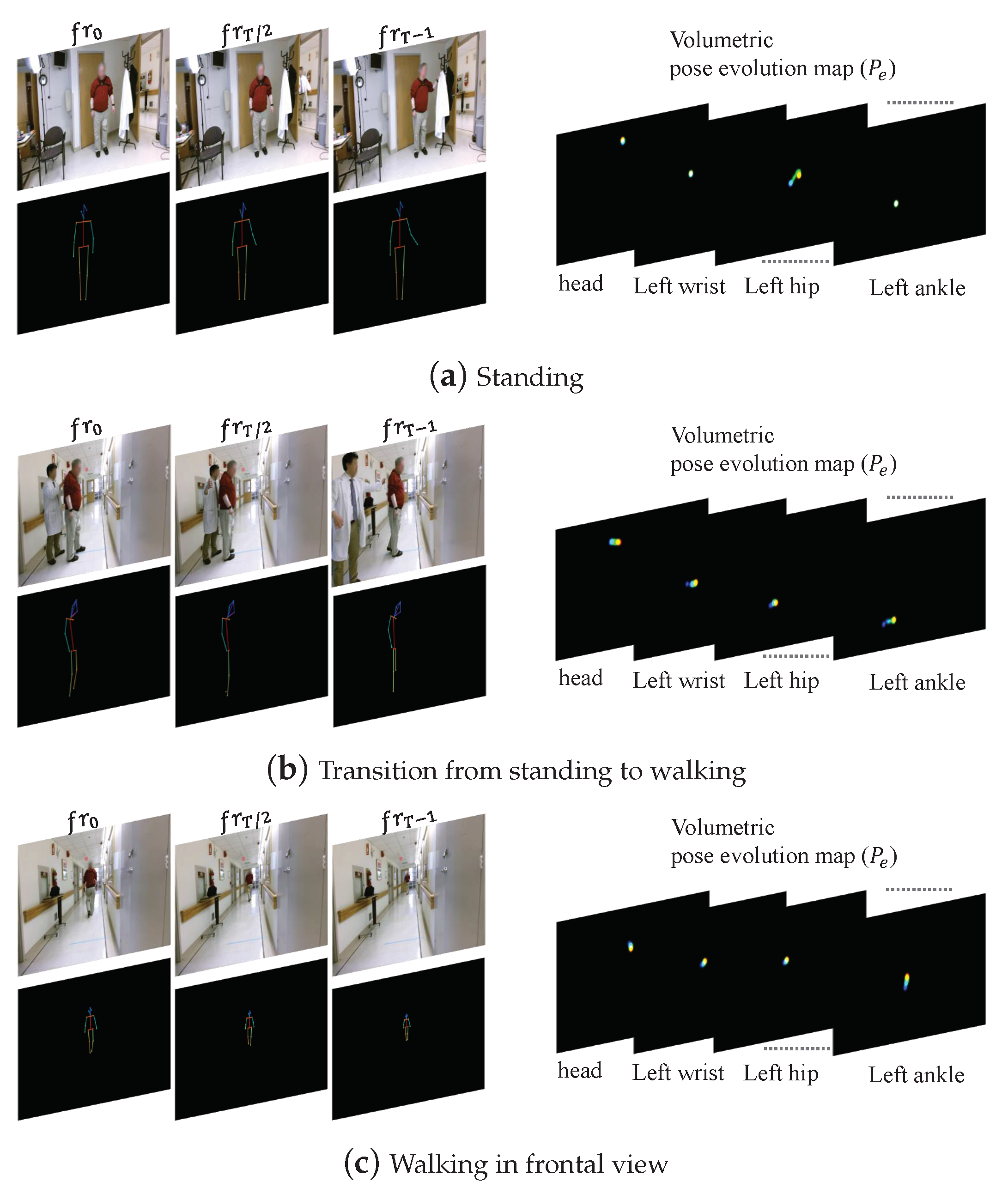
3.1. Pose Evolution Representation
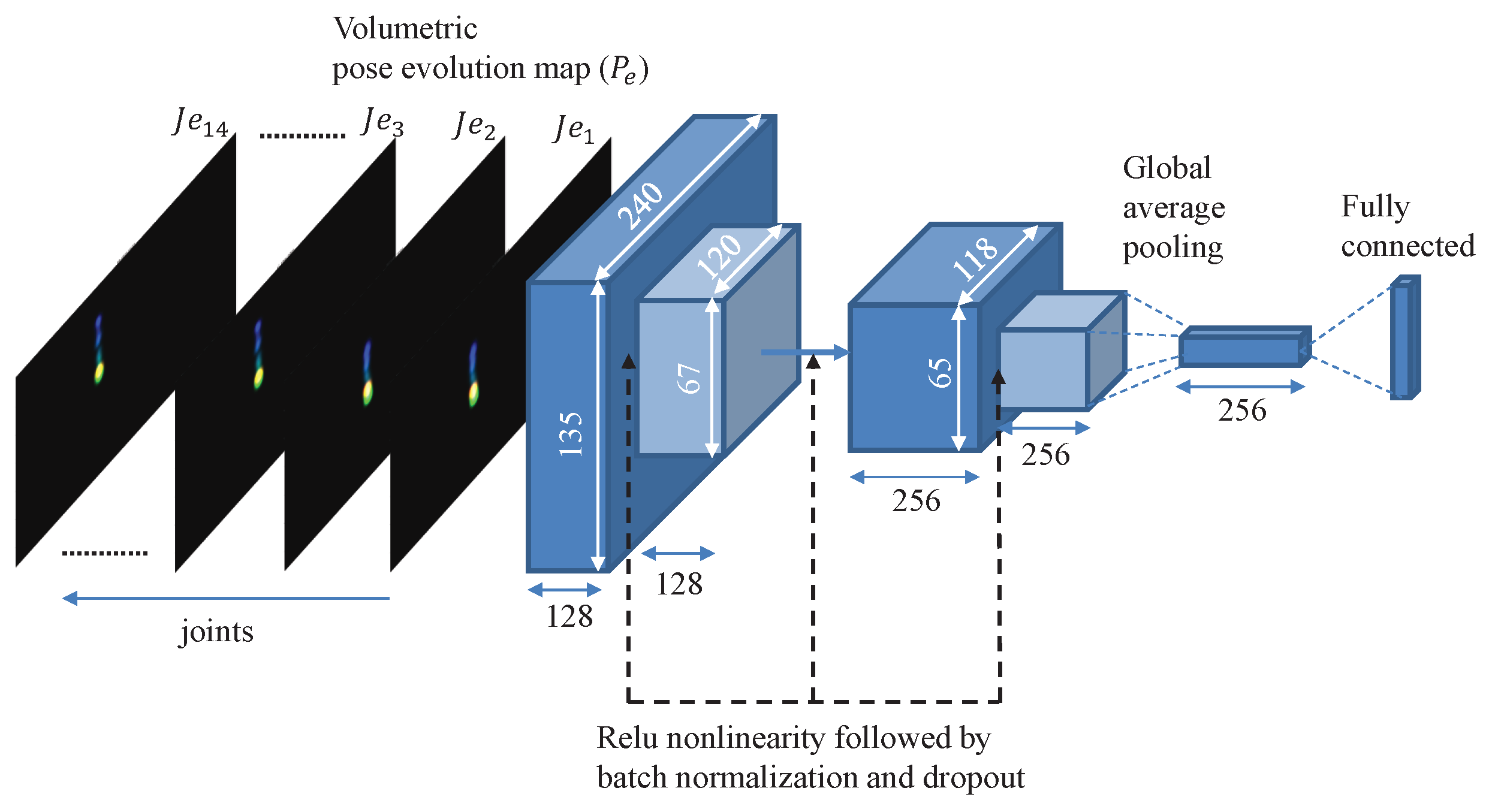
3.2. Classification Network
4. Experiments
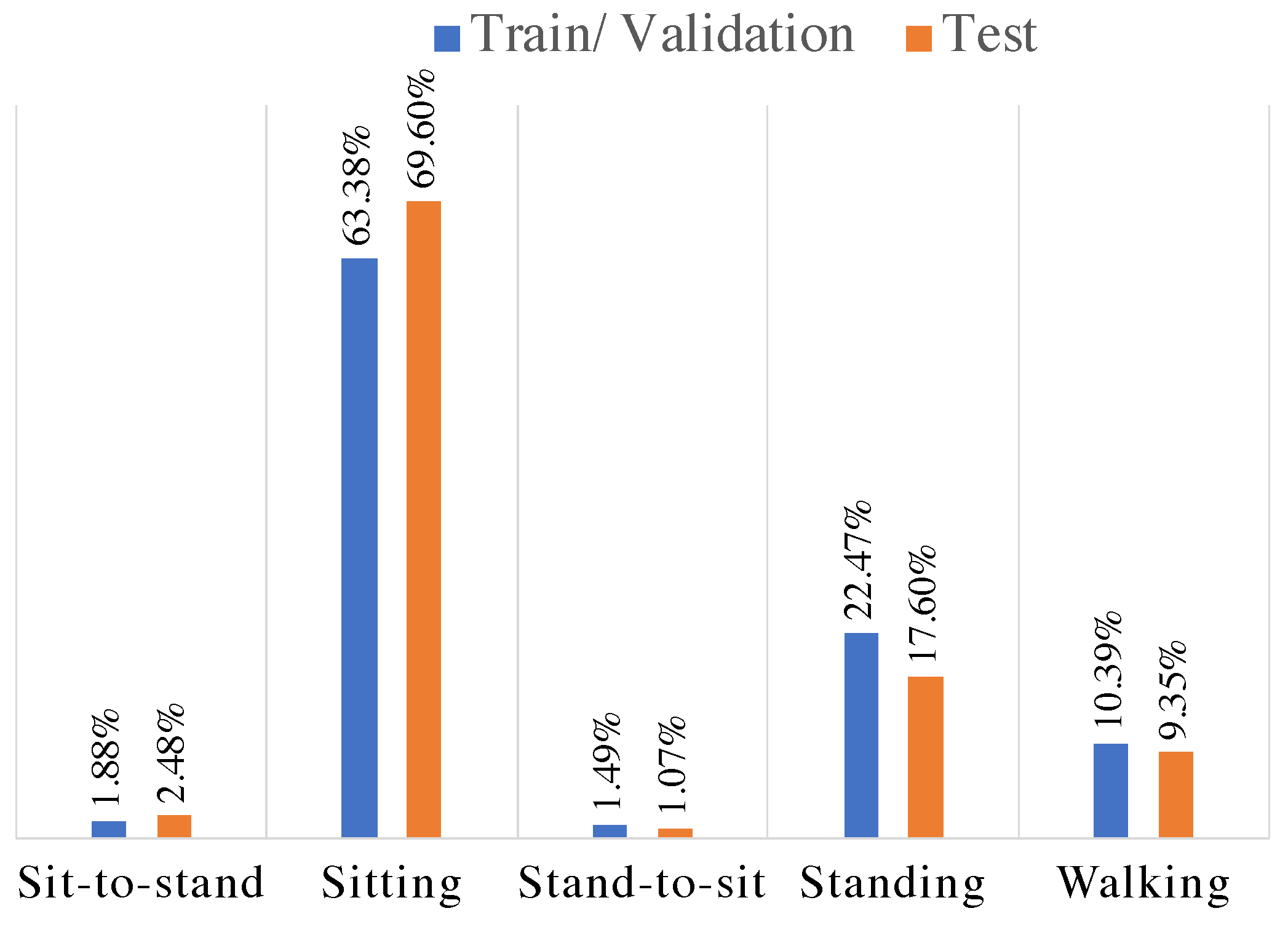
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Tracking Target Human and Pose
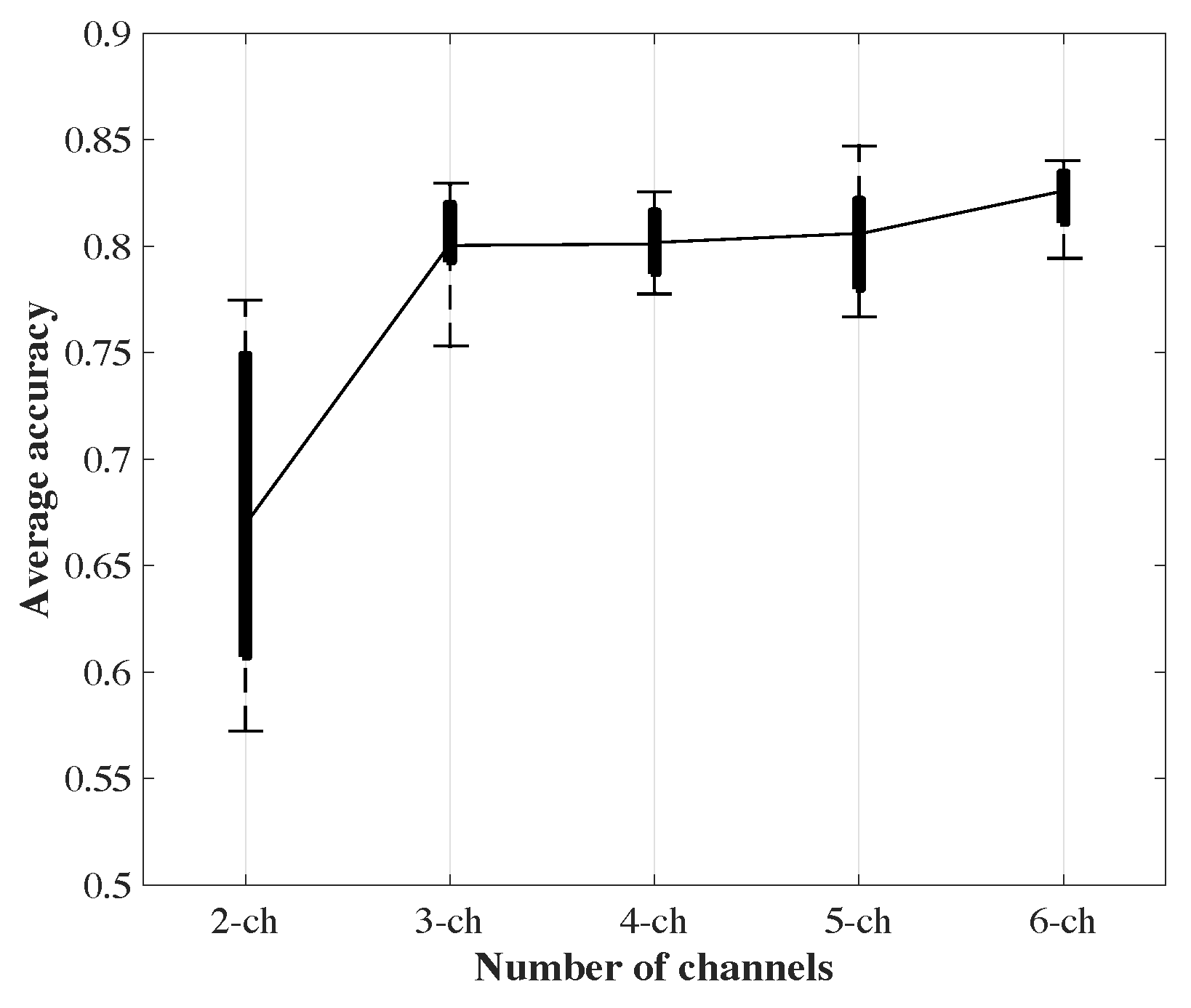
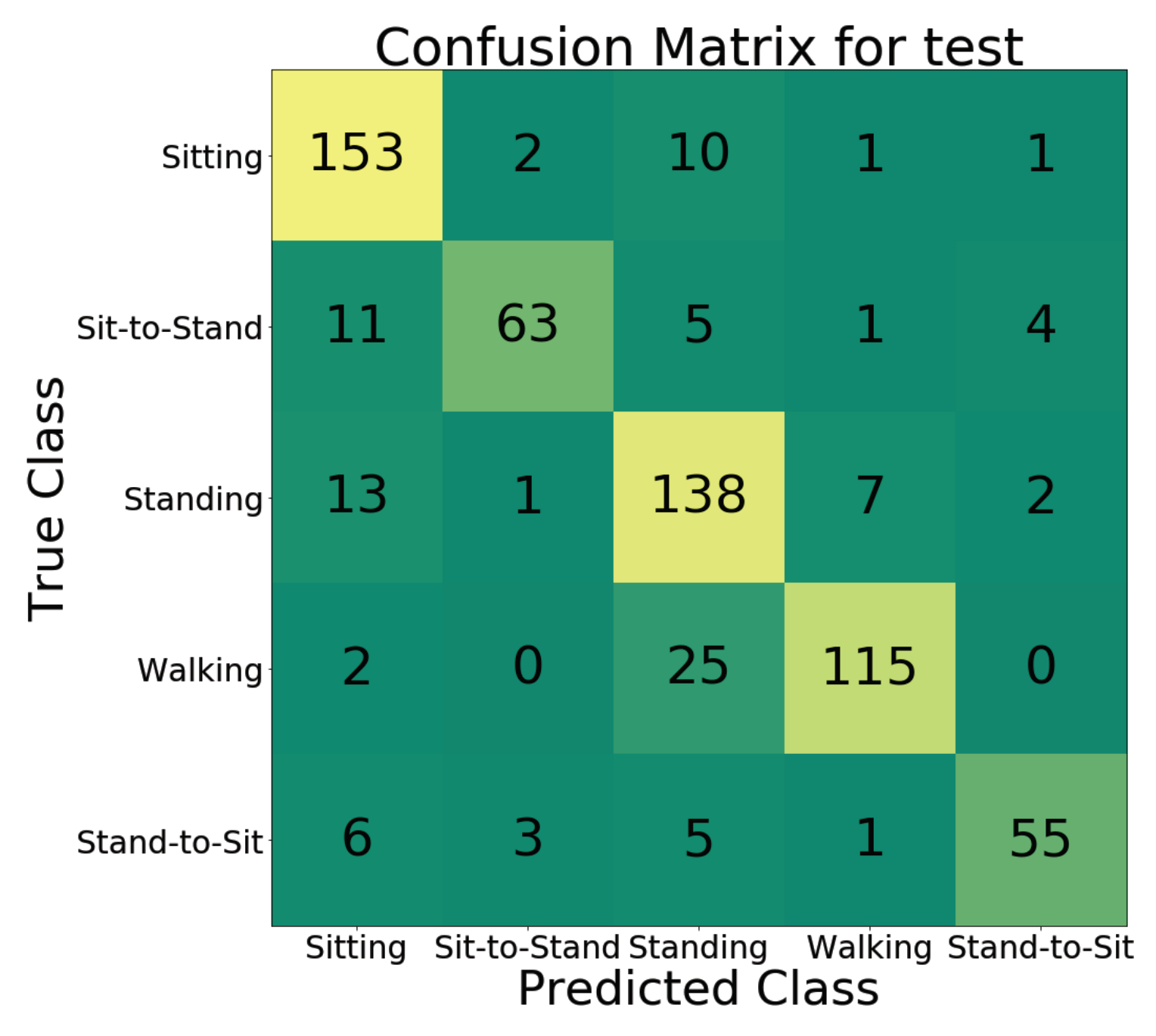
4.3. Action Classification
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Post, B.; Merkus, M.P.; de Bie, R.M.; de Haan, R.J.; Speelman, J.D. Unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale motor examination: Are ratings of nurses, residents in neurology, and movement disorders specialists interchangeable? Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2005, 20, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espay, A.J.; Bonato, P.; Nahab, F.B.; Maetzler, W.; Dean, J.M.; Klucken, J.; Eskofier, B.M.; Merola, A.; Horak, F.; Lang, A.E.; et al. Movement Disorders Society Task Force on Technology. Technology in Parkinson’s disease: Challenges and opportunities. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorp, J.E.; Adamczyk, P.G.; Ploeg, H.L.; Pickett, K.A. Monitoring Motor Symptoms During Activities of Daily Living in Individuals With Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, O.D.; Labrador, M.A. A survey on human activity recognition using wearable sensors. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 1192–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Nimwegen, M.; Speelman, A.D.; Hofman-van Rossum, E.J.M.; Overeem, S.; Deeg, D.J.H.; Borm, G.F.; van der Horst, M.H.L.; Bloem, B.R.; Munneke, M. Physical inactivity in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 2214–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaaraoui, A.A.; Climent-Pérez, P.; Flórez-Revuelta, F. A review on vision techniques applied to human behaviour analysis for ambient-assisted living. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 10873–10888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrigkas, M.; Nikou, C.; Kakadiaris, I.A. A review of human activity recognition methods. Front. Robot. AI 2015, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, L.; Ota, K.; Dong, M. Robust Activity Recognition for Aging Society. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 22, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.H.; Mestre, T.A.; Fox, S.H.; Taati, B. Vision-based assessment of parkinsonism and levodopa-induced dyskinesia with pose estimation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brattoli, B.; Buchler, U.; Wahl, A.S.; Schwab, M.E.; Ommer, B. LSTM Self-Supervision for Detailed Behavior Analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6466–6475. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Shen, L.; Valstar, M. Human behaviour-based automatic depression analysis using hand-crafted statistics and deep learned spectral features. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi’an, China, 15–19 May 2018; pp. 158–165. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, F.; Bieg, H.J.; Herman, M.; Rothkopf, C.A. I see what you see: Inferring sensor and policy models of human real-world motor behavior. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.T.; Biglari-Abhari, M.; Wang, K.I. Trusting the Computer in Computer Vision: A Privacy-Affirming Framework. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1360–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, B.; Ostadabbas, S. Background Subtraction via Fast Robust Matrix Completion. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1871–1879. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, B.; Huang, X.; Yee, J.R.; Ostadabbas, S. Long-term non-contact tracking of caged rodents. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 1952–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, B.; Ostadabbas, S. Moving Object Detection through Robust Matrix Completion Augmented with Objectness. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2018, 12, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, S.; Harandi, M.; Porikli, F. Going deeper into action recognition: A survey. Image Vis. Comput. 2017, 60, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dawar, N.; Ostadabbas, S.; Kehtarnavaz, N. Data Augmentation in Deep Learning-Based Fusion of Depth and Inertial Sensing for Action Recognition. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2018, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girdhar, R.; Carreira, J.; Doersch, C.; Zisserman, A. Video action transformer network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–21 June 2019; pp. 244–253. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.B.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhong, B.; Lei, Q.; Yang, L.; Du, J.X.; Chen, D.S. A comprehensive survey of vision-based human action recognition methods. Sensors 2019, 19, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Huang, J.; Li, T.; Guo, H.; Li, G. Detecting action tubes via spatial action estimation and temporal path inference. Neurocomputing 2018, 311, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, ON, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 568–576. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Sun, X.; Zha, Z.J.; Zeng, W. MiCT: Mixed 3D/2D Convolutional Tube for Human Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 449–458. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Wang, H.; Torresani, L.; Ray, J.; LeCun, Y.; Paluri, M. A Closer Look at Spatiotemporal Convolutions for Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6450–6459. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4489–4497. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Yuan, J. Recognizing Human Actions as the Evolution of Pose Estimation Maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Choutas, V.; Weinzaepfel, P.; Revaud, J.; Schmid, C. PoTion: Pose MoTion Representation for Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cherian, A.; Sra, S.; Gould, S.; Hartley, R. Non-Linear Temporal Subspace Representations for Activity Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 2197–2206. [Google Scholar]
- Zolfaghari, M.; Oliveira, G.L.; Sedaghat, N.; Brox, T. Chained Multi-stream Networks Exploiting Pose, Motion, and Appearance for Action Classification and Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Girdhar, R.; Gkioxari, G.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M.; Tran, D. Detect-and-Track: Efficient Pose Estimation in Videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 350–359. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Andriluka, M.; Iqbal, U.; Milan, A.; Insafutdinov, E.; Pishchulin, L.; Gall, J.; Schiele, B. Posetrack: A benchmark for human pose estimation and tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 5167–5176. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June 26–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, M.; Wu, Z.; Rates-Borras, A.; Camps, O.; Radke, R.J. A systematic evaluation and benchmark for person re-identification: Features, metrics, and datasets. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 523–536. [Google Scholar]
- Gou, M.; Camps, O.; Sznaier, M. Mom: Mean of moments feature for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1294–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, S.Z. Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 2197–2206. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, E.; Jones, M.; Marks, T.K. An improved deep learning architecture for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3908–3916. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhu, X.; Gong, S. Unsupervised person re-identification by deep learning tracklet association. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 737–753. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.; Chen, W.; Li, Q.; Yang, C. Unsupervised cross-dataset person re-identification by transfer learning of spatial-temporal patterns. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7948–7956. [Google Scholar]
- Pirsiavash, H.; Ramanan, D.; Fowlkes, C.C. Globally-optimal greedy algorithms for tracking a variable number of objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 1201–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, H.W. The Hungarian method for the assignment problem. Nav. Res. Logist. 2005, 52, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erb, K.; Daneault, J.; Amato, S.; Bergethon, P.; Demanuele, C.; Kangarloo, T.; Patel, S.; Ramos, V.; Volfson, D.; Wacnik, P.; et al. The BlueSky Project: Monitoring motor and non-motor characteristics of people with Parkinson’s disease in the laboratory, a simulated apartment, and home and community settings. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Congress, Hong Kong, China, 5–9 October 2018; Volume 33, p. 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Goetz, C.G.; Tilley, B.C.; Shaftman, S.R.; Stebbins, G.T.; Fahn, S.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Poewe, W.; Sampaio, C.; Stern, M.B.; Dodel, R.; et al. Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): Scale presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2008, 23, 2129–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, C.; Eden, G.; Chang, A.; Demanuele, C.; Kelley Erb, M.; Shaafi Kabiri, N.; Moss, M.; Bhangu, J.; Thomas, K. Quantification of discrete behavioral components of the MDS-UPDRS. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 61, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrouillet, P.; Bernardin, S.; Camos, V. Time constraints and resource sharing in adults’ working memory spans. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2004, 133, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insel, T.R. Digital Phenotyping: Technology for a New Science of Behavior. JAMA 2017, 318, 1215–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arigo, D.; Jake-Schoffman, D.E.; Wolin, K.; Beckjord, E.; Hekler, E.B.; Pagoto, S.L. The history and future of digital health in the field of behavioral medicine. J. Behav. Med. 2019, 42, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attal, F.; Mohammed, S.; Dedabrishvili, M.; Chamroukhi, F.; Oukhellou, L.; Amirat, Y. Physical Human Activity Recognition Using Wearable Sensors. Sensors 2015, 15, 31314–31338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Sit | Sit-to-Stand | Stand | Walk | Stand-to-Sit | Weighted | Mean ± Std. of | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Accuracy | Average Accuracy | ||||||
| With long-term tracking | |||||||
| Validation | 92.8 | 68.1 | 81.5 | 78.9 | 70.7 | 82.00 | 79.85 ± 2.38 |
| Test | 91.6 | 75.0 | 85.7 | 81.0 | 78.6 | 83.97 | - |
| Without long-term tracking | |||||||
| Validation | 90.9 | 88.1 | 91.0 | 71.8 | 75.8 | 84.04 | 71.42 ± 10.32 |
| Test | 72.6 | 63.9 | 81.6 | 51.7 | 16.3 | 63.14 | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rezaei, B.; Christakis, Y.; Ho, B.; Thomas, K.; Erb, K.; Ostadabbas, S.; Patel, S. Target-Specific Action Classification for Automated Assessment of Human Motor Behavior from Video. Sensors 2019, 19, 4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194266
Rezaei B, Christakis Y, Ho B, Thomas K, Erb K, Ostadabbas S, Patel S. Target-Specific Action Classification for Automated Assessment of Human Motor Behavior from Video. Sensors. 2019; 19(19):4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194266
Chicago/Turabian StyleRezaei, Behnaz, Yiorgos Christakis, Bryan Ho, Kevin Thomas, Kelley Erb, Sarah Ostadabbas, and Shyamal Patel. 2019. "Target-Specific Action Classification for Automated Assessment of Human Motor Behavior from Video" Sensors 19, no. 19: 4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194266
APA StyleRezaei, B., Christakis, Y., Ho, B., Thomas, K., Erb, K., Ostadabbas, S., & Patel, S. (2019). Target-Specific Action Classification for Automated Assessment of Human Motor Behavior from Video. Sensors, 19(19), 4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194266





