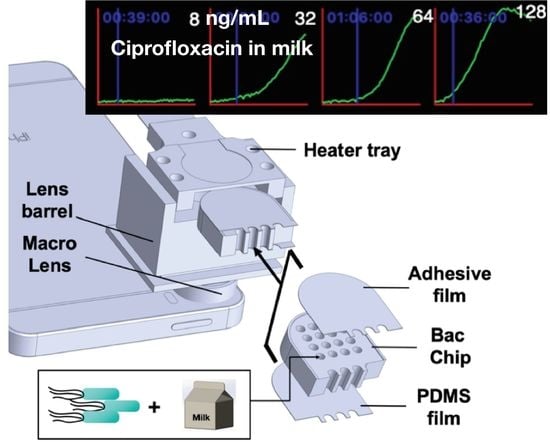
A Smartphone-Based Whole-Cell Array Sensor for Detection of Antibiotics in Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
2.1. LCS System Design
2.2. Fabrication of PDMS Layer on BacChip
2.3. Preparation of Bacteria
2.4. CIP Preparation and Bioreporter Stimulation
2.5. Smartphone Application for Image Capture, Processing, and Analysis
2.6. Measurement of Absolute Sensitivity of the LCS System
3. Results
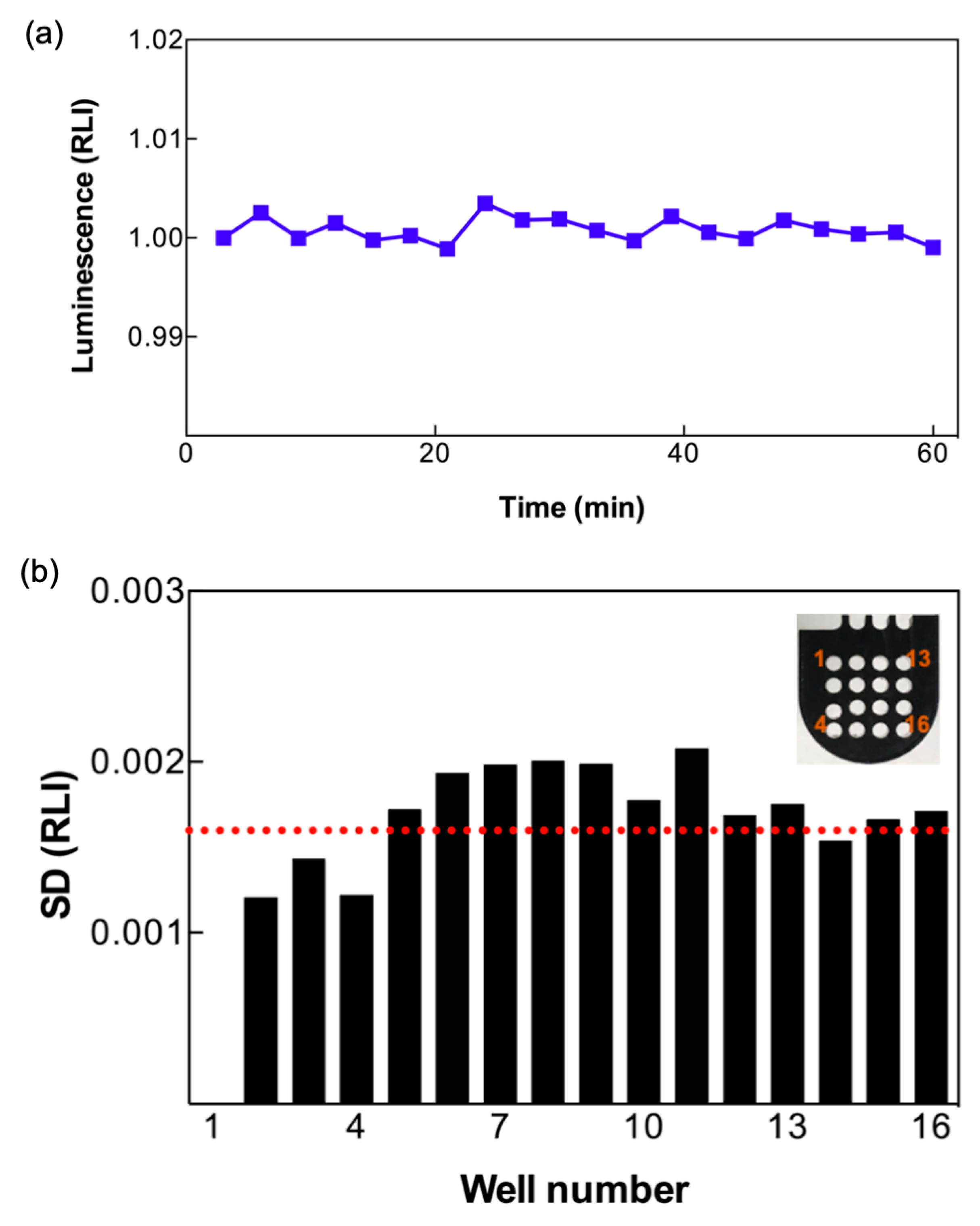
3.1. Photon Sensitivity of LCS System
3.2. Stability and Homogeneity of Bioluminescence Detection in the LCS System
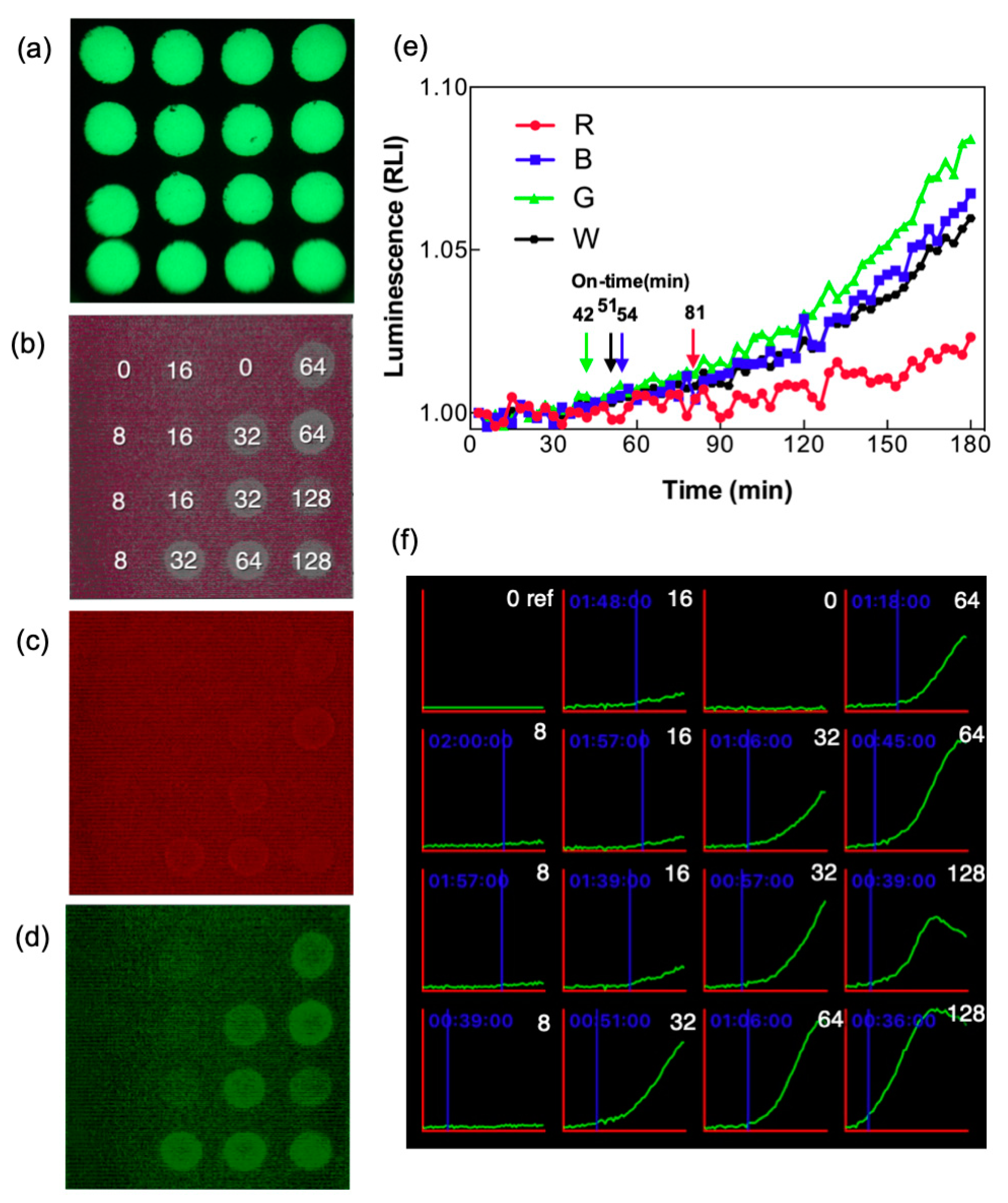
3.3. Enhancement of Signal Using Color Separation for Image Analysis
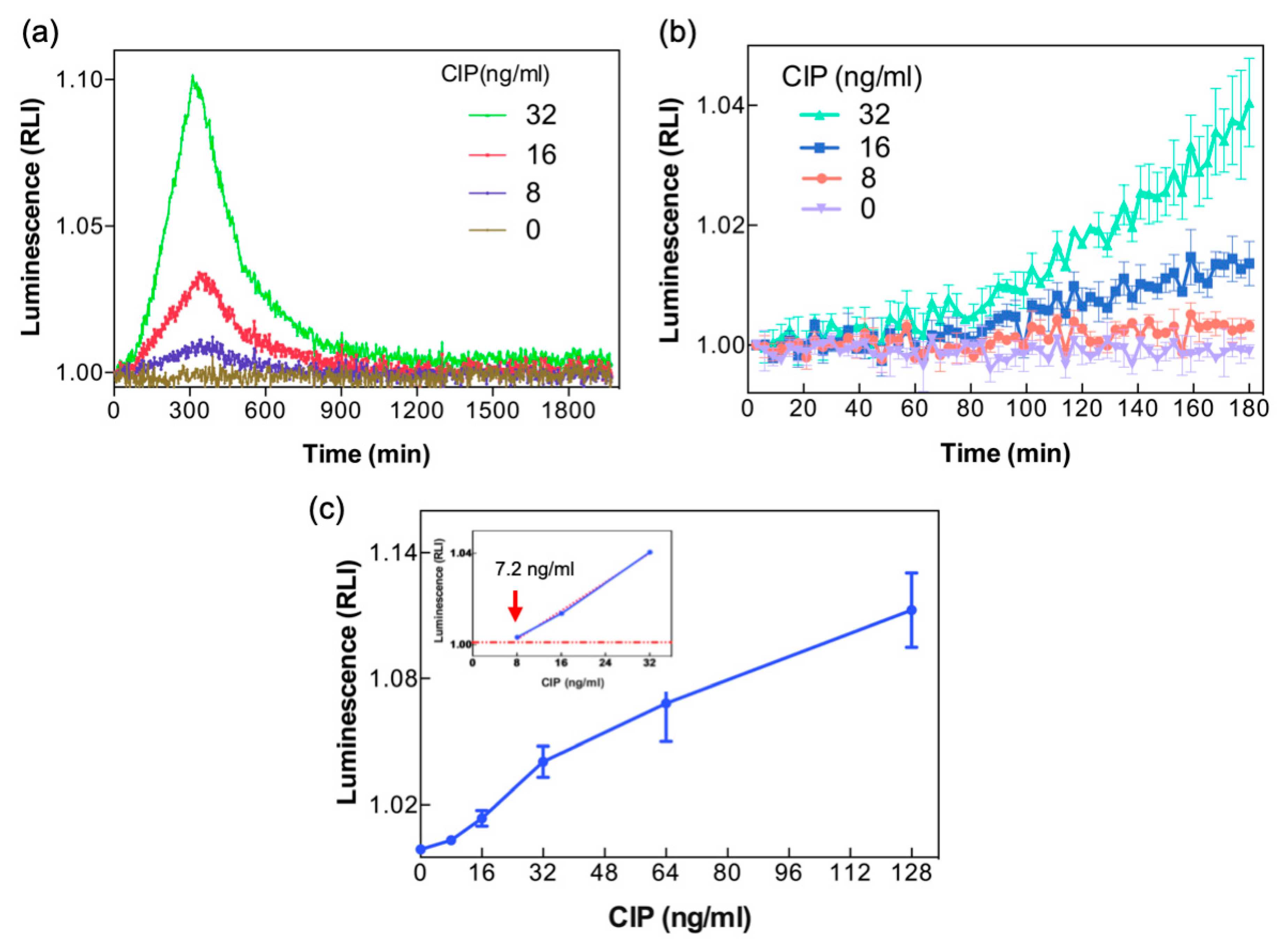
3.4. Detection of CIP in Whole Milk
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bbosa, G.S.; Mwebaza, N. Global irrational antibiotics/antibacterial drugs use: A current and future health and environmental consequences. In Microbial Pathogens and Strategies for Combating Them: Science, Technology and Education; Méndez-Vilas, A., Ed.; Formatex Research Center: Badajoz, Spain, 2013; pp. 1645–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Gandra, S.; Ashok, A.; Caudron, Q.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global antibiotic consumption 2000 to 2010: An analysis of national pharmaceutical sales data. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union Commission Regulation No 37/2010. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/health/files/files/eudralex/vol-5/reg_2010_37/reg_2010_37_en.pdf (accessed on 8 September 2019).
- Tang, Q.; Yang, T.; Tan, X.; Luo, J. Simultaneous determination of fluoroquinolone antibiotic residues in milk sample by solid-phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 4535–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiesa, L.M.; Nobile, M.; Panseri, S.; Biolatti, B.; Cannizzo, F.T.; Pavlovic, R.; Arioli, F.A. Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Detection of Antimicrobial Agents from Seven Classes in Calf Milk Replacers: Validation and Application. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2635–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valtonen, S.J.; Kurittu, J.S.; Karp, M.T. A luminescent Escherichia coli biosensor for the high throughput detection of beta-lactams. J. Biomol. Screen. 2002, 7, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virolainen, N.E.; Pikkemaat, M.G.; Elferink, J.W.; Karp, M.T. Rapid detection of tetracyclines and their 4-epimer derivatives from poultry meat with bioluminescent biosensor bacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 11065–11070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Meer, J.R.; Belkin, S. Where microbiology meets microengineering: Design and applications of reporter bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melamed, S.; Lalush, C.; Elad, T.; Yagur-Kroll, S.; Belkin, S.; Pedahzur, R. A bacterial reporter panel for the detection and classification of antibiotic substances. Microb. Biotechnol. 2012, 5, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamed, S.; Naftaly, S.; Belkin, S. Improved detection of antibiotic compounds by bacterial reporter strains achieved by manipulations of membrane permeability and efflux capacity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 2267–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Yoav, H.; Melamed, S.; Freeman, A.; Shacham-Diamand, Y.; Belkin, S. Whole-cell biochips for bio-sensing: Integration of live cells and inanimate surfaces. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2011, 31, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.F.; Tsai, Y.C.; Yagur-Kroll, S.; Palevsky, N.; Belkin, S.; Cheng, J.Y. Water pollutant monitoring by a whole cell array through lens-free detection on CCD. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, W.C.; Belkin, S.; Cheng, J.Y. Microbial biosensing of ciprofloxacin residues in food by a portable lens-free CCD-based analyzer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roda, A.; Mirasoli, M.; Michelini, E.; Di Fusco, M.; Zangheri, M.; Cevenini, L.; Roda, B.; Simoni, P. Progress in chemical luminescence-based biosensors: A critical review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Q. Biosensors and bioelectronics on smartphone for portable biochemical detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Z.; Lv, X.; Su, Y.; Chen, H. Recent Progress in Optical Biosensors Based on Smartphone Platforms. Sensors 2017, 17, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkel, J.M. Pocket laboratories. Nature 2017, 545, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesada-Gonzalez, D.; Merkoci, A. Mobile phone-based biosensing: An emerging diagnostic and communication technology. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xu, D.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Ma, X.; Guo, J. Smartphone-based analytical biosensors. Analyst 2018, 143, 5339–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchi, S.; Sabela, M.I.; Mdluli, P.S.; Inamuddin; Bisetty, K. Smartphone based bioanalytical and diagnosis applications: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Chakravarty, S.; Choi, W.; Lee, K.; Han, D.; Hwang, H.; Choi, J.; Jung, H.I. Mobile diagnostics: Next-generation technologies for in vitro diagnostics. Analyst 2018, 143, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wu, J.; Santos, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Lin, F. Recent development of portable imaging platforms for cell-based assays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 124–125, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevenini, L.; Calabretta, M.M.; Tarantino, G.; Michelini, E.; Roda, A. Smartphone-interfaced 3D printed toxicity biosensor integrating bioluminescent “sentinel cells”. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 225, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevenini, L.; Lopreside, A.; Calabretta, M.M.; D’Elia, M.; Simoni, P.; Michelini, E.; Roda, A. A novel bioluminescent NanoLuc yeast-estrogen screen biosensor (nanoYES) with a compact wireless camera for effect-based detection of endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Jung, Y.; Doh, I.J.; Lozano-Mahecha, R.A.; Applegate, B.; Bae, E. Smartphone-based low light detection for bioluminescence application. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escher, A.; O’Kane, D.J.; Lee, J.; Szalay, A.A. Bacterial luciferase alpha beta fusion protein is fully active as a monomer and highly sensitive in vivo to elevated temperature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 6528–6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregor, C.; Gwosch, K.C.; Sahl, S.J.; Hell, S.W. Strongly enhanced bacterial bioluminescence with the ilux operon for single-cell imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddings, M.A.; Gale, B.K. A PDMS-based gas permeation pump for on-chip fluid handling in microfluidic devices. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 2396–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagur-Kroll, S.; Bilic, B.; Belkin, S. Strategies for enhancing bioluminescent bacterial sensor performance by promoter region manipulation. Microb. Biotechnol. 2010, 3, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Method of Test for Veterinary Drug Residues in Foods-Method for Multiresidue Analysis. Available online: https://www.fda.gov.tw/tc/includes/GetFile.ashx?mid=189&id=28380 (accessed on 8 September 2019).
- Kamberi, M.; Tsutsumi, K.; Kotegawa, T.; Nakamura, K.; Nakano, S. Determination of ciprofloxacin in plasma and urine by HPLC with ultraviolet detection. Clin. Chem. 1998, 44, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pinacho, D.G.; Sánchez-Baeza, F.; Pividori, M.-I.; Marco, M.-P. Electrochemical Detection of Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics in Milk Using a Magneto Immunosensor. Sensors 2014, 14, 15965–15980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Sheng, W.; Wang, S. Development and Validation of a Reproducible and Label-Free Surface Plasmon Resonance Immunosensor for Enrofloxacin Detection in Animal-Derived Foods. Sensors 2017, 17, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Luo, L.; Suryoprabowo, S.; Peng, J.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. Development of an immunochromatographic strip test for rapid detection of ciprofloxacin in milk samples. Sensors 2014, 14, 16785–16798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Wong, H. Predicting Oral Drug Absorption: Mini Review on Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Models. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuvonen, P.J.; Kivistö, K.T.; Lehto, P. Interference of dairy products with the absorption of ciprofloxacin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1991, 50, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rateni, G.; Dario, P.; Cavallo, F. Smartphone-Based Food Diagnostic Technologies: A Review. Sensors 2017, 17, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, K.H.; Chen, P.H.; Lin, C.; Chen, C.F.; Lee, I.R.; Yeh, Y.C. Determination of Gold Ions in Human Urine Using Genetically Engineered Microorganisms on a Paper Device. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes-Halldorson, V.D.S.; Duran, N.L. Bioluminescent bacteria: Lux genes as environmental biosensors. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2003, 34, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheerer, S.; Gomez, F.; Lloyd, D. Bioluminescence of Vibrio fischeri in continuous culture: Optimal conditions for stability and intensity of photoemission. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2006, 67, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, M.-Y.; Kao, W.-C.; Belkin, S.; Cheng, J.-Y. A Smartphone-Based Whole-Cell Array Sensor for Detection of Antibiotics in Milk. Sensors 2019, 19, 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19183882
Lu M-Y, Kao W-C, Belkin S, Cheng J-Y. A Smartphone-Based Whole-Cell Array Sensor for Detection of Antibiotics in Milk. Sensors. 2019; 19(18):3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19183882
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Mei-Yi, Wei-Chen Kao, Shimshon Belkin, and Ji-Yen Cheng. 2019. "A Smartphone-Based Whole-Cell Array Sensor for Detection of Antibiotics in Milk" Sensors 19, no. 18: 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19183882
APA StyleLu, M.-Y., Kao, W.-C., Belkin, S., & Cheng, J.-Y. (2019). A Smartphone-Based Whole-Cell Array Sensor for Detection of Antibiotics in Milk. Sensors, 19(18), 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19183882