Raman Analysis of Tear Fluid Alteration Following Contact Lense Use
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Contact Lenses
2.3. Experimental Set-Up
2.4. Raman Spectra Acquisition and Processing
3. Results and Discussion
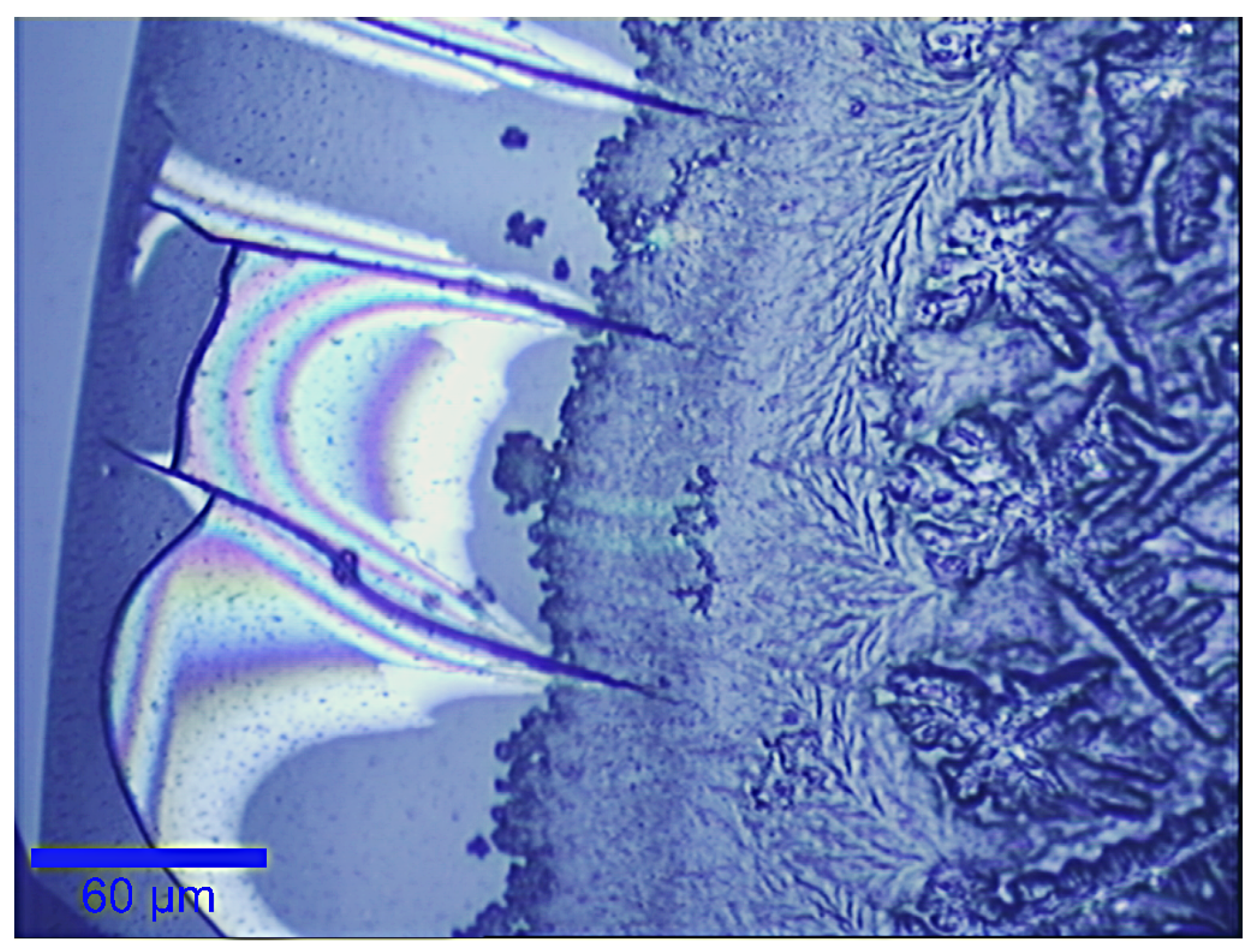
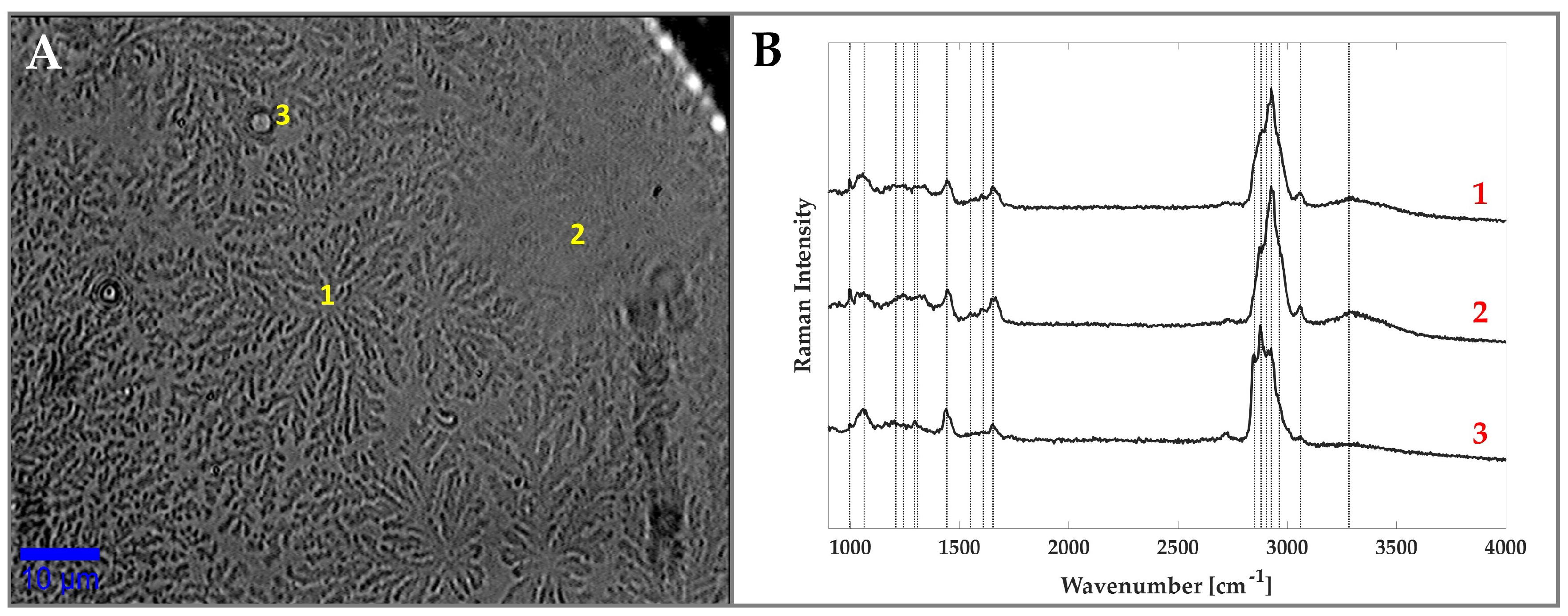
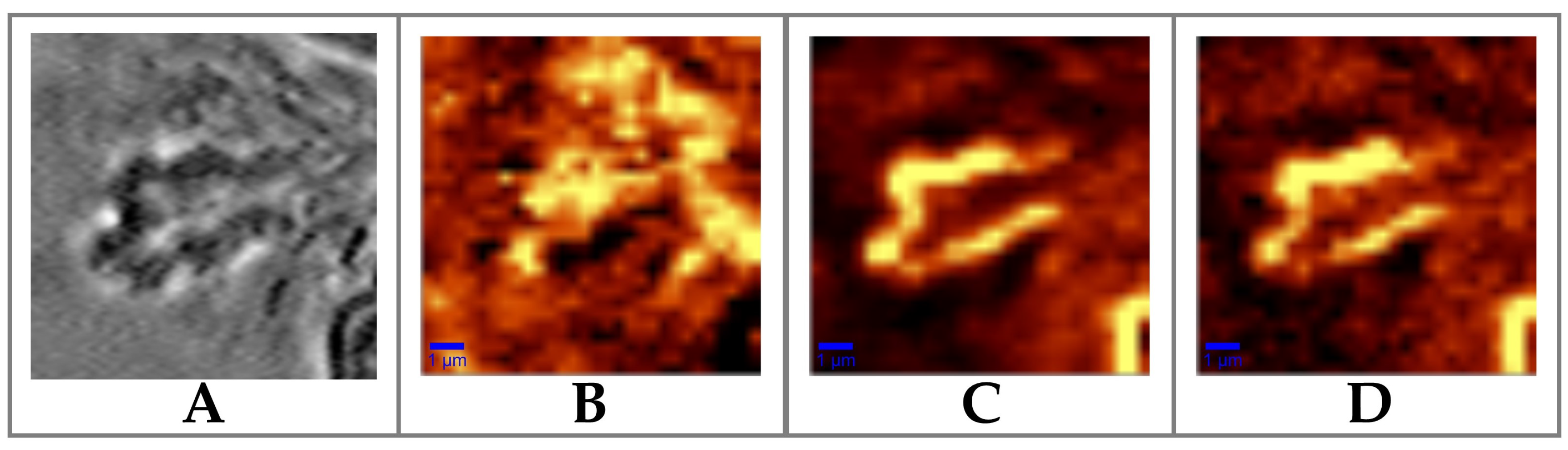
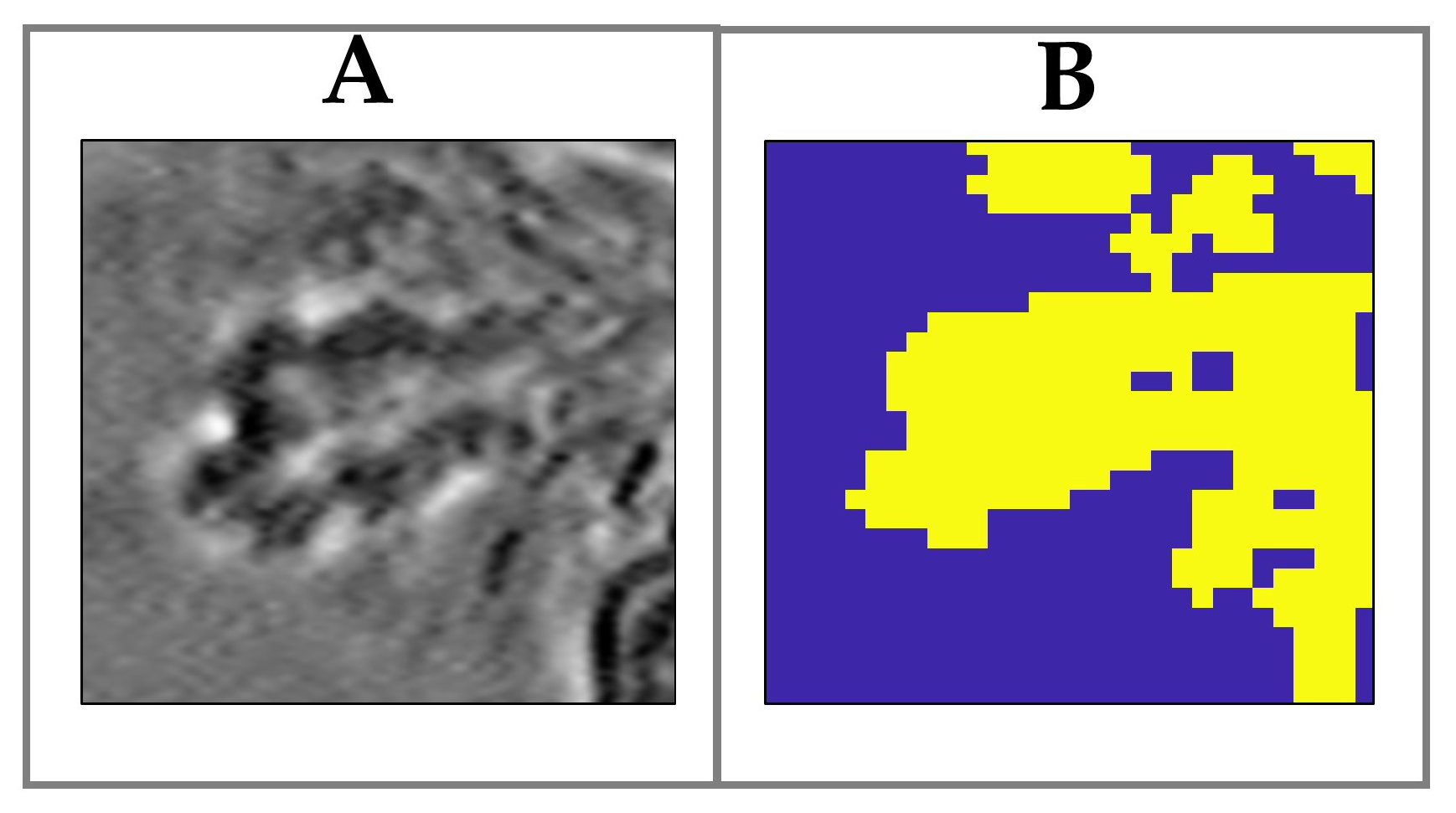
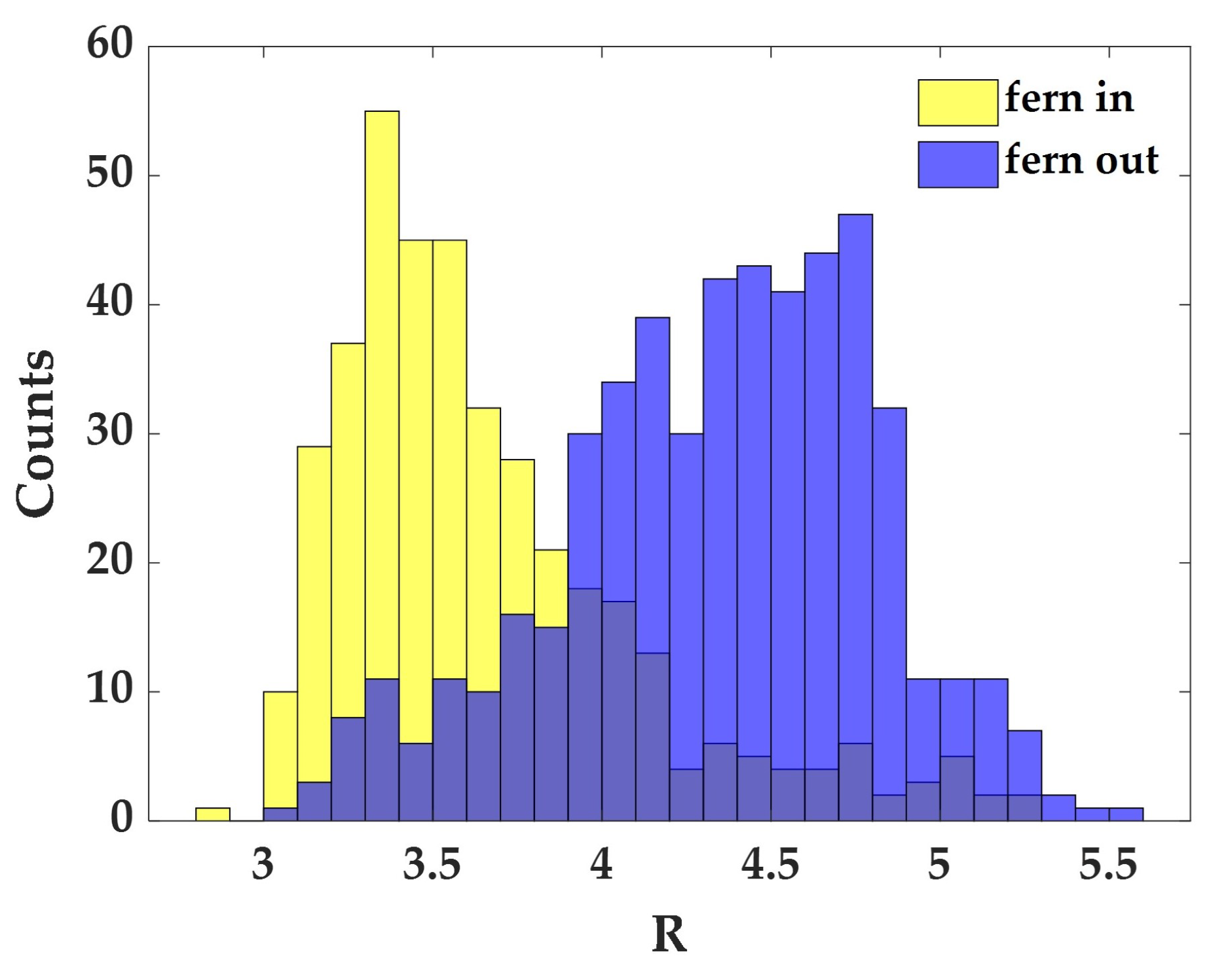
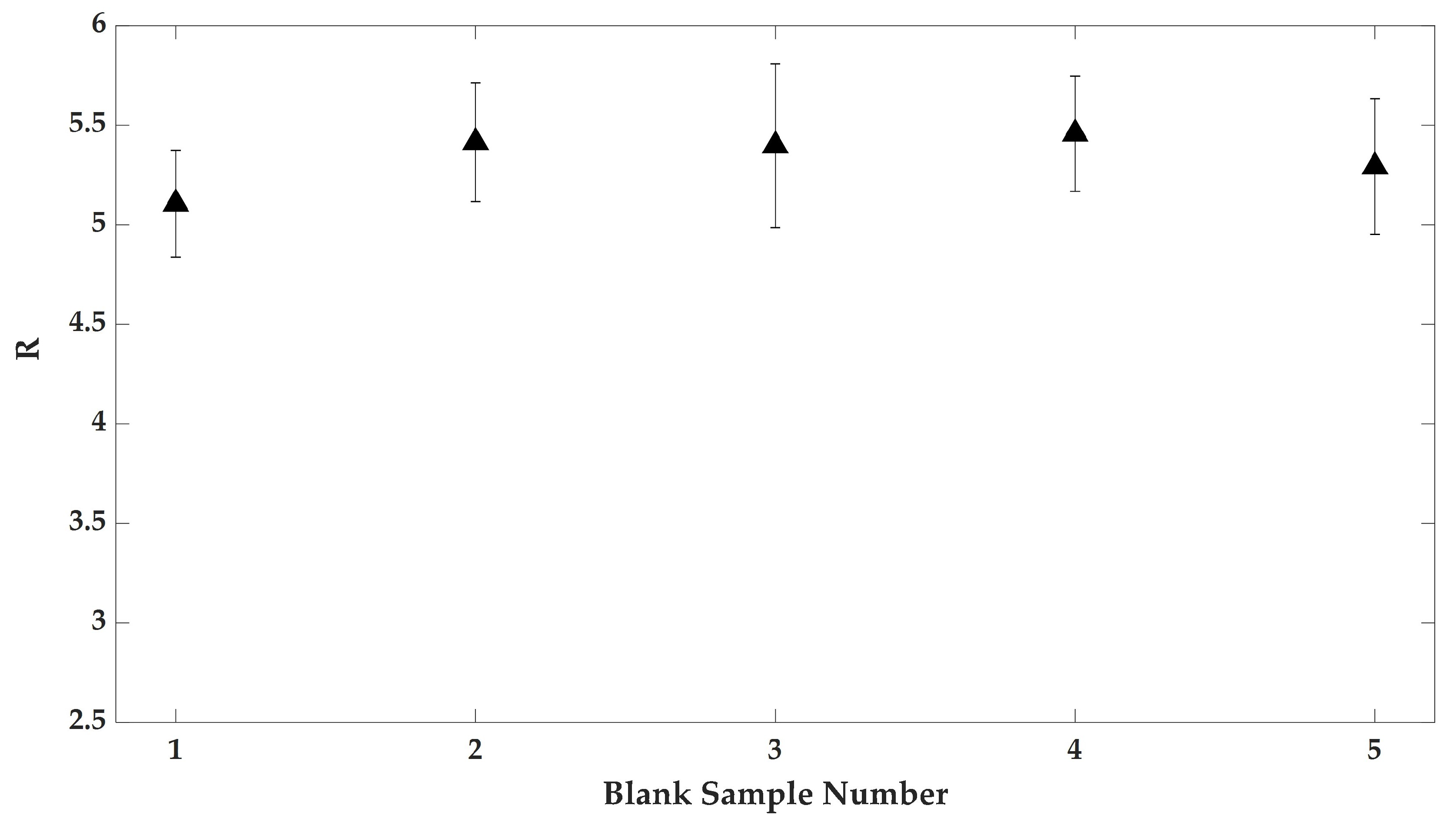
3.1. Raman Analysis of Human Tears
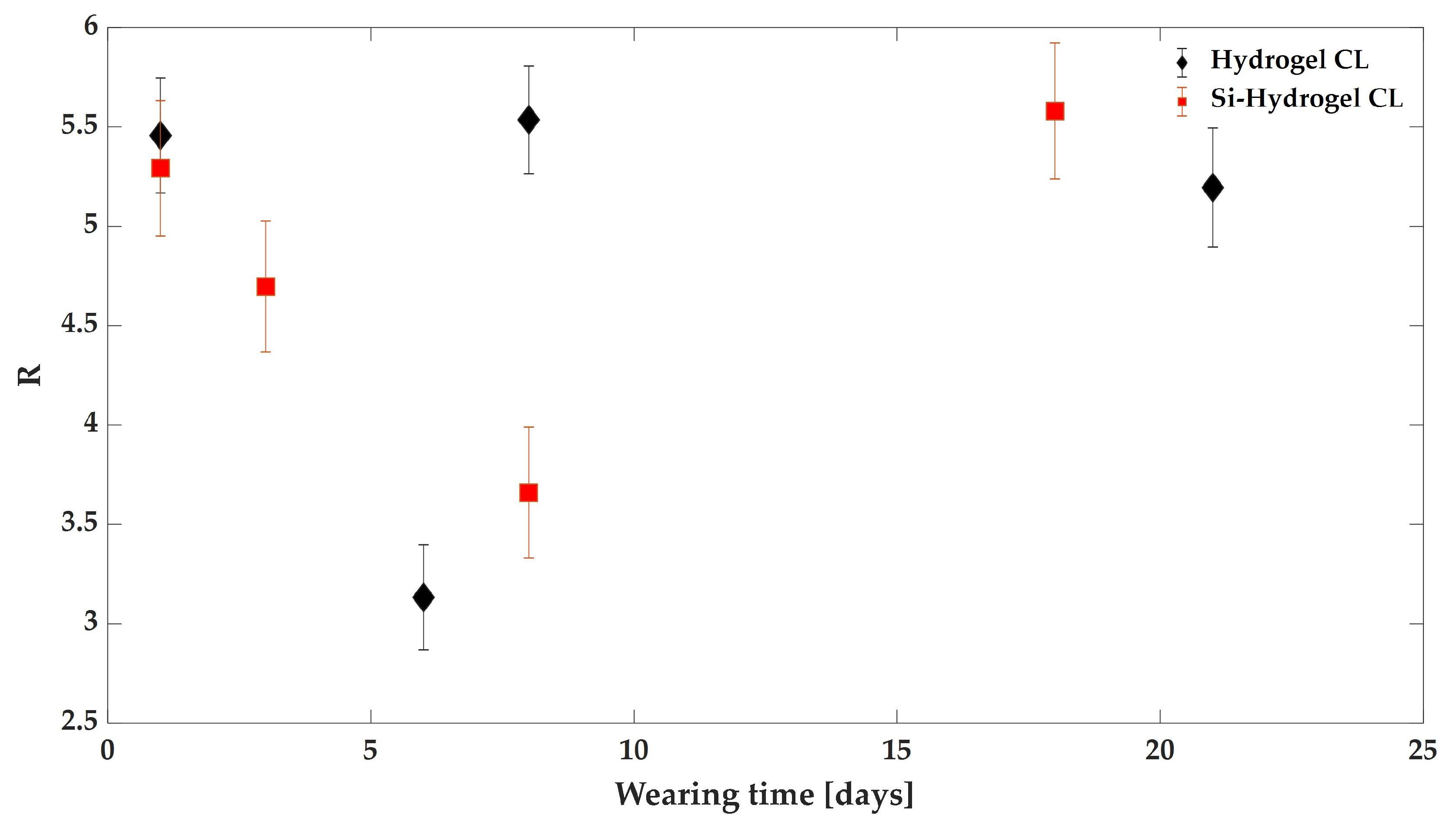
3.2. The Effect of Wearing CLs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CLs | Contact Lenses |
| RS | Raman Spectroscopy |
| DCDRS | Drop Coating Deposition Raman Spectroscopy |
| H-CLs | Hydrogel Contact Lens |
| SH-CLs | Silicon Hydrogel Contact Lens |
References
- Rantamaki, A.H.; Seppanen-Laakso, T.; Oresic, M.; Jauhiainen, M.; Holopainen, J.M. Human Tear Fluid Lipidome: From Composition to Function. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.M.; Tong, L.; Duan, X.; Petznick, A.; Wenk, M.R.; Shui, G. Extensive characterization of human tear fluid collected using different techniques unravels the presence of novel lipid amphiphiles. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jae Hun, J.; Yong Woo, J.; Ho Sik, H.; Jae Won, O.; Hyun Chang, K.; Hyung Keun, L.; Kwang Pyo, K. Proteomic analysis of human lacrimal and tear fluid in dry eye disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13363. [Google Scholar]
- Cwiklik, L. Tear film lipid layer: A molecular level view. BBA Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 2421–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, A.; Tighe, B. Contact lens interactions with the tear film. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 117, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiner, J.; Allansmith, M. Effect of Contact Lens Wear on the Conjunctival Mucous System. Ophthalmology 1981, 88, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.; Senchyna, M.; Glasier, M.; Schickler, J.; Forbes, I.; Louie, D.; May, C. Lysozyme and Lipid Deposition on Silicone Hydrogel Contact Lens Materials. Eye Contact Lens 2003, 29, S75–S79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaud, L.; van der Worp, E.; Brazeau, D.; Warde, R.; Giasson, C. Predicting estimates of oxygen transmissibility for scleral lenses. Cont. Lens. Anterior Eye 2012, 35, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maissa, C.; Franklin, V.; Guillon, M.; Tighe, B. Influence of contact lens material surface characteristics and replacement frequency on protein and lipid deposition. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1998, 75, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picarazzi, S.; Bergamaschi, D.; Tavazzi, S. Differences between tears of contact lens wearers studied by photon correlation spectroscopy. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2019, 42, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntz, A.; Subbaraman, L.; Sorbara, L.; Jones, L. Tear exchange and contact lenses: A review. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2015, 8, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammer, R. Effect of Contact Lens Wear on Tear Film Break up Time (TBUT) among Contact Lenses Users. Pak. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 33, 182–186. [Google Scholar]
- Filik, J.; Stone, N. Raman point mapping of tear ferning patterns. Proc. SPIE 2008, 6853, 685309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filik, J.; Stone, N. Analysis of human tear fluid by Raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 616, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filik, J.; Stone, N. Investigation into the protein composition of human tear fluid using centrifugal filters and drop coating deposition Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2008, 40, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Zheng, X.; Zong, C.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Ren, B. Drop-coating deposition and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopies (DCDRS and SERS) provide complementary information of whole human tears. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2014, 45, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camerlingo, C.; Lisitskiy, M.; Lepore, M.; Portaccio, M.; Montorio, D.; Del Prete, S.; Cennamo, G. Characterization of Human Tear Fluid by Means of Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Sensors 2019, 19, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Moon, S.; Shin, J.; Park, H.; Jin, K. Label-free biochemical method for early detection of Adenoviral conjuctivitis using human tear biofluids. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 11093–11099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omali, N. Quantification of individual proteins in silicone hydrogel contact lens deposits. Mol. Vis. 2013, 19, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Golding, T.; Brennan, N. The basis of tear ferning. Clin. Exp. Optom. 1989, 72, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murube, J. Tear Crystallization Test: Two Centuries of History. Ocul. Surf. 2004, 2, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, E.; Tomlinson, A. Spatial location studies on the chemical composition of human tear ferns. Ophthal. Physiol. Opt. 2000, 20, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, K.; Carpenter, S.; Freyer, J.; Mourant, J. Raman Spectroscopy Detects Biochemical Changes Due to Proliferation in Mammalian Cell Cultures. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 4274–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gniadecka, M.; Faurskov Nielsen, O.; Christensen, D.; Wulf, H. Structure of Water, Proteins, and Lipids in Intact Human Skin, Hair, and Nail. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1998, 4, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, N.; Kendall, C.; Smith, J.; Crow, P.; Barr, H. Raman spectroscopy for identification of epithelial cancers. Faraday Discuss. 2004, 126, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnier, R.; Byrne, H. Understanding the Molecular Information Contained in Principal Component Analysis of Vibrational Spectra of Biological Systems. Analyst 2012, 137, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schie, I.; Huser, T. Methods and applications of Raman microspectroscopy to single-cell analysis. Appl. Spectrosc. 2013, 67, 813–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polis, B.; Imiela, A.; Polis, L.; Abramczyk, H. Raman spectroscopy for medulloblastoma. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2018, 34, 2425–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Proprietary Name | LAC Monthly Wet | AirHydra |
| United States Adopted Name (USAN) | Wetafilcon | Genifilcon A |
| Classification | Hydrogel | Silicon Hydrogel |
| Water Content [%] | 55 | 45 |
| Dk/t | 19.5 | 70.0 |
| Wavenumber (cm) | Assignment | Wavenumber (cm) | Assignment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | Phe | 1605 | Phe |
| 1064 | Skeletal (CC)(l) | 1665 | Amide I |
| 1206 | Aromatic Amino Acids | 2845 | (CH) |
| 1242 | Amide III | 2875 | (CH) |
| 1296 | (CH) | 2930 | (CH) |
| 1301 | CH deformation (l) | 2960 | (CH) |
| 1440 | (CH)(p,l),(CH)(p) | 3057 | aromatic (CH) |
| 1553 | Trp | 3300 | (OH) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Capaccio, A.; Sasso, A.; Rusciano, G. Raman Analysis of Tear Fluid Alteration Following Contact Lense Use. Sensors 2019, 19, 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19153392
Capaccio A, Sasso A, Rusciano G. Raman Analysis of Tear Fluid Alteration Following Contact Lense Use. Sensors. 2019; 19(15):3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19153392
Chicago/Turabian StyleCapaccio, Angela, Antonio Sasso, and Giulia Rusciano. 2019. "Raman Analysis of Tear Fluid Alteration Following Contact Lense Use" Sensors 19, no. 15: 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19153392
APA StyleCapaccio, A., Sasso, A., & Rusciano, G. (2019). Raman Analysis of Tear Fluid Alteration Following Contact Lense Use. Sensors, 19(15), 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19153392






