Pure SH1 Guided-Wave Generation Method with Dual Periodic-Permanent-Magnet Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducers for Plates Inspection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Transduction Mechanism
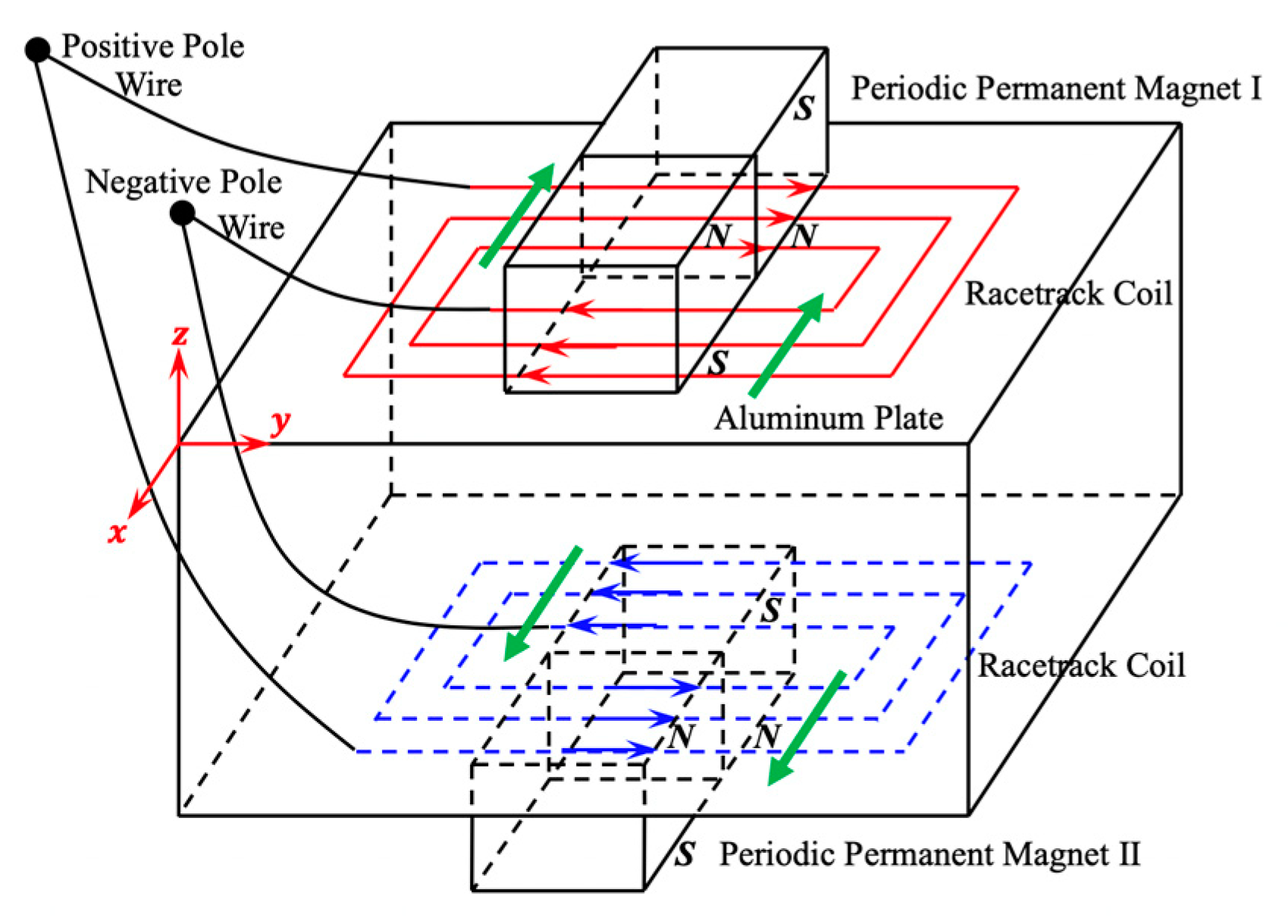
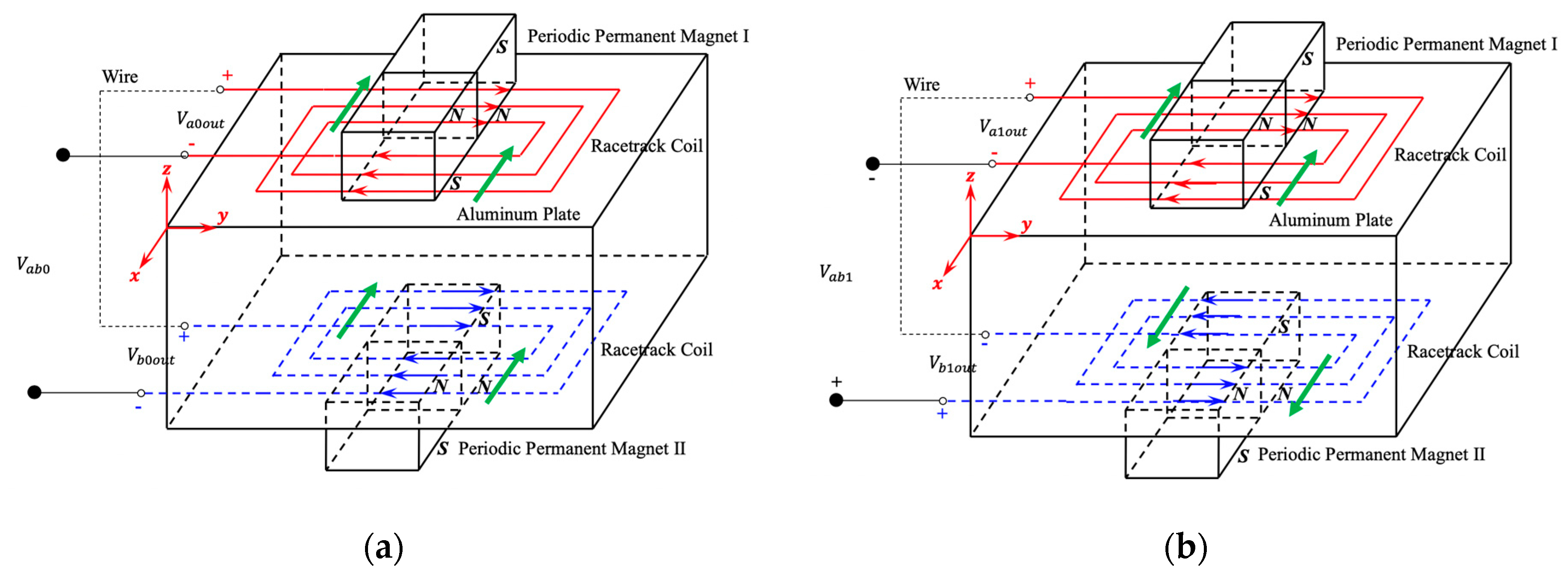
2.1. Excitation Mechanism
2.2. Receiving Mechanism
3. Simulation Analysis
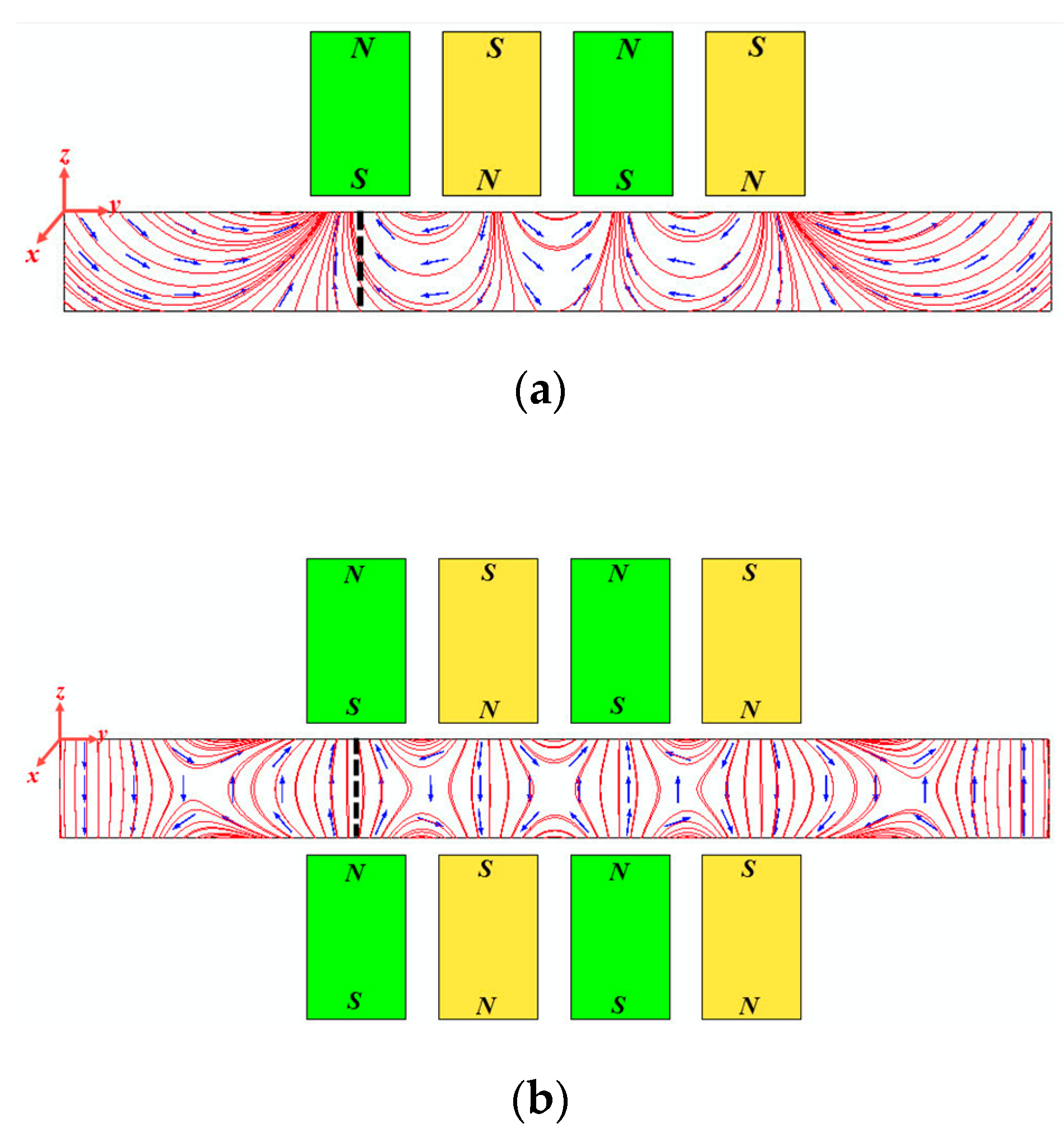
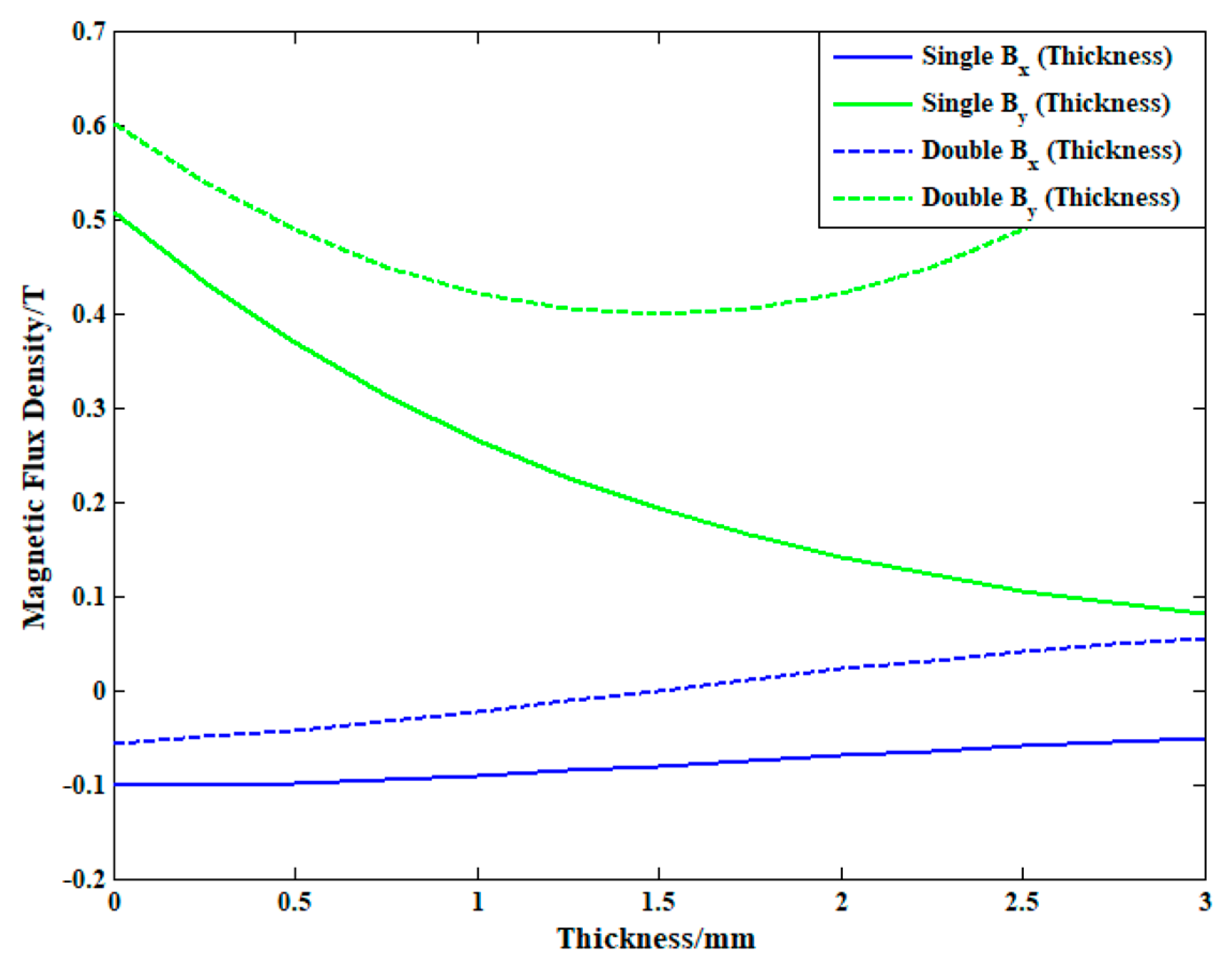
3.1. Distribution of Static Magnetic Field Induced by Conventional PPM EMATs and Dual PPM EMATs
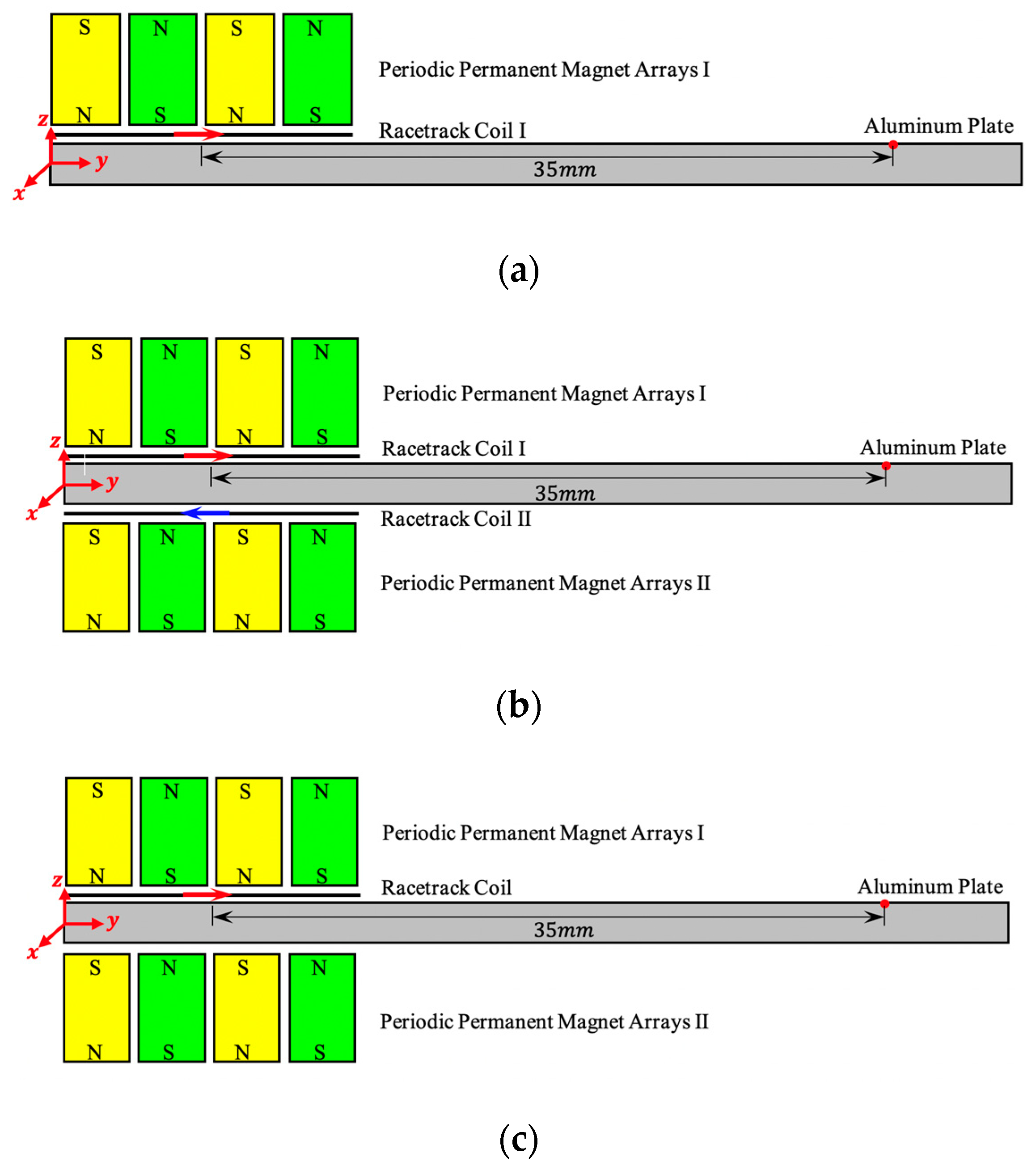
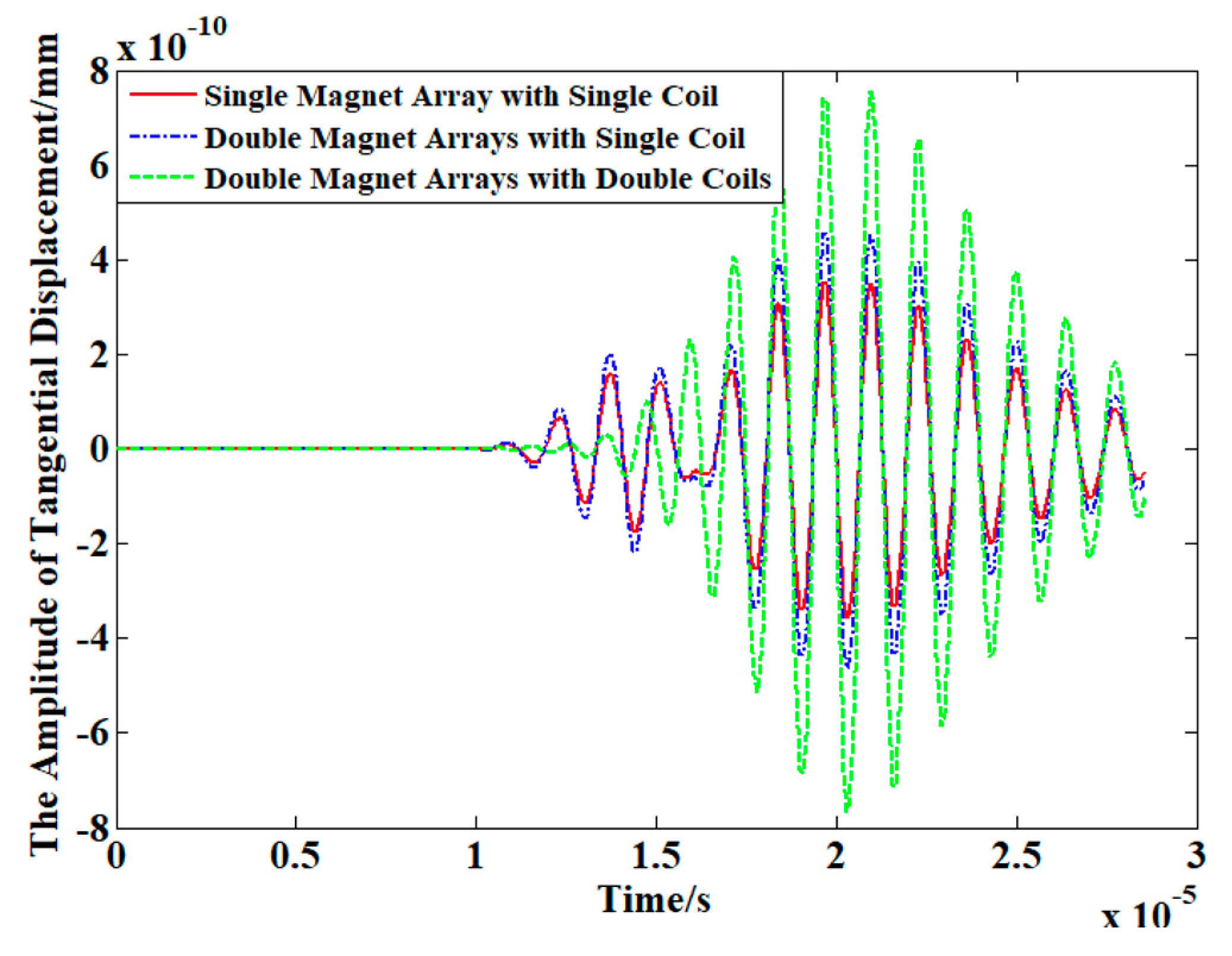
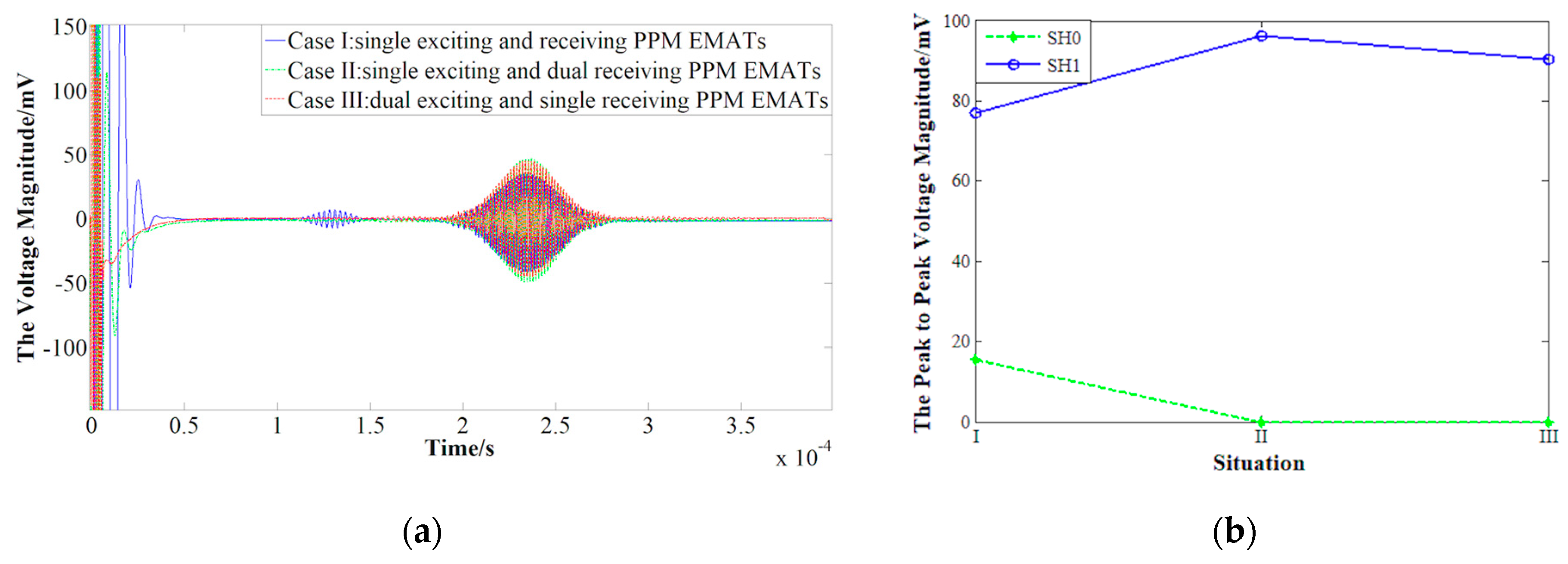
3.2. Signals Excited by Three PPM EMATs with Different Configurations
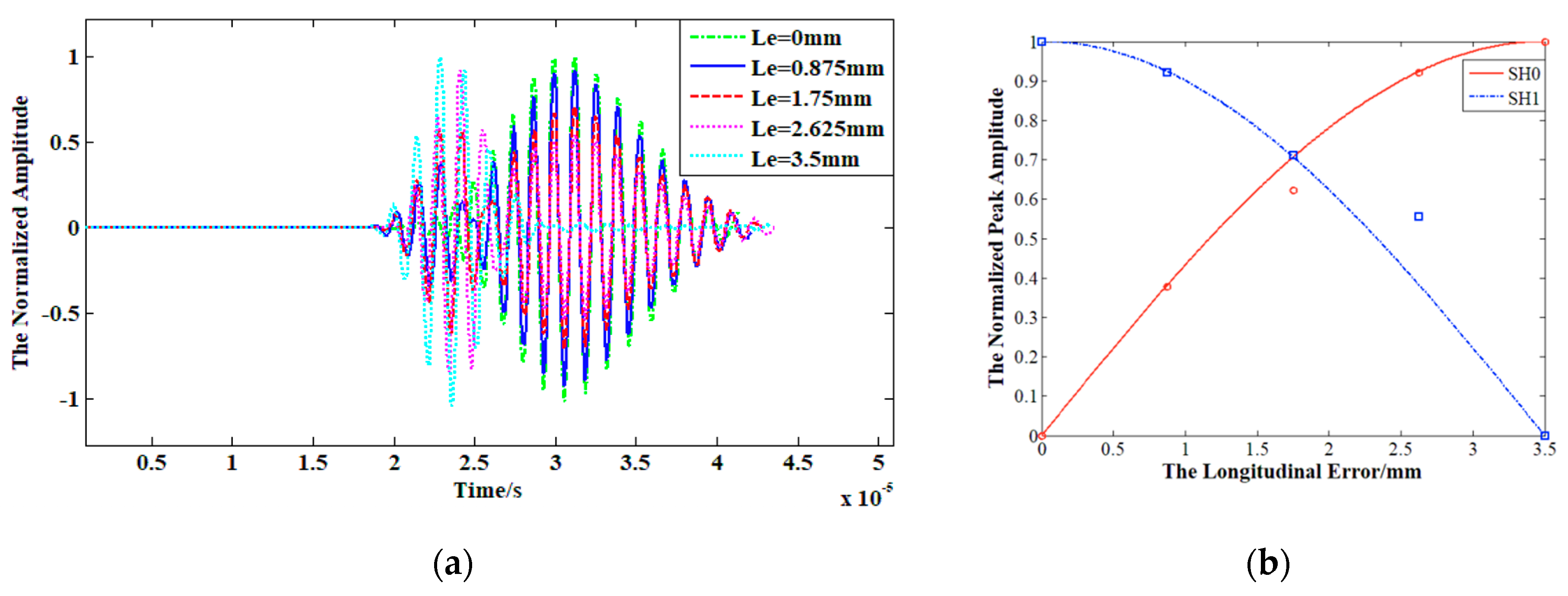
3.3. Effects of Position Errors of Dual PPM EMATs on Its Performances
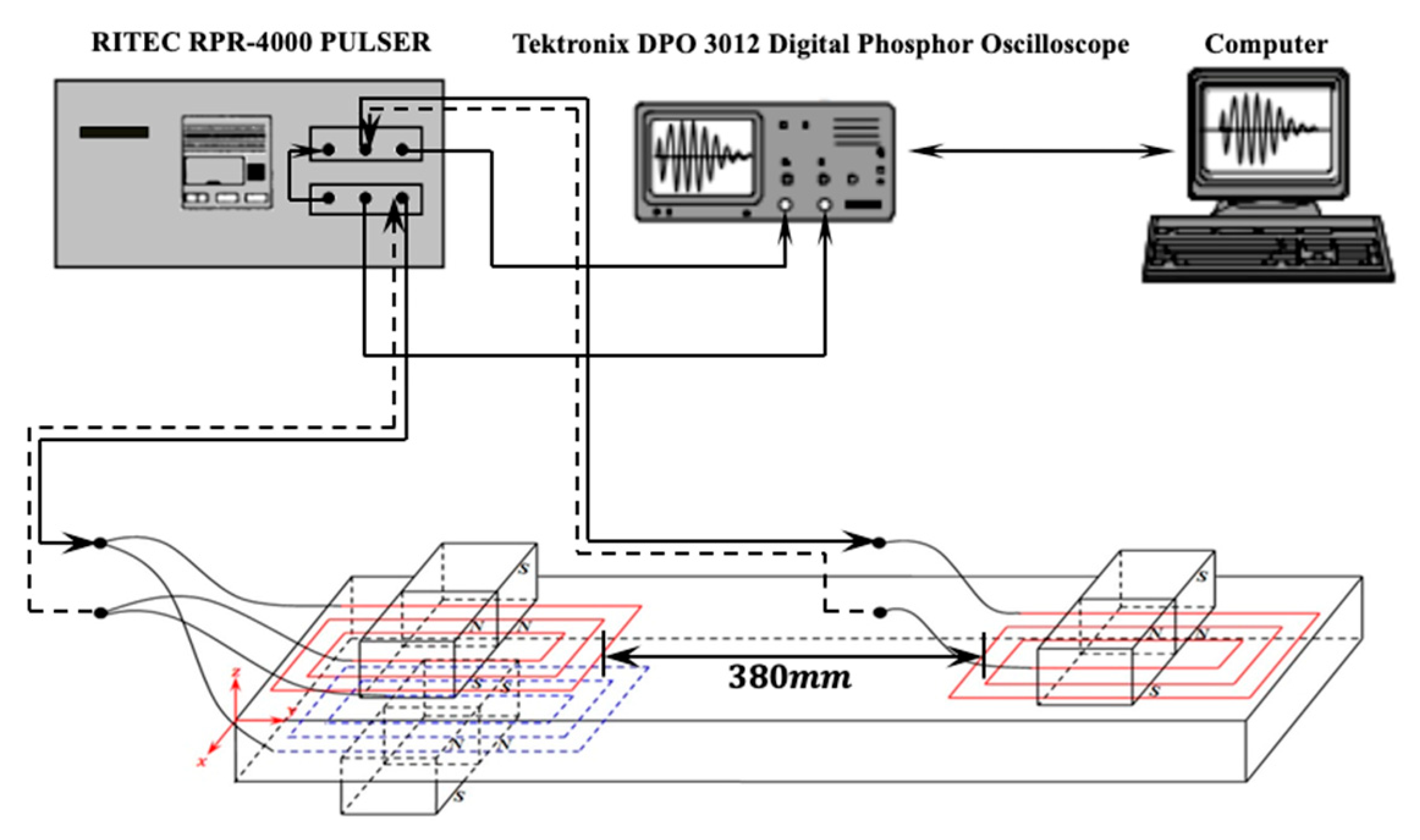
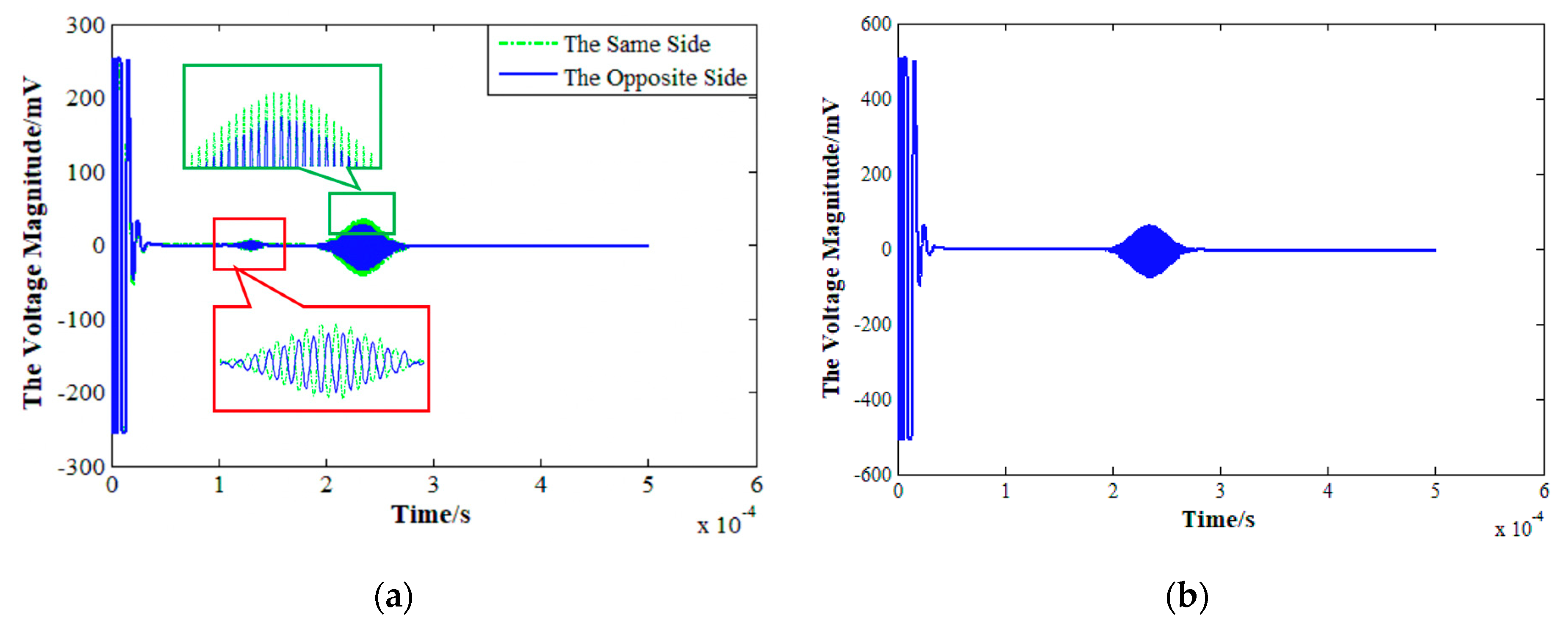
4. Experimental Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gajdacsi, A.; Cegla, F. High accuracy wall thickness loss monitoring. AIP Conf. Proc. 2014, 1581, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar]
- Alleyne, D.N.; Pavlakovic, B.; Lowe, M.J.S.; Cawley, P. Rapid, long range inspection of chemical plant pipework using guided waves. AIP Conf. Proc. 2001, 557, 180–187. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, P.B.; Simonetti, F.; Instanes, G. Corrosion and erosion monitoring in plates and pipes using constant group velocity lamb wave inspection. Ultrasonics 2014, 54, 1832–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Royer, R.L., Jr.; Rose, J.L. Ultrasonic guided wave imaging techniques in structural health monitoring. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2010, 21, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volker, A.; Bloom, J.; Thompson, D.O.; Chimenti, D.E. Experimental results of guided wave travel time tomography. Rev. Prog. Quant. Nondestruct. Eval. 2011, 30, 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Huthwaite, P.; Simonetti, F. High-resolution guided wave tomography. Wave Motion 2013, 50, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instanes, G.; Lakshminarayan, B.; Toppe, M.; Nagy, P.B. The use of non-intrusive ultrasonic intelligent sensors for corrosion and erosion monitoring. In Proceedings of the SPE International Conference on Oilfield Corrosion, Aberdeen, UK, 24–25 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Volker, A.; Van Zon, T.; Hsu, M.; Boogert, L. 1-D profiling using highly dispersive guided waves. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1706, 30001. [Google Scholar]
- Jenot, F.; Ouaftouh, M.; Ourak, M.; Duquennoy, M. Corrosion thickness gauging in plates using Lamb wave group velocity measurements. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunko, C.; King, R.; Tan, M. Nondestructive evaluation of planar defects in plates using low frequency shear horizontal waves. J. Appl. Phys. 1982, 53, 3450–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribichini, R. Modelling of Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducers. Ph.D. Thesis, Imperial College London, London, UK, October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ribichini, R.; Cegla, F.; Nagy, P.B.; Cawley, P. Study and Comparison of Different EMAT Configurations for SH Wave Inspection. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2011, 58, 2571–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, S.A.; Nakamura, N.; Ogi, H.; Hirao, M. Mode conversion of SH guided waves at defects for pipeline inspection. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Review of Progress in Quantitative Nondestructive Evaluation, Chicago, IL, USA, 20–25 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nurmalia, H.; Nakamura, N.; Ogi, H.; Hirao, M. Detection of SH guided waves propagating in aluminum plate with thinning region. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 50, 07HC17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmalia, H.; Nakamura, N.; Ogi, H.; Hirao, M.; Nakahata, K. Mode conversion behavior of SH guided wave in a tapered plate. NDT E Int. 2012, 45, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirao, M.; Ogi, H. An SH-wave EMAT technique for gas pipeline inspection. NDT E Int. 1999, 32, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carandente, R.; Ma, J.; Cawley, P. The scattering of the fundamental torsional mode from axi-symmetric defects with varying depth profile in pipes. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 127, 3440–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andruschak, N.; Saletes, I.; Filleter, T.; Sinclair, A. An NDT guided wave technique for the identification of corrosion defects at support locations. NDT E Int. 2015, 75, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, R.; Cegla, F. Detectability of corrosion damage with circumferential guided waves in reflection and transmission. NDT E Int. 2017, 91, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, R.; Cegla, F. On the probability of detecting wall thinning defects with dispersive circumferential guided waves. NDT E Int. 2017, 86, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Sun, P.; Li, J. Enhancement of the excitation efficiency of a torsional wave PPM EMAT array for pipe inspection by optimizing the element number of the array based on 3-D FEM. Sensors 2015, 15, 3471–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubrusly, A.C.; Freitas, M.A.; Von Der Weid, J.P.; Dixon, S. Mode selectivity of SH guided waves by dual excitation and reception applied to mode conversion analysis. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2018, 65, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maclauchlan, D.; Clark, S.; Cox, B. Recent advancements in the application of EMATs to NDE. In Proceedings of the 16th World Conference on NDT, Montreal, QC, Canada, 30 August–3 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Isla, J.; Cegla, F. Optimization of the bias magnetic field of shear wave EMATs. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2016, 63, 1148–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Zhang, C.; Dixon, S.; Zhao, H.; Hill, S.; Liu, M. Enhancement of ultrasonic signal using a new design of Rayleigh-wave electromagnetic acoustic transducer. NDT E Int. 2017, 86, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Jin, Z.; Yu, H. Influences of magnetic circuit structure of magnetostrictive guided wave transducer on the homogeneity of bias magnetic field. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2010, 33, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W. Multiphysics modeling of a Lorentz force-based meander coil electromagnetic acoustic transducer via steady-state and transient analyses. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 6641–6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, B.; Boonsang, S.; Dewhurst, R.J. A new magnetic configuration for a small in-plane electromagnetic acoustic transducer applied to laser-ultrasound measurements: Modelling and validation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 125, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, P.; Drozdz, M.; Skelton, E.A.; Lowe, M.J.; Craster, R.V. On the use of absorbing layers to simulate the propagation of elastic waves in unbounded isotropic media using commercially available Finite Element packages. NDT E Int. 2012, 51, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, M.J.; Cawley, P.; Kao, J.Y.; Diligent, O. The low-frequency reflection characteristics of the fundamental anti-symmetric Lamb wave a0 from a rectangular notch in a plate. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 112, 2612–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manogharan, P.; Yu, X.; Fan, Z.; Rajagopal, P. Interaction of shear horizontal bend (SHB) guided mode with defects. NDT E Int. 2015, 75, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Object | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Magnet | Width | 3 mm |
| Height | 5 mm | |
| Thickness | 4 mm | |
| Gap between adjacent magnets | 1 mm | |
| lift-off distance | 0.5 mm | |
| Magnetic flux density | 1.5 T | |
| Coil | Diameter | 0.3 mm |
| lift-off distance | 0.5 mm | |
| Resistivity | ||
| Aluminum Plate | Length | 50 mm |
| Width | 15 mm | |
| Thickness | 3 mm | |
| Density | 2700 | |
| Conductivity | ||
| Young’s modulus | 70 | |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.33 | |
| Excitation current | Amplitude | 1 A |
| Frequency | 700 kHz |
| Object | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Periodic Magnet Array | Width | 25 mm |
| Height | 25 mm | |
| Thickness | 3 mm | |
| Gap between adjacent magnets | 1 mm | |
| Lift-off distance | 0.3 mm | |
| Magnetic flux density | 250 mT | |
| Number of magnets in each periodic magnet array | 14 | |
| Racetrack Coil | Width | 30 mm |
| Length | 60 mm | |
| Thickness | 0.1 mm | |
| Copper layer width | 0.7 mm | |
| Copper layer depth | 0.035 mm | |
| Copper layer interval | 0.9 mm | |
| Turns of each coil | 13 | |
| Lift-off distance | 0.1 mm | |
| Aluminum Plate | Length | 500 mm |
| Width | 500 mm | |
| Thickness | 3 mm | |
| Excitation Signal | Voltage | 260 V |
| Operation Frequency | 700 kHz | |
| Duty Ratio | 20% | |
| Repetition Frequency | 50 Hz |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, G.; Song, X.; Zhang, X.; Tu, J.; Chen, T. Pure SH1 Guided-Wave Generation Method with Dual Periodic-Permanent-Magnet Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducers for Plates Inspection. Sensors 2019, 19, 3019. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19133019
Qiu G, Song X, Zhang X, Tu J, Chen T. Pure SH1 Guided-Wave Generation Method with Dual Periodic-Permanent-Magnet Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducers for Plates Inspection. Sensors. 2019; 19(13):3019. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19133019
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Gongzhe, Xiaochun Song, Xu Zhang, Jun Tu, and Tao Chen. 2019. "Pure SH1 Guided-Wave Generation Method with Dual Periodic-Permanent-Magnet Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducers for Plates Inspection" Sensors 19, no. 13: 3019. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19133019
APA StyleQiu, G., Song, X., Zhang, X., Tu, J., & Chen, T. (2019). Pure SH1 Guided-Wave Generation Method with Dual Periodic-Permanent-Magnet Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducers for Plates Inspection. Sensors, 19(13), 3019. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19133019





