An Improved Spatiotemporal Fusion Approach Based on Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
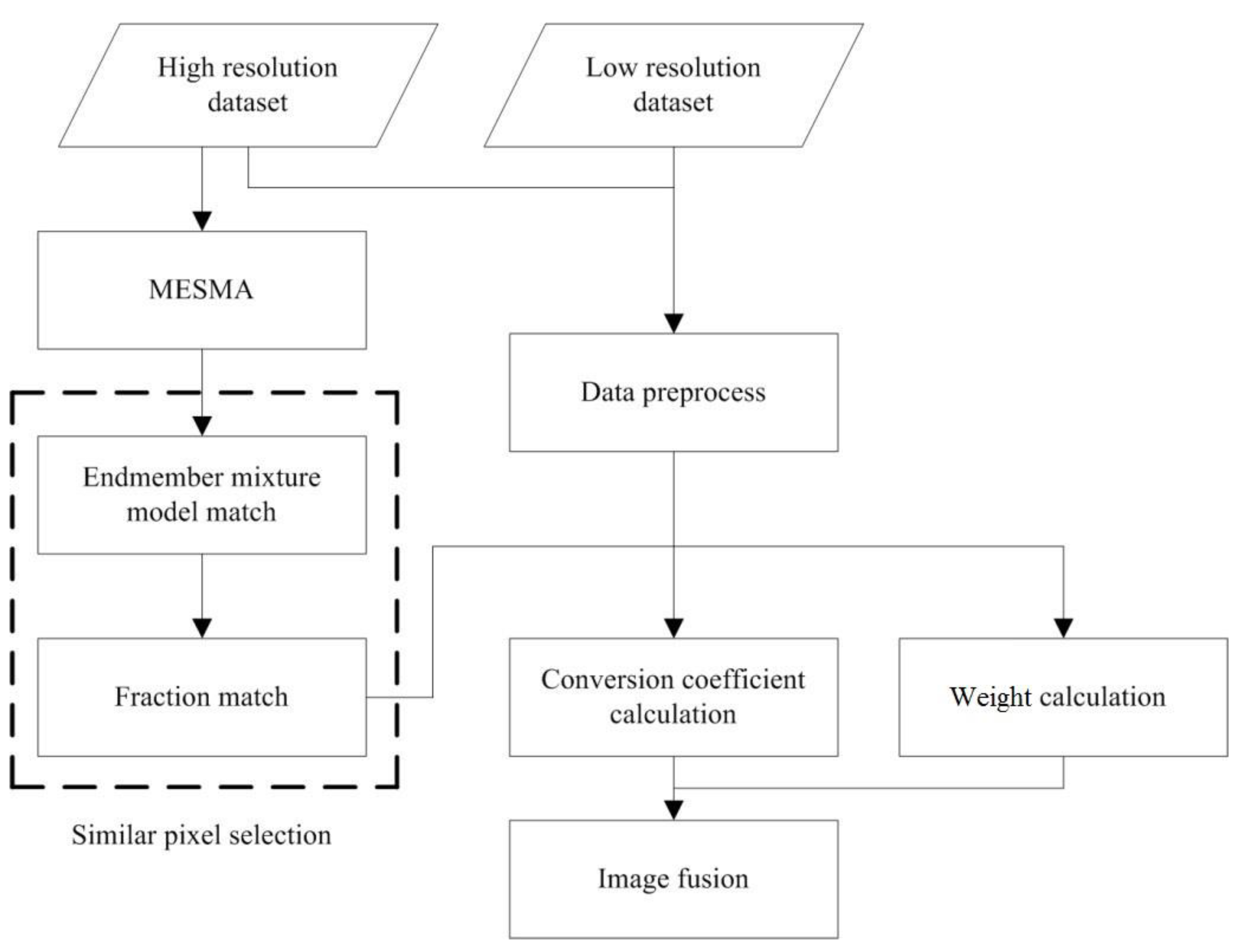
2. Description of IESTARFM
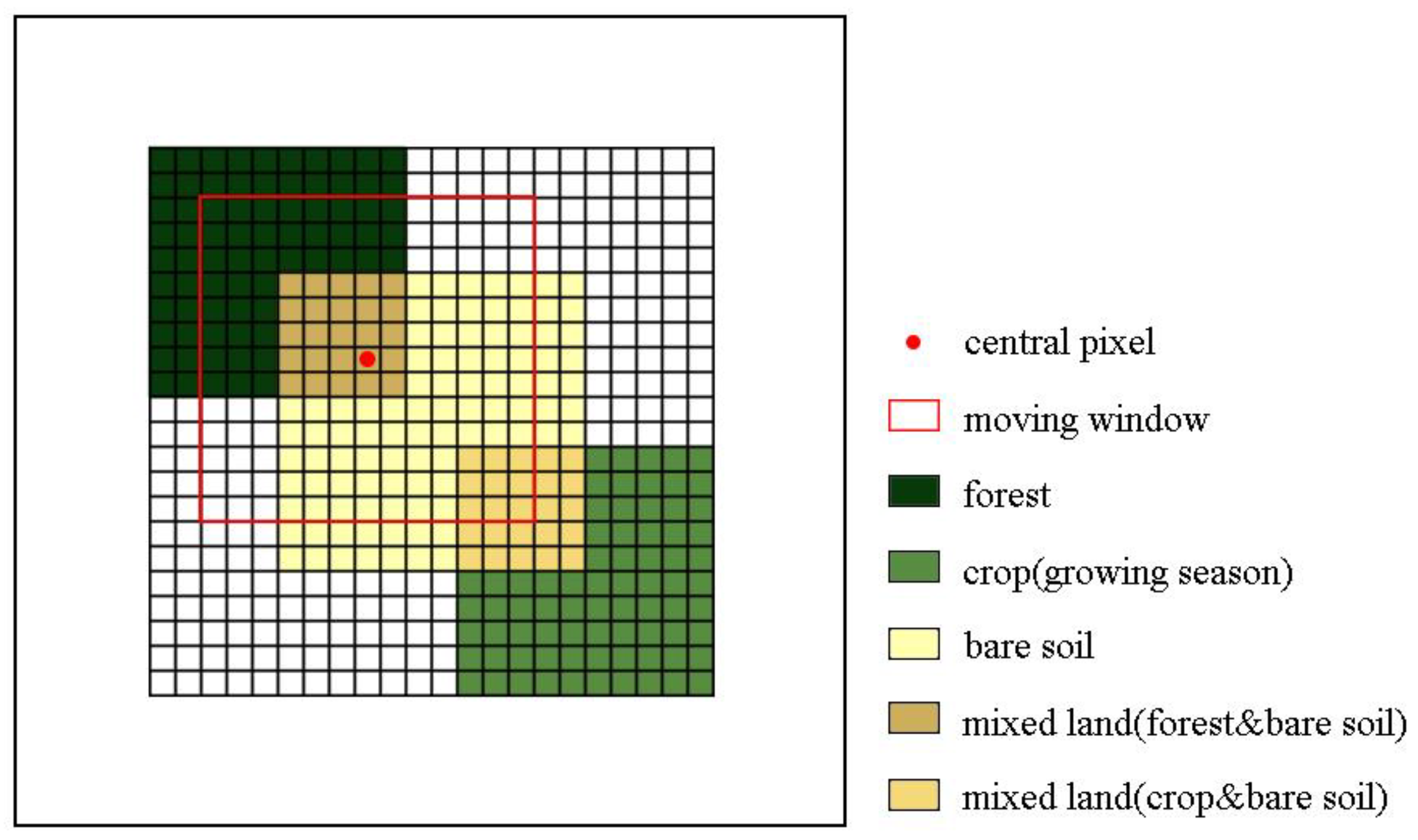
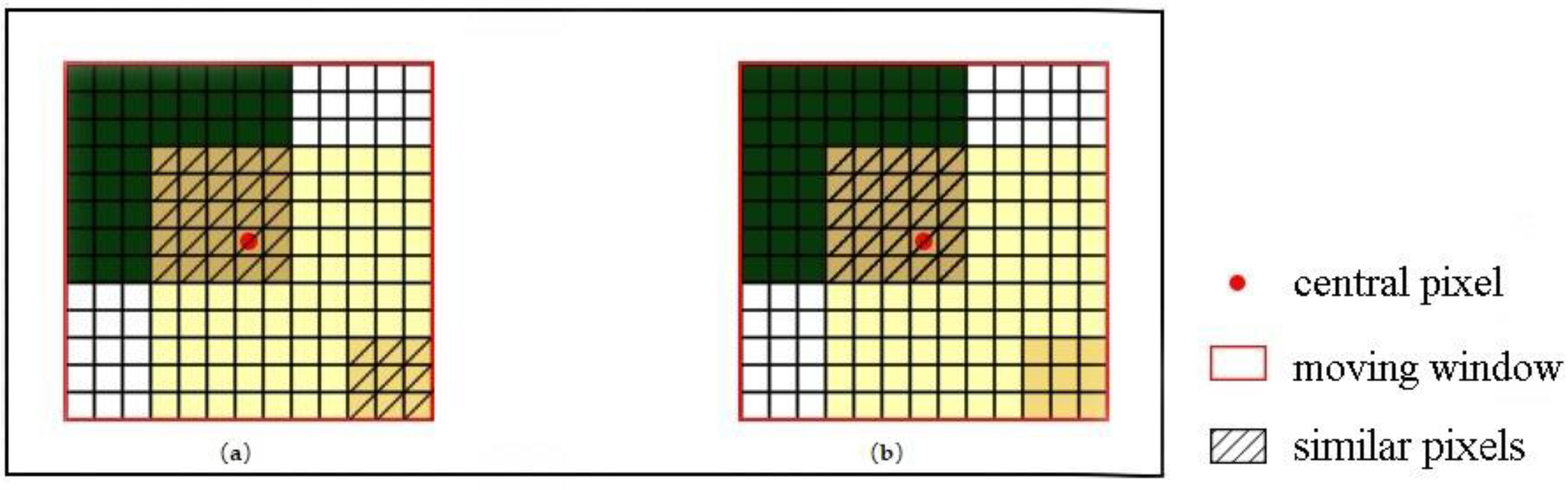
2.1. The Similar Pixel Selection Method in ESTARFM
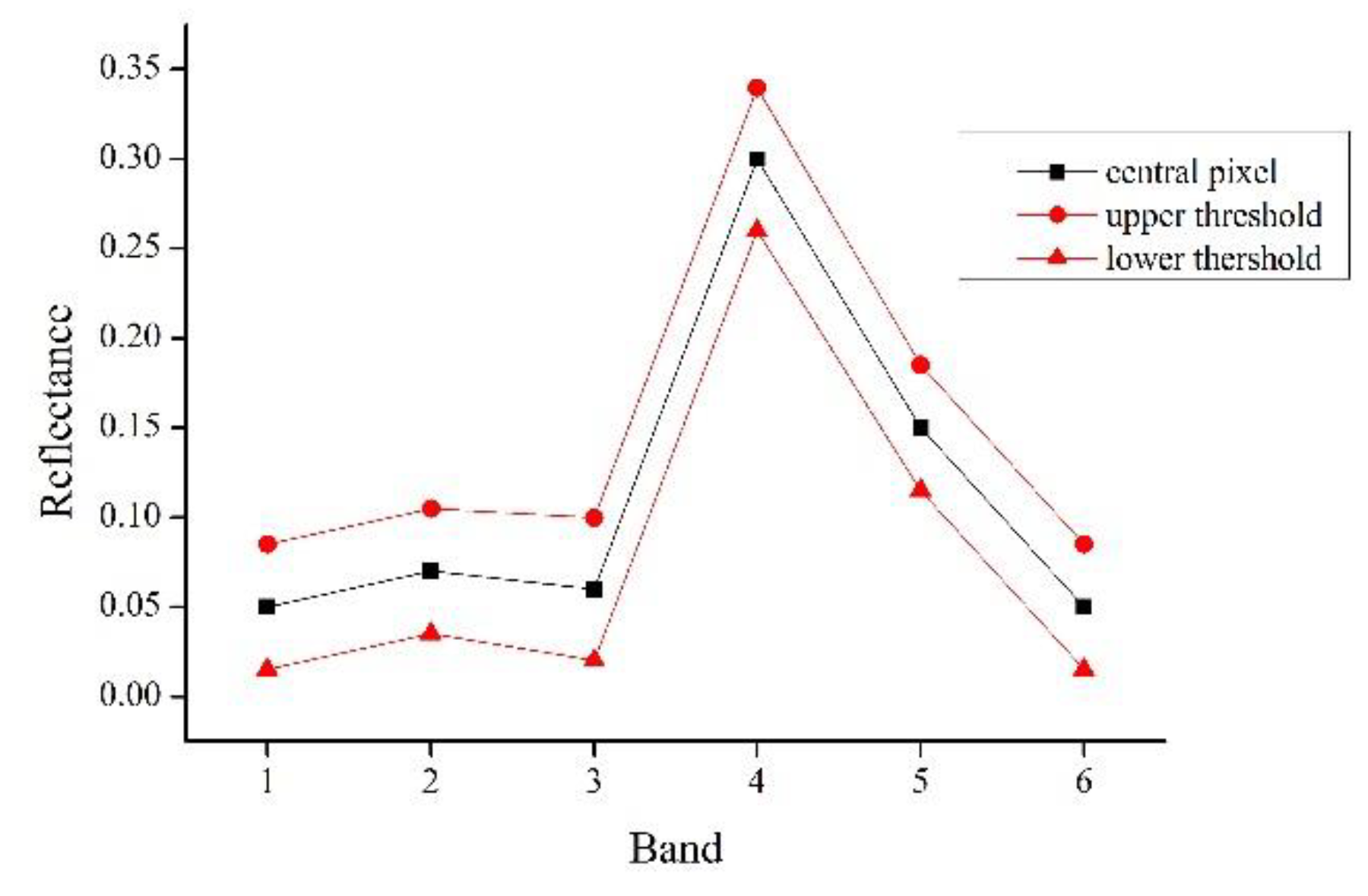
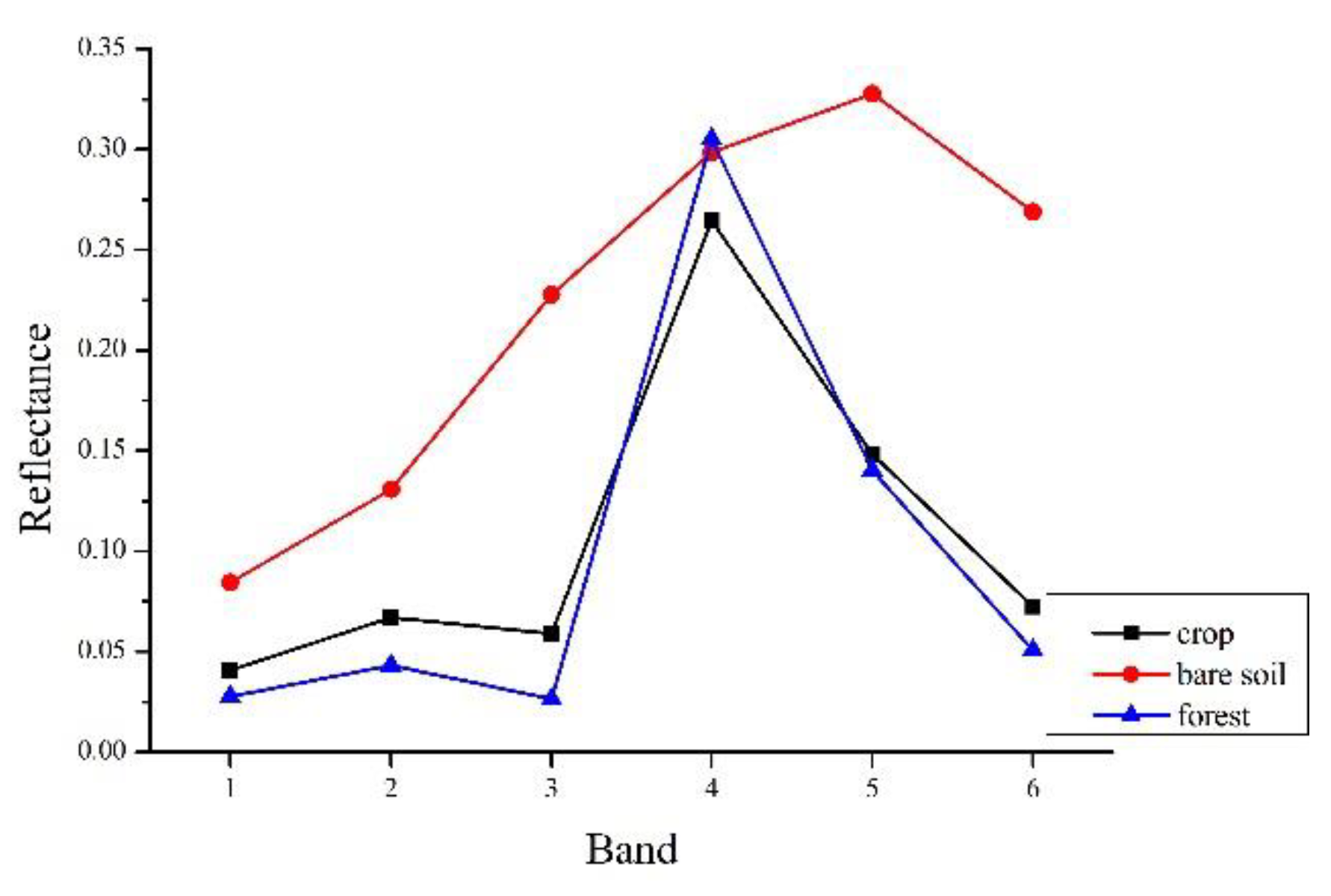
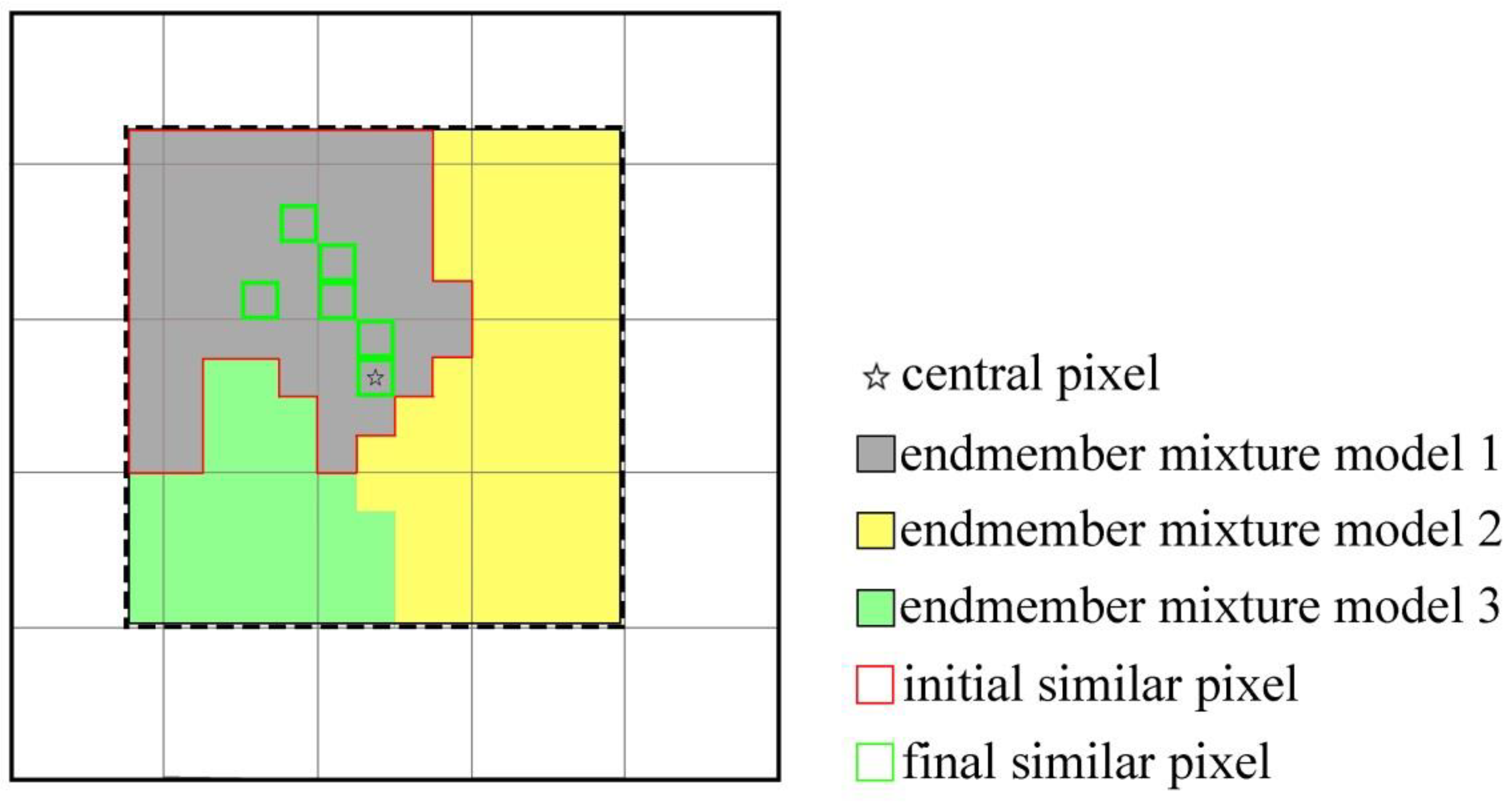
2.2. Improved Selection of Similar Pixels
2.3. Fused Data Generation
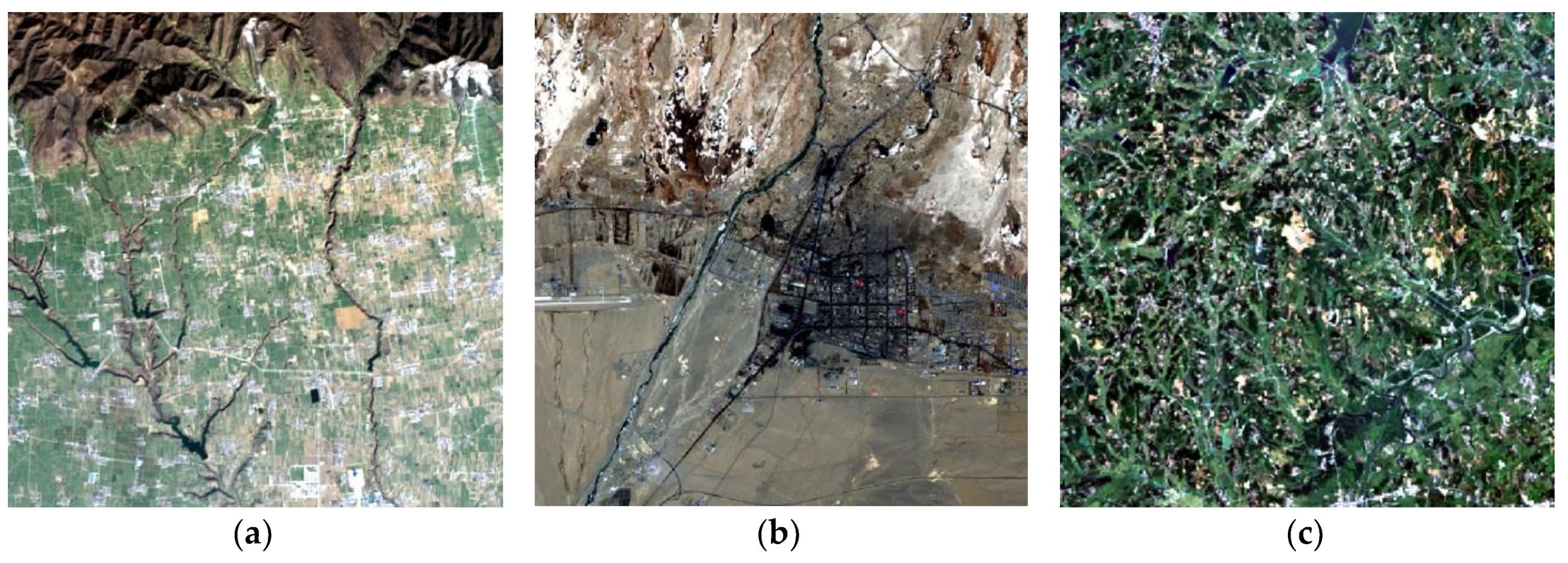
3. Data and Pre-Process
4. Result and Analysis
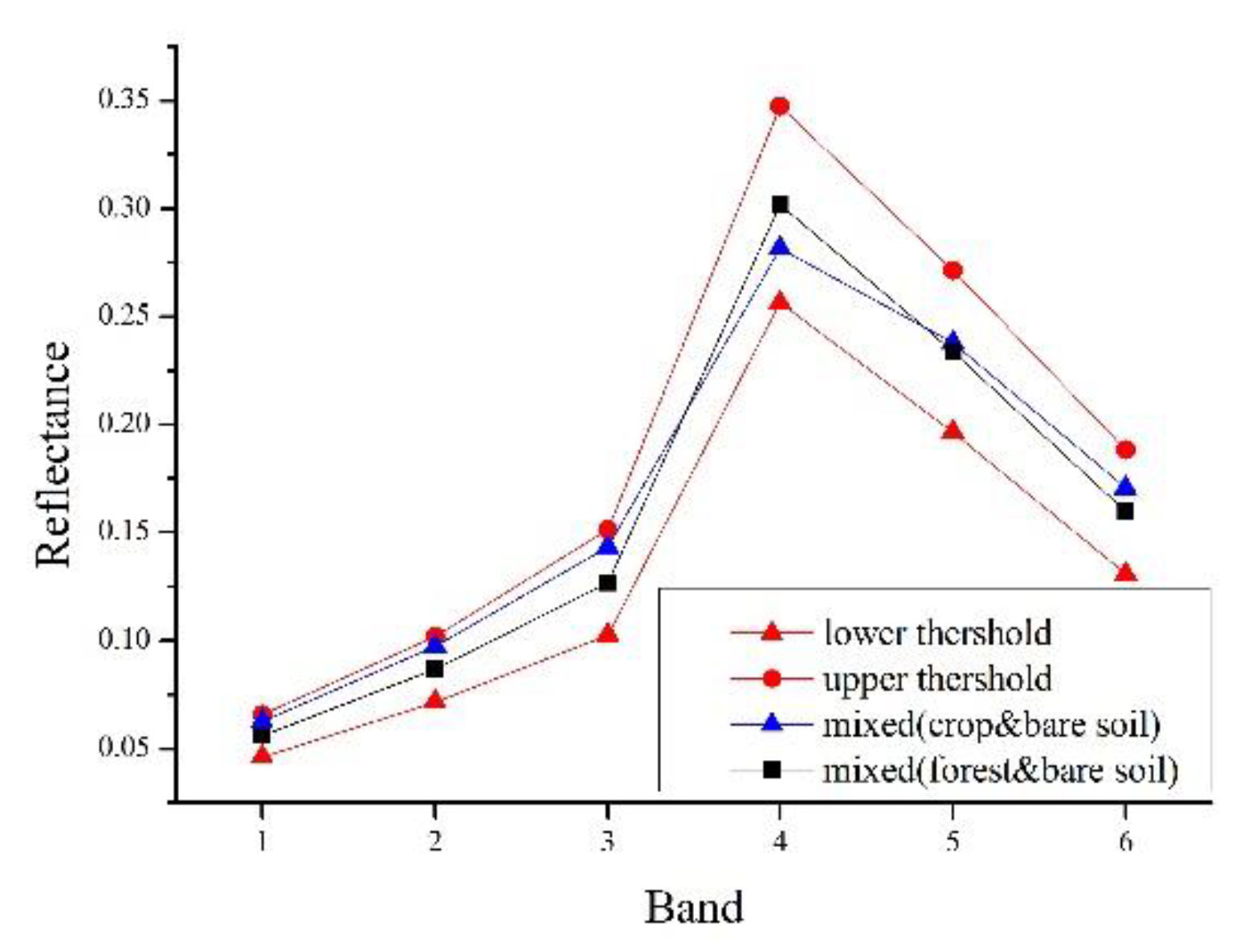
4.1. Spectral Mixture Analysis
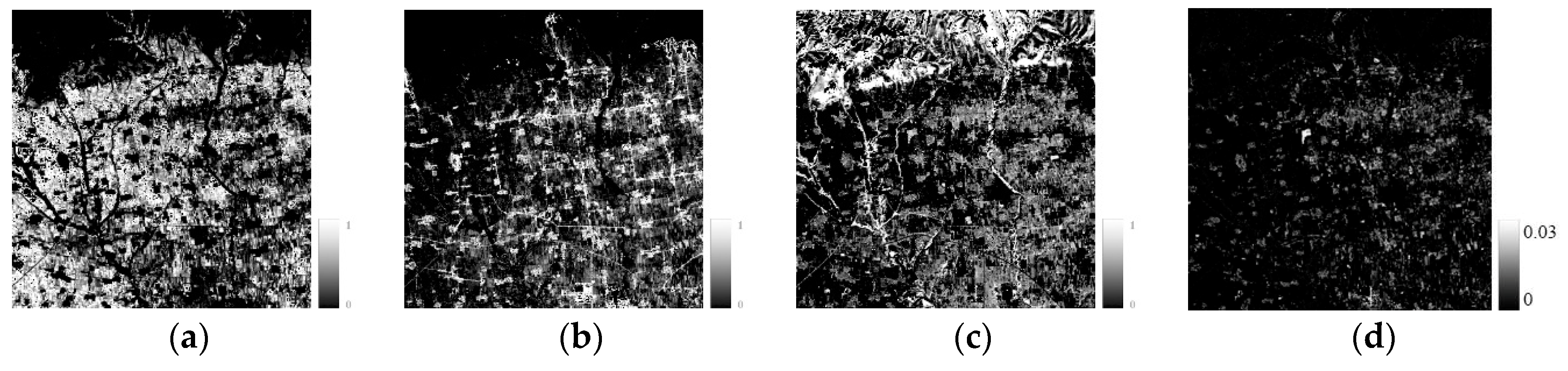
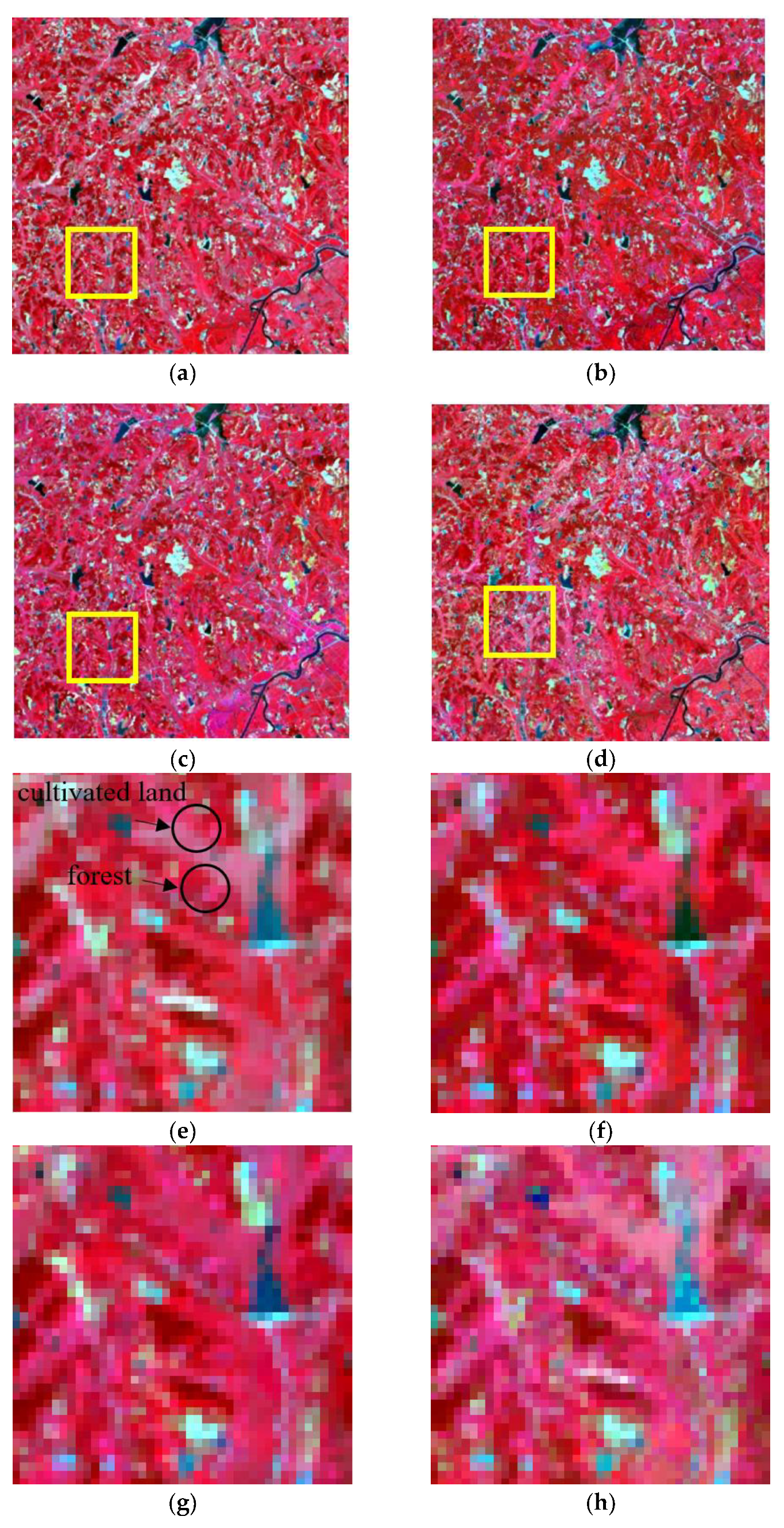
4.2. Fusion Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adachi, M.; Ito, A.; Yonemura, S.; Takeuchi, W. Estimation of global soil respiration by accounting for land-use changes derived from remote sensing data. J. Environ. Manage. 2017, 200, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senf, C.; Pflugmacher, D.; Heurich, M.; Krueger, T. A Bayesian hierarchical model for estimating spatial and temporal variation in vegetation phenology from Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.; Liu, D. Blending MODIS and Landsat images for urban flood mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 3237–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sanpedro, M.; Le Toan, T.; Moreno, J.; Kergoat, L.; Rubio, E. Seasonal variations of leaf area index of agricultural fields retrieved from Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 810–824. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, F. On the blending of the Landsat and MODIS surface reflectance: Predicting daily Landsat surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Wang, P.; Masek, J. Integrating remote sensing data from multiple optical sensors for ecological and crop condition monitoring. In Remote Sensing and Modeling of Ecosystems for Sustainability X; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; p. 886903. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, B.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, H. Crop phenology detection using high spatio-temporal resolution data fused from SPOT5 and MODIS products. Sensors 2016, 16, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, T.; Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C.; Linke, J.; McDermid, G.; Masek, J.G.; Gao, F.; White, J.C. A new data fusion model for high spatial-and temporal-resolution mapping of forest disturbance based on Landsat and MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Ju, J.; Lewis, P.; Schaaf, C.; Gao, F.; Hansen, M.; Lindquist, E. Multi-temporal MODIS–Landsat data fusion for relative radiometric normalization, gap filling, and prediction of Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3112–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Masek, J.G. An enhanced spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model for complex heterogeneous regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, C.; Zhu, X.; Gao, F.; Chou, B.; Perez, D.; Li, J.; Shen, Y.; Koperski, K.; Marchisio, G. Assessment of spatiotemporal fusion algorithms for planet and worldview images. Sensors 2018, 18, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, W.; Marinoni, A.; Gao, L.; Zhang, B. Performance assessment of ESTARFM with different similar-pixel identification schemes. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2018, 12, 025017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Chen, B.; Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Hilker, T. An improved image fusion approach based on enhanced spatial and temporal the adaptive reflectance fusion model. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6346–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Helmer, E.H.; Gao, F.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Lefsky, M.A. A flexible spatiotemporal method for fusing satellite images with different resolutions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 172, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauer, K.; Gessner, U.; Fensholt, R.; Kuenzer, C. An ESTARFM fusion framework for the generation of large-scale time series in cloud-prone and heterogeneous landscapes. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, C.M.; García-Haro, F.J. A comparison of STARFM and an unmixing-based algorithm for Landsat and MODIS data fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C. The Landsat ETM+ spectral mixing space. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.-K.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Chan, T.-H.; Gillis, N.; Gader, P.; Plaza, A.J.; Ambikapathi, A.; Chi, C.-Y. A signal processing perspective on hyperspectral unmixing: Insights from remote sensing. IEEE Signal Process Mag. 2014, 31, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C. Spectral mixture analysis for subpixel vegetation fractions in the urban environment: How to incorporate endmember variability? Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, J.; Roberts, D.A.; Halligan, K.; Menz, G. Hierarchical multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis (MESMA) of hyperspectral imagery for urban environments. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1712–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Gardner, M.; Church, R.; Ustin, S.; Scheer, G.; Green, R. Mapping chaparral in the Santa Monica Mountains using multiple endmember spectral mixture models. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 65, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridd, M.K. Exploring a VIS (vegetation-impervious surface-soil) model for urban ecosystem analysis through remote sensing: Comparative anatomy for cities. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 2165–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, A.; Garg, R. Systematic approach towards extracting endmember spectra from hyperspectral image using PPI and SMACC and its evaluation using spectral library. Appl. Geomatics 2015, 7, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, R.L.; Roberts, D.A.; Dennison, P.E.; Hess, L.L. Sub-pixel mapping of urban land cover using multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis: Manaus, Brazil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, T.; Anderson, G.P.; Felde, G.W.; Hoke, M.L.; Ratkowski, A.; Chetwynd, J.H.; Gardner, J.A.; Adler-Golden, S.; Matthew, M.W.; Berk, A.; et al. FLAASH, a MODTRAN4-based atmospheric correction algorithm, its application and validation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience & Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wayne, L. The IDL Astronomy User’s Library. Website; 2016. Available online: https://idlastro.gsfc.nasa.gov/ftp/pro/ image/correl_optimize.pro (accessed on 20 November 2018).
- Cui, J.; Zhang, X.; Luo, M. Combining Linear pixel unmixing and STARFM for spatiotemporal fusion of Gaofen-1 wide field of view imagery and MODIS imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Pan, Y.; Liu, H.; Yuan, Z.; Yun, Y. An improved STARFM with help of an unmixing-based method to generate high spatial and temporal resolution remote sensing data in complex heterogeneous regions. Sensors 2016, 16, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Peng, X. High-performance Spatio-temporal Fusion Models for Remote Sensing Images with Graphics Processing Units. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]

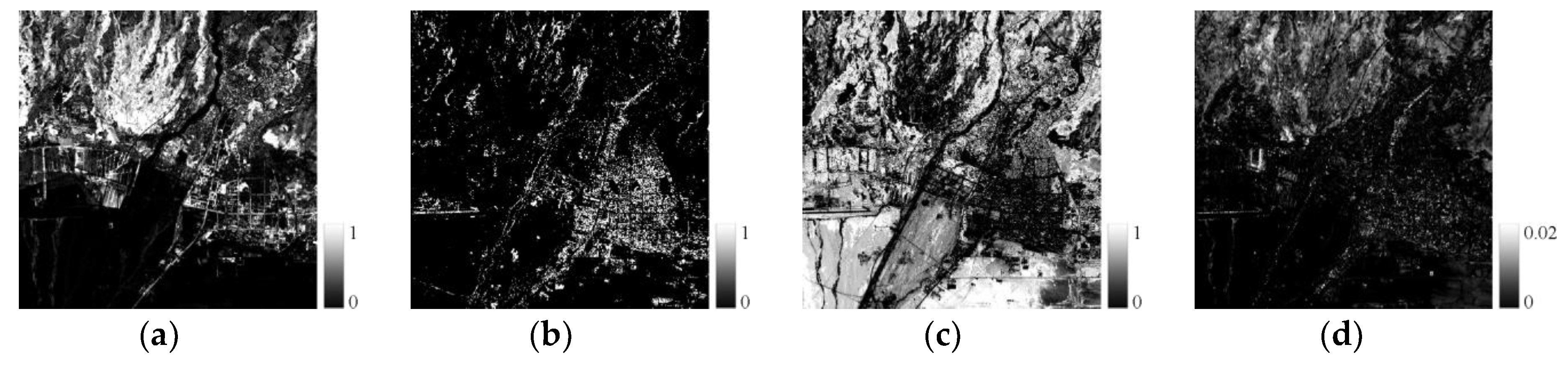
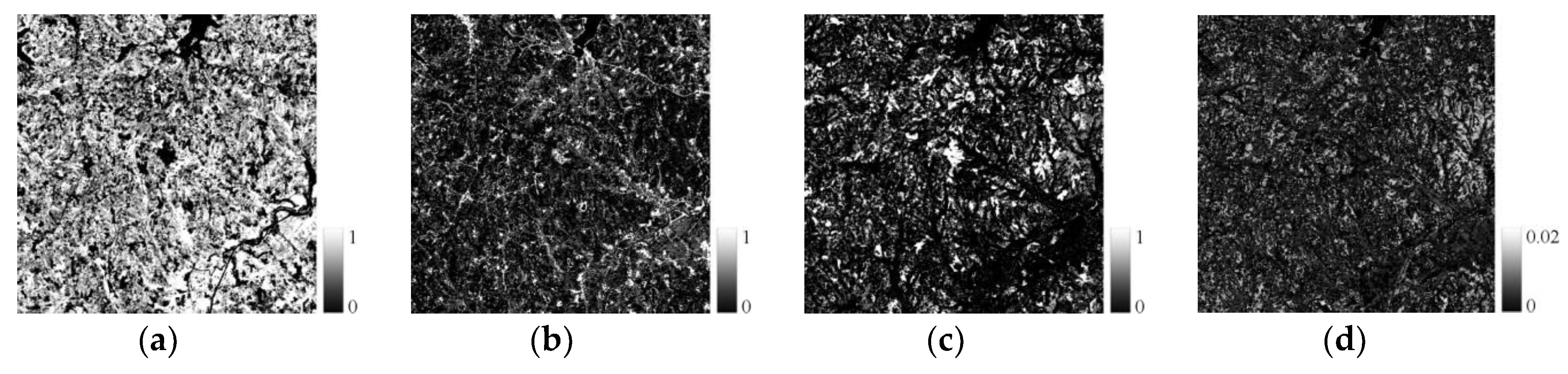
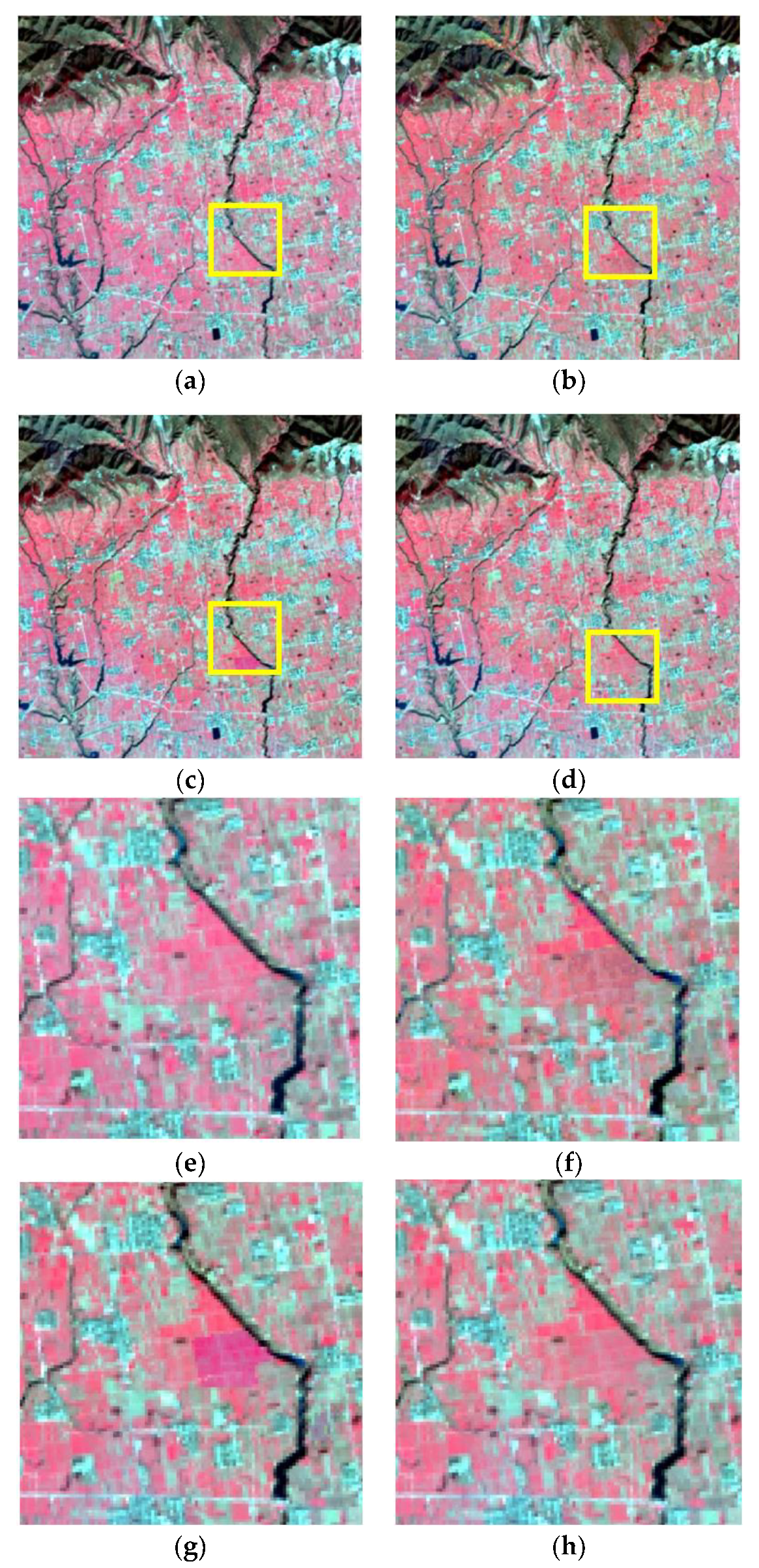
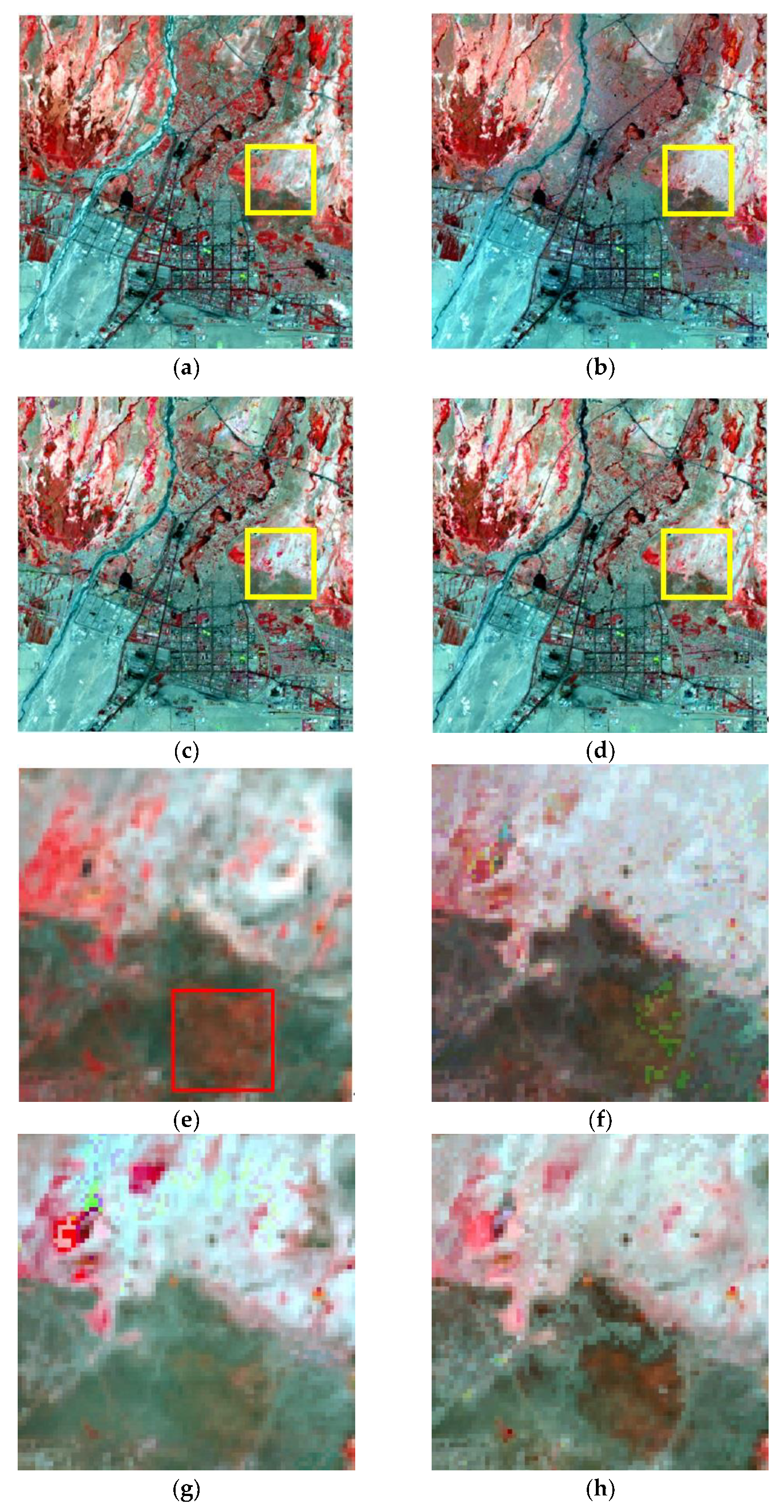
| Data Type | Row and Column | Study Area | Image Function | Acquired Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat8 OLI | 127/36 | Study area 1 | basis | 2014/12/5 |
| validation | 2014/12/21 | |||
| basis | 2015/1/22 | |||
| 136/35 | Study area 2 | basis | 2016/3/12 | |
| basis | 2016/6/16 | |||
| validation | 2016/9/20 | |||
| 122/39 | Study area 3 | basis | 2016/8/1 | |
| basis | 2016/8/17 | |||
| validation | 2016/9/2 | |||
| MODIS09GA | h27v05 | Study area 1 | basis | 2014/12/5 |
| predict | 2014/12/21 | |||
| basis | 2015/1/22 | |||
| h25v05 | Study area 2 | basis | 2016/3/12 | |
| basis | 2016/6/16 | |||
| predict | 2016/9/20 | |||
| h27v06 | Study area 3 | basis | 2016/8/1 | |
| basis | 2016/8/17 | |||
| predict | 2016/9/2 |
| Landsat OLI Band | Wavelength (nm) | MODIS Band | Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat8 OLI Band2 | 450–510 | MOD09GA Band3 | 459–479 |
| Landsat8 OLI Band3 | 530–590 | MOD09GA Band4 | 545–565 |
| Landsat8 OLI Band4 | 640–670 | MOD09GA Band1 | 620–670 |
| Landsat8 OLI Band5 | 850–880 | MOD09GA Band2 | 841–876 |
| Landsat8 OLI Band6 | 1570–1650 | MOD09GA Band6 | 1628–1652 |
| Landsat8 OLI Band7 | 2110–2290 | MOD09GA Band7 | 2105–2155 |
| Band | STARFM | ESTARFM | I-ESTARFM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | RMSE | r | RMSE | r | RMSE | |
| red | 0.88530 | 0.01895 | 0.90969 | 0.01812 | 0.92767 | 0.01769 |
| green | 0.83601 | 0.02431 | 0.93395 | 0.02283 | 0.94859 | 0.02236 |
| blue | 0.89573 | 0.02800 | 0.94181 | 0.02707 | 0.95345 | 0.02669 |
| NIR | 0.97119 | 0.07007 | 0.97123 | 0.06893 | 0.98162 | 0.06757 |
| SWIR 1 | 0.95649 | 0.04105 | 0.95477 | 0.04088 | 0.96558 | 0.04005 |
| SWIR 2 | 0.94699 | 0.03801 | 0.95653 | 0.03752 | 0.96634 | 0.03676 |
| Band | STARFM | ESTARFM | I-ESTARFM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | RMSE | r | RMSE | r | RMSE | |
| red | 0.82264 | 0.04239 | 0.83780 | 0.04076 | 0.86990 | 0.03919 |
| green | 0.81513 | 0.04930 | 0.84313 | 0.04788 | 0.86412 | 0.04519 |
| blue | 0.80664 | 0.05665 | 0.81788 | 0.05521 | 0.85654 | 0.05158 |
| NIR | 0.83907 | 0.06435 | 0.88136 | 0.06392 | 0.89616 | 0.06287 |
| SWIR 1 | 0.72223 | 0.05237 | 0.74327 | 0.05057 | 0.76800 | 0.04860 |
| SWIR 2 | 0.69582 | 0.04804 | 0.73173 | 0.04585 | 0.75836 | 0.04226 |
| Band | STARFM | ESTARFM | I-ESTARFM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | RMSE | r | RMSE | r | RMSE | |
| red | 0.80609 | 0.01420 | 0.81288 | 0.01403 | 0.85434 | 0.01296 |
| green | 0.83983 | 0.01709 | 0.84642 | 0.01575 | 0.90146 | 0.01482 |
| blue | 0.87306 | 0.02589 | 0.87751 | 0.02522 | 0.91762 | 0.02361 |
| NIR | 0.90136 | 0.05373 | 0.90889 | 0.05243 | 0.93467 | 0.04983 |
| SWIR 1 | 0.87413 | 0.04916 | 0.88579 | 0.04853 | 0.92770 | 0.04502 |
| SWIR 2 | 0.86640 | 0.03700 | 0.87866 | 0.03631 | 0.91614 | 0.03540 |
| Method | STARFM | ESTARFM | I-ESTARFM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Costing time (s) | 180 | 290 | 320 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Zeng, Y.; Li, S.; Pi, X.; Huang, W. An Improved Spatiotemporal Fusion Approach Based on Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis. Sensors 2019, 19, 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112443
Liu W, Zeng Y, Li S, Pi X, Huang W. An Improved Spatiotemporal Fusion Approach Based on Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis. Sensors. 2019; 19(11):2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112443
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wenjie, Yongnian Zeng, Songnian Li, Xinyu Pi, and Wei Huang. 2019. "An Improved Spatiotemporal Fusion Approach Based on Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis" Sensors 19, no. 11: 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112443
APA StyleLiu, W., Zeng, Y., Li, S., Pi, X., & Huang, W. (2019). An Improved Spatiotemporal Fusion Approach Based on Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis. Sensors, 19(11), 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112443







