Thermomechanical Noise Characterization in Fully Monolithic CMOS-MEMS Resonators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fabrication and Experimental Setup
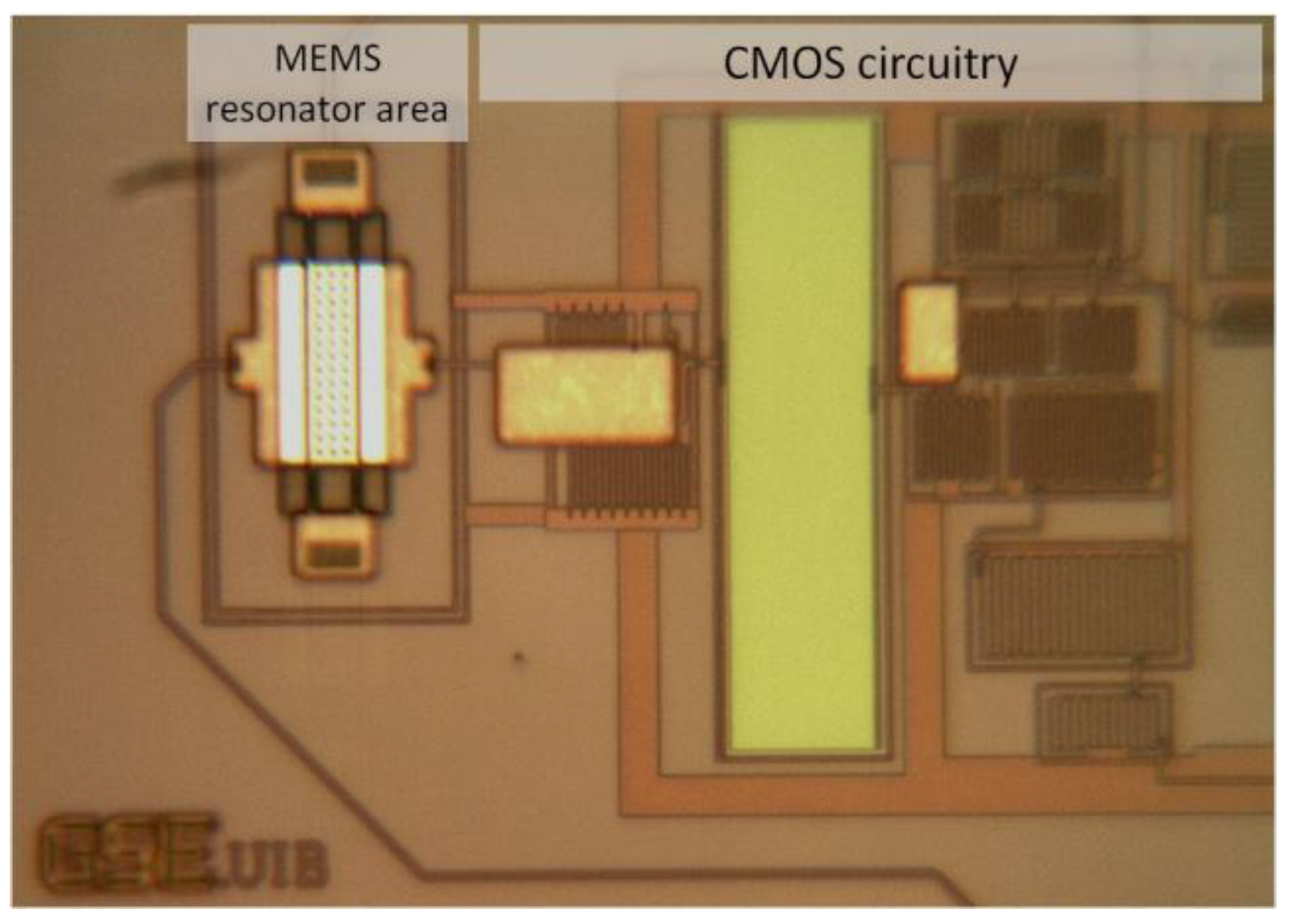
2.1. Fabrication
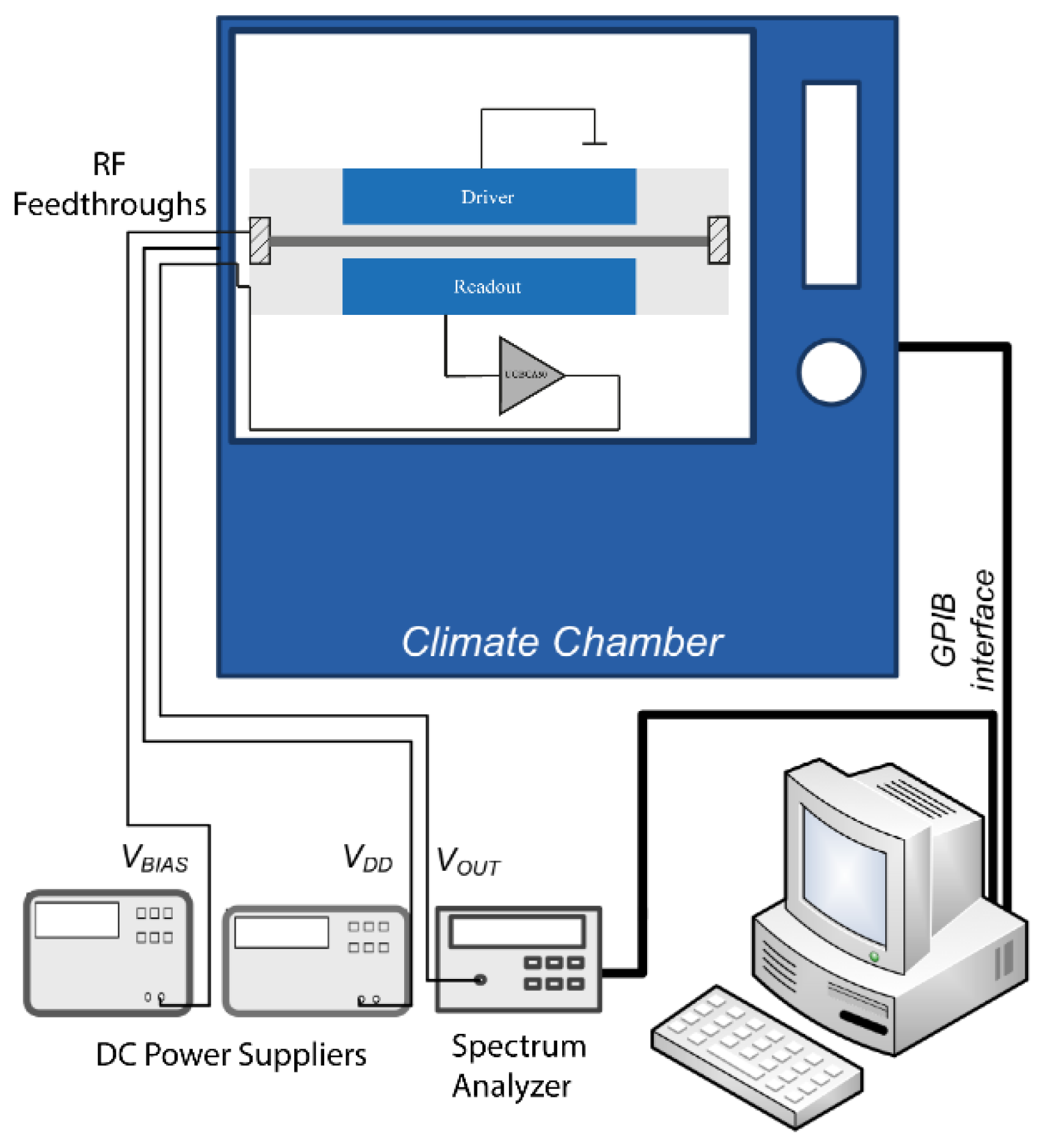
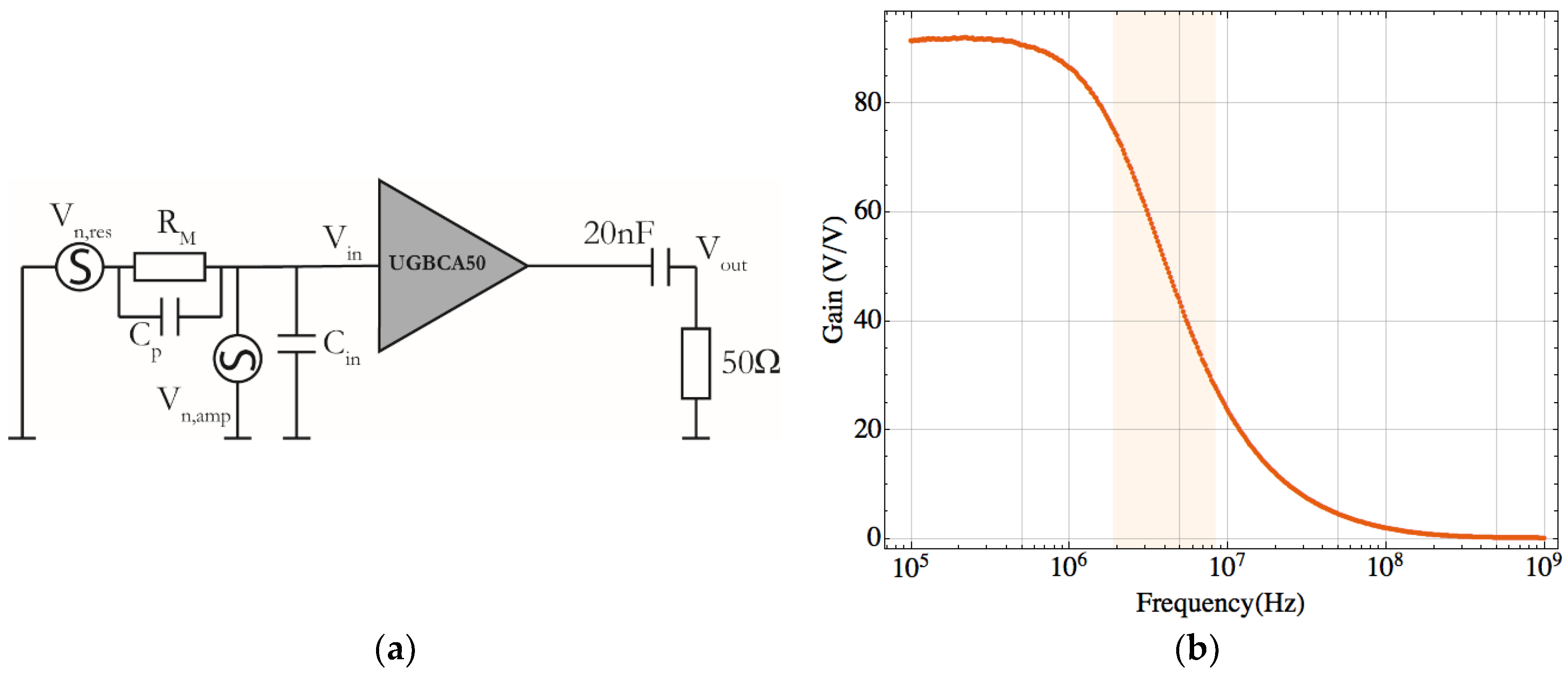
2.2. Experimental Setup
3. Noise Sources Model
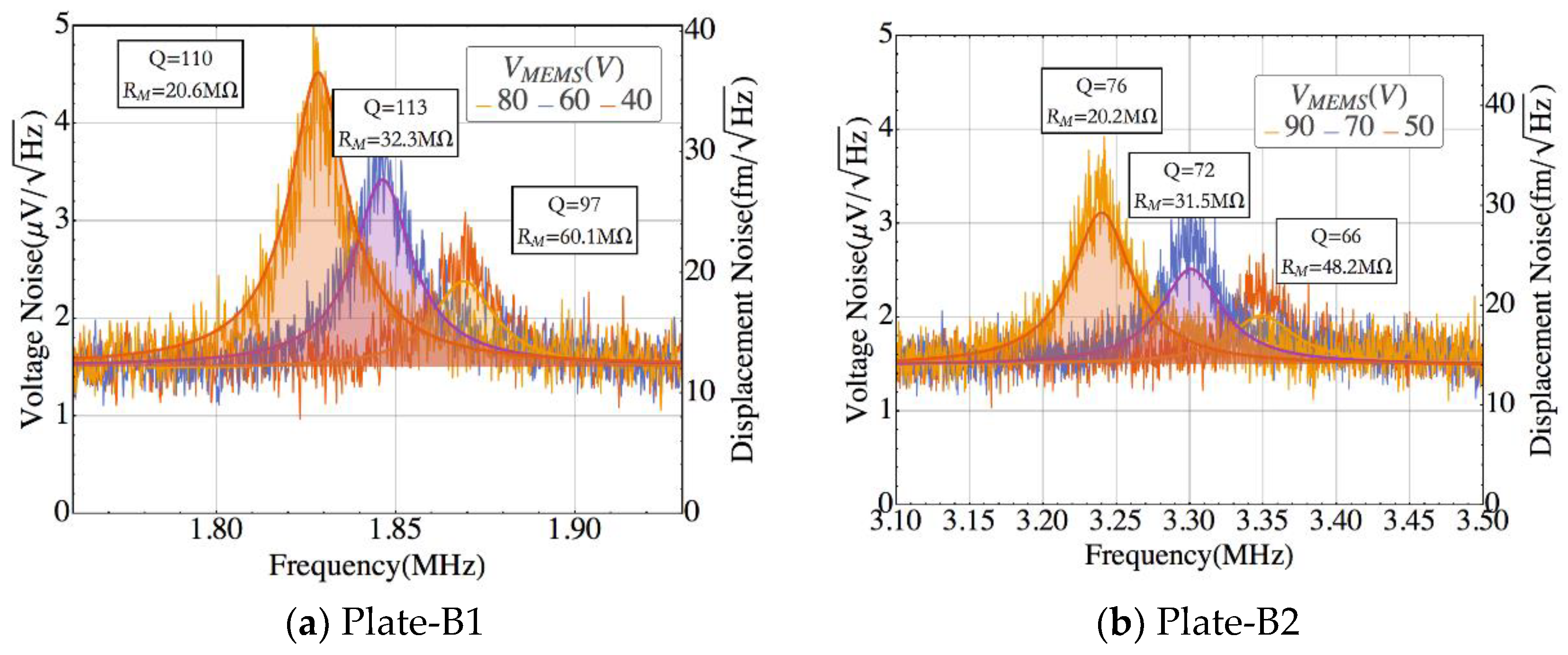
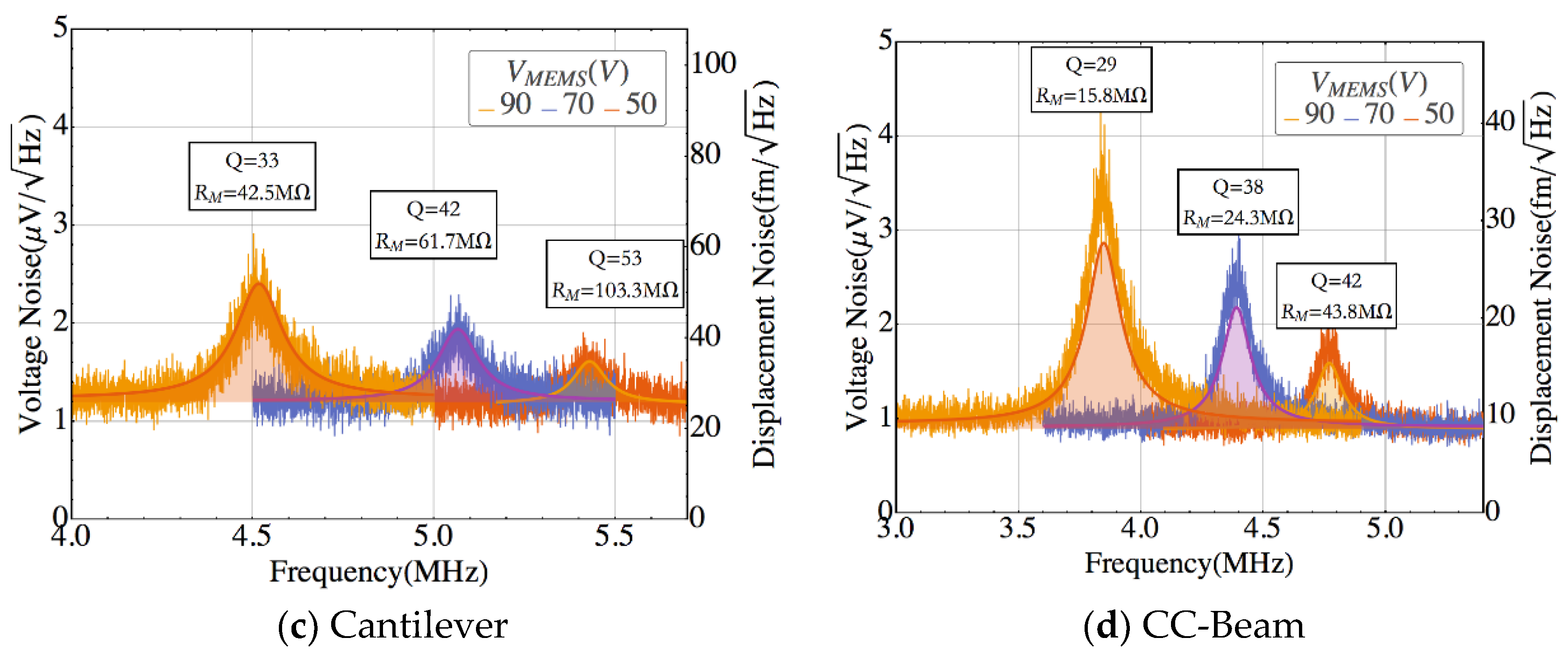
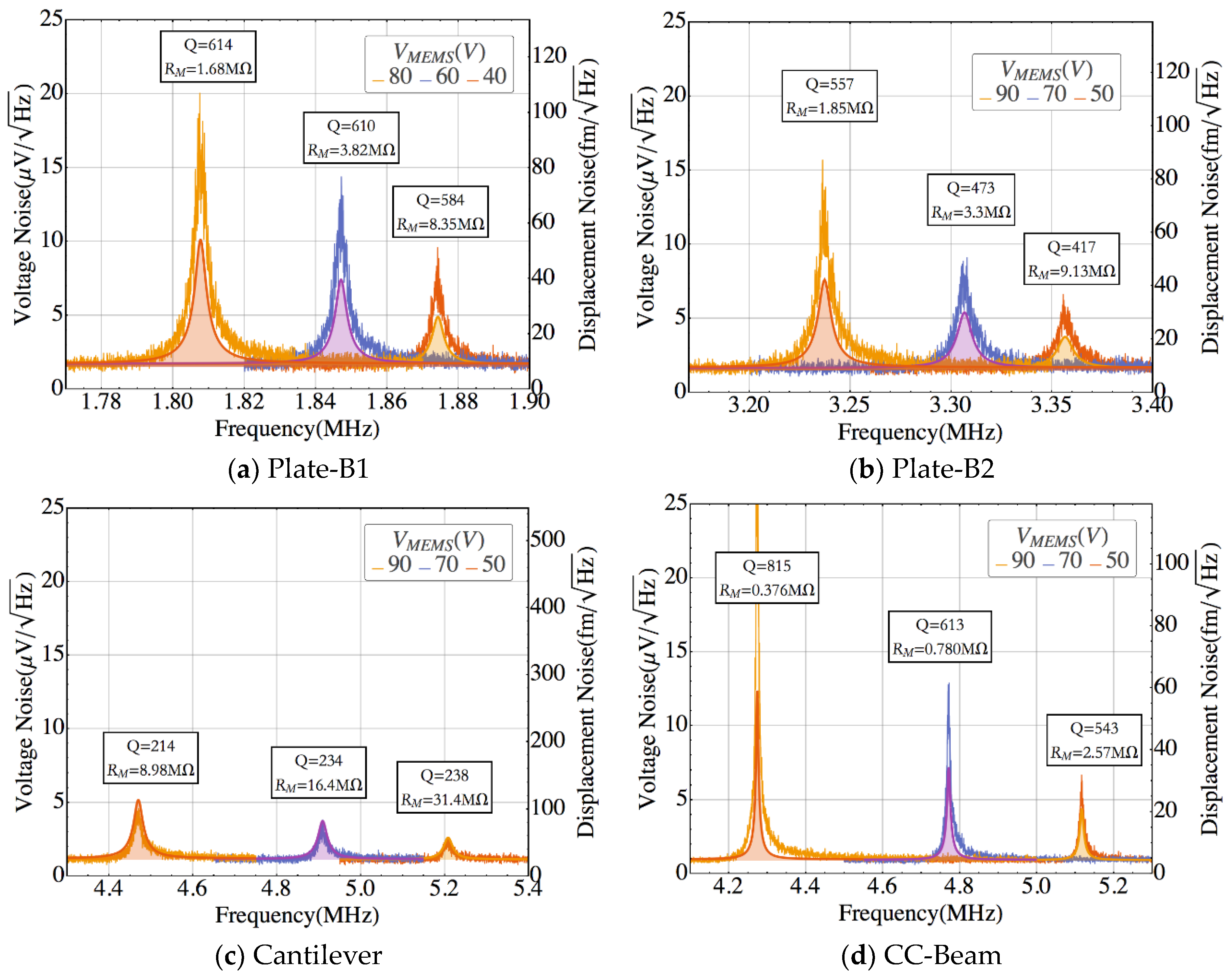
4. Results
Ultimate Resolution Limit
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Urasinska-Wojcik, B.; Vincent, T.A.; Chowdhury, M.F.; Gardner, J.W. Ultrasensitive WO3 gas sensors for NO2 detection in air and low oxygen environment. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc, N.; Cakmak, O.; Kosemen, A.; Ermek, E.; Ozturk, S.; Yerli, Y.; Ozturk, Z.Z.; Urey, H. Fabrication of 1D ZnO nanostructures on MEMS cantilever for VOC sensor application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 202, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verd, J.; Uranga, A.; Abadal, G.; Teva, J.L.; Torres, F.; López, J.; PÉrez-Murano, F.; Esteve, J.; Barinol, N. Monolithic CMOS MEMS oscillator circuit for sensing in the attogram range. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2008, 29, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaste, J.; Eichler, A.; Moser, J.; Ceballos, G.; Rurali, R.; Bachtold, A. A nanomechanical mass sensor with yoctogram resolution. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleland, A.N.; Roukes, M.L. Noise processes in nanomechanical resonators. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 2758–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, K.L.; Yang, Y.T.; Roukes, M.L. Ultimate limits to inertial mass sensing based upon nanoelectromechanical systems. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 2682–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouh, T.; Hanay, M.S.; Ekinci, K.L. Nanomechanical motion transducers for miniaturized mechanical systems. Micromachines 2017, 8, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Xia, G.M.; Qiu, A.P.; Su, Y.; Xu, Y.P. A sub-ug bias-instability MEMS oscillating accelerometer with an ultra-low-noise read-out circuit in CMOS. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2015, 50, 2113–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcamone, J.; Misischi, B.; Brugger, J.; Torres, F.; Abadal, G.; Barniol, N. A compact and low-power CMOS circuit for fully integrated NEMS resonators. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2007, 54, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colinet, E.; Durand, C.; Duraffourg, L.; Audebert, P.; Dumas, G.; Casset, F.; Ollier, E.; Ancey, P.; Carpentier, J.F.; Buchaillot, L.; et al. Ultra-sensitive capacitive detection based on SGMOSFET compatible with front-end CMOS process. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2009, 44, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.S.; Liu, C.Y.; Yeh, L.K.; Chiu, Y.H.; Lu, M.S.C.; Hsu, K.Y.J. An integrated low-noise sensing circuit with efficient bias stabilization for CMOS MEMS capacitive accelerometers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2011, 58, 2661–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Tang, H.X.; Roukes, M.L. Ultra-sensitive NEMS-based cantilevers for sensing, scanned probe and very high-frequency applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mile, E.; Jourdan, G.; Bargatin, I.; Labarthe, S.; Marcoux, C.; Andreucci, P.; Hentz, S.; Kharrat, C.; Colinet, E.; Duraffourg, L. In-plane nanoelectromechanical resonators based on silicon nanowire piezoresistive detection. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 165504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Baker, C.; Senellart, P.; Lemaitre, A.; Ducci, S.; Leo, G.; Favero, I. High frequency GaAs nano-optomechanical disk resonator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 263903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Xia, J. Femtogram scale high frequency nano-optomechanical resonators in water. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houmadi, S.; Legrand, B.; Salvetat, J.P.; Walter, B.; Mairiaux, E.; Aime, J.P.; Ducatteau, D.; Merzeau, P.; Buisson, L.; Elezgaray, J.; et al. When capacitive transduction meets the thermomechanical limit: Towards femto-newton force sensors at very high frequency. In Proceedings of the 28th IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Estoril, Portugal, 18–22 January 2015; pp. 150–153. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, P.; Güttinger, J.; Noury, A.; Vergara-Cruz, J.; Bachtold, A. Force sensitivity of multilayer graphene optomechanical devices. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verd, J.; Uranga, A.; Teva, J.; López, J.; Torres, F.; Esteve, J.; Abadal, G.; Perez-Murano, F.; Barinol, N. Integrated CMOS MEMS with on-chip readout electronics for high-frequency applications. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2006, 27, 495–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verd, J.; Uranga, A.; Abadal, G.; Teva, J.; Torres, F.; Pérez-Murano, F.; Fraxedas, J.; Esteve, J.; Barinol, N. Monolithic mass sensor fabricated using a conventional technology with attogram resolution in air conditions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 013501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verd, J.; Sansa, M.; Uranga, A.; Perez-Murano, F.; Segura, J.; Barniol, N. Metal microelectromechanical oscillator exhibiting ultra-high water vapor resolution. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2670–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verd, J.; Perello-Roig, R.; Bota, S.; Barceló, J.; Segura, J. Monolithic CMOS-MEMS capacitive plate resonator as a low-cost platform for high-resolution distributed mass detection. In Proceedings of the XXXI Design Circuits and Integrated Systems Conference, Granada, Spain, 23–25 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Do, C.; Erbes, A.; Yan, J.; Seshia, A.A. Design and implementation of a low-power hybrid capacitive MEMS oscillator. Microelectron. J. 2016, 56, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lübbe, J.; Temmen, M.; Rode, S.; Rahe, P.; Kühnle, A.; Reichling, M. Thermal noise limit for ultra-high vacuum noncontact atomic force microscopy. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imboden, M.; Mohanty, P. Dissipation in nanoelectromechanical systems. Phys. Rep. 2014, 534, 89–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olcum, S.; Cermak, N.; Wasserman, S.C.; Payer, C.; Shen, W.; Lee, J.; Manalis, S.R. Suspended nanochannel resonators at attogram precission. In Proceedings of the IEEE 27th International Conference on Micro Electro. Mechanical Systems (MEMS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 26–30 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
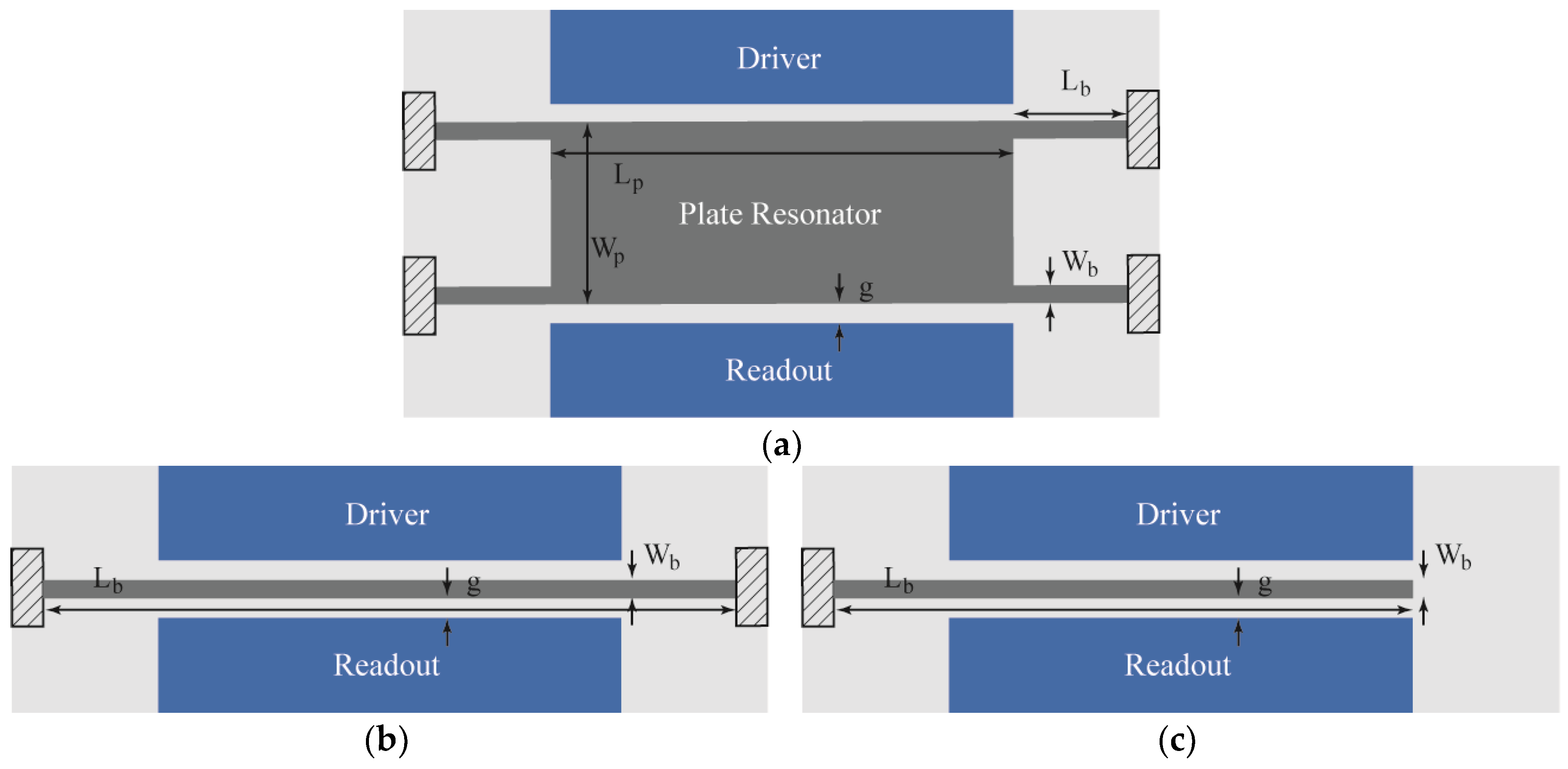
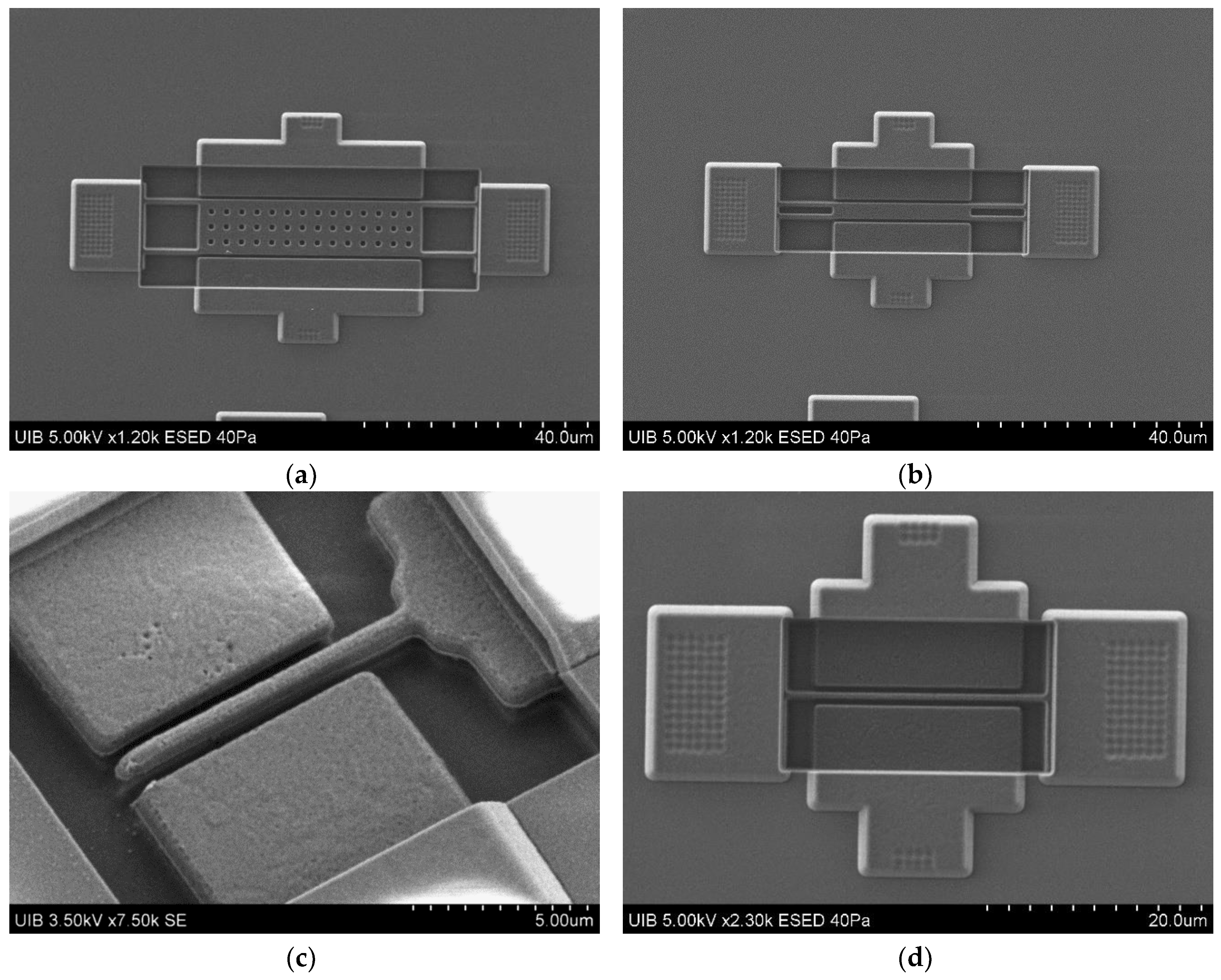
| Structure | Lb(μm) | Wb(μm) | Lp(μm) | Wp(μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plate-B1 | 10 | 0.8 | 41 | 10 |
| Plate-B2 | 10 | 0.8 | 25 | 3.0 |
| Cantilever | 10 | 0.6 | - | - |
| CC-Beam | 25 | 0.6 | - | - |
| Structure | Meff (pg) | K (Nm−1) | RM (MΩ) | F (MHz) | Q | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plate-B1 | 967 | 57.0 | 4.28·10−8 | 65.3 | 1.86 | 97 |
| 10.4 * | 1.87 * | 610 * | ||||
| Plate-B2 | 199 | 57.0 | 2.61·10−8 | 68.7 | 3.35 | 66 |
| 11.1 * | 3.36 * | 446 * | ||||
| Cantilever | 9.90 | 16.0 | 0.836·10−8 | 107.4 | 5.43 | 53 |
| 23.9 * | 5.21 * | 238 * | ||||
| CC-Beam | 29.3 | 49.3 | 2.01·10−8 | 71.5 | 4.78 | 42 |
| 5.53 * | 5.12 * | 543 * |
| Structure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plate-B1 | 0.053 | 154 | 65.3 | 60.1 |
| Plate-B2 | 0.045 | 92.5 | 68.7 | 48.2 |
| Cantilever | 0.070 | 90.4 | 107.4 | 103.3 |
| CC-Beam | 0.054 | 61.3 | 71.5 | 43.8 |
| Reference | Detection/SoC | (V·HZ−1/2) | (m·HZ−1/2) | (Vm−1) | (m·Hz−1/2) | (FHZ−1/2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 * | Capacitive/Monolithic | 1.85 MHz | 1.6 × 10−6 | 3.4 × 10−14 | 1.2 × 108 | 1.3 × 10−14 | 1.1 × 10−23 |
| 8.0 × 10−14 | 1.9 × 108 | 8.5 × 10−15 | 7.3 × 10−24 | ||||
| B2 * | Capacitive/Monolithic | 3.30 MHz | 1.5 × 10−6 | 2.4 × 10−14 | 1.1 × 108 | 1.4 × 10−14 | 7.4 × 10−24 |
| 6.1 × 10−14 | 1.8 × 108 | 8.3 × 10−15 | 4.3 × 10−24 | ||||
| Cantilever * | Capacitive/Monolithic | 5.00 MHz | 1.2 × 10−6 | 4.7 × 10−14 | 4.6 × 107 | 2.6 × 10−14 | 4.3 × 10−24 |
| 11 × 10−14 | 4.6 × 107 | 2.6 × 10−14 | 4.4 × 10−24 | ||||
| CC-Beam * | Capacitive/Monolithic | 4.50 MHz | 1.0 × 10−6 | 2.9 × 10−14 | 1.0 × 108 | 9.7 × 10−15 | 4.0 × 10−24 |
| 9.5 × 10−14 | 2.1 × 108 | 4.8 × 10−15 | 2.0 × 10−24 | ||||
| [8] | Capacitive/NOT | 21 kHz | 3.0 × 10−7 | - | - | - | 2.7 × 10−21 |
| [9] | Capacitive/Monolithic | 1.5 MHz | 3.5 × 10−8 | - | - | 1.5 × 10−11 | 2.6 × 10−21 |
| [10] | Capacitive/Hybrid | 13 MHz | 5.0 × 10−7 | - | - | - | 1.3 × 10−19 |
| [11] | Capacitive/Monolithic | 5.3 kHz | 2.5 × 10−5 | - | - | - | 1.6 × 10−20 |
| [12] | Piezo/Monolithic | 126 MHz | 1.5 × 10−9 | - | 3.8 × 104 | 3.9 × 10−14 | - |
| [13] | Piezo/Hybrid | 19 MHz | 1.3 × 10−8 | - | 4.2 × 104 | 3.1 × 10−13 | - |
| [14] | Optical/NOT | 860 MHz | 1.1 × 10−6 | - | 5.6 × 1010 | 2.0 × 10−17 | - |
| [15] | Optical/NOT | 5.4 GHz | - | - | - | 1.1 × 10−17 | - |
| [16] | Optical/NOT | 13 MHz | 2.0 × 10−8 | - | 2.0 × 107 | 1.0 × 10−15 | - |
| [17] | MW Cavity/NOT | 54 MHz | - | - | - | 1.3 × 10−15 | - |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perelló-Roig, R.; Verd, J.; Bota, S.; Segura, J. Thermomechanical Noise Characterization in Fully Monolithic CMOS-MEMS Resonators. Sensors 2018, 18, 3124. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093124
Perelló-Roig R, Verd J, Bota S, Segura J. Thermomechanical Noise Characterization in Fully Monolithic CMOS-MEMS Resonators. Sensors. 2018; 18(9):3124. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093124
Chicago/Turabian StylePerelló-Roig, Rafel, Jaume Verd, Sebastià Bota, and Jaume Segura. 2018. "Thermomechanical Noise Characterization in Fully Monolithic CMOS-MEMS Resonators" Sensors 18, no. 9: 3124. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093124
APA StylePerelló-Roig, R., Verd, J., Bota, S., & Segura, J. (2018). Thermomechanical Noise Characterization in Fully Monolithic CMOS-MEMS Resonators. Sensors, 18(9), 3124. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093124





