Extraction of High-Precision Urban Impervious Surfaces from Sentinel-2 Multispectral Imagery via Modified Linear Spectral Mixture Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
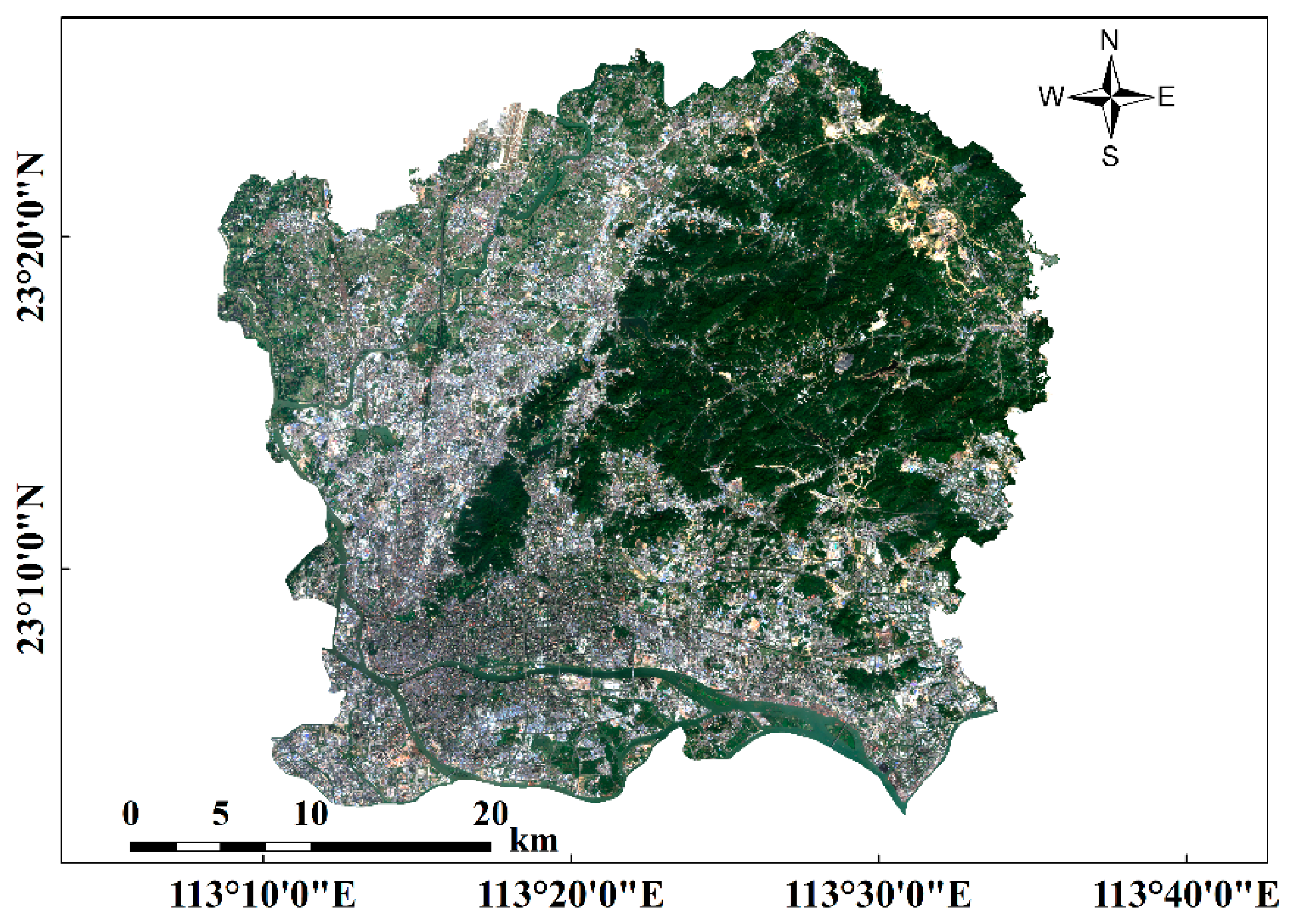
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sentinel-2A Image
3. Methods
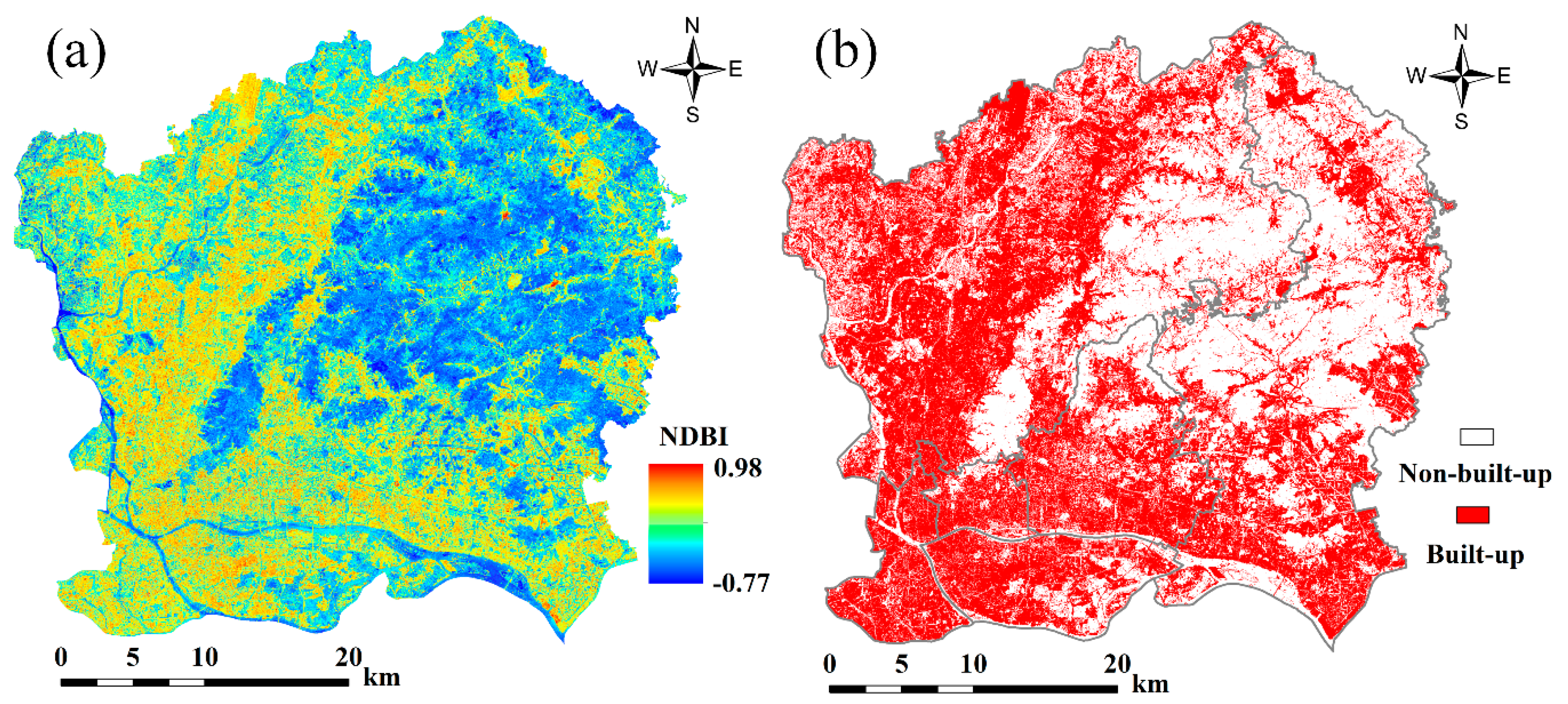
3.1. Automatic Extraction of Built-Up
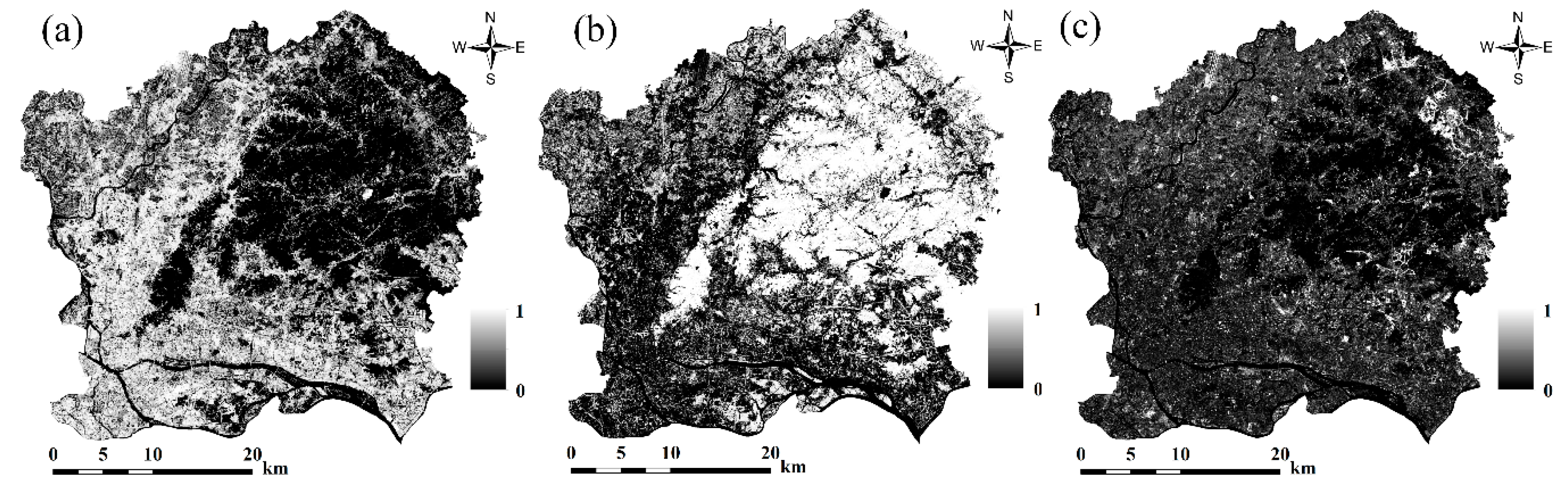
3.2. Modified Linear Spectral Mixture Analysis
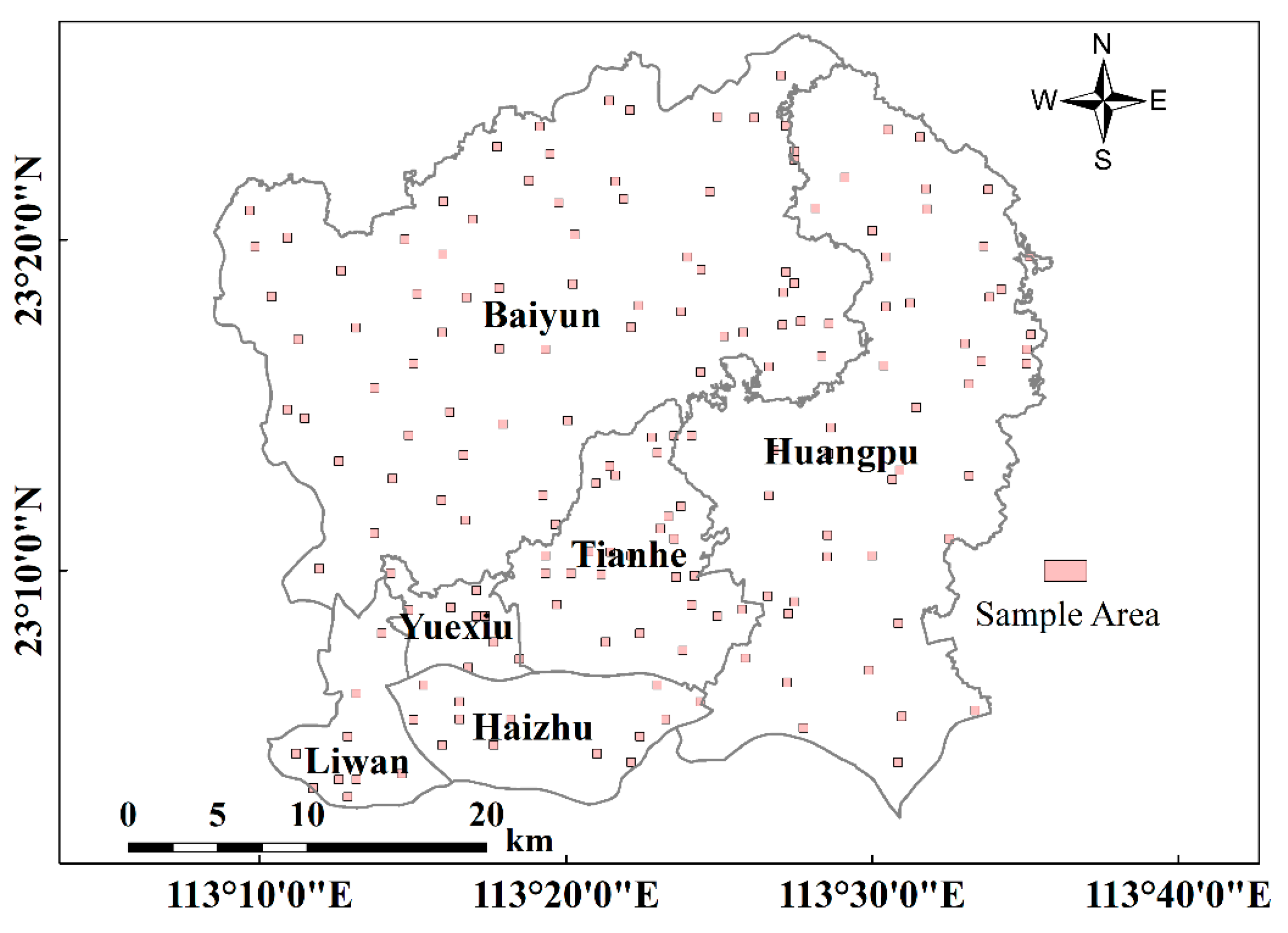
3.3. Accuracy Assessment
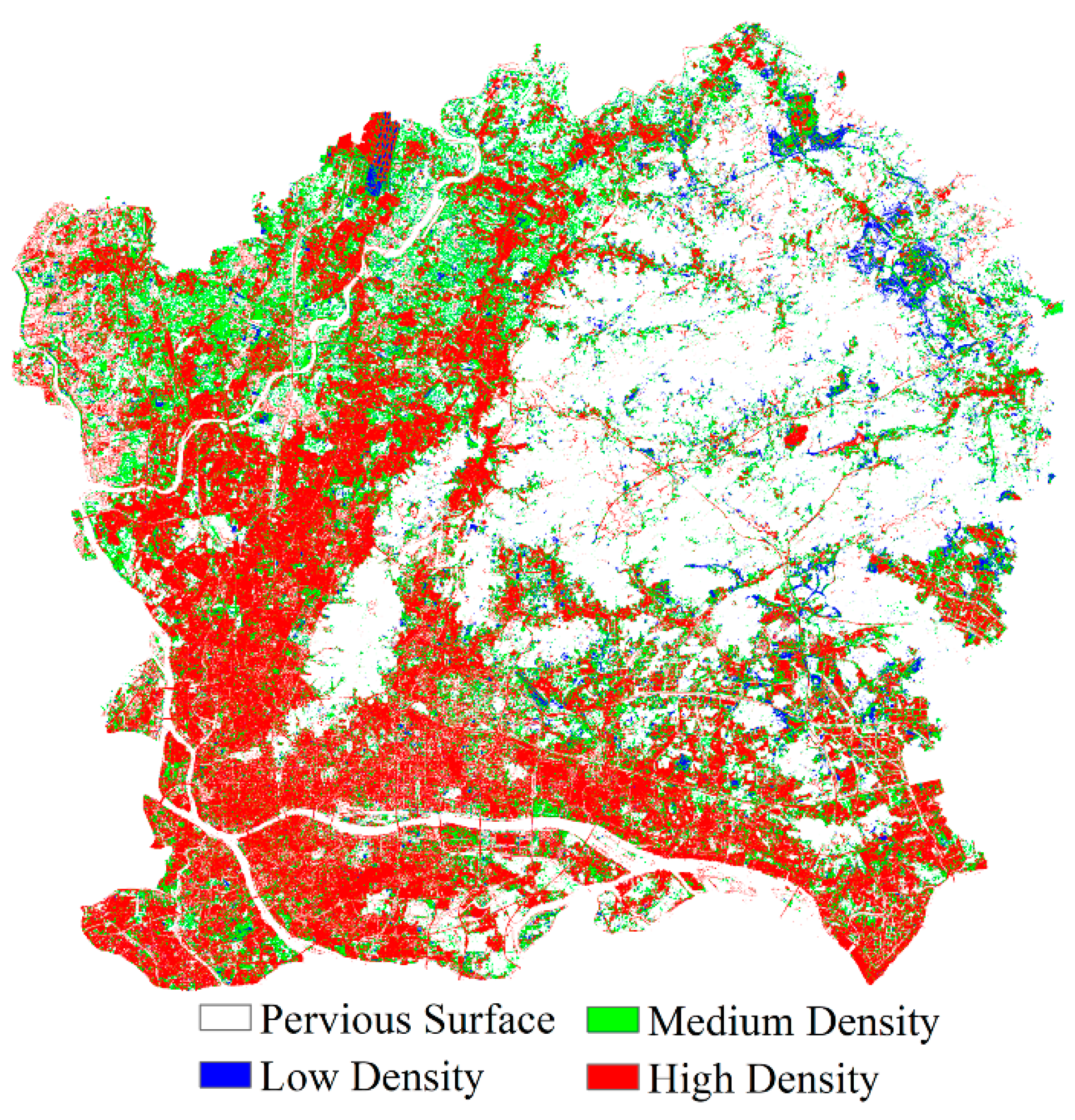
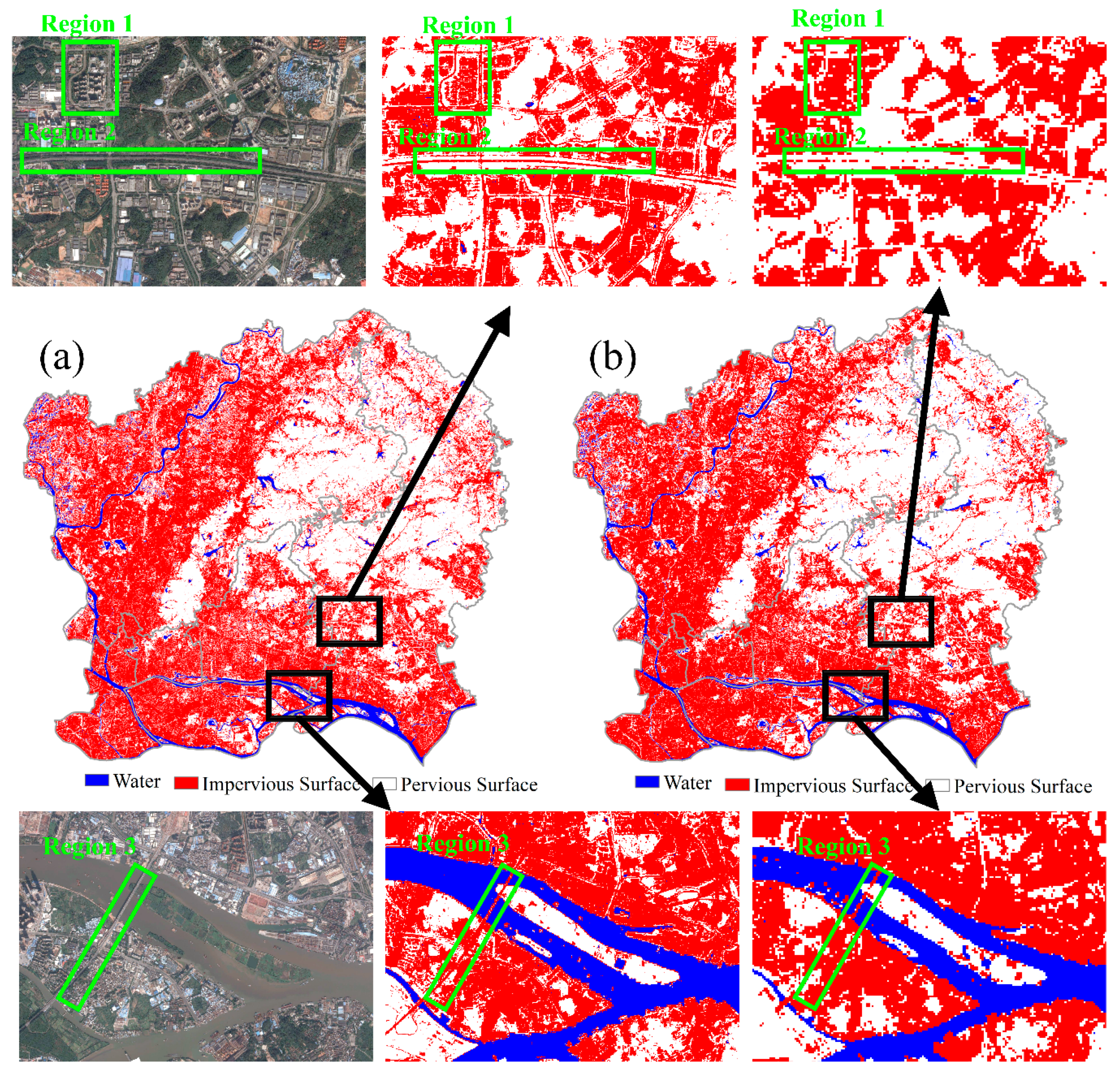
4. Results
5. Performance Assessment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, K.; Ruan, H.; Liu, X. Coupling modified linear spectral mixture analysis and soil conservation service curve number (SCS-CN) models to simulate surface runoff: Application to the main urban area of Guangzhou, China. Water 2016, 8, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Bauer, M.E. Comparison of impervious surface area and normalized difference vegetation index as indicators of surface urban heat island effects in landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabec, E.; Schulte, S.; Richards, P.L. Impervious surfaces and water quality: A review of current literature and its implications for watershed planning. J. Plan. Lit. 2002, 16, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Lu, D.; Liang, B. Urban surface biophysical descriptors and land surface temperature variations. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, M.; Dymond, R.L.; Goetz, S.J.; Jantz, C.; Goulet, N. Evaluation of impervious surface estimates in a rapidly urbanizing watershed. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2004, 70, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, K.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Sun, C. Measuring spatio-temporal dynamics of impervious surface in Guangzhou, China, from 1988 to 2015, using time-series landsat imagery. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 264–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Wu, C. Understanding population segregation from landsat ETM+ imagery: A geographically weighted regression approach. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2004, 41, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinn, S.R.; Stanford, M.; Scarth, P.; Murray, A.T.; Shyy, P.T. Monitoring the composition of urban environments based on the vegetation-impervious surface-soil (VIS) model by subpixel analysis techniques. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 4131–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henits, L.; Mucsi, L.; Liska, C.M. Monitoring the changes in impervious surface ratio and urban heat island intensity between 1987 and 2011 in Szeged, Hungary. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Lu, D.; Kuang, W. Examining urban impervious surface distribution and its dynamic change in Hangzhou metropolis. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Huang, C.; Homer, C.G.; Wylie, B.K.; Coan, M. An approach for mapping large-area impervious surfaces: Synergistic use of landsat-7 ETM+ and high spatial resolution imagery. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 29, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyoosh, A.K.; Ghosh, S.K. Semi-automatic mapping of anthropogenic impervious surfaces in an urban/suburban area using Landsat 8 satellite data. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2017, 54, 471–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Li, C.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, W.; Xi, L. Subpixel urban impervious surface mapping: The impact of input landsat images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 133, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Weng, Q.; Shao, Z. An evaluation of monthly impervious surface dynamics by fusing Landsat and MODIS time series in the Pearl River Delta, China, from 2000 to 2015. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 201, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cablk, M.E.; Minor, T.B. Detecting and discriminating impervious cover with high-resolution IKONOS data using principal component analysis and morphological operators. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4627–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Weng, Q. Extraction of urban impervious surfaces from an IKONOS image. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 1297–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, P. Impervious surface extraction in urban areas from high spatial resolution imagery using linear spectral unmixing. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2015, 1, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Hu, X.; Liu, H. Estimating impervious surfaces using linear spectral mixture analysis with multitemporal aster images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 4807–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, J.; Rahman, A.; Singh, C.K. Modeling urban heat islands in heterogeneous land surface and its correlation with impervious surface area by using night-time ASTER satellite data in highly urbanizing city, Delhi-India. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 52, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. Extracting urban impervious surface from GF-1 imagery using one-class classifiers. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.04824. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, C. Mapping urban impervious surface with dual-polarimetric SAR data: An improved method. Lands. Urban Plan. 2016, 151, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y. A new scheme for urban impervious surface classification from SAR images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 139, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tison, C.; Nicolas, J.; Tupin, F.; Maitre, H. A new statistical model for Markovian classification of urban areas in high-resolution SAR images. Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp. 2004, 42, 2046–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Liu, C. The integrated use of DMSP-OLS nighttime light and MODIS data for monitoring large-scale impervious surface dynamics: A case study in the yangtze river delta. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9359–9378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Lu, D.; Kuang, W. Improving fractional impervious surface mapping performance through combination of DMSP-OLS and MODIS NDVI data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Shao, Z.; Tu, C.; Zhang, Q. Impacts of Feature Selection for urban Impervious Surface Extraction Using Optical Image and SAR Data. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Earth Observation and remote Sensing Applications, Guangzhou, China, 4–6 July 2016; pp. 419–423. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Jiang, L.; Lin, H.; Liao, M. Quantifying sub-pixel urban impervious surface through fusion of optical and inSAR imagery. Mapp. Sci. Remote Sens. 2009, 46, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, H. Improving the impervious surface estimation with combined use of optical and SAR remote sensing images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 141, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, R. Exploring the optimal integration levels between SAR and optical data for better urban land cover mapping in the Pearl River Delta. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 64, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyong, H.U.; Chen, S.; Qiao, K.; Cao, S. Integrating CART algorithm and multi-source remote sensing data to estimate sub-pixel impervious surface coverage: A case study from Beijing municipality, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 614–625. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Q.; Hu, X. Medium spatial resolution satellite imagery for estimating and mapping urban impervious surfaces using LSMA and ANN. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 2397–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Chen, X.; Ren, J.; Zhang, A.; Jia, X. Stratified spectral mixture analysis of medium resolution imagery for impervious surface mapping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 60, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarchi, L.; Canters, F.; Chan, J.C.; De Voorde, T.V. Multiple endmember unmixing of CHRIS/Proba imagery for mapping impervious surfaces in urban and suburban environments. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3409–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, C. A geostatistical temporal mixture analysis approach to address endmember variability for estimating regional impervious surface distributions. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2016, 53, 102–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Shen, Z.; Cheng, X.; Xia, L.; Luo, J. Impervious surface extraction using coupled spectral–spatial features. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 035013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Murray, A.T. Estimating impervious surface distribution by spectral mixture analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Hu, X.; Lu, D. Extracting impervious surfaces from medium spatial resolution multispectral and hyperspectral imagery: A comparison. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3209–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; He, Y. Automated mapping of impervious surfaces in urban and suburban areas: Linear spectral unmixing of high spatial resolution imagery. Int. J. App. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 54, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, S.J.; Wright, R.; Smith, A.; Zinecker, E.; Schaub, E. IKONOS imagery for resource management: Tree cover, impervious surfaces, and riparian buffer analyses in the mid-atlantic region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Der Linden, S.V.; Hostert, P. The influence of urban structures on impervious surface maps from airborne hyperspectral data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2298–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayes, M.; Mustard, J.F.; Melillo, J.M. Forest cover change in miombo woodlands: Modeling land cover of African dry tropical forests with linear spectral mixture analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 165, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, S. Assessment of urban growth in Guangzhou using multi-temporal, multi-sensor landsat data to quantify and map impervious surfaces. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 5936–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thouvenin, P.; Dobigeon, N.; Tourneret, J. Hyperspectral unmixing with spectral variability using a perturbed linear mixing model. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X. Two-step constrained nonlinear spectral mixture analysis method for mitigating the collinearity effect. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2873–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, C. Incorporating land use land cover probability information into endmember class selections for temporal mixture analysis. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 101, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Fan, W.; Weng, Q. Improving urban impervious surface mapping by linear spectral mixture analysis and using spectral indices. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 41, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Bello, U.D.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P. Sentinel-2: ESA’s optical high-resolution mission for GMES operational services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagolle, O.; Sylvander, S.; Huc, M.; Claverie, M.; Clesse, D.; Dechoz, C.; Lonjou, V.; Poulain, V. SPOT-4 (Take 5): Simulation of Sentinel-2 time series on 45 large sites. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12242–12264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segl, K.; Guanter, L.; Gascon, F.; Kuester, T.; Rogass, C.; Mielke, C. S2eteS: An end-to-end modeling tool for the simulation of Sentinel-2 image products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 5560–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immitzer, M.; Vuolo, F.; Atzberger, C. First experience with Sentinel-2 data for crop and tree species classifications in central europe. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, A.; Sannier, C.; Corpetti, T. Monitoring urban areas with Sentinel-2A data: Application to the update of the copernicus high resolution layer imperviousness degree. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, M.; Corbane, C.; Julea, A.; Florczyk, A.J.; Syrris, V.; Soille, P. Assessment of the added-value of Sentinel-2 for detecting built-up areas. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, S.; Qin, X.; Zhao, N.; Liang, L. Mapping of urban surface water bodies from Sentinel-2 MSI imagery at 10 m resolution via NDWI-based image sharpening. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Li, X. Water bodies’ mapping from Sentinel-2 imagery with modified normalized difference water index at 10-m spatial resolution produced by sharpening the SWIR band. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Ni, S. Use of normalized difference built-up index in automatically mapping urban areas from tm imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, A.; Rajesh, E. A comparative study of built-up index approaches for automated extraction of built-up regions from remote sensing data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2014, 42, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Deng, R.; Xu, J.; Zhang, F. Coupling the modified linear spectral mixture analysis and pixel-swapping methods for improving subpixel water mapping: Application to the Pearl River Delta, China. Water 2017, 9, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Li, W.; Zhou, D.; Tian, L.; Ling, F.; Wang, H.; Gui, Y.; Sun, B. Analysis of landsat-8 OLI imagery for land surface water mapping. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Luo, X.; Xu, X.; Pan, H.; Tong, X. Automated subpixel surface water mapping from heterogeneous urban environments using Landsat 8 OLI imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanqiu, X.U. A study on information extraction of water body with the modified normalized difference water index (MNDWI). J. Remote Sens. 2005, 5, 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, J.B.; Sabol, D.E.; Kapos, V.; Filho, R.A.; Roberts, D.A.; Smith, M.O.; Gillespie, A.R. Classification of multispectral images based on fractions of endmembers: Application to land-cover change in the Brazilian Amazon. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 52, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Tang, L.; Wang, L. Influence of ecological factors on estimation of impervious surface area using Landsat 8 imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, C. Development of a class-based multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis (C-MESMA) approach for analyzing urban environments. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Bands | Central Wavelength (mm) | Spatial Resolution (m) |
|---|---|---|
| Band 1—Coastal aerosol | 0.443 | 60 |
| Band 2—Blue | 0.490 | 10 |
| Band 3—Green | 0.560 | 10 |
| Band 4—Red | 0.665 | 10 |
| Band 5—Vegetation Red Edge | 0.705 | 20 |
| Band 6—Vegetation Red Edge | 0.740 | 20 |
| Band 7—Vegetation Red Edge | 0.783 | 20 |
| Band 8a—Vegetation Red Edge | 0.865 | 20 |
| Band 8b—NIR | 0.842 | 10 |
| Band 9—Water vapor | 0.945 | 60 |
| Band 10—SWIR/Cirrus | 1.375 | 60 |
| Band 11—SWIR | 1.610 | 20 |
| Band 12—SWIR | 2.190 | 20 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, R.; Liu, J.; Xu, J. Extraction of High-Precision Urban Impervious Surfaces from Sentinel-2 Multispectral Imagery via Modified Linear Spectral Mixture Analysis. Sensors 2018, 18, 2873. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092873
Xu R, Liu J, Xu J. Extraction of High-Precision Urban Impervious Surfaces from Sentinel-2 Multispectral Imagery via Modified Linear Spectral Mixture Analysis. Sensors. 2018; 18(9):2873. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092873
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Rudong, Jin Liu, and Jianhui Xu. 2018. "Extraction of High-Precision Urban Impervious Surfaces from Sentinel-2 Multispectral Imagery via Modified Linear Spectral Mixture Analysis" Sensors 18, no. 9: 2873. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092873
APA StyleXu, R., Liu, J., & Xu, J. (2018). Extraction of High-Precision Urban Impervious Surfaces from Sentinel-2 Multispectral Imagery via Modified Linear Spectral Mixture Analysis. Sensors, 18(9), 2873. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18092873





