Handheld Real-Time LED-Based Photoacoustic and Ultrasound Imaging System for Accurate Visualization of Clinical Metal Needles and Superficial Vasculature to Guide Minimally Invasive Procedures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
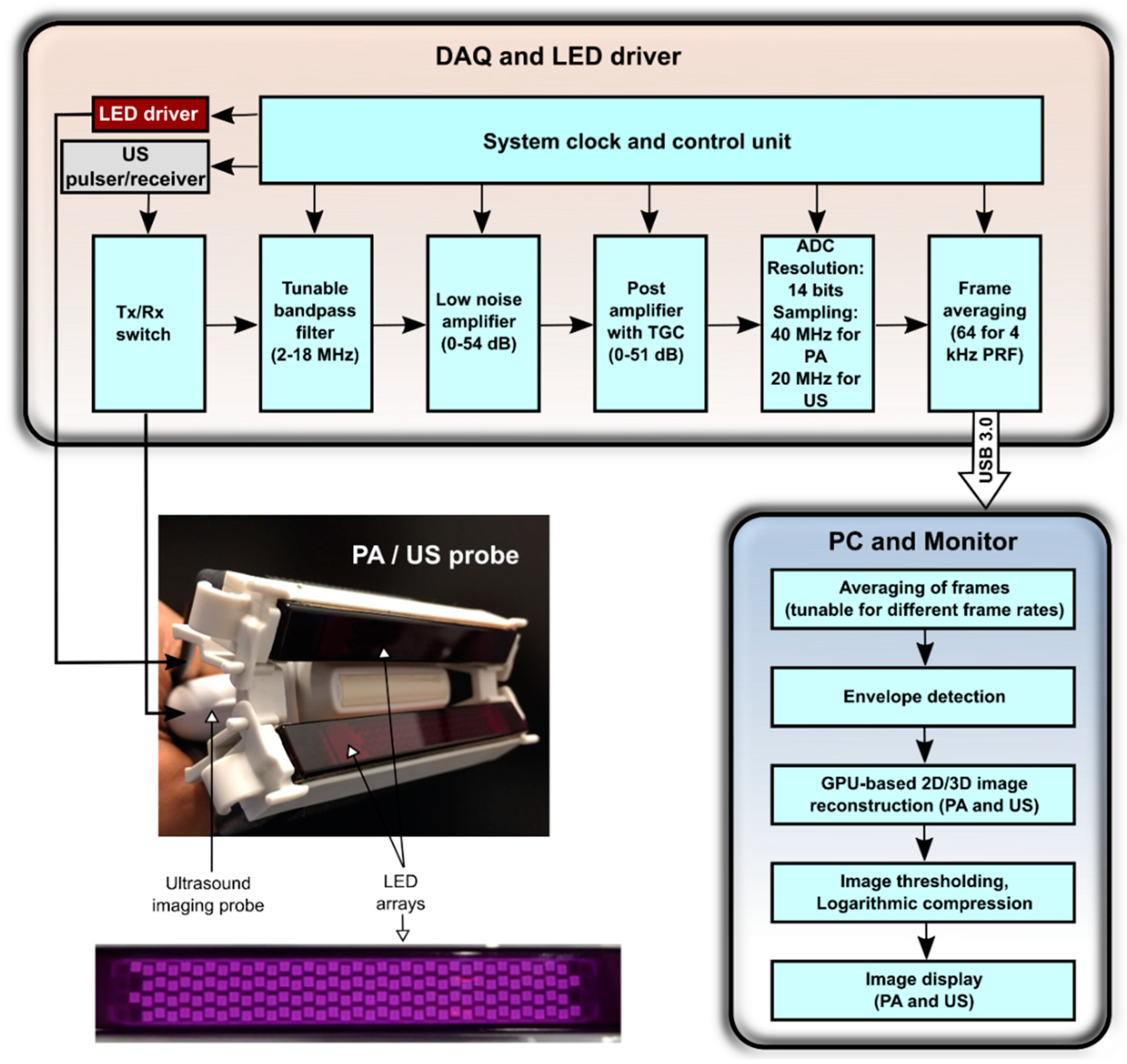
2.1. System Description
2.1.1. Light Illumination
2.1.2. Image Acquisition and Processing
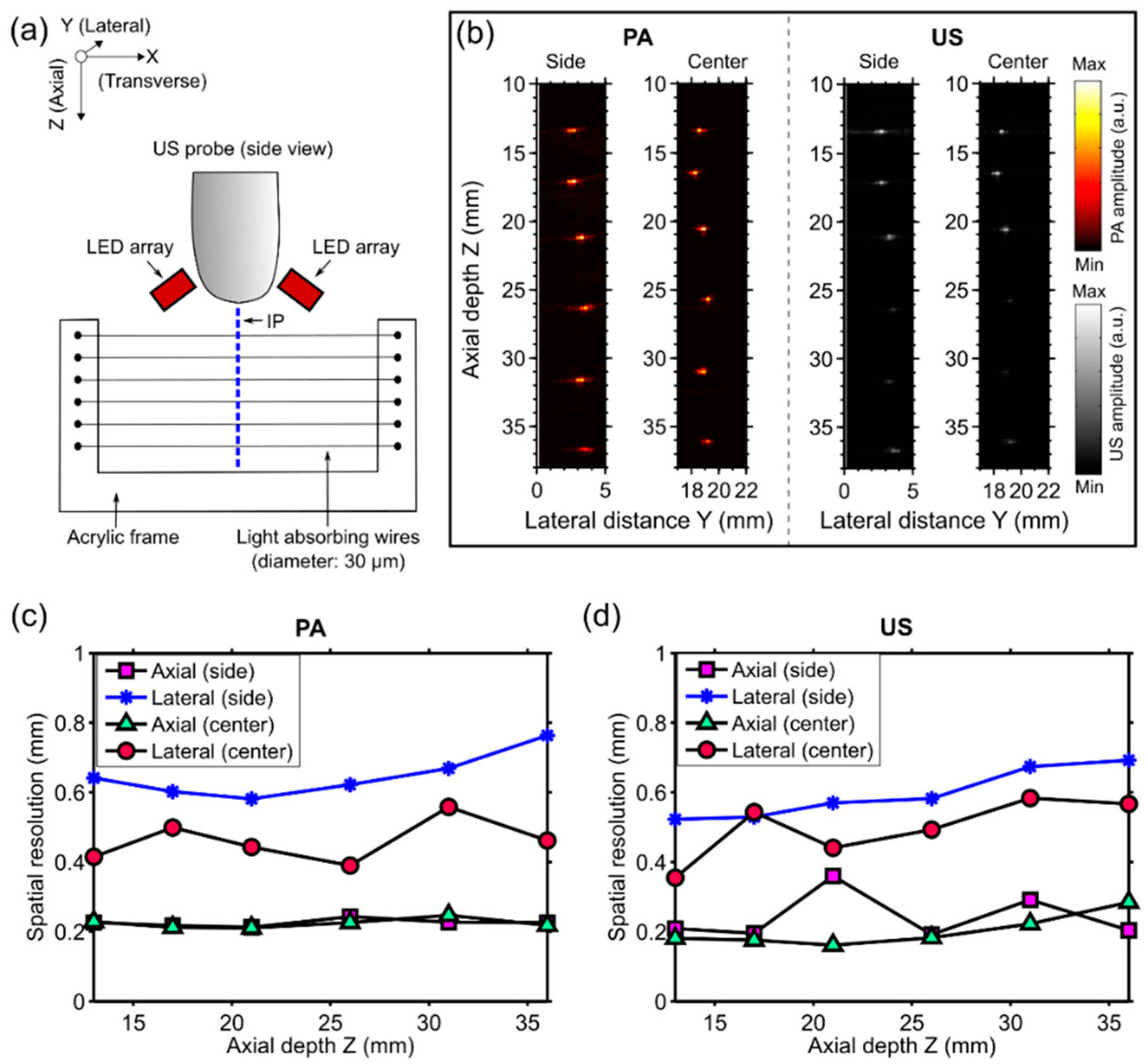
2.2. Spatial Resolution Measurements
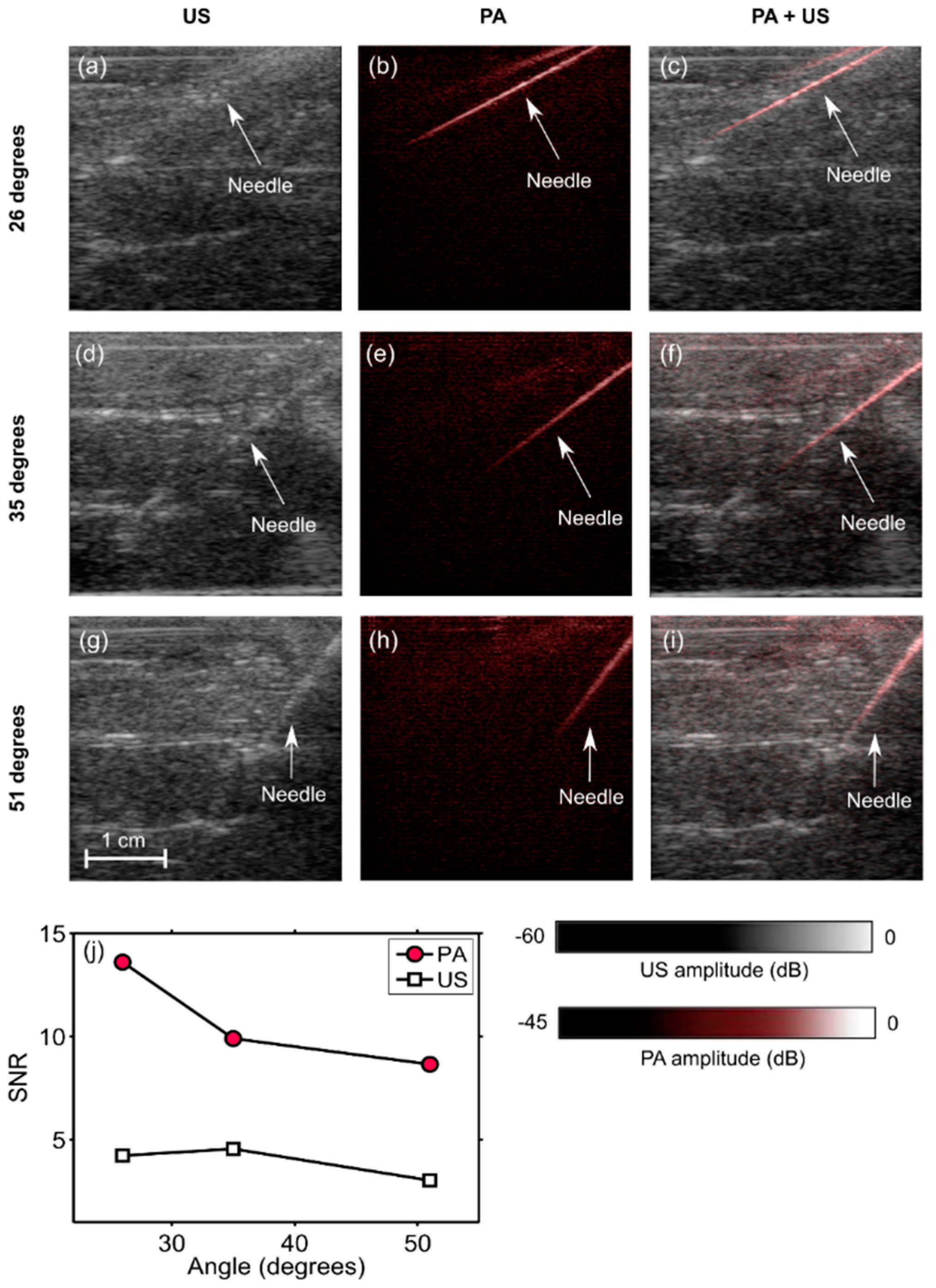
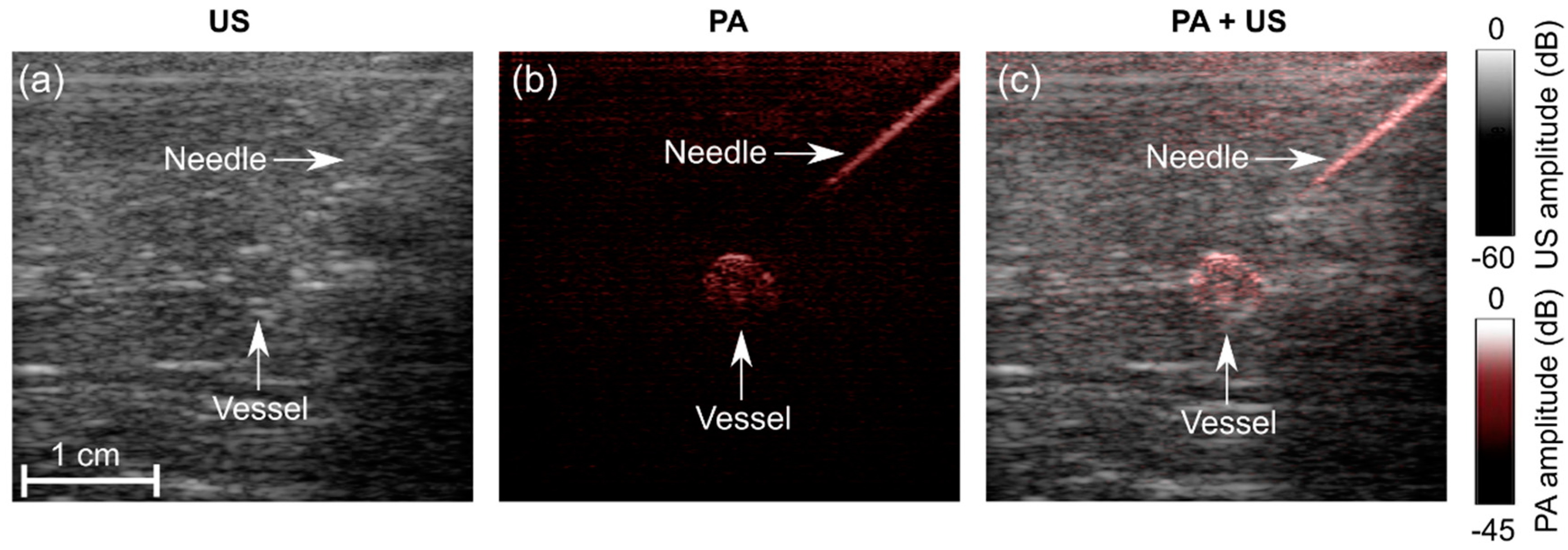
2.3. PA and US Imaging of Clinical Metal Needle Insertions
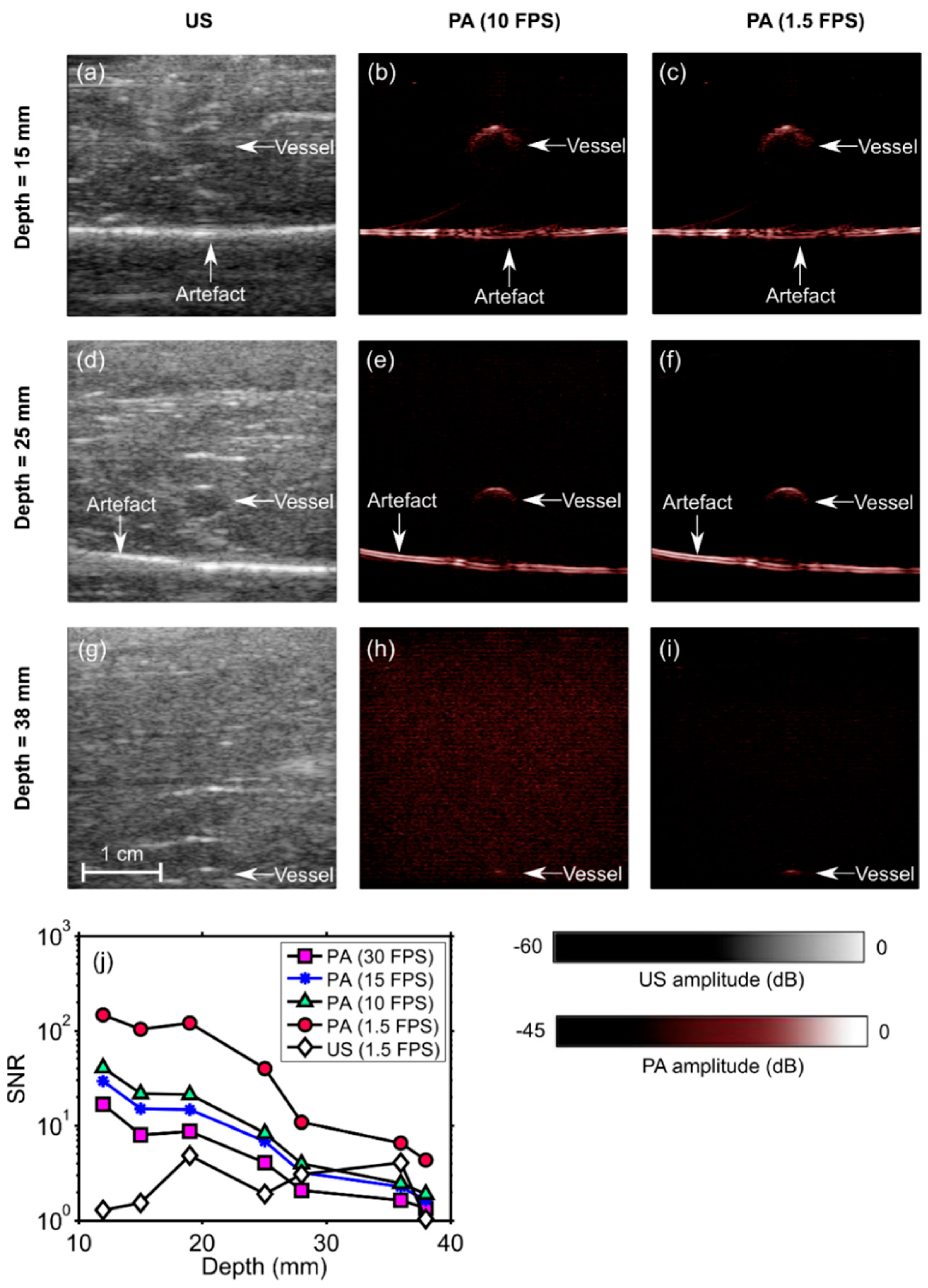
2.4. PA Imaging of a Blood-Vessel-Mimicking Phantom
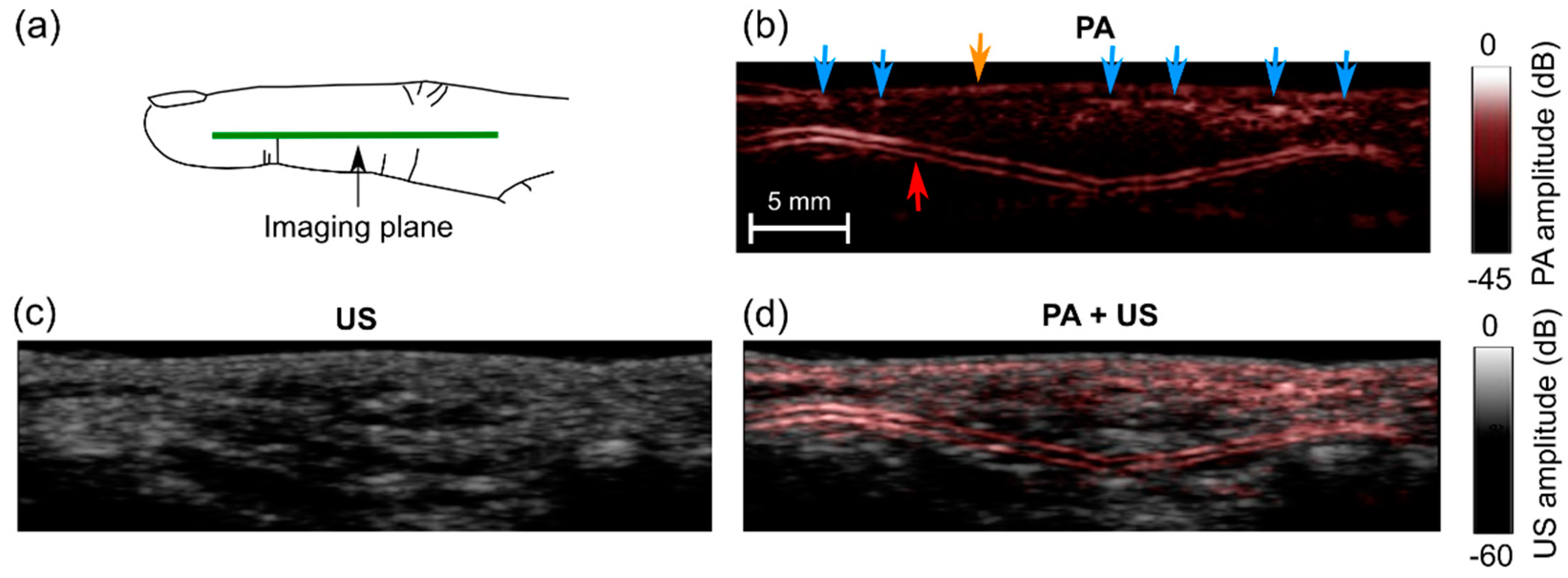
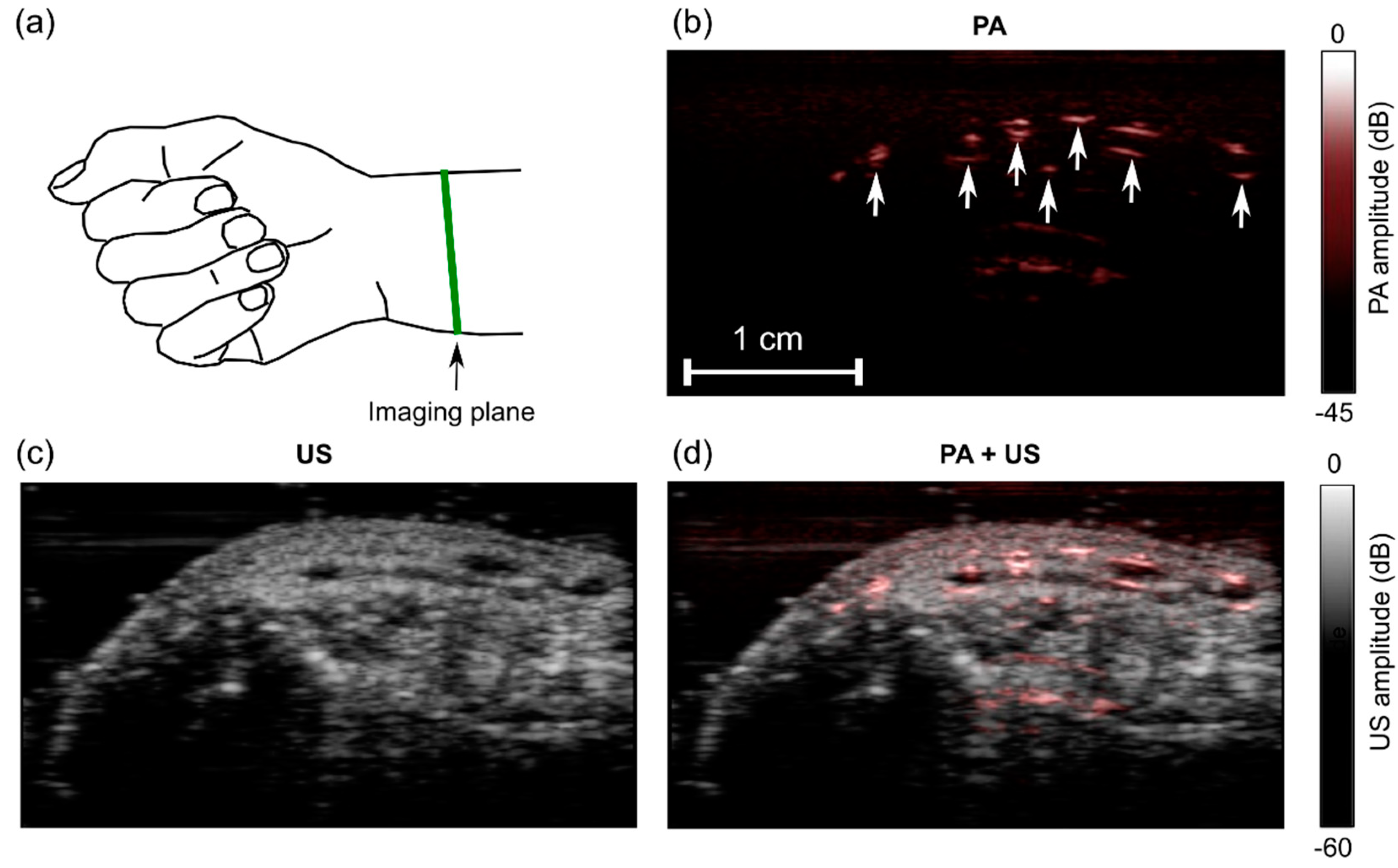
2.5. In Vivo Imaging
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Resolution
3.2. Angle Dependence of US and PA Imaging for In-Plane Needle Insertions
3.3. Imaging Depth—Phantom Experiment
3.4. In Vivo Imaging
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bluvol, M.K.; Bluvol, N.; Shaikh, A.; Kornecki, A.; Del Rey Fernandez, D.; Downey, D.; Fenster, A. A needle guidance system for biopsy and therapy using two-dimensional ultrasound. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randolph, A.G.; Cook, D.J.; Gonzales, C.A.; Pribble, C.G. Ultrasound guidance for placement of central venous catheters: A meta-analysis of the literature. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 24, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narouze, S.N. (Ed.) Atlas of Ultrasound-Guided Procedures in Interventional Pain Management; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rathmell, J.P.; Benzon, H.T.; Dreyfuss, P.; Huntoon, M.; Wallace, M.; Baker, R.; Riew, K.D.; Rosenquist, R.W.; Aprill, C.; Rost, N.S.; et al. Safeguards to Prevent Neurologic Complications after Epidural Steroid Injections: Consensus Opinions from a Multidisciplinary Working Group and National Organizations. Surv. Anesthesiol. 2016, 60, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yao, J.; Wang, L.V. Tutorial on photoacoustic tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 061007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, P. Biomedical photoacoustic imaging. Interface Focus 2011, 1, 602–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Favazza, C.; Wang, L.V. In vivo photoacoustic tomography of chemicals: High-resolution functional and molecular optical imaging at new depths. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2756–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntziachristos, V. Going deeper than microscopy: The optical imaging frontier in biology. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijblom, M.; Piras, D.; van den Engh, F.M.; van der Schaaf, M.; Klaase, J.M.; Steenbergen, W.; Manohar, S. The state of the art in breast imaging using the Twente Photoacoustic Mammoscope: Results from 31 measurements on malignancies. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 3874–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Daniele, P.; Mithun, K.A.S.; van Hespen, J.C.G.; van Leeuwen, T.G.; Steenbergen, W.; Manohar, S. Design and evaluation of a laboratory prototype system for 3D photoacoustic full breast tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 2555–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xia, W.; Steenbergen, W.; Manohar, S. Photoacoustic mammography: Prospects and promises. Breast Cancer Manag. 2014, 3, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermilov, S.A.; Khamapirad, T.; Conjusteau, A.; Leonard, M.H.; Lacewell, R.; Mehta, K.; Miller, T.; Oraevsky, A.A. Laser optoacoustic imaging system for detection of breast cancer. J. Biomed. Opt. 2009, 14, 024007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Es, P.; Biswas, S.K.; Bernelot Moens, H.J.; Steenbergen, W.; Manohar, S. Initial results of finger imaging using photoacoustic computed tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 060501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruizinga, P.; van der Steen, A.F.; de Jong, N.; Springeling, G.; Robertus, J.L.; van der Lugt, A.; van Soest, G. Photoacoustic imaging of carotid artery atherosclerosis. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 110504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean-Ben, X.L.; Razansky, D. Adding fifth dimension to optoacoustic imaging: Volumetric time-resolved spectrally enriched tomography. Nat. Light Sci. Appl. 2014, 3, e137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jathoul, A.P.; Laufer, J.; Ogunlade, O.; Treeby, B.; Cox, B.; Zhang, E.; Johnson, P.; Pizzey, A.R.; Philip, B.; Marafioti, T.; et al. Deep in vivo photoacoustic imaging of mammalian tissues using a tyrosinase-based genetic reporter. Nat. Photon. 2015, 9, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Rajian, J.R.; Girish, G.; Kaplan, M.J.; Fowlkes, J.B.; Carson, P.L.; Wang, X. Photoacoustic and ultrasound dual-modality imaging of human peripheral joints. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 18, 010502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.K.A.; Steenbergen, W.; Manohar, S. Handheld Probe-Based Dual Mode Ultrasound/Photoacoustics for Biomedical Imaging. In Frontiers in Biophotonics for Translational Medicine; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 209–247. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Park, S.; Jung, Y.; Chang, S.; Park, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lovell, J.F.; Kim, C. Programmable real-time clinical photoacoustic and ultrasound imaging system. Sci. Rep. 2016, 12, 35137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Jang, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, C. Real-time Triple-modal Photoacoustic, Ultrasound, and Magnetic Resonance Fusion Imaging of Humans. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 1912–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Erpelding, T.N.; Maslov, K.; Jankovic, L.; Akers, W.J.; Song, L.; Achilefu, S.; Margenthaler, J.A.; Pashley, M.D.; Wang, L.V. Handheld array-based photoacoustic probe for guiding needle biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 046010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Karpiouk, A.; Wang, B.; Emelianov, S. Photoacoustic imaging of clinical metal needles in tissue. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 021309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Nikitichev, D.I.; Mari, J.M.; West, S.J.; Pratt, R.; David, A.L.; Ourselin, S.; Beard, P.C.; Desjardins, A.E. Performance characteristics of an interventional multispectral photoacoustic imaging system for guiding minimally invasive procedures. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 086005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Maneas, E.; Nikitichev, D.I.; Mosse, C.A.; Sato dos Santos, G.; Vercauteren, T.; David, A.L.; Deprest, J.; Ourselin, S.; Beardet, P.C.; et al. Interventional photoacoustic imaging of the human placenta with ultrasonic tracking for minimally invasive fetal surgeries. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 371–378. [Google Scholar]
- Martial, J.-M.; Xia, W.; West, S.J.; Desjardins, A.E. Interventional multispectral photoacoustic imaging with a clinical ultrasound probe for discriminating nerves and tendons: An ex vivo pilot study. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 110503. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W.; West, S.J.; Nikitichev, D.I.; Ourselin, S.; Beard, P.C.; Desjardins, A.E. Interventional multispectral photoacoustic imaging with a clinical linear array ultrasound probe for guiding nerve blocks. Proc. SPIE 2016, 9708, 97080C1–97080C6. [Google Scholar]
- Piras, D.; Grijsen, C.; Schütte, P.; Steenbergen, W.; Manohar, S. Photoacoustic needle: Minimally invasive guidance to biopsy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 070502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lediju Bell, M.A.; Kuo, N.P.; Song, D.Y.; Kang, J.U.; Boctor, E.M. In vivo visualization of prostate brachytherapy seeds with photoacoustic imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 126011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lediju Bell, M.A.; Guo, X.; Song, D.Y.; Boctor, E.M. Transurethral light delivery for prostate photo-acoustic imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 036002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.K.A.; Parameshwarappa, V.; Hendriksen, E.; Steenbergen, W.; Manohar, S. Identification and removal of reflection artifacts in minimally-invasive photoacoustic imaging for accurate visualization of brachytherapy seeds. Proc. SPIE 2017, 10064, 100640G. [Google Scholar]
- Eddins, B.; Lediju Bell, M.A. Design of a multifiber light delivery system for photoacoustic-guided surgery. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 041011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoudi, K.; van den Berg, P.J.; Rabot, O.; Kohl, A.; Tisserand, S.; Brands, P.; Steenbergen, W. Handheld probe integrating laser diode and ultrasound transducer array for ultrasound/photoacoustic dual modality imaging. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 26365–26374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivasubramanian, K.; Pramanik, M. High frame rate photoacoustic imaging at 7000 frames per second using clinical ultrasound system. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.J.; Beard, P.C. Light emitting diodes as an excitation source for biomedical photoacoustics. Proc. SPIE 2013, 8581, 85811F. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, T.J.; Beard, P.C. High power visible light emitting diodes as pulsed excitation sources for biomedical photoacoustics. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, R.S. Using high-power light emitting diodes for photoacoustic imaging. Proc. SPIE 2011, 7968, 79680A. [Google Scholar]
- Kolkman, R.G.M.; Steenbergen, W.; van Leeuwen, T.G. In vivo photoacoustic imaging of blood vessels with a pulsed laser diode. Lasers Med. Sci. 2016, 21, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshitaro, A.; Tsutomu, H. Photoacoustic Imaging with Multiple-Wavelength Light-Emitting Diodes. Jpn. J. Appl. Phy. 2013, 52, 07HB06. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Yang, H.; Jiang, H. In vivo photoacoustic imaging of vasculature with a low-cost miniature light emitting diode excitation. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 1456–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alles, E.J.; Colchester, R.J.; Desjardins, A.E. Adaptive Light Modulation for Improved Resolution and Efficiency in All-Optical Pulse-Echo Ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelect. Freq. 2016, 63, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.V.; Yao, J. A practical guide to photoacoustic tomography in the life sciences. Nat. Meth. 2016, 13, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeger, M.; Schupbach, S.; Gertsch, A.; Kitz, M.; Frenz, M. Fourier reconstruction in optoacoustic imaging using truncated regularized inverse k-space interpolation. Inverse Probl. 2007, 23, S51–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneas, E.; Xia, W.; Nikitichev, D.I.; Daher, B.; Manimaran, M.; Wong, R.Y.J.; Chang, C.W.; Rahmani, B.; Capelli, C.; Schievano, S.; et al. Anatomically realistic ultrasound phantoms using gel wax with 3D printed moulds. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 015033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maneas, E.; Xia, W.; Ogunlade, O.; Fonseca, M.; Nikitichev, D.I.; David, A.L.; West, S.J.; Ourselin, S.; Hebden, J.C.; Vercauteren, T.; et al. Gel wax-based tissue-mimicking phantoms for multispectral photoacoustic imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, M.; Sundaram, T.; Holladay, D.; Nakitende, D. Ultrasound-Guided Peripheral Intravenous Line Placement: A Narrative Review of Evidence-based Best Practices. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 18, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.K.A.; Steenbergen, W. Photoacoustic-guided focused ultrasound (PAFUSion) for identifying reflection artifacts in photoacoustic imaging. Photoacoustics 2015, 3, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.A.; Jaeger, M.; Frenz, M.; Steenbergen, W. In vivo demonstration of reflection artifact reduction in photoacoustic imaging using synthetic aperture photoacoustic-guided focused ultrasound (PAFUSion). Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 2955–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.K.A.; Jaeger, M.; Frenz, M.; Steenbergen, W. Photoacoustic reflection artifact reduction using photoacoustic-guided focused ultrasound: Comparison between plane-wave and element-by-element synthetic backpropagation approach. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 2245–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, E.R.; Xia, W.; Clarkson, M.J.; Desjardins, A.E. Identification and removal of laser-induced noise in photoacoustic imaging using singular value decomposition. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Liu, C.; Gong, X.; Zheng, R.; Bei, Y.; Xing, M.; Du, X.; Liu, X.; Zeng, J.; Lin, R.; et al. Linear array-based real-time photoacoustic imaging system with a compact coaxial excitation handheld probe for noninvasive sentinel lymph node mapping. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 1408–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Noimark, S.; Ourselin, S.; West, S.J.; Finlay, M.C.; David, A.L.; Desjardins, A.E. Ultrasonic Needle Tracking with a Fibre-Optic Ultrasound Transmitter for Guidance of Minimally Invasive Fetal Surgery. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 10–14 September 2017; pp. 637–645. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Guo, X.; Kang, H.-J.; Etienne-Cummings, R.; Boctor, E.M. Active ultrasound pattern injection system (AUSPIS) for interventional tool guidance. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Mari, J.M.; West, S.J.; Ginsberg, Y.; David, A.L.; Ourselin, S.; Desjardins, A.E. In-plane ultrasonic needle tracking using a fiber-optic hydrophone. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 5983–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Ginsberg, Y.; West, S.J.; Nikitichev, D.I.; Ourselin, S.; David, A.L.; Desjardins, A.E. Coded excitation ultrasonic needle tracking: An in vivo study. Med. Phys. 2016, 43, 4065–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; West, S.J.; Mari, J.M.; Ourselin, S.; David, A.L.; Desjardins, A.E. 3D ultrasonic needle tracking with a 1.5 D transducer array for guidance of fetal interventions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Athens, Greece, 17–21 October 2016; pp. 353–361. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W.; Finlay, M.C.; Mari, J.M.; West, S.J.; Ourselin, S.; David, A.L.; Desjardins, A.E. Looking beyond the imaging plane: 3D needle tracking with a linear array ultrasound probe. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3674–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, W.; Kuniyil Ajith Singh, M.; Maneas, E.; Sato, N.; Shigeta, Y.; Agano, T.; Ourselin, S.; J. West, S.; E. Desjardins, A. Handheld Real-Time LED-Based Photoacoustic and Ultrasound Imaging System for Accurate Visualization of Clinical Metal Needles and Superficial Vasculature to Guide Minimally Invasive Procedures. Sensors 2018, 18, 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051394
Xia W, Kuniyil Ajith Singh M, Maneas E, Sato N, Shigeta Y, Agano T, Ourselin S, J. West S, E. Desjardins A. Handheld Real-Time LED-Based Photoacoustic and Ultrasound Imaging System for Accurate Visualization of Clinical Metal Needles and Superficial Vasculature to Guide Minimally Invasive Procedures. Sensors. 2018; 18(5):1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051394
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Wenfeng, Mithun Kuniyil Ajith Singh, Efthymios Maneas, Naoto Sato, Yusuke Shigeta, Toshitaka Agano, Sebastian Ourselin, Simeon J. West, and Adrien E. Desjardins. 2018. "Handheld Real-Time LED-Based Photoacoustic and Ultrasound Imaging System for Accurate Visualization of Clinical Metal Needles and Superficial Vasculature to Guide Minimally Invasive Procedures" Sensors 18, no. 5: 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051394
APA StyleXia, W., Kuniyil Ajith Singh, M., Maneas, E., Sato, N., Shigeta, Y., Agano, T., Ourselin, S., J. West, S., & E. Desjardins, A. (2018). Handheld Real-Time LED-Based Photoacoustic and Ultrasound Imaging System for Accurate Visualization of Clinical Metal Needles and Superficial Vasculature to Guide Minimally Invasive Procedures. Sensors, 18(5), 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051394




