Non-Contact Smartphone-Based Monitoring of Thermally Stressed Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
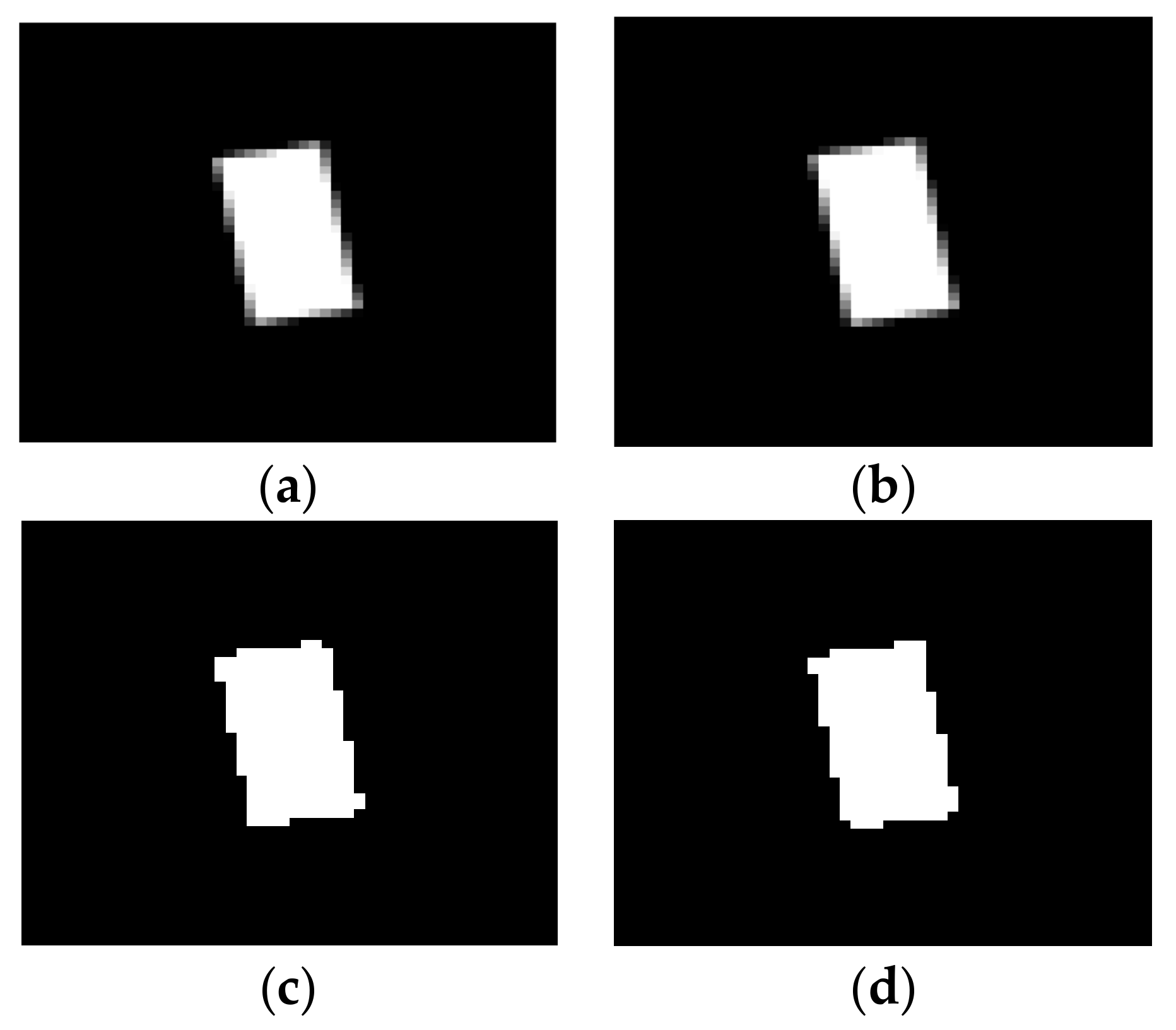
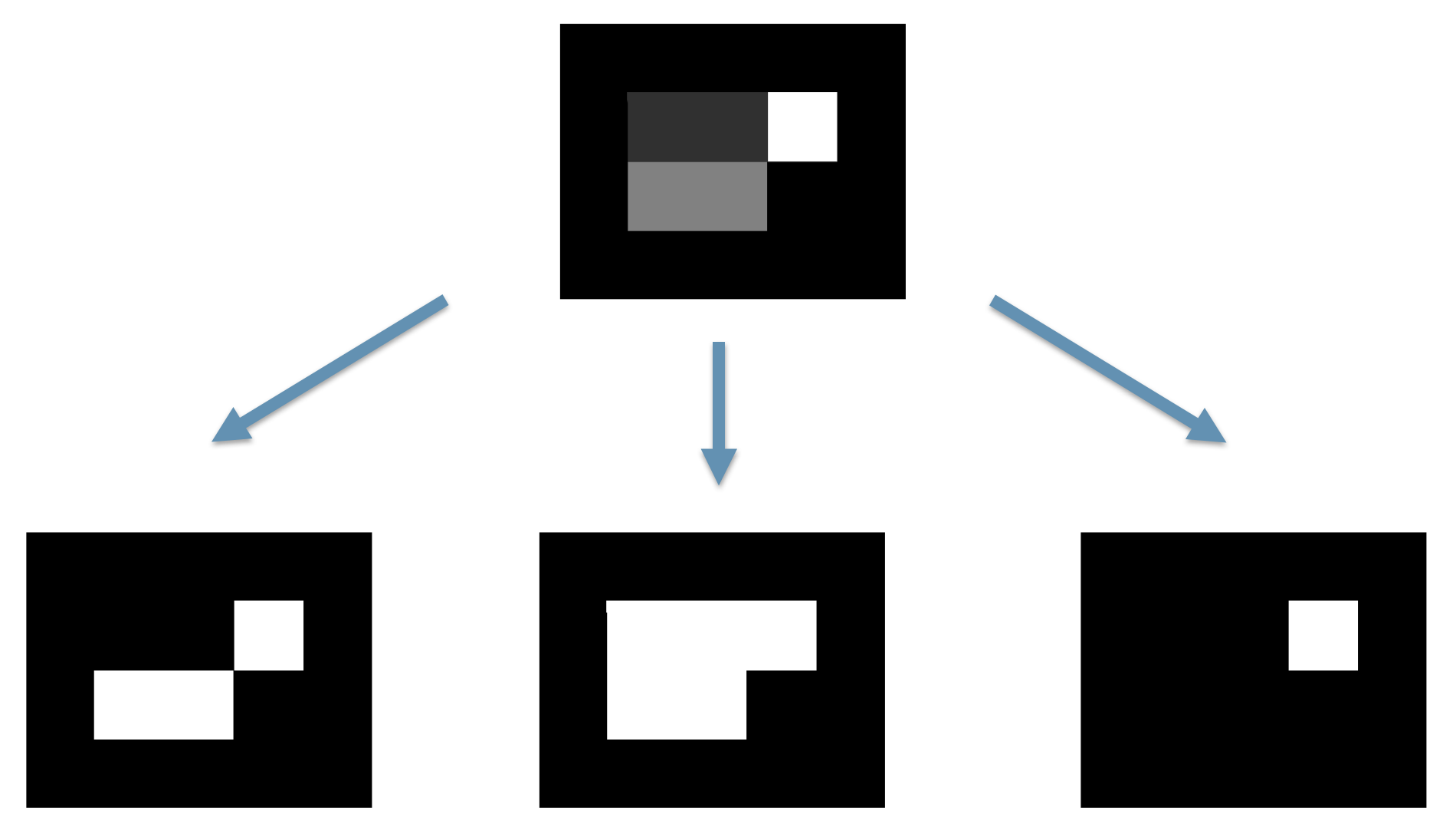
2. Image Processing Algorithm
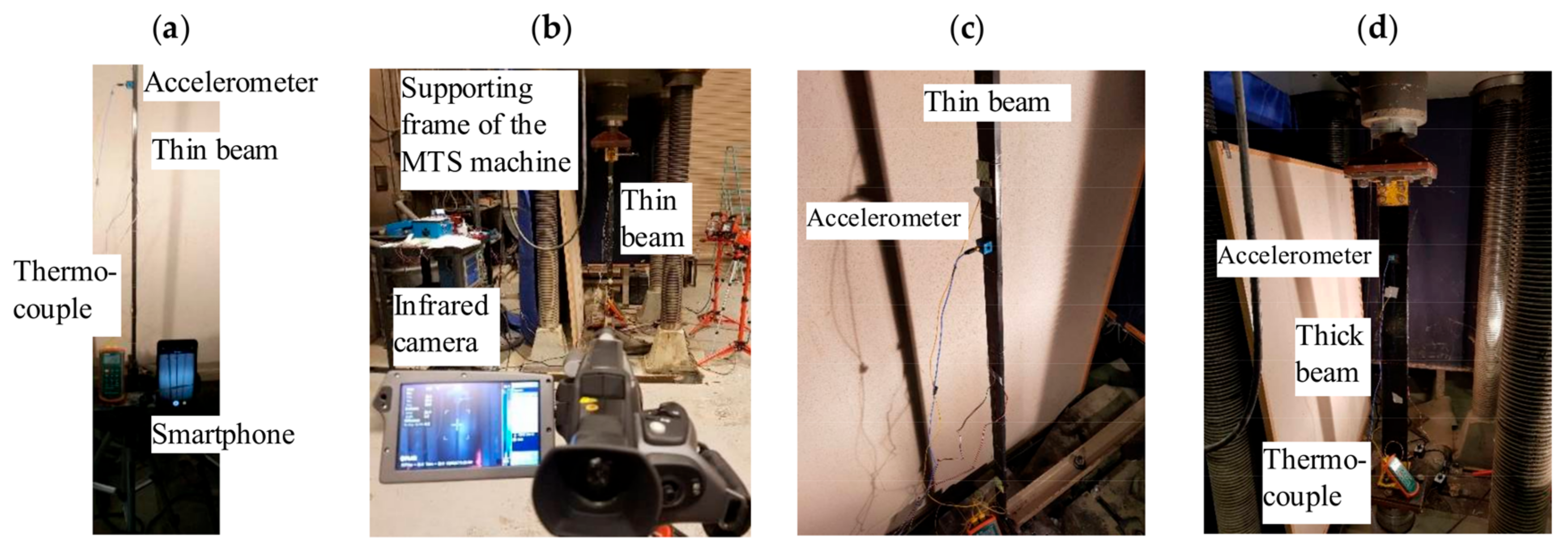
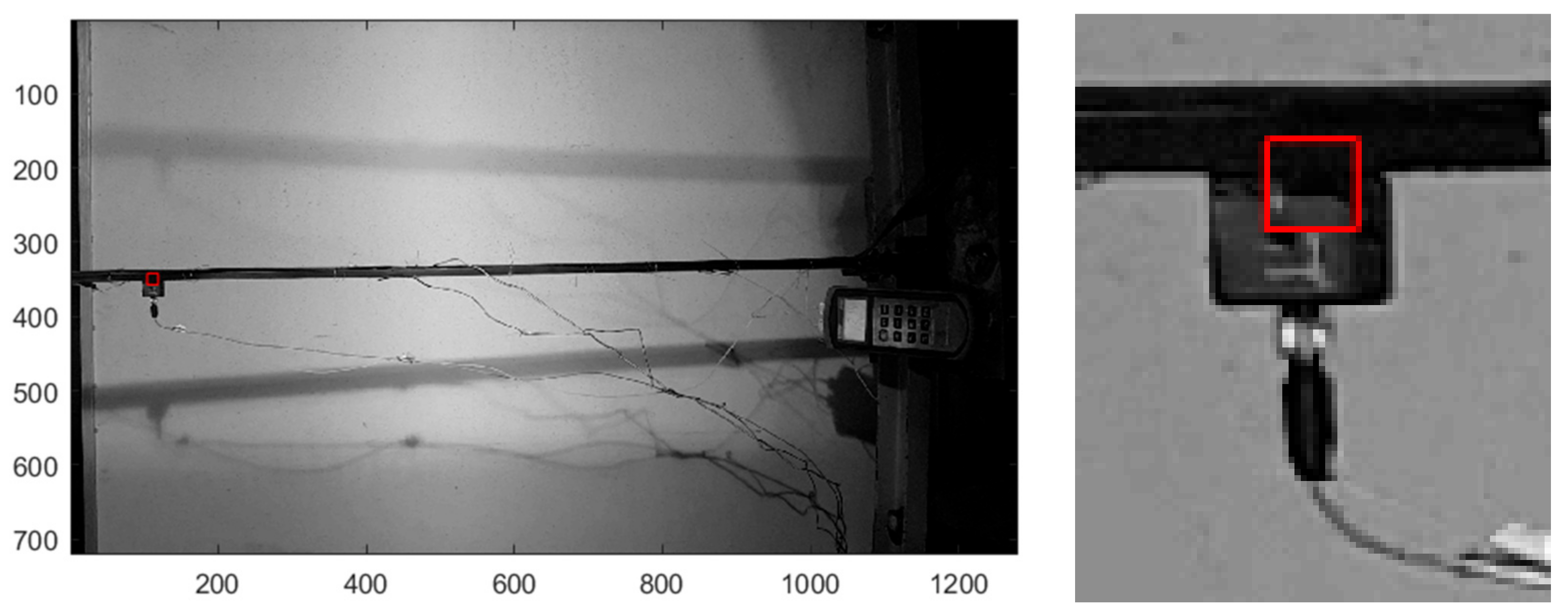
3. Experimental Setup
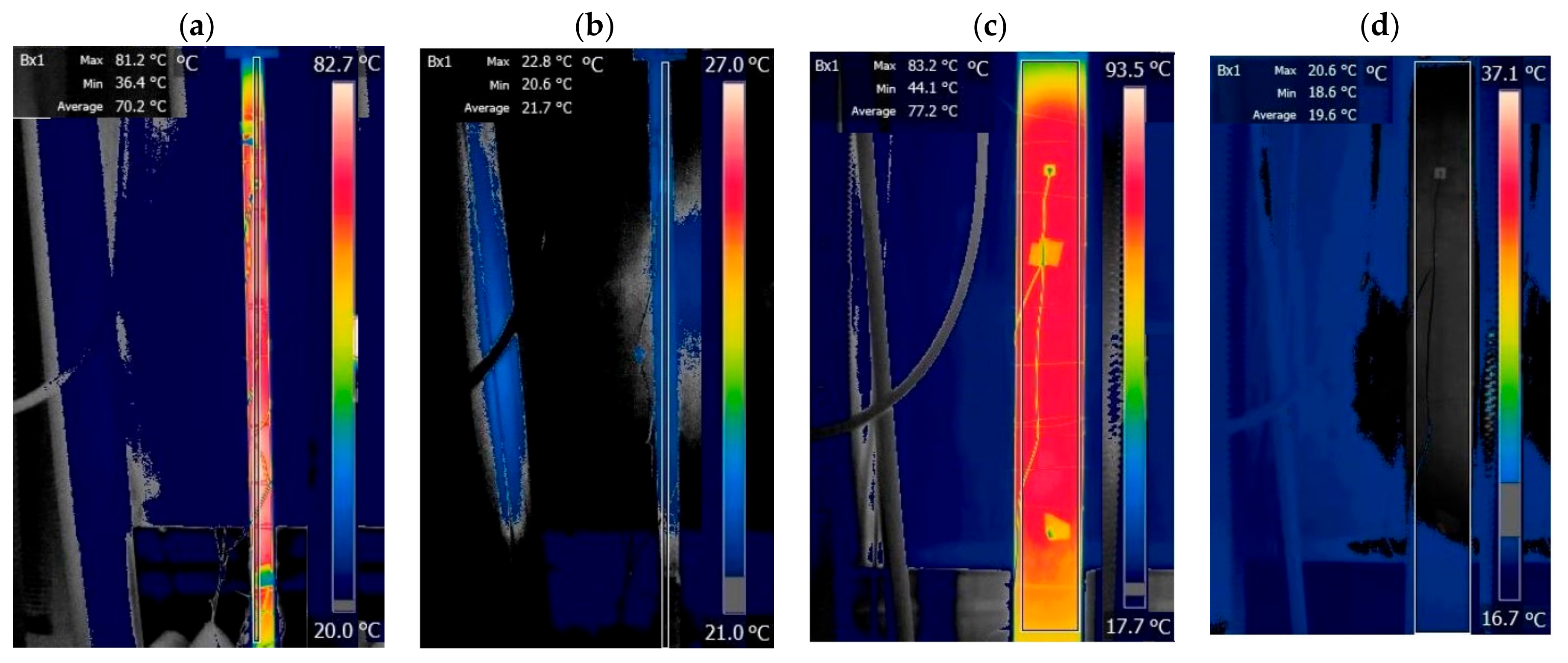
4. Results
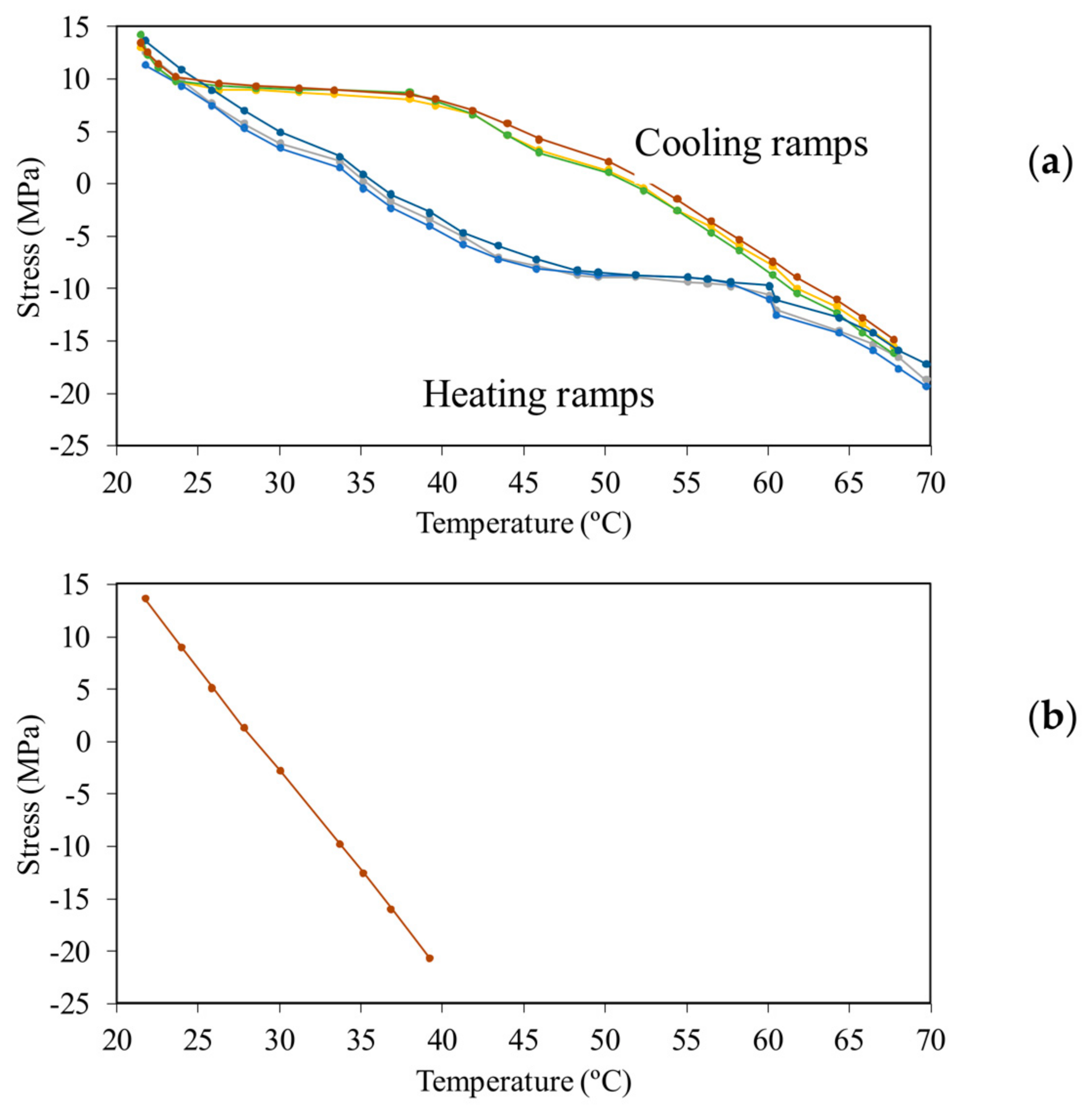
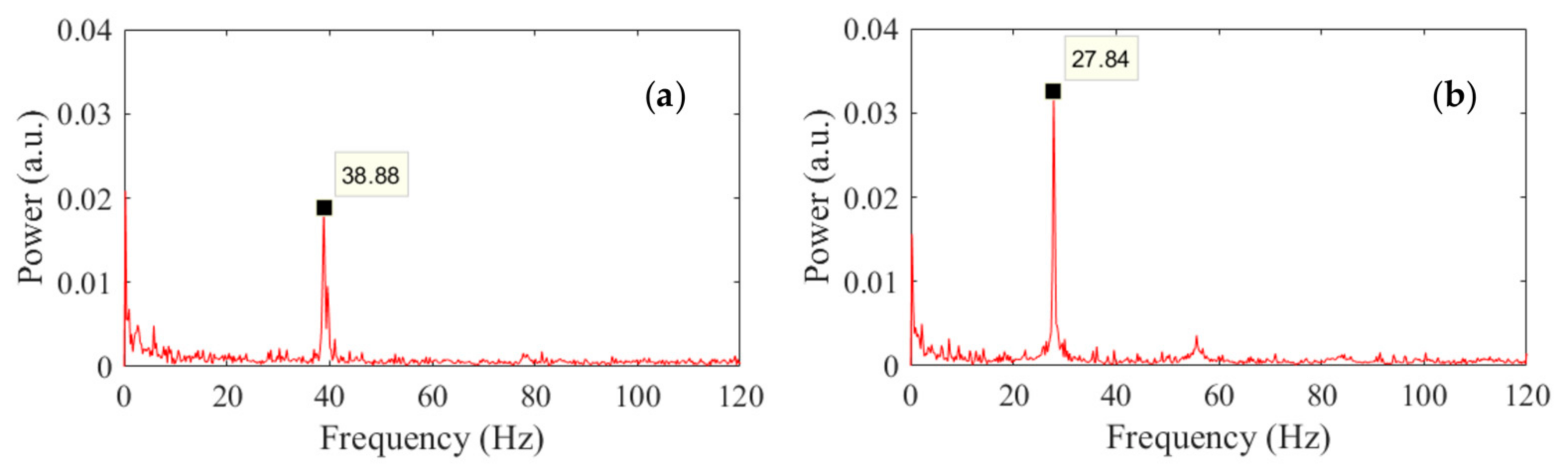
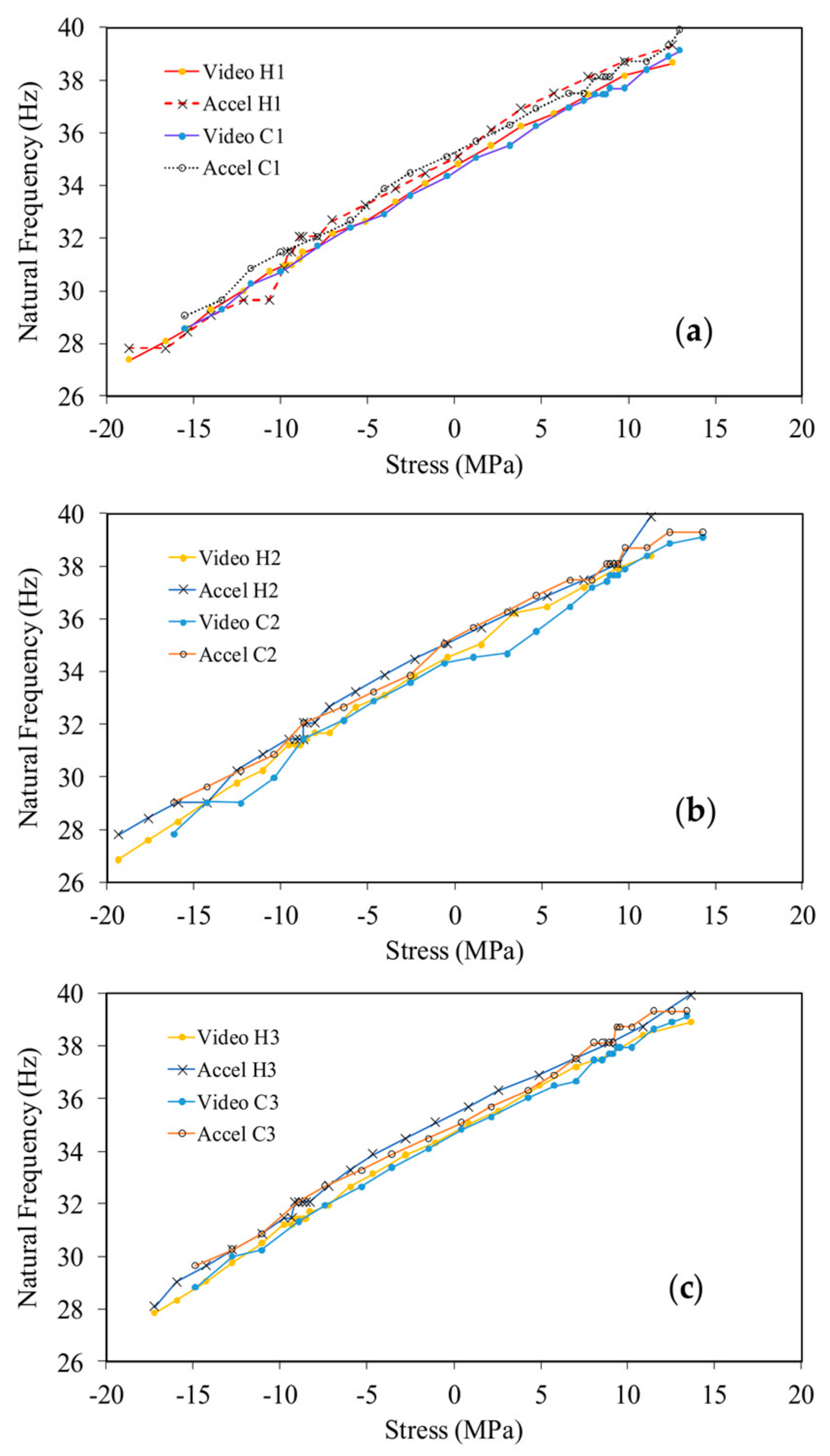
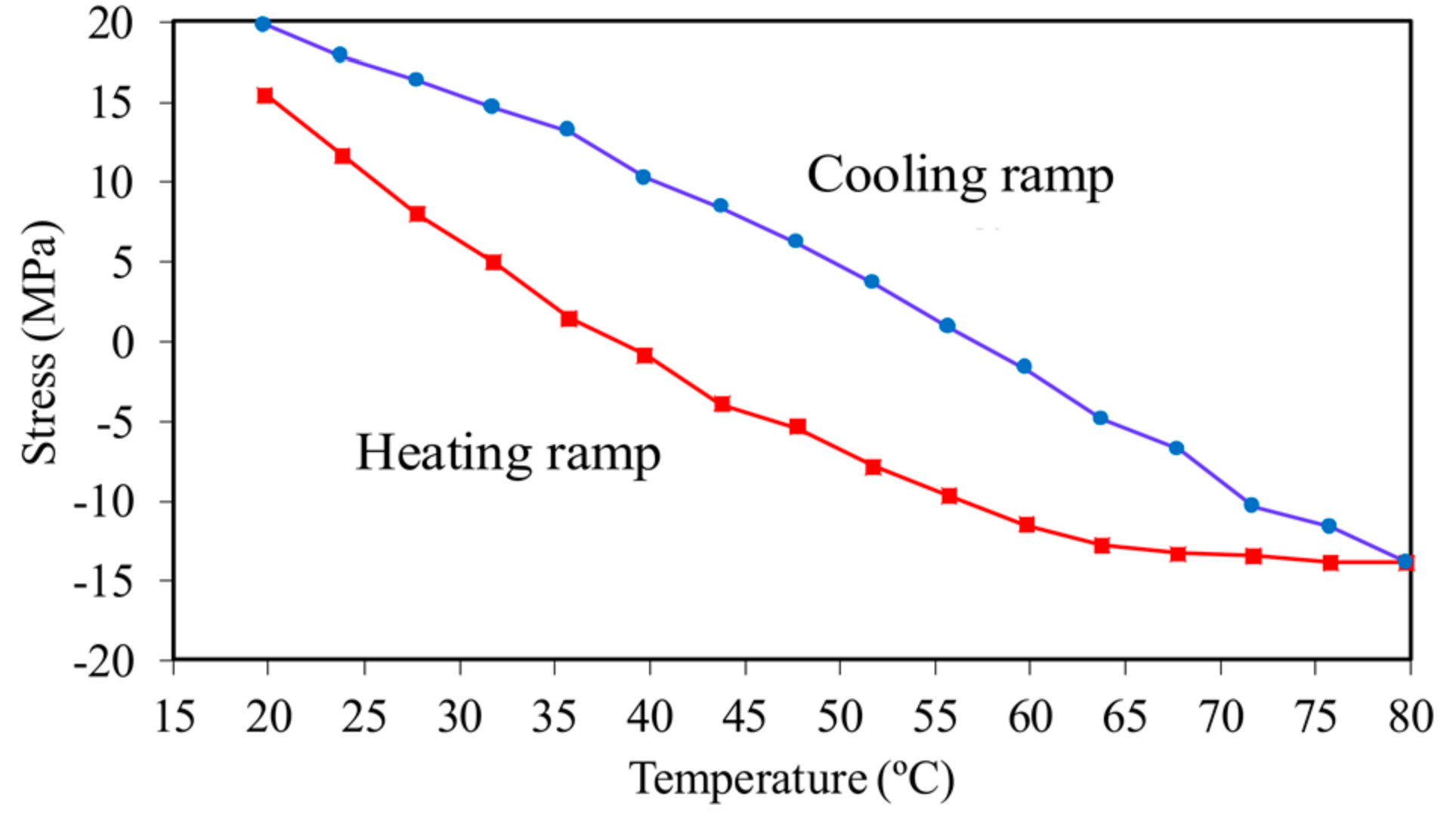
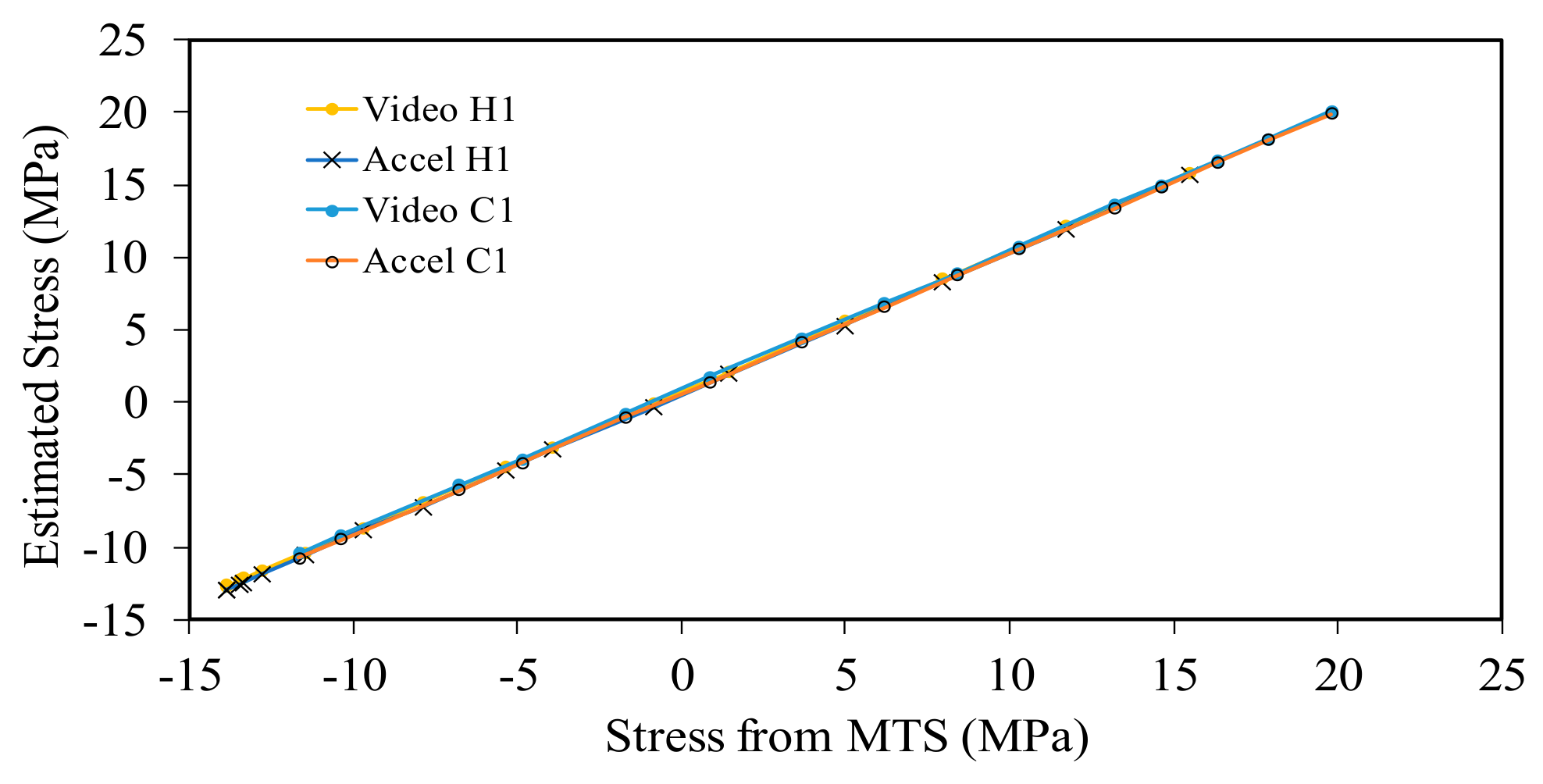
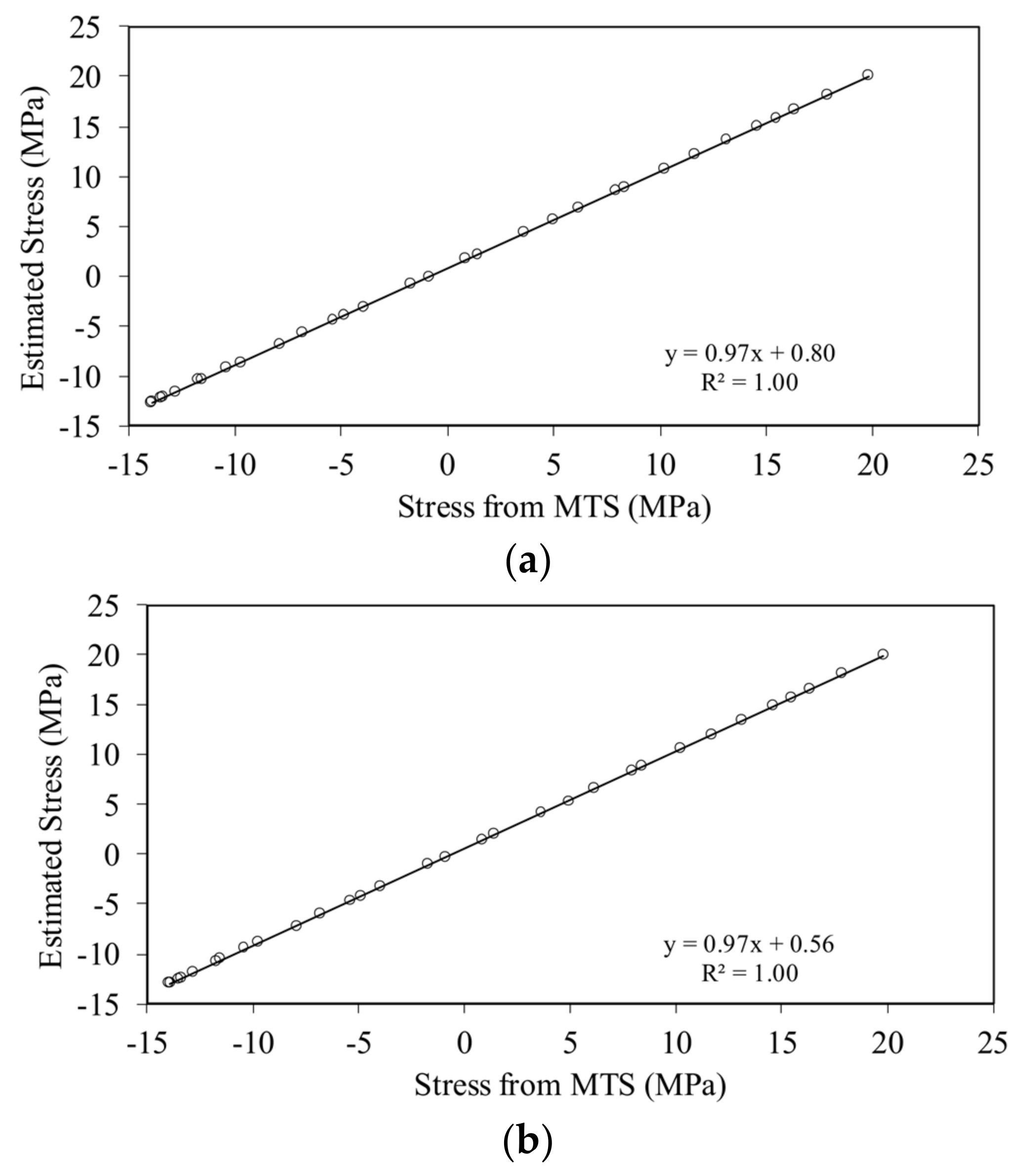
4.1. Thin Beam
4.2. Thick Beam
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vortok International and AEA Technology. Available online: http://www.vortok.com/uploads/catalogerfiles/verse/Verse_Technical_Pack_11.07.pdf (accessed on 17 April 2018).
- Kish, A.; Samavedam, G. Longitudinal Force Measurement in Continuous Welded Rail from Beam Column Deflection Response. Am. Railw. Eng. Assoc. 1987, 88, 280–301. [Google Scholar]
- QINETIQ North America. Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/6xPqWZFdS (accessed on 22 February 2018).
- Phillips, R.; Zhu, X.; Lanza di Scalea, F. The influence of stress on Electro-mechanical impedance measurements in rail steel. Mater. Eval. 2012, 70, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Lanza di Scalea, F. Sensitivity to Axial Stress of Electro-Mechanical Impedance Measurements. Experimental Mechanics. Exp. Mech. 2016, 56, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Nucera, C.; Scalea, L.D. Nonlinear wave propagation in constrained solids subjected to thermal loads. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nucera, C.; Lanza di Scalea, F. Nondestructive measurement of neutral temperature in continuous welded rails by nonlinear ultrasonic guided waves. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 136, 2561–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, A.; La Malfa Ribolla, E.; Rizzo, P.; Al-Nazer, L.; Giambanco, G. On the Use of L-shaped Granular Chains for the Assessment of Thermal Stress in Slender Structures. Exp. Mech. 2014, 55, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Ribolla, E.L.M.; Rizzo, P.; Al-Nazer, L. On the coupling dynamics between thermally stressed beams and granular chains. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2015, 86, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Rizzo, P.; Al-Nazer, L. Determination of the Neutral Temperature of Slender Beams by Using Nonlinear Solitary Waves. J. Eng. Mech. ASCE 2015, 141, 04014163. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Rizzo, P.; Al-Nazer, L. On the coupling mechanism between nonlinear solitary waves and slender beams. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 50, 4173–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maio, D.; Ewins, D.J. Continuous Scan, a method for performing modal testing using meaningful measurement parameters; Part I. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2011, 25, 3027–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanbridge, A.B.; Ewins, D.J. Modal testing using a scanning laser doppler vibrometer. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 1999, 13, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Feng, M.Q. Vision-based multipoint displacement measurement for structural health monitoring. Struct. Control Health 2016, 23, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Feng, M.Q. Identification of structural stiffness and excitation forces in time domain using noncontact vision-based displacement measurement. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 406, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.Q.; Fukuda, Y.; Feng, D.; Mizuta, M. Nontarget vision sensor for remote measurement of bridge dynamic response. J. Bridge Eng. 2015, 20, 04015023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, D.; Calçada, R.; Ferreira, J.; Martins, T. Non-contact measurement of the dynamic displacement of railway bridges using an advanced video-based system. Eng. Struct. 2014, 75, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigada, A.; Mazzoleni, P.; Zappa, E. Vibration monitoring of multiple bridge points by means of a unique vision-based measuring system. Exp. Mech. 2014, 54, 255–271. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.; Scarangello, T.; Feng, M.Q.; Ye, Q. Cable tension force estimate using novel noncontact vision-based sensor. Measurement 2017, 99, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Elanwar, H.; Choi, H.; Golparvar-Fard, M.; Spencer, B.F. Target-free approach for vision-based structural system identification using consumer-grade cameras. Struct. Control Health 2016, 23, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.G.; Wadhwa, N.; Cha, Y.-J.; Durand, F.; Freeman, W.T.; Buyukozturk, O. Modal identification of simple structures with high-speed video using motion magnification. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 345, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, N.; Freeman, W.T.; Durand, F.; Wu, H.-Y.; Davis, A.; Rubinstein, M.; Shih, E.; Mysore, G.J.; Chen, J.G.; Buyukozturk, O.; et al. Eulerian video magnification and analysis. Commun. ACM 2016, 60, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.-J.; Chen, J.; Buyukozturk, O. Motion Magnification Based Damage Detection Using High Speed Video. In Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring (IWSHM), Stanford, CA, USA, 1 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, A.; Bouman, K.L.; Chen, J.G.; Rubinstein, M.; Buyukozturk, O.; Durand, F.; Freeman, W.T. Visual Vibrometry: Estimating Material Properties from Small Motions in Video. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.; Rubinstein, M.; Wadhwa, N.; Mysore, G.J.; Durand, F.; Freeman, W.T. The visual microphone: Passive recovery of sound from video. ACM Trans. Graph. 2014, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Feng, M.Q. Computer vision for SHM of civil infrastructure: From dynamic response measurement to damage detection—A review. Eng. Struct. 2018, 156, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poozesh, P.; Sarrafi, A.; Mao, Z.; Avitabile, P.; Niezrecki, C. Feasibility of extracting operating shapes using phase-based motion magnification technique and stereo-photogrammetry. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 407 (Suppl. C), 350–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.G.; Wadhwa, N.; Durand, F.; Freeman, W.T.; Buyukozturk, O. Developments with Motion Magnification for Structural Modal Identification through Camera Video. In Dynamics of Civil Structures, Proceedings of the 33rd IMAC, A Conference and Exposition on Structural Dynamics, Orlando, FL, USA, 2–5 February 2015; Caicedo, J., Pakzad, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 2, pp. 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Gautama, T.; Hulle, M.A.V. A phase-based approach to the estimation of the optical flow field using spatial filtering. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2002, 13, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleet, D.J.; Jepson, A.D. Computation of component image velocity from local phase information. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1990, 5, 77–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, N.; Rubinstein, M.; Durand, F.; Freeman, W.T. Phase-based video motion processing. ACM Trans. Graph. 2013, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dorn, C.; Mancini, T.; Talken, Z.; Kenyon, G.; Farrar, C.; Mascareñas, D. Blind identification of full-field vibration modes from video measurements with phase-based video motion magnification. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 85, 567–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Viedma, A.J.; Felipe-Sesé, L.; López-Alba, E.; Díaz, F. High frequency mode shapes characterisation using Digital Image Correlation and phase-based motion magnification. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 102 (Suppl. C), 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Nagarajaiah, S.; Li, H.; Zhou, P. Real-Time Output-Only Identification of Time-Varying Cable Tension from Accelerations via Complexity Pursuit. J. Struct. Eng. 2016, 142, 04015083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dorn, C.; Farrar, C.; Mascarenas, D. Full-field imaging and modeling of structural dynamics with digital video cameras. In Structural Health Monitoring: Real-Time Material State Awareness and Data-Driven Safety Assurance, Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring, IWSHM, Stanford, CA, USA, 2–14 September 2017; DEStech Publications, Inc.: Lancaster, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer, B.; Espinosa, J.; Roig, A.B.; Perez, J.; Mas, D. Vibration frequency measurement using a local multithreshold technique. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 26198–26208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mas, D.; Ferrer, B.; Acevedo, P.; Espinosa, J. Methods and algorithms for video-based multi-point frequency measuring and mapping. Measurement 2016, 85, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MATLAB. R2017a; The MathWorks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Test Software and a Video Example. Available online: http://rua.ua.es/dspace/handle/10045/53429 (accessed on 17 April 2018).
- Tedesco, J.W.; McDougal, W.G.; Ross, C.A. Structural Dynamics: Theory and Applications; Addison Wesley Longman: Boston, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Amba-Rao, C.L. Effect of End Conditions on the Lateral Frequencies of Uniform Straight Columns. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1967, 42, 900–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fässler, S. Axial Load Determination Using Modal Analysis. Master’s Thesis, Lunds Tekniska Högskola, Lund, Skåne, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]




| Geometric/Mechanical Properties | Thin Beam | Thick Beam |
|---|---|---|
| Steel type | 416 steel | A36 steel |
| Length (mm) | 1402 | 1395 |
| Free length L (mm) | 1207 | 1200 |
| Cross-section (mm2) | 10.12 × 41.34 | 15.88 × 127 |
| Young’s Modulus E (GPa) | 200 | 200 |
| Density ρ (kg/m3) | 7750 | 7850 |
| Poisson’s ratio v | 0.28 | 0.28 |
| Yield stress σY (MPa) | 276 | 250 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion α (m/m°C) | 9.9 × 10−6 | 9.9 × 10−6 |
| Critical (Euler) load (kN) | 19.35 | 238.0 |
| Critical (Euler) stress (MPa) | 46.25 | 118.0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sefa Orak, M.; Nasrollahi, A.; Ozturk, T.; Mas, D.; Ferrer, B.; Rizzo, P. Non-Contact Smartphone-Based Monitoring of Thermally Stressed Structures. Sensors 2018, 18, 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041250
Sefa Orak M, Nasrollahi A, Ozturk T, Mas D, Ferrer B, Rizzo P. Non-Contact Smartphone-Based Monitoring of Thermally Stressed Structures. Sensors. 2018; 18(4):1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041250
Chicago/Turabian StyleSefa Orak, Mehmet, Amir Nasrollahi, Turgut Ozturk, David Mas, Belen Ferrer, and Piervincenzo Rizzo. 2018. "Non-Contact Smartphone-Based Monitoring of Thermally Stressed Structures" Sensors 18, no. 4: 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041250
APA StyleSefa Orak, M., Nasrollahi, A., Ozturk, T., Mas, D., Ferrer, B., & Rizzo, P. (2018). Non-Contact Smartphone-Based Monitoring of Thermally Stressed Structures. Sensors, 18(4), 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041250






