Development of Highly Sensitive Immunosensor for Clenbuterol Detection by Using Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/Graphene Oxide Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Buffers and Solutions
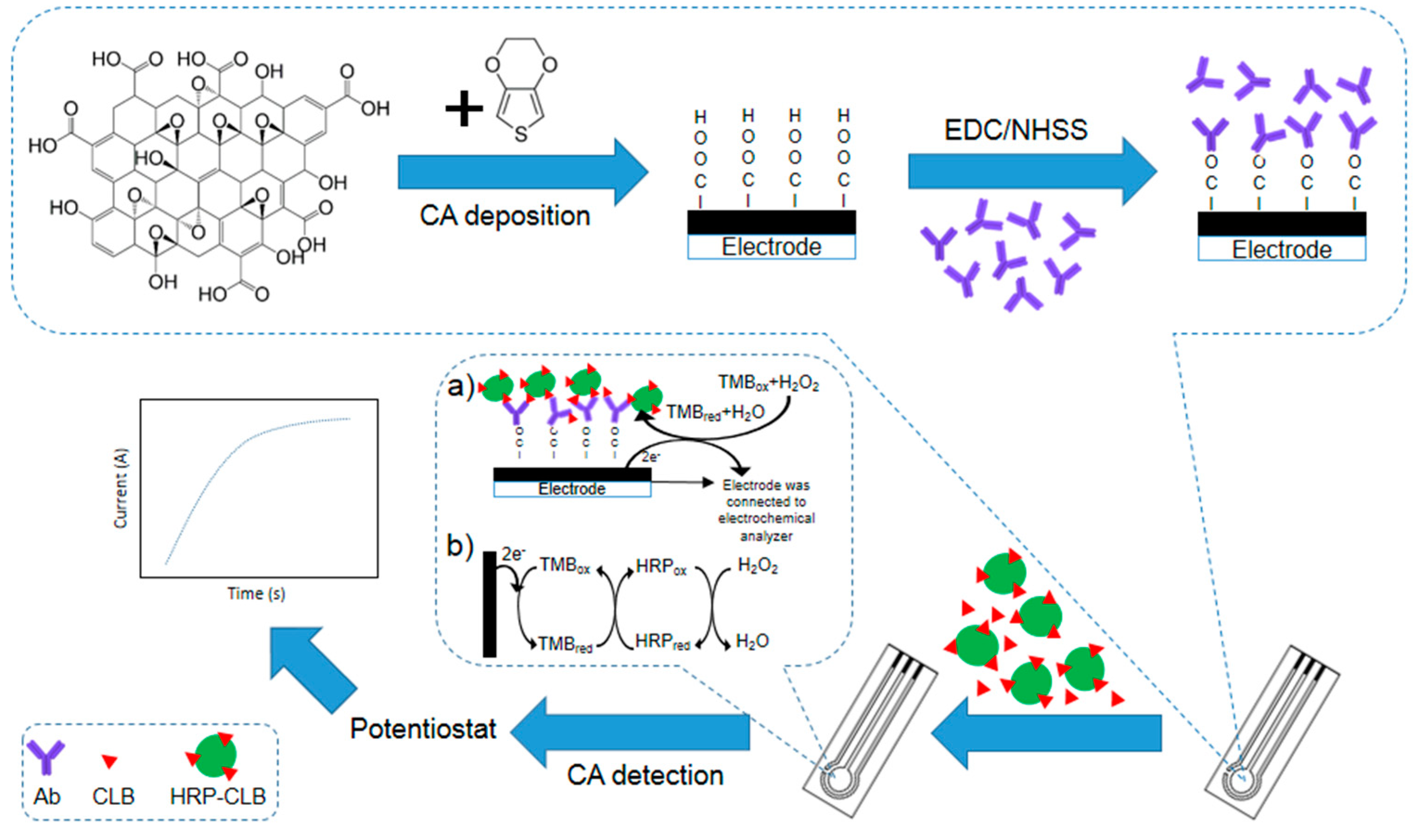
2.3. Preparation of Clenbuterol Immunosensor
2.3.1. Preparation of Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/graphene Oxide Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode
2.3.2. Preparation of Clenbuterol Immunosensor
- SD = standard deviation of zero value;
- a = maximum values of calibration curve;
- d = minimum values of calibration curve;
- x = concentration of the EC50 value; and,
- k = curve hill’s slope.
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Determination of Potential Applied
2.6. Optimization of Antibody Concentration
2.7. Preparation of Real Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Principle of the Immunosensor
3.2. Characterization
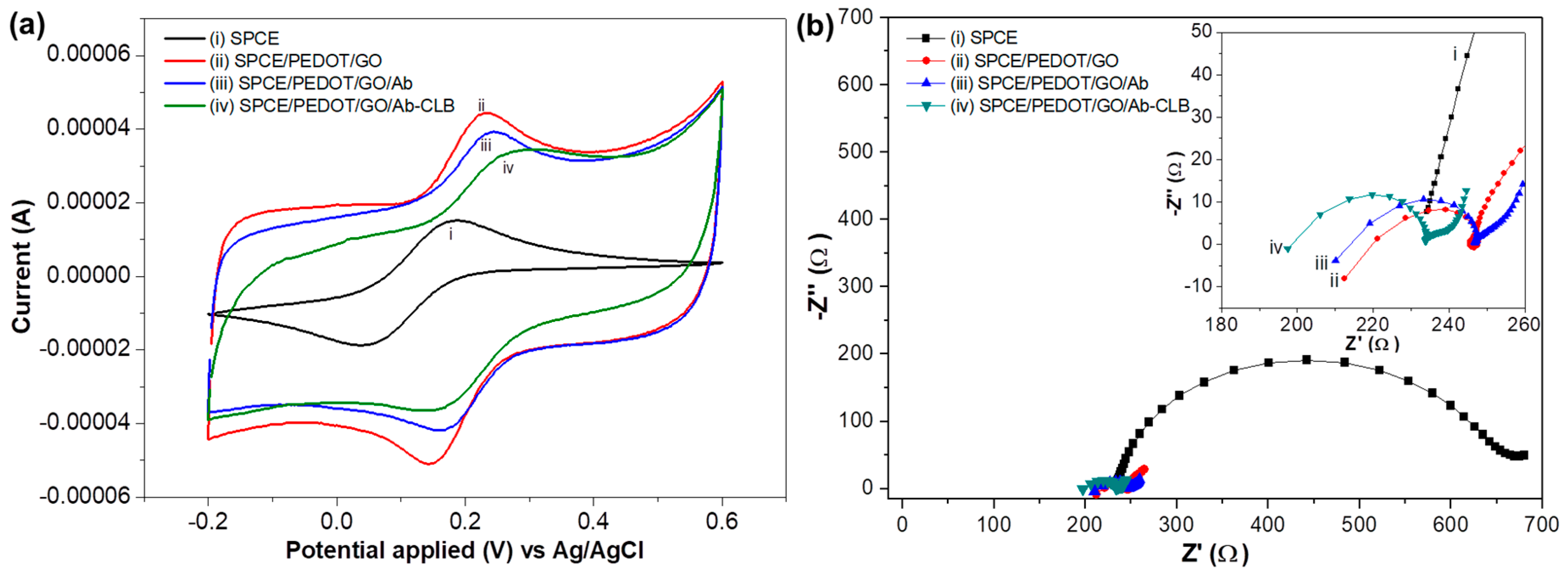
3.2.1. Cyclic Voltammetry
3.2.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
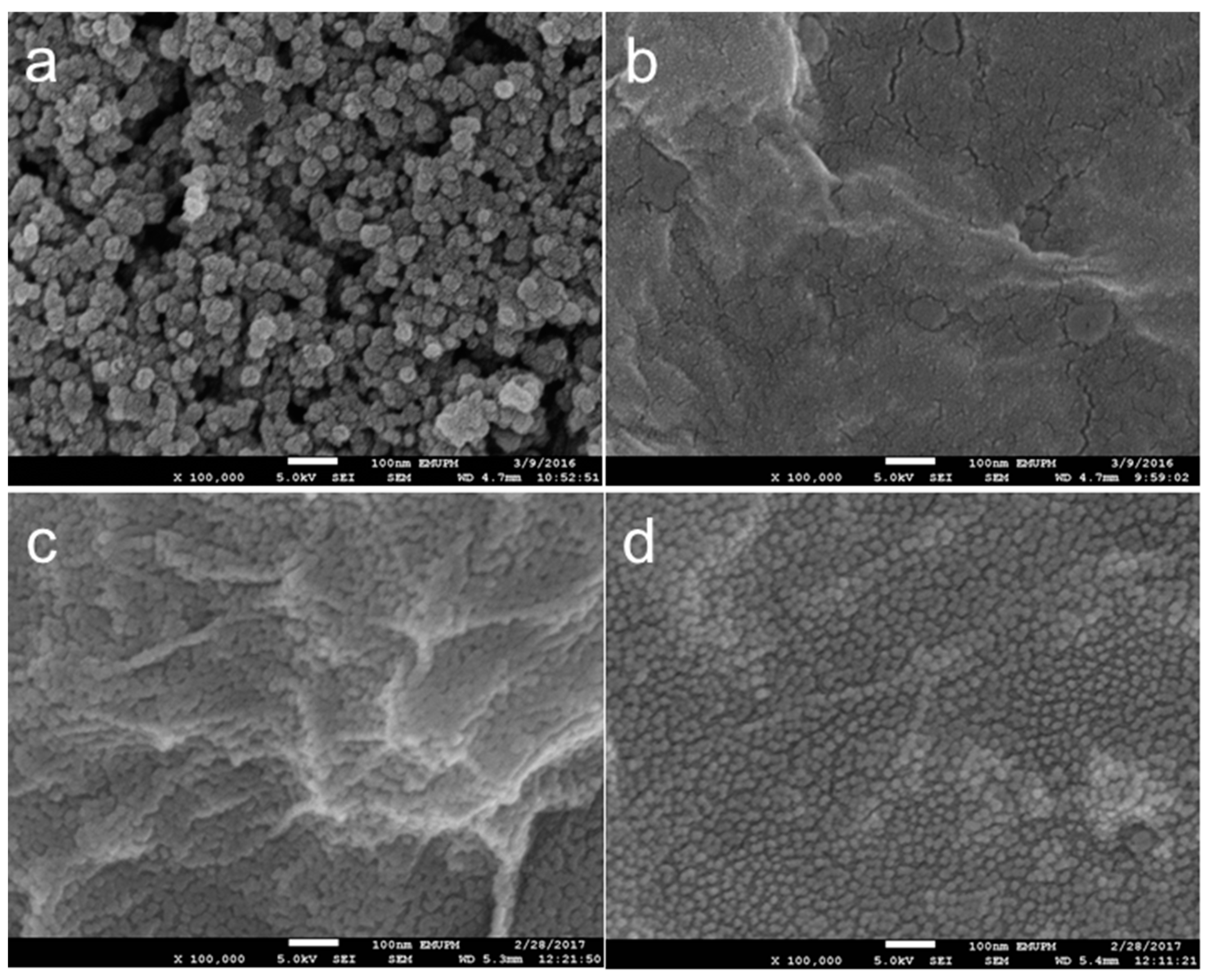
3.2.3. Morphology
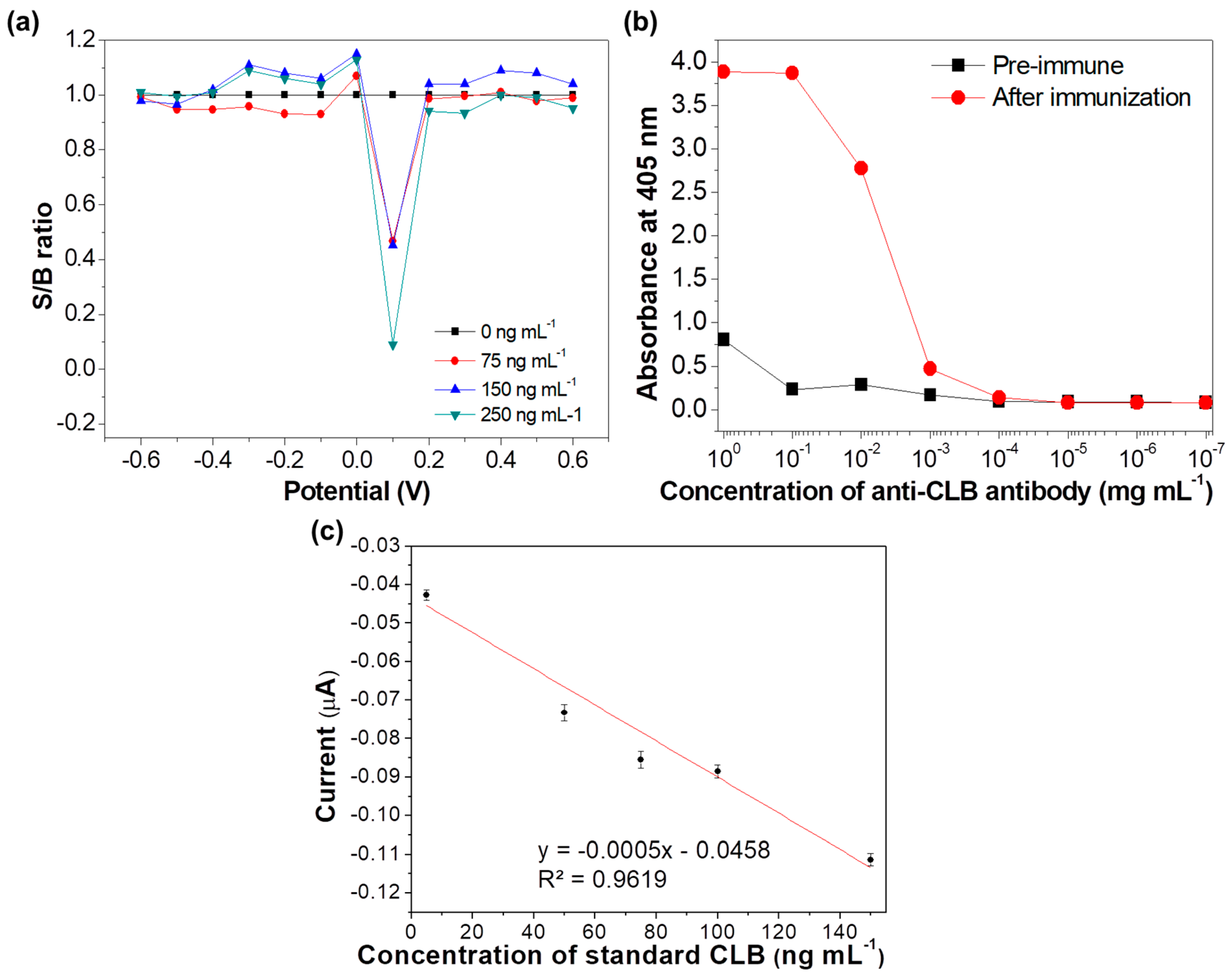
3.3. Determination of Potential Applied
3.4. Optimization of Antibody Concentration
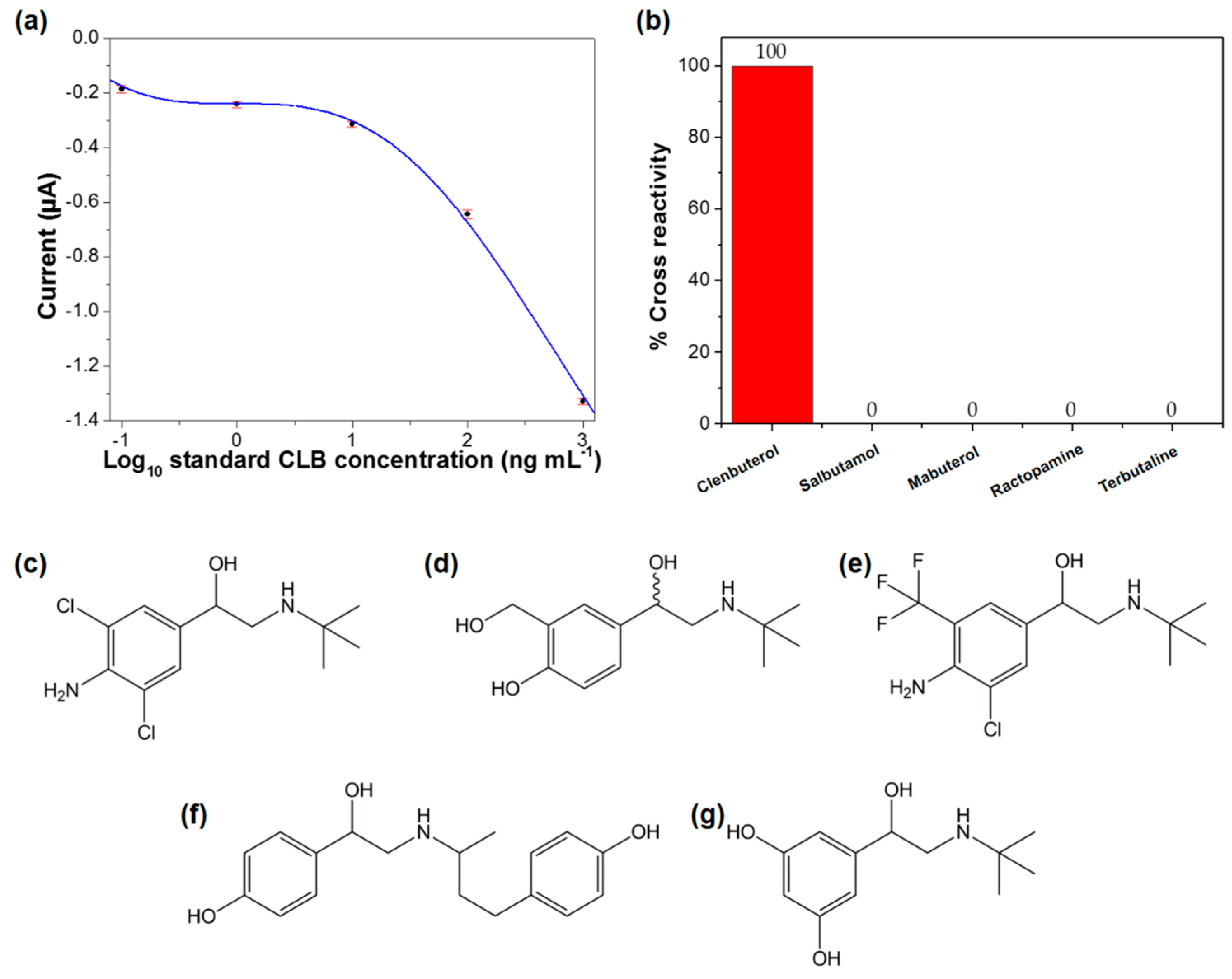
3.5. Analytical Performance of the Immunosensor
3.6. Real Samples Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, Y.; Jiao, X.; Han, Y.; Bai, L.; Liu, H.; Qiao, F.; Yan, H. One-pot synthesis of ethylenediamine-connected graphene/carbon nanotube composite material for isolation of clenbuterol from pork. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Nilghaz, A.; Choi, J.R.; Liu, X.; Lu, X. Rapid detection of clenbuterol in milk using microfluidic paper-based ELISA. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, G.; Cenci, T.; Franconi, F.; Galarini, R.; MacRì, A.; Rondoni, F.; Strozzi, M.; Loizzo, A. Clinical and pharmacological profile in a clenbuterol epidemic poisoning of contaminated beef meat in Italy. Toxicol. Lett. 2000, 114, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unusan, N. Determination of clenbuterol in UHT milk in Turkey. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Y.L.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Huang-Fu, W.G. Simultaneous determination of clenbuterol, salbutamol and ractopamine in milk by reversed-phase liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry with isotope dilution. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7873–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furusawa, N. An isocratic solvent-free mobile phase HPLC-PDA analysis of clenbuterol and ractopamine. Int. J. Chem. Anal. Sci. 2013, 4, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fu, Y.; Han, X.; Li, X.; Li, C. Metabolomic investigation of porcine muscle and fatty tissue after Clenbuterol treatment using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1456, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, B.P.; Manjunatha Prabhu, B.H.; Chandan, S.; Ranjith, D.; Shivakumar, V. Rapid Methods for detection of Veterinary Drug residues in Meat. Vet. World 2010, 3, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahnau, S.; Jülicher, B. Evaluation of commercially available ELISA test kits for the detection of clenbuterol and other beta 2-agonists. Food Addit. Contam. 1996, 13, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Yan, P.; Tang, Q.; Deng, A.; Li, J. Quantum dots based electrochemiluminescent immunosensor by coupling enzymatic amplification for ultrasensitive detection of clenbuterol. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 798, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Chen, H.; Peng, H.; Song, S.; Gao, J.; Lu, J.; Ding, M.; Li, L.; Ren, S.; Zou, Z.; et al. A carbon nanotube-based high-sensitivity electrochemical immunosensor for rapid and portable detection of clenbuterol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, W. Development of a label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on carbon nanotube for rapid determination of clenbuterol. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Lei, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, M.; Wang, F.; Hao, Q. Electrodeposition of graphene oxide doped poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) film and its electrochemical sensing of catechol and hydroquinone. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 85, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, F.; Volpe, G.; Micheli, L.; Palleschi, G. A review on novel developments and applications of immunosensors in food analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 605, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, A.; Marty, L.J. Disposable Screen Printed Electrochemical Sensors: Tools for Environmental Monitoring. Sensors 2014, 14, 10432–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zen, J.-M.; Chung, H.-H.; Kumar, A.S. Selective Detection of o-Diphenols on Copper-Plated Screen-Printed Electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1202–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, C.W.; Metters, J.P.; Kampouris, D.K.; Banks, C.E. Ultraflexible Screen-Printed Graphitic Electroanalytical Sensing Platforms. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honeychurch, K.C. Screen-printed Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors for Monitoring Metal Pollutants. Insci. J. 2012, 2, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, G.; Westmacott, K.; Honeychurch, K.C.; Crew, A.; Pemberton, R.M.; Hart, J.P. Recent Advances in the Fabrication and Application of Screen-Printed Electrochemical (Bio)Sensors Based on Carbon Materials for Biomedical, Agri-Food and Environmental Analyses. Biosensors 2016, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sołoducho, J.; Cabaj, J. Conducting Polymers in Sensor Design. In Conducting Polymers; Yilmaz, F., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 27–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Han, R.; Su, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, G.; Luo, X. Zwitterionic peptide anchored to conducting polymer PEDOT for the development of antifouling and ultrasensitive electrochemical DNA sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán, T.; Prieto-Simón, B.; Alvira, M.; Eritja, R.; Götz, G.; Bäuerle, P.; Samitier, J. Label-free electrochemical DNA sensor using “click”-functionalized PEDOT electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson-Burns, S.M.; Hendricks, J.L.; Foster, B.; Povlich, L.K.; Kim, D.H.; Martin, D.C. Polymerization of the conducting polymer poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) around living neural cells. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1539–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Huang, H. Electrochemical immunosensor for alpha-fetoprotein determination based on ZnSe quantum dots/Azure I/gold nanoparticles/poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) modified Pt electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 114, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaidi, F.S.; Civélas, A.; Castagnola, V.; Tsopela, A.; Mazenq, L.; Gros, P.; Launay, J.; Temple-Boyer, P. PEDOT-modified integrated microelectrodes for the detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 214, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Sheng, K.; Zhang, P.; Li, C.; Shi, G. Graphene oxide/conducting polymer composite hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 18653–18658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Bi, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, X.; Su, S.; Yin, K.; Sun, L. Graphene oxide as high-performance dielectric materials for capacitive pressure sensors. Carbon 2017, 114, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azman, N.H.N.; Ngee, L.H.; Sulaiman, Y. Effect of electropolymerization potential on the preparation of PEDOT/graphene oxide hybrid material for supercapacitor application. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 188, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Bhattacharyya, P. Recent developments on graphene and graphene oxide based solid state gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 173, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borini, S.; White, R.; Wei, D.; Astley, M.; Haque, S.; Spigone, E.; Harris, N.; Kivioja, J.; Ryhänen, T. Ultrafast Graphene Oxide Humidity Sensors. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 11166–11173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Singh, A.; Wu, H.; Kroe-Barrett, R. Comparison of biosensor platforms in the evaluation of high affinity antibody-antigen binding kinetics. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 508, 78–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, N.A.A.; Salam, F.; Sulaiman, Y. Development of Polyclonal Antibody against Clenbuterol for Immunoassay Application. Molecules 2018, 23, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talib, N.A.A.; Salam, F.; Yusof, N.A.; Ahmad, S.A.A.; Sulaiman, Y. Modeling and optimization of electrode modified with poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/graphene oxide composite by response surface methodology/Box-Behnken design approach. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 787, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, N.A.A.; Salam, F.; Yusof, N.A.; Alang Ahmad, S.A.; Azid, M.Z.; Mirad, R.; Sulaiman, Y. Enhancing a clenbuterol immunosensor based on poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/multi-walled carbon nanotube performance using response surface methodology. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 15522–15532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijssen, P. Practice and Theory of Immunoassay; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Salam, F.; Hazana, R.; Gayah, A.R.; Norzaili, Z.; Azima, A.; Nur Azura, M.S.; Zamri, I. Electrochemical sensors for detection of tetracycline antibiotics. Malays. Soc. Anim. Prod. 2012, 15, 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, J.M. The Bicinchoninic Acid (BCA) Assay for Protein Quantitation. In The Protein Protocols Handbook; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Conzuelo, F.; Gamella, M.; Campuzano, S.; Reviejo, A.J.; Pingarrón, J.M. Disposable amperometric magneto-immunosensor for direct detection of tetracyclines antibiotics residues in milk. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 737, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, I.G.; Daxenberger, A.; Meyer, H.H.D. Studies on the antibody response of Lama glama—Evaluation of the binding capacity of different IgG subtypes in ELISAs for clenbuterol and BSA. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2001, 83, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleadin, J.; Vulic, A.; Persi, N.; Vahcic, N. Clenbuterol residues in pig muscle after repeat administration in a growth-promoting dose. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Österholm, A.; Lindfors, T.; Kauppila, J.; Damlin, P.; Kvarnström, C. Electrochemical incorporation of graphene oxide into conducting polymer films. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 83, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Pei, S.; Ren, W.; Gao, L.; Cheng, H.M. Efficient preparation of large-area graphene oxide sheets for transparent conductive films. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5245–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Davis, J.J.; Bueno, P.R. Fundamentals and Applications of Impedimetric and Redox Capacitive Biosensors. J. Anal. Bioanal. Tech. 2014, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahaut, P. Immunisation—Choice of host, adjuvants and boosting schedules with emphasis on polyclonal antibody production. Methods 2017, 116, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, F.; Zheng, J.; Qin, P.; Han, T.; Zhao, D. A novel quartz crystal microbalance sensor array based on molecular imprinted polymers for simultaneous detection of clenbuterol and its metabolites. Talanta 2017, 167, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, I.M.; Robbins, E.M.; Catt, K.A.; Cody, P.A.; Happe, C.L.; Cui, X.T. Enhanced dopamine detection sensitivity by PEDOT/graphene oxide coating on in vivo carbon fiber electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89 Pt 1, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, X.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Wu, M.; He, Z.; Zhao, J. Detection of Clenbuterol at Trace Levels in Doping Analysis Using Different Gas Chromatographic–Mass Spectrometric Techniques. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2012, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Su, X.-O.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y. Highly Sensitive Detection of Clenbuterol in Animal Urine Using Immunomagnetic Bead Treatment and Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J. Simultaneous detection of clenbuterol and ractopamine based on multiplexed competitive surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) immunoassay. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 10407–10414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, R.; Wang, S.; Wang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, X.; Liang, H.; Zhu, J.; Sun, X.; et al. Detection of Clenbuterol Hydrochloride Residuals in Pork Liver Using a Customized Surface Plasmon Resonance Bioanalyzer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Shen, F.; Luo, Y.; Sun, C. Fluorescent detection of clenbuterol using fluorophore functionalized gold nanoparticles based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Food Control 2014, 46, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Ni, Y.; Kokot, S. A novel electrochemical sensor for the analysis of β-agonists: The poly(acid chrome blue K)/graphene oxide-nafion/glassy carbon electrode. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Deng, W.; Su, J.; Chen, S.; Song, H.; Aldalbahi, A.; Zuo, X.; Song, S.; Shi, J.; et al. Portable detection of clenbuterol using a smartphone-based electrochemical biosensor with electric field-driven acceleration. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 781, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, R.; Sun, L.; Yao, Q.; Chen, X. A sensitive solid-state electrochemiluminescence sensor for clenbuterol relying on a PtNPs/RuSiNPs/Nafion composite modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 781, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, C.; Yang, D.; Jia, N. Electrochemical non-enzyme sensor for detecting clenbuterol (CLB) based on MoS2-Au-PEI-hemin layered nanocomposites. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89 Pt 1, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Techniques | Detection Limit | Linear Range | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| GC-MS | 2 ng mL−1 | 0.06 to 8.0 ng mL−1 | [47] |
| Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) | 0.5 ng mL−1 | 0.5 to 20 ng mL−1 | [48] |
| Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) | NA | 1 to 1000 pg mL−1 | [49] |
| Surface plasmon resonance | 1.26 ng mL−1 | NA | [50] |
| Quartz crystal microbalance sensor | 3.0 ng mL−1 | NA | [45] |
| Fluorometry/FRET | 3.96 ng mL−1 | 200 to 1800 ng mL−1 | [51] |
| Electrochemical sensor | 0.64 ng mL−1 | 1.0 to 26.0 ng mL−1 | [52] |
| Electrochemical sensor | 0.076 ng mL−1 | 0.3 to 100 ng mL−1 | [53] |
| Electrochemiluminescence sensor | 0.8 ng mL−1 | 5 to 100 ng mL−1 | [54] |
| Electrochemical sensor | 1.92 ng mL−1 | 10 ng mL−1 to 2 μg mL−1 | [55] |
| Electrochemical immunosensor | 0.196 ng mL−1 | 5 to 150 ng mL−1 | This work |
| Immunosensor | ELISA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples | Spiked (ng mL−1) | Average Recovery (ng mL−1) | Percentage Recovery (%) | Average Recovery (ng mL−1) | Percentage Recovery (%) |
| Milk A | 50 | 44.6 ± 3.23 | 89.2 | 69.1 ± 0.59 | 138 |
| Milk B | 50 | 53.8 ± 9.71 | 107.6 | 57.6 ± 0.22 | 115 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Talib, N.A.A.; Salam, F.; Sulaiman, Y. Development of Highly Sensitive Immunosensor for Clenbuterol Detection by Using Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/Graphene Oxide Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode. Sensors 2018, 18, 4324. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124324
Talib NAA, Salam F, Sulaiman Y. Development of Highly Sensitive Immunosensor for Clenbuterol Detection by Using Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/Graphene Oxide Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode. Sensors. 2018; 18(12):4324. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124324
Chicago/Turabian StyleTalib, Nurul Ain A., Faridah Salam, and Yusran Sulaiman. 2018. "Development of Highly Sensitive Immunosensor for Clenbuterol Detection by Using Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/Graphene Oxide Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode" Sensors 18, no. 12: 4324. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124324
APA StyleTalib, N. A. A., Salam, F., & Sulaiman, Y. (2018). Development of Highly Sensitive Immunosensor for Clenbuterol Detection by Using Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/Graphene Oxide Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode. Sensors, 18(12), 4324. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124324





