Protection of Superconducting Industrial Machinery Using RNN-Based Anomaly Detection for Implementation in Smart Sensor †
Abstract
1. Introduction
- development of a neural algorithm dedicated to detecting anomaly occurring in the voltage time series acquired on the terminals of superconducting machines in electrical circuits,
- design and verification of the complete processing flow,
- introduction of the RNN-based solution for edge computing which paves the way for low-latency and low-throughput hardware implementation of the presented solution,
- development of a system level model suited for future experiments with the adaptive grid-based approach; the software is available online (see Supplementary Material section).
1.1. Protection System for Superconducting Machinery
1.2. State of the Art
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Quantization Algorithm
2.1.1. Previous Work
2.1.2. Other Quantization Approaches
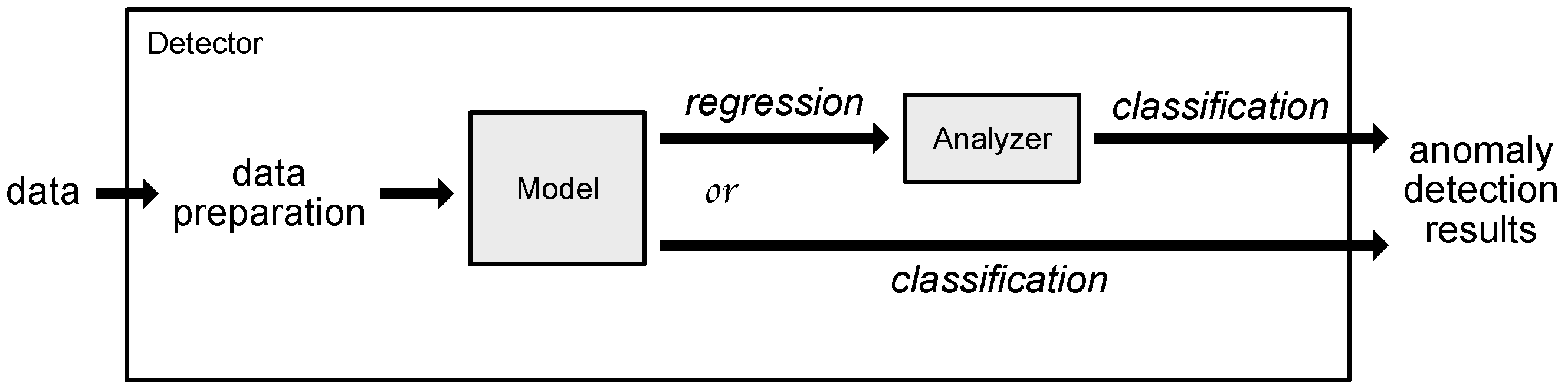
2.2. Implementation Overview
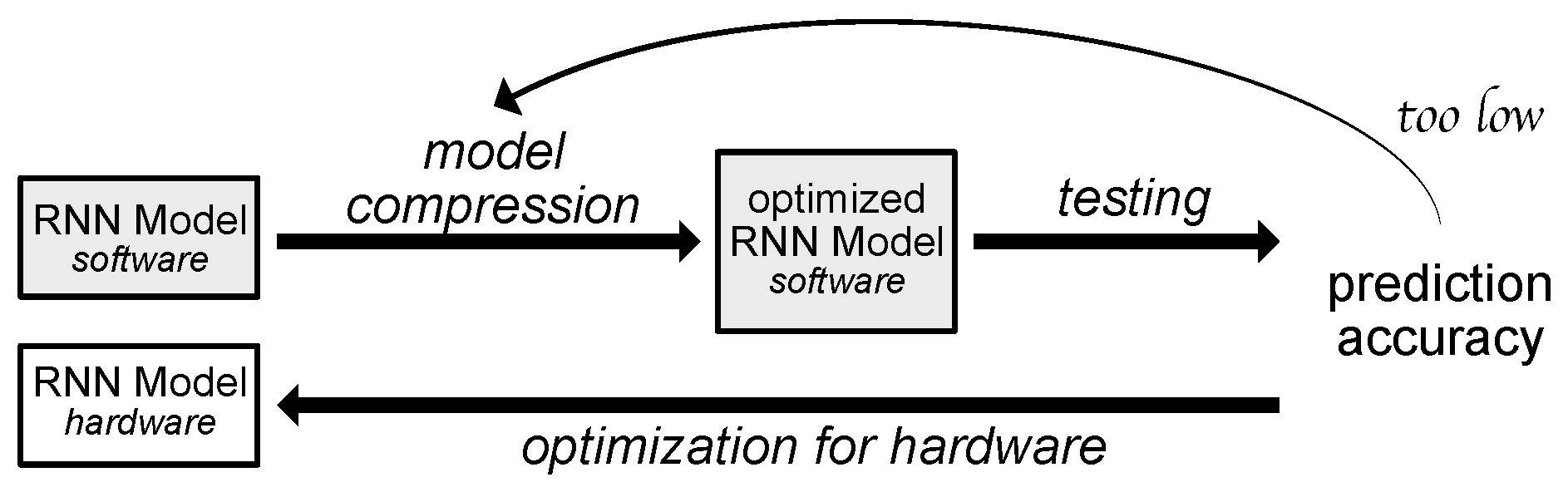
2.3. Model Complexity Reduction
2.3.1. Linear Quantization
2.3.2. MinMax Quantization
2.3.3. Hyperbolic Tangent Quantization
3. Results
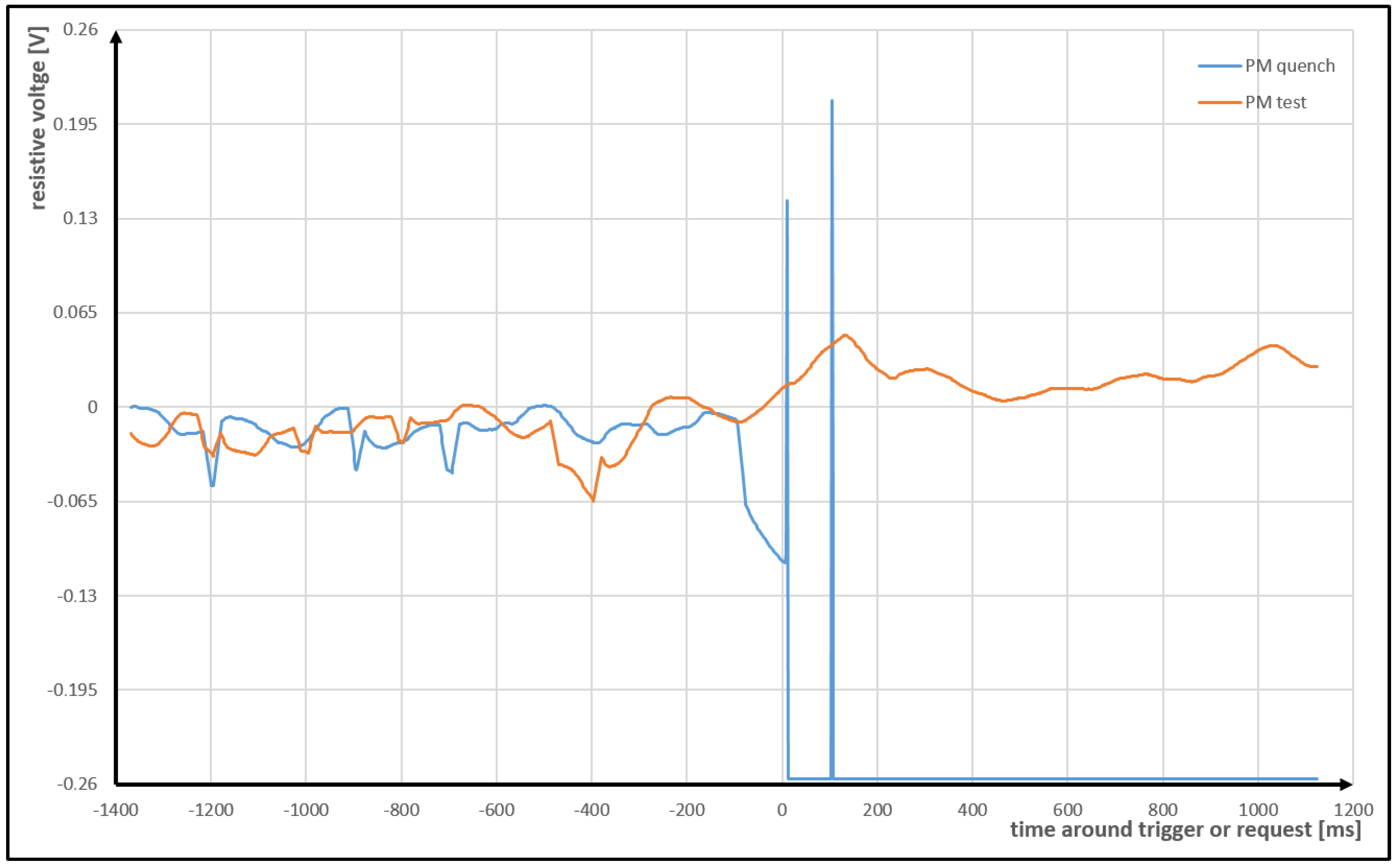
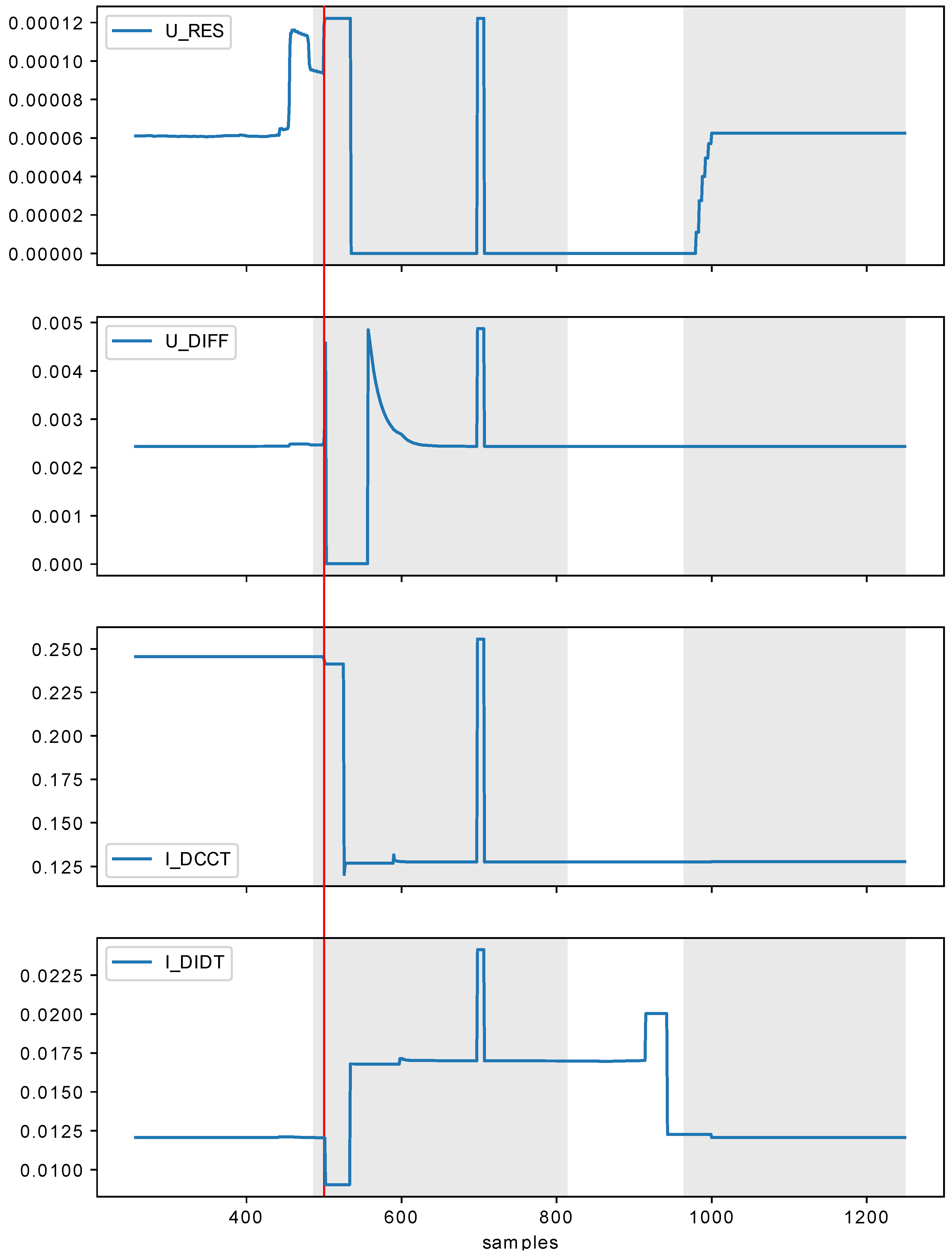
3.1. Dataset
- —total voltage measured between terminals of superconducting coil,
- —resistive voltage extracted from the total voltage using the electric current ,
- —current flowing through superconducting coil measured using Hall sensor, and
- —time derivative of the electric current calculated numerically.
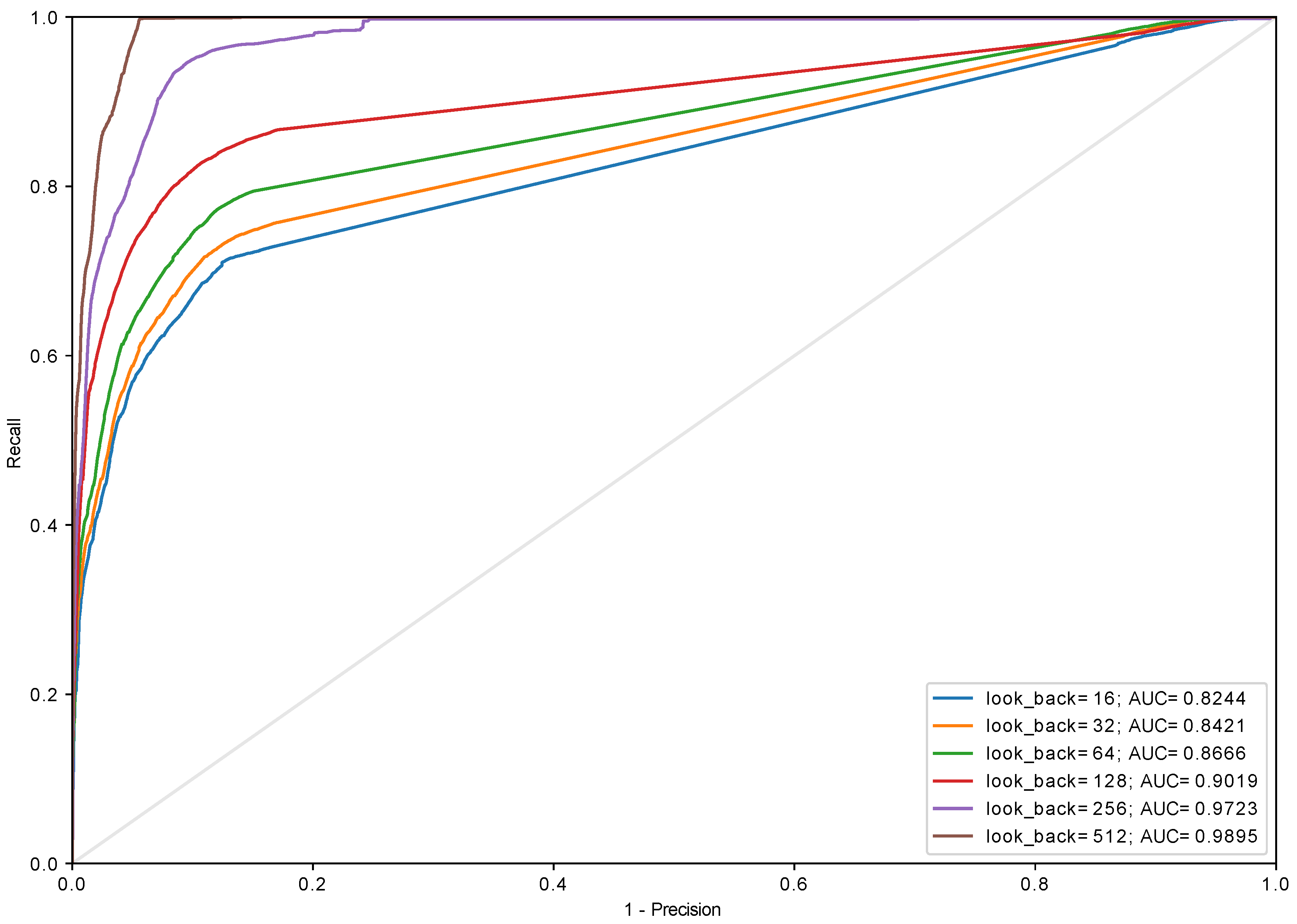
3.2. Quality Measures
- —true positive—item correctly classified as an anomaly,
- —true negative—item correctly classified as a part of normal operation,
- —false positive—item incorrectly classified as an anomaly,
- —false negative—item incorrectly classified as a part of normal operation.
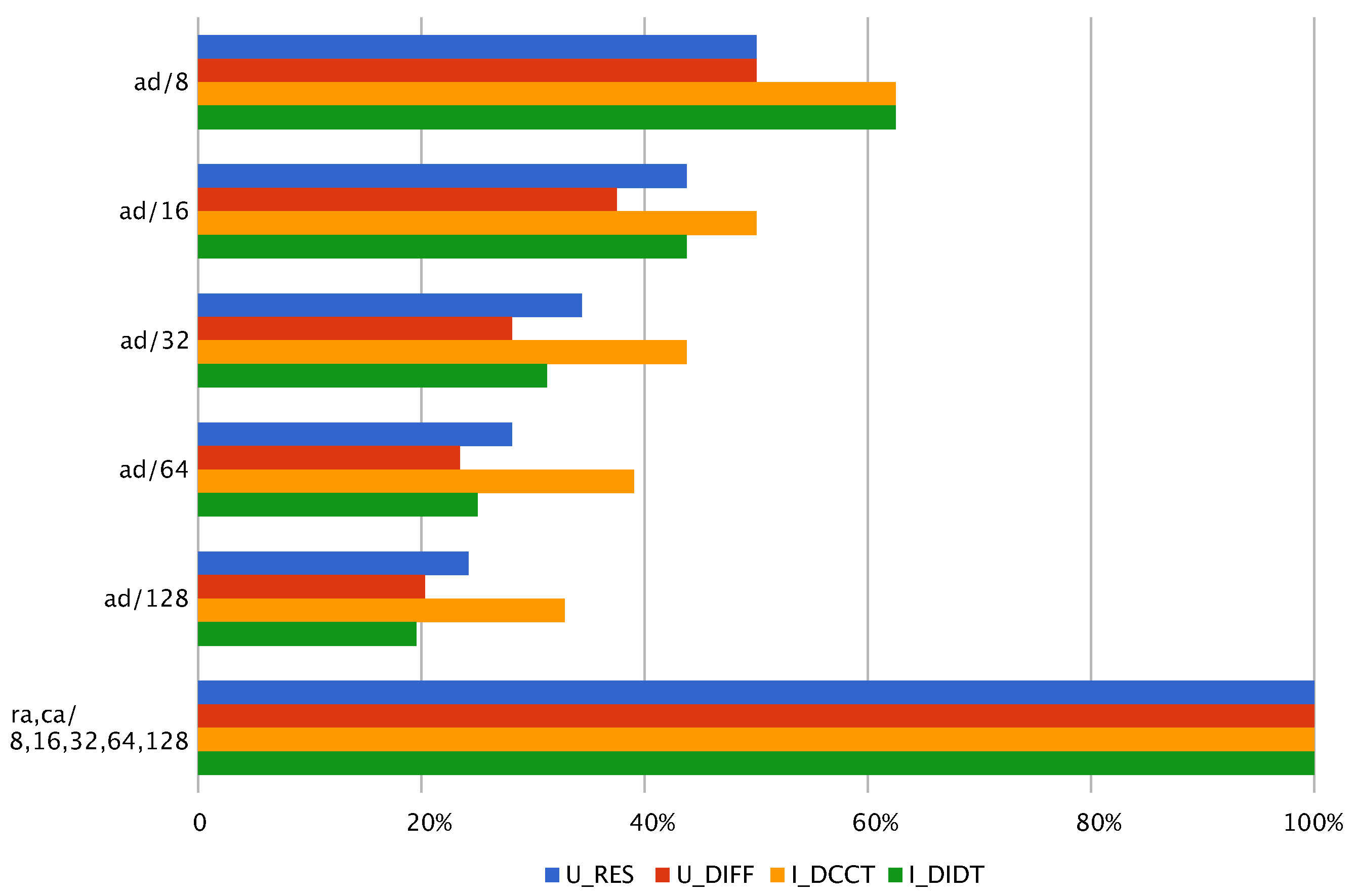
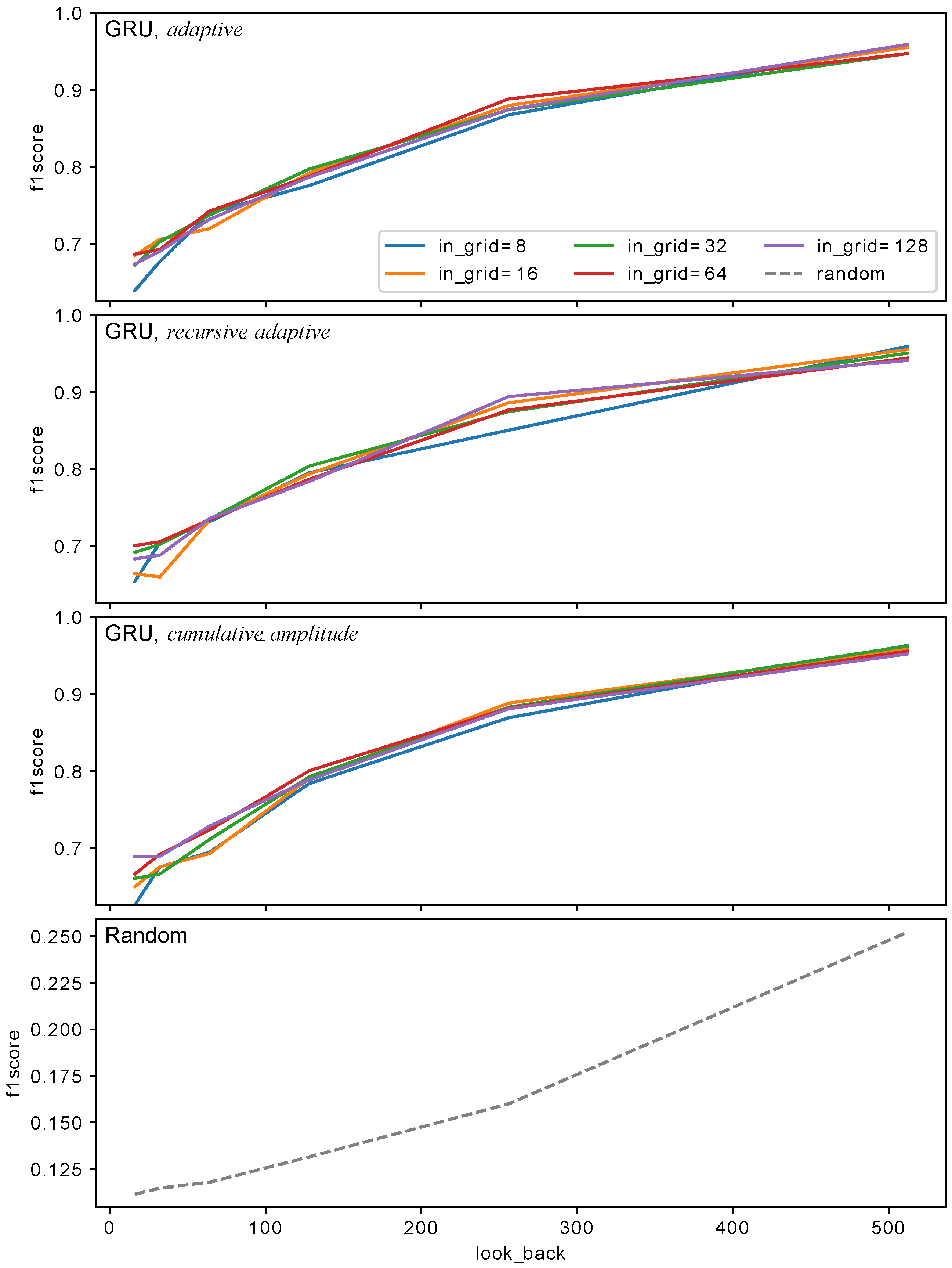
3.3. History Length and Data Quantization
3.4. Coefficients Quantization
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADC | Analog-to-Digital Converter |
| ASIC | Application-Specific Integrated Circuit |
| AUC | Area Under Curve |
| CALS | CERN Accelerator Logging Service |
| CERN | European Organization for Nuclear Research |
| EP | Electronics for Protection Section |
| FPGA | Field-Programmable Gate Array |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| IF | Isolation Forest |
| LHC | Large Hadron Collider |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MCD | Minimum Covariance Determinant |
| MPE | Machine Protection and Electrical Integrity Group |
| NN | Neural Network |
| OC-SVM | One-Class Support Vector Machine |
| PM | Post Mortem |
| QPS | Quench Protection System |
| RBF | Radial Basis Function |
| RMSE | Root-Mean-Square Error |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| TE | Technology Department |
Appendix A. Data Quantization
Appendix A.1. Adaptive Data Quantization
Appendix A.2. Cumulative Amplitude Data Quantization
References
- Wielgosz, M.; Skoczeń, A.; Wiatr, K. Looking for a Correct Solution of Anomaly Detection in the LHC Machine Protection System. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Signals and Electronic Systems (ICSES), Kraków, Poland, 10–12 September 2018; pp. 257–262. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, L.; Bryant, P. LHC Machine. J. Instrum. 2008, 3, S08001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denz, R. Electronic Systems for the Protection of Superconducting Elements in the LHC. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2006, 16, 1725–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckert, J.; Skoczen, A. Design of FPGA-based Radiation Tolerant Quench Detectors for LHC. J. Instrum. 2017, 12, T04005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandola, V.; Mithal, V.; Kumar, V. Comparative Evaluation of Anomaly Detection Techniques for Sequence Data. In Proceedings of the 2008 Eighth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Pisa, Italy, 15–19 December 2008; pp. 743–748. [Google Scholar]
- Chandola, V.; Banerjee, A.; Kumar, V. Anomaly Detection: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2009, 41, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.A.; Clifton, D.A.; Clifton, L.; Tarassenko, L. A Review of Novelty Detection. Signal Process. 2014, 99, 215–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A. Supervised Sequence Labelling with Recurrent Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, J.; Wheeler, T.A.; Kochenderfer, M.J. Analysis of Recurrent Neural Networks for Probabilistic Modelling of Driver Behaviour. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 18, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouladi, F.; Salehinejad, H.; Gilani, A.M. Recurrent Neural Networks for Sequential Phenotype Prediction in Genomics. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Developments of E-Systems Engineering (DeSE), Duai, UAE, 13–14 December 2015; pp. 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Gales, M.J.F.; Woodland, P.C. Efficient Training and Evaluation of Recurrent Neural Network Language Models for Automatic Speech Recognition. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2016, 24, 2146–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Perkins, S. Time-series Novelty Detection Using One-Class Support Vector Machines. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Portland, OR, USA, 20–24 July 2003; Volume 3, pp. 1741–1745. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, S.; Muthuraman, S.; Jiang, J. One Class Support Vector Machine for Anomaly Detection in the Communication Network Performance Data. In Proceedings of the 5th Conference on Applied Electromagnetics, Wireless and Optical Communications; World Scientific and Engineering Academy and Society (WSEAS) ELECTROSCIENCE’07, Stevens Point, WI, USA, 14–16 December 2007; pp. 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Long, Y.; Qiu, X.; Li, S.; Liu, D. Anomaly Detection of Single Sensors Using OCSVM_KNN. In Proceedings of the Big Data Computing and Communications: First International Conference, BigCom 2015, Taiyuan, China, 1–3 August 2015; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 217–230. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Gonzalez, R.; Gomez-Gil, J.; Gomez-Gil, F.J.; Martínez-Martínez, V. An SVM-Based Classifier for Estimating the State of Various Rotating Components in Agro-Industrial Machinery with a Vibration Signal Acquired from a Single Point on the Machine Chassis. Sensors 2014, 14, 20713–20735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornero, R.; Escudero, J.; Fernández, A.; Poza, J.; Gómez, C. Spectral and Nonlinear Analyses of MEG Background Activity in Patients With Alzheimer’s Disease. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 1658–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schölkopf, B.; Williamson, R.C.; Smola, A.J.; Shawe-Taylor, J.; Platt, J.C. Support Vector Method for Novelty Detection. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 29 November–4 December 2000; pp. 582–588. [Google Scholar]
- Schölkopf, B.; Platt, J.C.; Shawe-Taylor, J.C.; Smola, A.J.; Williamson, R.C. Estimating the Support of a High-Dimensional Distribution. Neural Comput. 2001, 13, 1443–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masnan, M.J.; Mahat, N.I.; Shakaff, A.Y.M.; Abdullah, A.H.; Zakaria, N.Z.I.; Yusuf, N.; Subari, N.; Zakaria, A.; Aziz, A.H.A. Understanding Mahalanobis distance criterion for feature selection. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 1660, 050075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.T.; Ting, K.M.; Zhou, Z.H. Isolation Forest. In Proceedings of the 2008 Eighth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Pisa, Italy, 15–19 December 2008; pp. 413–422. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Viswanathan, K.; Choudur, L.; Talwar, V.; Satterfield, W.; Schwan, K. Statistical Techniques for Online Anomaly Detection in Data Centers. In Proceedings of the 12th IFIP/IEEE International Symposium on Integrated Network Management (IM 2011) and Workshops, Dublin, Ireland, 23–27 May 2011; pp. 385–392. [Google Scholar]
- Ekberg, J.; Ylinen, J.; Loula, P. Network behaviour anomaly detection using Holt-Winters algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 11–14 December 2011; pp. 627–631. [Google Scholar]
- Wielgosz, M.; Skoczeń, A. Recurrent Neural Networks with Grid Data Quantization for Modeling LHC Superconducting Magnets Behaviour. In Contemporary Computational Science; Kulczycki, P., Kowalski, P.A., Łukasik, S., Eds.; AGH University of Science and Technology: Kraków, Poland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wielgosz, M.; Skoczeń, A.; Mertik, M. Using LSTM recurrent neural networks for detecting anomalous behavior of LHC superconducting magnets. Nuclear Inst. Methods Phys. Res. A 2017, 867, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielgosz, M.; Mertik, M.; Skoczeń, A.; Matteis, E.D. The model of an anomaly detector for HiLumi LHC magnets based on Recurrent Neural Networks and adaptive quantization. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 74, 166–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Wen, H.; Zhou, S.; Wu, Y.; Yao, C.; Zhou, X.; Zou, Y. Effective Quantization Methods for Recurrent Neural Networks. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1611.10176. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, S.; Hwang, K.; Sung, W. Fixed-Point Performance Analysis of Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 976–980. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Keras. 2015. Available online: https://keras.io (accessed on 10 November 2018).
- Theano Development Team. Theano: A Python Framework for Fast Computation of Mathematical Expressions. 2016. Available online: http://deeplearning.net/software/theano/ (accessed on 10 November 2018).
- Abadi, M. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems. 2015. Available online: https://tensorflow.org (accessed on 10 November 2018).
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Sze, V.; Chen, Y.H.; Emer, J.; Suleiman, A.; Zhang, Z. Hardware for Machine Learning: Challenges and Opportunities. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), Austin, TX, USA, 30 April–3 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Leng, C.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Cheng, J. Quantized Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4820–4828. [Google Scholar]





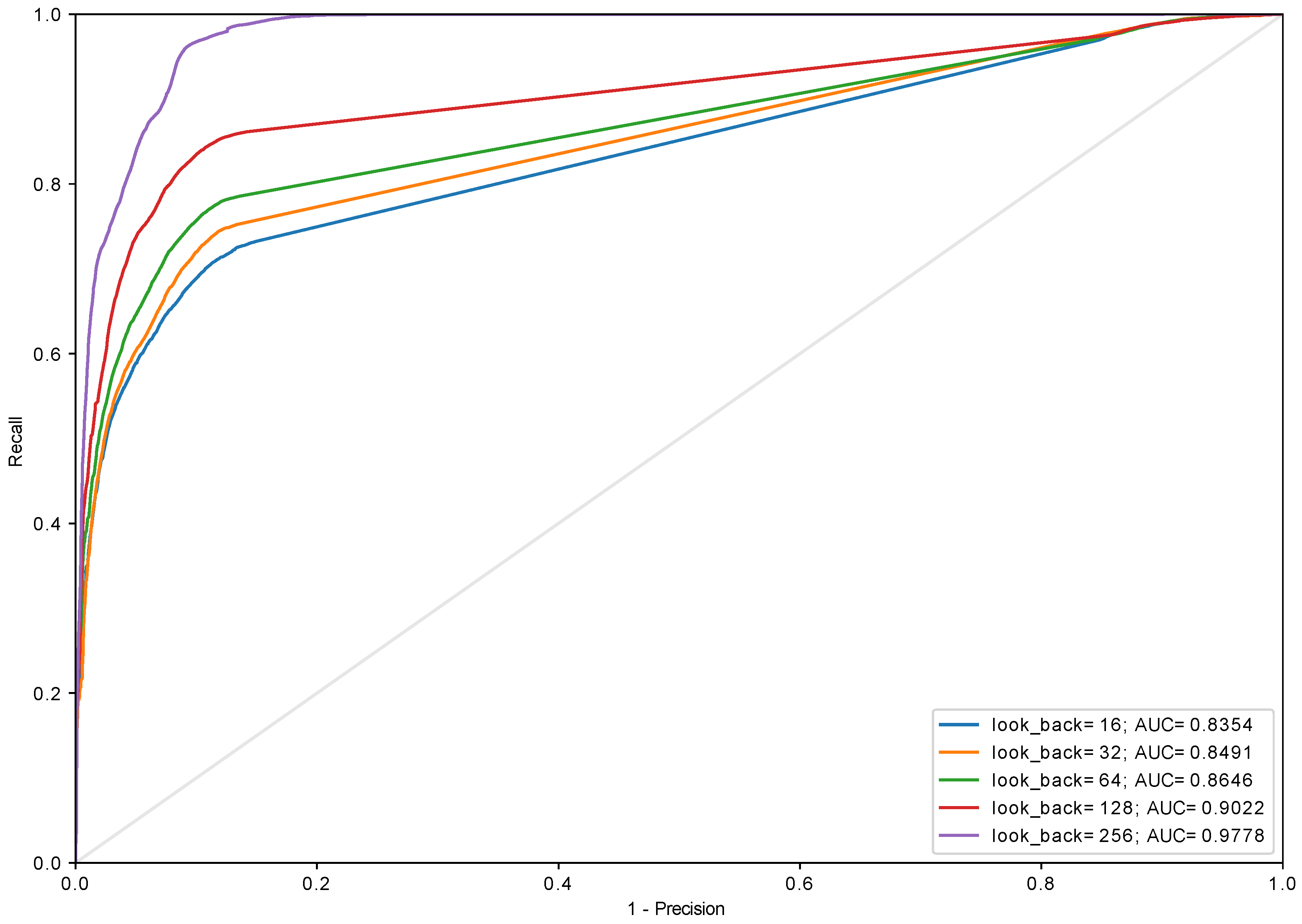
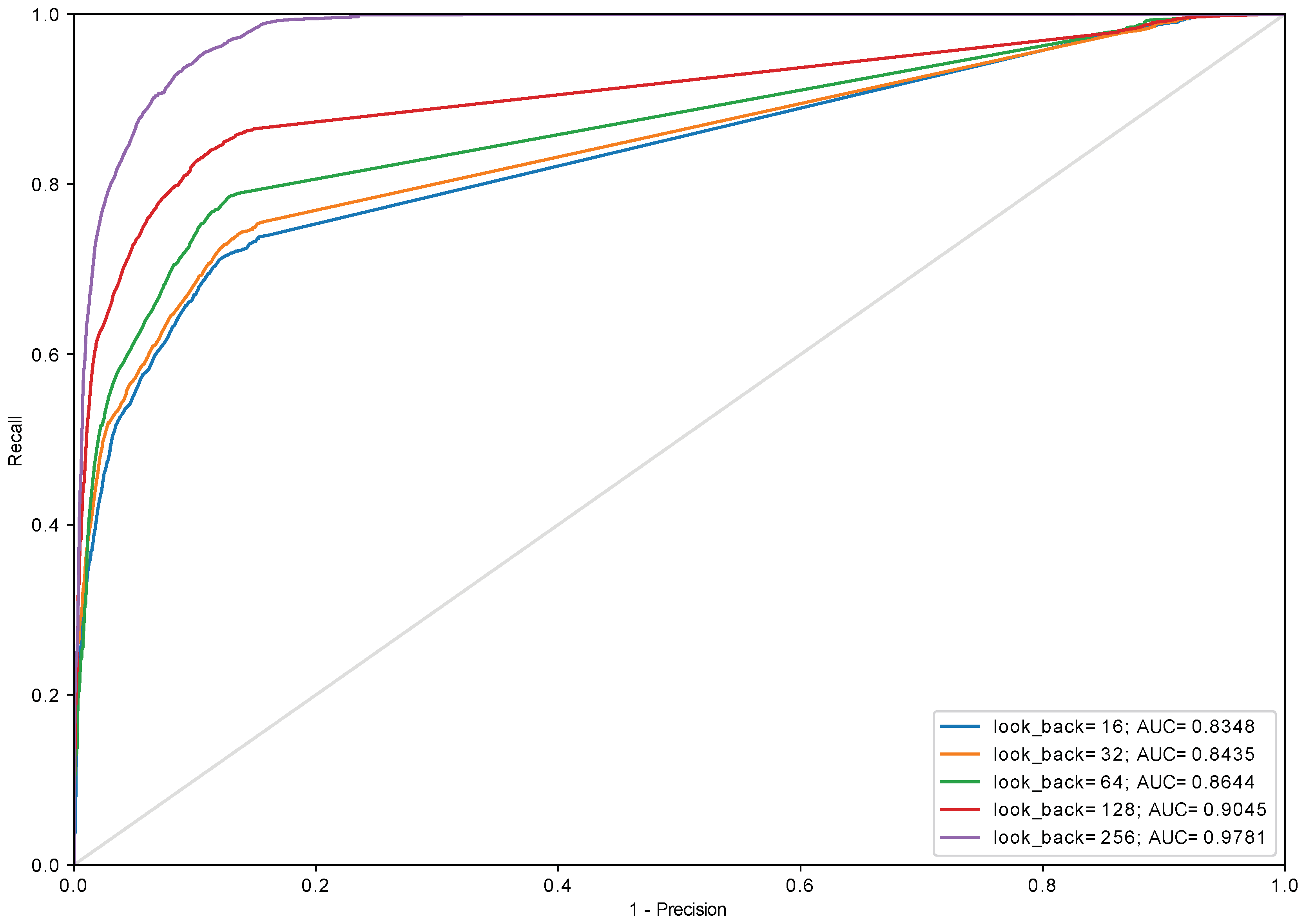
| Accuracy | Score | Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| adaptive | 16 | 0.8462 | 0.6722 | 0.6167 |
| 32 | 0.8506 | 0.7031 | 0.6687 | |
| 64 | 0.8611 | 0.7376 | 0.7124 | |
| 128 | 0.8838 | 0.7973 | 0.7835 | |
| 256 | 0.9162 | 0.8743 | 0.8796 | |
| 512 | 0.9543 | 0.9474 | 0.9522 | |
| recursive_adaptive | 16 | 0.8507 | 0.6920 | 0.6481 |
| 32 | 0.8543 | 0.7022 | 0.6561 | |
| 64 | 0.8652 | 0.7350 | 0.6928 | |
| 128 | 0.8868 | 0.8040 | 0.7939 | |
| 256 | 0.9172 | 0.8746 | 0.8749 | |
| 512 | 0.9571 | 0.9506 | 0.9560 | |
| cumulative_amplitude | 16 | 0.8436 | 0.6609 | 0.5999 |
| 32 | 0.8473 | 0.6664 | 0.5968 | |
| 64 | 0.8562 | 0.7115 | 0.6620 | |
| 128 | 0.8853 | 0.7927 | 0.7622 | |
| 256 | 0.9231 | 0.8830 | 0.8805 | |
| 512 | 0.9669 | 0.9625 | 0.9779 |
| Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Adaptive | Recursive_Adaptive | Cumulative_Amplitude | |
| Random (stratified) | 0.6334 | 0.6334 | 0.6334 |
| Elliptic Envelope | 0.6700 | 0.7775 | 0.6700 |
| Isolation Forest | 0.7947 | 0.7596 | 0.8094 |
| OC-SVM (RBF kernel) | 0.3300 | 0.8232 | 0.3300 |
| OC-SVM (linear kernel) | 0.2959 | 0.7881 | 0.2528 |
| GRU (two layers, 64 and 32 cells) | 0.8928 | 0.9005 | 0.8842 |
| LSTM (two layers, 64 and 32 cells) | 0.8271 | 0.8552 | 0.7402 |
| Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Adaptive | Recursive_Adaptive | Cumulative_Amplitude | |
| GRU (two layers, 64 and 32 cells) | 0.9235 | 0.9300 | 0.8842 |
| LSTM (two layers, 64 and 32 cells) | 0.9194 | 0.9092 | 0.9023 |
| Bits | Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adaptive | Recursive_Adaptive | Cumulative_Amplitude | ||
| Original Model | 0.9235 | 0.9300 | 0.8842 | |
| 10 | linear | 0.9236 | 0.9287 | 0.8841 |
| minmax | 0.9233 | 0.9300 | 0.8841 | |
| log_minmax | 0.9235 | 0.9298 | 0.8842 | |
| tanh | 0.9232 | 0.9283 | 0.9232 | |
| 9 | linear | 0.9236 | 0.9279 | 0.8838 |
| minmax | 0.9237 | 0.9295 | 0.8842 | |
| log_minmax | 0.9231 | 0.9293 | 0.8843 | |
| tanh | 0.9219 | 0.9260 | 0.8842 | |
| 8 | linear | 0.9206 | 0.9257 | 0.8830 |
| minmax | 0.9238 | 0.9311 | 0.8838 | |
| log_minmax | 0.9207 | 0.9283 | 0.8844 | |
| tanh | 0.9161 | 0.9143 | 0.8836 | |
| 7 | linear | 0.9177 | 0.3989 | 0.8850 |
| minmax | 0.9194 | 0.9250 | 0.8841 | |
| log_minmax | 0.9218 | 0.9236 | 0.8833 | |
| tanh | 0.9131 | 0.9033 | 0.8851 | |
| 6 | linear | 0.8952 | 0.9008 | 0.8871 |
| minmax | 0.9144 | 0.8839 | 0.8842 | |
| log_minmax | 0.9111 | 0.9076 | 0.8844 | |
| tanh | 0.8702 | 0.8782 | 0.8788 | |
| 5 | linear | 0.3722 | 0.8442 | 0.8802 |
| minmax | 0.9031 | 0.9058 | 0.8810 | |
| log_minmax | 0.3948 | 0.8878 | 0.8812 | |
| tanh | 0.8247 | 0.3306 | 0.8670 | |
| 4 | linear | 0.8500 | 0.2745 | 0.8587 |
| minmax | 0.8678 | 0.8702 | 0.8775 | |
| log_minmax | 0.8649 | 0.3848 | 0.8734 | |
| tanh | 0.7491 | 0.8464 | 0.3017 | |
| 3 | linear | 0.7928 | 0.8135 | 0.8190 |
| minmax | 0.3391 | 0.7900 | 0.8530 | |
| log_minmax | 0.7664 | 0.8023 | 0.8564 | |
| tanh | 0.6922 | 0.2833 | 0.7985 | |
| 2 | linear | 0.3006 | 0.6700 | 0.7065 |
| minmax | 0.7371 | 0.3391 | 0.3466 | |
| log_minmax | 0.7908 | 0.7369 | 0.3110 | |
| tanh | 0.7216 | 0.7549 | 0.2309 | |
| 1 | linear | 0.6700 | 0.3300 | 0.3300 |
| minmax | 0.6706 | 0.7003 | 0.6717 | |
| log_minmax | 0.7171 | 0.7459 | 0.2121 | |
| tanh | 0.7171 | 0.7459 | 0.2121 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wielgosz, M.; Skoczeń, A.; De Matteis, E. Protection of Superconducting Industrial Machinery Using RNN-Based Anomaly Detection for Implementation in Smart Sensor. Sensors 2018, 18, 3933. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113933
Wielgosz M, Skoczeń A, De Matteis E. Protection of Superconducting Industrial Machinery Using RNN-Based Anomaly Detection for Implementation in Smart Sensor. Sensors. 2018; 18(11):3933. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113933
Chicago/Turabian StyleWielgosz, Maciej, Andrzej Skoczeń, and Ernesto De Matteis. 2018. "Protection of Superconducting Industrial Machinery Using RNN-Based Anomaly Detection for Implementation in Smart Sensor" Sensors 18, no. 11: 3933. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113933
APA StyleWielgosz, M., Skoczeń, A., & De Matteis, E. (2018). Protection of Superconducting Industrial Machinery Using RNN-Based Anomaly Detection for Implementation in Smart Sensor. Sensors, 18(11), 3933. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113933





