Conductometric Soot Sensors: Internally Caused Thermophoresis as an Important Undesired Side Effect
Abstract
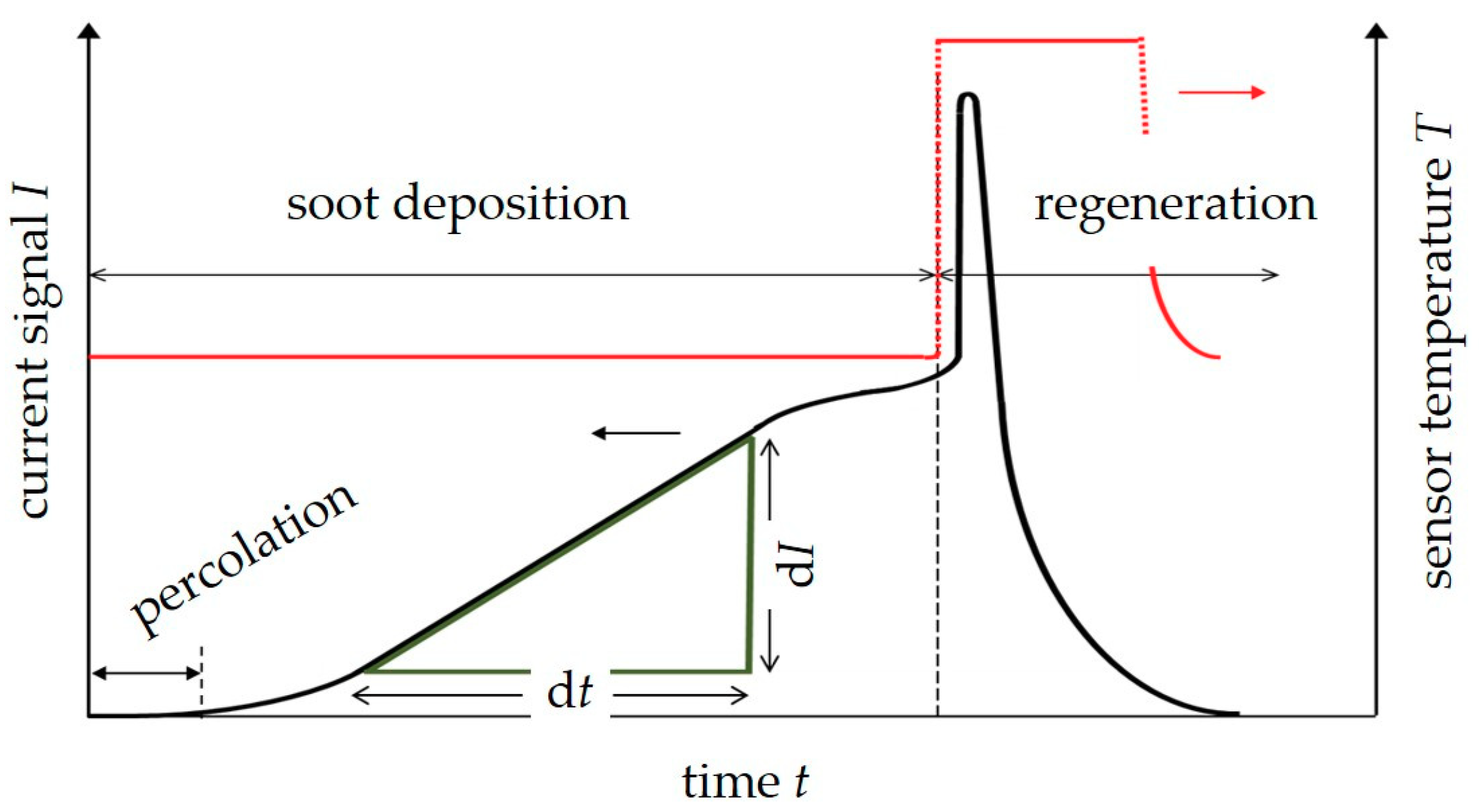
1. Introduction
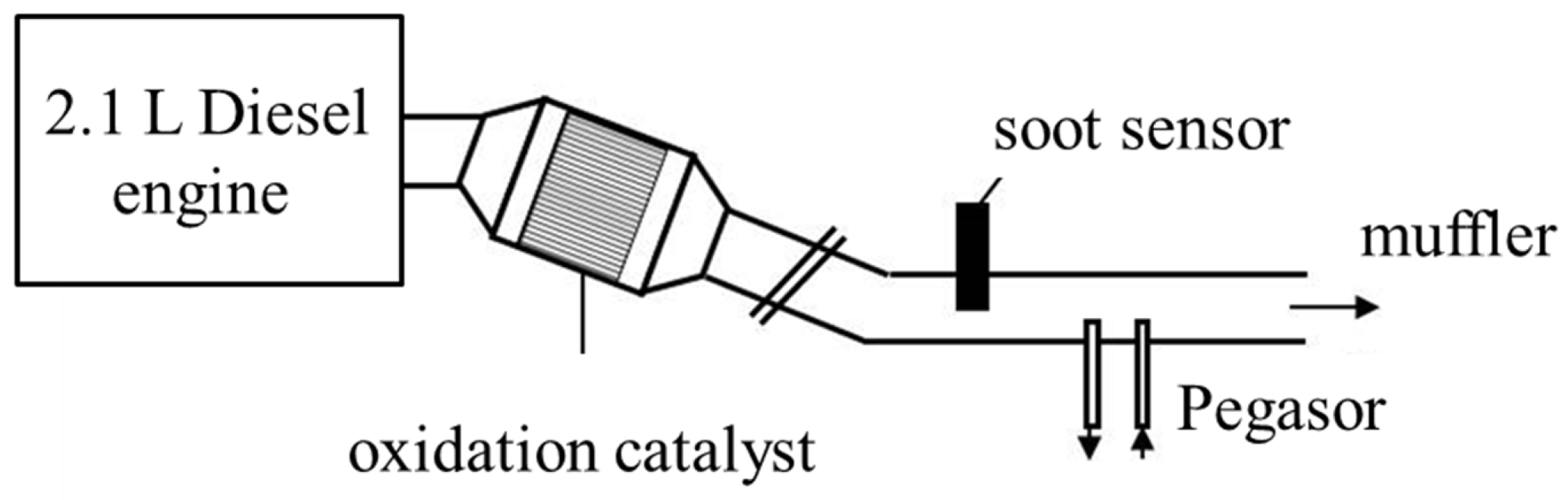
2. Sensor Design and Experimental Setup
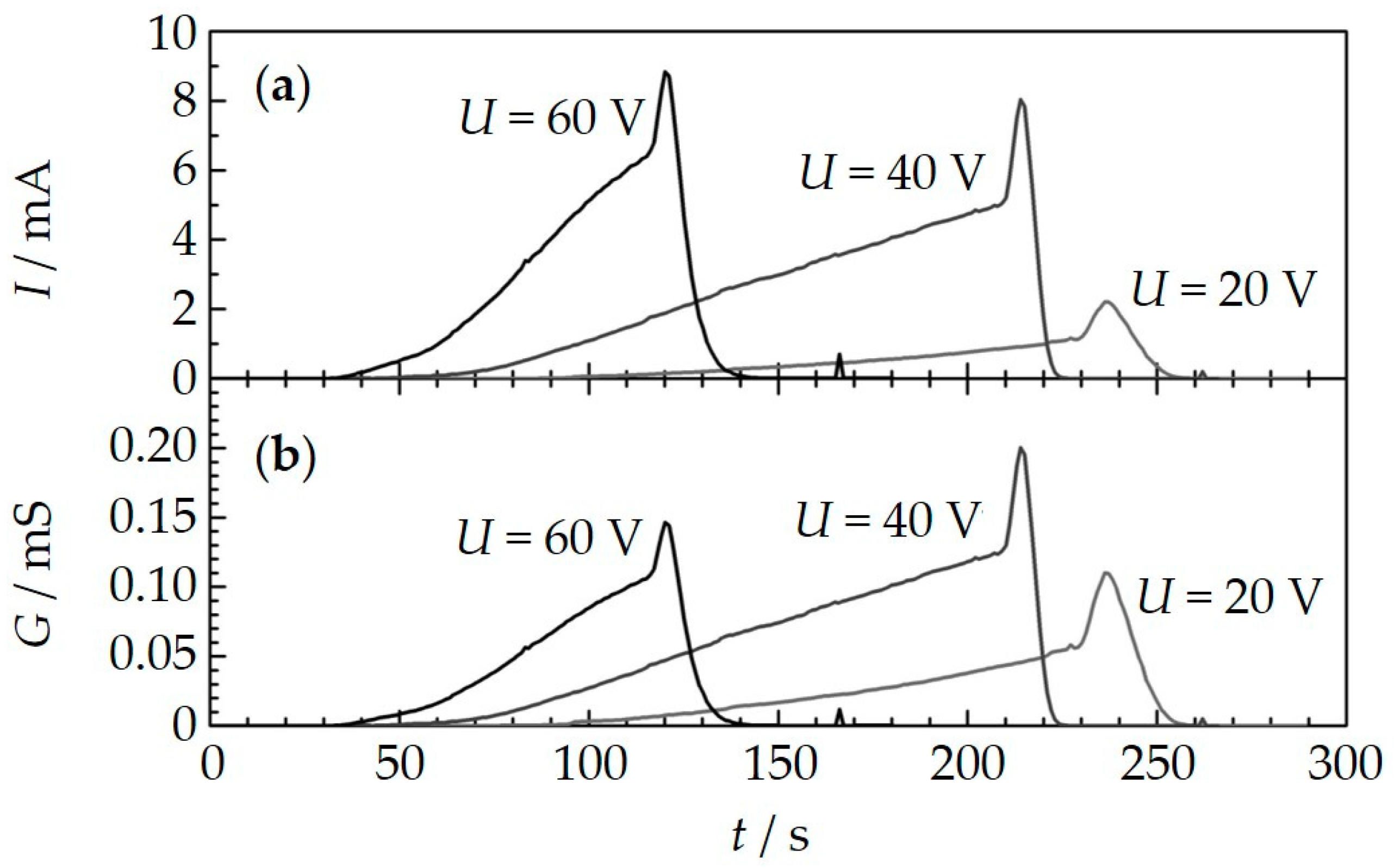
3. Results and Discussion for Real Exhaust Measurements
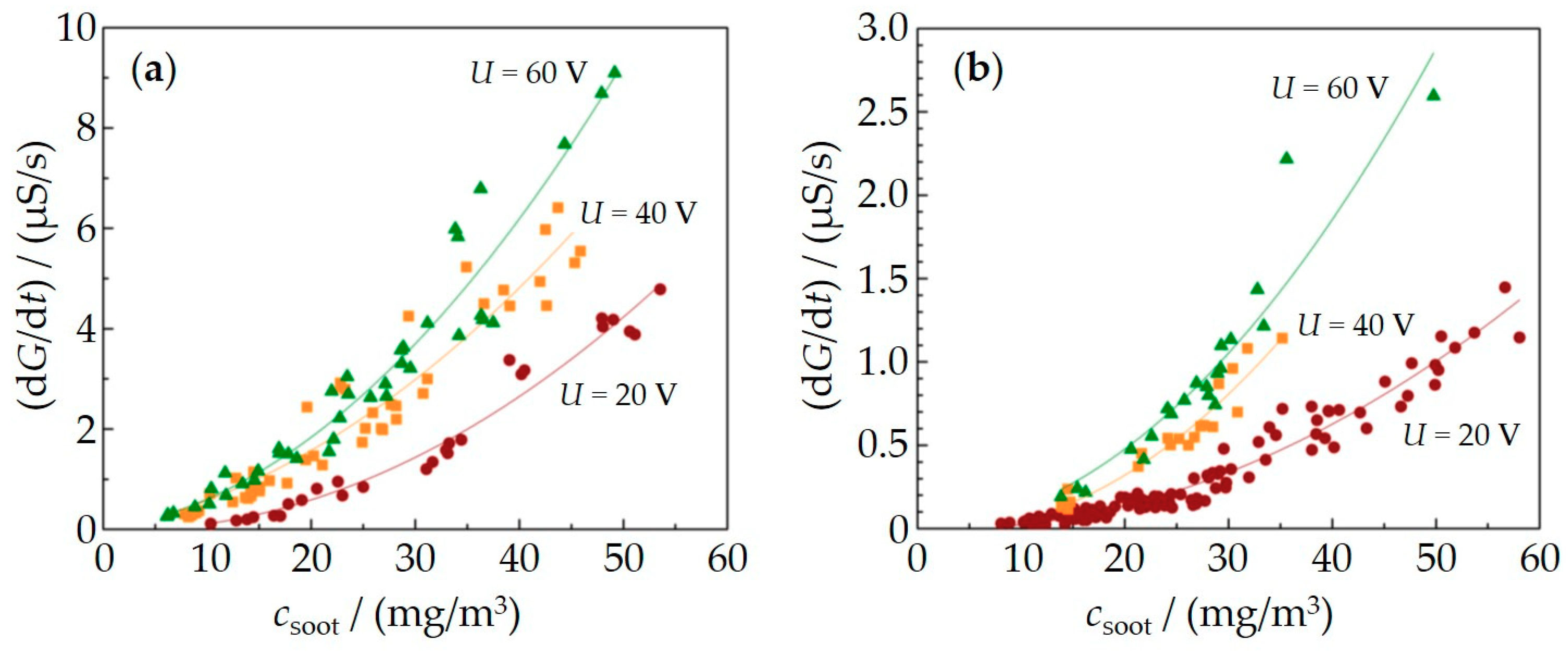
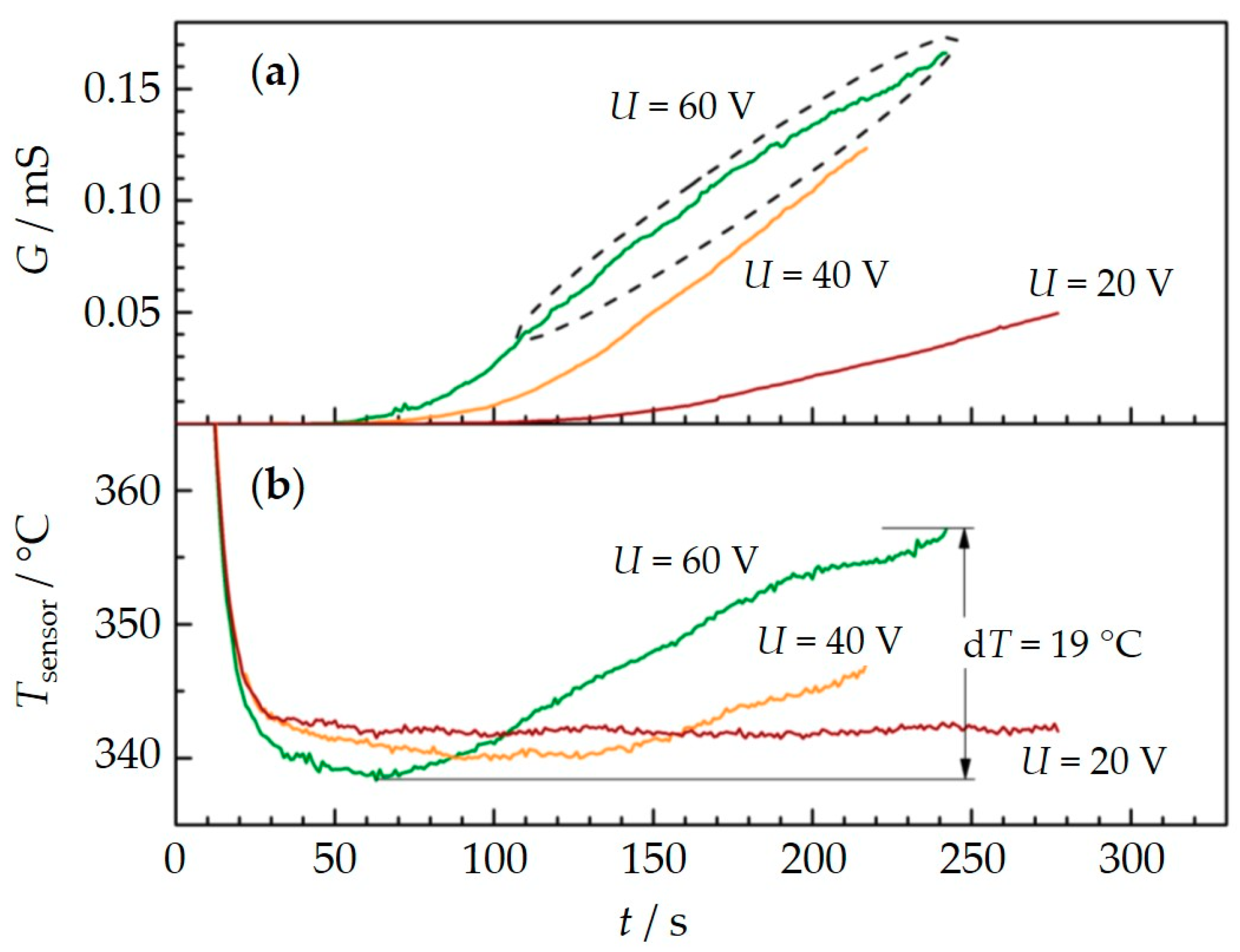
3.1. Influence of the Applied Voltage/Electrophoresis
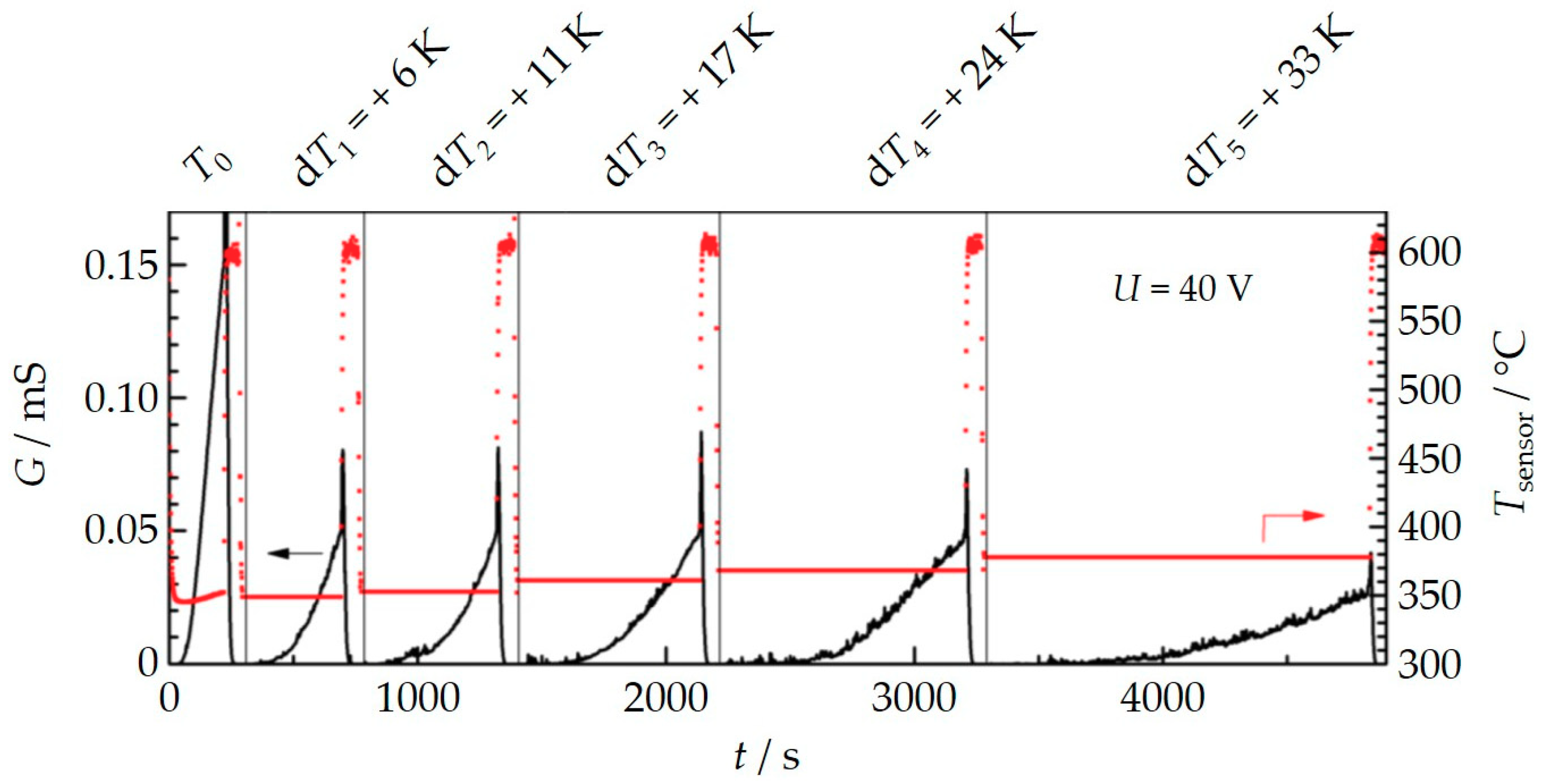
3.2. Influence of Thermophoresis
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maricq, M. Chemical characterization of particulate emissions from diesel engines: A review. J. Aerosol Sci. 2007, 38, 1079–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twigg, M.V.; Phillips, P.R. Cleaning the Air We Breathe—Controlling Diesel Particulate Emissions from Passenger Cars. Platin. Met. Rev. 2009, 53, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkemade, U.; Schumann, B. Engines and Exhaust after Treatment Systems for Future Automotive Applications. Solid State Ion. 2006, 177, 2291–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, V.; Kousoulidou, M.; Muntean, M.; Ntziachristos, L.; Hausberger, S.; Dilara, P. Road vehicle emission factors development: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 70, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtscher, H.; Majewski, W.A.; Jääskeläinen, H. PM Measurement: In-Situ Methods. DieselNet 2014, 7, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Mohr, M.; Lehmann, U.; Rütter, J. Comparison of Mass-Based and Non-Mass-Based Particle Measurement Systems for Ultra-Low Emissions from Automotive Sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 2229–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, S.J.; Maricq, M. Signature Size Distributions for Diesel and Gasoline Engine Exhaust Particulate Matter. J. Aerosol Sci. 2001, 32, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittelson, D.B. Engines and Nanoparticles: A Review. J. Aerosol Sci. 1998, 29, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Reggie, Z.; He, L.; Huang, Z. Review of the state-of-the-art of exhaust particulate filter technology in internal combustion engines. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 154, 225–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigl, M.; Roduner, C.; Lauer, T. Particulate Filter Onboard Diagnostics by Means of a Particulate Sensor. In Proceedings of the FISITA 2010 World Automotive Congress, Budapest, Hungary, 30 May–4 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Brunel, O.; Duault, F.; Lavy, J.; Creff, Y.; Youssef, B. Smart Soot Sensor for Particulate Filter OBD. SAE Int. J. Passeng. Cars Electron. Electr. Syst. 2013, 6, 307–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimoto, T. A review of soot sensors considered for on-board diagnostics application. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2016, 18, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, T.; Fujie, H.; Aso, M. DPF Failure Detection Method and DPF Failure Detection Device. U.S. Patent 8,770,016 B2, 20 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- DieselNet, On-Board Diagnostics. Available online: https://www.dieselnet.com/standards/us/obd.php (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- Johnson, T. Review of Diesel Emissions and Control. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2010, 3, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.; Boger, T. Different Approaches to Soot Estimation as Key Requirement for DPF Applications. SAE Tech. Pap. 2009, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sappok, A.; Bromberg, L. Loading and Regeneration Analysis of a Diesel Particulate Filter with a Radio Frequency-Based Sensor. SAE Tech. Pap. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feulner, M.; Hagen, G.; Piontkowski, A.; Müller, A.; Fischerauer, G.; Brüggemann, D.; Moos, R. In-Operation Monitoring of the Soot Load of Diesel Particulate Filters—Initial Tests. Top. Catal. 2013, 56, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feulner, M.; Hagen, G.; Hottner, K.; Redel, S.; Müller, A.; Moos, R. Comparative Study of Different Methods for Soot Sensing and Filter Monitoring in Diesel Exhausts. Sensors 2017, 17, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husted, H.; Roth, G.; Nelson, S.; Hocken, L.; Fulks, G.; Racine, D. Sensing of Particulate Matter for on-Board Diagnosis of Particulate Filters. SAE Int. J. Eng. 2012, 5, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostedt, A.; Marjamäki, M.; Yli-Ojanperä, J.; Keskinen, J.; Janka, K.; Niemelä, V.; Ukkonen, A. Non-Collecting Electrical Sensor for Particle Concentration Measurement. Aerosol Air Q. Res. 2009, 9, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiß, S. Continental ePM sensor for detecting particle emission. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference Sensors for Exhaust Gas Cleaning and CO2 Reduction, Leipzig, Germany, 29–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, A.; Yokoi, S.; Sakurai, T.; Nishikawa, S.; Egami, T.; Tokuda, M.; Sakuma, T. New Particulate Matter Sensor for On Board Diagnosis. SAE Int. J. Eng. 2011, 4, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, G.; Feulner, M.; Werner, R.; Schubert, M.; Müller, A.; Rieß, G.; Brüggemann, D.; Moos, R. Capacitive soot sensor for diesel exhausts. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasisto, H.S.; Merzsch, S.; Uhde, E.; Waag, A.; Peiner, E. Partially Integrated Cantilever-Based Airborne Nanoparticle Detector for Continuous Carbon Aerosol Mass Concentration Monitoring. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2015, 4, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Abdulhamid, H.; Pagels, J.; Rissler, J.; Lindskog, M.; Nilsson, P.; Bjorklund, R.; Jozsa, P.; Visser, J.; Spetz, A.; et al. A Potential Soot Mass Determination Method from Resistivity Measurement of Thermophoretically Deposited Soot. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi, M.; Sappok, A.G. Soot (PM) Sensors. DieselNet 2014, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ochs, T.; Schittenhelm, H.; Genssle, A.; Kamp, B. Particulate Matter Sensor for On Board Diagnostics (OBD) of Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF). SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2010, 3, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartscherer, P.; Moos, R. Improvement of the Sensitivity of a Conductometric Soot Sensor by Adding a Conductive Cover Layer. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2013, 2, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, G.; Feistkorn, C.; Wiegärtner, S.; Heinrich, A.; Brüggemann, D.; Moos, R. Conductometric Soot Sensor for Automotive Exhausts: Initial Studies. Sensors 2010, 10, 1589–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd Spetz, A.; Huotari, J.; Bur, C.; Bjorklund, R.; Lappalainen, J.; Jantunen, H.; Schütze, A.; Andersson, M. Chemical sensor systems for emission control from combustions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 187, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grob, B.; Schmid, J.; Ivleva, N.P.; Niessner, R. Conductivity for Soot Sensing: Possibilities and Limitations. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3586–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischer, M.; Pohle, R.; Wiesner, K.; Meixner, H. Soot sensor for exhaust gase. In Proceedings of the Eurosensors XIX, Barcelona, Spain, 11–14 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wiegärtner, S.; Hagen, G.; Kita, J.; Reitmeier, W.; Hien, M.; Grass, P.; Moos, R. Thermoelectric hydrocarbon sensor in thick-film technology for on-board-diagnostics of a diesel oxidation catalyst. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 214, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, G.; Müller, A.; Feulner, M.; Schott, A.; Zöllner, C.; Brüggemann, D.; Moos, R. Determination of the Soot Mass by Conductometric Soot Sensors. Procedia Eng. 2014, 87, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feulner, M.; Hagen, G.; Müller, A.; Schott, A.; Zöllner, C.; Brüggemann, D.; Moos, R. Conductometric Sensor for Soot Mass Flow Detection in Exhausts of Internal Combustion Engines. Sensors 2015, 15, 28796–28806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marr, I.; Groß, A.; Moos, R. Overview on Conductometric Solid-State Gas Dosimeters. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2014, 3, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grondin, D.; Breuil, P.; Viricelle, J.P.; Vernoux, P. Development of a particulate matter sensor for diesel engine. Procedia Eng. 2015, 120, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grondin, D.; Geara, S.; Breuil, P.; Viricelle, J.P.; Vernoux, P. Influence of Electrodes Polarization on the Response of Resistive Soot Sensor. Procedia Eng. 2016, 168, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grondin, D.; Westermann, A.; Breuil, P.; Viricelle, J.P.; Vernoux, P. Influence of key parameters on the response of a resistive soot sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittelson, D.B.; Pui, D.Y.H.; Moon, K.C. Electrostatic Collection of Diesel Particles. SAE Tech. Pap. 1986, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricq, M. On the electrical charge of motor vehicle exhaust particles. Aerosol Sci. 2006, 37, 858–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilby, D.; Kubinski, D.J.; Maricq, M. Current amplification in an electrostatic trap by soot dendrite growth and fragmentation: Application to soot sensors. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 98, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtscher, H. Physical Characterization of Particulate Emissions from Diesel Engines: A Review. J. Aerosol Sci. 2005, 36, 896–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, L.J.; Sarkar, A.K.; Kroto, H.W.; Munn, J.; Kathirgamanathan, P.; Heinen, U.; Fernandez, J.; Hare, J.; Reid, D.G.; Clark, A.D. Electrical, Magnetic and Structural Characterization of Fullerene Soots. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1996, 8, 2127–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sielicki, P.; Janik, H.; Guzman, A.; Namieśnik, J. Grain Type and Size of Particulate Matter from Diesel Vehicle Exhausts Analysed by Transmission Electron Microscopy. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huffman, G.P.; Huggins, F.E.; Shah, N.; Huggins, R.; Linak, W.P.; Miller, C.A.; Pugmire, R.J.; Meuzelaar, H.L.; Seehra, M.S.; Manivannan, A. Characterization of Fine Particulate Matter Produced by Combustion of Residual Fuel Oil. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2000, 50, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.H.; Lee, W.M.; Liaw, J.J. Morphological and Semi-Quantitative Characteristics of Diesel Soot Agglomerates Emitted from Commercial Vehicles and a Dynamometer. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, P. Cleaning Up Diesel Pollution: Emissions from Off-Highway Engines by State; Union of Concerned Scientists: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Krinke, T.J.; Deppert, K.; Magnusson, M.H.; Schmidt, F.; Fissan, H. Microscopic Aspects of the Deposition of Nanoparticles from the Gas Phase. J. Aerosol Sci. 2002, 33, 1341–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, T.; Wiegärtner, S.; Hagen, G.; Moos, R. Simulation of a thermoelectric gas sensor that determines hydrocarbon concentrations in exhausts and the light-off temperature of catalyst materials. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2017, 6, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messerer, A.; Niessner, R.; Pöschl, U. Thermophoretic Deposition of Soot Aerosol Particles under Experimental Conditions Relevant for Modern Diesel Engine Exhaust Gas Systems. J. Aerosol Sci. 2003, 34, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutic, D.; Pagels, J.; Bjorklund, R.; Josza, P.; Visser, J.H.; Grant, A.W.; Johansson, M.L.; Paaso, J.; Fägerman, P.-E.; Sanati, M.; et al. Detection of Soot Using a Resistivity Sensor Device Employing Thermophoretic Particle Deposition. J. Sens. 2010, 2010, 421072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, G.; Spannbauer, C.; Moos, R. Electrophoretic and thermophoretic effects on conductometric soot sensing: Special challenges when using synthetic soot. In Proceedings of the 17th International Meeting on Chemical Sensors (IMCS 17), Vienna, Austria, 15–19 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkiadoulakis, P.; Geivanidis, S.; Samaras, Z. Modeling a resistive soot sensor by particle deposition mechanisms. J. Aerosol Sci. 2018, 123, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hagen, G.; Spannbauer, C.; Feulner, M.; Kita, J.; Müller, A.; Moos, R. Conductometric Soot Sensors: Internally Caused Thermophoresis as an Important Undesired Side Effect. Sensors 2018, 18, 3531. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103531
Hagen G, Spannbauer C, Feulner M, Kita J, Müller A, Moos R. Conductometric Soot Sensors: Internally Caused Thermophoresis as an Important Undesired Side Effect. Sensors. 2018; 18(10):3531. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103531
Chicago/Turabian StyleHagen, Gunter, Christoph Spannbauer, Markus Feulner, Jaroslaw Kita, Andreas Müller, and Ralf Moos. 2018. "Conductometric Soot Sensors: Internally Caused Thermophoresis as an Important Undesired Side Effect" Sensors 18, no. 10: 3531. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103531
APA StyleHagen, G., Spannbauer, C., Feulner, M., Kita, J., Müller, A., & Moos, R. (2018). Conductometric Soot Sensors: Internally Caused Thermophoresis as an Important Undesired Side Effect. Sensors, 18(10), 3531. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103531




