Interference-Aware Adaptive Beam Alignment for Hyper-Dense IEEE 802.11ax Internet-of-Things Networks
Abstract
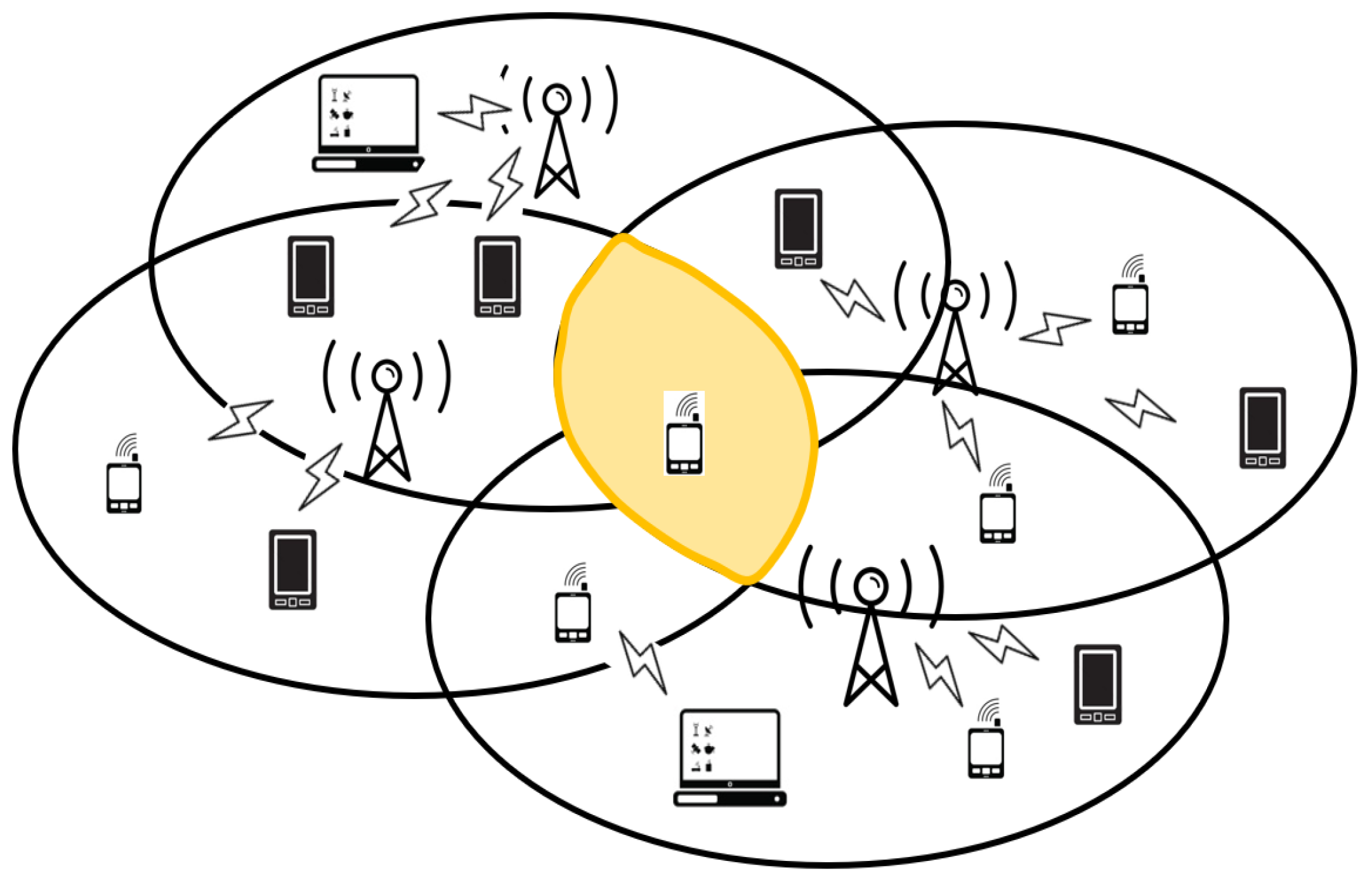
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. IEEE 802.11ax Features
3.1. PPDU Frame Structure
3.2. Error Correction and Modulation
4. Proposed Opportunistic Medium Access
4.1. System Model and Assumptions
- Each STA has exactly the same performances with OFDMA and MU-MIMO for mathematical performance analysis.
- In addition, antennas which are installed in each IEEE 802.11ax IoT device are full-duplex vouching simultaneous U/DL transmission.
- Detailed parameter setting of antennas for beamforming including azimuth, half power beam width (HPBW), and antenna gains are not associated with the proposed algorithm.
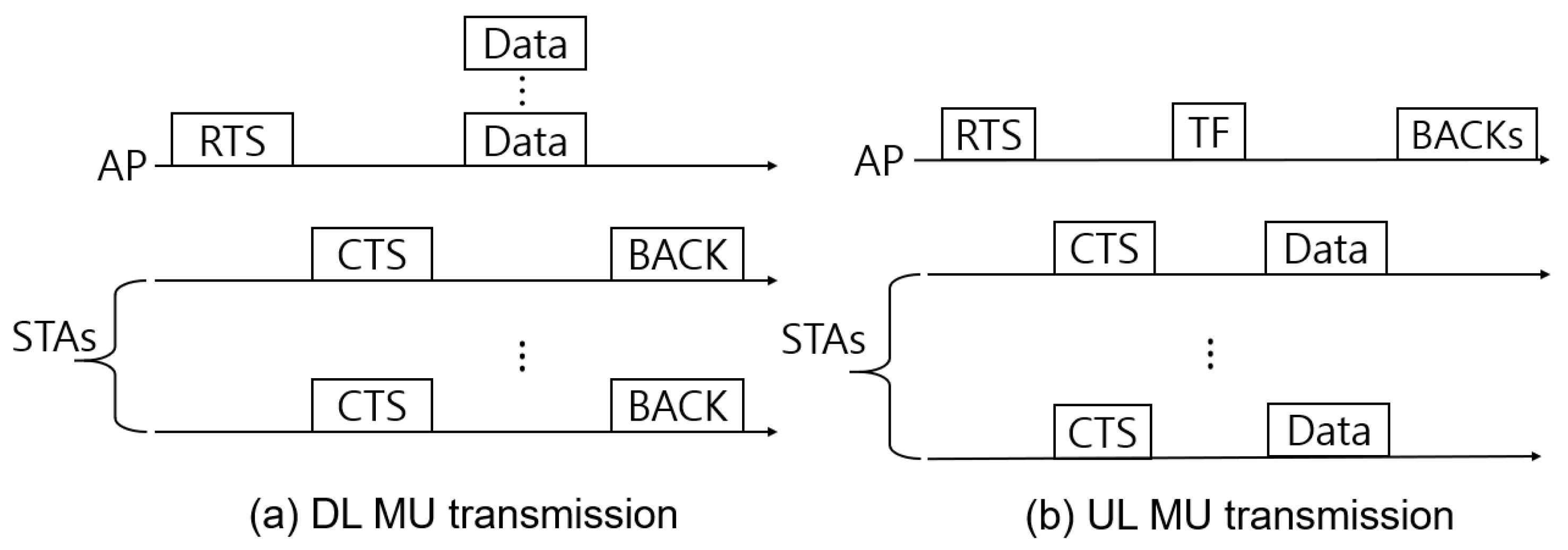
- U/DL MU transmissions are considered in this paper.
- In our proposed algorithm, NAV is set to 0 if the corresponding AP is idle and vice versa.
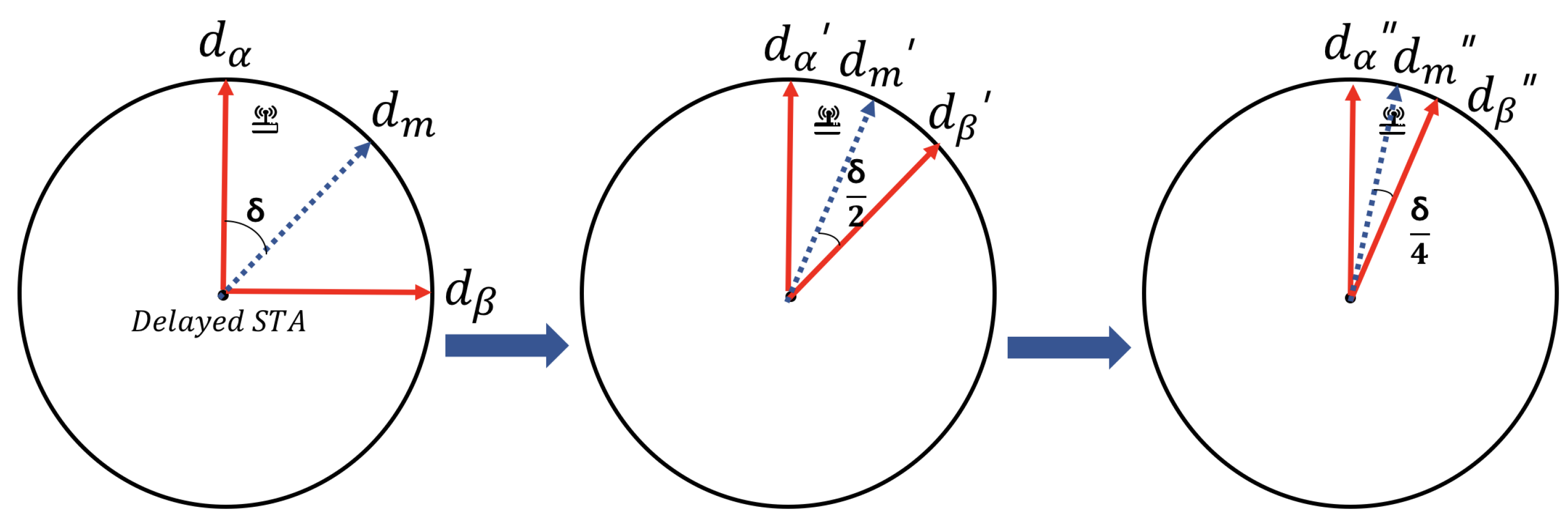
4.2. Beam Direction Selection and Beamforming Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 Proposed beamforming algorithm |
Input: 〈, 〉, , ,
|
| Algorithm 2 Joint searching for direction and CSI |
| Input:, , , , , , Output: Appropriate for beamforming
|
4.3. Analytical Model
4.3.1. Total Elapsed Time of D/UL MU Transmission
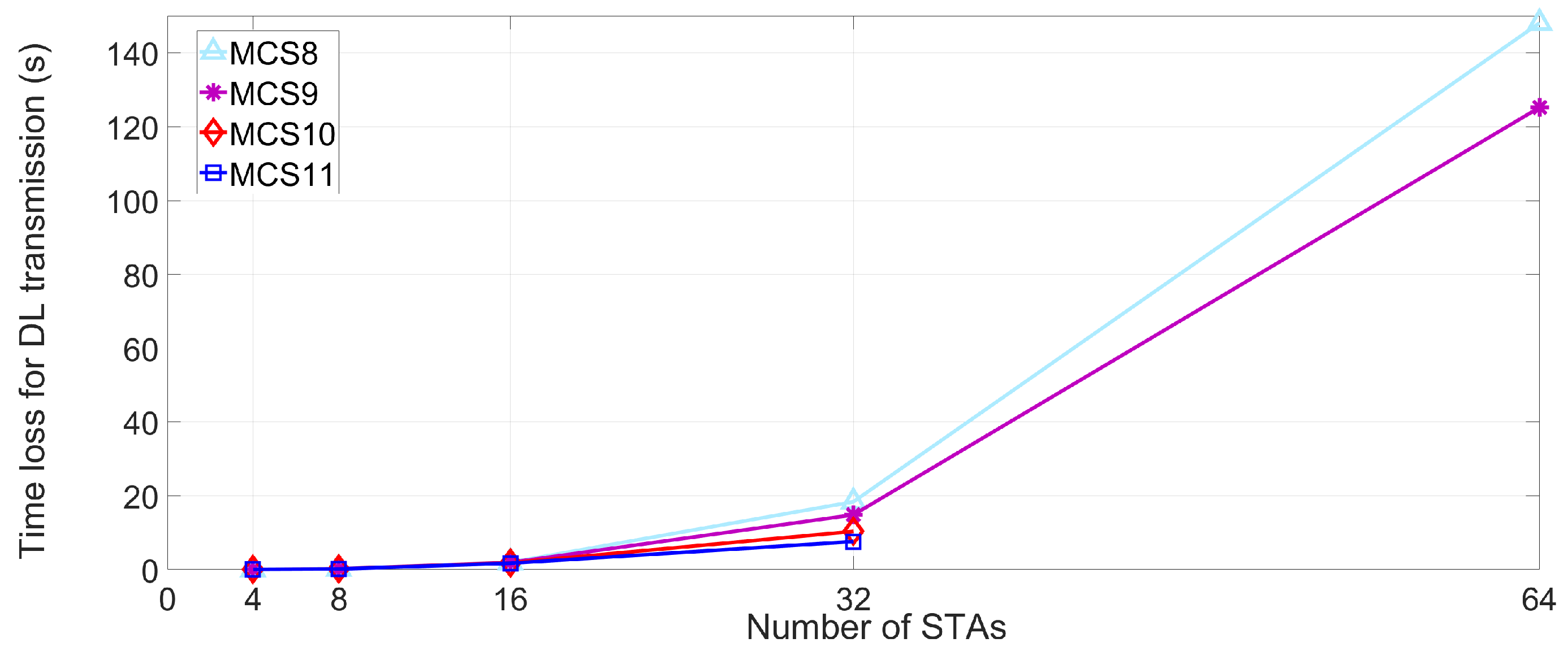
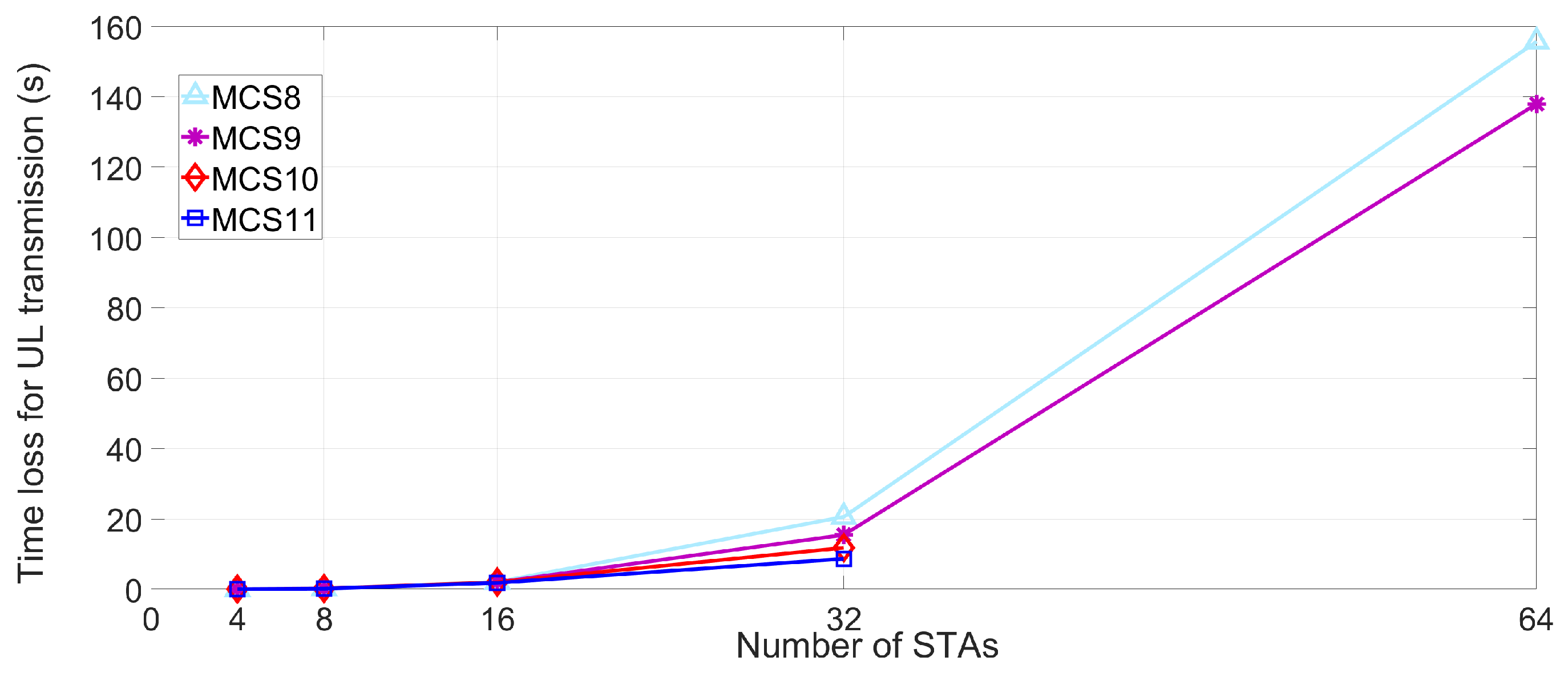
4.3.2. Expected Lost Time,
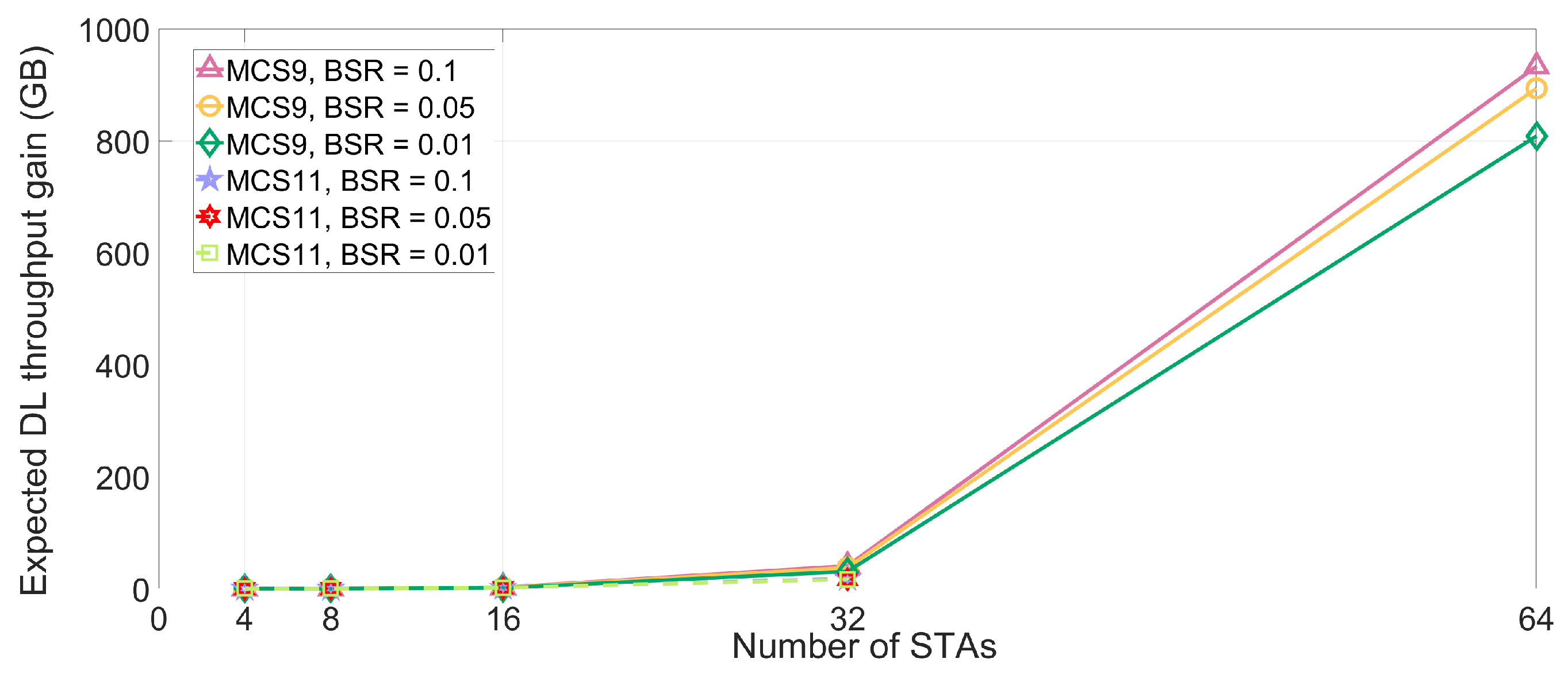
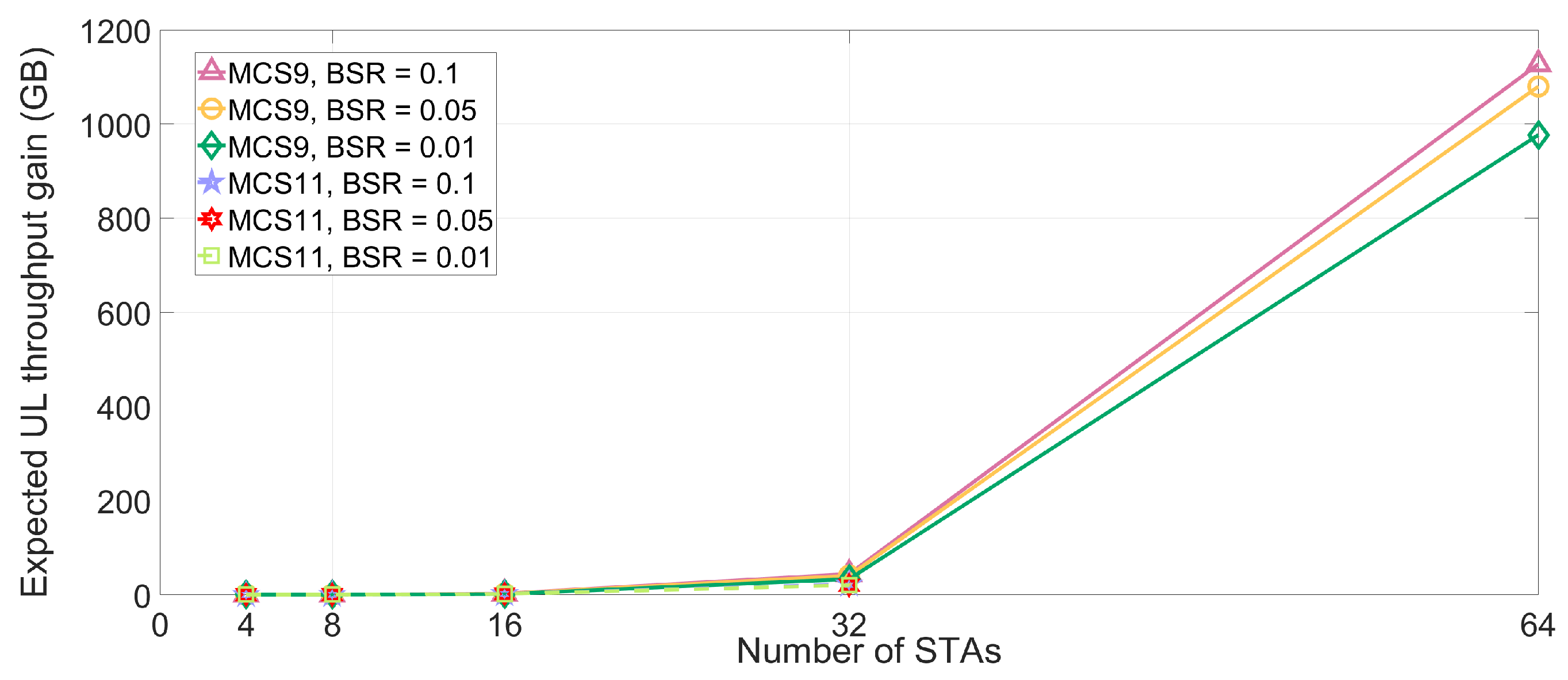
4.3.3. Expected Throughput Loss,
4.3.4. Jain’s Index for Fairness
5. Performance Evaluation
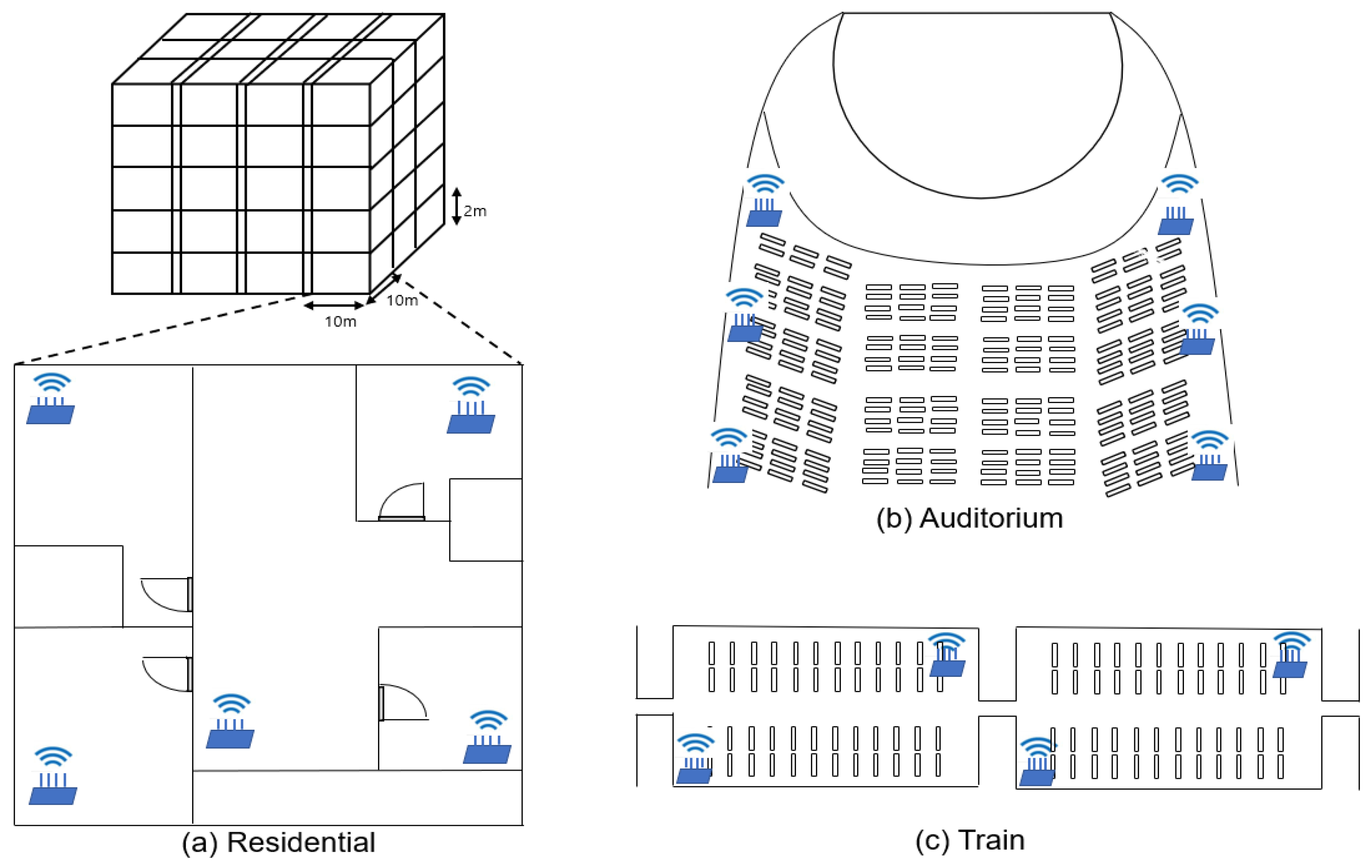
5.1. Simulation Setting and Overview
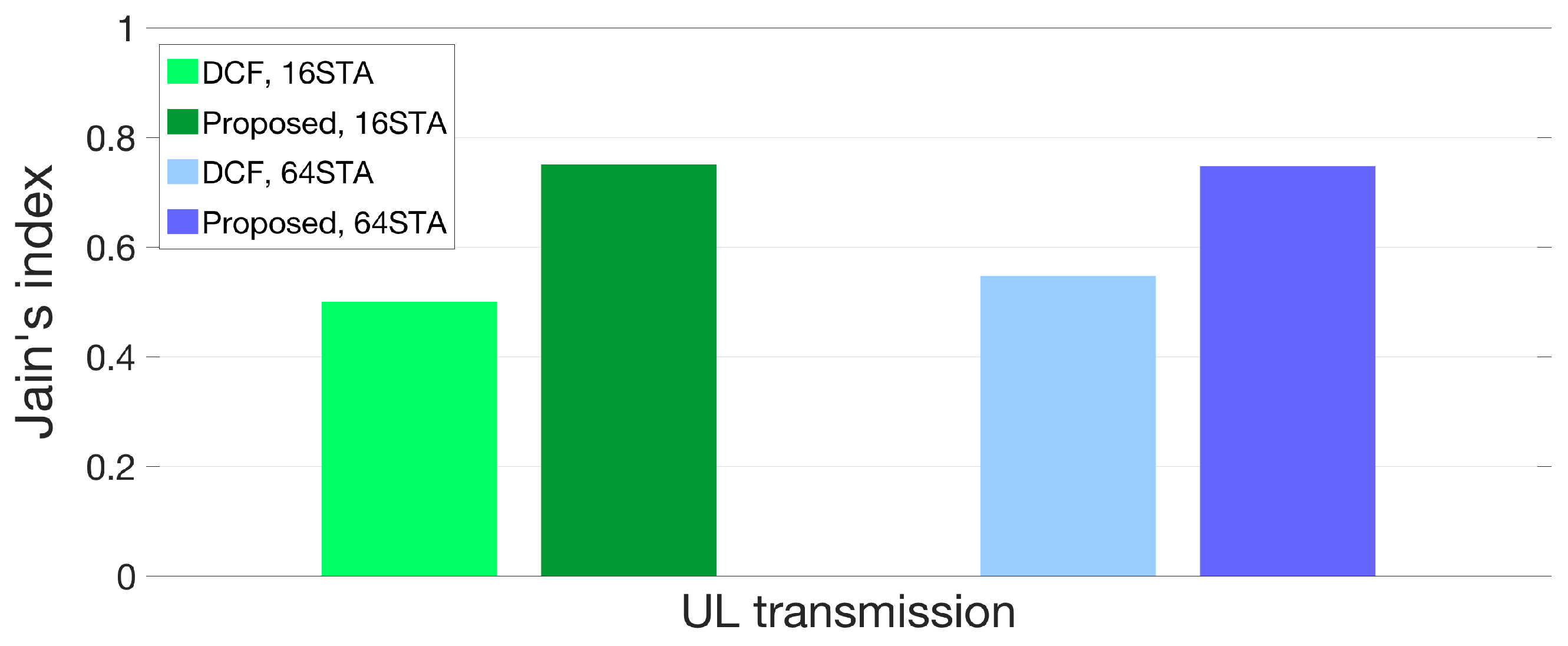
5.2. Simulation Results and Discussions
6. Conclusions Remarks and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cisco Visual Networking Index: Forecast and Methodology 2016–2021. 2017. Available online: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/service-provider/visual-networking-index-vni/complete-white-paper-c11-481360.html (accessed on 25 July 2018).
- Afaqui, M.S.; Villegas, E.G.; Aguilera, E.L. IEEE 802.11ax: Challenges and Requirements for Future High Efficiency WiFi. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorov, E.; Kiryanov, A.; Lyakhov, A. IEEE 802.11ax: How to Build High Efficiency WLANs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Engineering and Telecommunication (EnT), Moscow, Russia, 18–19 November 2015; pp. 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, H.A.; Abboud, K.; Cheng, N.; Malekshan, K.R.; Gamage, A.T.; Zhuang, W. A Survey on High Efficiency Wireless Local Area Networks: Next Generation WiFi. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 2315–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellalta, B. IEEE 802.11ax: High-Efficiency WLANs. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2016, 23, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellalta, B.; Kosek-Szott, K. AP-initiated Multi-User Transmissions in IEEE 802.11ax WLANs. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1702.05397. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, M.X.; Hart, B.; Mao, S. Advanced Wireless LAN Technologies: IEEE 802.11AC and Beyond. In ACM GetMobile: Mobile Computing and Communications; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 18, pp. 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Qu, Q.; Yan, Z.; Yang, M. Survey on OFDMA based MAC Protocols for the Next Generation WLAN. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference Workshop (WCNC WKSHPS), Istanbul, Turkey, 9–12 May 2015; pp. 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Q.; Li, B.; Yang, M.; Yan, Z. An OFDMA based Concurrent Multiuser MAC for Upcoming IEEE 802.11ax. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference Workshop (WCNC WKSHPS), Istanbul, Turkey, 9–12 May 2015; pp. 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Afaqui, M.S.; Villegas, E.G.; Lopez-Aguilera, E. Dynamic Sensitivity Control Algorithm Leveraging Adaptive RTS/CTS for IEEE 802.11ax. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Doha, Qatar, 3–6 April 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Afaqui, M.S.; Garcia-Villegas, E.; Lopez-Aguilera, E.; Smith, G.; Camps, D. Evaluation of Dynamic Sensitivity Control Algorithm for IEEE 802.11ax. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Istanbul, Turkey, 9–12 May 2015; pp. 1060–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Li, B.; Yang, M.; Qu, Q.; Yan, Z.; Zuo, X.; Yang, B. Integrated Link-System Level Simulation Platform for the Next Generation WLAN-IEEE 802.11ax. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Washington, DC, USA, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, D.J.; Lien, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Chen, K.C. On Quality-of-Service Provisioning in IEEE 802.11 ax WLANs. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 6086–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, S.Y.; Deng, D.J.; Tsai, H.L.; Lin, Y.P.; Chen, K.C. Vehicular Radio Access to Unlicensed Spectrum. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajami, A.K.; Artail, H. On The Modeling and Analysis of Uplink and Downlink IEEE 802.11 ax Wi-Fi with LTE in Unlicensed Spectrum. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 5779–5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurchis, M.; Bellalta, B. Target Wake Time: Scheduled access in IEEE 802.11 ax WLANs. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1804.07717. [Google Scholar]
- Sharon, O.; Alpert, Y. Scheduling Strategies and Throughput Optimization for the Uplink for IEEE 802.11 ax and IEEE 802.11 ac Based Networks. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1803.10657. [Google Scholar]
- Sharon, O.; Alpert, Y. Advanced IEEE 802.11 ax TCP aware scheduling under unreliable channels. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1803.10649. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, T.; Wen, X.; Lu, Z.; Li, Y. A Semi-Matching Based Load Balancing Scheme for Dense IEEE 802.11 WLANs. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 15332–15339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aijaz, A.; Kulkarni, P. Simultaneous Transmit and Receive Operation in Next Generation IEEE 802.11 WLANs: A MAC Protocol Design Approach. arXiv, arXiv:1706.07544.
- Kwon, H.; Seo, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, B.G. Generalized CSMA/CA for OFDMA Systems: Protocol Design, Throughput Analysis, and Implementation Issues. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2009, 8, 4176–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, B.G. Opportunistic Multi-Channel CSMA Protocol for OFDMA Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2010, 9, 1552–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Wang, X.; Fang, J.; Ghosh, M.; Zhang, G.; Olesen, R. Multi-User Parallel Channel Access for High Efficiency Carrier Grade Wireless LANs. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 10–14 June 2014; pp. 3868–3870. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.; Lim, J. Group Contention-Based OFDMA MAC Protocol for Multiple Access Interference-Free in WLAN Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2012, 11, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.K.; Chiu, D.M.W.; Hawe, W.R. A Quantitative Measure of Fairness and Discrimination for Resource Allocation. 1984. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Raj_Jain3/publication/220486705_A_Quantitative_Measure_Of_Fairness_And_Discrimination_For_Resource_Allocation_In_Shared_Computer_Systems/links/09e4150c0274cec7b2000000.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2018).



| IEEE 802.11ac | IEEE 802.11ax | |
|---|---|---|
| Band (GHz) | 5 | 2.4 and 5 |
| Channel bandwidth (MHz) | 20, 40, 80, 80 + 80, 160 | 20, 40, 80, 80 + 80, 160 |
| Modulation | BPSK, QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM, 256QAM | 1024QAM is newly added |
| FFT size | 64, 128, 256, 512 | 256, 512, 1024, 2048 |
| Subcarrier spacing (KHz) | 312.5 | 78.12 |
| Symbol duration (us) | 3.2 | 12.8 |
| CP (us) | 0.4 and 0.8 | 0.8, 1.6, and 3.2 |
| FEC | BCC, LDPC (optional) | LDPC |
| Spatial stream (SS) | Up to 8 SS for each AP | Up to 8 SS for each AP |
| Up to 4 SS for each STA | Up to 4 SS for each STA | |
| MU-MIMO | DL MU-MIMO | UL/DL MU-MIMO |
| Proposed | [21] | [22] | [23] | [24] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MU transmission | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| MU access | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| MU diversity | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Simple signal exchange | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| CSI measurement | ✓ |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Number of APs | |
| Number of STAs | |
| Number of MU STAs | |
| Return time when | |
| NAV | i-th inter-BSS NAV |
| NAV | intra-BSS NAV |
| Length of control frame | |
| Length of data frame | |
| Beamforming search rate | |
| Throughput of i-th STA in time t | |
| n | Required count to find appropriate beamformees |
| Number of SU-MIMO spatial streams per STA | |
| Number of MU-MIMO spatial streams per STA | |
| Data rate | |
| Bandwidth of RU | |
| Packet size | |
| Number of aggregated packets in A-MPDU |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| B | 160 MHz |
| FFT | 256 |
| 1460 bytes | |
| 256 | |
| 32 | |
| 1024 | |
| SIFS | 16 s |
| aSlotTime | 9 s |
| 16 s | |
| 8 | |
| from 8 up to 64 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, D.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, J.; Mohaisen, A. Interference-Aware Adaptive Beam Alignment for Hyper-Dense IEEE 802.11ax Internet-of-Things Networks. Sensors 2018, 18, 3364. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103364
Kwon D, Kim S-W, Kim J, Mohaisen A. Interference-Aware Adaptive Beam Alignment for Hyper-Dense IEEE 802.11ax Internet-of-Things Networks. Sensors. 2018; 18(10):3364. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103364
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Dohyun, Sang-Wook Kim, Joongheon Kim, and Aziz Mohaisen. 2018. "Interference-Aware Adaptive Beam Alignment for Hyper-Dense IEEE 802.11ax Internet-of-Things Networks" Sensors 18, no. 10: 3364. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103364
APA StyleKwon, D., Kim, S.-W., Kim, J., & Mohaisen, A. (2018). Interference-Aware Adaptive Beam Alignment for Hyper-Dense IEEE 802.11ax Internet-of-Things Networks. Sensors, 18(10), 3364. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103364





