Gas Sensors Based on Molecular Imprinting Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Significance of Gas Sensors
1.2. Molecular Imprinting Technology in Gas Sensors
1.3. Synthesis Strategies of Molecularly Imprinted Gas Sensors
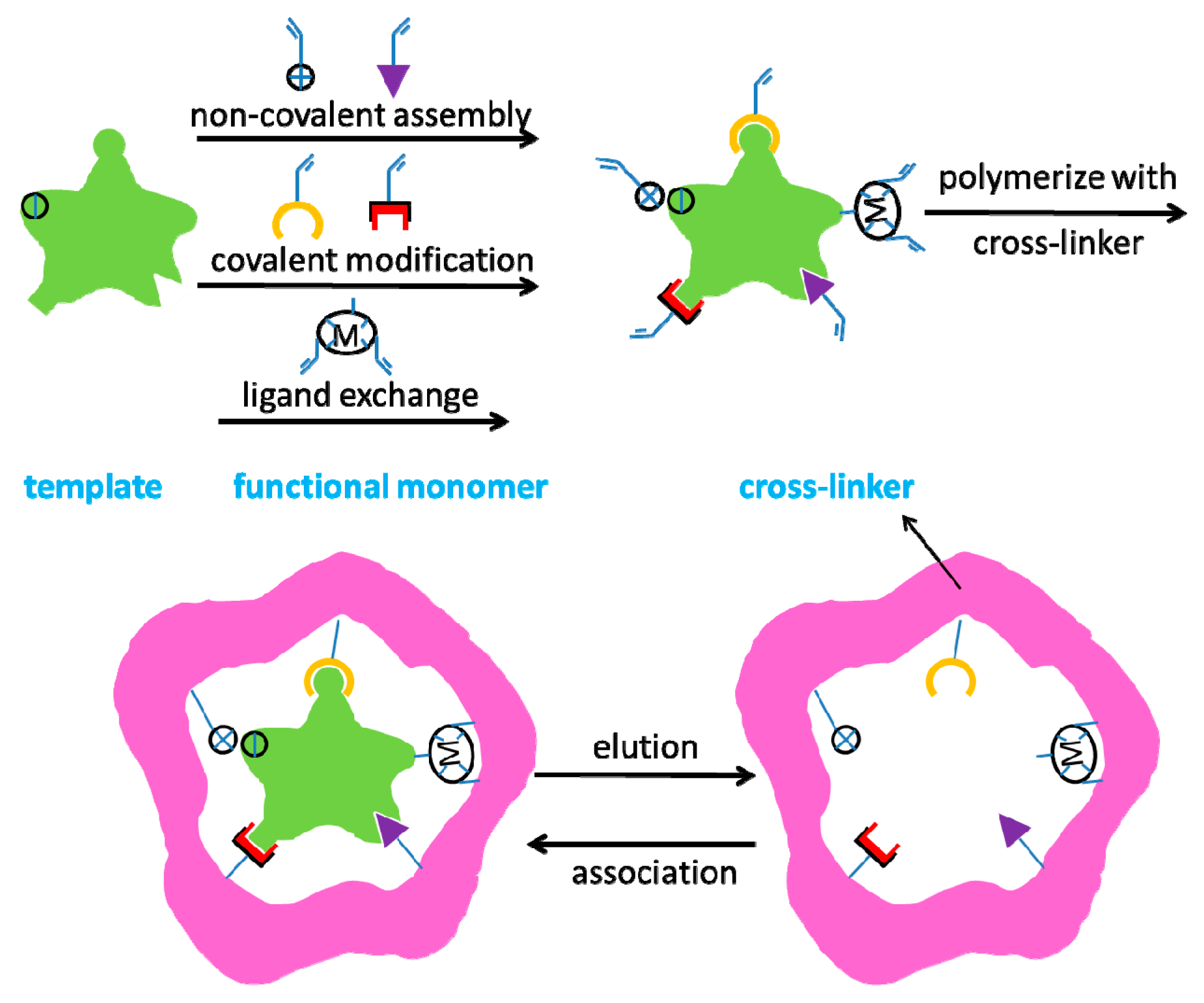
1.3.1. Molecular Imprinting Method
1.3.2. Quasi-Molecular Imprinting Method
2. Molecularly Imprinted Gas Sensors
2.1. Molecularly Imprinted Organic Gas Sensors
2.2. Molecularly Imprinted Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Gas Sensors
3. Quasi-Molecularly Imprinted Gas Sensors
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shah, R.R.; Abbott, N.L. Principles for measurement of chemical exposure based on recognition–driven anchoring transitions in liquid crystals. Science 2001, 293, 1296–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talin, A.A.; Centrone, A.; Ford, A.C.; Foster, M.E.; Stavila, V.; Haney, P.; Léonard, F.; Allendor, M.D. Tunable Electrical Conductivity in Metal-Organic Framework Thin-Film Devices. Science 2014, 343, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potyrailo, R.A.; Ghiradella, H.; Vertiatchikh, A.; Dovidenko, K.; Cournoyer, J.; Olson, R.E. Morpho butterfly wing scales demonstrate highly selective vapour response. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, G.; Zečević, J.; Friedrich, H.; Jong, K.P.; Jongh, P.E. Towards stable catalysts by controlling collective properties of supported metal nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghaddam, A.; Olszewska, W.; Wang, B.; Tregoning, J.S.; Helson, R.; Sattentau1, Q.J.; Openshaw, P.J.M. A potential molecular mechanism for hypersensitivity caused by formalin-inactivated vaccines. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 905–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.Q.; Saijo, K.; Todoroki, T.; Ohno, T. Induction of human autologous cytotoxic T lymphocytes on formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tumour sections. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bricker, C.E.; Johnson, H.R. Spectrophotometric method for determining formaldehyde. Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 1945, 17, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, R.K.; Hoffmann, C.E.; Rueppel, M.L.; Worley, J.W. Sampling of formaldehyde in air with coated solid sorbent and determination by high performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1980, 52, 1110–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herschkovitz, Y.; Eshkenazi, I.; Campbell, C.E.; Rishpon, J. An electrochemical biosensor for formaldehyde. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2000, 491, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.W.; Ji, X.L.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, X.R. On-line monitoring of formaldehyde in air by cataluminescence-based gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 119, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.L.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Liu, Q.J. Improvement of response to formaldehyde at Ag–LaFeO3 based gas sensors through incorporation of SWCNTs. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 195, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.X.; Qiu, Z.M.; Ding, S.J. Bio-Analytical Chemistry; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 272–290. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Mosbach, K. Molecular Imprinting: Synthetic Materials as Substitutes for Biological Antibodies and Receptors. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Lu, W.H.; Wu, X.Q.; Li, J.H. Molecular imprinting: Perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupt, K.; Mosbach, K. Molecularly imprinted polymers and their use in biomimetic sensors. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Ma, Y.; Pan, J.; Meng, Z.; Pan, G.; Sellergren, B. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers with Stimuli-Responsive Affinity: Progress and Perspectives. Polymers 2015, 7, 1689–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
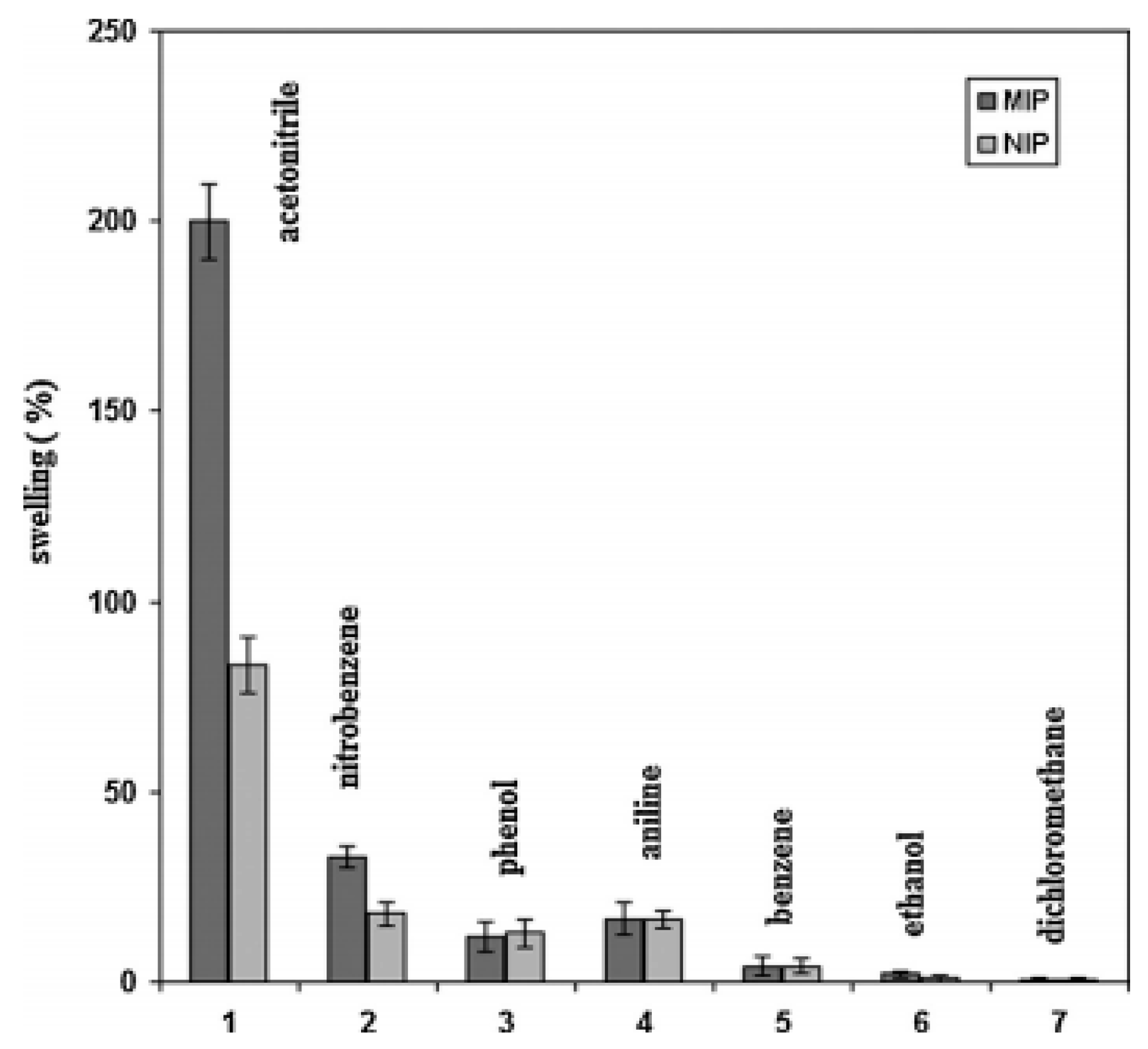
- Liu, R.; Guan, G.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z. Core-shell nanostructured molecular imprinting fluorescent chemosensor for selective detection of atrazine herbicide. Analyst 2011, 136, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Li, B.; Liew, K.Y.; Li, C. Electrochemical fabrication of molecularly imprinted porous silicate film electrode for fast and selective response of methyl parathion. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, C.N.; Campbell, S.E.; Gibson, U.J. Phenylalanine detection using matrix assisted pulsed laser evaporation of molecularly imprinted amphiphilic block copolymer films. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamayo, F.G.; Casillas, J.L.; Martin-Esteban, A. Evaluation of new selective molecularly imprinted polymers prepared by precipitation polymerisation for the extraction of phenylurea herbicides. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1069, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, C.C.; Chang, P.H.; Lin, C.C.; Hong, C.L. A disposable microfluidic biochip with on-chip molecularly imprinted biosensors for optical detection of anesthetic propofol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2058–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, C.J.; Shimizu, K.D. Colorimetric and fluorometric molecularly imprinted polymer sensors and binding assays. Polym. Int. 2007, 56, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, I.; Chiono, V.; Vozzi, G.; Ciardelli, G.; Silvestri, D.; Giusti, P. Molecularly imprinted submicronspheres for applications in a novel model biosensor-film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 150, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
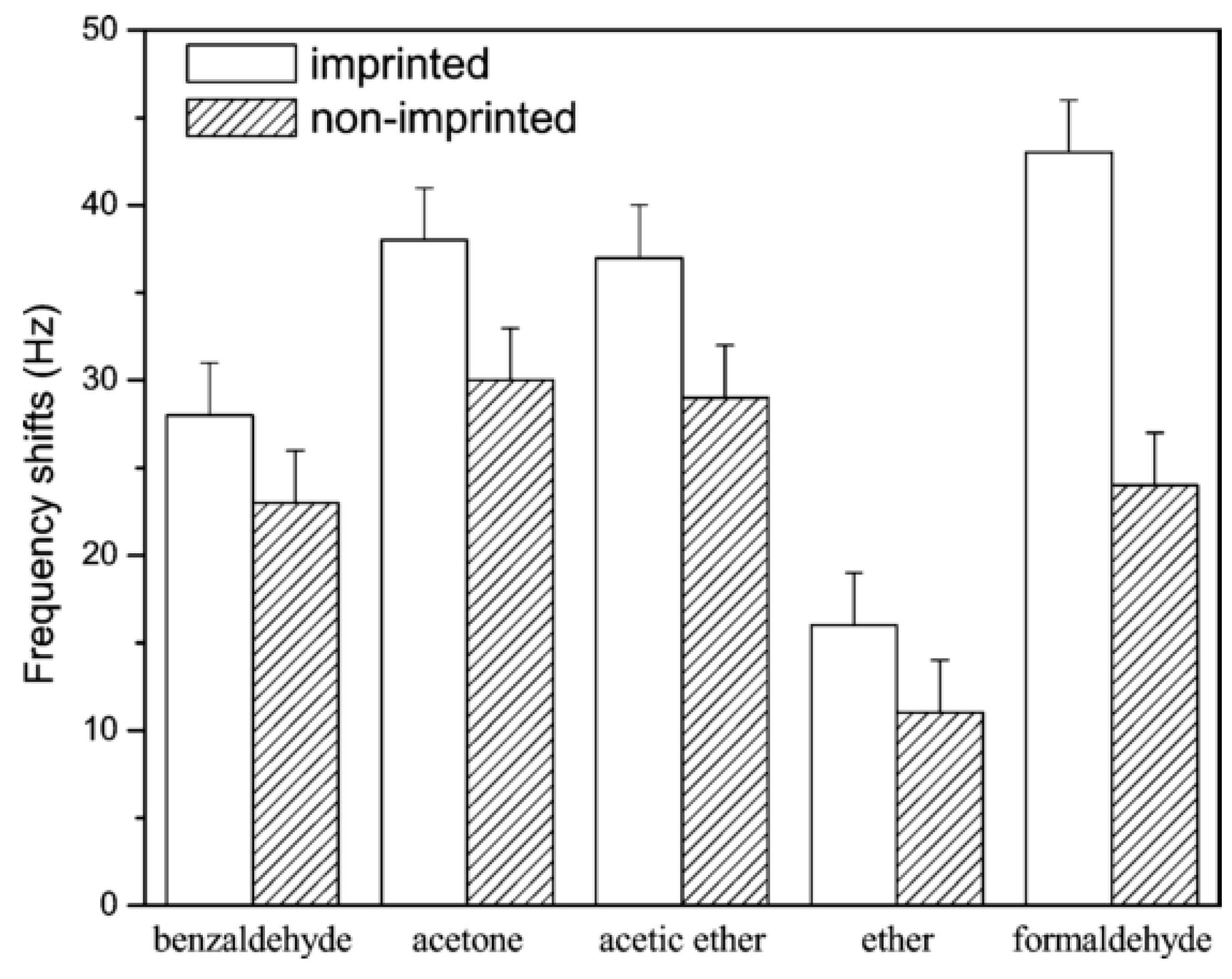
- Feng, L.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhou, X.D.; Hu, J.M. The fabrication and characterization of a formaldehyde odor sensor using molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 284, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuguchi, M.; Uno, T. Molecular imprinting strategy for solvent molecules and its application for QCM-based VOC vapor sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 113, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawari, H.F.; Samsudin, N.M.; Ahmad, M.N.; Shakaff, A.Y.M.; Ghani, S.A.; Wahab, Y. Recognition of Limonene Volatile Using Interdigitated Electrode Molecular Imprinted Polymer Sensor. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Intelligent Systems Modelling and Simulation, Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 8–10 February 2012; pp. 723–726. [Google Scholar]
- Hawari, H.F.; Samsudin, N.M.; Md Shakaff, A.Y.; Ghani, S.A.; Ahmad, M.N.; Wahab, Y.; Hashim, U. Development of Interdigitated Electrode Molecular Imprinted Polymer Sensor for Monitoring Alpha Pinene Emissions from Mango Fruit. Procedia Eng. 2013, 53, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
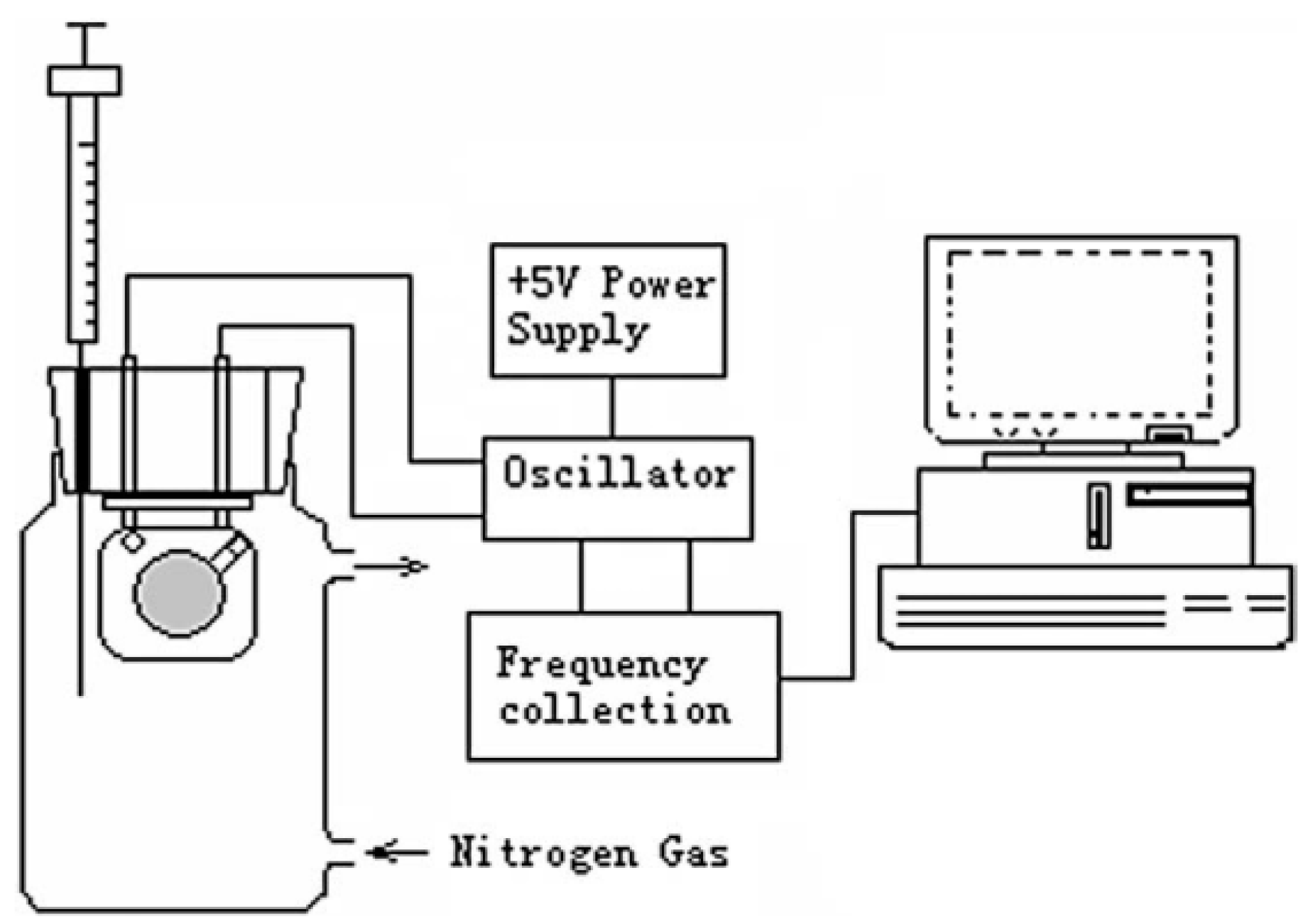
- Ji, H.-S.; McNiven, S.; Ikebukuro, K.; Karube, I. Selective piezoelectric odor sensors using molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 390, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunte, G.; Hurttlen, J.; Pontius, H.; Hartlieb, K.; Krause, H. Gas phase detection of explosives such as 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene by molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 591, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
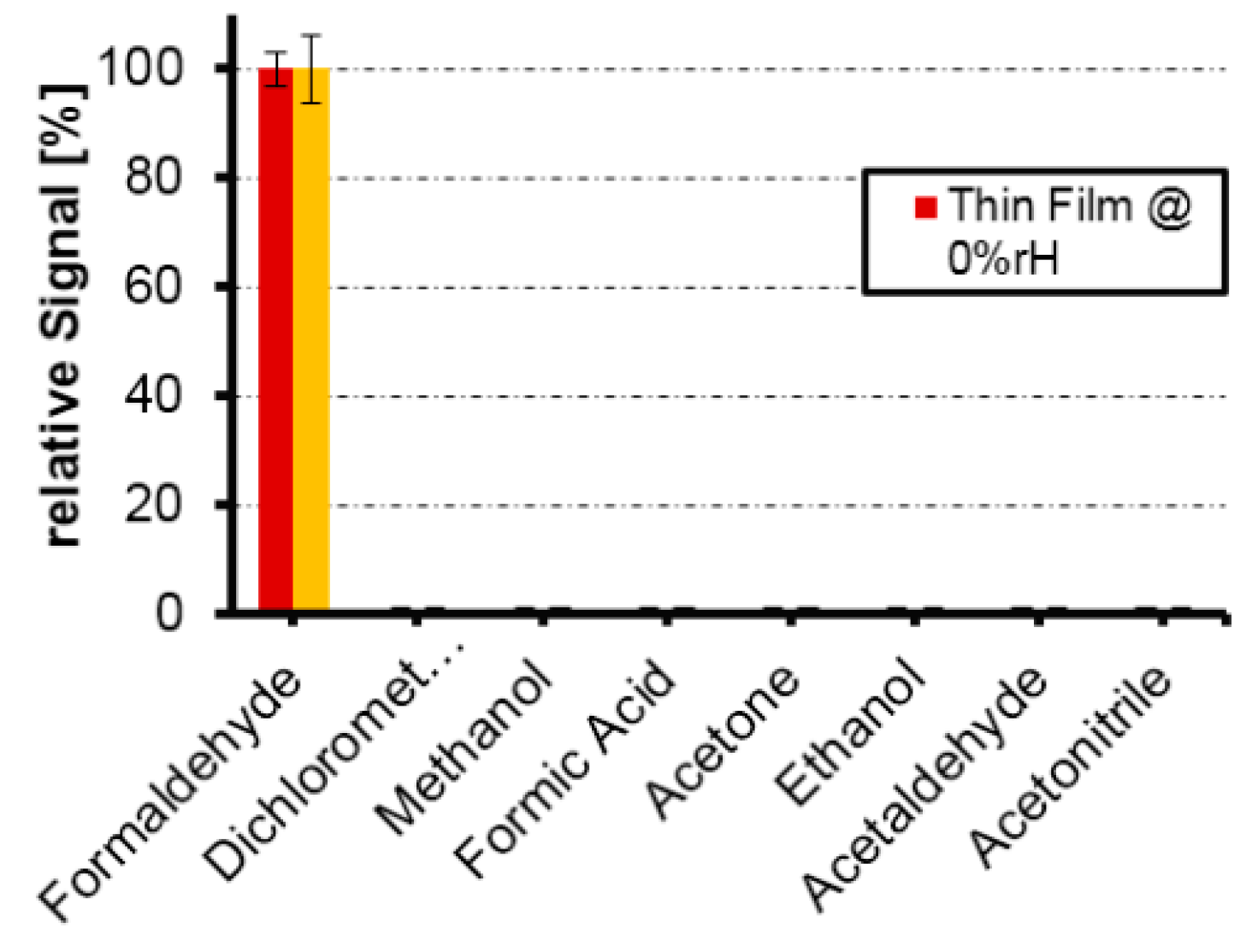
- Hussain, M.; Kotova, K.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for Formaldehyde Sensing with QCM. Sensors 2016, 16, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, T.; Hamedsoltani, L. Graphene/graphite/molecularly imprinted polymer nanocomposite as the highly selective gas sensor for nitrobenzene vapor recognition. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1514–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Shitang, H.; Shunzhou, L.; Minghua, L.; Yong, P. Enhanced sensitivity of SAW gas sensor coated molecularly imprinted polymer incorporating high frequency stability oscillator. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 125, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.R.; Linman, M.J.; Timmers, M.M.; Dean, S.L.; Burkett, C.M.; Lloyd, J.A.; Keelor, J.D.; Baughman, B.M.; Edmiston, P.L. Selective detection of gas-phase TNT by integrated optical waveguide spectrometry using molecularly imprinted sol-gel sensing films. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 593, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Vila, Á.; Debliquy, M.; Lahem, D.; Zhang, C.; Mégret, P.; Caucheteur, C. Molecularly imprinted electropolymerization on a metal-coated optical fiber for gas sensing applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 244, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakoby, B.; Ismail, G.; Byfield, M.; Vellekoop, M. A novel molecularly imprinted thin film applied to a Love wave gas sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1999, 76, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, M.; Amalya, Z.; Iva Turyan, A.; Mandler, D. Parathion Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Sol–Gel Films. Anal. Chem. 2005, 76, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, S.K.; Liu, C.; Hayashi, K. Molecular imprinted polyacrylic acids based QCM sensor array for recognition of organic acids in body odor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.K.; Hayashi, K. A quick responding quartz crystal microbalance sensor array based on molecular imprinted polyacrylic acids coating for selective identification of aldehydes in body odor. Talanta 2015, 134, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imahashi, M.; Chiyomaru, Y.; Hayashi, K. Ultrathin reconfigurable molecular filter for gas-selective sensing. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Sensors, Baltimore, MD, USA, 3–6 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
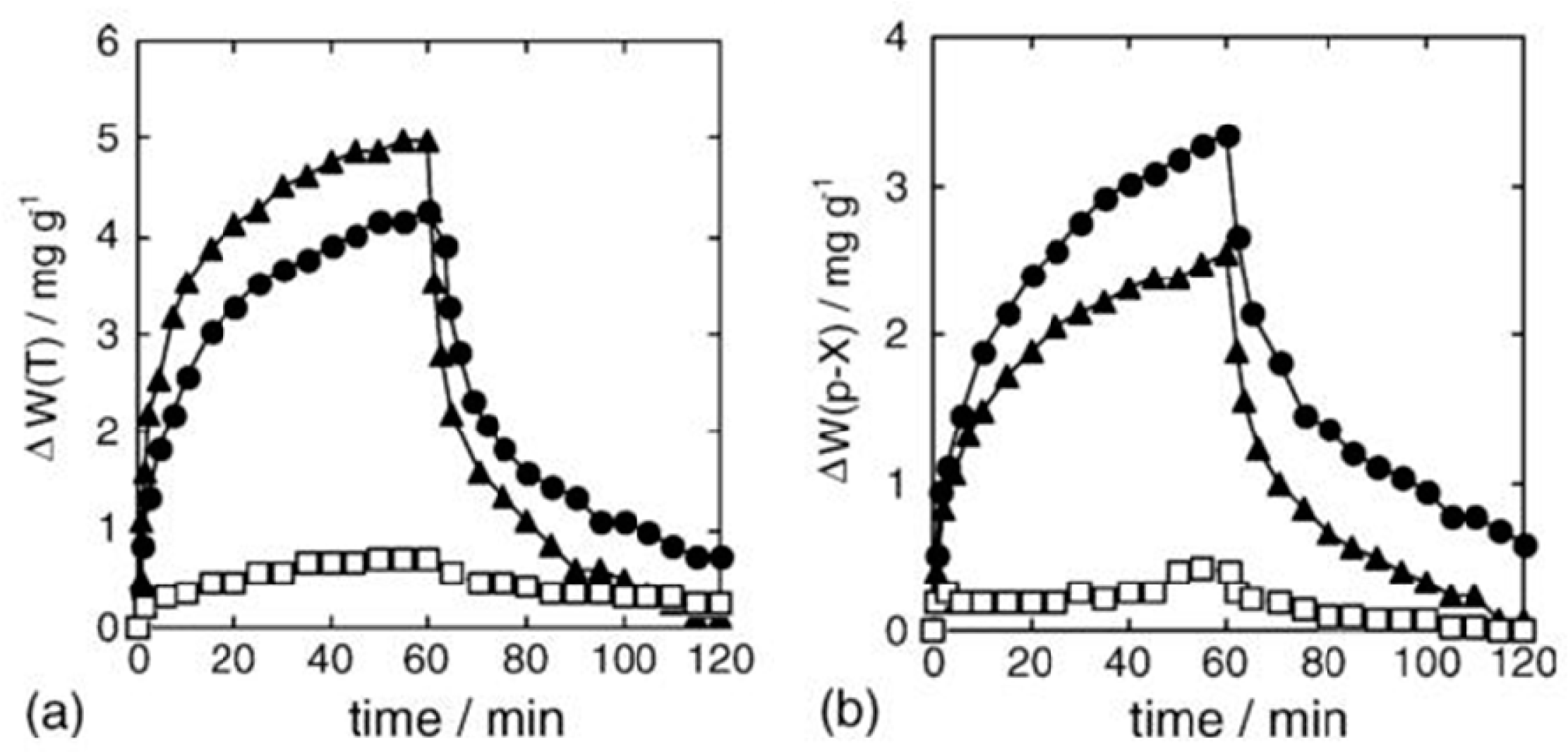
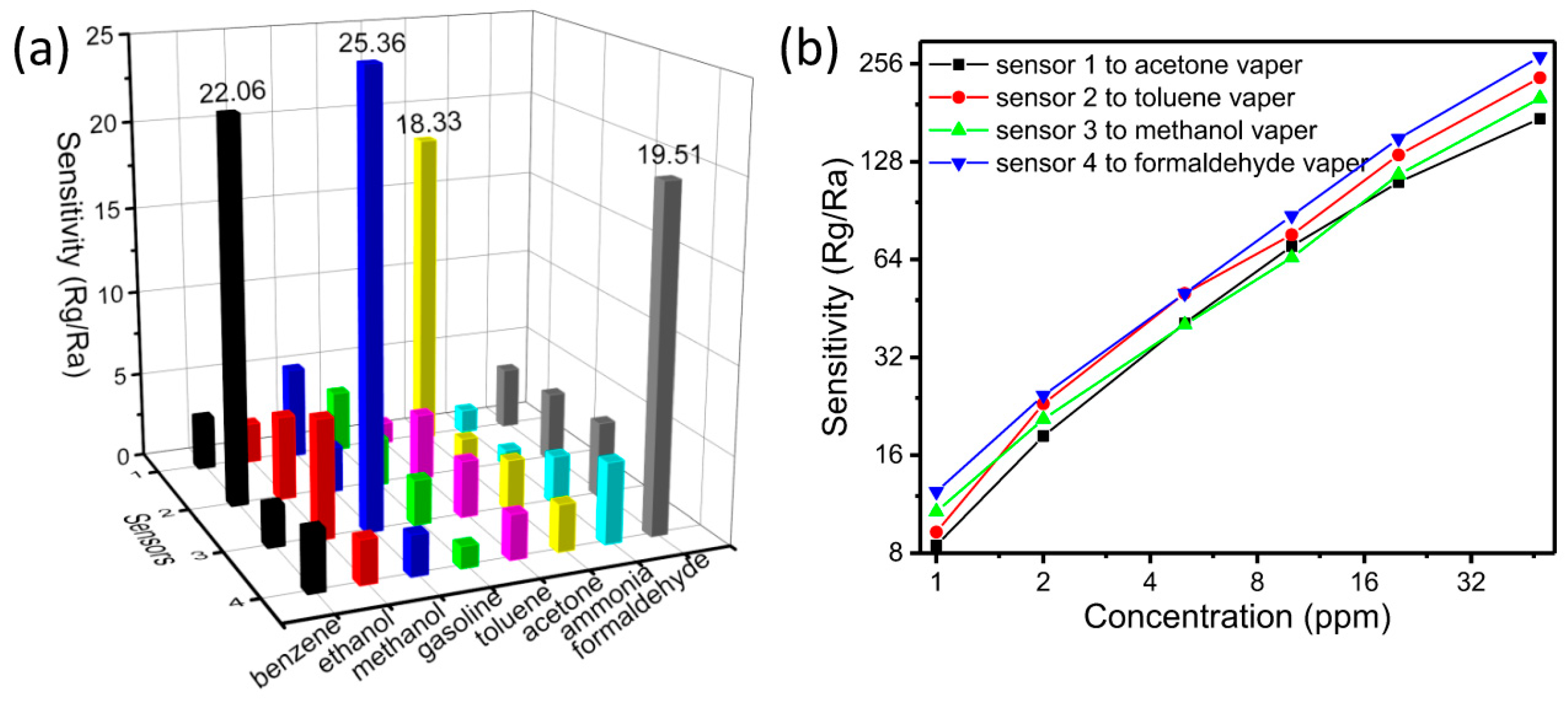
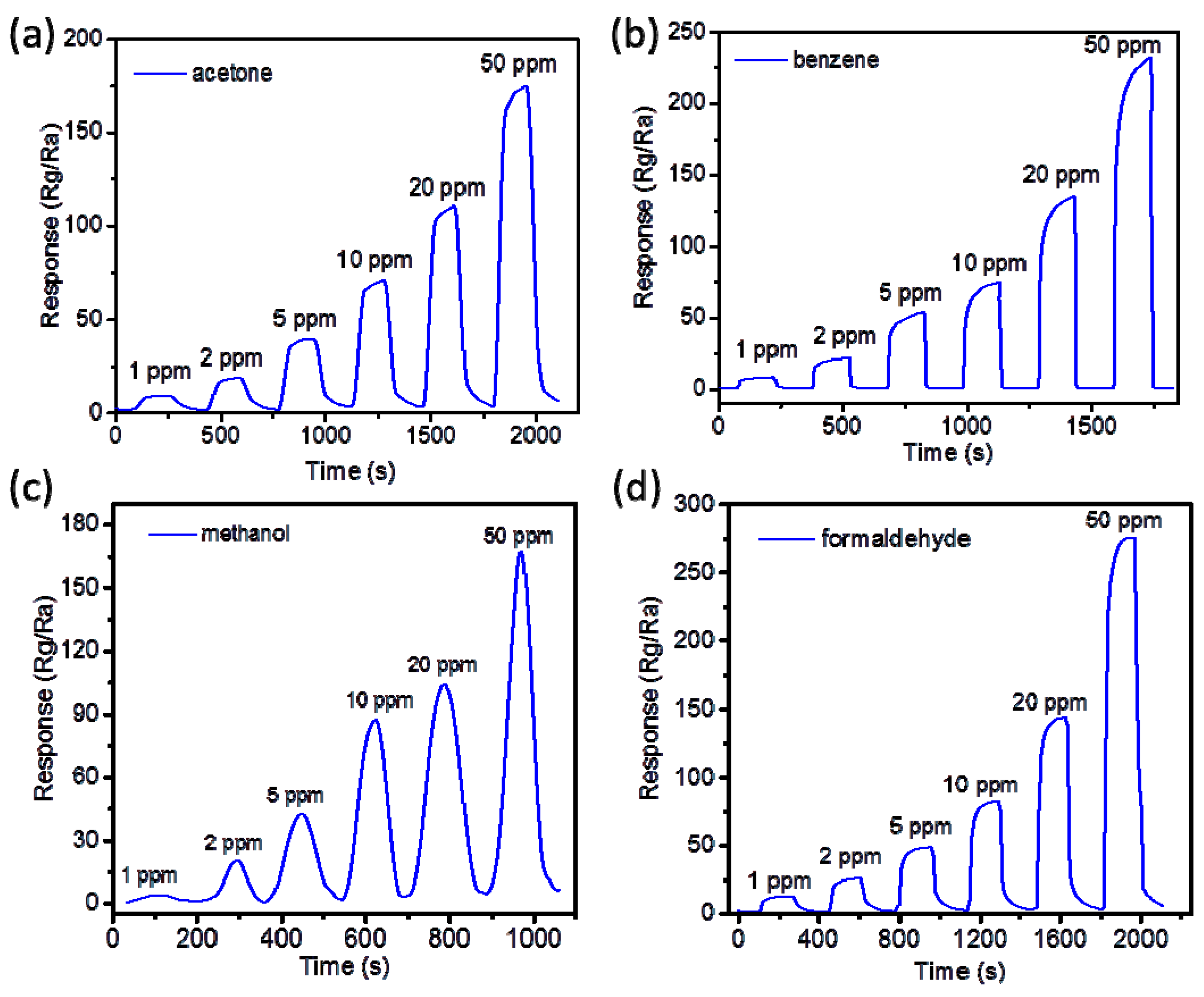
- Zhang, Y.M.; Liu, Q.J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, Z.Q. A highly sensitive and selective formaldehyde gas sensor using a molecular imprinting technique based on Ag–LaFeO3. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 10067–10072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Liu, Q.J. A new and high response gas sensor for methanol using molecularly imprinted technique. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversa, E.; Matsushuma, S.; Okada, G.; Sadaoka, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Watanabe, K. NO2 sensitive LaFeO3 thin films prepared by r.f. sputtering. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 1995, 24, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetchakun, K.; Samerjai, T.; Tamaekong, N.; Liewhiran, C.; Siriwong, C.; Kruefu, V.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Tuantranont, A.; Phanichphant, S. Semiconducting metal oxides as sensors for environmentally hazardous gases. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natile, M.M.; Ponzoni, A.; Concina, I.; Glisenti, A. Chemical Tuning versus Microstructure Features in Solid-State Gas Sensors: LaFe1-xGaxO3, a Case Study. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toan, N.N.; Saukko, S.; Lantto, V. Gas sensing with semiconducting perovskite oxide LaFeO3. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2003, 327, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Qin, H.W.; Sun, L.H.; Hu, J.F. CO2 sensing properties and mechanism of nanocrystalline LaFeO3 sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiglusz, R.J.; Kordek, K.; Malecka, M.; Ciupa, A.; Ptak, M.; Pazik, R.; Pohl, P.; Kaczorowski, D. A new approach in the synthesis of La1−xGdxFeO3 perovskite nanoparticles-structural and magnetic characterization. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 20067–20074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murade, P.A.; Sangawar, V.S.; Chaudhari, G.N.; Kapse, V.D.; Bajpeyee, A.U. Acetone gas-sensing performance of Sr-doped nanostructured LaFeO3 semiconductor prepared by citrate sol–gel route. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2011, 11, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroftei, C.; Popa, P.D.; Iacomi, F. Synthesis of nanocrystalline La-Pb-Fe-O perovskite and methanol-sensing characteristics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 161, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Lin, Y.T.; Chen, J.L.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Liu, Q.J. A high sensitivity gas sensor for formaldehyde based on silver doped lanthanum ferrite. Sen. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
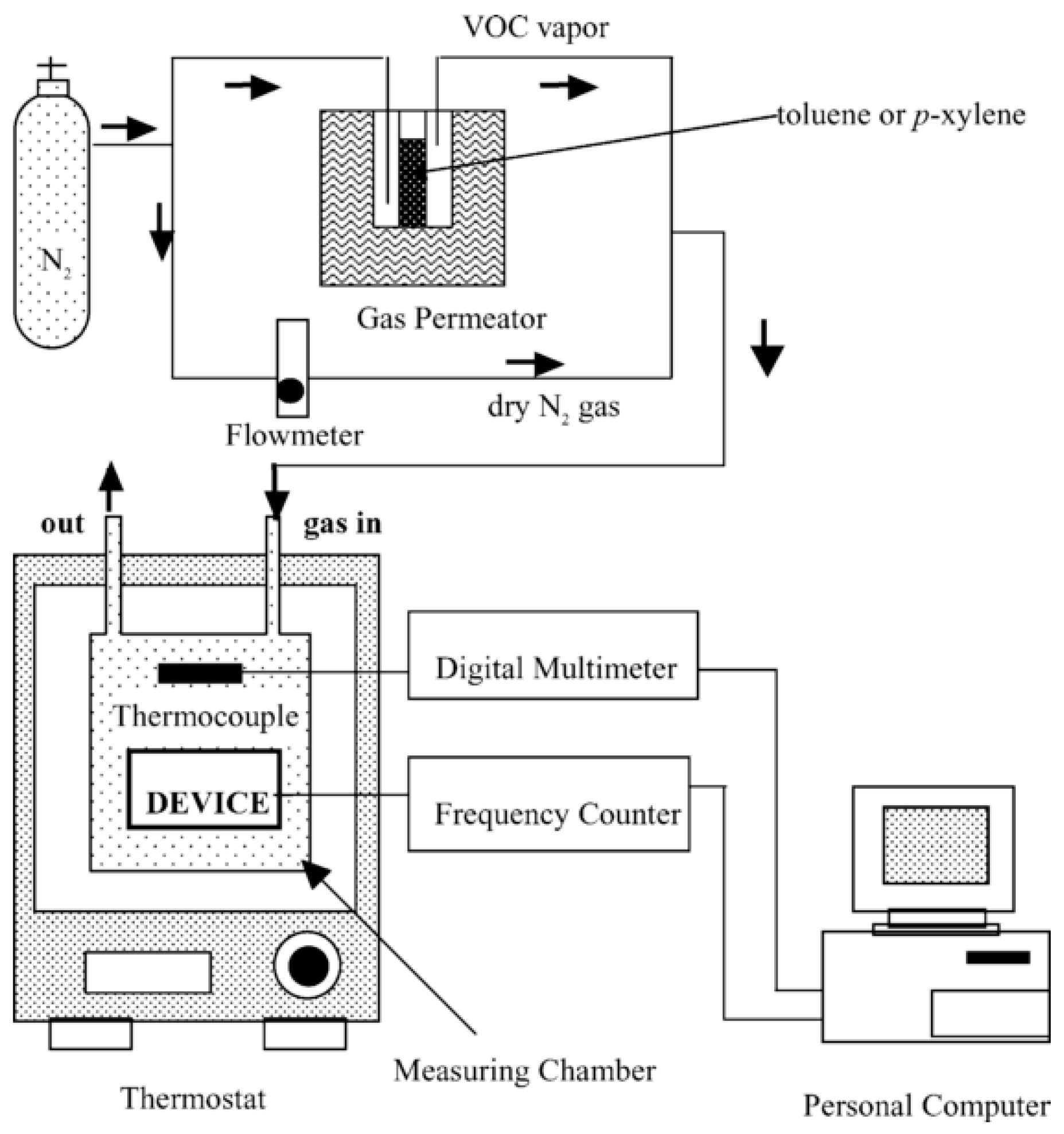
- Tang, X.; Raskin, J.P.; Lahem, D.; Krumpmann, A.; Decroly, A.; Debliquy, M. A Formaldehyde Sensor Based on Molecularly-Imprinted Polymer on a TiO2 Nanotube Array. Sensors 2017, 17, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
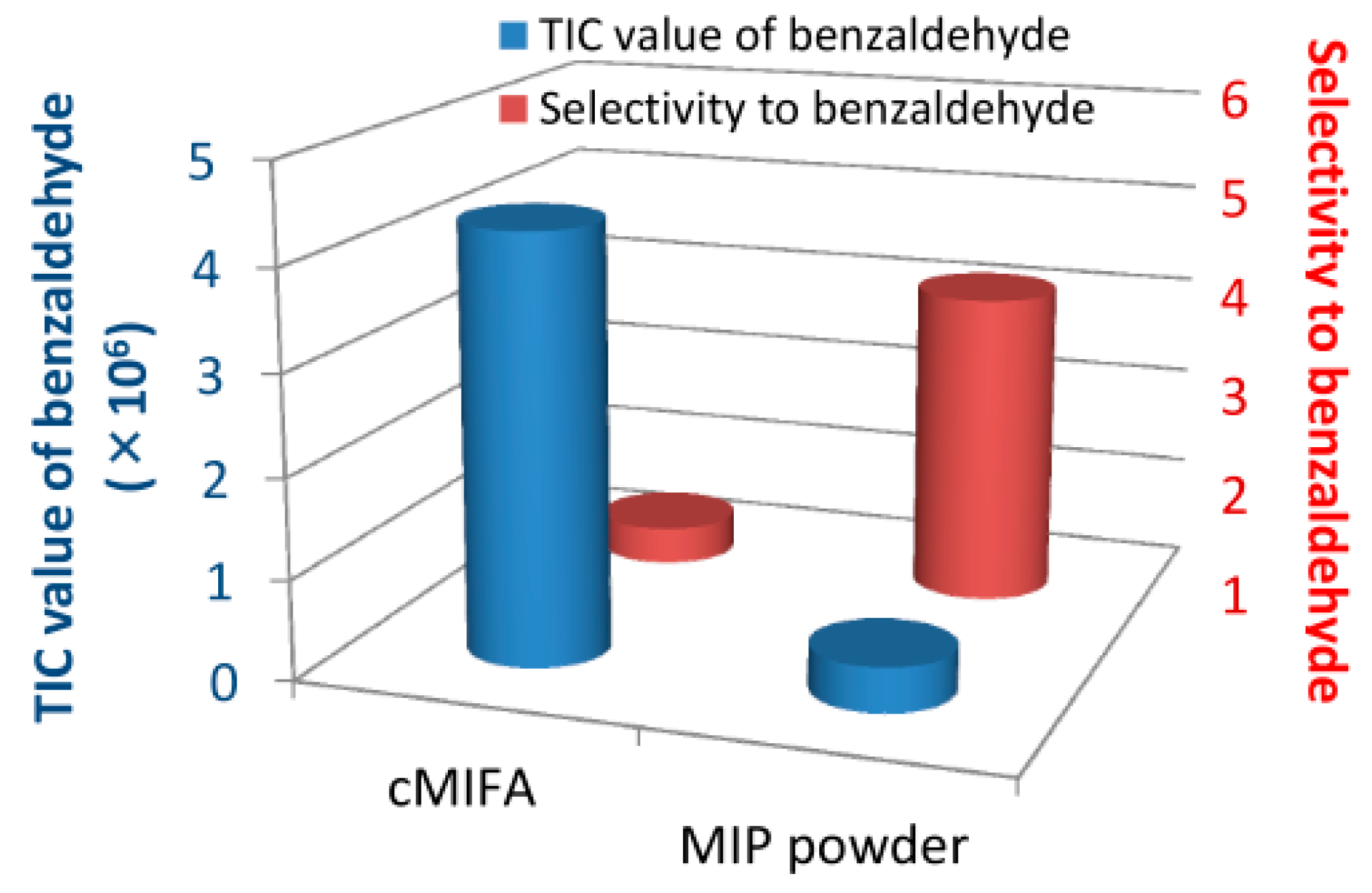
- Li, C.J.; Lv, M.; Zuo, J.L.; Huang, X.T. SnO2 Highly Sensitive CO Gas Sensor Based on Quasi-Molecular-Imprinting Mechanism Design. Sensors 2015, 15, 3789–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.H.; Yu, Q.X.; Ruan, X.F.; Huang, X.T. Design of SnO2-based highly sensitive ethanol gas sensor based on quasi molecular-cluster imprinting mechanism. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 212, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.H.; Ruan, X.F.; Yu, Q.X.; Yu, Z.T.; Huang, X.T. Fabrication of a SnO2-based acetone gas sensor enhanced by molecular imprinting. Sensors 2015, 15, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q. Gas Sensors Based on Molecular Imprinting Technology. Sensors 2017, 17, 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17071567
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Liu Q. Gas Sensors Based on Molecular Imprinting Technology. Sensors. 2017; 17(7):1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17071567
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yumin, Jin Zhang, and Qingju Liu. 2017. "Gas Sensors Based on Molecular Imprinting Technology" Sensors 17, no. 7: 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17071567
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhang, J., & Liu, Q. (2017). Gas Sensors Based on Molecular Imprinting Technology. Sensors, 17(7), 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17071567



