Development towards Compact Nitrocellulose-Based Interferometric Biochips for Dry Eye MMP9 Label-Free In-Situ Diagnosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
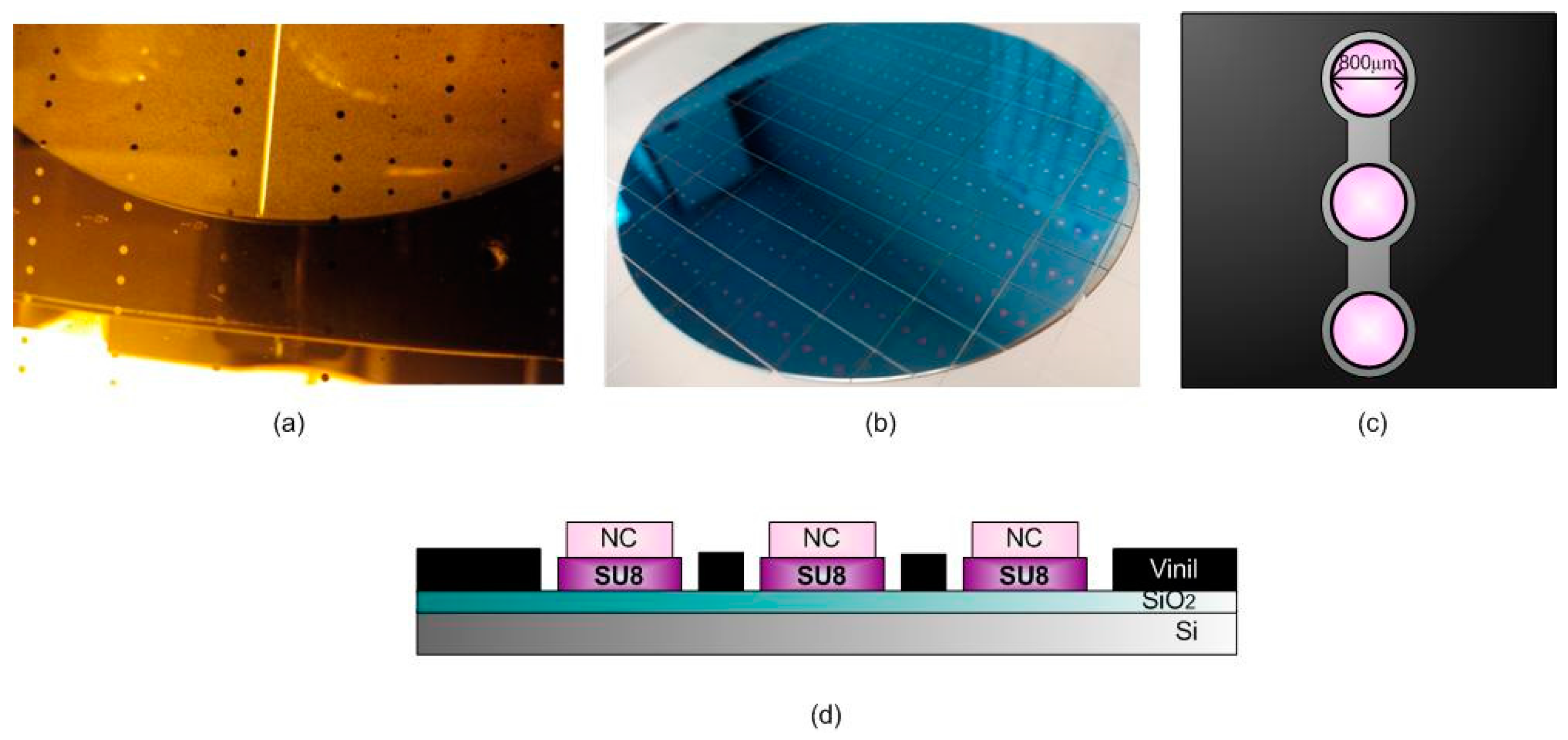
2.1. BICELL Fabrication and Materials
2.2. Optical Characterization of the Biosensor
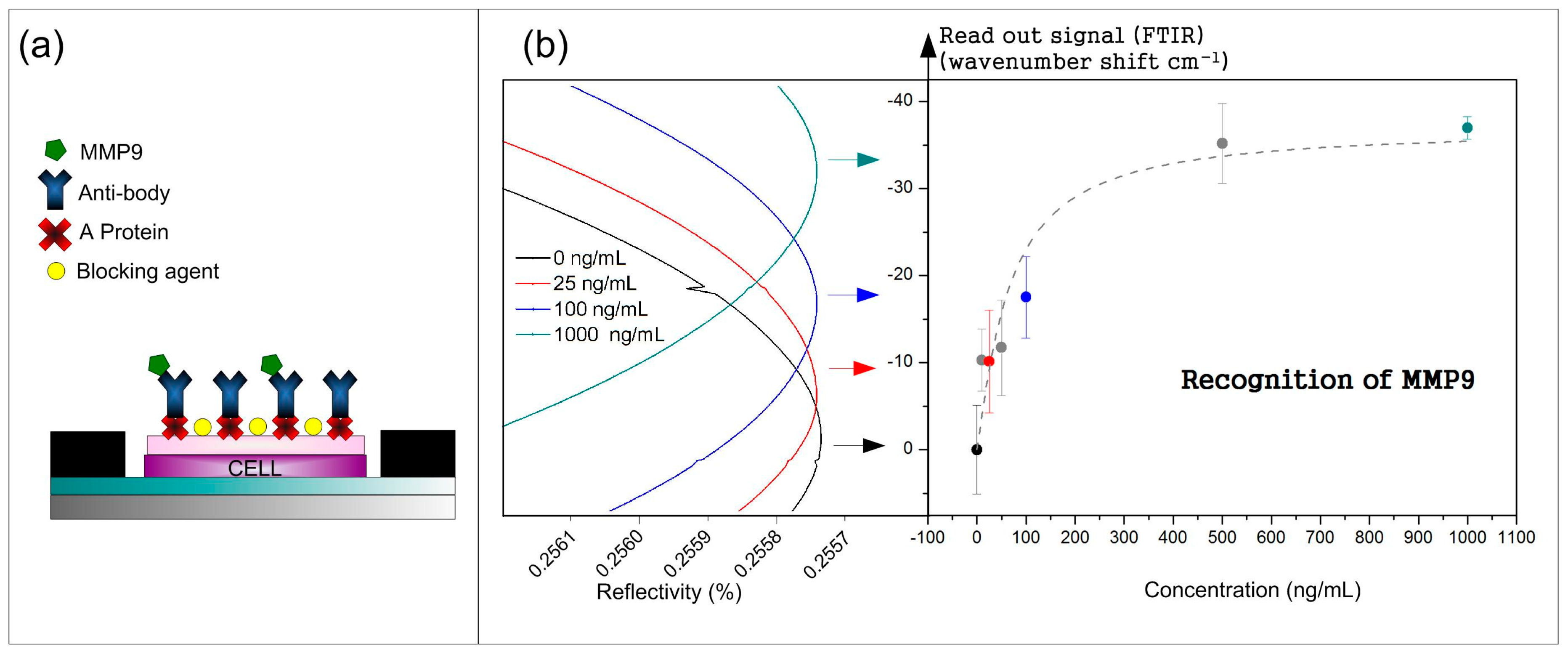
2.3. Biofunctionalization of the BICELLs
3. Results
3.1. Recognition Curve Response to Detect MMP9
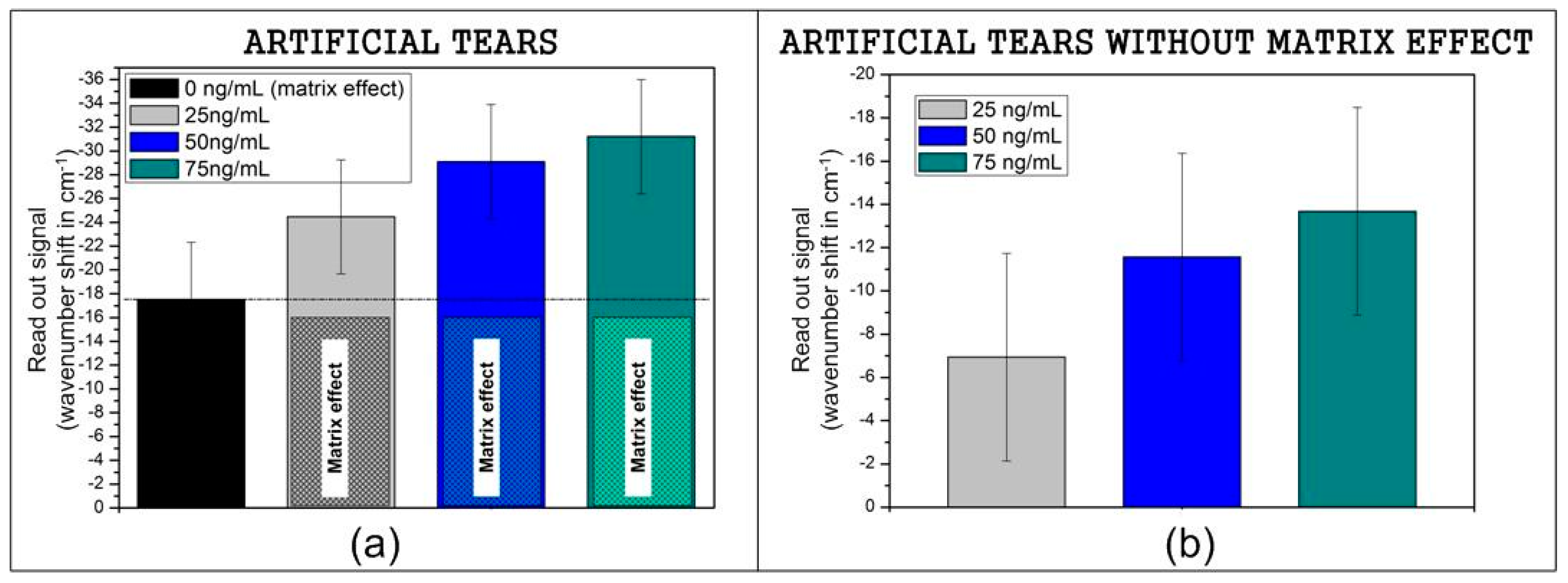
3.2. Recognition of Model Samples
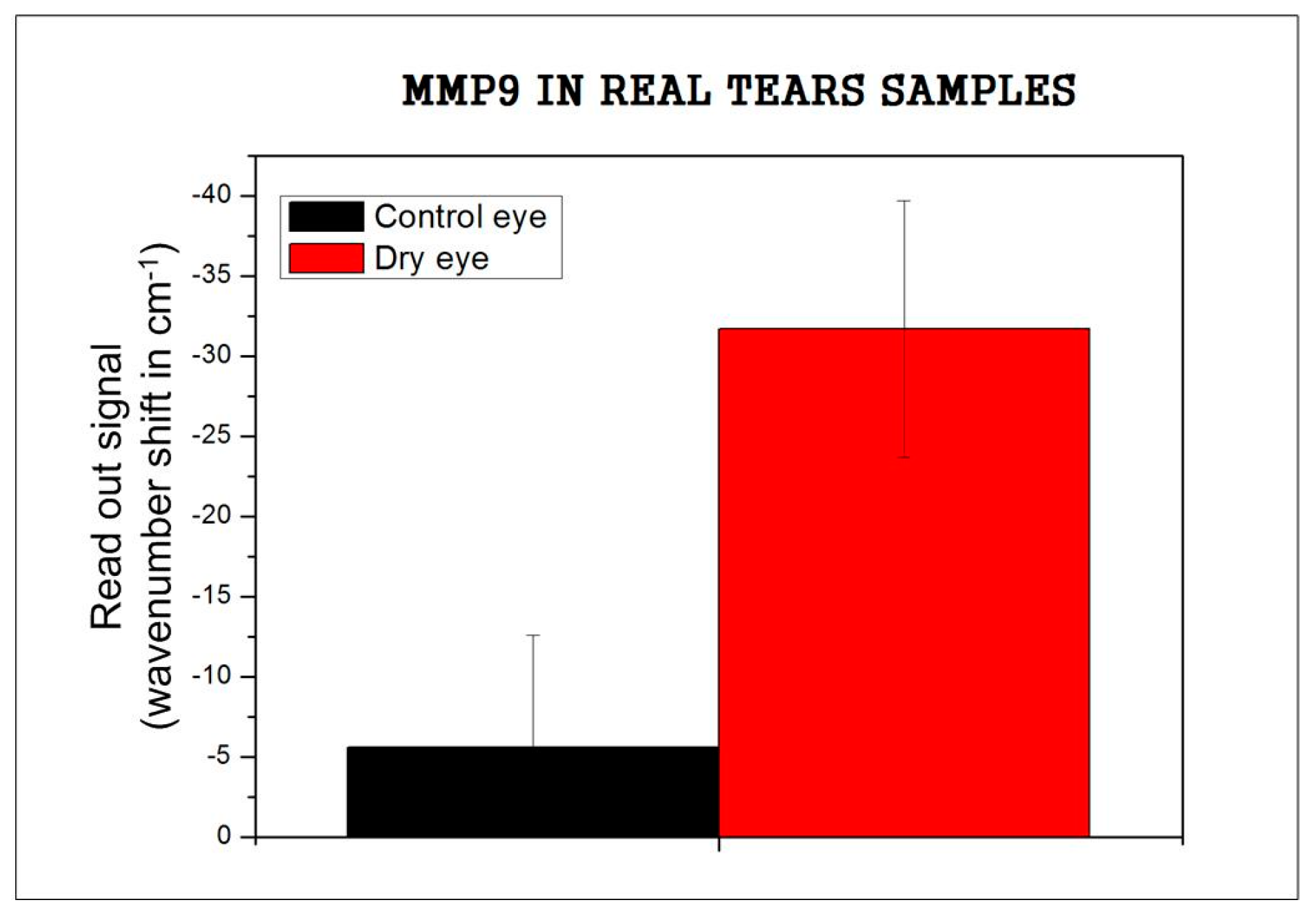
3.3. Recognition of Real Tears
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soria, J.; Durán, J.; Etxebarria, J.; Merayo, J.; González, N.; Reigada, R.; García, I.; Acera, A.; Suárez, T. Tear proteome and protein network analyses reveal a novel pentamarker panel for tear film characterization in dry eye and meibomian gland dysfunction. J. Proteom. 2013, 78, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanza, N.L.; Valenzuela, F.; Perez, V.L.; Galor, A. The matrix metalloproteinase 9 point-of-care test in dry eye. Ocul. Surf. 2016, 14, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acera, A.; Rocha, G.; Vecino, E.; Lema, I.; Duran, J.A. Inflammatory markers in the tears of patients with ocular surface disease. Ophthalmic Res. 2008, 40, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pflugfelder, S.C. Antiinflammatory therapy for dry eye. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 137, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Li, D.; Doshi, A.; Farley, W.; Corrales, R.M.; Pflugfelder, S.C. Experimental Dry Eye Stimulates Production of Inflammatory Cytokines and MMP-9 and Activates MAPK Signaling Pathways on the Ocular Surface. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 4293–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holgado, M.; Barrios, C.A.; Ortega, F.J.; Sanza, F.J.; Casquel, R.; Laguna, M.F.; Bañuls, M.J.; López-Romero, D.; Puchades, R.; Maquieira, A. Label-free biosensing by means of periodic lattices of high aspect ratio SU-8 nano-pillars. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2553–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laguna, M.F.; Sanza, F.J.; Soria, J.; Jara, M.; Lavín, Á.; Casquel, R.; López, A.; Suarez, T.; Holgado, M. Label-free biosensing by means of BICELLs for dry eye. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MicroChem SU-8 2000 Permanent Epoxy Negative Photoresist. Available online: http://www.microchem.com/pdf/SU-82000DataSheet2000_5thru2015Ver4.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2016).
- Laguna, M.; Holgado, M.; Hernandez, A.L.; Santamaría, B.; Lavín, A.; Soria, J.; Suarez, T.; Bardina, C.; Jara, M.; Sanza, F.J.; et al. Antigen-antibody affinity for dry eye biomarkers by label free biosensing. Comparison with the ELISA technique. Sensors 2015, 15, 19819–19829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Romero, D.; Barrios, C.A.; Holgado, M.; Laguna, M.F.; Casquel, R. High aspect-ratio SU-8 resist nano-pillar lattice by e-beam direct writing and its application for liquid trapping. Microelectron. Eng. 2010, 87, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.J.; Bañuls, M.; Sanza, F.J.; Laguna, M.F.; Holgado, M.; Casquel, R.; Barrios, C.A.; López-Romero, D.; Maquieira, Á.; Puchades, R. Development of a versatile biotinylated material based on SU-8. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2750–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holgado, M.; Casquel, R.; Sánchez, B.; Molpeceres, C.; Morales, M.; Ocaña, J.L. Optical characterization of extremely small volumes of liquid in sub-micro-holes by simultaneous reflectivity, ellipsometry and spectrometry. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 13318–13329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanza, F.; Holgado, M.; Ortega, F.; Casquel, R.; López-Romero, D.; Bañuls, M.; Laguna, M.; Barrios, C.; Puchades, R.; Maquieira, A. Bio-photonic sensing cells over transparent substrates for anti-gestrinone antibodies biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4842–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, A.L.; Casquel, R.; Holgado, M.; Cornago, I.; Sanza, F.; Santamaría, B.; Maigler, M.; Fernández, F.; Lavín, A.; Laguna, M. Arrays of Resonant Nanopillars for Biochemical Sensing. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 2370–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phadatare, S.P.; Momin, M.; Nighojkar, P.; Askarkar, S.; Singh, K.K. A Comprehensive Review on Dry Eye Disease: Diagnosis, Medical Management, Recent Developments, and Future Challenges. Adv. Pharm. 2015, 2015, 704946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelson, M.B.; Lafond, A. 3500 Years of Artificial Tears. Available online: https://www.reviewofophthalmology.com/article/3500-years-of-artificial-tears (accessed on 25 January 2017).
- Ursa BioScience-Contriever Tears with MMP9. Available online: http://www.ursabioscience.com/online-store/consumables/contrived-tears-with-mmp-9/contrived-tears-with-mmp-9-5-ml-detail (accessed on 3 September 2016).
- Kalló, G.; Emri, M.; Varga, Z.; Ujhelyi, B.; Tözsér, J.; Csutak, A.; Csösz, É. Changes in the Chemical Barrier Composition of Tears in Alzheimer’s Disease Reveal Potential Tear Diagnostic Biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santamaría, B.; Laguna, M.F.; López-Romero, D.; Hernandez, A.L.; Sanza, F.J.; Lavín, Á.; Casquel, R.; Maigler, M.V.; Espinosa, R.L.; Holgado, M. Development towards Compact Nitrocellulose-Based Interferometric Biochips for Dry Eye MMP9 Label-Free In-Situ Diagnosis. Sensors 2017, 17, 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051158
Santamaría B, Laguna MF, López-Romero D, Hernandez AL, Sanza FJ, Lavín Á, Casquel R, Maigler MV, Espinosa RL, Holgado M. Development towards Compact Nitrocellulose-Based Interferometric Biochips for Dry Eye MMP9 Label-Free In-Situ Diagnosis. Sensors. 2017; 17(5):1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051158
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantamaría, Beatriz, María F. Laguna, David López-Romero, Ana L. Hernandez, Francisco J. Sanza, Álvaro Lavín, Rafael Casquel, María V. Maigler, Rocío L. Espinosa, and Miguel Holgado. 2017. "Development towards Compact Nitrocellulose-Based Interferometric Biochips for Dry Eye MMP9 Label-Free In-Situ Diagnosis" Sensors 17, no. 5: 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051158
APA StyleSantamaría, B., Laguna, M. F., López-Romero, D., Hernandez, A. L., Sanza, F. J., Lavín, Á., Casquel, R., Maigler, M. V., Espinosa, R. L., & Holgado, M. (2017). Development towards Compact Nitrocellulose-Based Interferometric Biochips for Dry Eye MMP9 Label-Free In-Situ Diagnosis. Sensors, 17(5), 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051158







