Real-Time Gait Event Detection Based on Kinematic Data Coupled to a Biomechanical Model †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Data Collection and Processing
2.2. Reference Events
2.3. RTGSD Structure
| Algorithm 1: Real-time detection layer: Example of detecting event as a maximum |
 |
| Algorithm 2: Update layer: Example event corresponding to a maximum |
 |
2.4. RTGSD-Min
2.5. RTGSD-B6
2.6. RTGSD-G6
3. Results and Discussion
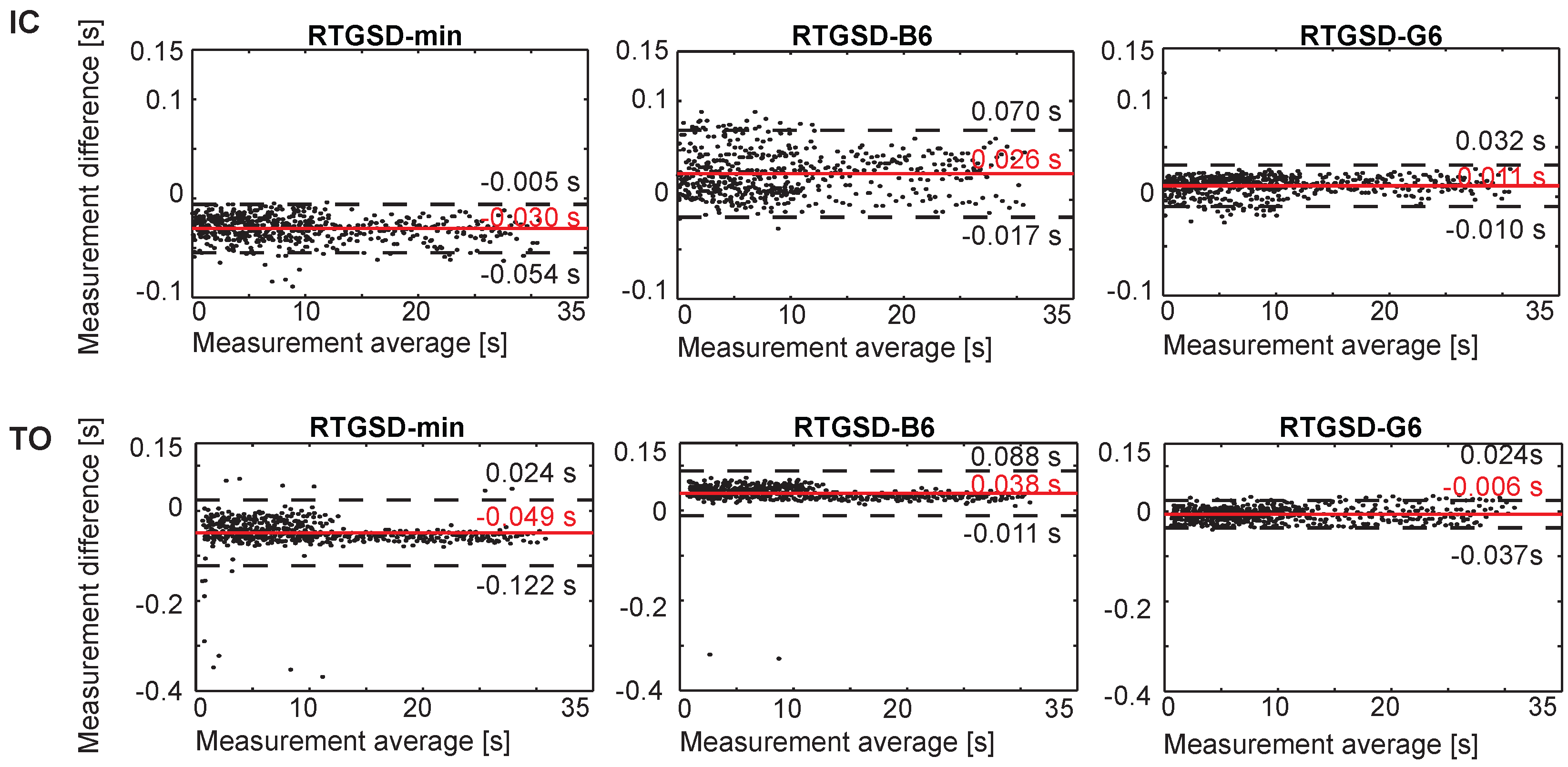
3.1. Results
3.2. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFO | Ankle-Foot Orthoses |
| FF | Foot Flat |
| FSR | Force Sensitive Resistor |
| GRF | Ground Reaction Forces |
| HO | Heel Off |
| IC | Initial Contact |
| LPF | Low-Pass Filtered |
| MS | Mid Swing |
| NP | NeuroProsthetics |
| NR | NeuroRobotics |
| piIC | post ipsilateral IC |
| RT | Real-Time |
| RTGSD | Real-Time Gait and Stance Detection |
| TO | Toe Off |
| ZC | Zero-Crossing |
References
- Reinkensmeyer, D.J.; Hogan, N.; Krebs, H.I.; Lehman, S.L.; Lum, P.S.; Newman, D.J. Rehabilitators, Robots, and Guides: New Tools for Neurological Rehabilitation. In Biomechanics and Neural Control of Posture and Movement; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 516–534. [Google Scholar]
- Hesse, S.; Uhlenbrock, D. A mechanized gait trainer for restoration of gait. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2000, 37, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blaya, J.A.; Herr, H. Adaptive control of a variable-impedance ankle-foot orthosis to assist drop-foot gait. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2004, 12, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoussayni, S.; Stevens, C.; Durham, S.; Ewins, D. Assessment and validation of a simple automated method for the detection of gait events and intervals. Gait Posture 2004, 20, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminian, K.; Najafi, B.; Büla, C.; Leyvraz, P.F.; Robert, P. Spatio-temporal parameters of gait measured by an ambulatory system using miniature gyroscopes. J. Biomech. 2002, 35, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia Bejarano, N.; Ambrosini, E.; Pedrocchi, A.; Ferrigno, G.; Monticone, M.; Ferrante, S. A Novel Adaptive, Real-Time Algorithm to Detect Gait Events From Wearable Sensors. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2015, 23, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bötzel, K.; Marti, F.M.; Rodríguez, M.Á.C.; Plate, A.; Vicente, A.O. Gait recording with inertial sensors—How to determine initial and terminal contact. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueterbories, J.; Spaich, E.G.; Larsen, B.; Andersen, O.K. Methods for gait event detection and analysis in ambulatory systems. Med. Eng. Phys. 2010, 32, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, B.R.; McGrath, D.; O’Neill, R.; O’Donovan, K.J.; Burns, A.; Caulfield, B. An adaptive gyroscope-based algorithm for temporal gait analysis. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2010, 48, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, S.; Berniker, M.; Herr, H. Powered ankle-foot prosthesis to assist level-ground and stair-descent gaits. Neural Netw. 2008, 21, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotiadis, D.; Hermens, H.J.; Veltink, P.H. Inertial Gait Phase Detection for control of a drop foot stimulator Inertial sensing for gait phase detection. Med. Eng. Phys. 2010, 32, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, I.P.; Popovic, M.R.; Keller, T.; Dietz, V.; Morari, M. A reliable gait phase detection system. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2001, 9, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, G.M.; Sinkjaer, T.; Burridge, J.H.; Wilcox, D.J. A review of portable FES-based neural orthoses for the correction of drop foot. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2002, 10, 260–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, E.; Munih, M.; Benko, H.; Kralj, A. Comparison of foot-switch and hand-switch triggered FES correction of foot drop. In Proceedings of the 6th Vienna Inter- national Workshop on Functional Electrostimulation, Vienna, Austria, 22–24 September 1998; pp. 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Cutti, A.G.; Ferrari, A.; Garofalo, P.; Raggi, M.; Cappello, A.; Ferrari, A. ‘Outwalk’: A protocol for clinical gait analysis based on inertial and magnetic sensors. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2010, 48, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, T.R.; Weir, R.F. The Optimal Controller Delay for Myoelectric Prostheses. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doxon, A.J.; Johnson, D.E.; Tan, H.Z.; Provancher, W.R. Human Detection and Discrimination of Tactile Repeatability, Mechanical Backlash, and Temporal Delay in a Combined Tactile-Kinesthetic Haptic Display System. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2013, 6, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delp, S.L.; Anderson, F.C.; Arnold, A.S.; Loan, P.; Habib, A.; John, C.T.; Guendelman, E.; Thelen, D.G. OpenSim: Open-source software to create and analyze dynamic simulations of movement. IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 2007, 54, 1940–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamner, S.R.; Seth, A.; Delp, S.L. Muscle contributions to propulsion and support during running. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 2709–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groote, F.; de Laet, T.; Jonkers, I.; de Schutter, J. Kalman smoothing improves the estimation of joint kinematics and kinetics in marker-based human gait analysis. J. Biomech. 2008, 41, 3390–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia Bejarano, N.; Lambrecht, S.; Urendes, E.; Moreno, J.C.; Ambrosini, E.; Ferrante, S.; Pons, J.L. Real-time detection of gait and stance events from WR embedded sensors. In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Wearable Robotics (WeRob), Baiona, Spain, 14–19 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 1, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


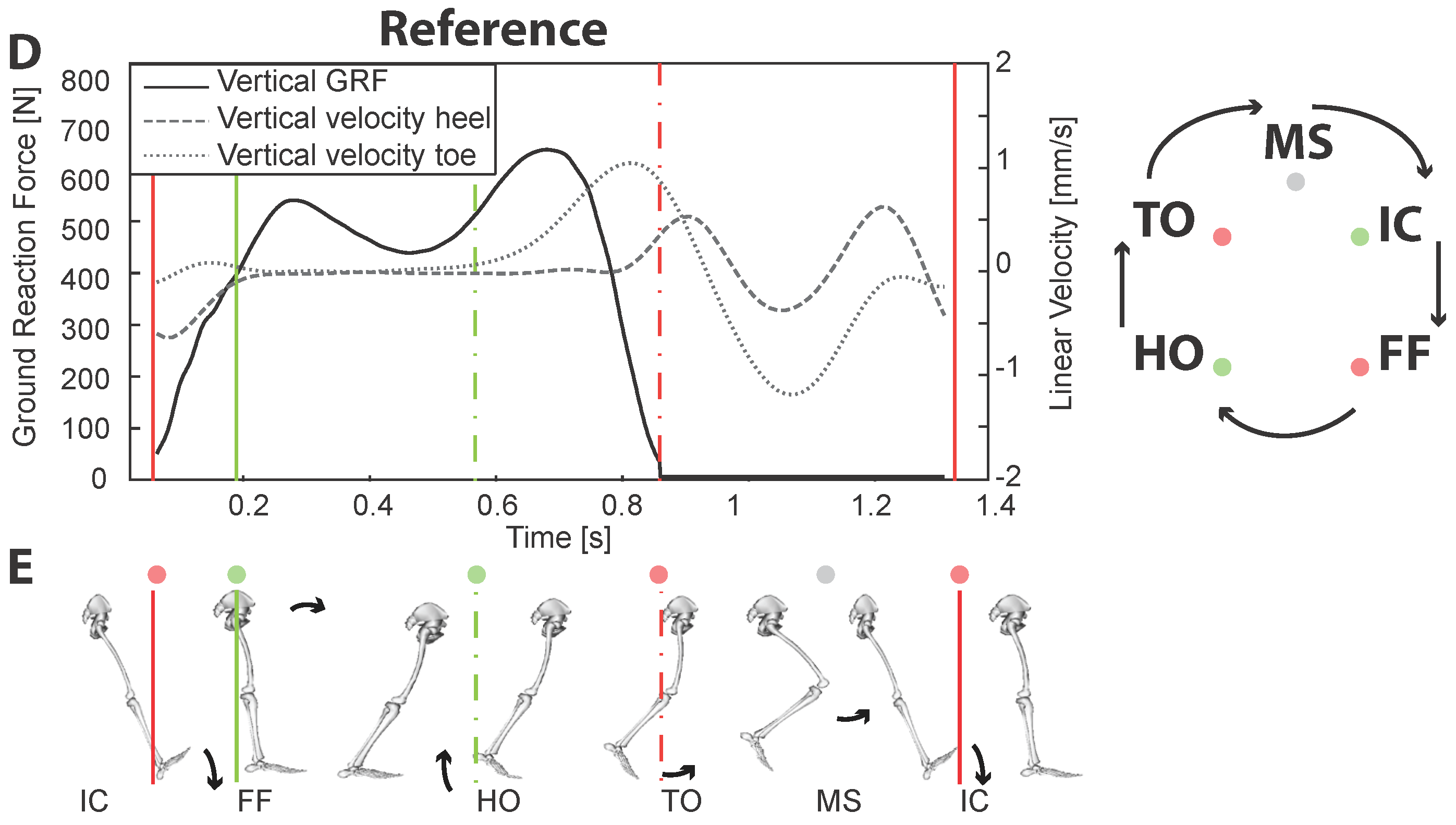

| Event | RTGSD-Min | RTGSD-B6 | RTGSD-G6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC | max. tibia angle | min. tibia angular vel. | calcaneus vertical vel. > −50 mm/s |
| FF | 1st min. ankle angle, piIC | min. foot angular acc. | toes vertical vel. > −50 mm/s |
| HO | 1st max. ankle angle, piIC | min. tibia vertical position | calcaneus vertical vel. > 50 mm/s |
| TO | min. tibia angular vel. | midpoint min. and ZC tibia angular vel. | toes vertical vel. > 50 mm/s |
| Algorithm | IC (ms) | FF (ms) | HO (ms) | TO (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RTGSD-min | −30.45 (12.45) | 5.83 (95.15) | ||
| RTGSD-B6 | 26.53 (22.43) | 26.21 (12.48) | 3.63 (110.37) | 38.52 (25.35) |
| RTGSD-G6 | 11.10 (10.72) | 189.39 (44.99) | 6.40 (15.49) | |
| Chia [6] | 13 | N.A. | N.A. | 10 |
| Pappas [12] | 70 | 70 | 40 | 35 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lambrecht, S.; Harutyunyan, A.; Tanghe, K.; Afschrift, M.; De Schutter, J.; Jonkers, I. Real-Time Gait Event Detection Based on Kinematic Data Coupled to a Biomechanical Model †. Sensors 2017, 17, 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040671
Lambrecht S, Harutyunyan A, Tanghe K, Afschrift M, De Schutter J, Jonkers I. Real-Time Gait Event Detection Based on Kinematic Data Coupled to a Biomechanical Model †. Sensors. 2017; 17(4):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040671
Chicago/Turabian StyleLambrecht, Stefan, Anna Harutyunyan, Kevin Tanghe, Maarten Afschrift, Joris De Schutter, and Ilse Jonkers. 2017. "Real-Time Gait Event Detection Based on Kinematic Data Coupled to a Biomechanical Model †" Sensors 17, no. 4: 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040671
APA StyleLambrecht, S., Harutyunyan, A., Tanghe, K., Afschrift, M., De Schutter, J., & Jonkers, I. (2017). Real-Time Gait Event Detection Based on Kinematic Data Coupled to a Biomechanical Model †. Sensors, 17(4), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040671





