Lab-on-a-Chip Platforms for Detection of Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer Biomarkers
Abstract
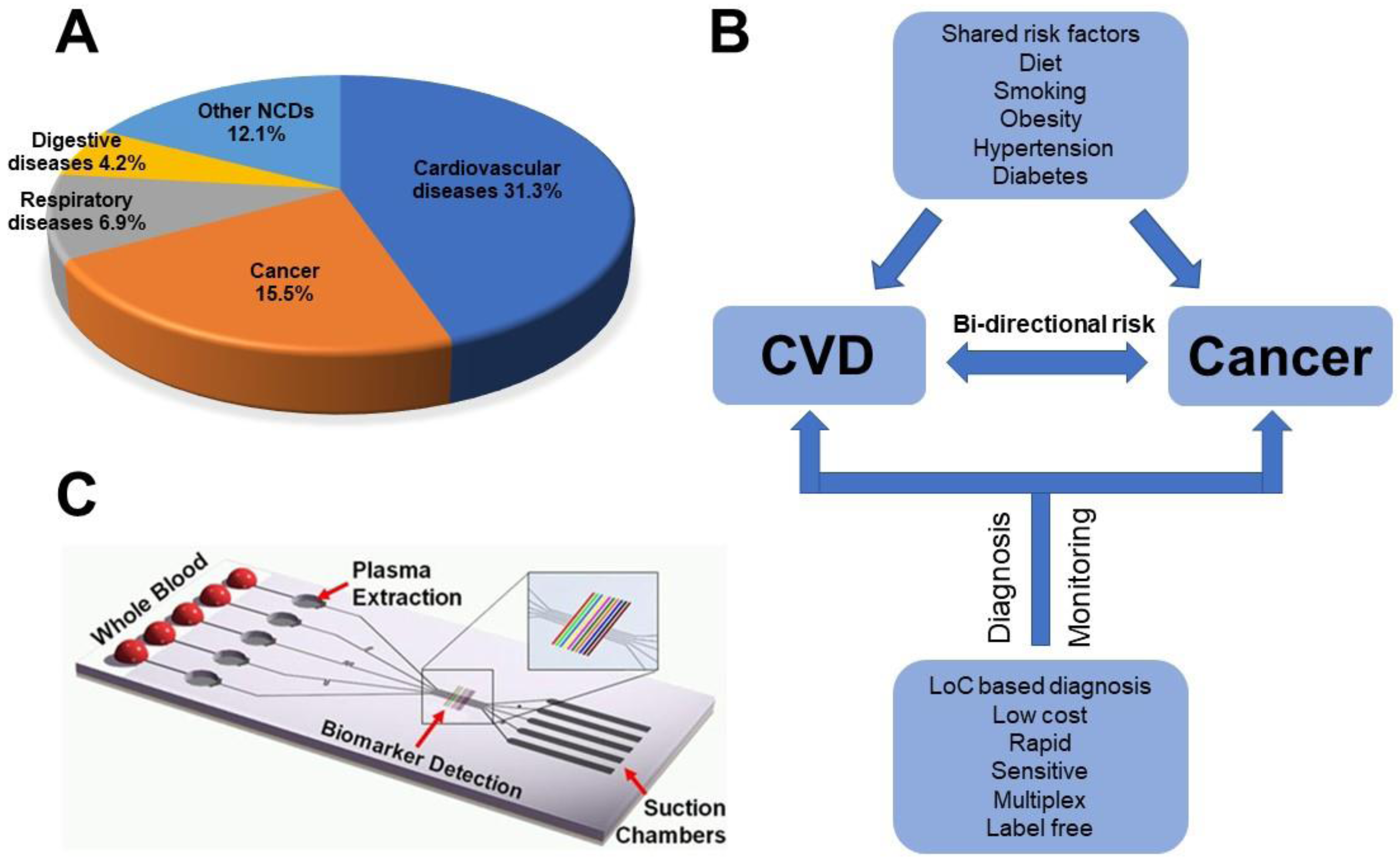
1. Introduction
2. LoC Platforms for Detection of Cardiovascular Disease Biomarkers
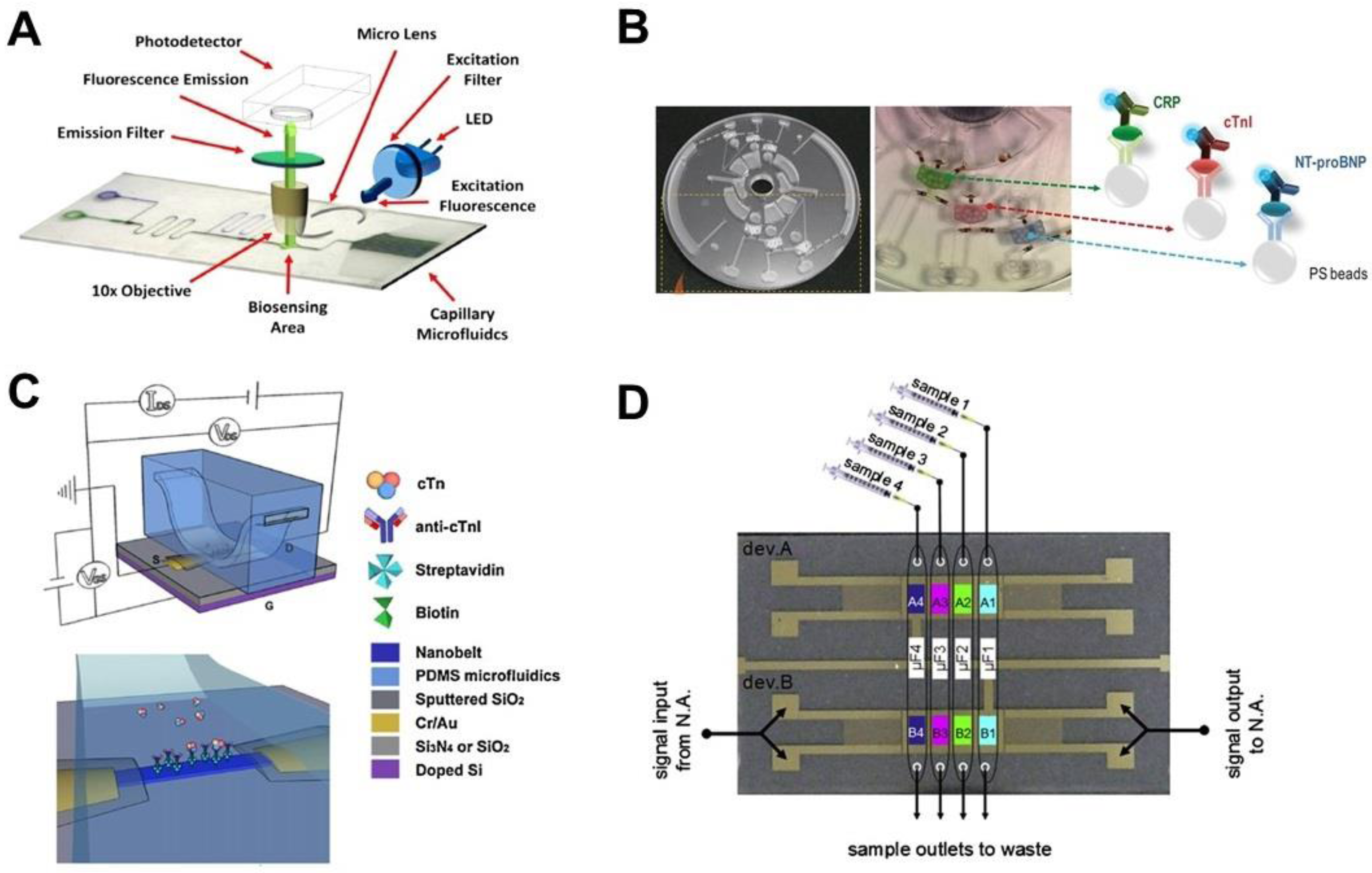
2.1. Detection of Protein Biomarkers
2.2. Detection of Cell-Based Biomarkers
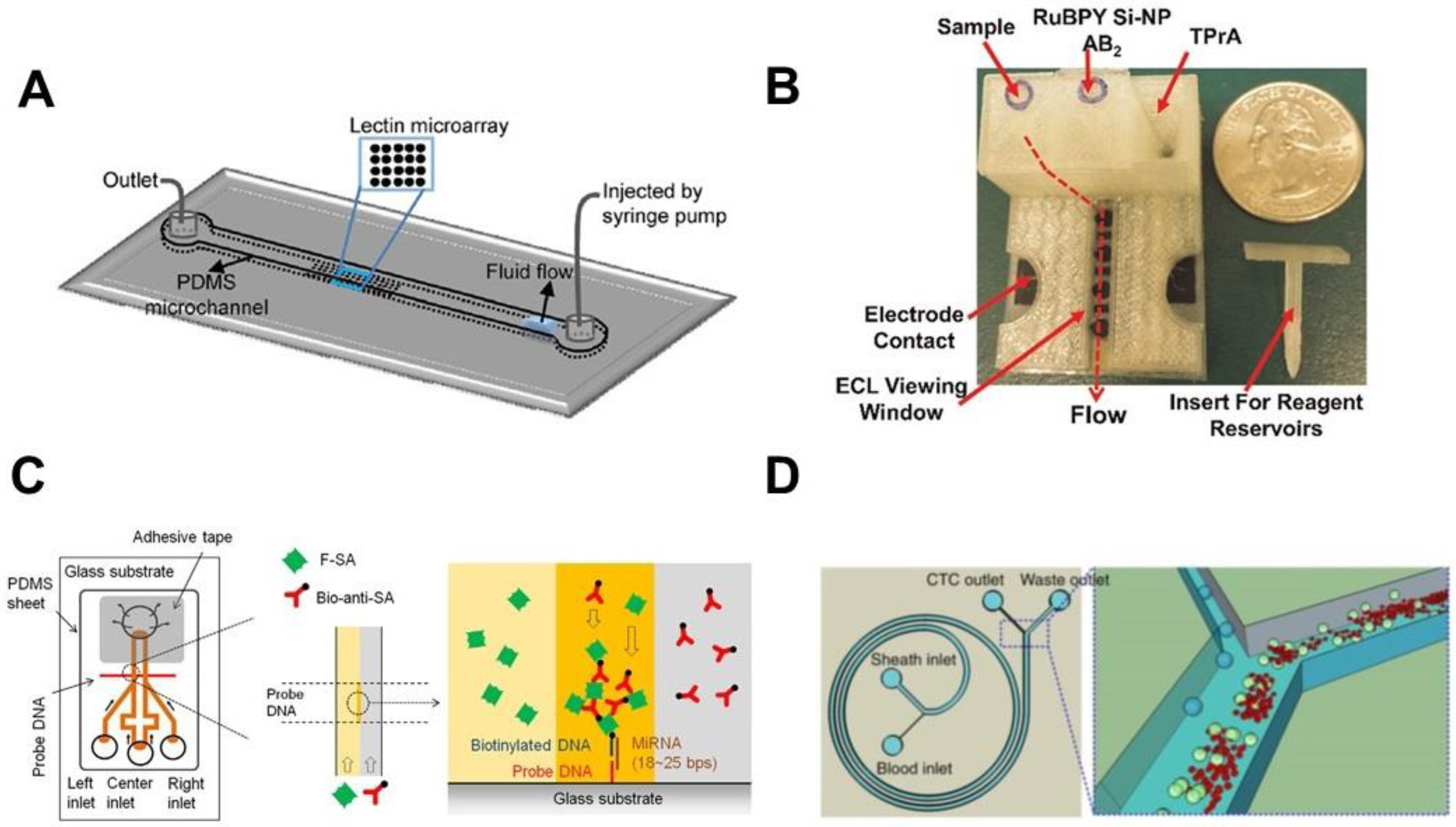
3. LoC Platforms for Detection of Cancer Biomarkers
3.1. Detection of Protein Biomarkers
3.2. Detection of Nucleic Acid Biomarkers
3.3. Detection of Exosomes as Cancer Biomarkers
3.4. Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTC) as Cancer Biomarkers
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D | three-dimensional |
| CA | carbohydrate antigen |
| CF | cystic fibrosis |
| Cfc | cell free circulating |
| CK-MB | creatine kinase MB |
| CLL | chronic lymphocytic leukemia |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CTC | circulating tumor cell |
| CTI | cleavable tag immunoassay |
| cTn | cardiac troponin |
| CVD | cardiovascular diseases |
| DEP | dielectrophoretic |
| ECL | electrochemiluminescent |
| EGF | epidermal growth factor |
| ELISA | enzyme linked immunosorbent assay |
| EPC | endothelial progenitor cells |
| FETs | field-effect transistors |
| FISH | fluorescence in-situ hybridization |
| HDL3 | high density lipoprotein-3 |
| HE4 | human epididymis protein 4 |
| hs-CRP | high-sensitivity C-reactive protein |
| LoC | lab-on-a-chip |
| LOD | limit of detection |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| MRD | minimal residual disease |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| MS | mass spectrometry |
| MS2 | mobile sensing based on microfluidic devices and smartphone |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal pro-B type natriuretic peptide |
| PAI-1 | plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| PDMS | polydimethylsiloxane |
| pM | picomolar |
| PSA | prostate specific antigen |
| PSMA | prostate specific membrane antigen |
| qPCR | quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| RBC | red blood cell |
| SAW | surface acoustic wave |
| WBC | white blood cells |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Koene, R.J.; Prizment, A.E.; Blaes, A.; Konety, S.H. Shared risk factors in cardiovascular disease and cancer. Circulation 2016, 133, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimov, I.K.; Basabe-Desmonts, L.; Garcia-Cordero, J.L.; Ross, B.M.; Ricco, A.J.; Lee, L.P. Stand-alone self-powered integrated microfluidic blood analysis system (SIMBAS). Lab Chip 2011, 11, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yager, P.; Edwards, T.; Fu, E.; Helton, K.; Nelson, K.; Tam, M.R.; Weigl, B.H. Microfluidic diagnostic technologies for global public health. Nature 2006, 442, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitesides, G.M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhavan, B.; Yue, S.; Galli, U.; Rana, S.; Gross, W.; Müller, M.; Giese, N.A.; Kalthoff, H.; Becker, T.; Büchler, M.W.; et al. Combined evaluation of a panel of protein and miRNA serum-exosome biomarkers for pancreatic cancer diagnosis increases sensitivity and specificity. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 2616–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackmann, E.K.; Fulton, A.L.; Beebe, D.J. The present and future role of microfluidics in biomedical research. Nature 2014, 507, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, W.; Han, J.; Choi, J.-W.; Ahn, C.H. Point-of-care testing (POCT) diagnostic systems using microfluidic lab-on-a-chip technologies. Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 132, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebauer, A.; Schmidt, S.; Hoffmann, W. Status and perspective of lab-on-a-chip systems for common diseases: A systematic review from 2003 to 2013. Pers. Med. 2016, 13, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.N.; Ingber, D.E. Microfluidic organs-on-chips. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrero, M.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical biosensors for the determination of cardiovascular markers: A review. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 1132–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.-I.; Desmulliez, M.P. Lab-on-a-chip based immunosensor principles and technologies for the detection of cardiac biomarkers: A review. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 569–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Zhang, W. Cancer-on-a-chip systems at the frontier of nanomedicine. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghavi, M.; Wang, H.; Lozano, R.; Davis, A.; Liang, X.; Zhou, M.; Vollset, S.E.; Ozgoren, A.A.; Abdalla, S.; Abd-Allah, F. Global, regional, and national age–sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 385, 117–171. [Google Scholar]
- McGill, H.C.; McMahan, C.A.; Gidding, S.S. Preventing heart disease in the 21st century implications of the pathobiological determinants of atherosclerosis in youth (PDAY) study. Circulation 2008, 117, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amundson, B.E.; Apple, F.S. Cardiac troponin assays: A review of quantitative point-of-care devices and their efficacy in the diagnosis of myocardial infarction. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2015, 53, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Sunkara, V.; Kim, T.-H.; Hwang, H.; Cho, Y.-K. Lab-on-a-Disc for Fully Integrated Multiplex Immunoassays. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2133–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, S.; Li, X.; Niu, M.; Ge, B.; Yu, H.-Z. Blu-ray Technology-Based Quantitative Assays for Cardiac Markers: From Disc Activation to Multiplex Detection. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6889–6896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsakakis, K.; Gizeli, E. Detection of multiple cardiac markers with an integrated acoustic platform for cardiovascular risk assessment. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 699, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekin, D.; Skhiri, Y.; Baret, J.-C.; Le Corre, D.; Mazutis, L.; Ben Salem, C.; Millot, F.; El Harrak, A.; Hutchison, J.B.; Larson, J.W.; et al. Quantitative and sensitive detection of rare mutations using droplet-based microfluidics. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2156–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, J.; Wu, H.; Ying, J.Y. Trapping cells in paper for white blood cell count. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 69, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansmann, G.; Plouffe, B.D.; Hatch, A.; Gise, A.; Sallmon, H.; Zamanian, R.T.; Murthy, S.K. Design and validation of an endothelial progenitor cell capture chip and its application in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 89, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadimisetty, K.; Mosa, I.M.; Malla, S.; Satterwhite-Warden, J.E.; Kuhns, T.M.; Faria, R.C.; Lee, N.H.; Rusling, J.F. 3D-printed supercapacitor-powered electrochemiluminescent protein immunoarray. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadfan, B.H.; Simmons, A.R.; Simmons, G.W.; Ho, A.; Wong, J.; Lu, K.H.; Bast, R.C., Jr.; McDevitt, J.T. A multiplexable, microfluidic platform for the rapid quantitation of a biomarker panel for early ovarian cancer detection at the point-of-care. Cancer Prev. Res. 2015, 8, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arata, H.; Komatsu, H.; Hosokawa, K.; Maeda, M. Rapid and Sensitive MicroRNA Detection with Laminar Flow-Assisted Dendritic Amplification on Power-Free Microfluidic Chip. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Crow, J.; Roth, M.; Zeng, Y.; Godwin, A.K. Integrated immunoisolation and protein analysis of circulating exosomes using microfluidic technology. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3773–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; He, M. A microfluidic ExoSearch chip for multiplexed exosome detection towards blood-based ovarian cancer diagnosis. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnenberg, A.; Marciniak, J.Y.; McCanna, J.; Krishnan, R.; Rassenti, L.; Kipps, T.J.; Heller, M.J. Dielectrophoretic isolation and detection of cfc-DNA nanoparticulate biomarkers and virus from blood. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mughal, F.; Baldock, S.J.; Karimiani, E.G.; Telford, N.; Goddard, N.J.; Day, P.J.R. Microfluidic channel-assisted screening of hematopoietic malignancies. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014, 53, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuara, D.; Ginesta, M.M.; Gausachs, M.; Rodriguez-Moranta, F.; Fabregat, J.; Busquets, J.; Pelaez, N.; Boadas, J.; Galter, S.; Moreno, V. Nanofluidic digital PCR for KRAS mutation detection and quantification in gastrointestinal cancer. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 1332–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warkiani, M.E.; Khoo, B.L.; Wu, L.; Tay, A.K.P.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Han, J.; Lim, C.T. Ultra-fast, label-free isolation of circulating tumor cells from blood using spiral microfluidics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, M.I.; Desmulliez, M.P.Y. Autonomous capillary microfluidic system with embedded optics for improved troponin I cardiac biomarker detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Chen, K.-S.; Meyer, N.L.; Yuan, J.; Hirst, L.S.; Chase, P.B.; Xiong, P. Functionalized SnO2 nanobelt field-effect transistor sensors for label-free detection of cardiac troponin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4538–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.N.; Li, C.A.; Seong, G.H. Microfluidic Chips for Immunoassays. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2013, 6, 119–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.; Ng, A.H.C.; Fobel, R.; Chang-Yen, D.A.; Yarnell, L.E.; Pearson, E.L.; Oleksak, C.M.; Fischer, A.T.; Luoma, R.P.; Robinson, J.M.; et al. Automated Digital Microfluidic Platform for Magnetic-Particle-Based Immunoassays with Optimization by Design of Experiments. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 9638–9646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, W.; Shim, J.; Lee, D.-Y.; Dutta, P.; Kim, J.-R.; Cho, K.-H. Rapid detection of dysfunctional high-density lipoproteins using isoelectric focusing-based microfluidic device to diagnose senescence-related disease. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 3415–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.R.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, K.; Chung, D.S. On-chip immunoassay of a cardiac biomarker in serum using a polyester-toner microchip. Talanta 2013, 109, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.R.; Zhang, Y.S.; Kim, D.-J.; Manbohi, A.; Avci, H.; Silvestri, A.; Aleman, J.; Hu, N.; Kilic, T.; Keung, W. Aptamer-based microfluidic electrochemical biosensor for monitoring cell-secreted trace cardiac biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10019–10027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, R.H., Jr.; Neaton, J.D.; Ludwig, W. PRognostic importance of the white blood cell count for coronary, cancer, and all-cause mortality. JAMA 1985, 254, 1932–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Cancer Fact Sheet N 297; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, B.; Wild, C.P. World Cancer Report 2014; IARC Publications: Lyon, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, J.M.; Yeo, C.J.; Brody, J.R. Diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive biomarkers in pancreatic cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 107, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, A.J.; Harris, C.C. Biomarker development in the precision medicine era: Lung cancer as a case study. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhavan, D.; Cuk, K.; Burwinkel, B.; Yang, R. Cancer diagnosis and prognosis decoded by blood-based circulating microRNA signatures. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, B.; Chattopadhyay, G.; Mishra, D.; Das, T.; Chakraborty, S.; Maiti, T.K. On-chip lectin microarray for glycoprofiling of different gastritis types and gastric cancer. Biomicrofluidics 2014, 8, 034107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Costa, J.J.; Goldsmith, J.C.; Wilson, J.S.; Bryan, R.T.; Ward, D.G. A Systematic Review of the Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Urinary Protein Biomarkers in Urothelial Bladder Cancer. Bladder Cancer 2016, 2, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohri, Y.; Toiyama, Y.; Kusunoki, M. Progress and prospects for the discovery of biomarkers for gastric cancer: A focus on proteomics. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2016, 13, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodahl, A.R.; Lyng, M.B.; Binder, H.; Cold, S.; Gravgaard, K.; Knoop, A.S.; Ditzel, H.J. Novel circulating microRNA signature as a potential non-invasive multi-marker test in ER-positive early-stage breast cancer: A case control study. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, M.N.; Chik, J.; Lee, L.; Anugraham, M.; Abrahams, J.L.; Packer, N.H. Cell surface protein glycosylation in cancer. Proteomics 2014, 14, 525–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilgunn, S.; Conroy, P.J.; Saldova, R.; Rudd, P.M.; O’Kennedy, R.J. Aberrant PSA glycosylation[mdash]a sweet predictor of prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2013, 10, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnal-Estapé, A.; Nguyen, D.X. Sweets for a Bitter End: Lung Cancer Cell–Surface Protein Glycosylation Mediates Metastatic Colonization. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wen, T.; Zhu, M.; Li, L.; Wei, J.; Wu, X.; Guo, M.; Liu, S.; Zhao, H.; Xia, S.; et al. Glycoproteomic analysis of tissues from patients with colon cancer using lectin microarrays and nanoLC-MS/MS. Mol. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, D. Quantification using real-time PCR technology: Applications and limitations. Trends Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagci, P.; Andea, A.A.; Basturk, O.; Jang, K.-T.; Erbarut, I.; Adsay, V. Large duct type invasive adenocarcinoma of the pancreas with microcystic and papillary patterns: A potential microscopic mimic of non-invasive ductal neoplasia. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Whitesides, G.M. Three-dimensional microfluidic devices fabricated in layered paper and tape. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19606–19611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arata, H.; Komatsu, H.; Han, A.; Hosokawa, K.; Maeda, M. Rapid microRNA detection using power-free microfluidic chip: Coaxial stacking effect enhances the sandwich hybridization. Analyst 2012, 137, 3234–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soung, Y.H.; Ford, S.; Zhang, V.; Chung, J. Exosomes in cancer diagnostics. Cancers 2017, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liga, A.; Vliegenthart, A.; Oosthuyzen, W.; Dear, J.; Kersaudy-Kerhoas, M. Exosome isolation: A microfluidic road-map. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2388–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohr, J.G.; Adalsteinsson, V.A.; Cibulskis, K.; Choudhury, A.D.; Rosenberg, M.; Cruz-Gordillo, P.; Francis, J.; Zhang, C.-Z.; Shalek, A.K.; Satija, R.; et al. Whole exome sequencing of circulating tumor cells provides a window into metastatic prostate cancer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baccelli, I.; Schneeweiss, A.; Riethdorf, S.; Stenzinger, A.; Schillert, A.; Vogel, V.; Klein, C.; Saini, M.; Bauerle, T.; Wallwiener, M.; et al. Identification of a population of blood circulating tumor cells from breast cancer patients that initiates metastasis in a xenograft assay. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haber, D.A.; Velculescu, V.E. Blood-Based Analyses of Cancer: Circulating Tumor Cells and Circulating Tumor DNA. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alix-Panabieres, C.; Pantel, K. Technologies for detection of circulating tumor cells: Facts and vision. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, W.; Ogunwobi, O.O.; Chen, T.; Zhang, J.; George, T.J.; Liu, C.; Fan, Z.H. Capture, release and culture of circulating tumor cells from pancreatic cancer patients using an enhanced mixing chip. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeilsabzali, H.; Beischlag, T.V.; Cox, M.E.; Parameswaran, A.M.; Park, E.J. Detection and isolation of circulating tumor cells: Principles and methods. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1063–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabacak, N.M.; Spuhler, P.S.; Fachin, F.; Lim, E.J.; Pai, V.; Ozkumur, E.; Martel, J.M.; Kojic, N.; Smith, K.; Chen, P.I.; et al. Microfluidic, marker-free isolation of circulating tumor cells from blood samples. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 694–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Jia, C.-P.; Jun, Y.; Sun, W.-J.; Wang, W.-T.; Zhang, H.-L.; Cong, H.; Jing, F.-X.; Mao, H.-J.; Jin, Q.-H.; et al. Highly sensitive enumeration of circulating tumor cells in lung cancer patients using a size-based filtration microfluidic chip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 51, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sollier, E.; Go, D.E.; Che, J.; Gossett, D.R.; O’Byrne, S.; Weaver, W.M.; Kummer, N.; Rettig, M.; Goldman, J.; Nickols, N.; et al. Size-selective collection of circulating tumor cells using Vortex technology. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.W.; Warkiani, M.E.; Khoo, B.L.; Li, Z.R.; Soo, R.A.; Tan, D.S.-W.; Lim, W.-T.; Han, J.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Lim, C.T. Isolation and retrieval of circulating tumor cells using centrifugal forces. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantel, K.; Brakenhoff, R.H.; Brandt, B. Detection, clinical relevance and specific biological properties of disseminating tumour cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, B.; Zu, Y.L. Detecting Circulating Tumor Cells: Current Challenges and New Trends. Theranostics 2013, 3, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Gonzalez, V.H.; Gallo-Villanueva, R.C.; Camacho-Leon, S.; Gomez-Quinones, J.I.; Rodriguez-Delgado, J.M.; Martinez-Chapa, S.O. Emerging microfluidic devices for cancer cells/biomarkers manipulation and detection. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 10, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Zeng, Y. Microfluidic Exosome Analysis toward Liquid Biopsy for Cancer. JALA 2016, 21, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickey, D.D.; Giangrande, P.H. Oligonucleotide aptamers: A next-generation technology for the capture and detection of circulating tumor cells. Methods 2016, 97, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.L.; Chung, J.; Issadore, D. Diagnostic technologies for circulating tumour cells and exosomes. Biosci. Rep. 2016, 36, e00292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.H.; Tang, M.; Li, M.; Gao, F.; Shi, C.; Hou, J.; Zeng, W.B. Circulating Tumor Cells: A New Window for Diagnosis and Evaluation of Cancer. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, K.; Fan, Z.H. Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation and Analysis. In Advances in Clinical Chemistry; Makowski, G.S., Ed.; Elsevier Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; Volume 75, pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Myung, J.H.; Hong, S. Microfluidic devices to enrich and isolate circulating tumor cells. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 4500–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, P.; Madhuprasad; Kumeria, T.; Losic, D.; Kurkuri, M. Isolation of circulating tumour cells by physical means in a microfluidic device: A review. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 89745–89762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.F.; Gouw, N.E.; Gao, Z.Q. Quantification techniques for circulating tumor cells. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 64, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ng, S.R.; Xu, Y.; Dong, H.; Wang, Y.J.; Li, C.M. Advances of lab-on-a-chip in isolation, detection and post-processing of circulating tumour cells. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 3163–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, K.A.; Jung, H.I. Advances and critical concerns with the microfluidic enrichments of circulating tumor cells. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajba, L.; Guttman, A. Circulating tumor-cell detection and capture using microfluidic devices. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 59, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Chen, J.F.; Lu, Y.T.; Zhang, Y.; Song, J.Z.; Hou, S.; Ke, Z.F.; Tseng, H.R. Nanostructure Embedded Microchips for Detection, Isolation, and Characteriiation of Circulating Tumor Cells. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2941–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; Nagrath, S.; Toner, M.; Haber, D.A.; Lynch, T.J. The CTC-Chip: An Exciting New Tool to Detect Circulating Tumor Cells in Lung Cancer Patients. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Peretz-Soroka, H.; Liu, Y.; Lin, F. Novel developments in mobile sensing based on the integration of microfluidic devices and smartphones. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 943–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Disease | Marker | Technique | LOD | Detector | Assay Time | Sample Volume | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVD | hs-CRP | bead-based ELISA | 0.30 ng/mL (saliva); 0.27 ng/mL (blood) | CCD | <20 min | 200 μL | [16] |
| cTnI | 0.51 ng/mL (saliva); 0.27 ng/mL (blood) | ||||||
| NT-proBNP | 0.24 ng/mL (saliva); 0.32 ng/mL (blood) | ||||||
| myoglobin | aptamer-antibody hybrid assay | - | Blu-ray optical drive | - | - | [17] | |
| troponin I | |||||||
| CRP | |||||||
| CK-MB | surface acoustic wave | <1 nM | vector network analyzer | <30 min | - | [18] | |
| D-dimer | |||||||
| PAPP-A | |||||||
| CRP | fluorescence | 0.54 μg/mL | fluorescent microscope | 5 min | ~4.5 μL | [19] | |
| WBC | colorimetric assays | - | naked eye | ~35 min | 15 μL | [20] | |
| EPC | immunofluorescence | - | fluorescent microscope | 1 h | 200 μL | [21] | |
| Cancer | PSA | ECL | 300–500 fg/mL | CCD | 35 min | 2–5 μL | [22] |
| PSMA | |||||||
| PF-4 | |||||||
| CA125 | bead-based immunoassay | 1.8 U/mL | fluorescent microscope | 43 min | 50 μL | [23] | |
| HE4 | 2.3 pmol/L | ||||||
| MMP-7 | 0.2 ng/mL | ||||||
| CA72-4 | 1.7 U/mL | ||||||
| miRNA-21 | sandwich hybridization | 0.5 pmol/L | fluorescent microscope | 20 min | 500 μL | [24] | |
| IGF-1R | Exosome immunoisolation and protein analysis | 0.281 pg/mL | fluorescent microscope | ~100 min | 30 μL | [25] | |
| p-IGF-1R | 0.383 pg/mL | ||||||
| CA-125 | immunomagnetic beads exosome isolation and immunofluorescence protein analysis | - | fluorescent microscope | 40 min | 20 μL | [26] | |
| EpCAM | |||||||
| CD24 | |||||||
| cfc-DNA | DEP isolation | 8–16 ng/mL | fluorescent microscope | - | 20 μL | [27] | |
| cancer cell | FISH | 1:100 (MRD) | microscope | 1 h | 0.2 μL | [28] | |
| KRAS | digital PCR | 0.05–0.1% (mutant alleles) | real-time PCR | ~1 h | 1.8 μL | [29] | |
| CTC | lateral migration | - | a microscope equipped with a high-speed camera | ~2 min | 1 mL | [30] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Dong, M.; Santos, S.; Rigatto, C.; Liu, Y.; Lin, F. Lab-on-a-Chip Platforms for Detection of Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer Biomarkers. Sensors 2017, 17, 2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122934
Wu J, Dong M, Santos S, Rigatto C, Liu Y, Lin F. Lab-on-a-Chip Platforms for Detection of Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer Biomarkers. Sensors. 2017; 17(12):2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122934
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jiandong, Meili Dong, Susy Santos, Claudio Rigatto, Yong Liu, and Francis Lin. 2017. "Lab-on-a-Chip Platforms for Detection of Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer Biomarkers" Sensors 17, no. 12: 2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122934
APA StyleWu, J., Dong, M., Santos, S., Rigatto, C., Liu, Y., & Lin, F. (2017). Lab-on-a-Chip Platforms for Detection of Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer Biomarkers. Sensors, 17(12), 2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122934





