Repetitively Mode-Locked Cavity-Enhanced Absorption Spectroscopy (RML-CEAS) for Near-Infrared Gas Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
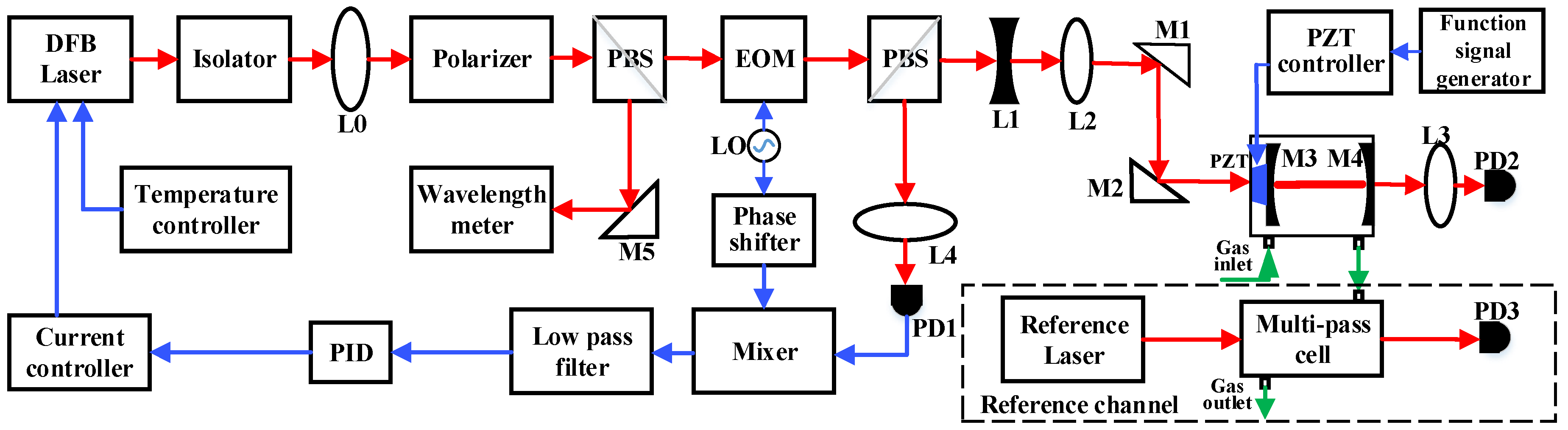
2. Sensor System Configuration
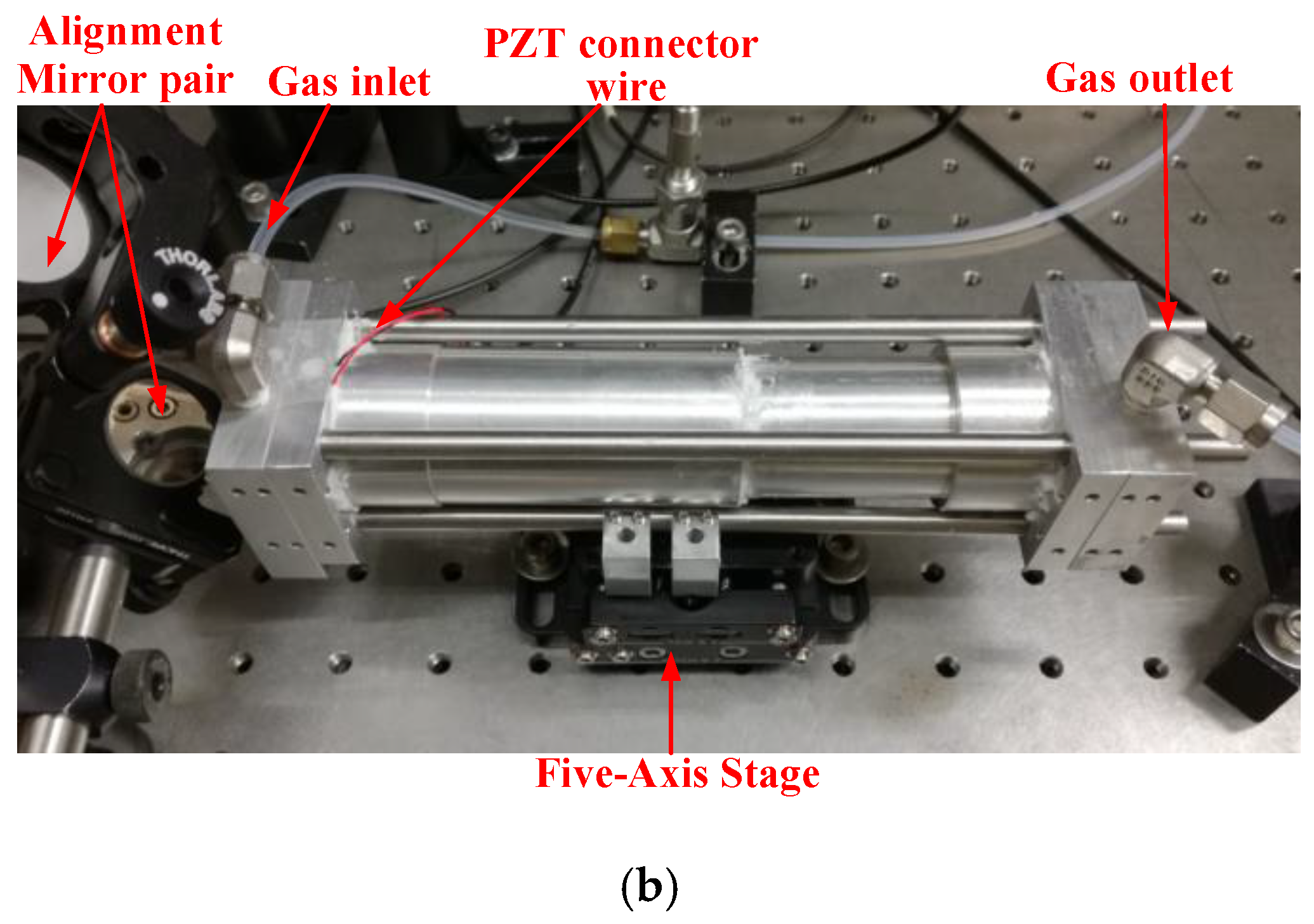
2.1. Sensor Structure
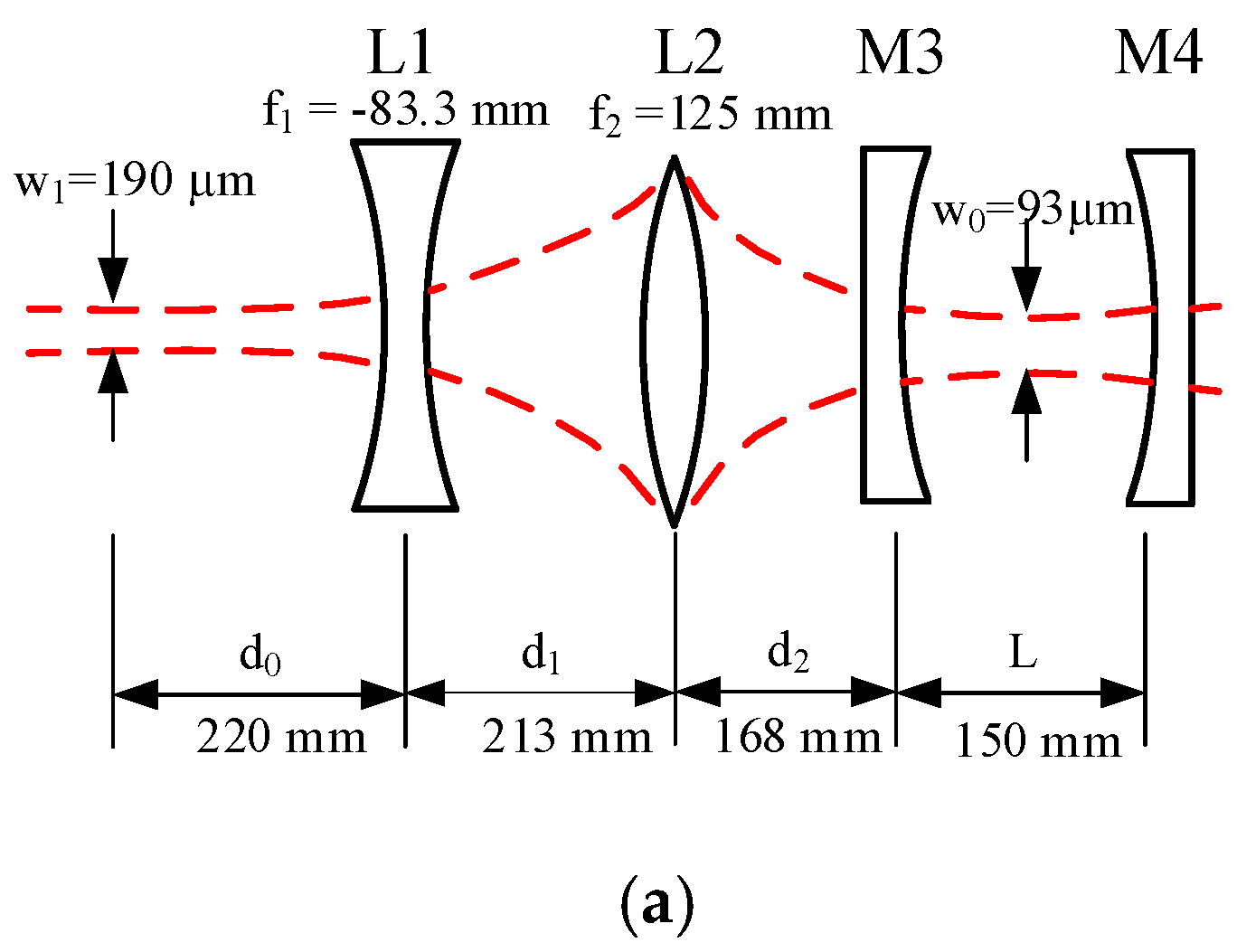
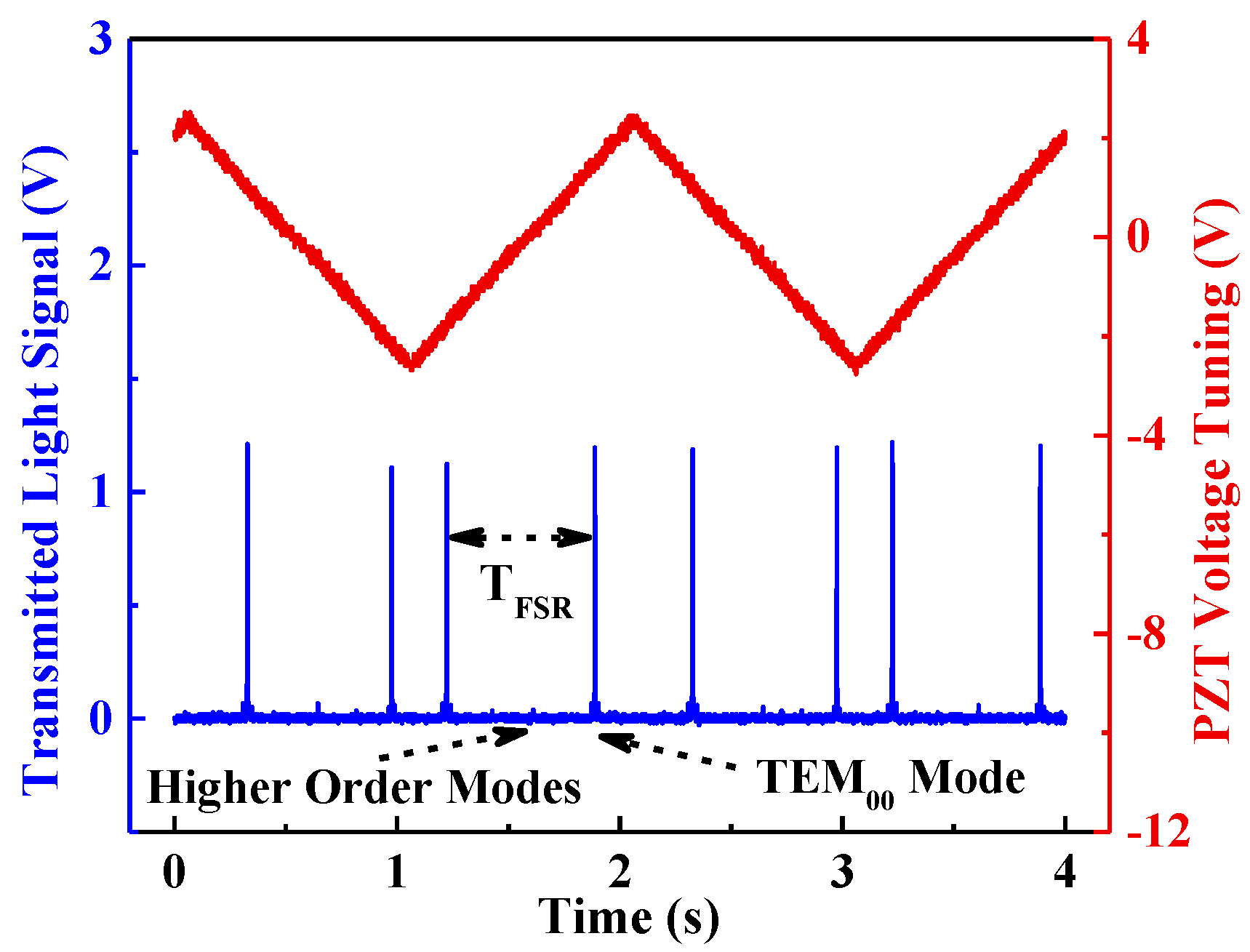
2.2. Fabry-Perot Cavity
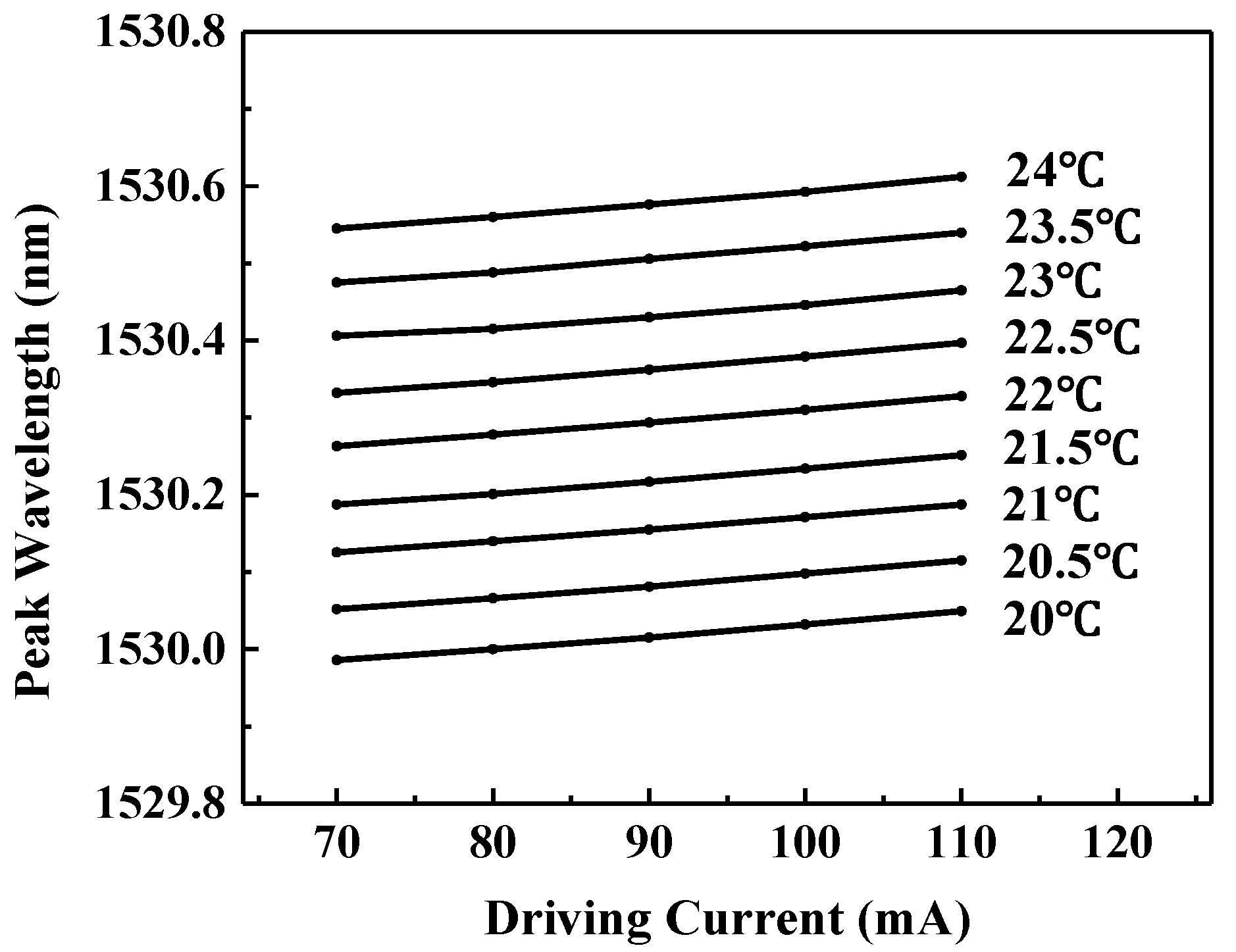
2.3. Tuning Characteristics of the Laser
3. Experiments and Results
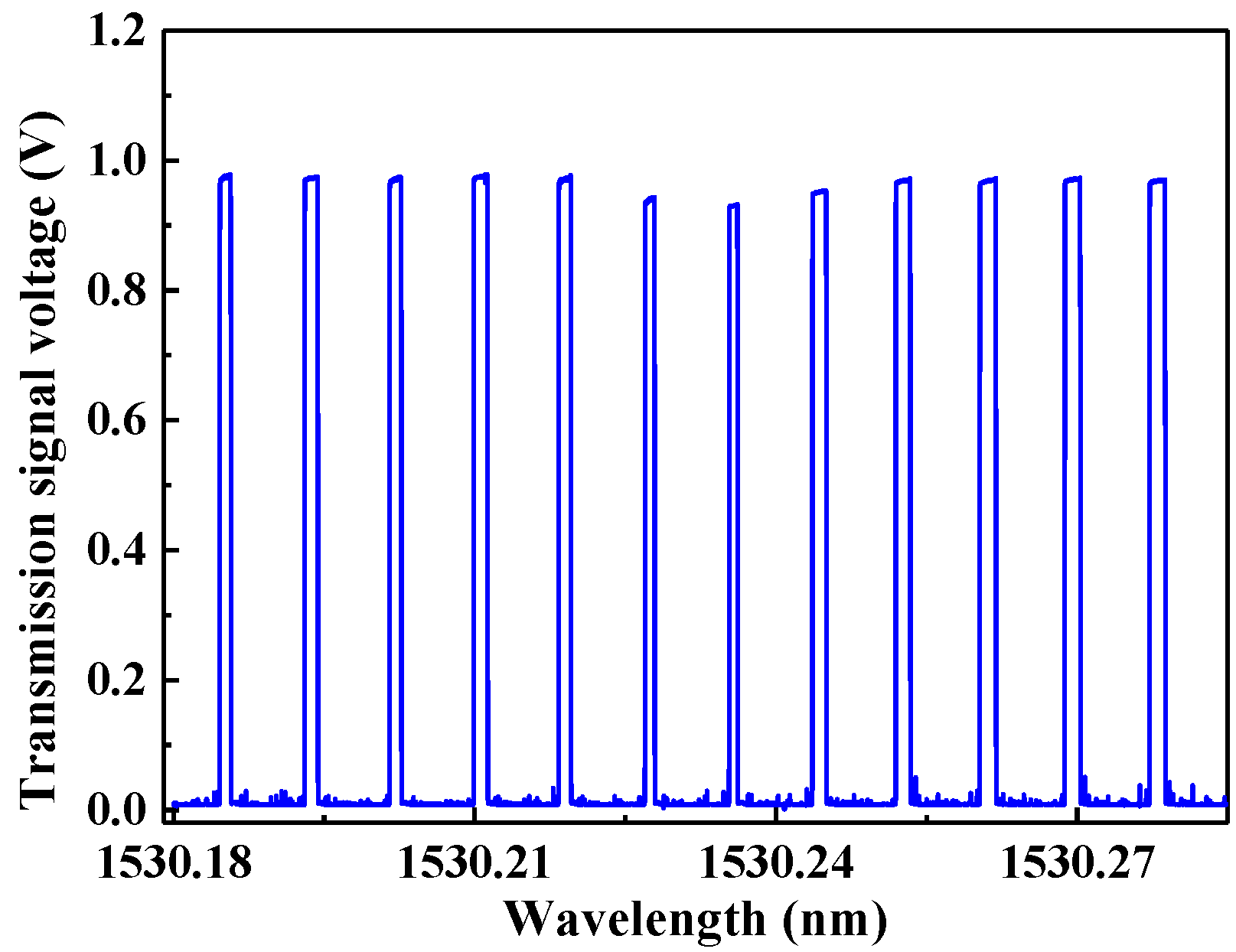
3.1. Cavity Transmission Spectrum
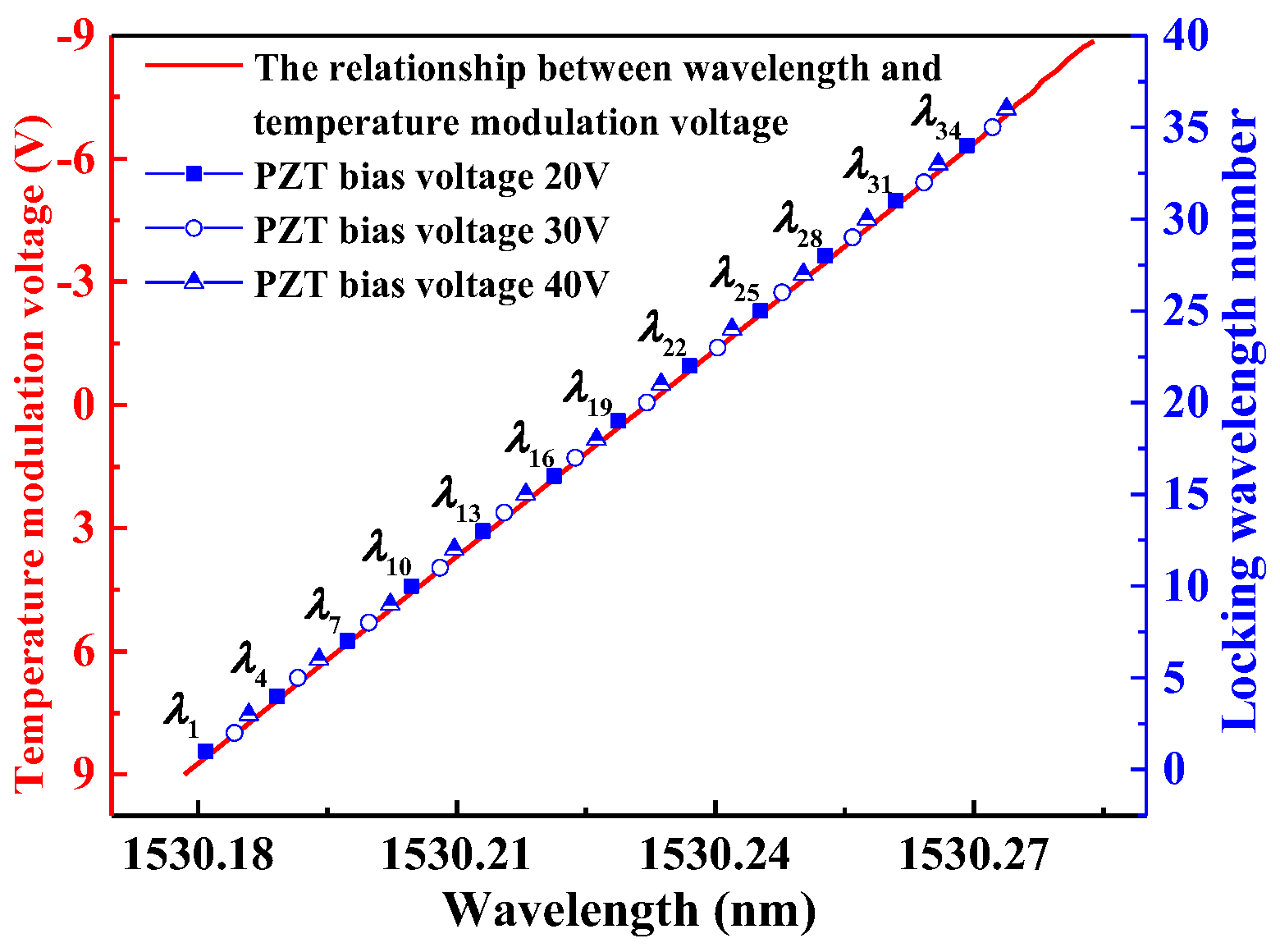
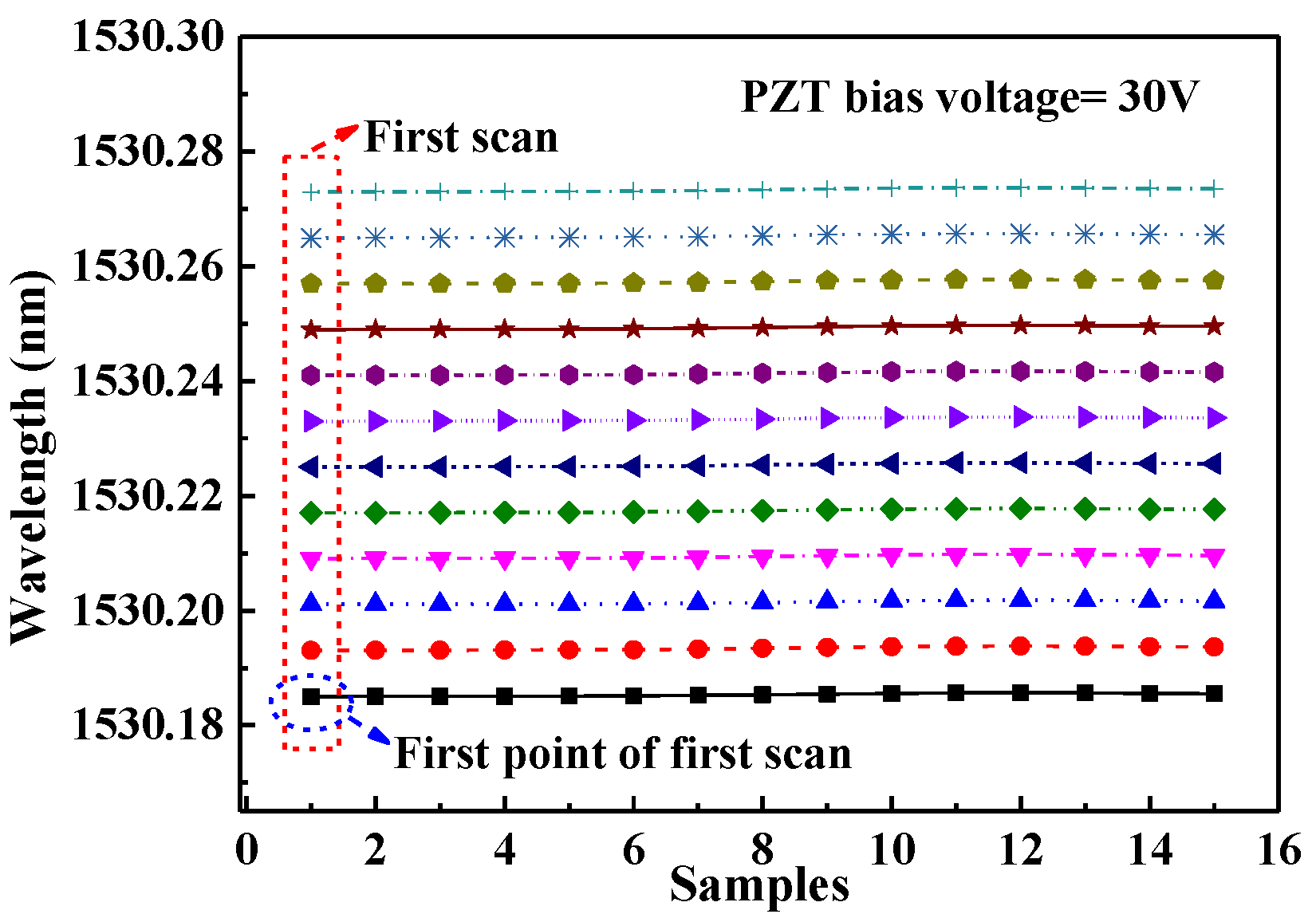
3.2. Locked Wavelength with PZT Bias
3.3. H2O Detection
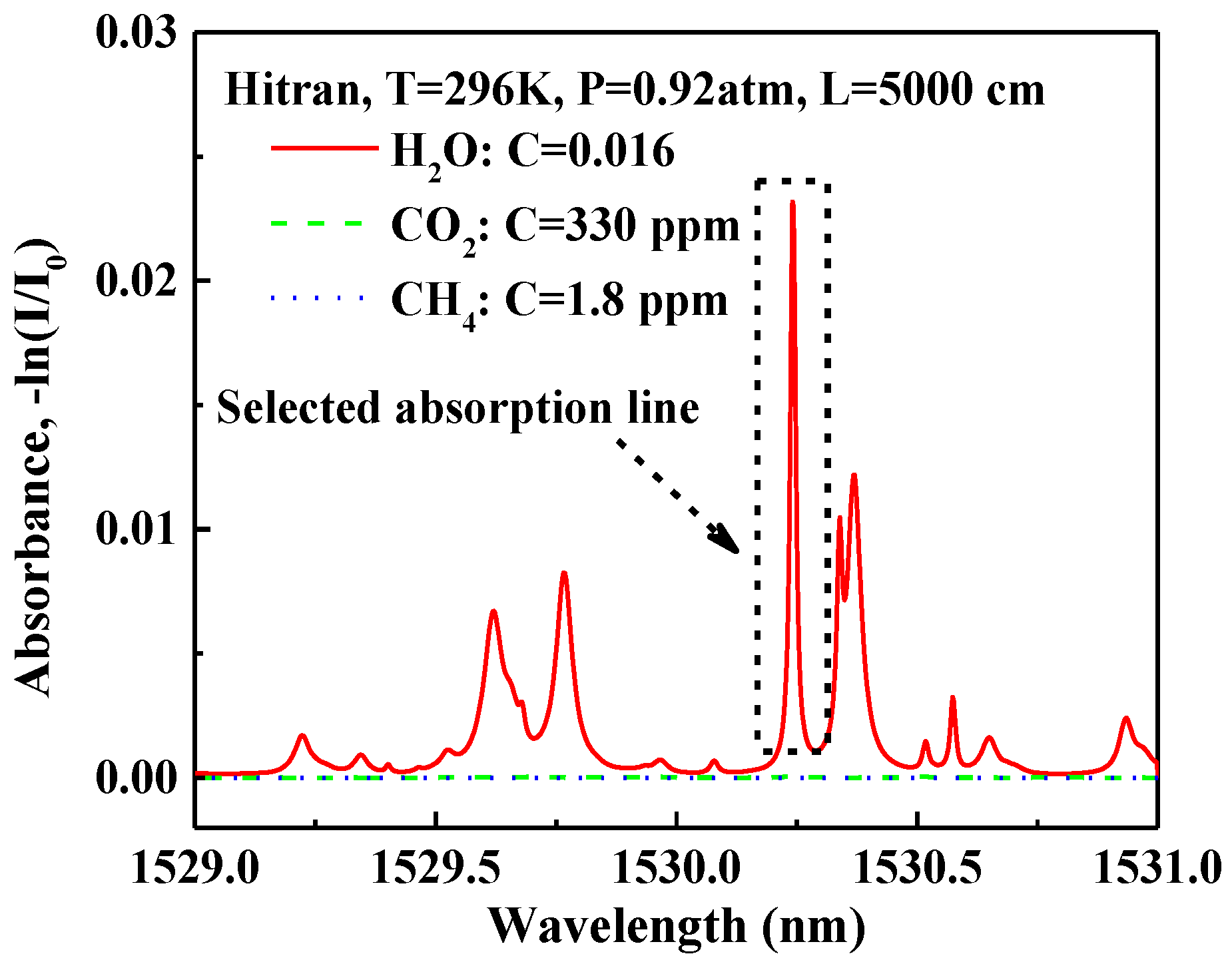
3.3.1. H2O Absorption Spectroscopy in the Near-Infrared
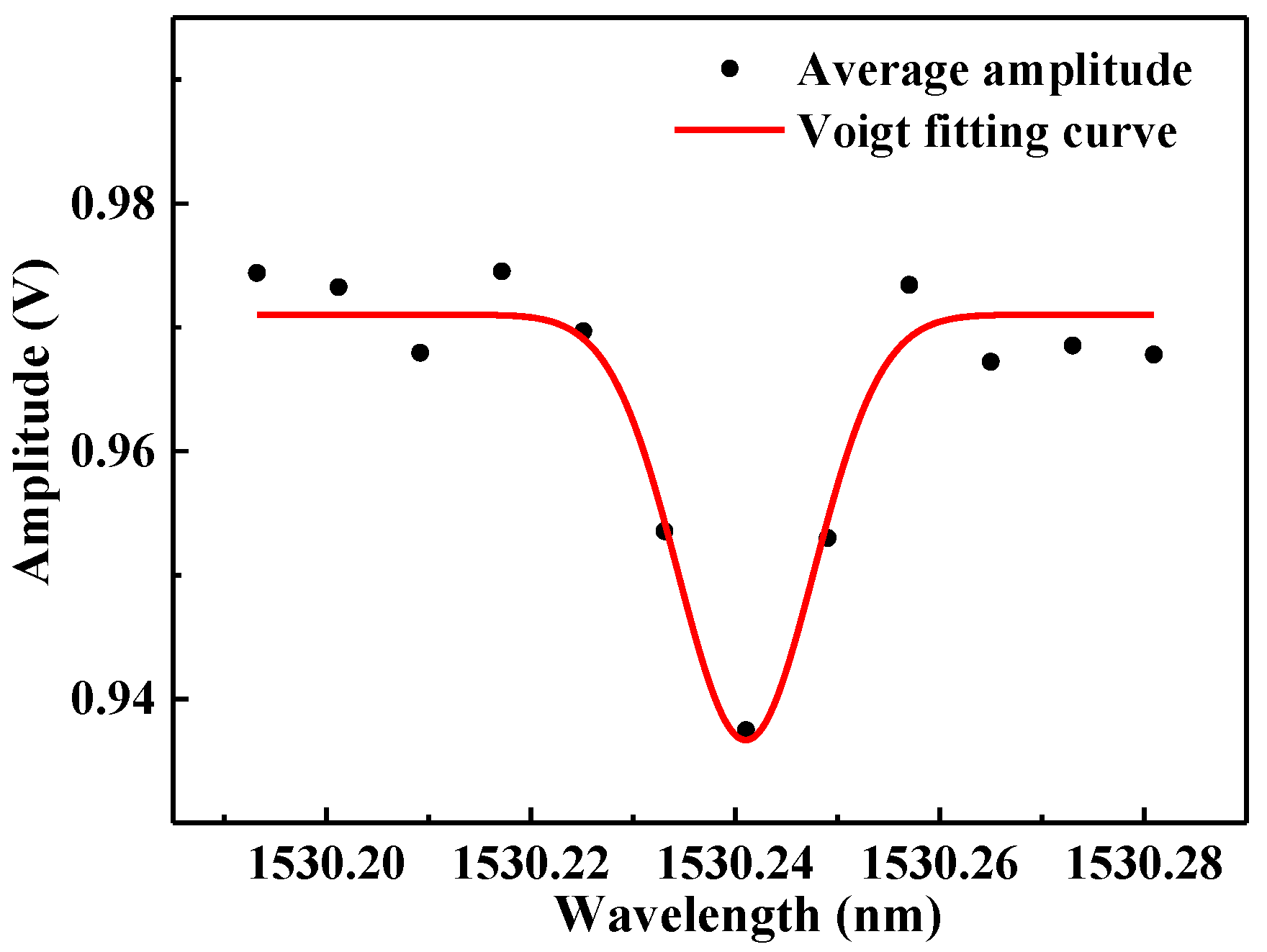
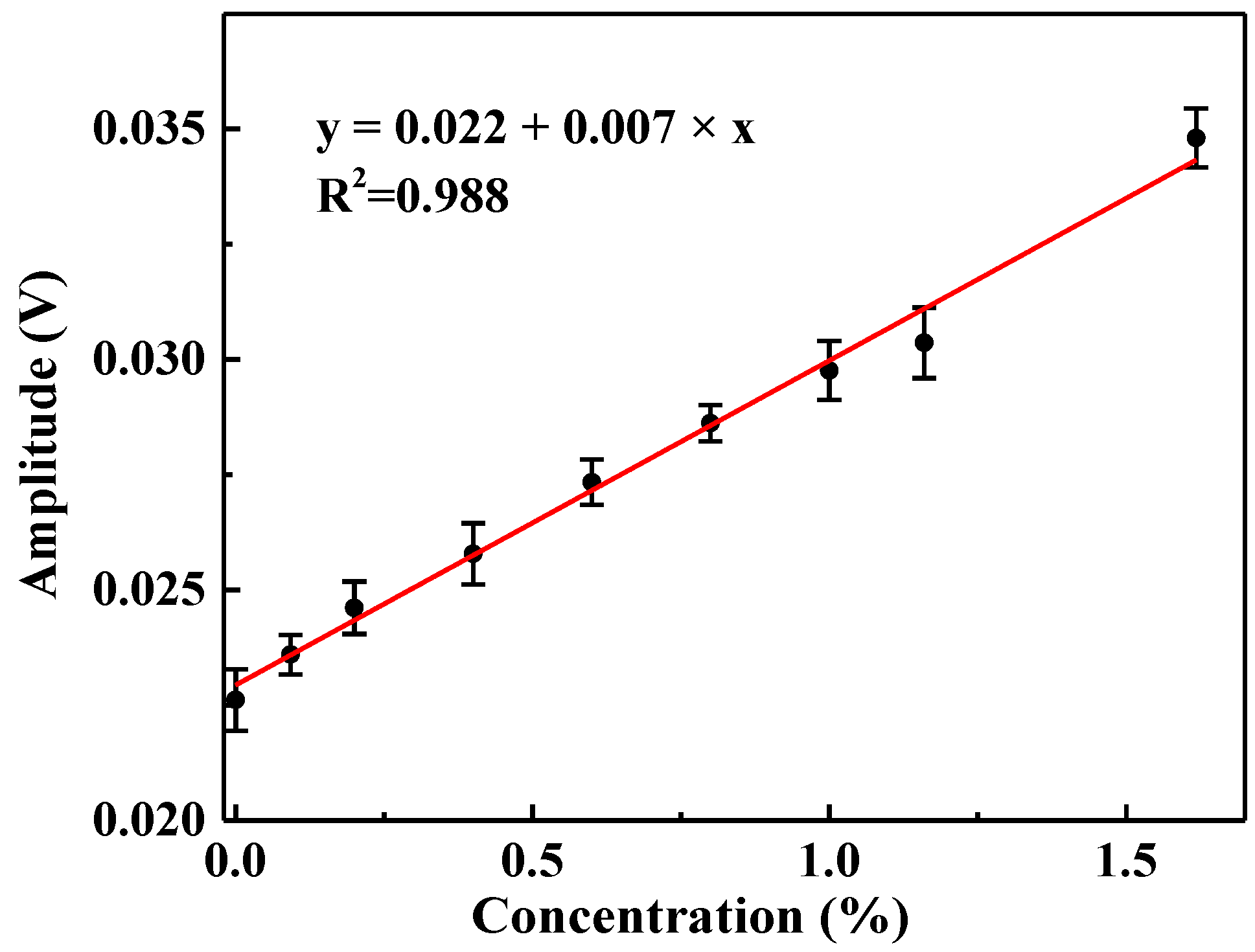
3.3.2. Experimental Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamilton, D.J.; Orr-Ewing, A.J. A quantum cascade laser-based optical feedback cavity-enhanced absorption spectrometer for the simultaneous measurement of CH4 and N2O in air. Appl. Phys. B 2011, 102, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Li, C.; Sanchez, N.P.; Gluszek, A.K.; Griffin, R.J.; Tittel, F.K. Compact CH4 sensor system based on a continuous-wave, low power consumption, room temperature interband cascade laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 011106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Sanchez, N.P.; Griffin, R.J.; Tittel, F.K. CW EC-QCL-based sensor for simultaneous detection of H2O, HDO, N2O and CH4 using multi-pass absorption spectroscopy. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 10391–10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, L.; Ventrillard, I.; Chau, G.; Jaulin, K.; Kerstel, E.; Romanini, D. Optical-feedback cavity-enhanced absorption spectroscopy with an interband cascade laser: Application to SO2 trace analysis. Appl. Phys. B 2016, 122, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianella, M.; Ritchie, G.A.D. Cavity-Enhanced Near-Infrared Laser Absorption Spectrometer for the Measurement of Acetonitrile in Breath. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6881–6889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morville, J.; Kassi, S.; Chenevier, M.; Romanini, D. Fast, low-noise, mode-by-mode, cavity-enhanced absorption spectroscopy by diode-laser self-locking. Appl. Phys. B 2005, 80, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanini, D.; Chenevier, M.; Kassi, S.; Schmidt, M.; Valant, C.; Ramonet, M.; Jost, H.J. Optical–feedback cavity–enhanced absorption: A compact spectrometer for real–time measurement of atmospheric methane. Appl. Phys. B 2006, 83, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowzan, G.; Lee, K.F.; Paradowska, M.; Borkowski, M.; Ablewski, P.; Wójtewicz, S.; Masłowski, P. Self-referenced, accurate and sensitive optical frequency comb spectroscopy with a virtually imaged phased array spectrometer. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, M.; Iwakuni, K.; Okubo, S.; Sasada, H. Design of cavity-enhanced absorption cell for reducing transit-time broadening. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 5277–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nation, M.; Wang, S.; Goldedstein, C.S.; Sun, K.; Davidson, D.F.; Jeffries, J.B.; Hanson, R.K. Shock-tube measurements of exciter oxygen atoms using cavity-enhanced absorption spectroscopy. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 8766–8775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyson, T.K.; Dagdigian, P.J.; Pavey, K.D.; FitzGerald, N.J.; Spence, T.G.; Moore, D.S.; Harb, C.C. Real-time multiplexed digital cavity-enhanced spectroscopy. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 4560–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, S.G.; Hancock, G.; Peverall, R.; Ritchie, G.A.; Leeuwen, N.J.V. Optical feedback cavity enhanced absorption spectroscopy with diode lasers. Analyst 2009, 134, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, P.S.; Lehmann, K.K. Cavity enhanced absorption spectroscopy using a broadband prism cavity and a supercontinuum source. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 15013–15023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.; Wu, T.; Wang, G.; Zhao, W.; Fertein, E.; Coeur, C.; Chen, W. Sensing atmospheric reactive species using light emitting diode by incoherent broadband cavity enhanced absorption spectroscopy. Opt. Express 2016, 24, A781–A790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, H.; Ropcke, J.; Helden, J.H.V.; Wiese, M.; Lang, N.; Macherius, U. Sensitive CH4 detection applying quantum cascade laser based optical feedback cavity-enhanced absorption spectroscopy. Opt. Express 2016, 24, A536–A543. [Google Scholar]
- Gianella, M.; Reuter, S.; Aguila, A.L.; Ritchie, G.A.D.; van Helden, J.P.H. Detection of HO2 in an atmospheric pressure plasma jet using optical feedback cavity-enhanced absorption spectroscopy. New J. Phys. 2016, 18, 113027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassi, S.; Campargue, A.; Mondelain, D.; Tran, H. High pressure Cavity Ring Down Spectroscopy: Application to the absorption continuum of CO2 near 1.7 µm. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 2015, 167, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xu, X.; Fang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Qian, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, P.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Huang, Y. Development of an incoherent broad-band cavity-enhanced aerosol extinction spectrometer and its application to measurement of aerosol optical hygroscopicity. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, E16–E22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherman, T.; Venables, D.S.; Vaughan, S.; Orphal, J.; Ruth, A.A. Incoherent broadband cavity-enhanced absorption spectroscopy in the near-ultraviolet: Application to HONO and NO2. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasyutich, V.L.; Canosa-Mas, C.E.; Pfrang, C.; Vaughan, S.; Wayne, R.P. Off-axis continuous-wave cavity-enhanced absorption spectroscopy of narrow-band and broadband absorbers using red diode lasers. Appl. Phys. B 2002, 75, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leen, J.B.; Yu, X.Y.; Gupta, M.; Baer, D.S.; Hubbe, J.M.; Kluzek, C.D.; Tomlinson, J.M.; Hubbell, M.R. Fast in situ airborne measurement of ammonia using a mid-infrared off-axis ICOS spectrometer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10446–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centeno, R.; Mandon, J.; Cristescu, S.M.; Axner, O.; Harren, F.J.M. External cavity diode laser-based detection of trace gases with NICE-OHMS using current modulation. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 6277–6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foltynowicz, A.; Schmidt, F.M.; Ma, W.; Axner, O. Noise-immune cavity-enhanced optical heterodyne molecular spectroscopy: Current status and future potential. Appl. Phys. B 2008, 92, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, E.D. An introduction to Pound–Drever–Hall laser frequency stabilization. Am. J. Phys. 2001, 69, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langridge, J.M.; Laurila, T.; Watt, R. S.; Jones, R.L.; Kaminski, C.F.; Hult, J. Cavity enhanced absorption spectroscopy of multiple trace gas species using a supercontinuum radiation source. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 10178–10188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cygan, A.; Lisak, D.; Masłowski, P.; Bielska, K.; Wojtewicz, S.; Domyslawska, J.; Trawinski, R.S.; Ciurylo, R.; Abe, H.; Hodges, J.T. Pound-Drever-Hall-locked, frequency-stabilized cavity ring-down spectrometer. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2011, 82, 063107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drever, R.; Hall, J.L.; Kowalski, F.; Hough, J.; Ford, G.; Munley, A.; Ward, H. Laser phase and frequency stabilization using an optical resonator. Appl. Phys. B 1983, 31, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Ye, W.; Sanchez, N.P.; Li, C.; Dong, L.; Wang, Y.; Griffin, R. J.; Tittel, F.K. Development and field deployment of a mid-infrared methane sensor without pressure control using interband cascade laser absorption spectroscopy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 244, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogelnik, H.; Li, T. Laser beams and resonators. Proc. IEEE 1966, 54, 1312–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothman, L.S.; Gordon, I.E.; Babikov, Y.; Barbe, A.; Benner, D.C.; Bernath, P.F.; Birk, M.; Bizzocchi, L.; Boudon, V.; Brown, L.R.; et al. The HITRAN2012 molecular spectroscopic database. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2013, 130, 4–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Q.; Lou, M.; Zheng, C.; Ye, W.; Wang, Y.; Tittel, F.K. Repetitively Mode-Locked Cavity-Enhanced Absorption Spectroscopy (RML-CEAS) for Near-Infrared Gas Sensing. Sensors 2017, 17, 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122792
He Q, Lou M, Zheng C, Ye W, Wang Y, Tittel FK. Repetitively Mode-Locked Cavity-Enhanced Absorption Spectroscopy (RML-CEAS) for Near-Infrared Gas Sensing. Sensors. 2017; 17(12):2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122792
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Qixin, Minhan Lou, Chuantao Zheng, Weilin Ye, Yiding Wang, and Frank K. Tittel. 2017. "Repetitively Mode-Locked Cavity-Enhanced Absorption Spectroscopy (RML-CEAS) for Near-Infrared Gas Sensing" Sensors 17, no. 12: 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122792
APA StyleHe, Q., Lou, M., Zheng, C., Ye, W., Wang, Y., & Tittel, F. K. (2017). Repetitively Mode-Locked Cavity-Enhanced Absorption Spectroscopy (RML-CEAS) for Near-Infrared Gas Sensing. Sensors, 17(12), 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122792






