Impedance-Based Living Cell Analysis for Clinical Diagnosis of Type I Allergy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Lines
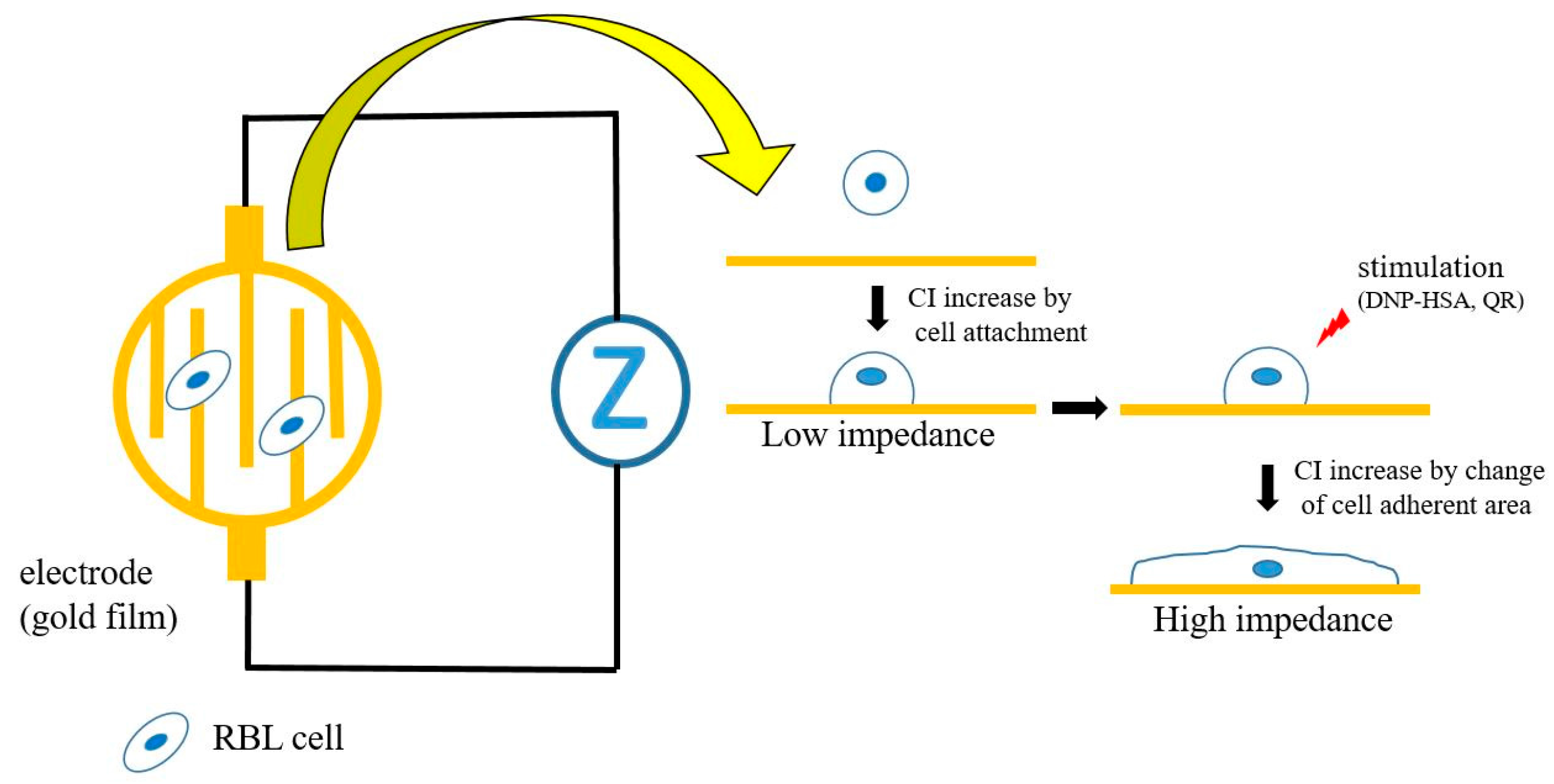
2.3. Impedance Measurement
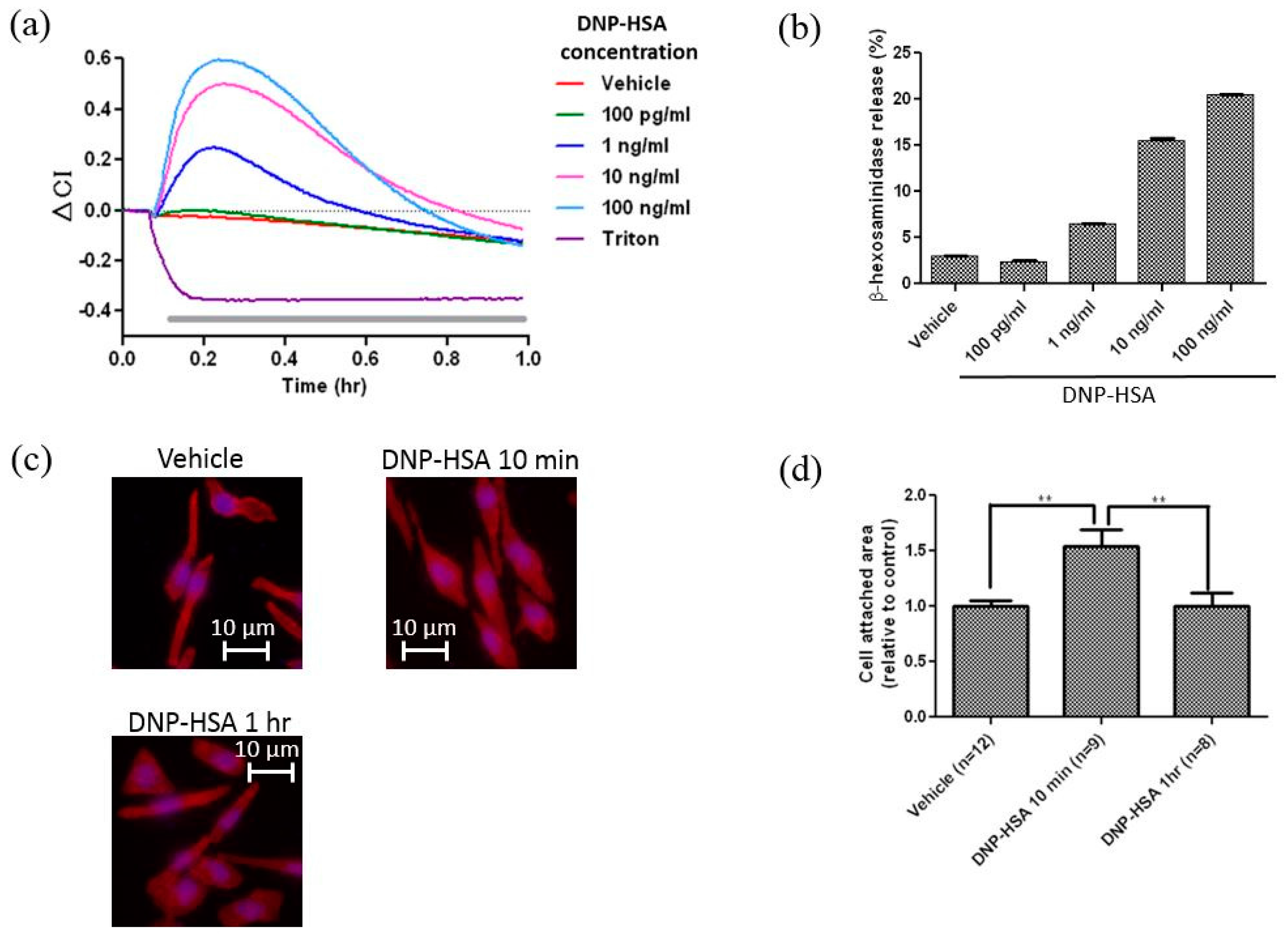
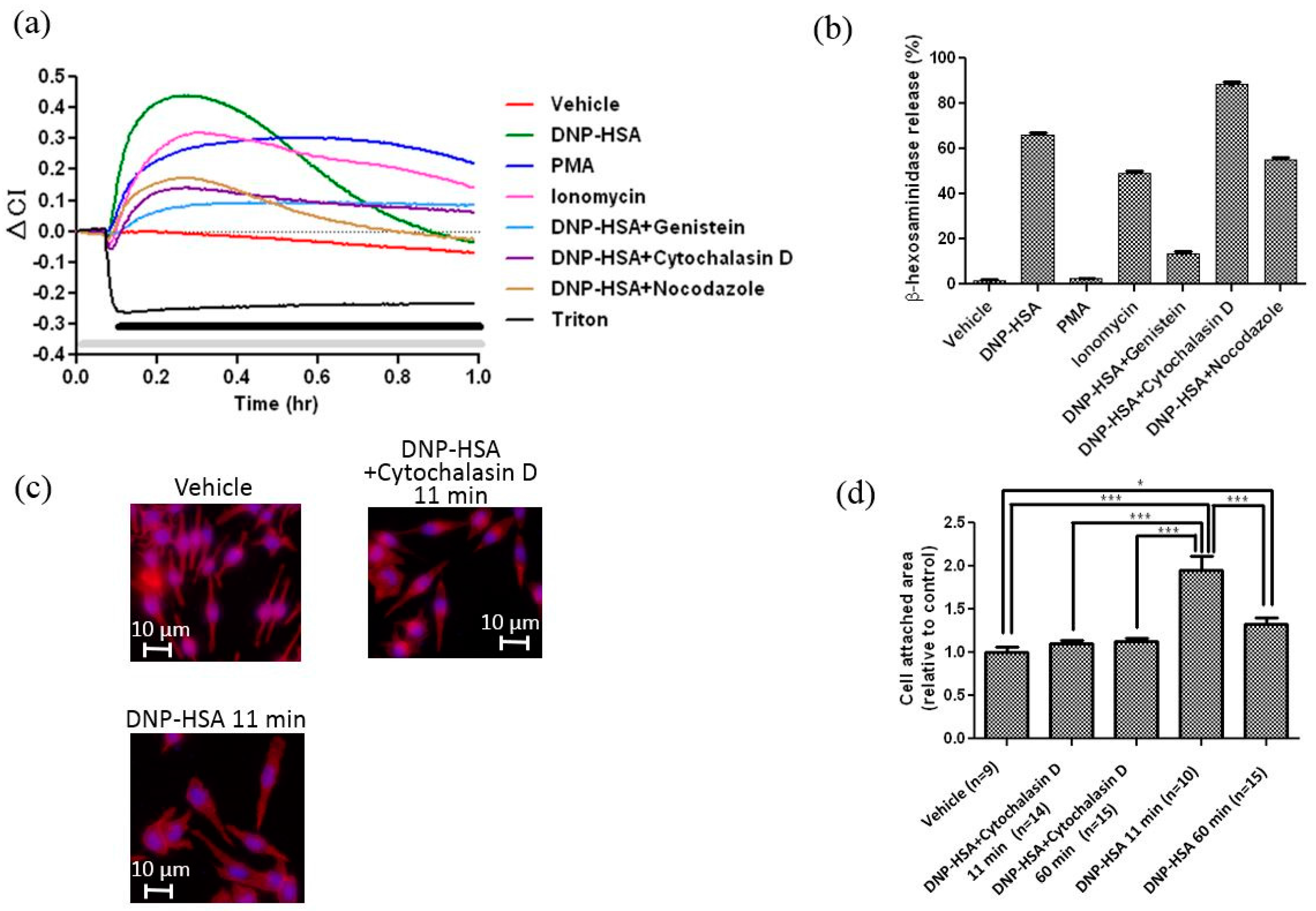
2.4. Assays of Mast Cell and Basophil Degranulations (Release of β–Hexosaminidase and Histamine)
2.5. Subjects
2.6. Actin Cytoskeleton and Nuclei Staining, and Calculation of the Area of Cell Attachment
2.7. Measurement of QR-Specific Antibodies
3. Results
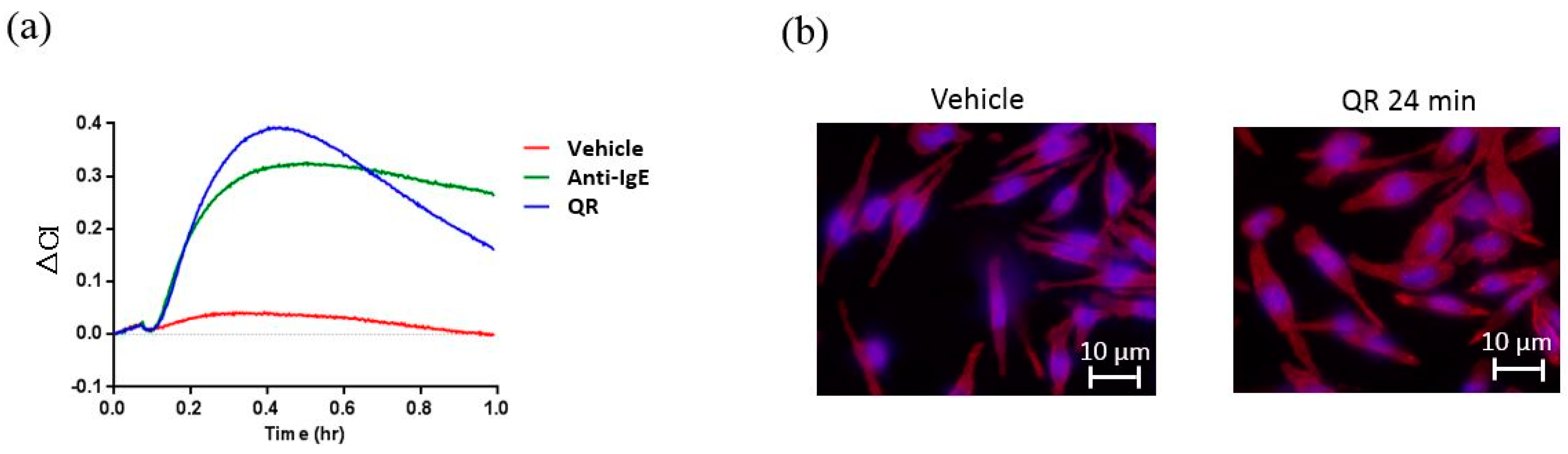
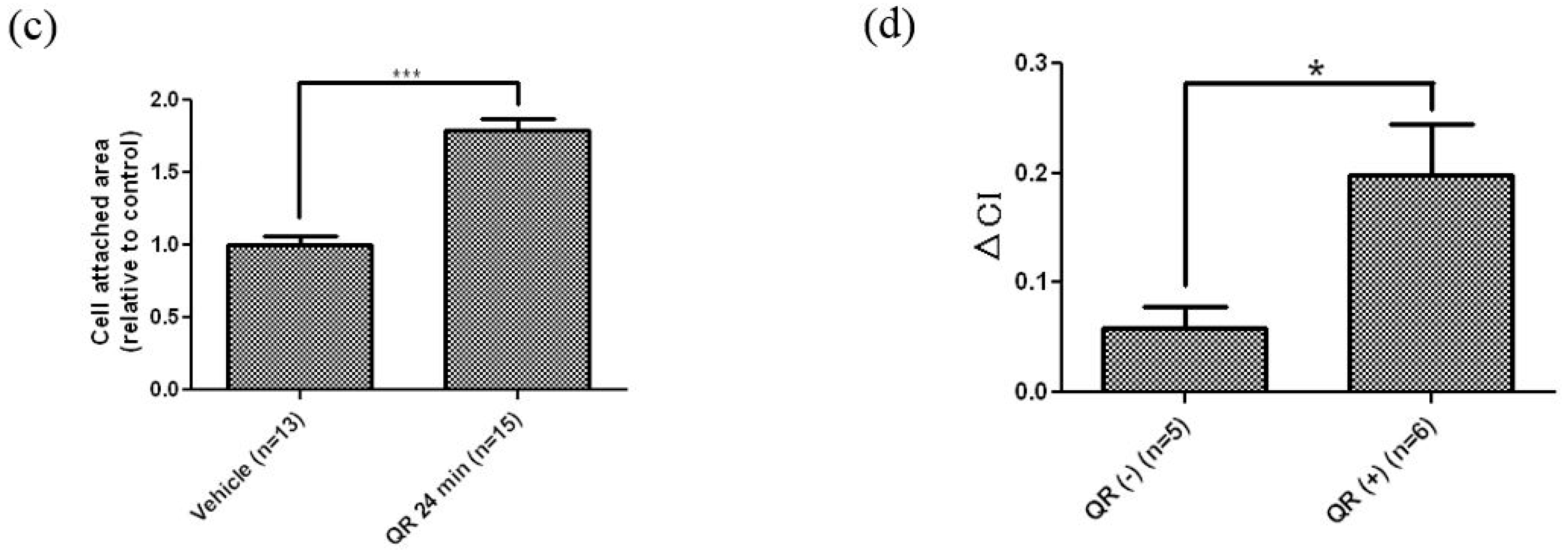
3.1. Real-Time and Label-Free Monitoring of Living Cell Activations by Means of Impedance Sensor
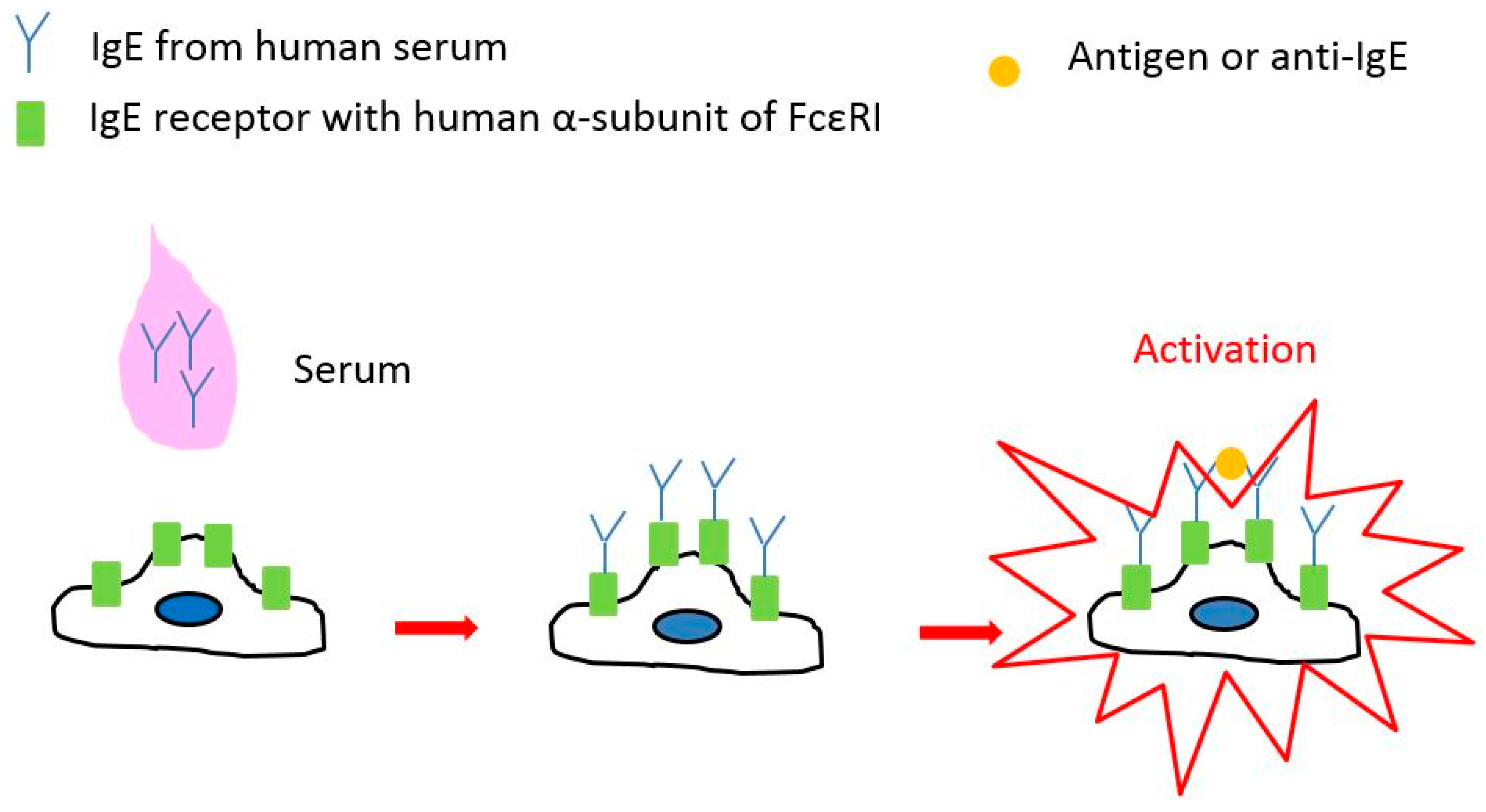
3.2. Clinical Diagnosis of Type I Allergy with Serum by Means of Impedance Sensor and RBL-48 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Statements
References
- Marx, K.A.; Zouh, T.; Montrone, A.; Schulze, H.; Braunhut, S.J. A quartz crystal microbalance cell biosensor: Detection of microtubule alterations in living cells at nM nocodazole concentrations. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitakis, M.; Gizeli, E. Acoutic sensors as a biophysical tool for probing cell attachment and cell/surface interactions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, T.; Miyahara, Y. Noninvasive monitoring of transporter-substrate interaction at cell membrane. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 1493–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanase, Y.; Hiragun, T.; Yanase, T.; Kawaguchi, T.; Ishii, K.; Kumazaki, N.; Obara, T.; Hide, M. Clinical diagnosis of type I allergy by means of SPR imaging with less than a microliter of peripheral blood. Sens. Biosens. Res. 2014, 2, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Ferrie, A.M.; Fontaine, N.H.; Yuen, P.K. Characteristics of dynamic mass redistribution of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in living cells measured with label-free optical biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 5720–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urcan, E.; Haertel, U.; Styllou, M.; Hickel, R.; Scherthan, H.; Reichl, F.X. Real-time xCELLigence impedance analysis of the cytotoxity of dental composite components on human gingival fibroblasts. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, N.; Deng, J.; Li, T.; Xu, X.; Irelan, J.T.; Wang, M.W. Label-free monitoring of T cell activation by the impedance-based xCELLigence system. Mol. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barni, S.; Fort, A.; Becatti, M.; Fiorillo, C.; Mugnaini, M.; Vignoli, V.; Addabbo, T.; Pucci, N.; Novembre, E. Detection of allergen-IgE interaction in allergic children through combined iimpedance and ROS measurements. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hide, M.; Yanase, Y.; Greaves, M.W. Cutaneous mast cell receptors. Dermatol. Clin. 2007, 25, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plebani, M. Clinical value and measurement of specific IgE. Clin. Biochem. 2003, 36, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gasse, A.L.; Mangodt, E.A.; Faber, M.; Sabato, V.; Bridts, C.H.; Ebo, D.G. Molecular allergy diagnosis: Status anno 2015. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 444, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahagi, S.; Tanaka, T.; Ishii, K.; Suzuki, H.; Kameyoshi, Y.; Shindo, H.; Hide, M. Sweat antigen induces histamine release from basophils of patients with cholinergic urticaria associated with atopic diathesis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 160, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGowan, E.C.; Saini, S. Update on the performance and application of basophil activation tests. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2013, 13, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griese, M.; Kusenbach, G.; Reinhardt, D. Histamine release test in comparison to standard tests in diagnosis of childhood allergic asthma. Ann. Allergy 1990, 65, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sturm, E.M.; Kranzelbinder, B.; Heinemann, A.; Groselj-Strele, A.; Aberer, W.; Sturm, G.J. CD203c-based basophil activation test in allergy diagnosis: Characteristics and differences to CD63 upregulation. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2010, 78, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codreanu, F.; Morisset, M.; Cordebar, V.; Kanny, G.; Moneret-Vautrin, D.A. Risk of allergy to food proteins in topical medicinal agents and cosmetics. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 38, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gilfillan, A.M.; Kado-Fong, H.; Wiggan, G.A.; Hakimi, J.; Kent, U.; Kochan, J.P. Conservation of signal transduction mechanisms via the human Fc epsilon RI alpha after transfection into a rat mast cell line, RBL 2H3. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 2445–2451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yanase, Y.; Hide, I.; Mihara, S.; Shirai, Y.; Saito, N.; Nakata, Y.; Hide, M.; Sakai, N. A critical role of conventional protein kinase C in morphological changes of rodent mast cells. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2011, 89, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, A.; Tanaka, T.; Suzuki, H.; Ishii, K.; Kameyoshi, Y.; Hide, M. Semi-purification of the immunoglobulin E-sweat antigen acting on mast cells and basophils in atopic dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2006, 15, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, K.; Hiragun, M.; Hiragun, T.; Kan, T.; Kawaguchi, T.; Yanase, Y.; Tanaka, A.; Takahagi, S.; Hide, M. A human monoclonal IgE antibody that binds to MGL_1304, a major allergen in human sweat, without activation of mast cells and basophils. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuspa, S.H.; Hawley-Nelson, P.; Koehler, B.; Stanley, J.R. A Survey of Transformation Markers in Differentiating Epidermal Cell Lines in Culture. Cancer Res. 1980, 40, 4694–4703. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hiragun, T.; Ishii, K.; Hiragun, M.; Suzuki, H.; Kan, T.; Mihara, S.; Yanase, Y.; Bartels, J.; Schröder, J.M.; Hide, M. Fungal protein MGL_1304 in sweat is an allergen for atopic dermatitis patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hide, M.; Tsutsui, T.; Sato, H.; Nishimura, T.; Morimoto, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Yoshizato, K. Real-time analysis of ligand-induced cell surface and intracellular reactions of living mast cells using a surface plasmon resonance-based biosensor. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 302, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanase, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Tsutsui, T.; Hiragun, T.; Kameyoshi, Y.; Hide, M. The SPR signal in living cells reflects changes other than the area of adhesion and the formation of cell constructions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Yanase, Y.; Tsutsui, T.; Ishii, K.; Hiragun, T.; Hide, M. Applying surface plasmon resonance to monitor the IgE-mediated activation of human basophils. Allergol. Int. 2008, 57, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanase, Y.; Hiragun, T.; Kaneko, S.; Gould, H.J.; Greaves, M.W.; Hide, M. Detection of refractive index changes in individual living cells by means of surface plasmon resonance imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanase, Y.; Hiragun, T.; Yanase, T.; Kawaguchi, T.; Ishii, K.; Hide, M. Evaluation of peripheral blood basophil activation by means of surface plasmon resonance imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 32, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanase, Y.; Hiragun, T.; Ishii, K.; Kawaguchi, T.; Yanase, T.; Kawai, M.; Sakamoto, K.; Hide, M. Surface plasmon resonance for cell-based clinical diagnosis. Sensors 2014, 14, 4948–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanase, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Hide, M. Diagnosis of immediate-type allergy using surface plasmon resonance. Opt. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Subjects | Age | Sex | Reaction to QR (Histamine Release Test) | Reaction to QR (β-hexosaminidase Assay) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donor 1 | 22 | M | Positive | Positive |
| Donor 2 | 25 | F | Positive | Positive |
| Donor 3 | 15 | M | Positive | Positive |
| Donor 4 | 22 | M | Positive | Positive |
| Donor 5 | 56 | F | Positive | Positive |
| Donor 6 | 37 | F | Positive | Positive |
| Donor 7 | 19 | F | Negative | Negative |
| Donor 8 | 27 | F | Negative | Negative |
| Donor 9 | 44 | F | Negative | Negative |
| Donor 10 | 30 | M | Negative | Negative |
| Donor 11 | 50 | M | Negative | Negative |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Irifuku, R.; Yanase, Y.; Kawaguchi, T.; Ishii, K.; Takahagi, S.; Hide, M. Impedance-Based Living Cell Analysis for Clinical Diagnosis of Type I Allergy. Sensors 2017, 17, 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112503
Irifuku R, Yanase Y, Kawaguchi T, Ishii K, Takahagi S, Hide M. Impedance-Based Living Cell Analysis for Clinical Diagnosis of Type I Allergy. Sensors. 2017; 17(11):2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112503
Chicago/Turabian StyleIrifuku, Reiko, Yuhki Yanase, Tomoko Kawaguchi, Kaori Ishii, Shunsuke Takahagi, and Michihiro Hide. 2017. "Impedance-Based Living Cell Analysis for Clinical Diagnosis of Type I Allergy" Sensors 17, no. 11: 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112503
APA StyleIrifuku, R., Yanase, Y., Kawaguchi, T., Ishii, K., Takahagi, S., & Hide, M. (2017). Impedance-Based Living Cell Analysis for Clinical Diagnosis of Type I Allergy. Sensors, 17(11), 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112503





