A Novel Semi-Supervised Method of Electronic Nose for Indoor Pollution Detection Trained by M-S4VMs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- (2)
- (3)
2. E-Nose System and Experiments
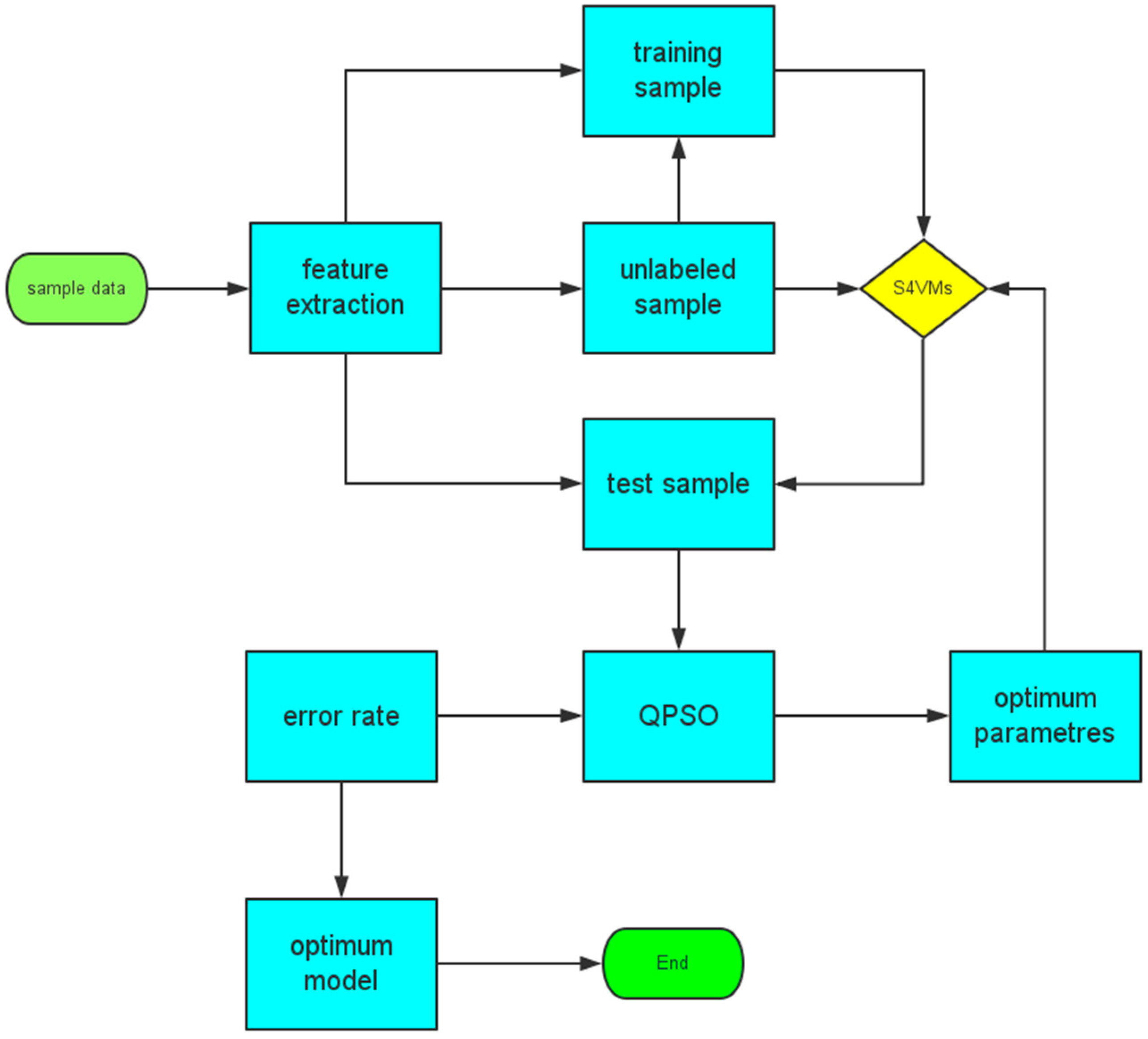
3. M-S4VMs Technique
3.1. S4VMs
3.2. Multi-Classifier Strategy
- (1)
- Winner-takes-all strategy SVM (WTA-SVM): this method needs M binary classifiers. Suppose the function is the output of the i-th classifier trained by the examples which comes from . divides the samples into two groups, in which the single type examples are the positive class and all other types are the negative class. Then, the positive class will be removed as one class, and the remaining part will repeat the classification and remove steps until all samples have been classified into their group, which often needs M times to classify as well as M binary classifiers.
- (2)
- Max-wins voting strategy SVM (MWV-SVM): This method requires constructing binary classifiers in which each binary classifier corresponds to every pair of distinct classes. Assuming that a binary classifier is , it is trained by the negative and positive samples taken from sample data . When there is a new sample x, will determine if this sample belongs to class , and the vote for class will add or decrease by one according to the result of . After each of the binary classifiers finishes its voting, MWV will allocate x to the class based on the side having the largest number of votes.
3.3. M-S4VMs Technique
| Algorithm 1 (M-S4VMs algorithm): |
|
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ciosek, P.; Wróblewski, W. The analysis of sensor array data with various pattern recognition techniques. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 114, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhuang, S.; Zhang, F. Impedance sensing and molecular modeling of an olfactory biosensor based on chemosensory proteins of honeybee. Biosensor. Bioelectron. 2012, 40, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, J.H.; Hudson, N.; Gallagher, E.; Dunlop, M.; Zeller, L.; Atzeni, M. Implementation of an electronic nose for continuous odor monitoring in a poultry shed. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 133, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameer, Q.; Adeloju, S.B. Polypyrrole-based electronic noses for environmental and industrial analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 106, 541–552. [Google Scholar]
- Lamagna, A.; Reich, S.; Rodríguez, D.; Boselli, A.; Cicerone, D. The use of an electronic nose to characterize emissions from a highly polluted river. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 131, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loutfi, A.; Coradeschi, S.; Mani, G.K.; Shankar, P.; Rayappan, J.B. Electronic noses for food quality: A review. J. Food Eng. 2015, 144, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbi, E.; Falasconi, M.; Zambotti, G.; Sberveglieri, V.; Pulvirenti, A.; Sberveglieri, G. Rapid diagnosis of Enterobacteriaceae, in vegetable soups by a metal oxide sensor based electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, G.; Wang, L.; Mo, Y.; Zhang, L. Study of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) quality predictive model based on electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 166–167, 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, A.; Stam, F.; Morrissey, A.; Hirschfelder, M.; Enderlein, D. Packaging effects of a novel explosion-proof gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 95, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, G.C.; Chan, A.C.; Dan, H.; Lin, M. Using a metal oxide sensor (MOS)-based electronic nose for discrimination of bacteria based on individual colonies in suspension. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 152, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, E.A.; Thomas, P.S.; Stone, E.; Lewis, C.; Yates, D.H. A breath test for malignant mesothelioma using an electronic nose. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 448–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, P.; Tian, F.; He, Q.; Fan, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.X. Feature extraction of wound infection data for electronic nose based on a novel weighted KPCA. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 201, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, A.; Di, N.C.; Falconi, C.; Martinelli, E.; Paolesse, R.; Pennazza, G. Detection and identification of cancers by the electronic nose. Expert Opin. Med. Diagn. 2012, 6, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.C.; Buttner, W.J.; Linnell, B.R.; Ramesham, R. Electronic nose for space program applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 93, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tian, F.; Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Hu, B.; Ye, Q. Chaos based neural network optimization for concentration estimation of indoor air contaminants by an electronic nose. Sens. Actuat. A Phys. 2013, 189, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tian, F.; Peng, X.; Dang, L.; Li, G.; Liu, S. Standardization of metal oxide sensor array using artificial neural networks through experimental design. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 177, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Pandey, R.A.; Jana, A. Application of electronic nose for industrial odors and gaseous emissions measurement and monitoring-An overview. Talanta 2015, 144, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khulal, U.; Zhao, J.; Hu, W.; Chen, Q. Intelligent evaluation of total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) content in chicken meat by an improved multiple level data fusion model. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Hu, W.; Su, J.; Li, H.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhao, J. Nondestructively sensing of total viable count (TVC) in chicken using an artificial olfaction system based colorimetric sensor array. J. Food Eng. 2015, 168, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Ren, W.; Huang, L. Geoherbalism evaluation of Radix Angelica sinensis, based on electronic nose. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 105, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Xiao, H.; Liu, M. Quality grade identification of green tea using the eigenvalues of PCA based on the E-nose signals. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 140, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.W.; Boilot, P.; Hines, E.L. Enhancing electronic nose performance by sensor selection using a new integer-based genetic algorithm approach. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 106, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Khan, N.S.; Mondal, S.; Tudu, B.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Bhattacharyya, N. Features extraction from electronic nose employing genetic algorithm for black tea quality estimation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Electronic Systems, Pinani, India, 21–23 September 2013; pp. 64–67.
- Jiang, M.J.; Liu, Y.X.; Yang, J.X.; Yu, W.J. A model of classification for e-nose based on genetic algorithm. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 475-476, 952–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosov, A.V. An Introduction to Support Vector Machines; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, J. A fast algorithm for training support vector machines. J. Inf. Technol. 1998, 2, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Haugen, J.E.; Kvaal, K. Electronic nose and artificial neural network. Meat Sci. 1998, 49, S273–S286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.K.; Kwon, C.H.; Kim, S.R.; Yun, D.H.; Lee, K.; Sung, Y.K. Portable electronic nose system with gas sensor array and artificial neural network. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 66, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boser, B.E.; Guyon, I.M.; Vapnik, V.N. A training algorithm for optimal margin classifiers. In Proceedings of the 5th Annual ACM Workshop on Computational Learning Theory, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 27–29 July 1992; pp. 144–152.
- Vapnik, V.N. Statistical Learning Theory. Encycl. Sci. Learn. 2010, 41, 3185–3185. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, J.C.; Cristianini, N.; Shawe-Taylor, J. Large margin DAGs for multiclass classification. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2010, 12, 547–553. [Google Scholar]
- Dietterich, T.G.; Bakiri, G. Solving multiclass learning problems via error-correcting output codes. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 1995, 2, 263–286. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Tian, F.; Feng, J.; Jia, P.; He, Q.; Shen, Y. A PSO-SVM Method for parameters and sensor array optimization in wound infection detection based on electronic nose. J. Comput. 2012, 7, 2663–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Yan, J.; Shen, Y.; Bi, Y.; Ye, G.; Tian, F.; Wang, Z. Classification of Electronic Nose Data in Wound Infection Detection Based on PSO-SVM Combined with Wavelet Transform. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2012, 18, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J. Hybrid feature matrix construction and feature selection optimization-based multi-objective QPSO for electronic nose in wound infection detection. Sensor Rev. 2016, 36, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Tian, F.; Fan, S.; He, Q.; Feng, J.; Yang, S.X. A novel sensor array and classifier optimization method of electronic nose based on enhanced quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization. Sensor Rev. 2014, 34, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Huang, T.; Duan, S.; Ge, L.; Yan, J.; Wang, L. A novel semi-supervised electronic nose learning technique: M-Training. Sensors 2016, 16, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Active Learning Literature Survey. Available online: http://s3.amazonaws.com/academia.edu.documents/30743174/settles_active_learning.pdf?AWSAccessKeyId=AKIAJ56TQJRTWSMTNPEA&Expires=1473420623&Signature=1HWPhuu2akUY9WNJyKgQ6e0aR7c%3D&response-content-disposition=inline%3B%20filename%3DActive_learning_literature_survey.pdf (accessed on 9 September 2016).
- Schohn, G.; Cohn, D. Less is more: Active learning with support vector machines. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–21 June 2013; pp. 839–846.
- Pan, S.J.; Yang, Q. A Survey on Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2010, 22, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; King, I.; Lyu, M.R. Multi-task Learning for one-class classification. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Barcelona, Spain, 18–23 July 2010; pp. 1–8.
- Yang, H.; Lyu, M.R.; King, I. Efficient online learning for multitask feature selection. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data. 2013, 7, 1693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.H.; Li, M. Semi-supervised learning by disagreement. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2010, 24, 415–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; King, I. Introduction to semi-supervised learning. Synth. Lect. Artif. Intell. Mach. Learn. 2009, 3, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.H. Towards making unlabeled data never hurt. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, S. Optimization by simulated annealing: Quantitative studies. J. Stat. Phys. 1984, 34, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černý, V. Thermodynamical approach to the traveling salesman problem: An efficient simulation algorithm. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1985, 45, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hajek, B. A tutorial survey of theory and applications of simulated annealing. In Proceedings of the 24th IEEE Conference on Decision & Control, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 11–13 December 1985; pp. 755–760.
- Sindhwani, V.; Keerthi, S.S.; Chapelle, O. Deterministic annealing for semi-supervised kernel machines. In Proceedings of the 23th International Conference on Machine Learning, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 25–29 June 2006; pp. 841–848.
- Duan, K.B.; Keerthi, S.S. Which is the best multiclass SVM method? An empirical study. Multi. Classif. Syst. 2005, 3541, 278–285. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, P.; Duan, S.; Yan, J. An enhanced quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization based on a novel computing way of local attractor. Information 2015, 6, 633–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Kwok, J.T.; Zhou, Z.H. Semi-supervised learning using label mean. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–18 June 2009; pp. 633–640.
- Goldman, S.A.; Zhou, Y. Enhancing supervised learning with unlabeled data. In Proceedings of the Seventeenth International Conference on Machine Learning, Stanford, CA, USA, 29 June–2 July 2000; pp. 327–334.
- Angluin, D.; Laird, P. Learning from noisy examples. Mach. Learn. 1988, 2, 343–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semi-Supervised Regression Using Spectral Techniques. Available online: https://www.ideals.illinois.edu-/bitstream/handle/2142/11232/SemiSupervised%20Regression%20using%20Spectral%20Techniques.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y (accessed on 8 September 2016).
- Cai, D.; He, X.; Han, J. Spectral regression: A unified subspace learning framework for content-based image retrieval. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia 2007, Augsburg, Germany, 24–29 September 2007; pp. 455–482.

| Gases | Concentration Range (ppm) |
|---|---|
| Carbon monoxide | [4, 12] |
| Toluene | [0.0668, 0.1425] |
| Formaldehyde | [0.0565, 1.2856] |
| Gases | Training Set | Unlabeled Set | Test Set |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon monoxide | 116 | 116 | 116 |
| Toluene | 132 | 132 | 132 |
| Formaldehyde | 253 | 253 | 253 |
| All-3 | 501 | 501 | 501 |
| Gases | Training Set | Unlabeled Set | Test Set |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon monoxide | 58 | 174 | 116 |
| Toluene | 66 | 198 | 132 |
| Formaldehyde | 126 | 380 | 253 |
| All-3 | 250 | 752 | 501 |
| Gases | Training Set | Unlabeled Set | Test Set |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon monoxide | 174 | 58 | 116 |
| Toluene | 198 | 66 | 132 |
| Formaldehyde | 380 | 126 | 253 |
| All-3 | 752 | 250 | 501 |
| Min | Max | Average | |
|---|---|---|---|
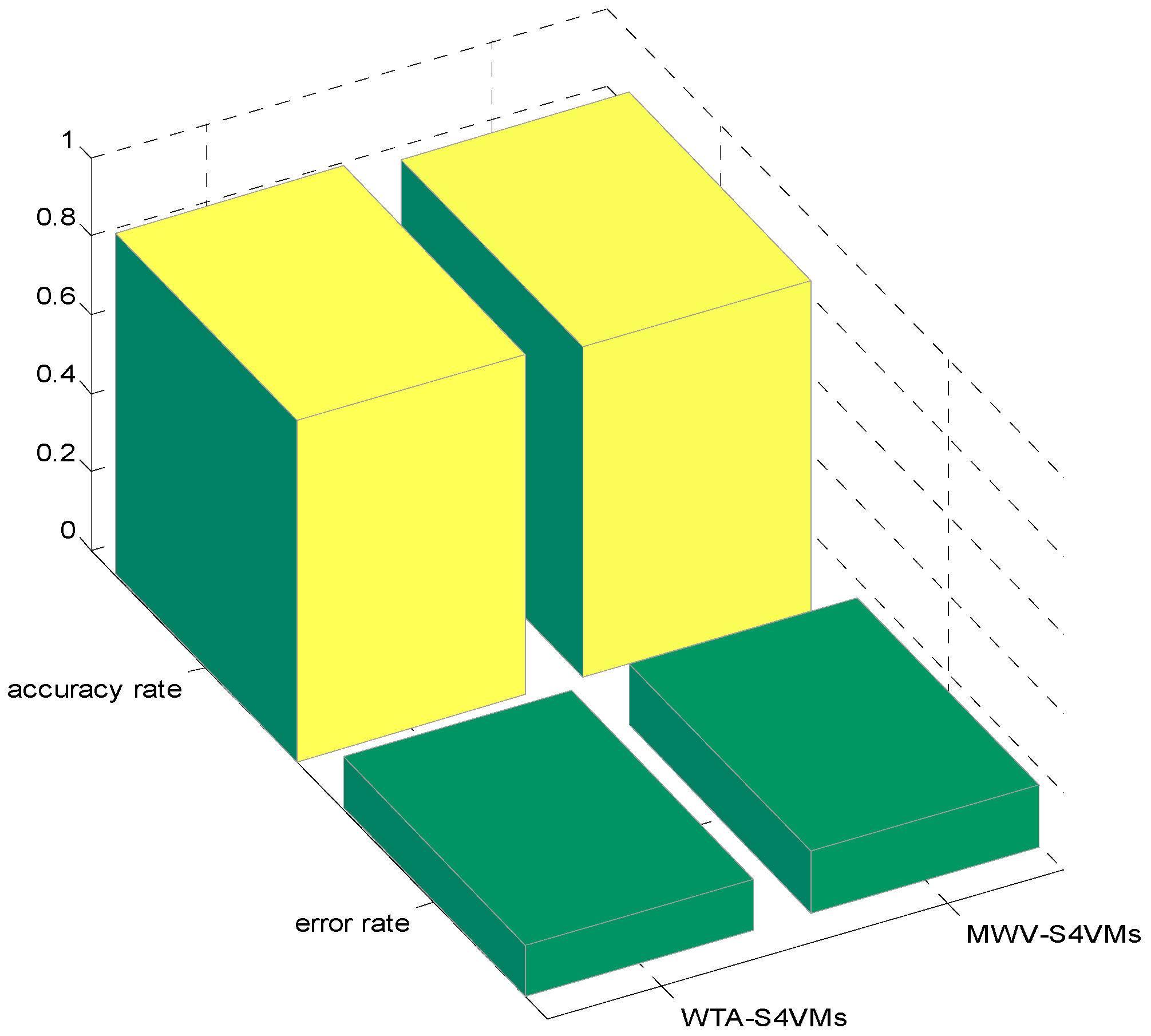
| WTA-S4VMs | 0.8524 | 0.8724 | 0.8692 |
| MWV-S4VMs | 0.8276 | 0.8678 | 0.8438 |
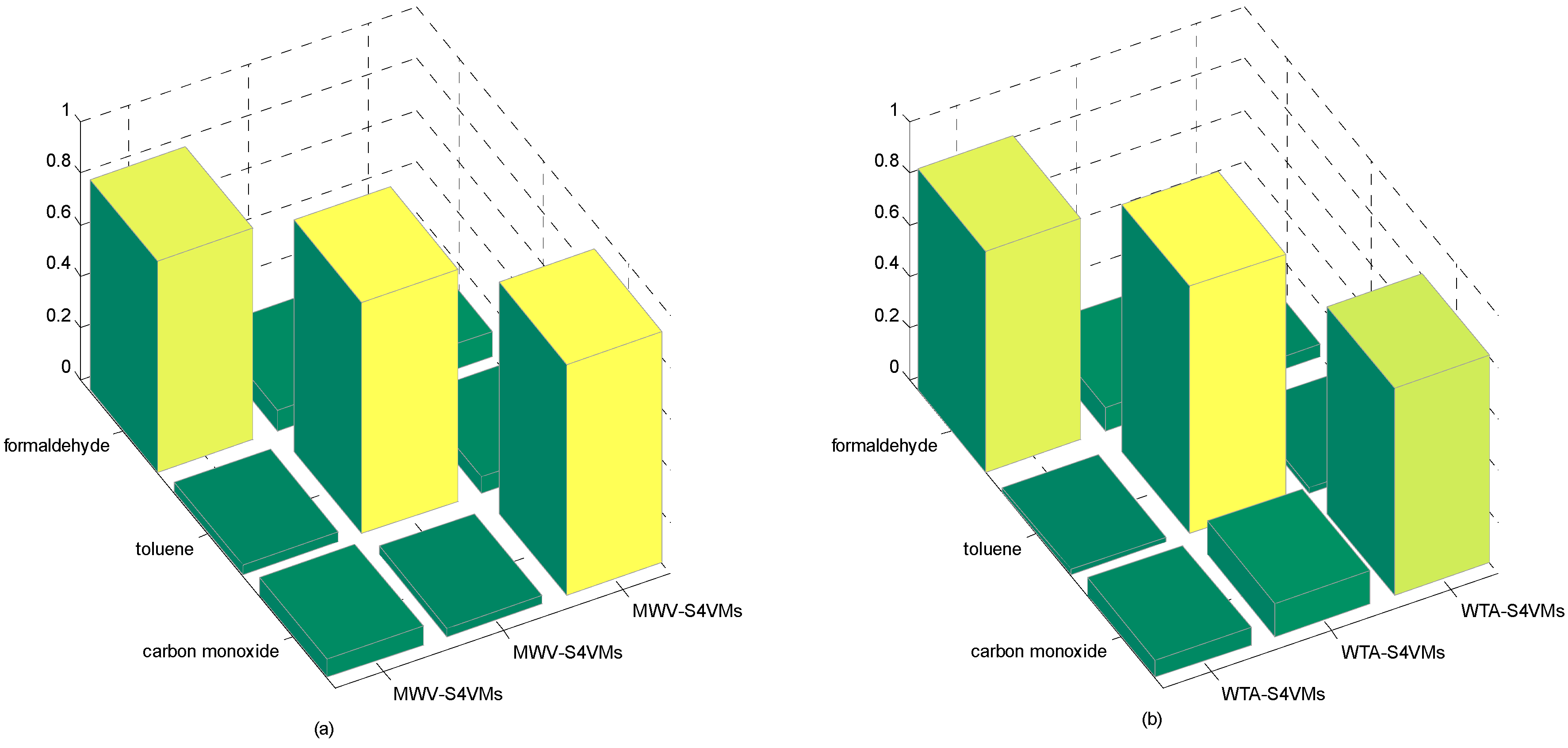
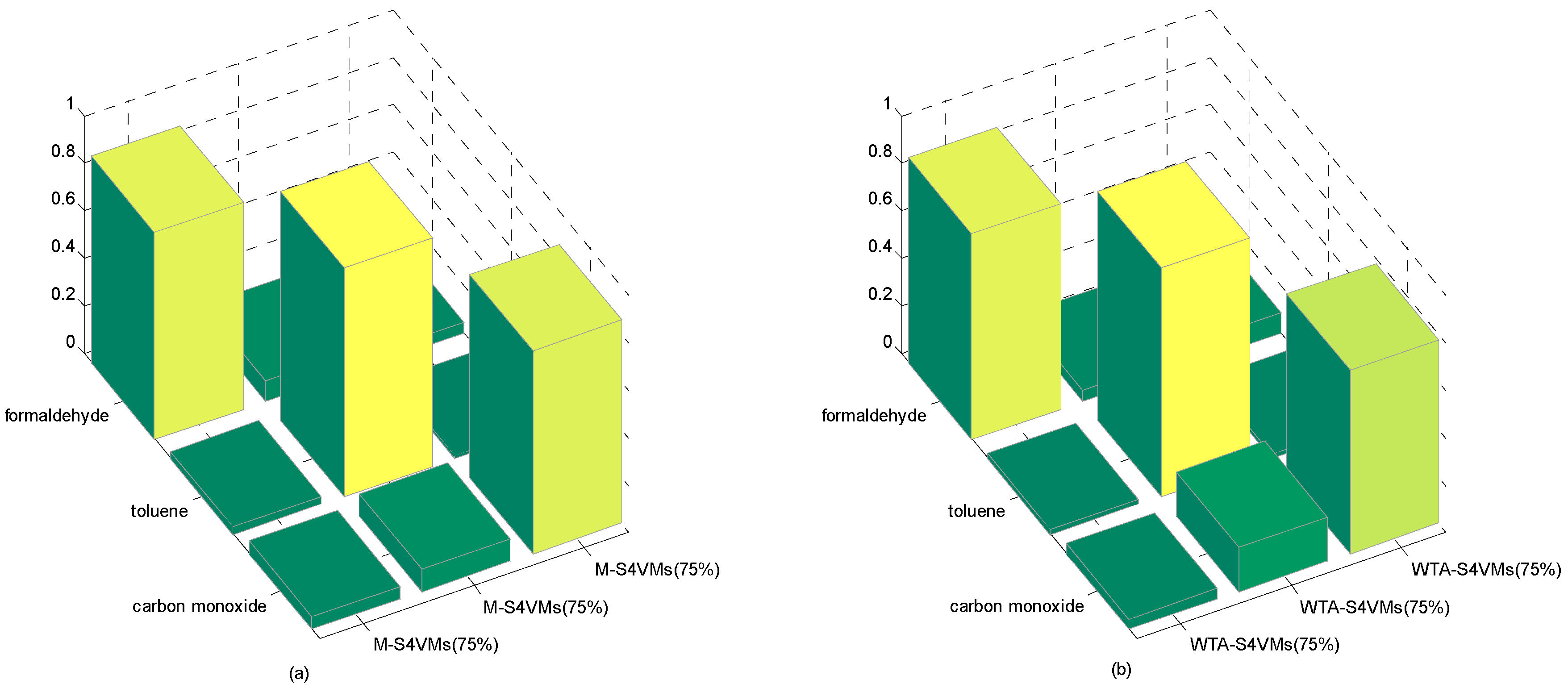
| Formaldehyde | Toluene | Carbon Monoxide | |
|---|---|---|---|
| WTA-S4VMs | 0.8575 | 0.9599 | 0.8049 |
| MWV-S4VMs | 0.8176 | 0.8998 | 0.8978 |
| Min | Max | Average | Improvement | Unlabeled Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WTA-S4VMs | 0.8424 | 0.8724 | 0.8592 | 5% | 50% |
| M-S4VMs | 0.8972 | 0.9140 | 0.9002 | ||
| WTA-S4VMs | 0.8324 | 0.8679 | 0.8579 | 3% | 25% |
| M-S4VMs | 0.8772 | 0.9070 | 0.8895 | ||
| WTA-S4VMs | 0.8324 | 0.8624 | 0.8592 | 3% | 75% |
| M-S4VMs | 0.8872 | 0.9143 | 0.8867 |
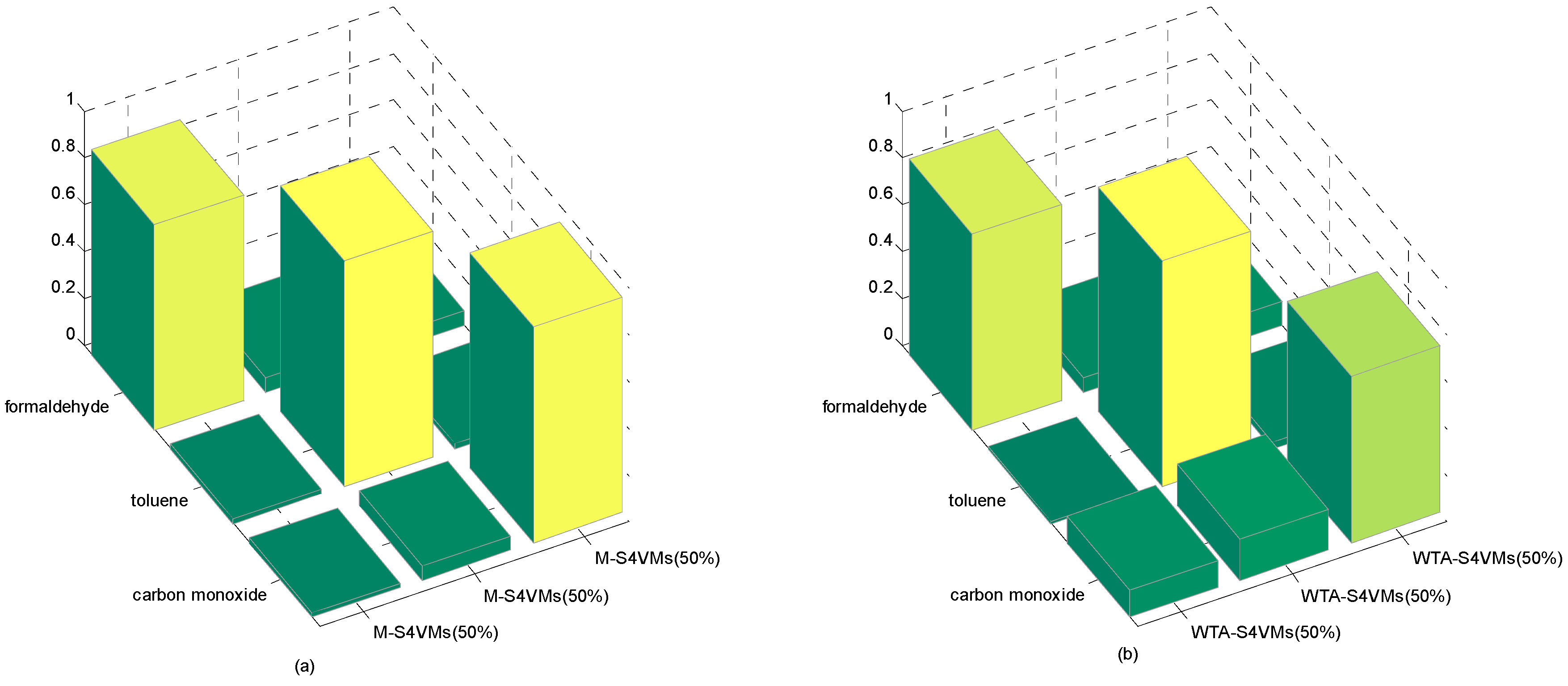
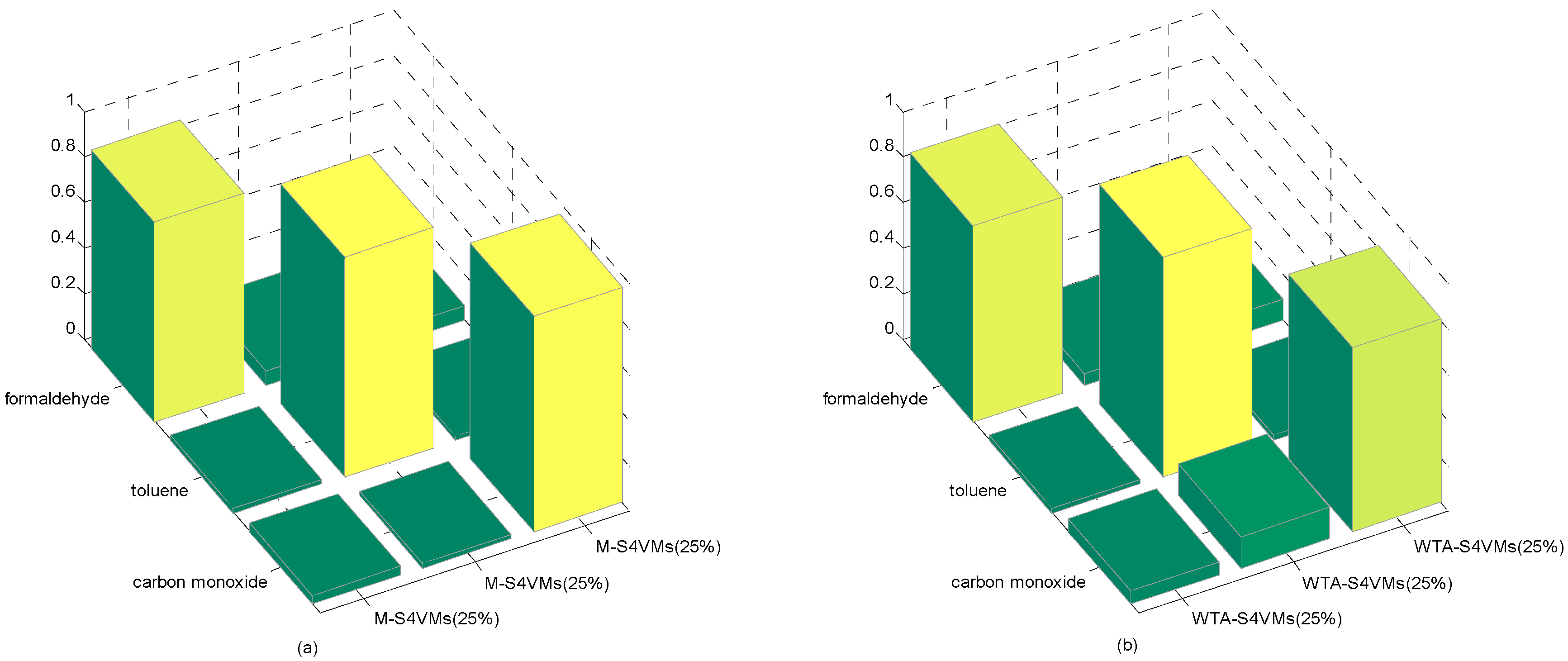
| Formaldehyde | Toluene | Carbon Monoxide | Unlabeled Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WTA-S4VMs | 0.8343 | 0.9588 | 0.7104 | 50% |
| M-S4VMs | 0.8742 | 0.9599 | 0.9188 | |
| WTA-S4VMs | 0.8575 | 0.9599 | 0.8049 | 25% |
| M-S4VMs | 0.8739 | 0.9639 | 0.9438 | |
| WTA-S4VMs | 0.8636 | 0.9602 | 0.7722 | 75% |
| M-S4VMs | 0.8687 | 0.9599 | 0.8537 |
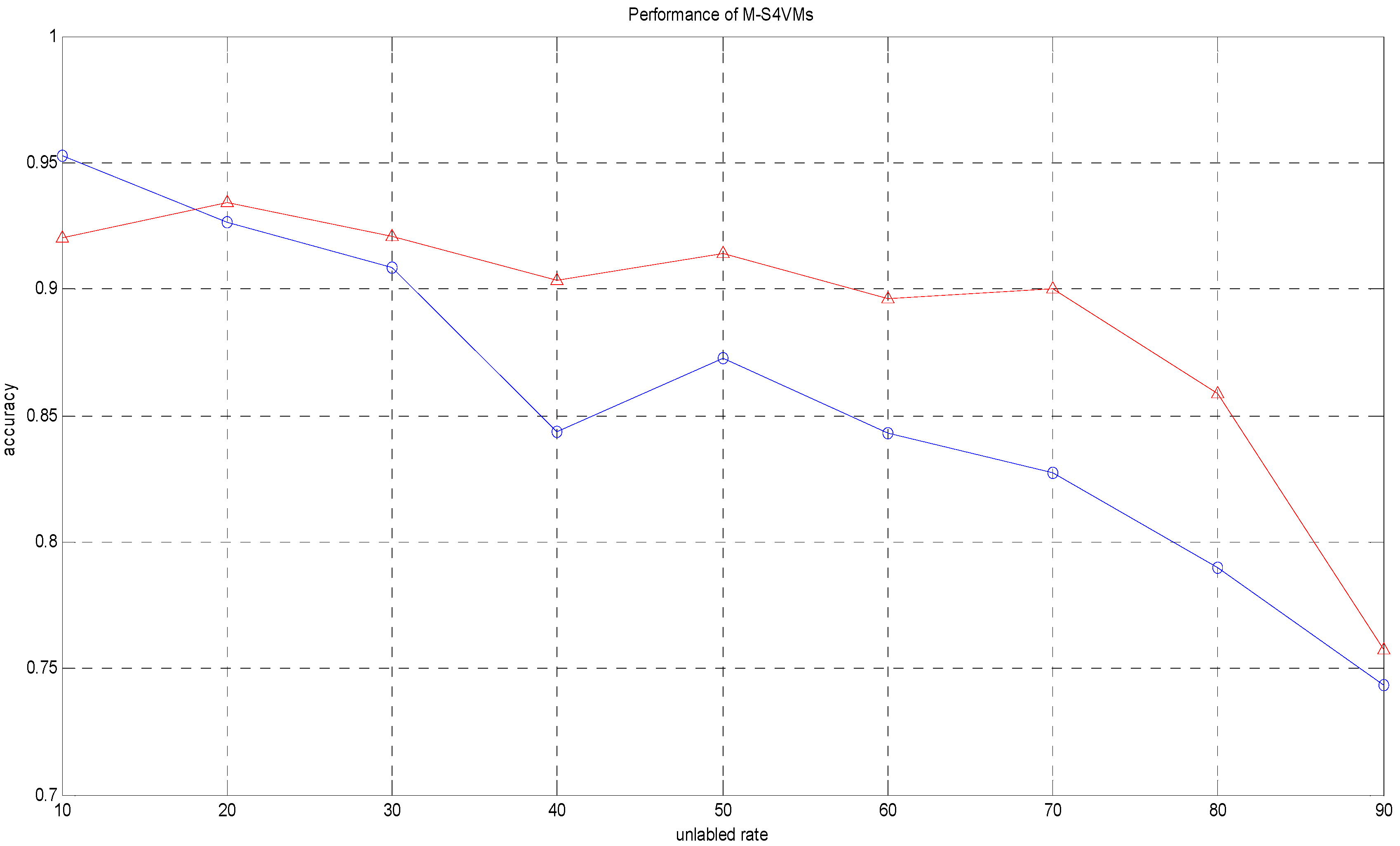
| Unlabeled Rate | Accuracy1 | Accuracy2 |
|---|---|---|
| 10% | 0.9527 | 0.9200 |
| 20% | 0.9262 | 0.9343 |
| 30% | 0.9086 | 0.9210 |
| 40% | 0.8438 | 0.9037 |
| 50% | 0.8728 | 0.9140 |
| 60% | 0.8430 | 0.8960 |
| 70% | 0.8271 | 0.8999 |
| 80% | 0.7896 | 0.8589 |
| 90% | 0.7435 | 0.7576 |
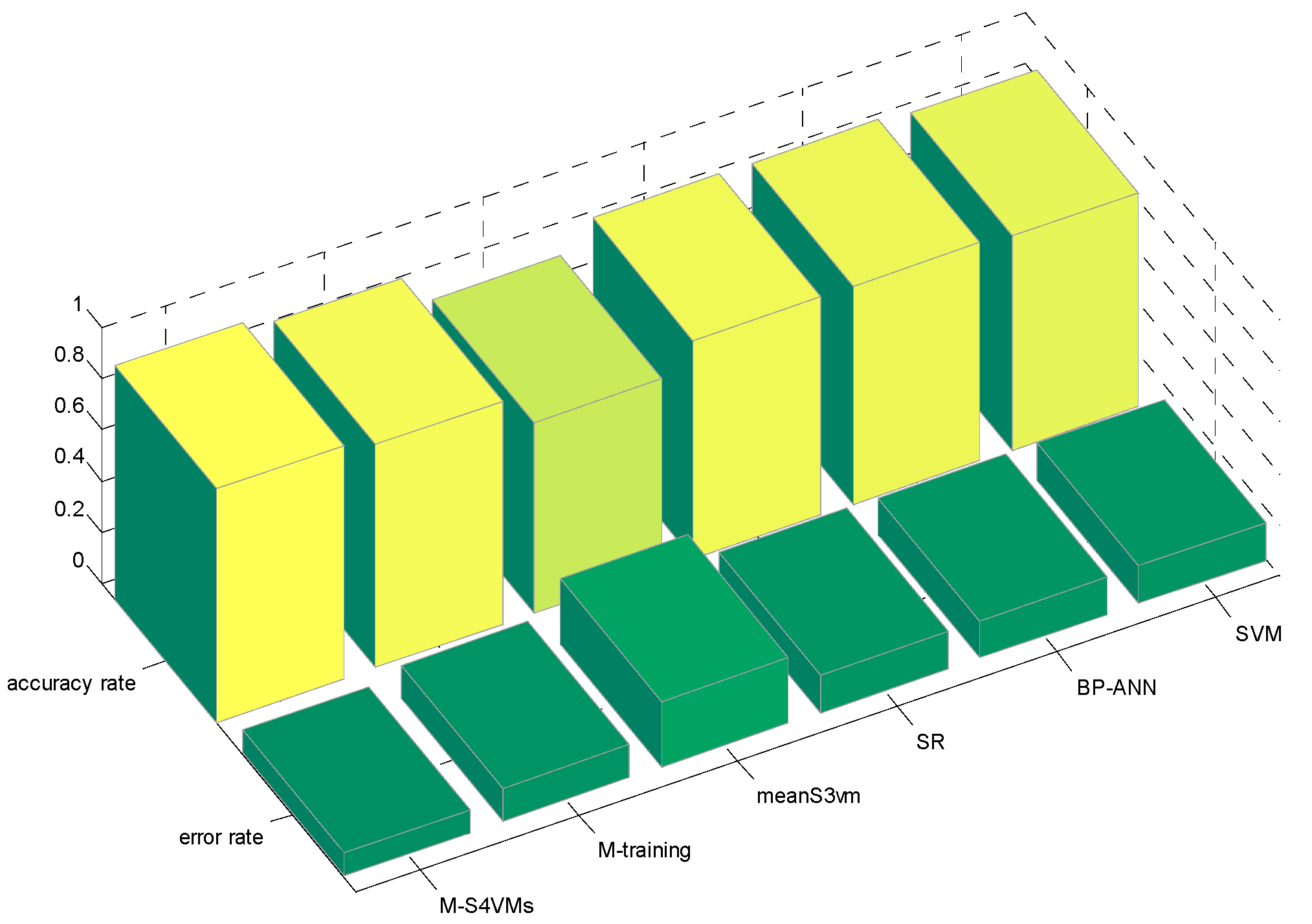
| Min | Max | Average | |
|---|---|---|---|
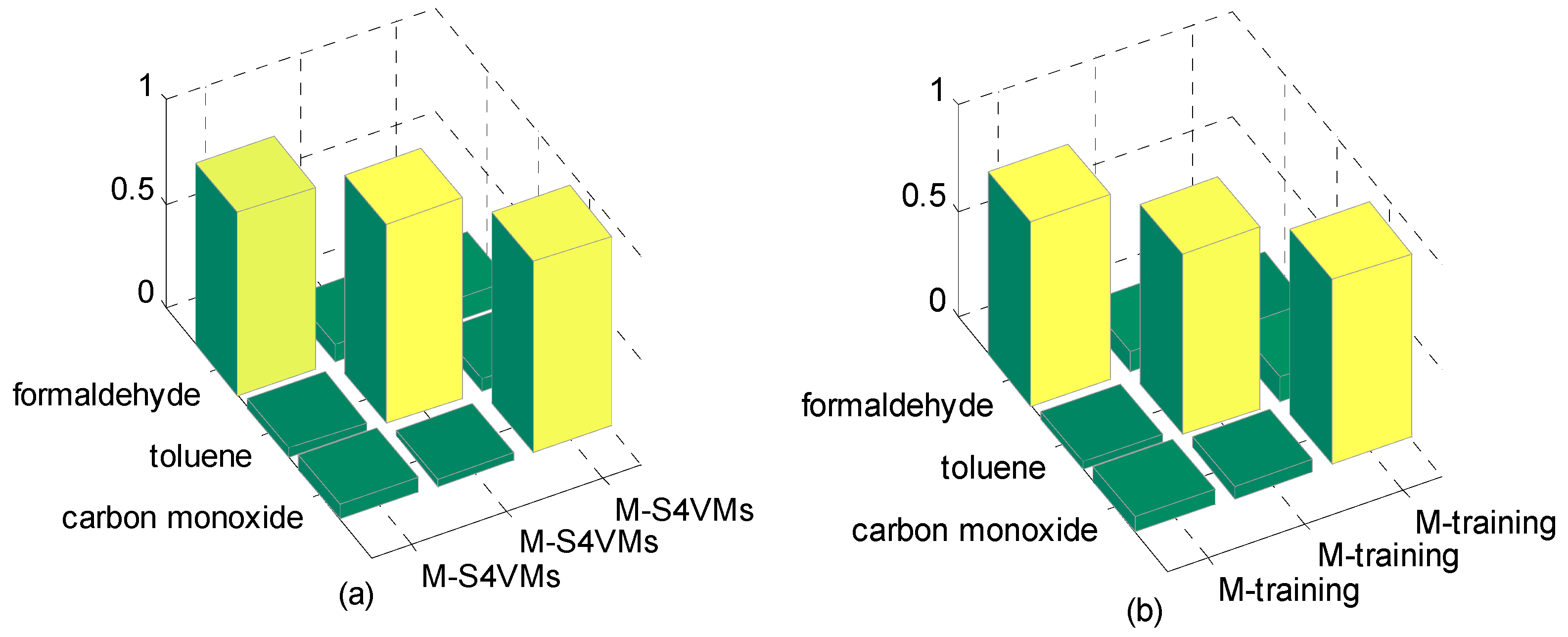
| M-S4VMs | 0.8967 | 0.9166 | 0.9102 |
| M-training | 0.8633 | 0.8755 | 0.8702 |
| meanS3vm | 0.7354 | 0.7632 | 0.7448 |
| SR | 0.8437 | 0.8637 | 0.8535 |
| BP-ANN | 0.8425 | 0.8764 | 0.8525 |
| SVM | 0.8430 | 0.8258 | 0.8335 |
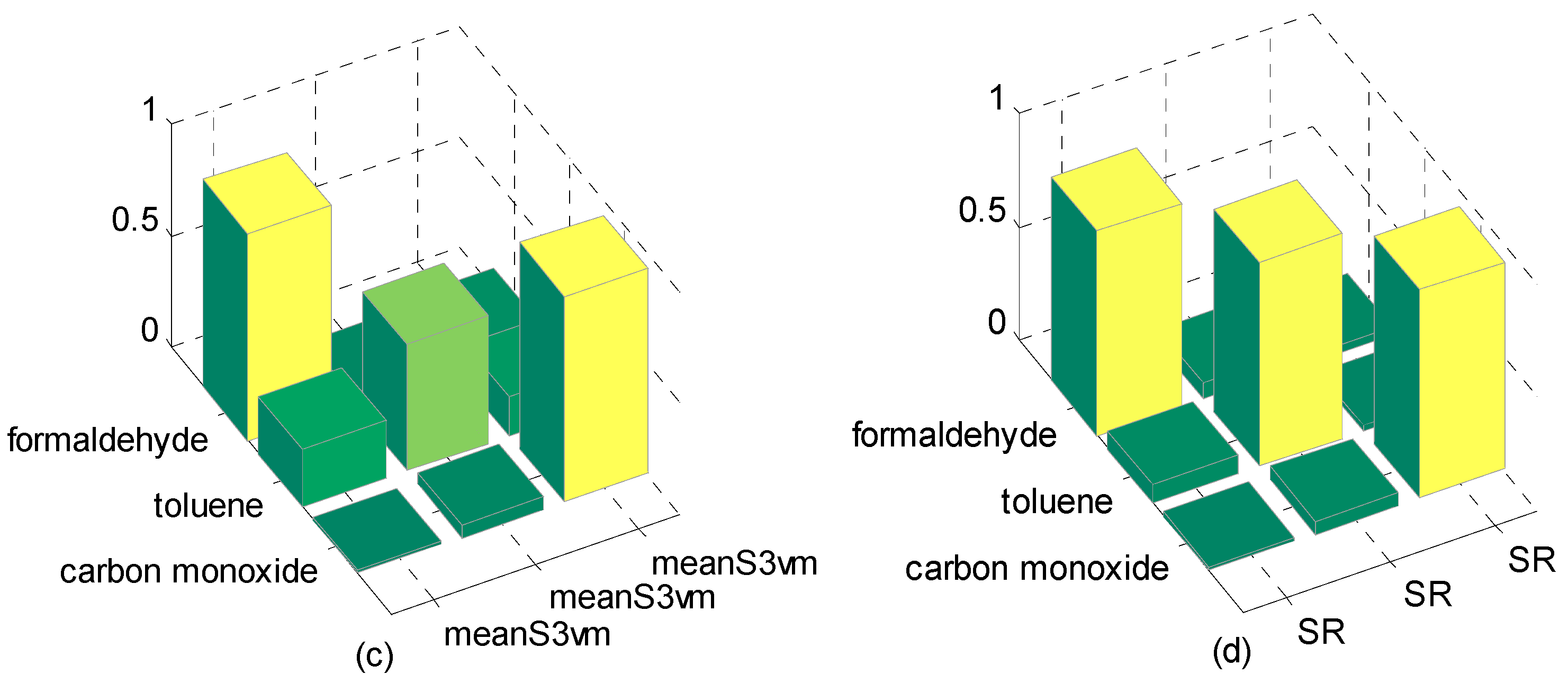
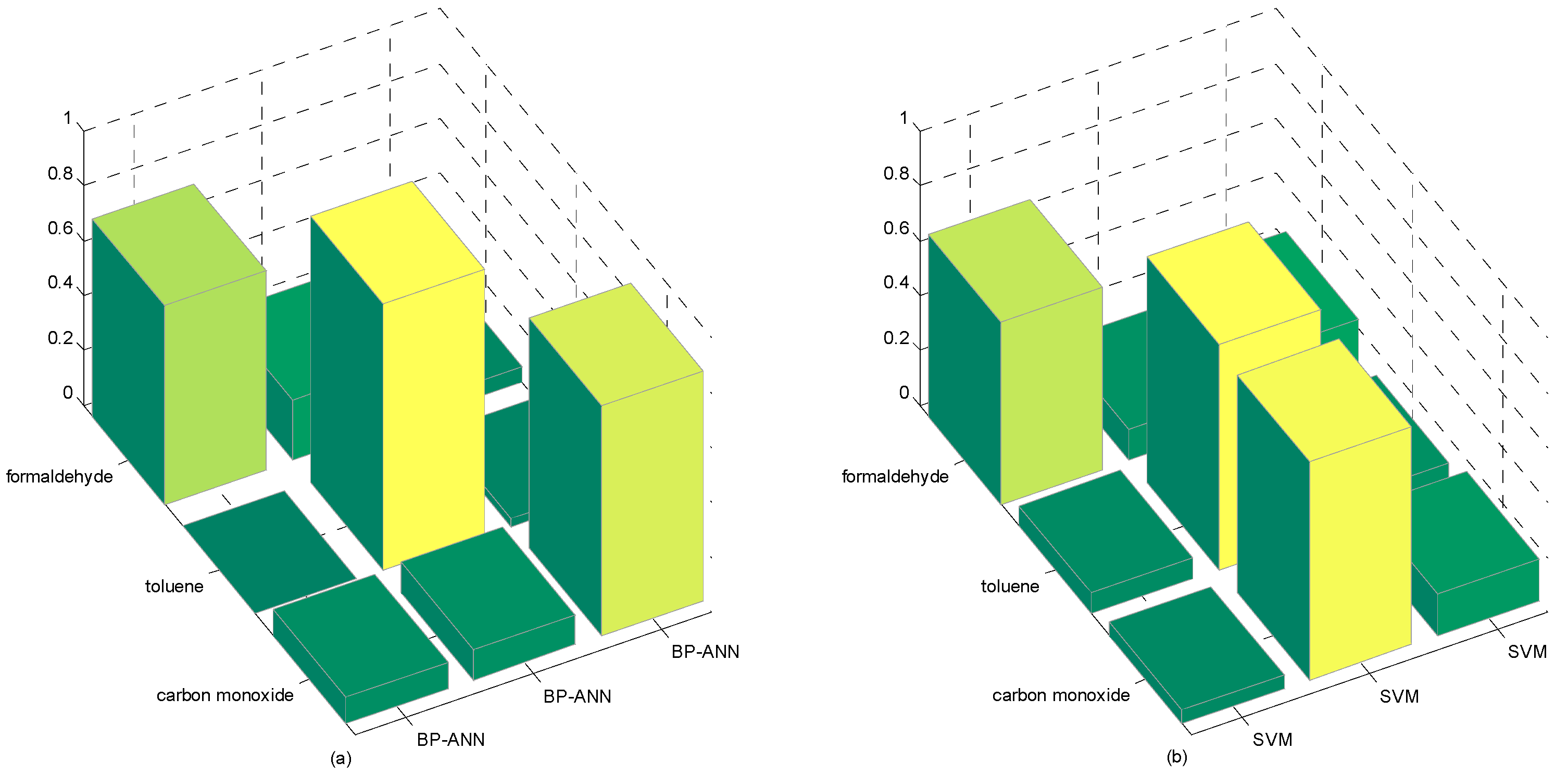
| Formaldehyde | Toluene | Carbon Monoxide | |
|---|---|---|---|
| M-S4VMs | 0.8742 | 0.9599 | 0.9188 |
| M-training | 0.8687 | 0.8555 | 0.8733 |
| meanS3vm | 0.9317 | 0.5682 | 0.9277 |
| SR | 0.8998 | 0.8988 | 0.9188 |
| BP-ANN | 0.7222 | 0.9697 | 0.8412 |
| SVM | 0.6652 | 0.8223 | 0.7932 |
| Running Time (s) | |
|---|---|
| M-S4VMs | 35.410543 |
| M-training | 48.008512 |
| meanS3vm | 179.690567 |
| SR | 21.677869 |
| BP-ANN | 18.648126 |
| SVM | 42.281541 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, T.; Jia, P.; He, P.; Duan, S.; Yan, J.; Wang, L. A Novel Semi-Supervised Method of Electronic Nose for Indoor Pollution Detection Trained by M-S4VMs. Sensors 2016, 16, 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091462
Huang T, Jia P, He P, Duan S, Yan J, Wang L. A Novel Semi-Supervised Method of Electronic Nose for Indoor Pollution Detection Trained by M-S4VMs. Sensors. 2016; 16(9):1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091462
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Tailai, Pengfei Jia, Peilin He, Shukai Duan, Jia Yan, and Lidan Wang. 2016. "A Novel Semi-Supervised Method of Electronic Nose for Indoor Pollution Detection Trained by M-S4VMs" Sensors 16, no. 9: 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091462
APA StyleHuang, T., Jia, P., He, P., Duan, S., Yan, J., & Wang, L. (2016). A Novel Semi-Supervised Method of Electronic Nose for Indoor Pollution Detection Trained by M-S4VMs. Sensors, 16(9), 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091462









