Wearable Sensors for eLearning of Manual Tasks: Using Forearm EMG in Hand Hygiene Training
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
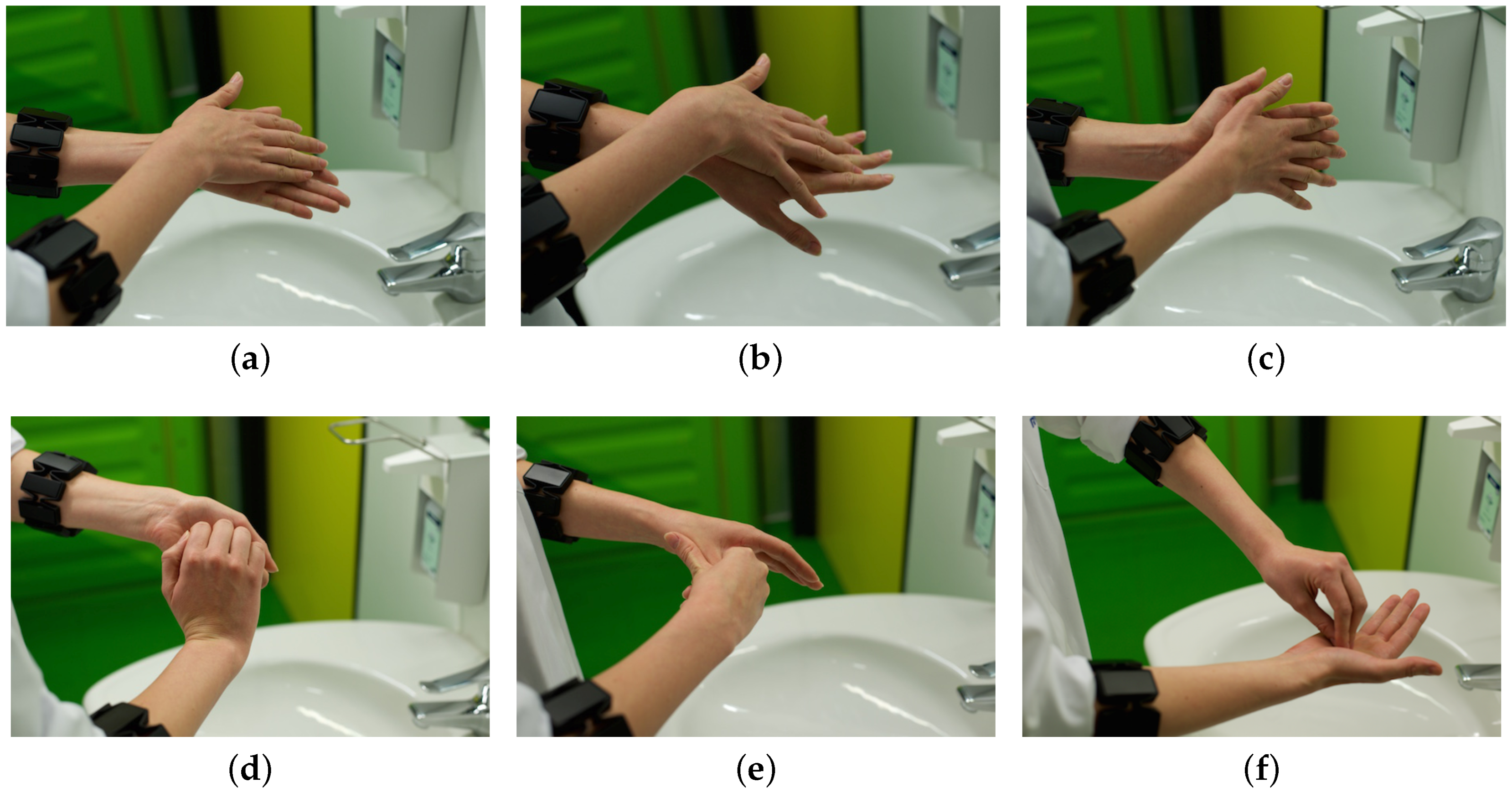
2.1. The WHO Standard
2.2. EMG Armband
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Pre-Processing and Feature Extraction
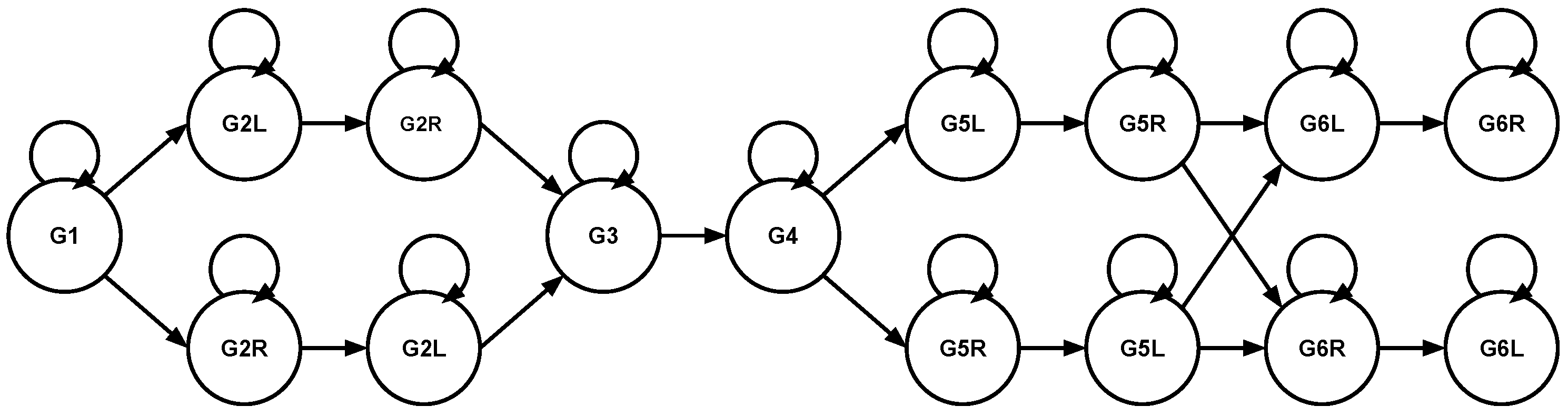
2.4.2. Classification
2.4.3. Post-Processing
2.5. The Software Employed
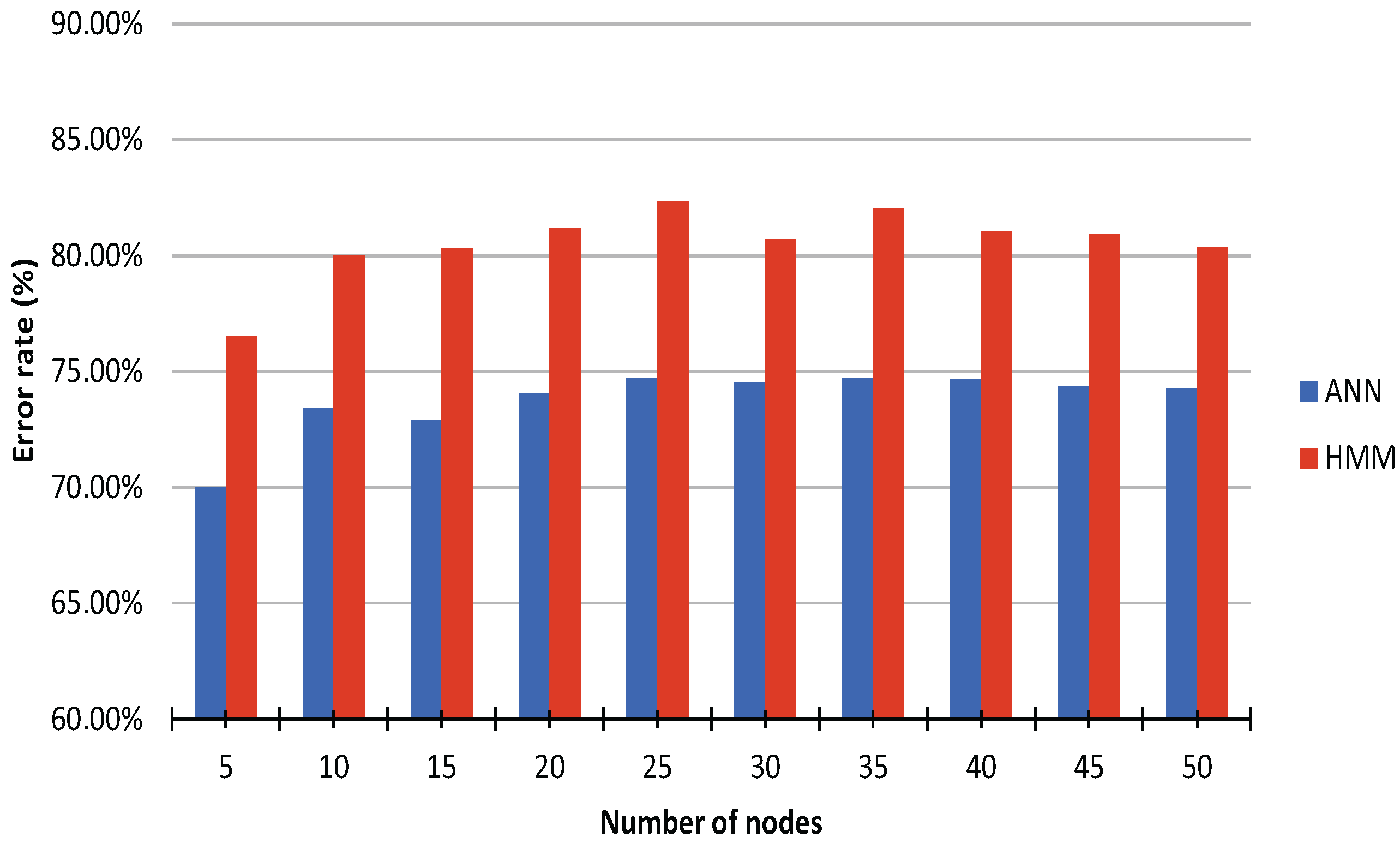
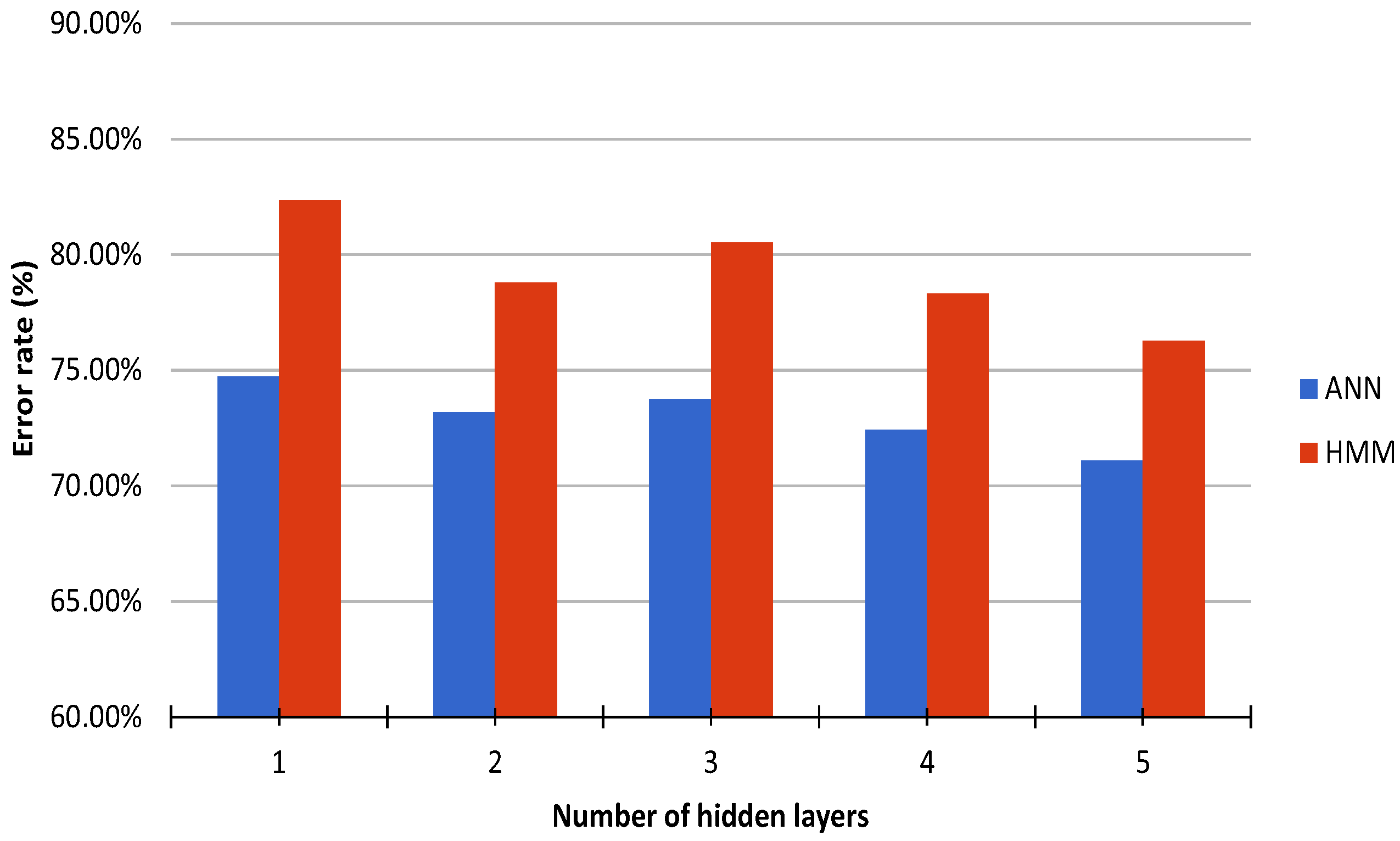
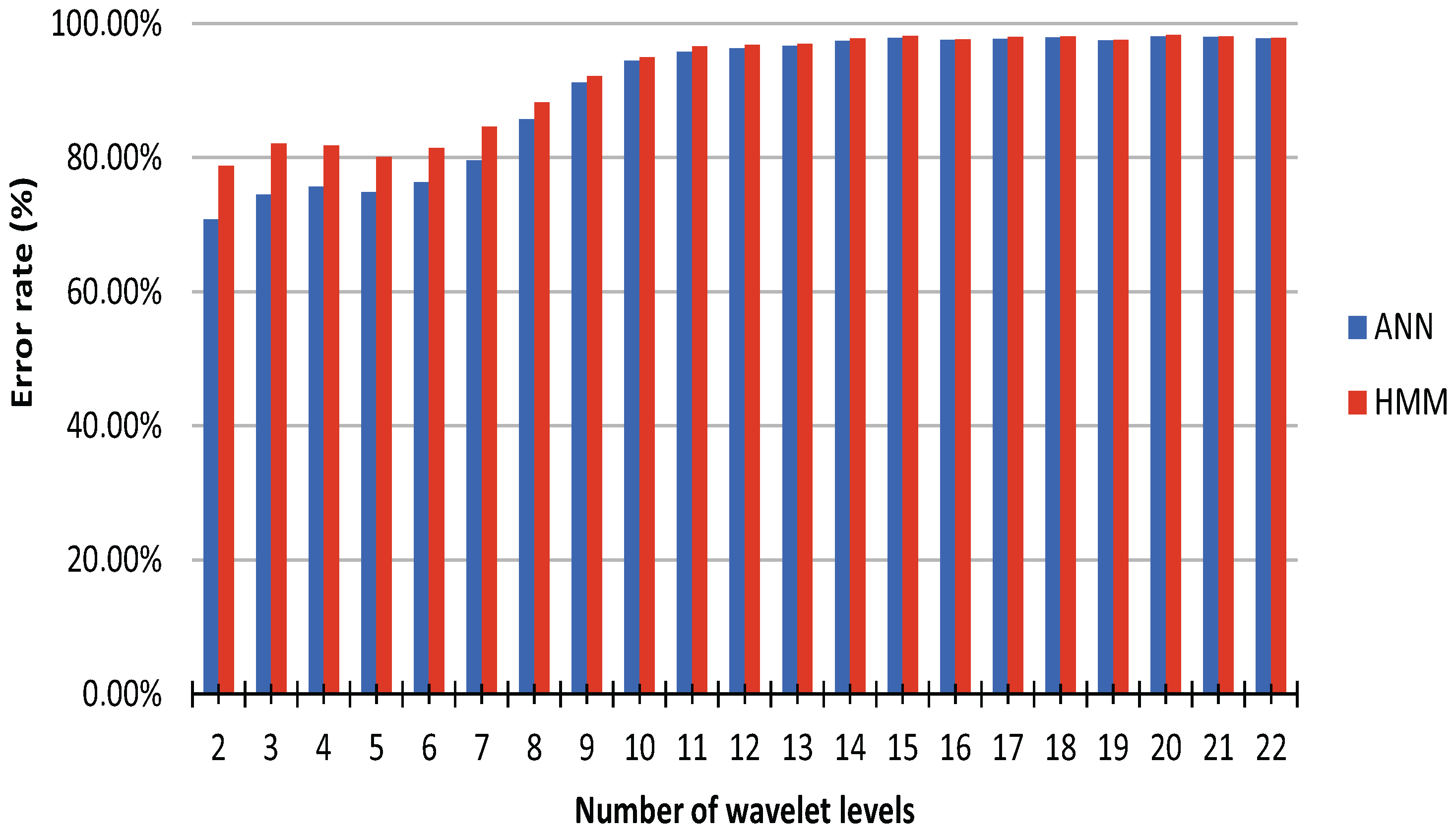
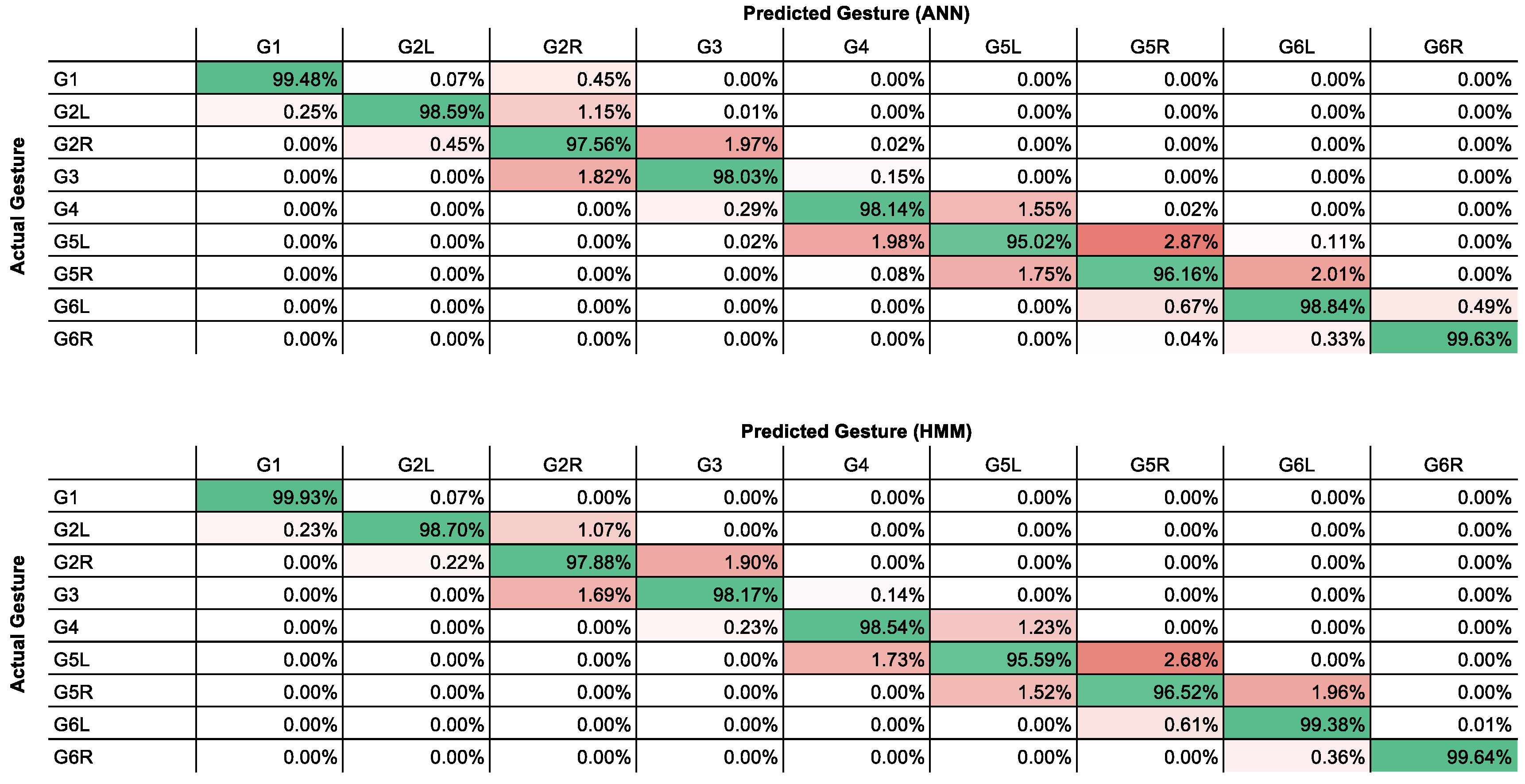
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| ECDC | European Center of Disease Prevention and Control |
| EMG | ElectroMyoGraph |
| HMM | Hidden Markov Model |
| IMU | Inertial Measurements Unit |
| SDK | Software Development Kit |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Marimuthu, K.; Pittet, D.; Harbarth, S. The effect of improved hand hygiene on nosocomial MRSA control. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erasmus, V.; Daha, T.J.; Brug, H.; Richardus, J.H.; Behrendt, M.D.; Vos, M.C.; van Beeck, E.F. Systematic Review of Studies on Compliance with Hand Hygiene Guidelines in Hospital Care. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2010, 31, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Surveillance of Healthcare-Associated Infections in Europe 2007; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Maria Malliarou, R.N.; Pavlos Sarafis, R.N.; Sofia Zyga, R.N.; Constantinidis, T.C. The Importance of Nurses Hand Hygiene. Int. J. Caring Sci. 2013, 6, 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- WHO Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care: First Global Patient Safety Challenge: Clean Care Is Safer Care; World Health Organization, Patient Safety: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Laukamp, D.; Kutafina, E.; Jonas, S.M. Wearables in der praktischen Ausbildung: Handhygienetraining mit dem Myo Armband. In Proceedings of the GMDS Annual Meeting, Krefeld, Germany, 6–9 September 2015.
- Webel, S.; Bockholt, U.; Engelke, T.; Gavish, N.; Olbrich, M.; Preusche, C. An augmented reality training platform for assembly and maintenance skills. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2013, 61, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shull, P.B.; Jirattigalachote, W.; Hunt, M.A.; Cutkosky, M.R.; Delp, S.L. Quantified self and human movement: A review on the clinical impact of wearable sensing and feedback for gait analysis and intervention. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawassizadeh, R.; Tomitsch, M.; Nourizadeh, M.; Momeni, E.; Peery, A.; Ulanova, L.; Pazzani, M. Energy-Efficient Integration of Continuous Context Sensing and Prediction into Smartwatches. Sensors 2015, 15, 22616–22645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hand Hygiene Australia. Available online: http://www.hha.org.au (accessed on 13 April 2016).
- SureWash|Mobile Hand Hygiene Training Units. Available online: http://www.surewash.com (accessed on 13 April 2016).
- Xia, B.; Dahyot, R.; Ruttle, J.; Caulfield, D.; Lacey, G. Hand Hygiene Poses Recognition with RGB-D Videos. In Proceedings of the Irish Machine Vision & Image Processing Conference, Dublin, Ireland, 26–28 August 2015.
- Lacey, G.; Llorca, D.F. Hand Washing Monitoring System. U.S. Patent US20090087028 A1, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Boyce, J.M. Measuring Healthcare Worker Hand Hygiene Activity: Current Practices and Emerging Technologies. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2011, 32, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.A.; Schweizer, M.L.; Polgreen, P.M.; Gupta, K.; Reisinger, H.S.; Perencevich, E.N. Automated and electronically assisted hand hygiene monitoring systems: A systematic review. Am. J. Infect. Control 2014, 42, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SwipeSense. Available online: http://www.swipesense.com (accessed on 13 April 2016).
- BIOVIGIL. Available online: http://www.biovigilsystems.com (accessed on 13 April 2016).
- Hyginex|Saving Lives through Better Hand Hygiene. Available online: http://www.hyginex.com (accessed on 13 April 2016).
- Klein, F.; Severijns, C.; Albiez, D.; Jovanovic, M.; Eyvazy Hesar, M. The hygiene games. In Proceedings of the NI2016, Geneva, Switzeland, 27 June 2016.
- Shhedi, Z.A.; Moldoveanu, A.; Moldoveanu, F.; Taslitchi, C. Real-time hand hygiene monitoring system for HAI prevention. In Proceedings of the E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB), Iasi, Romania, 19–21 November 2015; pp. 1–4.
- Galluzzi, V.; Herman, T.; Polgreen, P. Hand hygiene duration and technique recognition using wrist-worn sensors. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–16 April 2015; pp. 106–117.
- Kutafina, E.; Laukamp, D.; Jonas, S.M. Wearable Sensors in Medical Education: Supporting Hand Hygiene Training with a Forearm EMG. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2015, 211, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Møller, M.F. A scaled conjugate gradient algorithm for fast supervised learning. Neural Netw. 1993, 6, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifkin, R.; Klautau, A. In Defense of One-vs-All Classification. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2004, 5, 101–141. [Google Scholar]
- Rabiner, L.R. A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. IEEE Proc. 1989, 77, 257–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- mHealth Software. Available online: mhealth.imib.rwth-aachen.de/software (accessed on 1 August 2016).
- Hannig, A.; Kuth, N.; Özman, M.; Jonas, S.; Spreckelsen, C. eMedOffice: A web-based collaborative serious game for teaching optimal design of a medical practice. BMC Med. Educ. 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| EMG | IMU | |
|---|---|---|
| Sampling rate | 200 | 50 |
| #Values | 8 | 10 |
| Data type | int8 | float |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kutafina, E.; Laukamp, D.; Bettermann, R.; Schroeder, U.; Jonas, S.M. Wearable Sensors for eLearning of Manual Tasks: Using Forearm EMG in Hand Hygiene Training. Sensors 2016, 16, 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081221
Kutafina E, Laukamp D, Bettermann R, Schroeder U, Jonas SM. Wearable Sensors for eLearning of Manual Tasks: Using Forearm EMG in Hand Hygiene Training. Sensors. 2016; 16(8):1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081221
Chicago/Turabian StyleKutafina, Ekaterina, David Laukamp, Ralf Bettermann, Ulrik Schroeder, and Stephan M. Jonas. 2016. "Wearable Sensors for eLearning of Manual Tasks: Using Forearm EMG in Hand Hygiene Training" Sensors 16, no. 8: 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081221
APA StyleKutafina, E., Laukamp, D., Bettermann, R., Schroeder, U., & Jonas, S. M. (2016). Wearable Sensors for eLearning of Manual Tasks: Using Forearm EMG in Hand Hygiene Training. Sensors, 16(8), 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081221






