Time-Resolved Fluorescent Immunochromatography of Aflatoxin B1 in Soybean Sauce: A Rapid and Sensitive Quantitative Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Apparatus
2.2. Conjugation of Eu-Nanospheres to Antibody
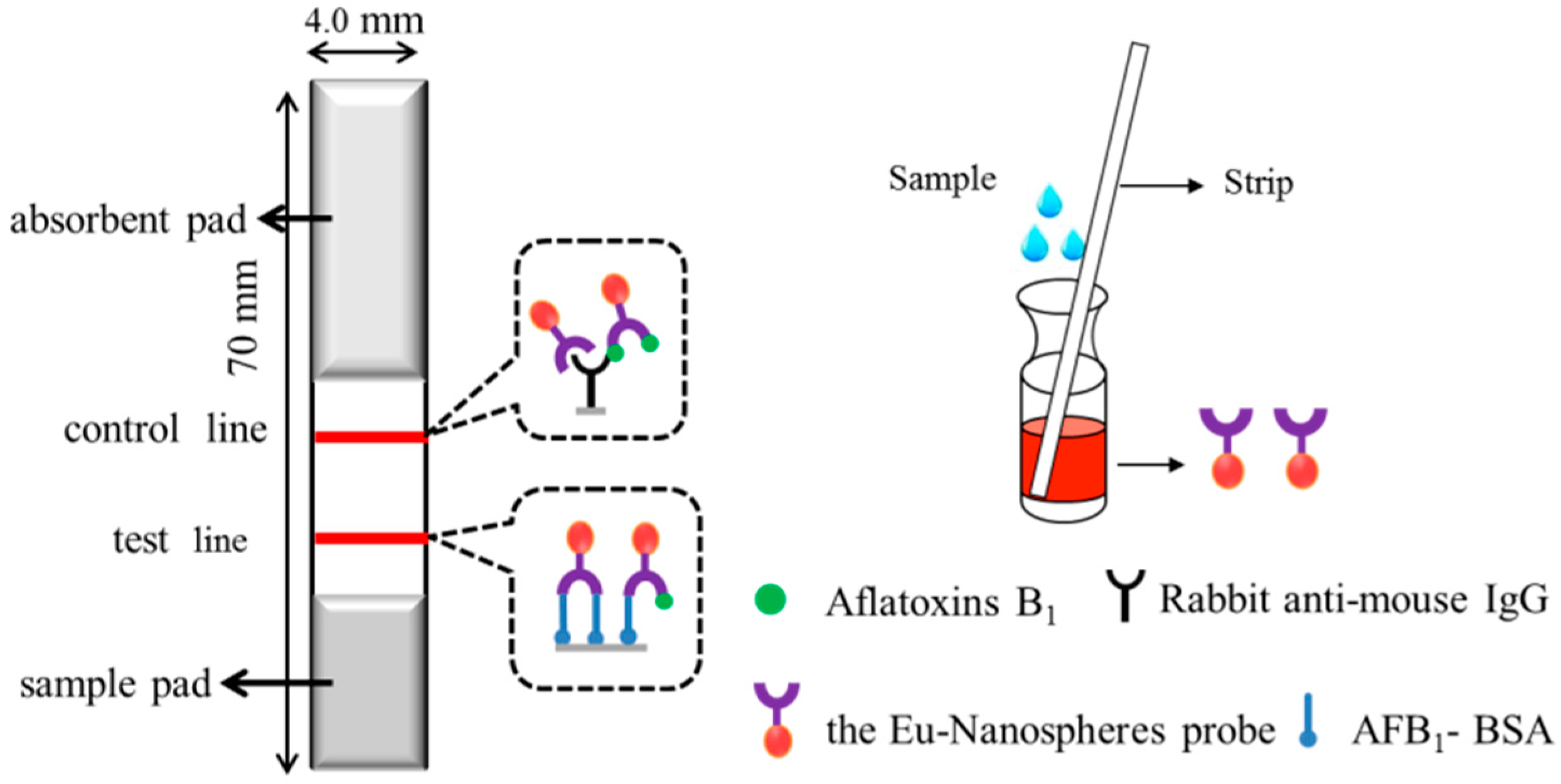
2.3. Preparation of the Immunochromatographic Strip
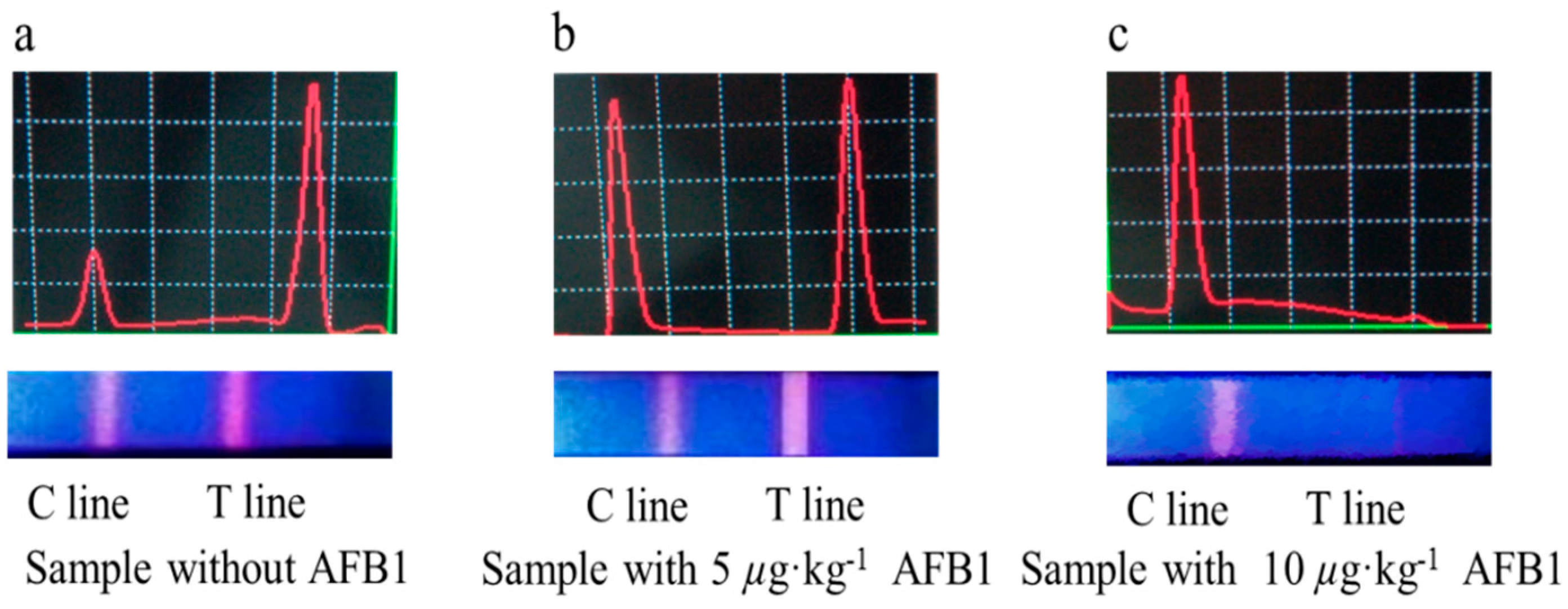
2.4. Evaluation of TRFIA
2.5. Sample Treatment for TRFIA
2.6. Sample Treatment for HPLC Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Eu-Probe
3.1.1. Optimal pH of Boric Acid Buffer Solution for Conjugation
3.1.2. Optimal Antibody Level Labeled with Eu-Nanospheres
3.2. Optimization of the IC Strip
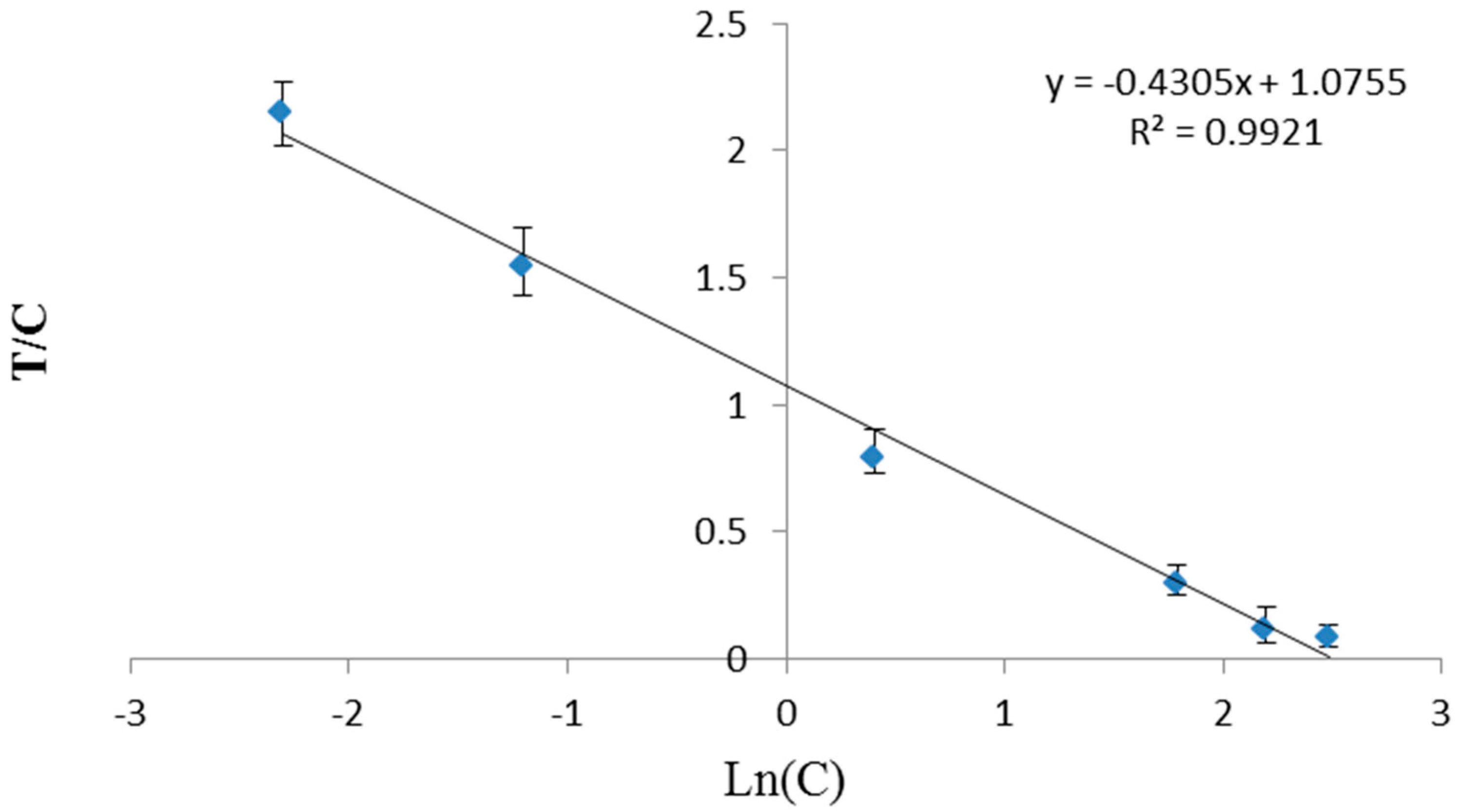
3.3. Optimization of TRFIA
3.4. Optimization of Sample for TRFIA
3.5. Validation by HPLC
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, D.H.; Li, P.W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W. Ultrasensitive nanogold probe-based immunochromatographic assay for simultaneous detection of total aflatoxins in peanuts. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2877–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacin, A.; Gonzalez, H.H.L.; Etcheverry, M.G.; Resnik, S.; Vivas, L.; Espin, S. Fungi associated with food and feed commodities from ecuador. Mycopathologia 2003, 156, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, K.W.; Baird, R.E.; Abney, T.S. A review of soybean (Glycine max) seed, pod and flower mycofloras in North America with methods and a key for identification of selected fungi. Mycopathologia 2010, 150, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. International agency for research on cancer. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 2002; Volume 82, pp. 171–300. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, E.Z. Impact of mycotoxins on humans and animals. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2011, 15, 129–144. [Google Scholar]
- Blesa, J.; Soriano, J.M.; Moltó, J.C.; Mañes, J. Absence ochratoxin A in soy sauce. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 97, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.L.; Cui, C.; Ren, J.Y.; Zhao, H.F.; Zhao, Q.Z.; Zhao, M.M. Changes in the chemical composition of traditional Chinese-type soy sauce at different stages of manufacture and its relation to taste. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.J.; Wild, C.P.; Eaton, D.L.; Groopman, J.D. Epidemiology of aflatoxin-related disease. In The Toxicology of Aflatoxins: Human Health, Veterinary and Agricultural Significance; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 233–258. [Google Scholar]
- Pleadin, J.; Vulić, A.; Perši, N.; Škrivanko, M.; Capek, B.; Cvetnic, Z. Aflatoxin B1 occurrence in maize sampled from Croatian farms and feed factories during 2013. Food Control 2014, 40, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W. Immunoassays for aflatoxins Review Article. Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajslova, J.; Zachariasova, M.; Cajka, T. Analysis of multiple mycotoxins in food. Mass Spectrom. Food Saf. 2011, 747, 233–258. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, H. Development of a microwave-assisted-extraction-based method for the determination of aflatoxins B1, G1, B2, and G2 in grains and grain products. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 1623–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urusov, A.E.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Immunochemical methods of mycotoxin analysis. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2010, 46, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Hashim, N.H.; Yoshizawa, T. Evaluation and application of a simple and rapid method for the analysis of aflatoxins in commercial foods from Malaysia and the Philippines. Food Addit. Contam. 1999, 16, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzantiev, B.B.; Byzova, N.; Urusov, A.; Zherdev, A.V. Immunochromatographic methods in food analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 55, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.F.; Huang, Y.M.; Chen, M.H.; Wang, S.Y.; Liu, K.; Lai, W.H. Rapid detection method for aflatoxin B1 in soybean sauce based on fluorescent microspheres probe. Food Control 2015, 50, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Huang, H.; Liu, T.; He, C.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Hou, J.; Ren, Z.; Dong, W.; Wu, Y. A time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay for the quantitation of rabies virus nucleoprotein in the rabies vaccine. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 206, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmilá, I.; Mukkala, V.M. Time-resolution in fluorometry: Technologies, labels, and applications in bioanalytical assays. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2001, 38, 441–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Xiao, H.L.; Zhang, X.R.; Zhu, L.; Liu, H.Y.; Jin, J. Ultrasensitive detection of pepsinogen I and pepsinogen II by a time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay and its preliminary. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 571, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Shi, W.M.; Liu, Y.B.; Zhang, S.X. A monoclonal antibody-based time- resolved fluoroimmunoassay for chloramphenicol in shrimp and chicken muscle. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 575, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, X.D.; Tan, M.Q.; Wang, G.L.; Ye, Z.Q.; Yuan, J.L.; Matsumoto, K. Preparation and a time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay application of new europium fluorescent nanoparticles. Anal. Sci. 2004, 20, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Tang, X.Q.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P.W.; Ding, X.X. Rapid on-site sensing aflatoxin B1 in food and feed via a chromatographic Time-Resolved Fluoroimmunoassay. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.H.; Li, P.W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, Z.; Ding, X.X. A high selective immunochromatographic assay for rapid detection of aflatoxin B1. Talanta 2011, 85, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.Q.; Zhang, Z.W.; Li, P.W.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, J.; Wang, D.; Lei, J.W. Sample-pretreatment-free based high sensitive determination of aflatoxin M1 in raw milk using a time-resolved fluorescent competitive immunochromatographic assay. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakala, H.; Mukkala, V.M.; Sutela, T.; Hovinen, J. Synthesis and properties of nanosphere copolymerized with luminescent europium (III) chelates. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 1383–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdinasab, M.; Sheikh-Zeinoddin, M.; Soleimanian-Zad, S.; Li, P.W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Tang, X.Q.; Li, J. A reliable and sensitive time-resolved fluorescent immunochromatographic assay (TRFICA) for ochratoxin A in agro-products. Food Control 2015, 47, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.W.; Li, P.W.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, X.X.; Zhang, W. Europium nanospheres based time-resolved fluorescence for rapid and ultrasensitive determination of total aflatoxin in feed. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10313–10318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanski, M.S.; Porter, R.A. Preparation and quality control of silver nanoparticle–antibody conjugate for use in electrochemical immunoassays. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 387, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Li, P.W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Ding, X.X. Graphene oxide: an adsorbent for the extraction and quantification of aflatoxins in peanuts by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1318, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese National Standard. GB/T 5009.22-2003 Determination of Aflatoxin B1in Foods. Available online: http://micor.agriculture.gov.au/Dairy/Documents/Pdfs/Food_Additives_Permitted_by_China_and_the_Corresponding_Applicable_Standards_List.pdf (accessed on 11 May 2003).
- Xie, F.; Lai, W.H.; Saini, J.; Shan, S.; Cui, X.; Liu, D.F. Rapid pretreatment and detection of trace aflatoxin B1 in traditional soybean sauce. Food Chem. 2014, 150, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample | Number | Spike µg·kg−1 | Result by TRFIA µg·kg−1 | CV% | Recovery % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Mean | |||||
| Soybean sauce | 1 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| 2 | 0.80 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.90 | 0.79 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 8.6 | 114.3 | |
| 3 | 4.00 | 4.57 | 3.88 | 3.69 | 4.33 | 4.22 | 4.14 | 8.5 | 103.5 | |
| 4 | 8.00 | 7.90 | 7.39 | 7.74 | 8.43 | 7.26 | 7.75 | 6.0 | 96.8 | |
| 5 | 12.00 | 11.45 | 11.98 | 13.01 | 12.89 | 12.87 | 12.44 | 5.7 | 103.7 | |
| Soybean sauce | 1 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | - | - | - |
| 2 | 2.00 | 2.10 | 2.07 | 1.93 | 2.20 | 2.29 | 2.12 | 6.4 | 105.9 | |
| 3 | 5.00 | 5.02 | 5.24 | 5.46 | 5.34 | 5.09 | 5.23 | 3.4 | 104.6 | |
| 4 | 10.00 | 9.42 | 9.89 | 9.65 | 10.37 | 10.57 | 9.98 | 4.5 | 99.8 | |
| 5 | 15.00 | 12.98 | 12.07 | 13.58 | 13.12 | 13.68 | 13.09 | 5.0 | 87.2 | |
| Average | 6.0 | 110.0 | ||||||||
| Soybean Sauce Sample | HPLC Detected AFB1 µg·kg−1 | Intra-Batch (n = 5) | Inter-Batch (n = 5) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Detected Value µg·kg−1 | Average CV % | Average Detected Value µg·kg−1 | Average CV % | ||
| 1# | ND | ND | - | ND | - |
| 2# | 0.8 | 0.69 | 7.9 | 0.68 | 8.7 |
| 3# | 3.2 | 3.43 | 4.6 | 3.58 | 5.2 |
| 4# | 8.9 | 9.30 | 5.3 | 9.20 | 5.6 |
| 5# | ND | ND | - | ND | - |
| 6# | 0.3 | 0.32 | 8.9 | 0.27 | 9.2 |
| 7# | 4.7 | 4.43 | 6.6 | 3.98 | 5.9 |
| 8# | 12.4 | 13.2 | 5.3 | 13.7 | 5.6 |
| 9# | 6.4 | 6.00 | 6.4 | 5.80 | 7.2 |
| 10# | 0.8 | 0.69 | 9.1 | 0.68 | 9.4 |
| Number | AFB1 Result by HPLC µg·kg−1 | AFB1 Result by TRFIA µg·kg−1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1# | 5.20 | 4.90 |
| 2# | 6.40 | 6.70 |
| 3# | 9.80 | 10.7 |
| 4# | 3.20 | 2.75 |
| 5# | 2.90 | 2.45 |
| 6# | 0.80 | 0.70 |
| 7# | 1.30 | 1.50 |
| 8# | 3.60 | 4.20 |
| 9# | 0.31 | 0.44 |
| 10# | 3.60 | 3.80 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W. Time-Resolved Fluorescent Immunochromatography of Aflatoxin B1 in Soybean Sauce: A Rapid and Sensitive Quantitative Analysis. Sensors 2016, 16, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071094
Wang D, Zhang Z, Li P, Zhang Q, Zhang W. Time-Resolved Fluorescent Immunochromatography of Aflatoxin B1 in Soybean Sauce: A Rapid and Sensitive Quantitative Analysis. Sensors. 2016; 16(7):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071094
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Du, Zhaowei Zhang, Peiwu Li, Qi Zhang, and Wen Zhang. 2016. "Time-Resolved Fluorescent Immunochromatography of Aflatoxin B1 in Soybean Sauce: A Rapid and Sensitive Quantitative Analysis" Sensors 16, no. 7: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071094
APA StyleWang, D., Zhang, Z., Li, P., Zhang, Q., & Zhang, W. (2016). Time-Resolved Fluorescent Immunochromatography of Aflatoxin B1 in Soybean Sauce: A Rapid and Sensitive Quantitative Analysis. Sensors, 16(7), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16071094









