Abstract
Despite all the significant advances in pedestrian detection brought by computer vision for driving assistance, it is still a challenging problem. One reason is the extremely varying lighting conditions under which such a detector should operate, namely day and nighttime. Recent research has shown that the combination of visible and non-visible imaging modalities may increase detection accuracy, where the infrared spectrum plays a critical role. The goal of this paper is to assess the accuracy gain of different pedestrian models (holistic, part-based, patch-based) when training with images in the far infrared spectrum. Specifically, we want to compare detection accuracy on test images recorded at day and nighttime if trained (and tested) using (a) plain color images; (b) just infrared images; and (c) both of them. In order to obtain results for the last item, we propose an early fusion approach to combine features from both modalities. We base the evaluation on a new dataset that we have built for this purpose as well as on the publicly available KAIST multispectral dataset.
1. Introduction
Visual pedestrian detection has received attention for more than a decade from computer vision researchers due to its multiple applications in Advance Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) [1,2,3], autonomous vehicles [4] and video surveillance [5,6,7], being nowadays still a challenging problem. The accuracy of pedestrian detection methods remains limited because of occlusions, cluttered backgrounds and, foremost, bad visibility because of the varying lighting conditions under which they must operate.
Most efforts on building pedestrian detectors have focused on two directions, each being a key component of the whole system. The first one is the design of the features on which the statistical classifiers will work. Since the breakthrough of histograms of oriented gradients (HOG) by Dalal et al. [8], many other features and combinations of features have been proposed in the last decade, like HOG plus local binary patterns (LBP) [9], HOG plus color self similarity (CSS) [10], Haar features plus histogram of edges [11], integral channels [12] or macrofeatures [13], just to name a few. These features are arranged to form models: holistic [8,9], part-based (e.g., the DPM) [14,15,16], or patch based [17,18] , many times taking into account also different views and resolutions [14,19,20]. Another recent trend has been to complement those appearance-based features, computed from single frames, with additional motion and depth features such as in [21,22,23,24,25].
The second main direction has been the design of the classifier itself. Since the plain binary max-margin discriminative classifiers were employed in the initial approaches, we now see a plethora of classification architectures like cascades of classifiers [26,27], random forests of local experts [17], and even alternative approaches like generative classifiers [28], active learning [29], and domain adaptation [30,31]. In the last three years, there has also been an explosion of end-to-end learning of object models based on deep convolutional neural networks (deep CNNs) [32]. These models are mainly operating in the visible spectrum to leverage object annotations from image classification datasets given the large number of annotated object examples these deep CNNs need to converge to a useful object model. The reason is the huge number of parameters to learn, on the order of millions.
In parallel to all these works, there is a relatively unexplored third direction, namely, image acquisition. Recent works have started to supplement or even replace images provided by monochrome and color cameras in the visible spectrum with images from other modalities, with the intent of improving the performance of the whole system but still keeping the same types of features and classifiers.
Near infrared cameras, sensing in the range 0.75–1.3 m, have been used for pedestrian detection in [33]. Far infrared cameras, instead, work in the range 7.5–13 m. They have the distinctive advantages of leveraging the fact that the human body emits radiation around 9.3 m [34] and their relative invariance to different illumination conditions (see Figure 1 and Figure 2), which may improve the detector robustness, as shown in [35,36,37,38,39,40].
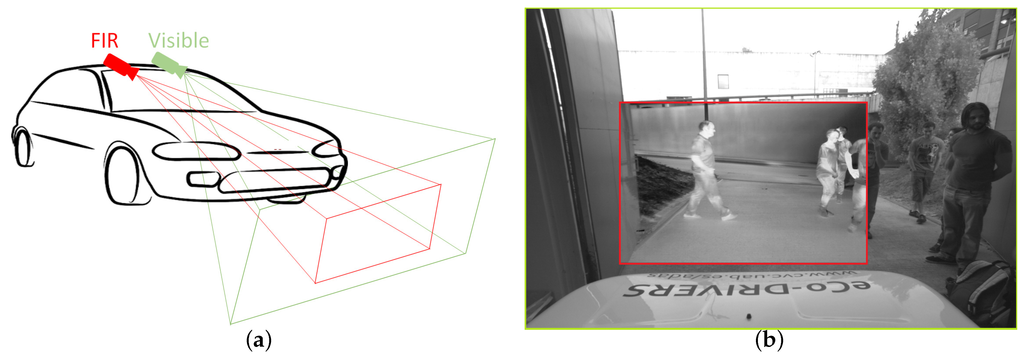
Figure 1.
Camera setup for the CVC-14 dataset and registered sample frames showing the different field of views. (a) Fields of view of the visible and far infrared cameras and (b) example images.
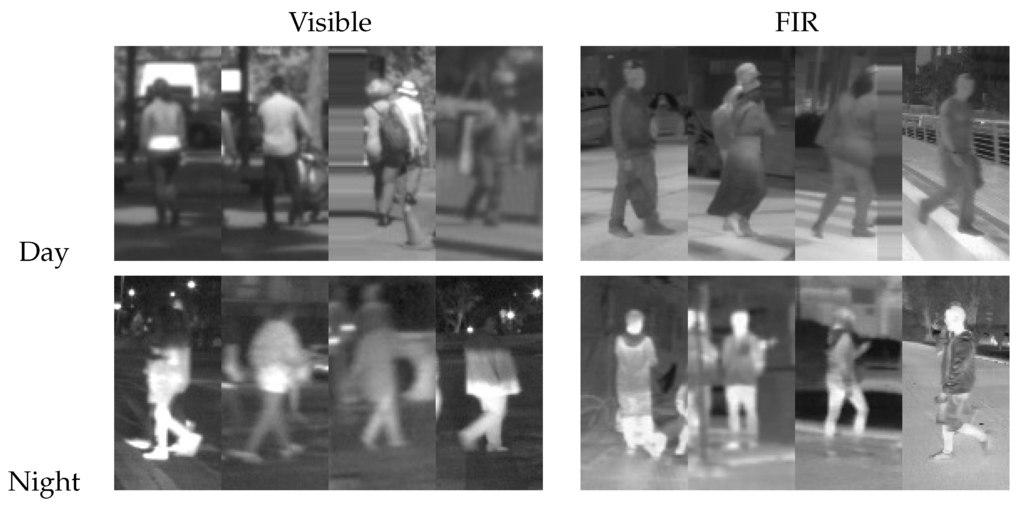

Figure 2.
Sample pedestrians from the CVC-14 dataset.
The goal of this paper is to assess the accuracy of a pedestrian detector with regard to (1) the imaging modalities; (2) strong baselines in terms of features and pedestrian models proposed for this task; and (3) the lighting conditions. Even though we expect to get better results on sequences recorded at night with a far infrared (FIR) camera than with a standard color or monochrome camera, there are still relevant open questions in relation to the design of a practical and affordable pedestrian detector system. For instance, how does an FIR camera perform at daytime? Is its performance similar to that of a regular camera? Is it worth to combine features extracted from a color and an FIR camera operating simultaneously? If so, what is then the gain in accuracy at day and nighttime?
The contributions of this paper are:
- An extensive evaluation of pedestrian detectors for a number of combinations of the former three factors: visible/FIR modalities, pedestrian models and lighting conditions.
- We make available the new CVC-14 dataset in the Dataset section of http://adas.cvc.uab.es. CVC-14 is a new dataset of multimodal (FIR plus visible) videosequences and the corresponding detection groundtruth, comparable to the only other publicly available KAIST dataset [36].
- We assess the relevance of simultaneously using two cameras of different modality (FIR, Visible) by applying early fusion, which is done on KAIST.
In the following, we will review the works most related to ours and point out the main differences (Section 2). Section 3 presents our new dataset and compares it to KAIST. Based on both of them, we have designed and run a number of experiments, and present the results in Section 5. Finally, Section 6 summarizes this work and draws the conclusions.
2. Related Works
Recently, a number of works have appeared that explore the application of FIR cameras to pedestrian detection. This has probably been fostered by a drastic reduction of their price, which may favor its adoption by the automotive industry in the future. We divide the approaches into two categories.
The first one includes the approaches mainly focused on the introduction of new features, specifically targeted to this imaging modality. In this group, we find works like Olmeda et al. [41], which presents a new descriptor, the histograms of oriented phase energy (HOPE) and an adaptation of the latent variable SVM approach to FIR images. HOPE is a contrast invariant descriptor that encodes a grid of local oriented histograms extracted from the phase congruency of the images computed from a joint of Gabor filters. Besbes et al. [39] propose a pipeline for pedestrian detection in FIR images using a hierarchical codebook of SURF in the head region, taking advantage of the brightness of this area inside the regions of interest (ROIs). Another nice work by Li et al. [38] employs sparse coding. Overall, these works try to show that FIR cameras and specialized features improve over standard cameras and “off-the-shelf” features previously employed in this and other domains. The problem is that, given the absence of benchmark datasets, it becomes difficult to do a fair quantitative comparison. For instance, the total number of pedestrians present in the sequences, number of occlusions, the distribution of the pedestrian distance to the camera (size in pixels), the type of background present, the frame resolution and the frame rate etc. are factors that clearly have an influence on the results.
In the second category, we consider those papers mainly addressing the evaluation and comparison of modalities and features, as we intend to do in this work. We have found just a few papers on this category, all of them published less than one year ago. Miron et al. [37] evaluate a set of different descriptors over visible and FIR sequences. This evaluation is performed in on-board sequences but recorded only in the daytime.
More interesting, Yuan et al. [36] are the first to perform a comprehensive study and make publicly available their dataset. They take as baselines pedestrian detectors based on the aggregated channel features (ACF) originally proposed by Dollar et al. [3], but adding several combinations of new gradient orientation-related features computed from the FIR image intensity, resulting in the combination of features of both modalities. However, differently from them, we perform an exhaustive experimental analysis to demonstrate the advantages in detection using different modalities in isolation for different state-of-the-art detectors during different time/illumination conditions. Then, these results are used to propose a multi-modal approach combining visible and FIR spectrum images. We are more interested in the performance of state-of-the-art features and classifiers for pedestrian detection, not in the introduction of new features. At most, we want to investigate the effect of combining in a simple way features from different modalities, in the event of visible and FIR sequences simultaneously recorded. Ultimately, we want to set a baseline for future research and also identify the source of the improvements if any: e.g., a given set of features, image modality, specific lighting conditions, etc., and for each case being able to perform a quantitative evaluation. Note that it is important to have a quantitative evaluation on the use of two different types of cameras simultaneously, since car manufacturers would like to use a single camera for ADAS to reduce overall cost and aesthetic impact.
3. Datasets
To build our new dataset we use both visible and FIR cameras to gather two long pairs of video sequences of day and night activity, respectively (see Figure 1). One pair was recorded at daytime, the other at night. We used an IDS UI-3240CP (IDS Imaging Development Systems GmbH, Obersulm, Germany) and an FLIR Tau 2 camera (FLIR Systems, Nashua, NH, USA), with the specifications in Table 1.

Table 1.
FLIR Tau 2 and UI-3240CP camera specifications.
Note that resolution and the field-of-view do not match. Hence, we needed to perform an automatic spatial alignment and crop. Even though the cameras are not at the same position, the baseline is small and, once registered, the disparity and occlusions of objects beyond a few meters are negligible.
Table 2 shows the number of frames and annotated pedestrian for each of the four sequences in the dataset (here called CVC-14): day/FIR, night/FIR, day/visible and night/visible. This dataset was acquired at 10 FPS. We have defined a threshold for the minimum height of pedestrians that we will take into account later in the experiments. That is, we have annotated all of them but, as it is usually done [3], we will consider as mandatory the detection of those whose bounding box is higher than 50 pixels, about 10% of the registered frames height.

Table 2.
New CVC-14 dataset summary of images and annotated pedestrians.
The KAIST multispectral pedestrian dataset [36] is a set of video sequences composed by 95 K frame pairs. The images from each pair have been recorded by an on-board color and thermal cameras at 20 Hz, both at a resolution of 640 × 480 pixels. Hence, it is well suited for pedestrian detection studies because the two underlying sequences, color and infrared, are synchronized. In addition, a beamsplitter in the acquisition setup makes each pair spatially registered so that the computed local features in both images correspond to the same region. Another important characteristic is the groundtruth with 103,128 dense annotations featuring people, cyclists and 1182 unique pedestrians.
4. Features and Classifiers
In this study, we have selected a short list with the most used and top scoring features and classifiers from the pedestrian detection literature. As for the features, they are HOG [8], LBP [9] and their aggregation as a single feature, which we will denote as HOG+LBP. As for the classifiers, we have selected three different types of models: holistic, learned by a linear SVM [42]; a patch-based classifier learned by a Random Forest of local experts [17]; and the popular DPM) [14]. Whereas the first one is probably well known for its wide application in many classification problems, we will shortly introduce the two latter, which may be more specific. The Random Forest of local experts (RF) [17] is a patch-based detector. RF is an ensemble of trees where each node is based on an SVM classifier learned on a random patch. In this way, different parts (patches) are selected to create a decision tree from which a classification score is computed on the basis of the probabilities of being a target object at the leaf node. The DPM [14] is a successful part-based detector that defines a fixed number of parts. Each of them are detected separately and a deformation cost is learned based on the part positions in the training samples. All of the part descriptions plus the deformation costs are concatenated to form a final descriptor, on which an SVM performs the final classification. The learning process is based on Latent SVM since the object parts are not supposed to be annotated, just the object as a whole is given.
We thus consider different combinations for the comparison: {HOG, LBP, HOG+LBP} × {Linear SVM, RF, DPM}. For each of them, we will assess the performance of the detector at day and night sequences separately. In addition, in each case, still, we will build a feature vector with the corresponding type of feature computed just on the visible frame, infrared frame, and the aggregation of both of these feature vectors.
In order to check whether complementarity information is better for pedestrian detection, we explore the integration of the two image modalities, visible and FIR. We thus propose to use an approach similar to [25]: for each candidate window, we extract HOG and LBP features over each modality and then combine them into a single feature vector to feed the classifier. We combine the features using an early fusion approach whereby the resulting descriptor is the plain concatenation of the features from each modality. It is worth mentioning also that, although for stereo-based systems it is possible to use a scene-based generation of candidate windows to be classified [1,2], in this paper, the visible and FIR modalities are treated as monocular systems regarding candidate generation. Thus, we use the scanning approaches defined in their respective works, which basically are the pyramidal sliding window [9,26] and the same for DPM but considering the detection of object parts at double the resolution of the whole object [14].
5. Experiments
5.1. Evaluation Protocol
As evaluation methodology, we follow the de-facto Caltech standard for pedestrian detection [3], i.e., we plot curves of false positives per image (FPPI) vs. miss rate. The average miss rate (AMR) in the range of to FPPI is taken as indicative of each detector accuracy, i.e., the lower the better.
5.2. Experiments on the CVC-14 Dataset
Table 3 summarizes the results in terms of AMR for the seven combinations of features and classifiers on the two lighting conditions and image modalities considered. For the holistic model (linear SVM), we test all of the features. For the patch-based one (RF of local experts), we keep HOG as reference, but the next test consists in directly combining HOG and LBP, since, for this model, we know from our previous work [17] (visible spectrum) that this combination works better than the two features in isolation. On the other hand, the standard (publicly available) DPM is based only in HOG, so following the same criterion as for RF, we have added LBP too, but it is not necessary to consider LBP alone. Overall, Table 3 plots the experiments that make more sense. We can appreciate that, as expected, all detectors perform quite badly on the images from the visible camera at night, in comparison to FIR. What is worth highlighting is that FIR gets similar results at day and night for two of the detectors (SVM and RF) for all of the features. However, perhaps the most interesting observation is that FIR beats visible also in the daytime for all detectors. Figure 3 shows the evolution of the miss rate as FPPI increases for the cases of using HOG and HOG+LBP.

Table 3.
Average miss rate (AMR) in the CVC-14 dataset.
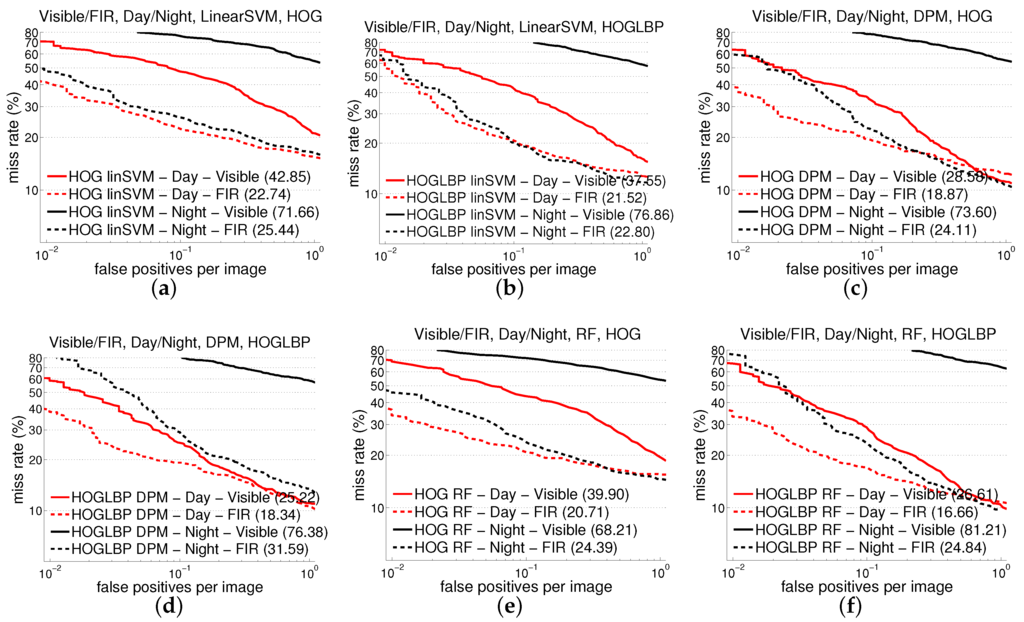
Figure 3.
Results using different detectors over CVC-14 dataset. First row plot results using detectors based on (a) SVM/HOG, (b) SVM/HOG+LBP, (c) DPM/HOG, (d) DPM/HOG+LBP, (e) RF/HOG and (f) RF/HOG+LBP.
5.3. Experiments on KAIST Dataset
For the CVC-14 dataset, each sequence consists of a pair of video streams, one per camera, which are not perfectly synchronized. This means that, for each frame of one of the streams, say the visible one, we can always locate the closest frame in time in the other (FIR) stream, but they were not captured at the same time so they contain slight differences because camera location and orientation were not the same. Such differences are so small that the visible vs. FIR comparison presented here remains fair according to our purposes. However, if we want to compare the accuracy with single modality features versus multimodality (visible plus FIR), we need to make sure that those features correspond exactly to the same region in the scene. Fortunately, the KAIST dataset [36] was recorded with this goal in mind.
From now on, we assume the use of RF/HOG+LBP, since, for the CVC-14 dataset, it was the best performing together with DPM/HOG+LBP in the daytime for visible and FIR, and it was better than DPM/HOG+LBP at nighttime using FIR (using the visible spectrum all the detectors are performing really bad). At this point, we introduce a new variation: concatenating the same features from visible and FIR. In addition, and for the sake of comparison, we run all the experiments, not only for the set of reasonable pedestrians but also to distinguish near from medium distance pedestrians.The near subset includes pedestrians with height equal to or higher than 75 pixels. The medium subset includes pedestrians between 50 and 75 pixel height. This is described in Table 4 while Figure 4 shows the complete curves when varying the number of false positives per image.

Table 4.
AMR (average miss rate) in the KAIST dataset. The three rows in each cell represent the AMR for near, medium and reasonable pedestrians, as explained in the text.
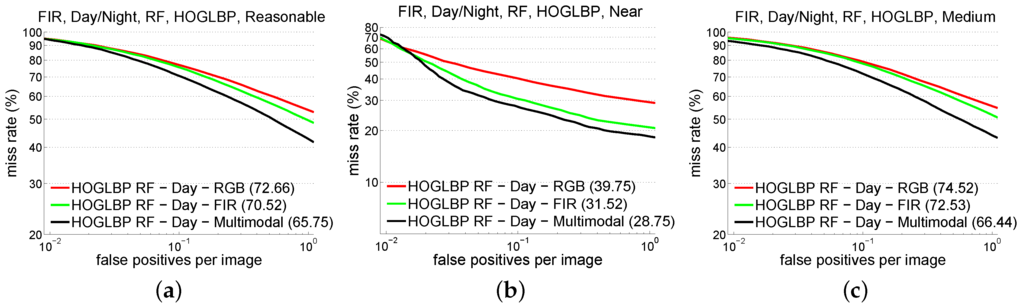
Figure 4.
Results using different test subsets over KAIST multispectral dataset during daytime. Results obtained with RF/HOG+LBP for (a) reasonable (b) near and (c) medium pedestrian subsets.
The same detector consistently gets the minimum AMR for all the cases. More significant is the fact that the best feature descriptor in the daytime results in the combination of visible and FIR features, whereas at night, FIR features achieve the maximum performance by themselves, closely followed by the combination of FIR and visible features (just about 3% more AMR on average). In this evaluation, we obtain competitive detectors in KAIST benchmark where state-of-the-art is, for daytime and reasonable pedestrians, AMR of in the Caltech evaluation protocol, while we obtain for the same subset .
In fact, the combination of visible + FIR at daytime is just scarcely better than using only FIR (see RF/HOG+LBP), specially for near pedestrians. Thus, from the viewpoint of the cost, it seems more reasonable to focus on improving FIR alone if the only purpose of the system is pedestrian detection. Of course, if other functionalities are required, such as traffic sign recognition in ADAS, then combining both systems is a good option as long as the synchronization of the cameras and the alignment of the images are cost effective.
As for the CVC-14 case, visible spectrum provides very poor results at nighttime (Qualitative results in Figure 5). Our dataset has been obtained using halogen headlights and the camera is not operating at high dynamic range. Thus, it seems that, to improve nighttime results, a more sophisticated illumination system and a very well set high dynamic range scheme must be designed if we want to use such types of camera for on-board pedestrian detection.
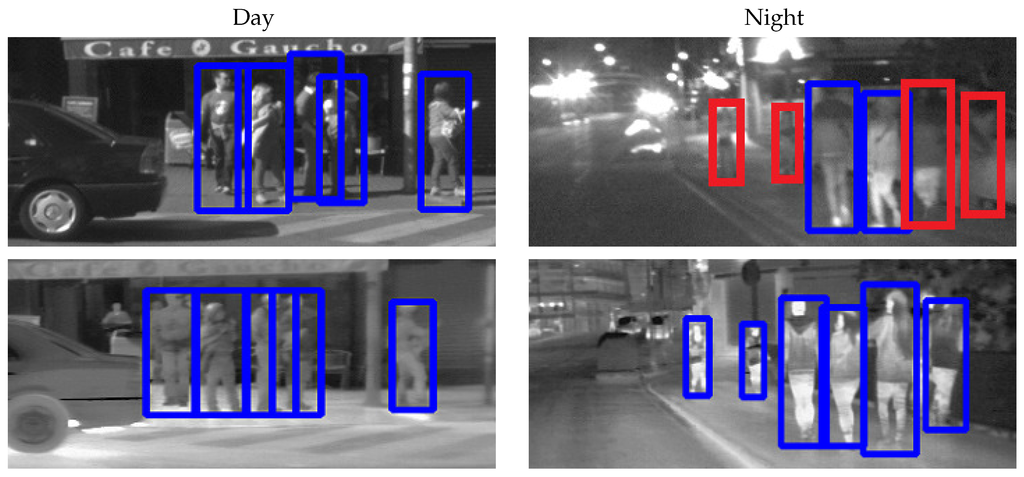

Figure 5.
Qualitative Results comparing HOG/LinSVM detectors in different time/sensor conditions. The top row shows results over visible spectrum images, the bottom row over far infrared images. Blue boxes represent correct detections (True Positive), while red boxes represent misdetections (False Negative).
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we have presented a study of pedestrian detection using commercial visible and FIR sensors operating during daytime and nighttime. This evaluation is based on well known features HOG and LBP and holistic (SVM), patch-based (RF), and part-based models (DPM), to train state-of-the-art classifiers.
The main conclusion is that the combination of features from FIR and visible images produces the best detector in the daytime by a notorious margin (about 5% less AMR) from just visible or just FIR features. This was originally unexpected since one would guess that the poor details observed in FIR images do not add discriminative power to features from visible images in the daytime. In fact, the FIR modality is as discriminative as the visible one, even not too far from the combined use of these sensors. At nighttime, FIR features get the best result and concatenating the two features’ vectors produces just a slight increase in AMR. Overall, we hope our results help to encourage the development of cheaper FIR cameras well integrated with those of the visible spectrum for developing more reliable ADAS and autonomous vehicles.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Spanish MICINN projects TRA2014-57088-C2-1-R, by the Secretaria d’Universitats i Recerca del Departament d’Economia i Coneixement de la Generalitat de Catalunya (2014-SGR-1506), by TECNIOspring with the FP7 of the EU and ACCIÓ, and also by DGT (SPIP2014-01352). Our research is also kindly supported by NVIDIA Corporation in the form of different GPU hardware. We thank also German Ros for his help reviewing the manuscript.
Author Contributions
D.V. and A.M.L. designed and supervised the study, and developed the RF of local experts in a previous work. Y.S. acquired and prepared the CVC-14 dataset. Z.F. and J.X. implemented and performed the experiments involving DPM. A.G. performed the experiments using SVM, RF and multi-modal approaches, decided the evaluation protocols, and analyzed the results. A.G. and J.S. prepared the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gerónimo, D.; López, A.M.; Sappa, A.D.; Graf, T. Survey of pedestrian detection for advanced driver assistance systems. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 1239–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enzweiler, M.; Gavrila, D.M. Monocular pedestrian detection: Survey and experiments. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 31, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dollár, P.; Wojek, C.; Schiele, B.; Perona, P. Pedestrian detection: An evaluation of the state of the art. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 743–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Urtasun, R. Are we ready for Autonomous Driving? The KITTI Vision Benchmark Suite. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012.
- Portmann, J.; Lynen, S.; Chli, M.; Siegwart, R. People detection and tracking from aerial thermal views. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014.
- Teutsch, M.; Mller, T.; Huber, M.; Beyerer, J. Low resolution person detection with a moving thermal infrared camera by hotspot classification. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014.
- Torabi, M.; Mass, G.; Bilodeau, G.A. An interative integrated framework for thermal-visible image registration, sensor fusion, and people tracking for video serveillance applications. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2012, 116, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of Oriented Gradients for Human Detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 25 June 2005.
- Wang, X.; Han, T.X.; Yan, S. An HOG-LBP human detector with partial occlusion handling. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 29 September–2 October 2009.
- Walk, S.; Majer, N.; Schindler, K.; Schiele, B. New features and insights for pedestrian detection. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Diego, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010.
- Gerónimo, D.; Sappa, A.; Ponsa, D.; López, A. 2D-3D based on-board pedestrian detection system. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2010, 114, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollár, P.; Tu, Z.; Perona, P.; Belongie, S. Integral channel features. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, London, UK, 7 September 2009.
- Nam, W.; Han, B.; Han, J. Improving object localization using macrofeature layout selection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision—Workshop on Visual Surveillance, Barcelona, Spain, 13 November 2011.
- Felzenszwalb, P.; Girshick, R.; McAllester, D.; Ramanan, D. Object detection with discriminatively trained part based models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 1627–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanan, D. Part-Based Models for Finding People and Estimating Their Pose; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty, J.; McCallum, A.; Pereira, F. Real-time Pedestrian Detection with Deformable Part Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Alcala de Henares, Spain, 3 June 2012.
- Marin, J.; Vázquez, D.; López, A.; Amores, J.; Leibe, B. Random Forests of Local Experts for Pedestrian Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Sydney, Australia, 1 December 2013.
- Shashua, A.; Gdalyahu, Y.; Hayun, G. Pedestrian detection for driving assistance systems: Single-frame classification and system level performance. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Parma, Italy, 14 June 2004; pp. 1–6.
- Park, D.; Ramanan, D.; Fowlkes, C. Multiresolution models for object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Greece, 5 September 2010.
- Benenson, R.; Mathias, M.; Timofte, R.; Van Gool, L. Pedestrian detection at 100 frames per second. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16 June 2012.
- Wojek, C.; Walk, S.; Schiele, B. Multi-cue onboard pedestrian detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 19 June 2009.
- Enzweiler, M.; Gavrila, D.M. A multi-level mixture-of-experts framework for pedestrian classification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 2967–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premebida, C.; Carreira, J.; Batista, J.; Nunes, U. Pedestrian Detection Combining RGB and Dense LIDAR Data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Chicago, IL, USA, 14 September 2014.
- González, A.; Vázquez, D.; Ramos, S.; López, A.M.; Amores, J. Spatiotemporal Stacked Sequential Learning for Pedestrian Detection. In Proceedings of the Iberian Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 17 June 2015.
- González, A.; Villalonga, G.; Xu, J.; Vázquez, D.; Amores, J.; López, A.M. Multiview Random Forest of Local Experts Combining RGB and LIDAR data for Pedestrian Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Seoul, Korea, 28 June 2015.
- Oliveira, L.; Nunes, U.; Peixoto, P. On exploration of classifier ensemble synergism in pedestrian detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2010, 11, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Chen, C.S. Fast human detection using a novel boosted cascading structure with meta stages. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2008, 17, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enzweiler, M.; Gavrila, D. A mixed generative-discriminative framework for pedestrian classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23 June 2008.
- Yang, T.; Li, J.; Pan, Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Y. Active Learning Based Pedestrian Detection in Real Scenes. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR’06), Hong Kong, China, 20 August 2006; Volume 4, pp. 904–907.
- Vázquez, D.; López, A.M.; Ponsa, D.; Marin, J. Cool World: Domain adaptation of virtual and real worlds for human detection usind active learning. In Proceedings of the Conference on NIPS Domain Adaptation Workshop: Theory and Application, Sierra Nevada, Spain, 17 December 2011.
- Xu, J.; Vázquez, D.; Ramos, S.; López, A.; Ponsa, D. Domain Adaptation of Deformable Part-Based Models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 2367–2380. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28, Proceedings of Neural Information Processing Systems 2015, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; pp. 91–99.
- Yuan, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, X. Multi-spectral pedestrian detection. Signal Process. 2015, 11, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Laurent, L.; Maldague, X.; Prévost, D. Combination of colour and thermal sensors for enhanced object detection. In Proceedings of the 2007 10th International Conference on Information Fusion, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 9–12 July 2007; pp. 1–8.
- Socarras, Y.; Ramos, S.; Vázquez, D.; López, A.M.; Gevers, T. Adapting Pedestrian Detection from Synthetic to Far Infrared Images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Workshop on Visual Domain Adaptation and Dataset Bias, Sydney, Australia, 7 December 2011.
- Hwang, S.; Park, J.; Kim, N.; Choi, Y.; So Kweon, I. Multispectral Pedestrian Detection: Benchmark Dataset and Baseline. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015.
- Miron, A.; Rogozan, A.; Ainouz, S.; Bensrhair, A.; Broggi, A. An Evaluation of the Pedestrian Classification in a Multi-Domain Multi-Modality Setup. Sensors 2015, 15, 13851–13873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Guo, R.; Chen, C. Robust Pedestrian Tracking and Recognition from FLIR Video: A Unified Approach via Sparse Coding. Sensors 2014, 14, 11245–11259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besbes, B.; Rogozan, A.; Rus, A.M.; Bensrhair, A.; Broggi, A. Pedestrian Detection in Far-Infrared Daytime Images Using a Hierarchical Codebook of SURF. Sensors 2015, 15, 8570–8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, J.S.; Jeon, E.S.; Kim, Y.G.; Le, T.T.; Shin, K.Y.; Lee, H.C.; Park, K.R. Robust Pedestrian Detection by Combining Visible and Thermal Infrared Cameras. Sensors 2015, 15, 10580–10615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmeda, D.; Premebida, C.; Nunes, U.; Armingol, J.M.; de la Escalera, A. Pedestrian detection in far infrared images. Integr. Comput. Aided Eng. 2013, 20, 347–360. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-Vector Networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).