Multi-Mode Electromagnetic Ultrasonic Lamb Wave Tomography Imaging for Variable-Depth Defects in Metal Plates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
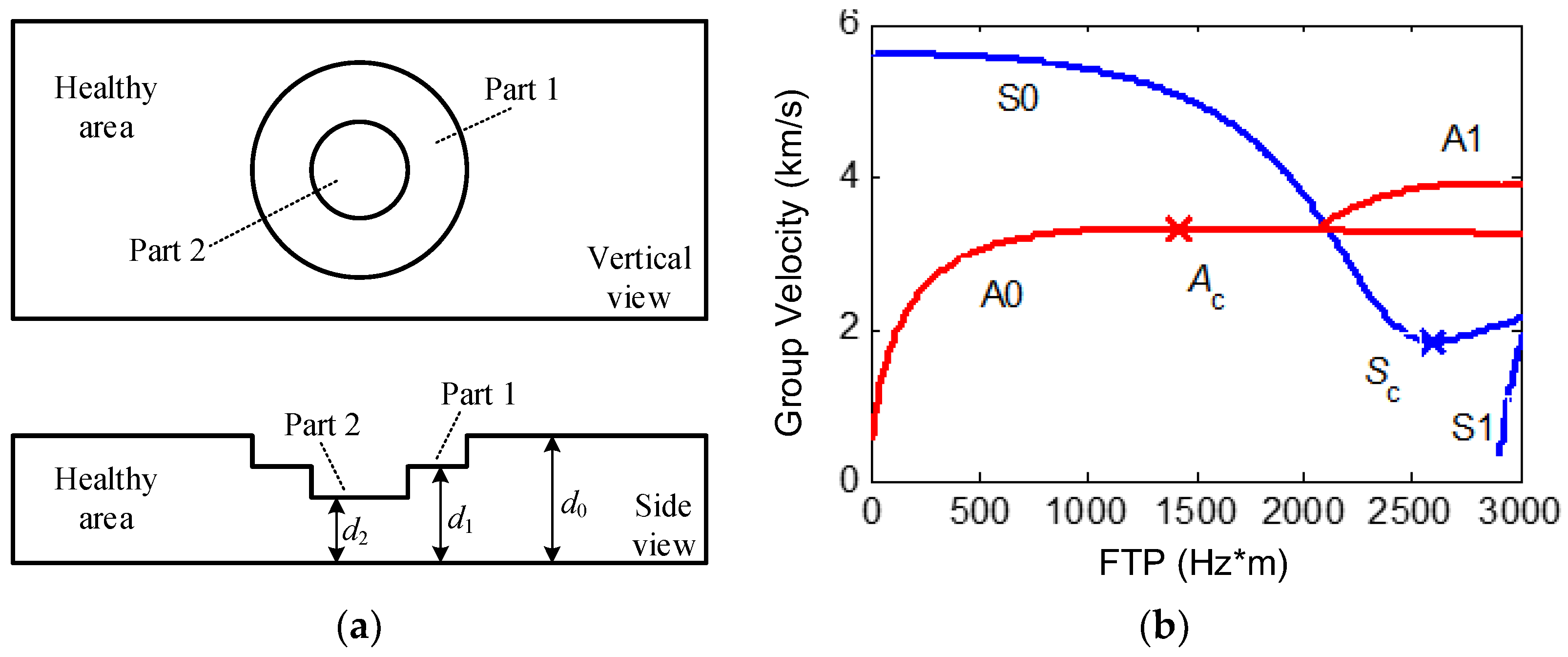
2. LW’s Sensitivity to Thickness
3. Principles and Procedures of Multi-Mode LW CTI
- (1)
- The FTP of an A0-mode LW and an S0-mode LW should be respectively less than xa and xs, which are respectively the cut-off FTP of an A0-mode LW and an S0-mode LW, in order to preserve the monotonicity of the LW group velocity.
- (2)
- Based on the sensitivity threshold STH, the working areas of an A0-mode LW and S0-mode LW should be respectively located in their own sensitive areas to increase the imaging sensitivity.
- (3)
- An A0-mode LW should be mainly applied in a small-thickness situation, and an S0-mode LW should be mainly applied in a large-thickness situation, according to the investigation results of LW’s sensitivity to thickness.
- (4)
- The working areas of an A0-mode LW and an S0-mode LW at their own working frequencies should partially overlap each other in order to guarantee that, for a given thickness, at least one mode of LW is sensitive. Specifically, the upper limit thickness of an A0-mode LW working area should be greater than the lower limit thickness of an S0-mode LW working area.
- (1)
- Set the sensitivity thresholds STH respectively for the A0-mode and S0-mode LWs.
- (2)
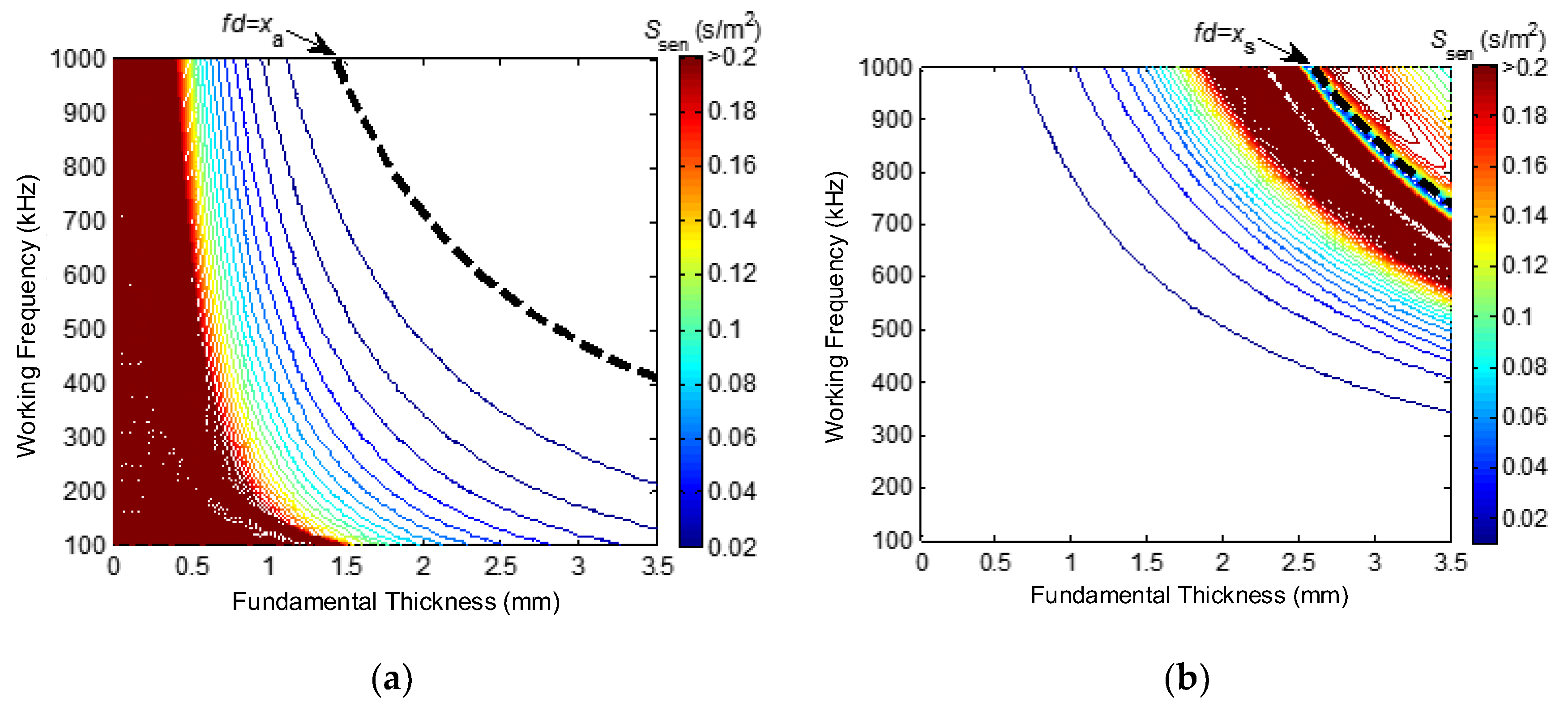
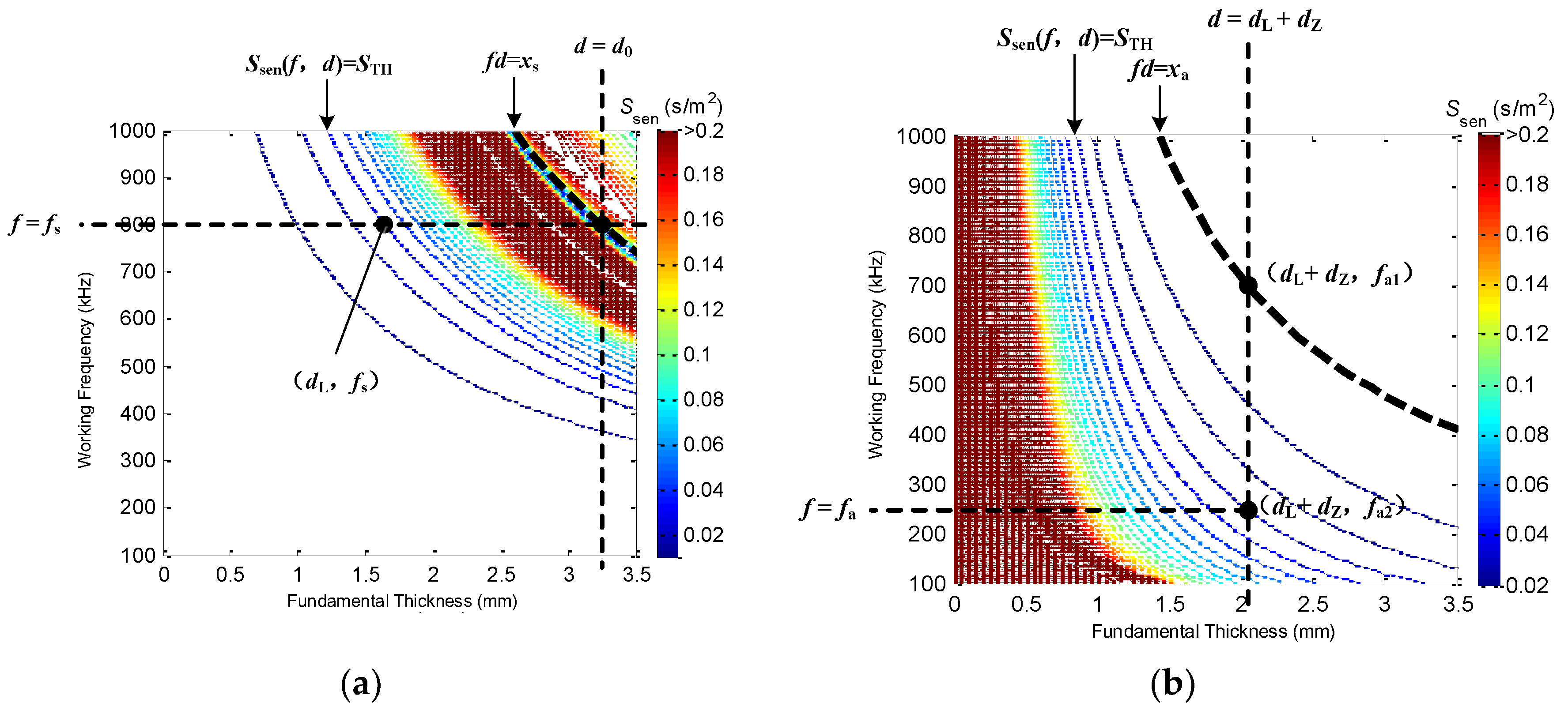
- Locate the curve fd = xs in Figure 3a, which is the sensitivity distribution of the S0-mode LW. The working area of the S0-mode LW should be at the lower left part of the curve.
- (3)
- Locate the straight line d = d0 in Figure 3a, where d0 is the thickness of the healthy area. The working area of the S0-mode LW should be confined to the left part of the straight line. Because the S0-mode LW is more sensitive when the thickness is relatively large, the thickness of the healthy area (known quantity) should be figured on the sensitivity distribution plane of the S0-mode LW, and the working areas of the S0-mode LW should firstly be determined.
- (4)
- Calculate the intersection point coordinates (d0, fs) of the curve fd = xs and the straight line d = d0, and take fs as the working frequency of the S0-mode LW. If the working frequency of the S0-mode LW is bigger than fs, then the working area will not cover the thickness of the healthy area, and, if the working frequency is smaller than fs, the sensitive thickness range that the S0-mode LW covers greatly decreases. Therefore, fs at the intersection point is almost the perfect working frequency of the S0-mode LW.
- (5)
- Locate the contour line Ssen(f, d) = STH in Figure 3a, and the working area of the S0-mode LW should be confined to the upper right part of the contour line, which is the sensitive area of the the S0-mode LW.
- (6)
- Calculate the intersection point coordinates (dL, fs) of the straight line f = fs and the contour line Ssen(f, d) = STH to obtain the lower limit dL, and the working area of the thickness of the S0-mode LW at working frequency fs is [dL, d0]. The sensitive-thickness range of the S0-mode LW is maximized by the method proposed above.
- (7)
- Set the overlapping width dZ(dZ > 0) of the A0-mode and S0-mode LWs working areas in Figure 3b to obtain the working area of the thickness of the A0-mode LW [0, dL + dZ]. The overlapping width is to ensure that the sensitive working thickness by the cooperation of the A0-mode and S0-mode LWs can completely cover the thickness of the variable-depth defect area.
- (8)
- Locate the curve fd = xa in Figure 3b. The working area of the A0-mode LW should be confined to the lower left part of the curve, which is the cut-off FTP of the A0-mode LW
- (9)
- Calculate the intersection point coordinates (dL + dZ, fa1) of the curve fd = xa and the straight line d = dL + dZ.
- (10)
- Locate the contour line Ssen(f, d) = STH in Figure 3b, and the working area of the A0-mode LW should be confined to the lower left part of the contour line, which is the sensitive area of the the A0-mode LW.
- (11)
- Calculate the intersection point coordinates (dL + dZ, fa2) of the contour line Ssen(f, d) = STH and the straight line d = dL + dZ.
- (12)
- Select the smallest of fa1 and fa2 as the working frequency fa of the A0-mode LW. If the contour line Ssen(f, d) = STH is under the curve fd = xa, fa2 is selected as the working frequency fa. Otherwise, if the contour line Ssen(f, d) = STH is above the curve fd = xa, fa1 is selected as the working frequency fa. This is to maximize the sensitive working thickness of the A0-mode LW to be [0, dL + dZ].
- (1)
- Calculate the working frequencies and working areas of the A0-mode and S0-mode LWs based on the proposed cooperation principles.
- (2)
- Respectively implement the single A0-mode and single S0-mode LWs to detect the defect area and obtain the TOF.
- (3)
- Conduct the CTI respectively based on the A0-mode and S0-mode LWs using the TOF.
- (4)
- Conduct data fusion of CTI results from the A0-mode and S0-mode LWs.
- (1)
- In the condition of da∈[0, dL + dZ] and ds∈[dL, d0], or in the condition of da∉[0, dL + dZ] and ds∉[dL, d0], the mesh thickness after fusion is dadd = 0.5da + 0.5ds. In this situation, da is in the sensitive thickness range of the A0-mode LW, and ds is in the sensitive thickness range of the S0-mode LW (or neither da nor ds is in the corresponding sensitive thickness range), which means the calculated thicknesses are both expected ones, so the weighted average value is selected as the final thickness of the mesh.
- (2)
- In the condition of da∈[0, dL + dZ] and ds∉[dL, d0], the mesh thickness after fusion is dadd = da. In this situation, only da is in the sensitive thickness range of the A0-mode LW, but ds is not in the sensitive thickness range of the S0-mode LW, so the calculated thickness ds should not be considered. That means the mesh thickness is in the sensitive thickness range of the A0-mode LW [0, dL + dZ]; therefore, da is selected as the final thickness of the mesh.
- (3)
- In the condition of da∉[0, dL + dZ] and ds∈[dL, d0], the mesh thickness after fusion is dadd = ds. In this situation, only ds is in the sensitive thickness range of the S0-mode LW, but da is not in the sensitive thickness range of the A0-mode LW, so the calculated thickness da should not be considered. That means the mesh thickness is in the sensitive thickness range of the S0-mode LW [dL, d0]; therefore, ds is selected as the final thickness of the mesh.
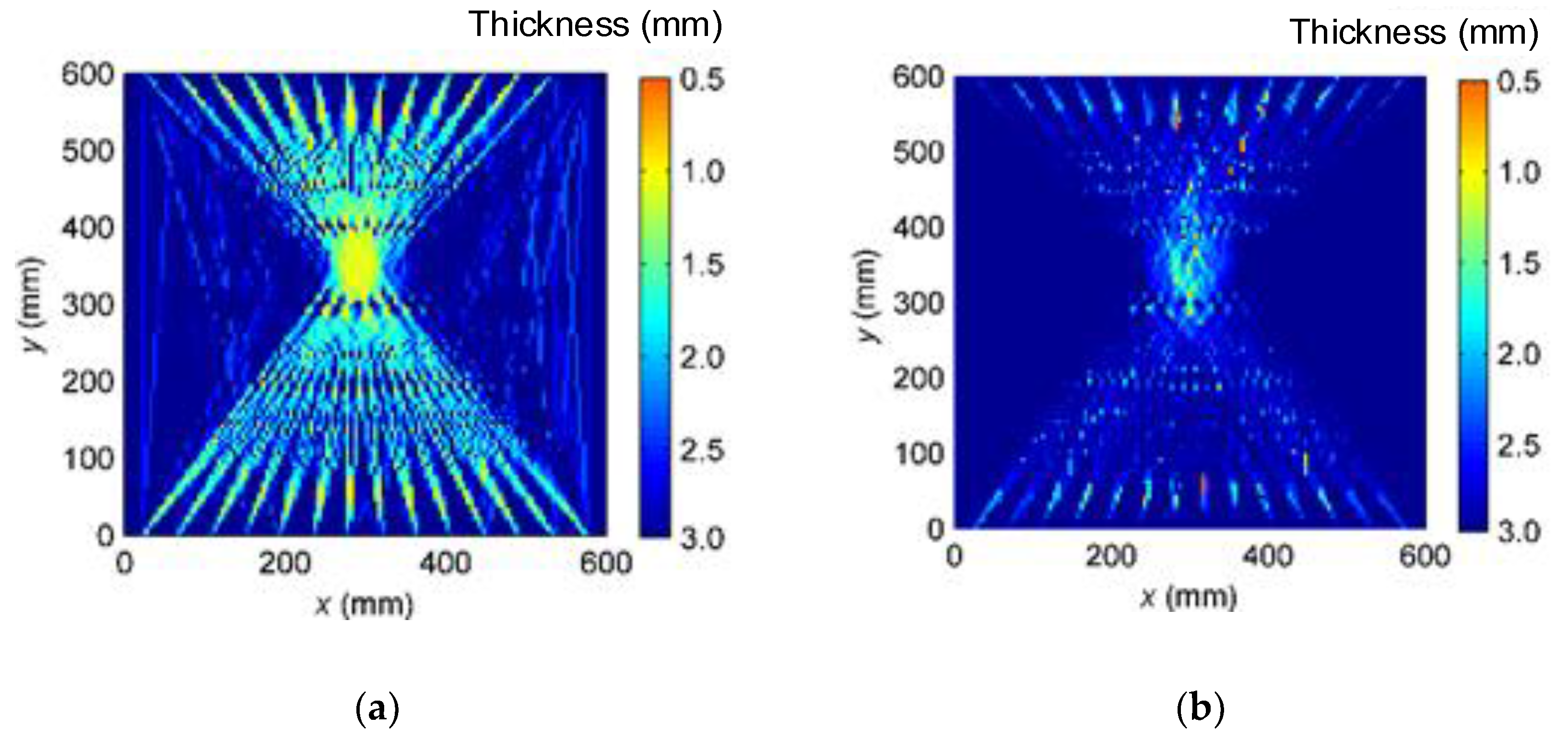
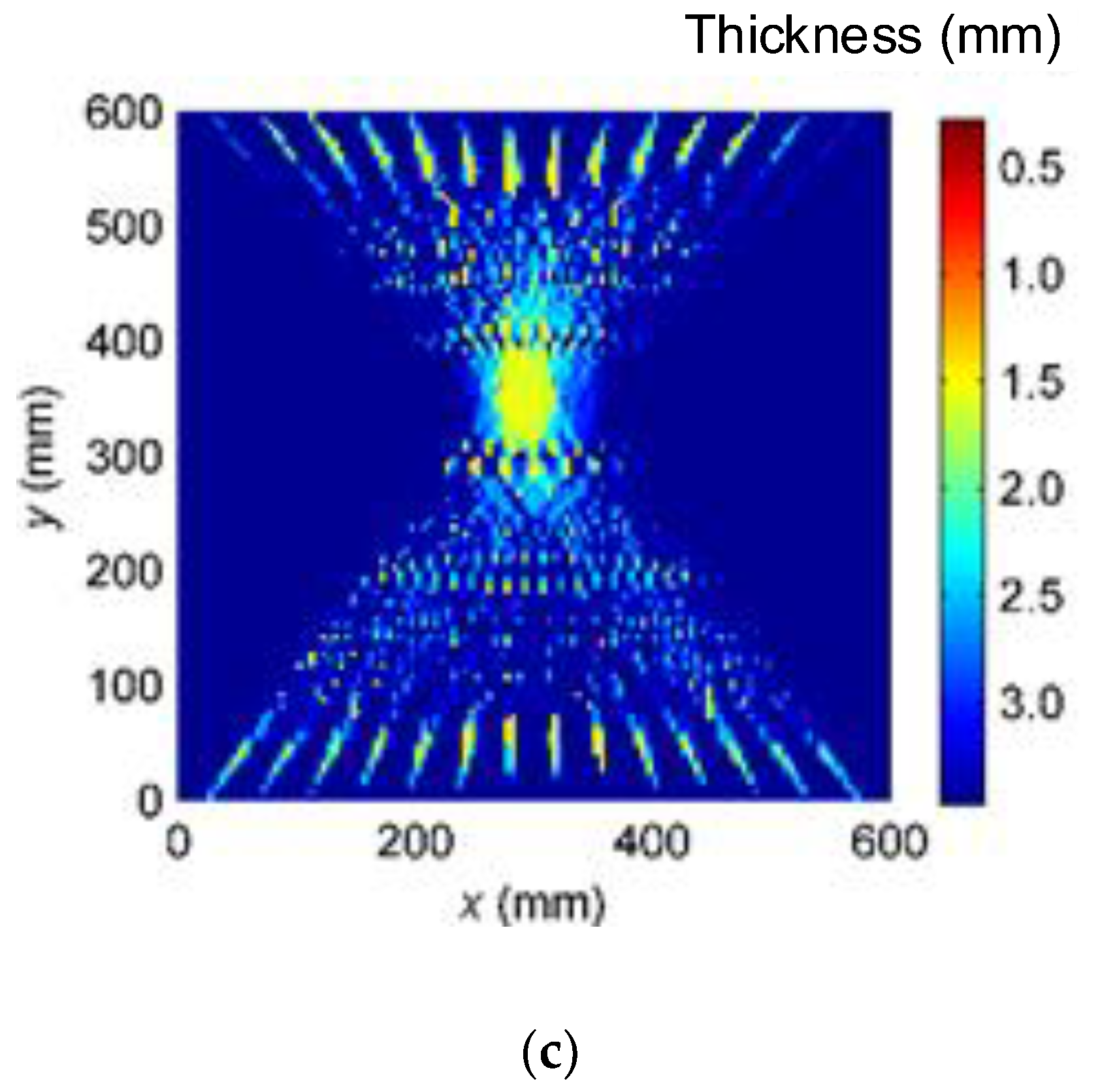
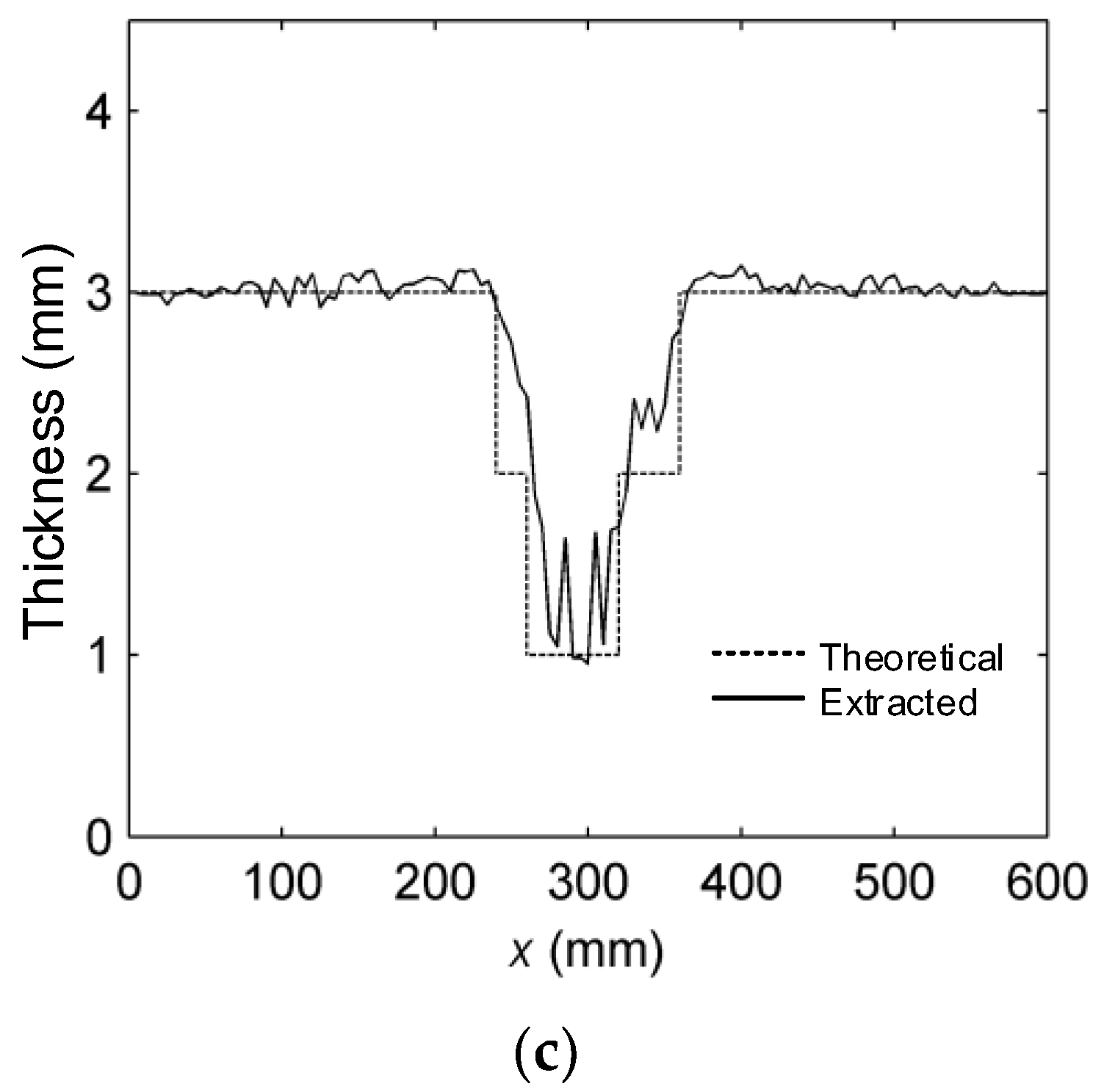
4. Experiments and Results
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, F.C.; Meng, G.; Ye, L.; Lu, Y.; Kageyama, K. Dispersion analysis of Lamb waves and damage detection for aluminum structures using ridge in the time-scale domain. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baid, H.; Schaal, C.; Samajder, H.; Mal, A. Dispersion of Lamb waves in a honeycomb composite sandwich panel. Ultrasonics 2015, 56, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeon, J.C.P.; Hinders, M.K. Parallel projection and crosshole Lamb wave contact scanning tomography. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 106, 2568–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyarenko, E.V.; Hinders, M.K. Fan beam and double crosshole Lamb wave tomography for mapping flaws in aging aircraft structures. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 108, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.M.; Balasubramaniam, K.; Krishnamurthy, C.V. Structural health monitoring of composite structures using Lamb wave tomography. Smart Mater. Struct. 2004, 13, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, K.R.; Hinders, M.K. Multi-mode Lamb wave tomography with arrival time sorting. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 117, 2028–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyadiji, S.O.; Feroz, T. Applications of PZT sensors and finite element analysis in defect detection in bars. In Proceedings of the 2nd International workshop on Structural health monitoring, Stanford, CA, USA, 8–10 September 1999; pp. 1048–1057.
- Sposito, G.; Cawley, P.; Nagy, P.B. Crack profile reconstruction by means of potential drop measurements. Rev. Prog. Quant. Nondestruct. Eval. 2007, 894, 733–740. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.N.; He, C.F.; Wu, B. Defect detection in helical and central wires of steel strands using advanced ultrasonic guided wave technique with new type magnetostrictive transducers. In Proceedings of IEEE 2008 Ultrasonics Symposium, Beijing, China, 2–5 November 2008; pp. 832–835.
- Miller, C.A.; Hinders, M.K. Classification of flaw severity using pattern recognition for guided wave-based structural health monitoring. Ultrasonics 2014, 54, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endoh, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Hiwatashi, Y.; Hoshimiya, T. Observation of tilted or wedge-shaped subsurface defects and their nondestructive evaluation by photoacoustic microscopy. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 42, 3052–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.S.; Billson, D.R.; Hutchins, D.A. Ultrasonic Lamb wave tomography using scanned EMATs and wavelet processing. Nondestr. Test. Eval. 2007, 22, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleyne, D.N.; Cawley, P. Optimization of Lamb wave inspection techniques. NDT E Int. 1992, 25, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.L.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, W.; Wang, S. A new omni-directional EMAT for ultrasonic Lamb wave tomography imaging of metallic plate defects. Sensors 2014, 14, 3458–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Structure Parameters | A0 Mode EMAT | S0 Mode EMAT |
|---|---|---|
| Working frequency (kHz) | 270 | 700 |
| l (mm) | 4.2 | 3.6 |
| Outer diameter of the coil (mm) | 37.8 | 32.4 |
| Inner diameter of the coil (mm) | 12.6 | 10.8 |
| Number of windings | 24 | 24 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, W. Multi-Mode Electromagnetic Ultrasonic Lamb Wave Tomography Imaging for Variable-Depth Defects in Metal Plates. Sensors 2016, 16, 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050628
Huang S, Zhang Y, Wang S, Zhao W. Multi-Mode Electromagnetic Ultrasonic Lamb Wave Tomography Imaging for Variable-Depth Defects in Metal Plates. Sensors. 2016; 16(5):628. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050628
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Songling, Yu Zhang, Shen Wang, and Wei Zhao. 2016. "Multi-Mode Electromagnetic Ultrasonic Lamb Wave Tomography Imaging for Variable-Depth Defects in Metal Plates" Sensors 16, no. 5: 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050628
APA StyleHuang, S., Zhang, Y., Wang, S., & Zhao, W. (2016). Multi-Mode Electromagnetic Ultrasonic Lamb Wave Tomography Imaging for Variable-Depth Defects in Metal Plates. Sensors, 16(5), 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050628






