A New, Scalable and Low Cost Multi-Channel Monitoring System for Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. A Brief Review of DAQ/SCADA Architectures
3. Developed Monitoring System
Real-Time Monitoring System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PE | Polymer Electrolyte |
| PEFC | Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell |
| DAQ | Data Acquisition |
| NI | National Instruments |
| BoP | Balance of Plant |
| RES | Renewable Energy Sources |
| SG | Smart Grid |
| PHM | Prognostics and Health Management |
| MTU | Master Terminal Unit |
| OPC | OLE for Process Control |
| SCADA | Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition |
| AMB | Amplifying and Multiplexing Board |
| IDE | Integrated Development Environment |
| VI | Virtual Instrument |
| GUI | Graphical User Interface |
| CSV | Comma Separated Values |
References
- Segura, F.; Andújar, J.M. Step by step development of a real fuel cell system. Design, implementation, control and monitoring. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 5496–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasallo, M.; Andújar, J.M.; Garcia, C.; Brey, J.J. A methodology for sizing back-up fuel cell/battery hybrid power systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 1964–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, F.; Durán, E.; Andújar, J.M. Design, building and testing of a stand alone fuel cell hybrid system. J. Power Sources 2009, 193, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.S.; Moghavvemi, M.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Muttaqi, K.M.; Moghavvemi, S. Effective utilization of excess energy in standalone hybrid renewable energy systems for improving comfortability and reducing cost of energy: A review and analysis. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2015, 42, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursúa, A.; Gandía, L.M.; Sanchis, P. Hydrogen production from water electrolysis: Current status and future trends. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 410–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicakova, O.; Straka, P. Production of hydrogen from renewable resources and its effectiveness. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 11563–11578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veziroğlu, T.N.; Şahin, S. 21st Century’s energy: Hydrogen energy system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 1820–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chan, S.; KweeHo, H.; Tan, S.C.; Li, M.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Feng, Z. Towards a smart energy network: The roles of fuel/electrolysis cells and technological perspectives. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 6866–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracco, S.; Delfino, F.; Pampararo, F.; Robba, M.; Rossi, M. The University of Genoa smart polygeneration microgrid test-bed facility: The overall system, the technologies and the research challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 2013, 18, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andújar, J.M.; Segura, F. Fuel cells: History and updating. A walk along two centuries. Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 2009, 13, 2309–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirami, H.; Zargar, A.; Mahdi, M. Optimal PID plus fuzzy controller design for a PEM fuel cell air feed system using self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 30, 9422–9434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliardini, F.; Capasso, C.; Corbo, P. Optimization of hydrogen feeding procedure in PEM fuel cell systems for transportation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 21746–21752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitwieser, M.; Klingele, M.; Britton, B.; Holdcroft, S.; Zengerle, R.; Thiele, S. Improved Pt-utilization efficiency of low Pt-loading PEM fuel cell electrodes using direct membrane deposition. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 60, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devrim, Y.; Albostan, A. Enhancement of PEM fuel cell performance at higher temperatures and lower humidities by high performance membrane electrode assembly based on Nafion/zeolite membrane. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 15328–15335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, T. Compact PEM fuel cell system combined with all-in-one hydrogen generator using chemical hydride as a hydrogen source. Appl. Energy 2015, 160, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moçoteguy, P.; Ludwig, B.; Yousfi, N. Application of current steps and design of experiments methodology to the detection of water management faults in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack. J. Power Sources 2016, 303, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damour, C.; Benne, M.; Grondin-Perez, B.; Bessafi, M.; Hissel, D.; Chabriat, J.P. Polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell fault diagnosis based on empirical mode decomposition. J. Power Sources 2015, 299, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechartier, E.; Laffly, E.; Péra, M.C.; Gouriveau, R.; Hissel, D.; Zerhouni, N. Proton exchange membrane fuel cell behavioural model suitable for prognostics. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 8384–8397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husar, A.; Strahl, S.; Riera, J. Experimental characterization methodology for the identification of voltage losses of PEMFC: Applied to an open cathode stack. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 7309–7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadet, C.; Jemeï, S.; Druart, F.; Hissel, D. Diagnostic tools for PEMFCs: From conception to implementation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 10613–10626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotelli, G.; Ferrero, R.; Gallo, P.; Latorrata, S.; Toscani, S. Testing of a Diagnostic Technique for a Single PEM Fuel Cell Based on a DC/DC Converter. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Applied Measurements for Power Systems (AMPS), Aachen, Germany, 24–26 September 2014; pp. 1–5.
- Kim, J.; Lee, I.; Tak, Y.; Cho, B.H. State-of-health diagnosis based on hamming neural network using output voltage pattern recognition for a PEM fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 4280–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrone, R.; Zheng, Z.; Hissel, D.; Péra, M.C.; Pianese, C.; Sorrentino, M.; Becherif, M.; Yousfi-Steiner, N. A review on model-based diagnosis methodologies for PEMFCs. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 7077–7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Outbib, R.; Hissel, D.; Giurgea, S. Online diagnosis of PEMFC by analyzing individual cell voltages. In Proceedings of the 2013 European Control Conference (ECC), Zurich, Switzerland, 17–19 July 2013; pp. 2439–2444.
- Li, Z.; Outbib, R.; Hissel, D.; Giurgea, S. Data-driven diagnosis of PEM fuel cell: A comparative study. Control Eng. Pract. 2014, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Outbib, R.; Giurgea, S.; Hissel, D. Diagnosis for PEMFC Systems: A Data-Driven Approach with the Capabilities of Online Adaptation and Novel Fault Detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 5164–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Outbib, R.; Giurgea, S.; Hissel, D.; Jemei, S.; Giraud, A.; Rosini, S. Online implementation of SVM based fault diagnosis strategy for PEMFC systems. Appl. Energy 2014, 164, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, F.J.; Valledor, M.; Campo, J.C.; Blanco, J.R.; Menéndez, J. Low-cost open-source multifunction data acquisition system for accurate measurements. Measurement 2014, 55, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonderware InTouch HMI Solutions. Available online: http://www.wonderware.es/contents/WonderwareInTouchHMI.asp (accessed on 10 December 2015).
- GE HMI/SCADA iFIX. Available online: http://www.geautomation.com/products/proficy-hmiscada-ifix (accessed on 10 December 2015).
- SIMATIC HMI Software. Available online: http://w3.siemens.com/mcms/human-machine-interface/en/visualization-software/pages/default.aspxt (accessed on 10 December 2015).
- NI LabVIEW. Available online: http://www.ni.com/labview/ (accessed on 12 December 2015).
- Rapid SCADA. Available online: http://rapidscada.org/ (accessed on 12 December 2015).
- OpenSCADA. Available online: http://openscada.org/ (accessed on 12 December 2015).
- EnSCADA—IndigoSCADA. Available online: http://www.enscada.com/a7khg9/IndigoSCADA.html (accessed on 12 December 2015).
- Arpaia, P.; De Matteis, E.; Inglese, V. Software for measurement automation: A review of the state of the art. Measurement 2015, 66, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitru, C.D.; Gligor, A. SCADA based software for renewable energy management System. Proc. Econ. Finance 2012, 3, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, Z.; Morais, H.; Faria, P.; Ramos, C. Distribution system operation supported by contextual energy resource management based on intelligent SCADA. Renew. Energy 2013, 52, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvial-Palavicino, C.; Garrido-Echeverría, N.; Jiménez-Estévez, G.; Reyes, L.; Palma-Behnke, R. A methodology for community engagement in the introduction of renewable based smart microgrid. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2011, 15, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, W.T.; Chung, H.Y. A distributed energy monitoring network system based on data fusion via improved PSO. Measurement 2014, 55, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.; Crespo, A.; Iung, B. On the concept of e-maintenance: Review and current research. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2008, 93, 1165–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, A.; Naveenkumar, B.; Balaji, A.; Bharathi, N. Experimental validation of PID based cascade control system through SCADA-PLC-OPC and internet architectures. Measurement 2012, 45, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherdantseva, Y.; Burnap, P.; Blyth, A.; Eden, P.; Jones, K.; Soulsby, H.; Stoddart, K. A review of cyber security risk assessment methods for SCADA systems. Comput. Secur. 2016, 56, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, P.; Walter, A.; Karnouskos, S. Industrial automation based on cyber-physical systems technologies: Prototype implementations and challenges. Comput. Ind. 2015, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, K.S.; Kumar, M.; Mallick, T.K.; Sharon, H.; Lokeswaran, S. A review of Integration, Control, Communication and Metering (ICCM) of renewable energy based smart grid. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Figueiredo, J.; Melicio, R.; Mendes, V.M.F.; Martins, J.; Quadrado, J.C. Consumer energy management system with integration of smart meters. Energy Rep. 2015, 1, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, D.; Russell, D.; Ferguson, I.; Isaacs, J.; MacLeod, A.; White, R. The Internet of Things—The future or the end of mechatronics. Mechatronics 2015, 27, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, R.; Dunkel, J.; Masbruch, H.; Stipkovic, S. Intelligent M2M: Complex event processing for machine-to-machine communication. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduino. Available online: https://www.arduino.cc/ (accessed on 25 November 2015).
- RaspberryPi. Available online: https://www.raspberrypi.org/ (accessed on 25 November 2015).
- Intel Edison. Available online: http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/do-it-yourself/edison.html (accessed on 25 November 2015).
- OpenDAQ. Available online: http://www.open-daq.com/ (accessed on 25 November 2015).
- Devaraju, J.T.; Suhas, K.R.; Mohana, H.K.; Patil, V.A. Wireless Portable Microcontroller based Weather Monitoring Station. Measurement 2015, 76, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay-Ekuakille, A.; Griffo, G.; Massaro, A.; Spano, F.; Gigli, G. Experimental characterization of an implantable neuro-packaging for EEG signal recording and measurement. Measurement 2016, 79, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faranda, R.; Lazzaroni, M. Industrial low cost temperature measurement in permanent electro-magnetic platens. Measurement 2013, 46, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, H.E.; Gad, H.E. Development of a new temperature data acquisition system for solar energy applications. Renew. Energy 2015, 74, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgas, P.; Piromalis, D.; Antonakoglou, K.; Vokas, G.; Tseles, D.; Arvanitis, K.G. Smart Solar Panels: In-situ monitoring of photovoltaic panels based on wired and wireless sensor networks. Energy Proc. 2013, 36, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdoush, S.; Li, X. Wireless Sensor Network System Design Using Raspberry Pi and Arduino for Environmental Monitoring Applications. Proc. Comput. Sci. 2014, 34, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, N.C.; Melício, R.; Matias, J.C.O.; Catalão, J.P.S. Photovoltaic and wind energy systems monitoring and building/home energy management using ZigBee devices within a smart grid. Energy 2013, 49, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.S.; Huang, C.F. Design, fabrication and performance test of a planar array module-type micro fuel cell stack. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 76, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanungkhid, P.; Piumsomboon, P. 200W PEM Fuel Cell Stack with Online Model-Based Monitoring System. Eng. J. 2014, 18, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moçoteguy, P.; Ludwig, B.; Yousfi, N. Influence of ageing on the dynamic behaviour and the electrochemical characteristics of a 500 We PEMFC stack. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 10230–10244. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, A.; Sasmito, A.P.; Shamim, T. Investigation of the purging effect on a dead-end anode PEM fuel cell-powered vehicle during segments of a European driving cycle. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 106, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, I.; Calderón, A.J.; Calderón, M.; Herrero, J.L. Monitoring of Electric Power Systems: Application to Self-Sufficient Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th International Conference on Compatibility and Power Electronics (CPE), Caparica, Portugal, 24–26 June 2015; pp. 560–565.
- Lebreton, C.; Benne, M.; Damour, C.; Yousfi-Steiner, N.; Grondin-Perez, B.; Hissel, D.; Chabriat, J.P. Fault Tolerant Control Strategy Applied to PEMFC Water Management. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 10636–10646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilavivat, V.; Shimpalee, S.; Van Zee, J.W.; Xu, H.; Mittelsteadt, C.K. Current Distribution Mapping for PEMFCs. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 174, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, F.; Andújar, J.M. Modular PEM Fuel Cell SCADA & Simulator System. Resources 2015, 4, 692–712. [Google Scholar]
- Andújar, J.M.; Segura, F. PEFC Simulator and Real Time Monitoring System. Fuel Cells 2015, 15, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, T.; Thi, P.; Babauta, J.T.; Trong, N.; Heo, D.; Beyenal, H. Scale-up of sediment microbial fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2014, 272, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.; Correia, J.H.; Carmo, J.P. A Low-Cost Flexible-Platform (LCFP) for characterization of photodetectors. Measurement 2015, 61, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, M.; Calderón, A.J.; Ramiro, A.; González, J.F. Automatic management of energy flows of a stand-alone renewable energy supply with hydrogen support. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 2226–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, I.; Ramiro, A.; Calderón, M.; Calderón, A.J.; González, J.F. Estimation of the state-of-charge of gel lead-acid batteries and application to the control of a stand-alone wind-solar test-bed with hydrogen support. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 11090–11103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H-TEC Education Fuel Cell Stack Experimentation System. Available online: http://www.h-tec.com/en/education/products-education/stack/stack-experimentation/ (accessed on 15 December 2015).

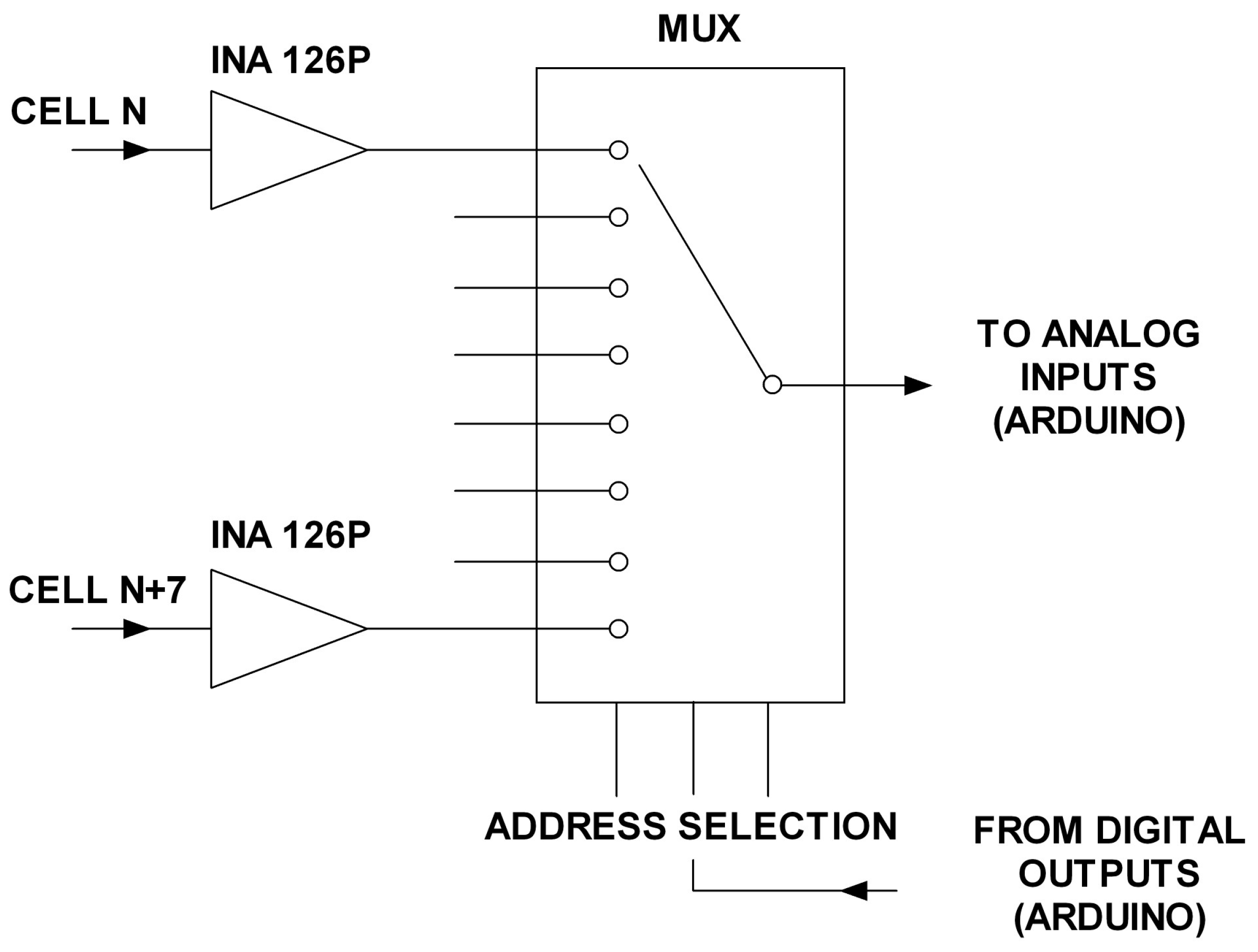
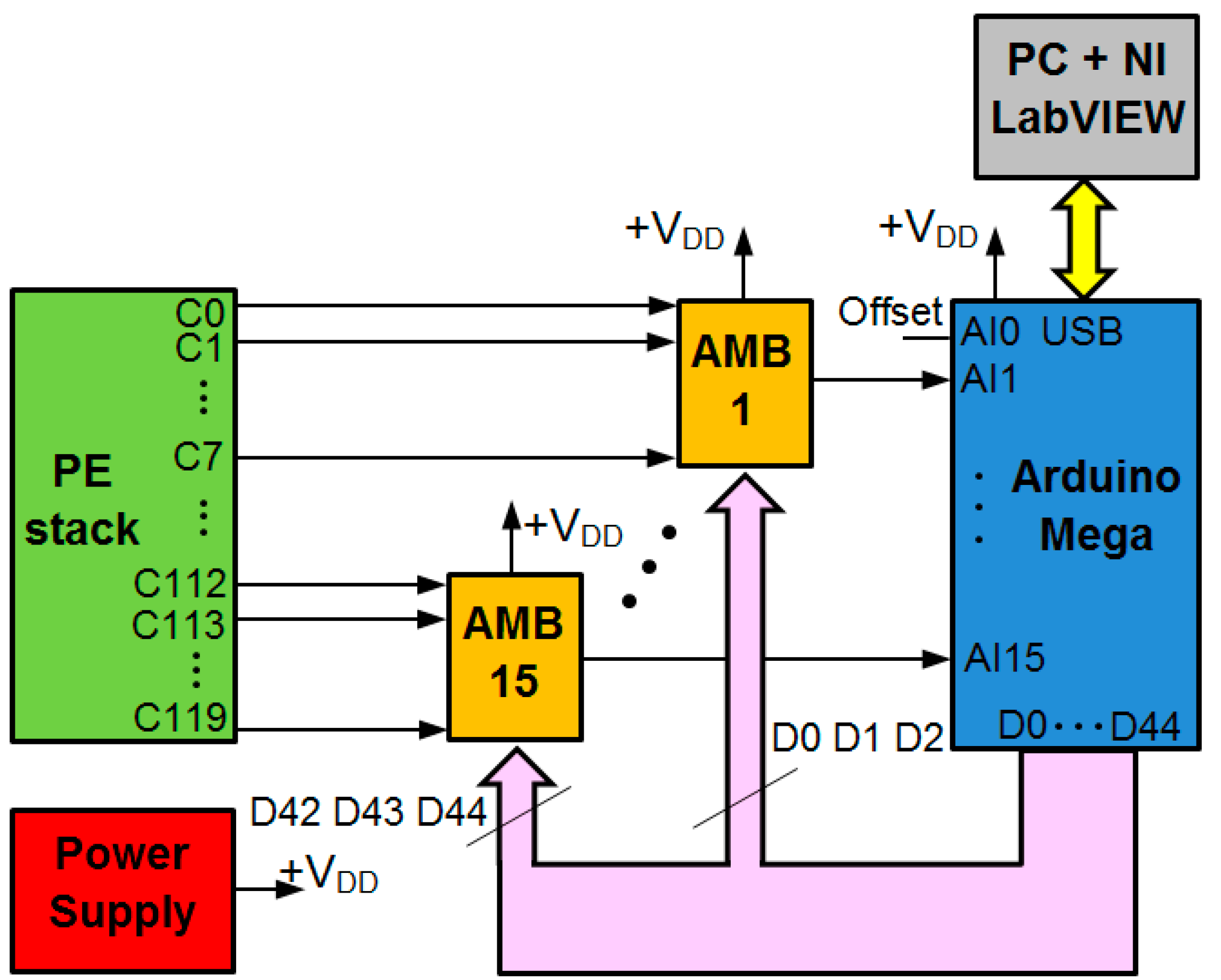

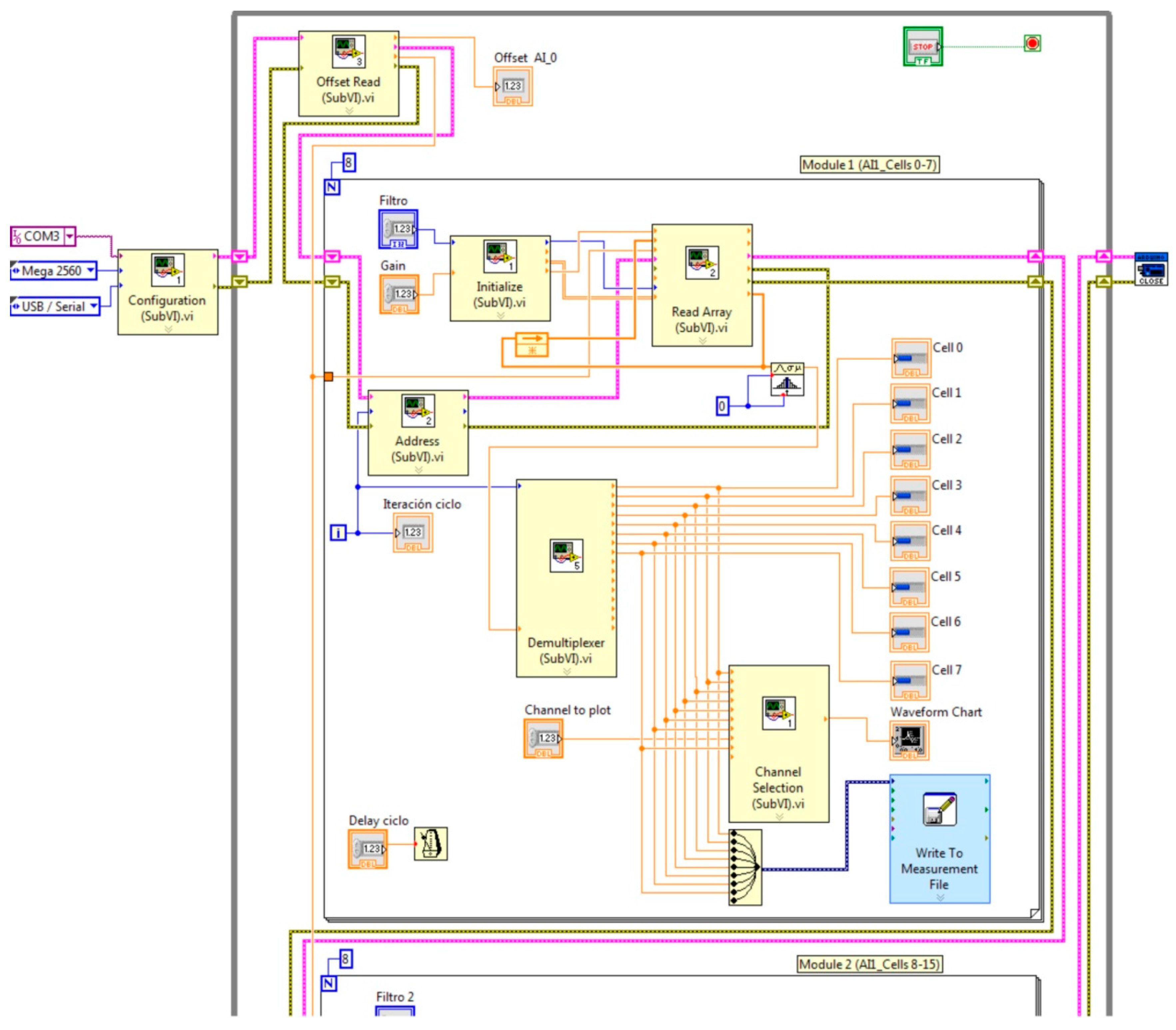
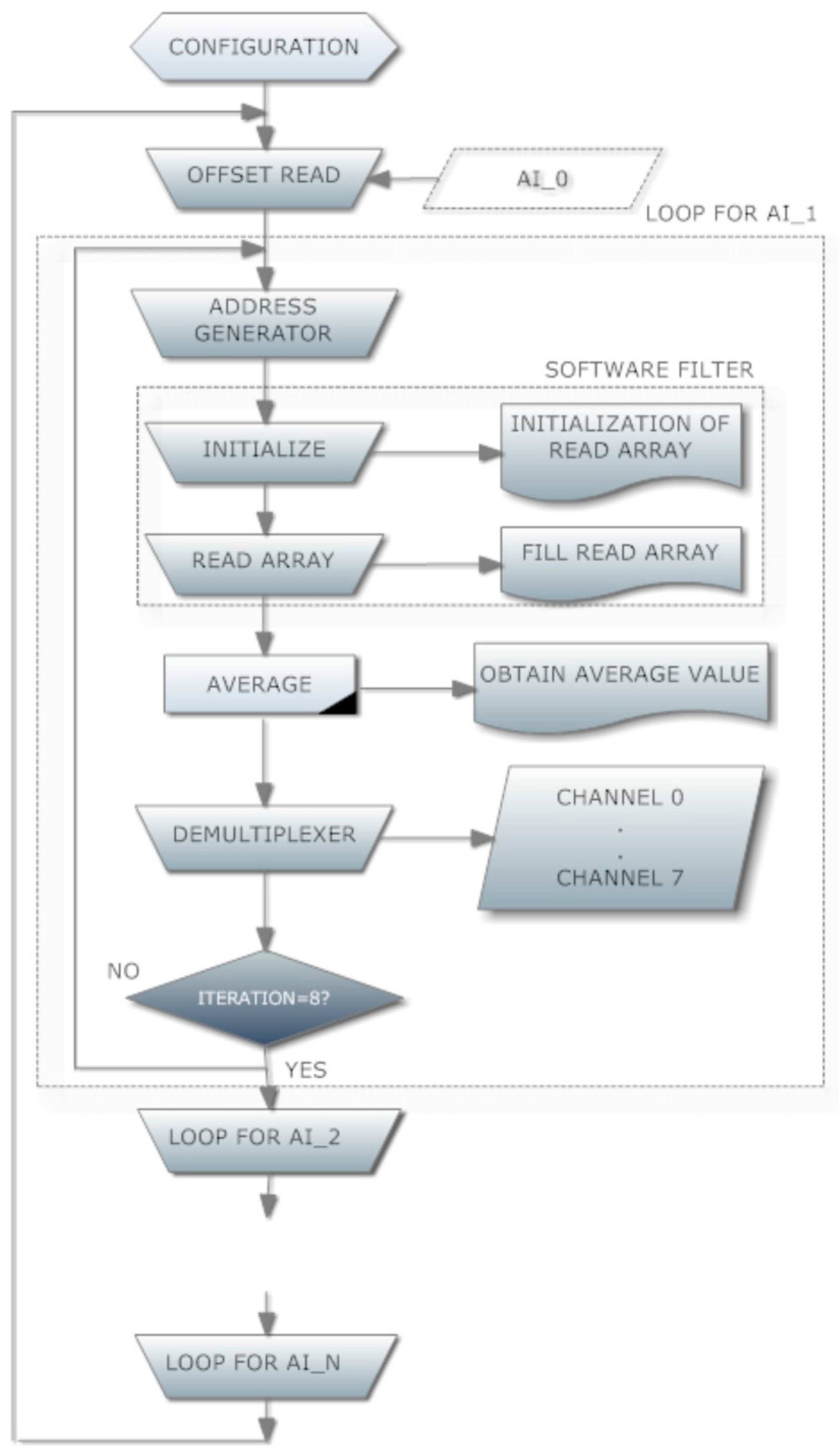

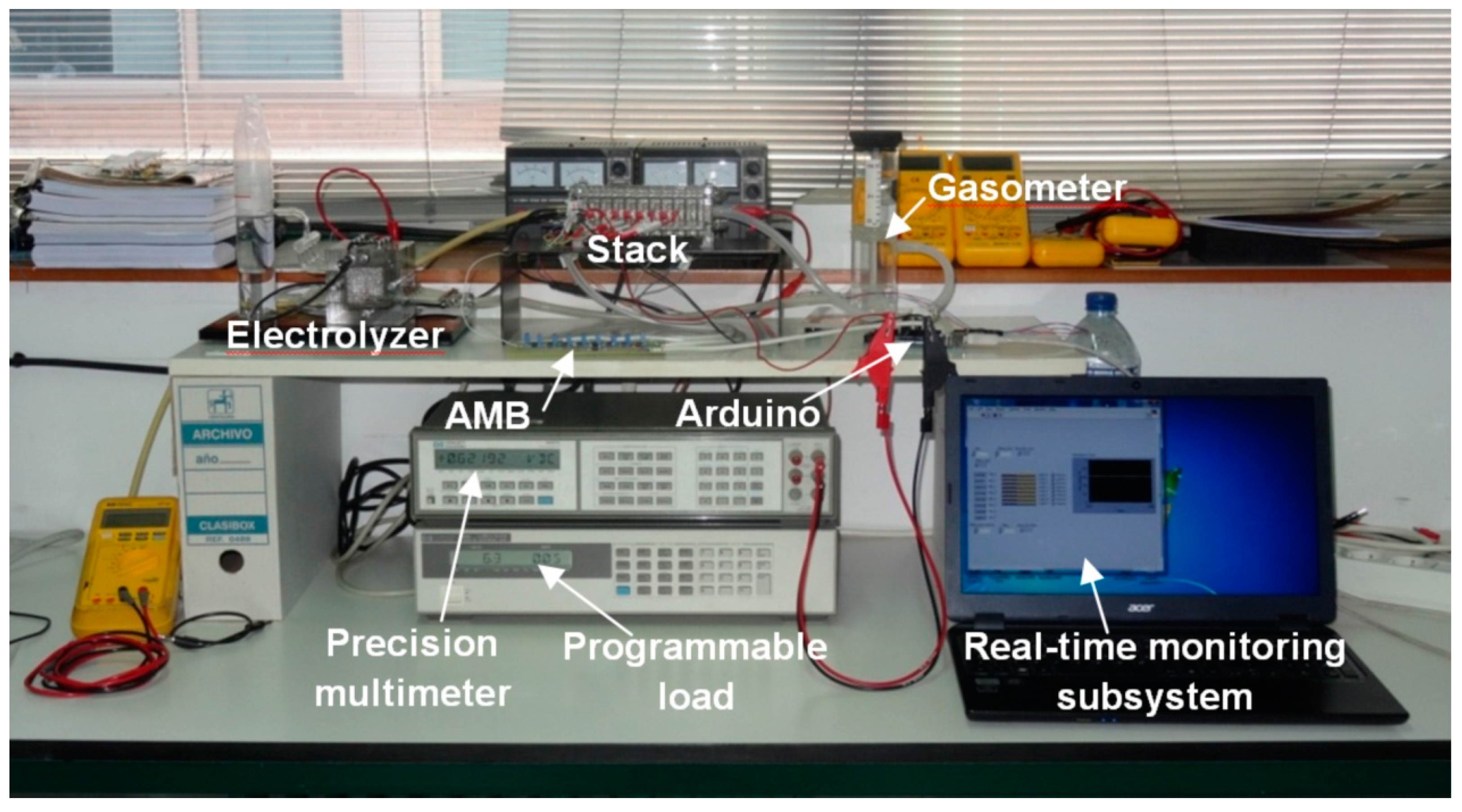

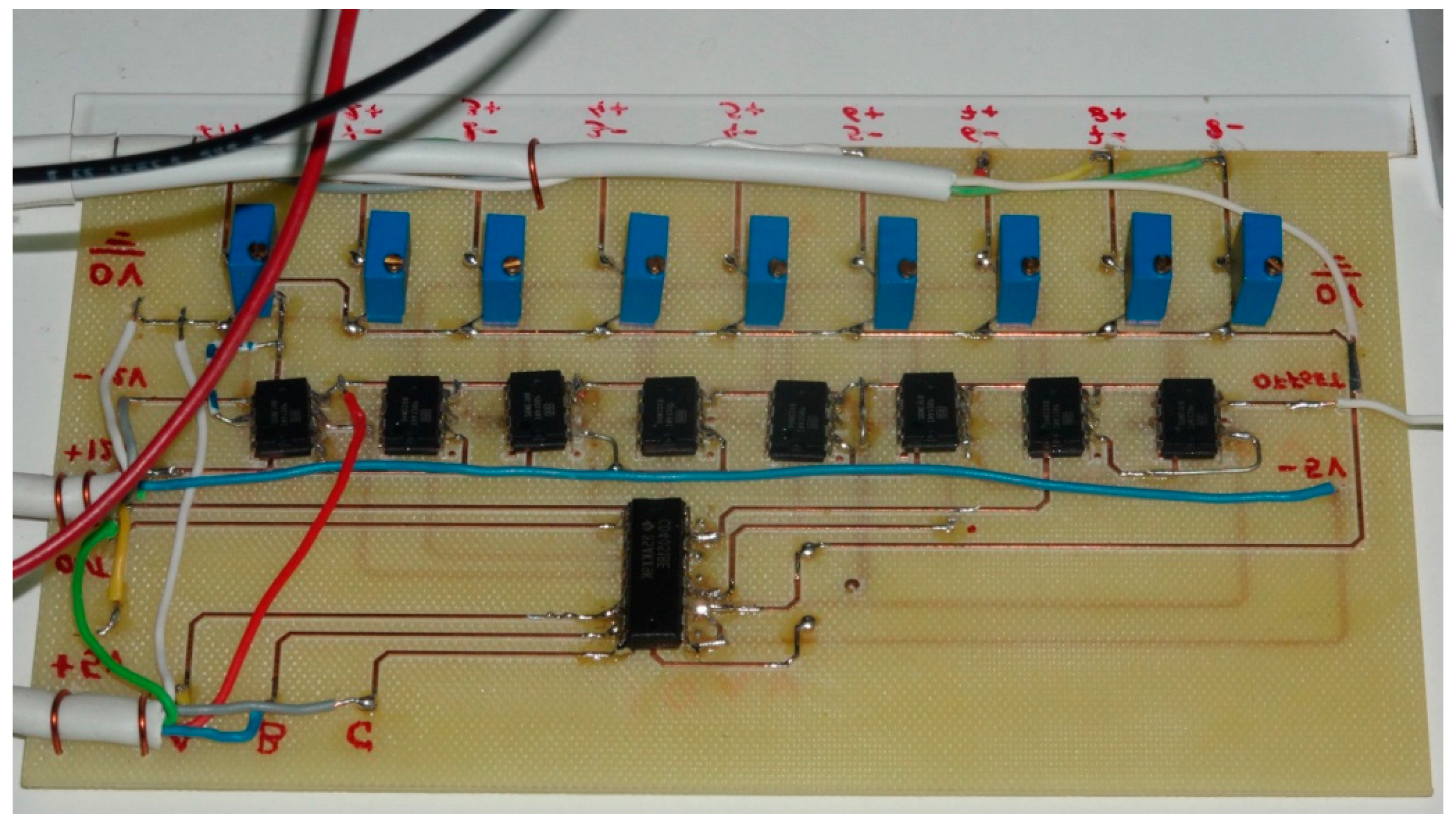
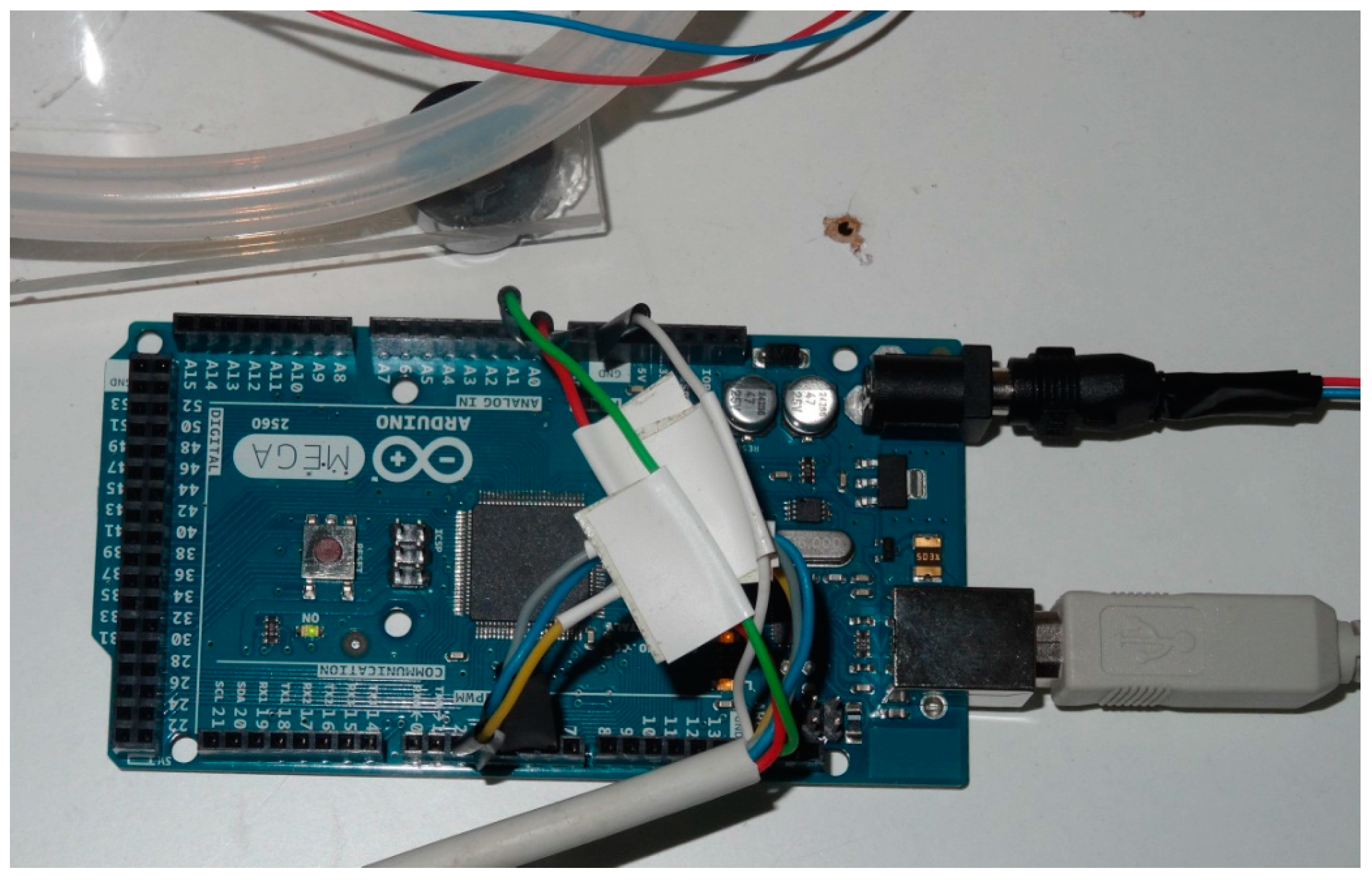
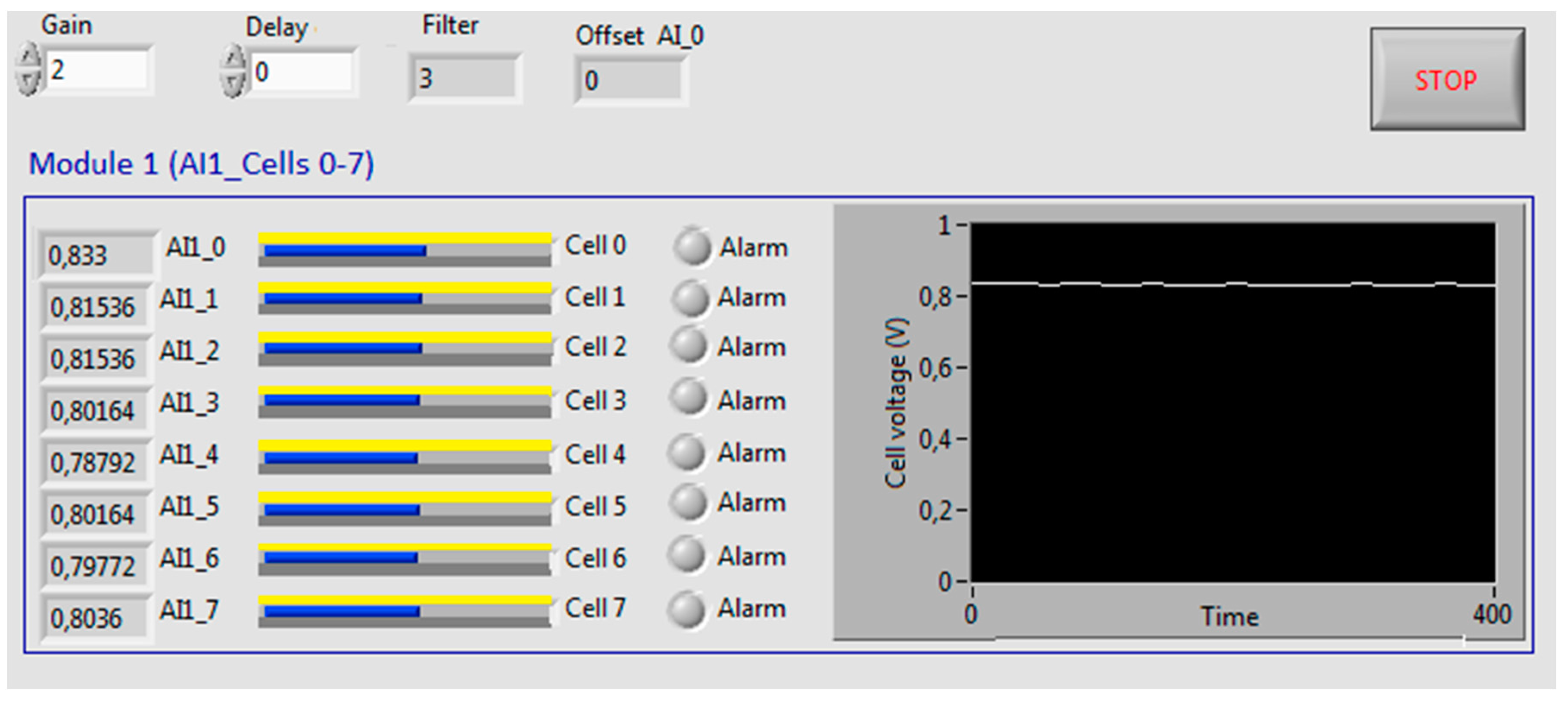
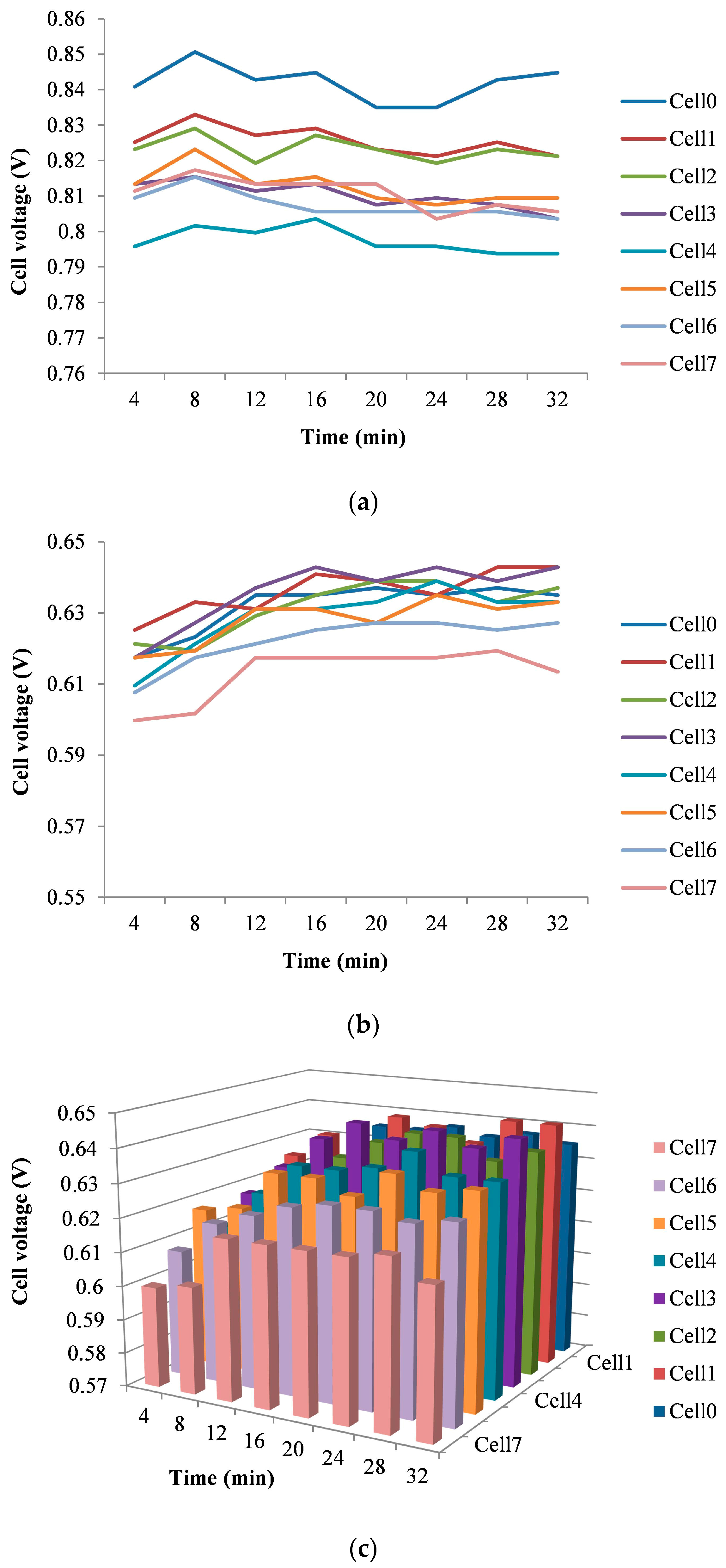
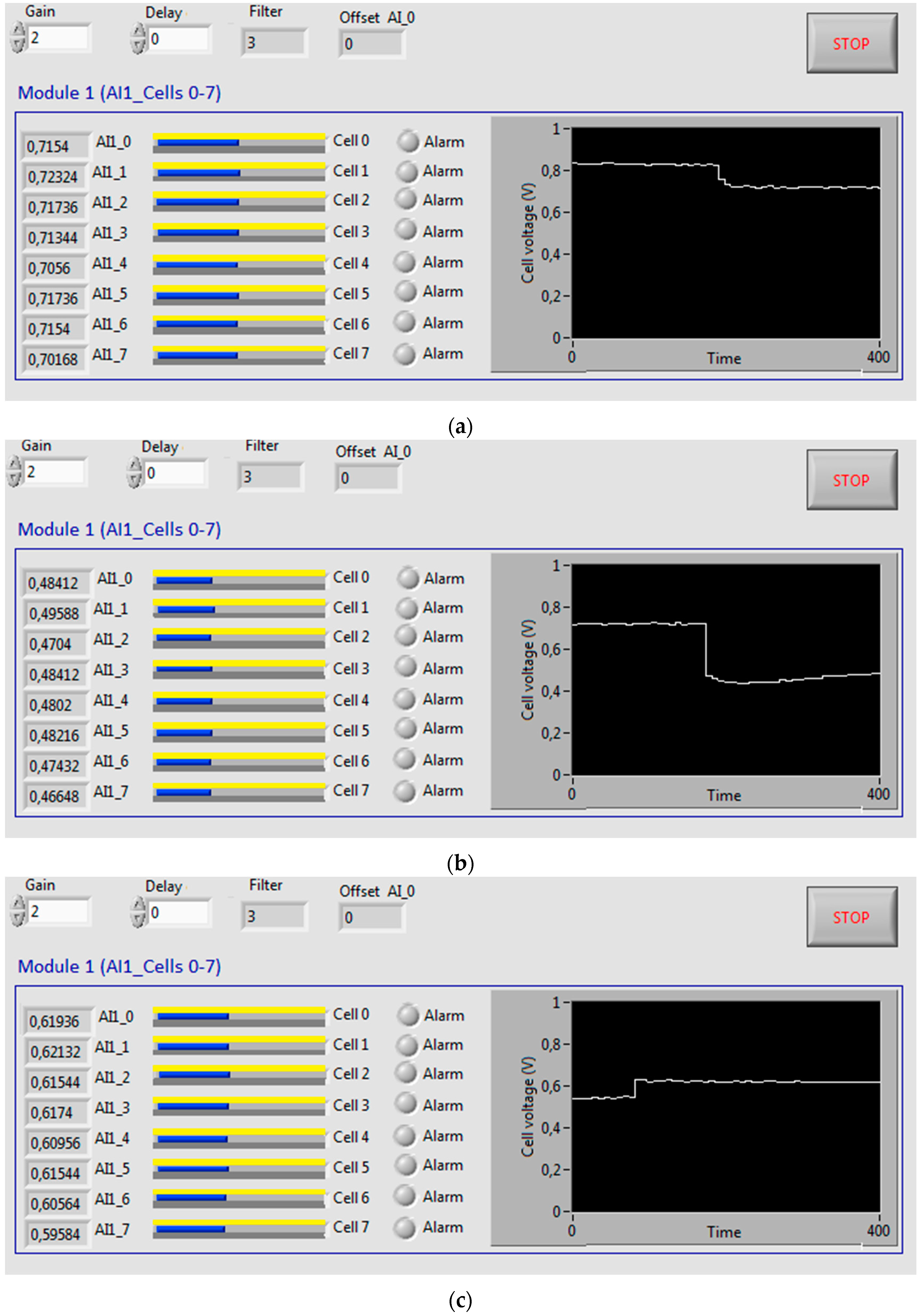
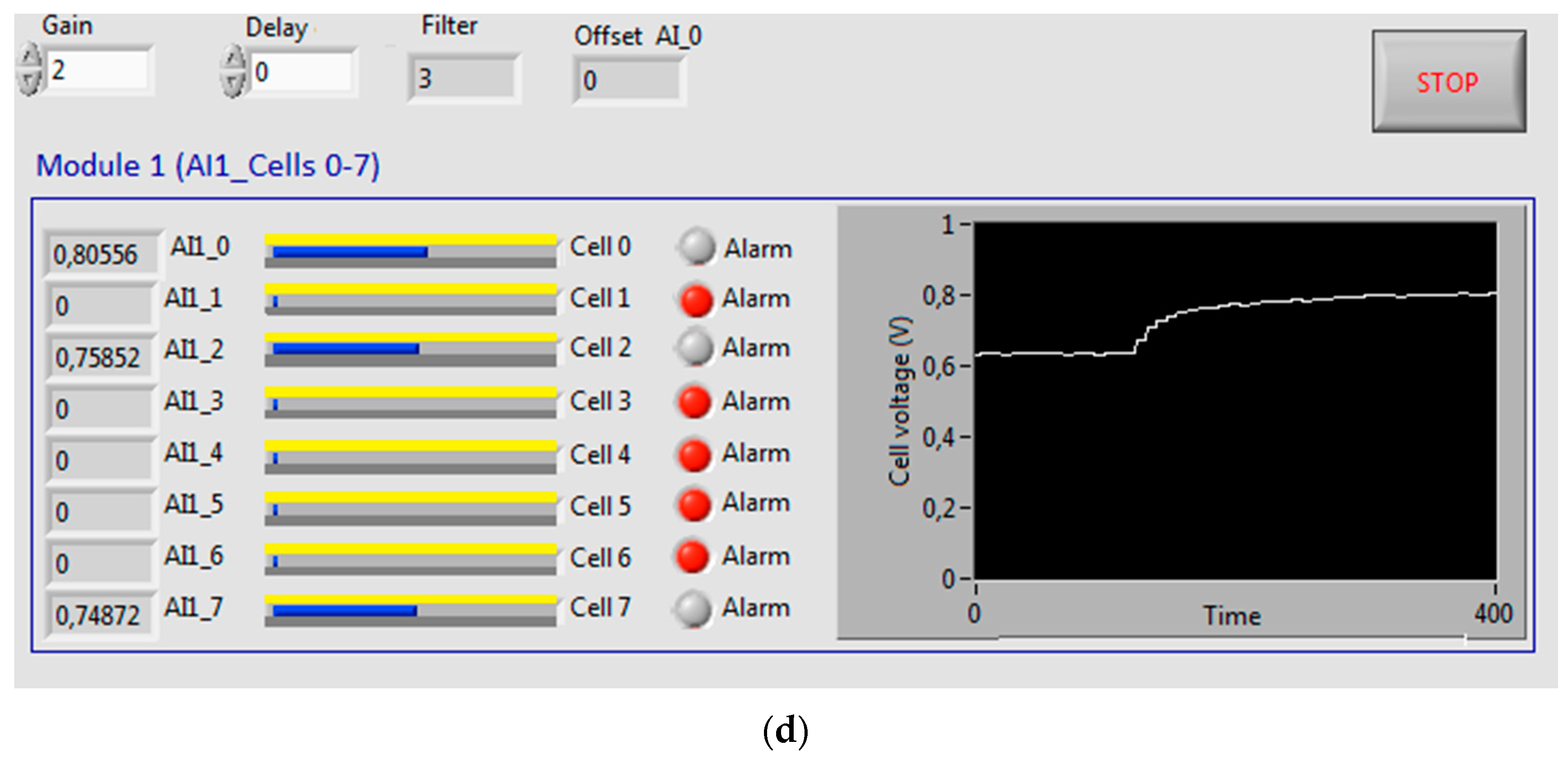
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of cells | 10 |
| Generated voltage | 0.4–0.96 V per cell |
| Power | 200 mW per cell |
| Electrode area | 4 cm2 per cell |
| Weight | 430 g |
| H × W × D | 60 × 70 × 175 mm |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calderón, A.J.; González, I.; Calderón, M.; Segura, F.; Andújar, J.M. A New, Scalable and Low Cost Multi-Channel Monitoring System for Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. Sensors 2016, 16, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16030349
Calderón AJ, González I, Calderón M, Segura F, Andújar JM. A New, Scalable and Low Cost Multi-Channel Monitoring System for Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. Sensors. 2016; 16(3):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16030349
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalderón, Antonio José, Isaías González, Manuel Calderón, Francisca Segura, and José Manuel Andújar. 2016. "A New, Scalable and Low Cost Multi-Channel Monitoring System for Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells" Sensors 16, no. 3: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16030349
APA StyleCalderón, A. J., González, I., Calderón, M., Segura, F., & Andújar, J. M. (2016). A New, Scalable and Low Cost Multi-Channel Monitoring System for Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. Sensors, 16(3), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16030349








