Multi-Axis Force/Torque Sensor Based on Simply-Supported Beam and Optoelectronics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Integration of optoelectronic force sensors in a bespoke mechanical structure for the purpose of force/torque measurement;
- A concept that lends itself to miniaturisation;
- Simplified manufacturability and customisation to fit a wide-range of robot systems;
- Low-cost fabrication and assembly of sensor structure; and
- Good sensitivity and sensor range for a wide range of manipulation tasks.
2. Design Methods and Fabrication
2.1. Design Requirements
- (1)
- (2)
- Be miniaturisable: The diameter of sensor structure should be less than 15 mm to be able to pass through the current commercialized trocars.
- (3)
- Be easily adaptable and integrateable with the given manipulator structure.
- (4)
- Impact on the robot structure as little as possible and provide space for necessary tubes and cables for other functions such as robot actuation, sensing, and tool actuation.
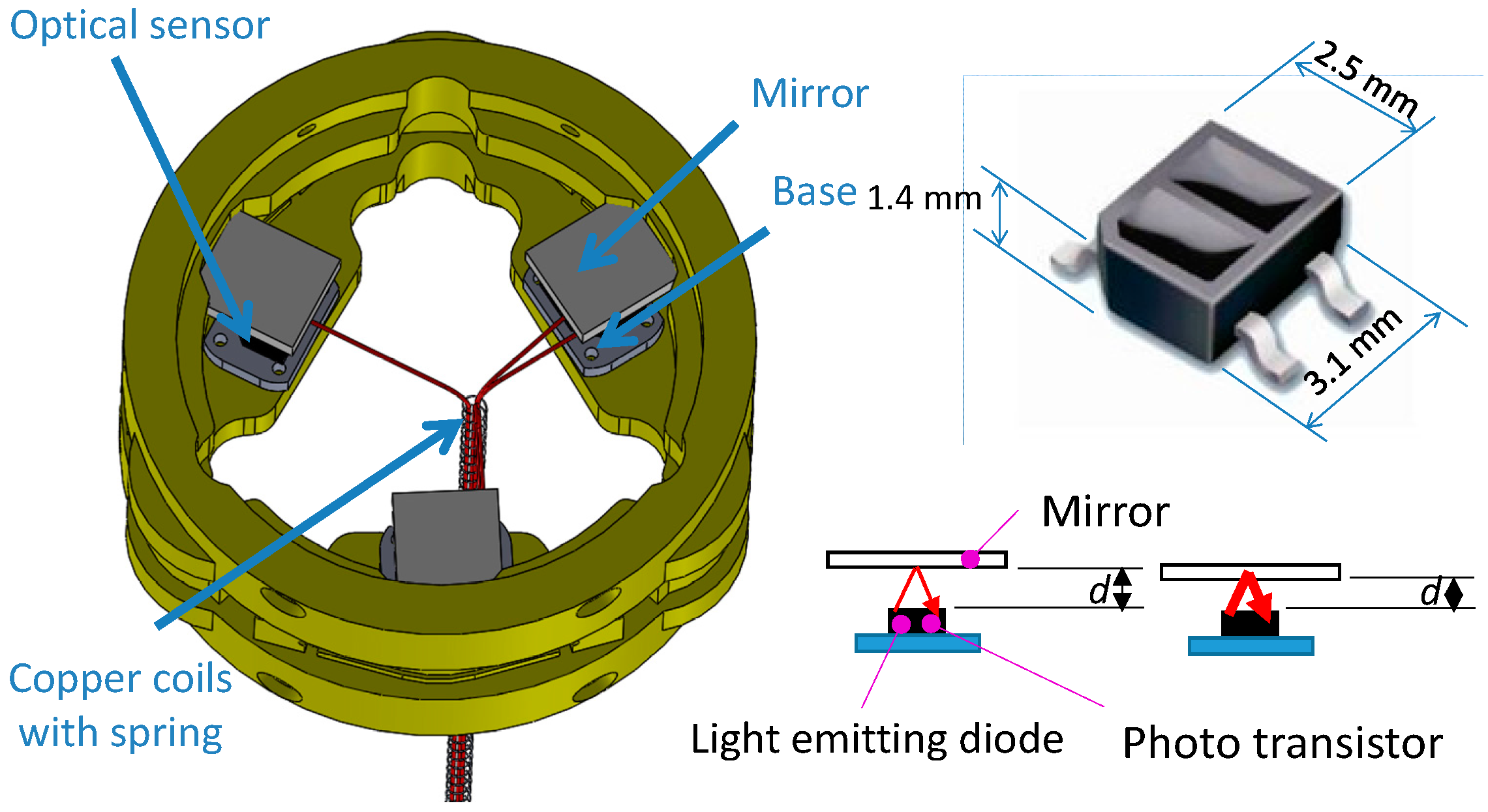
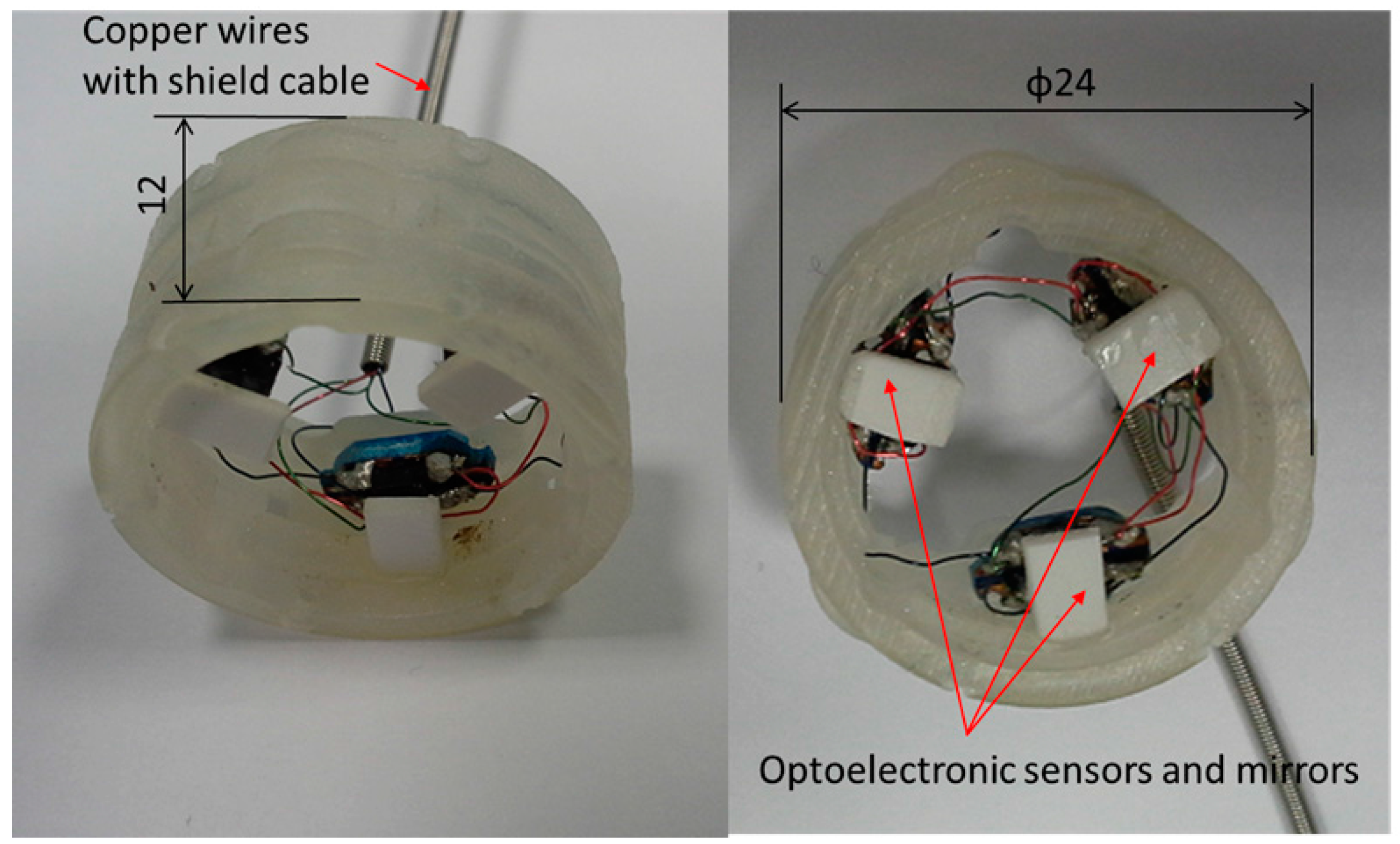
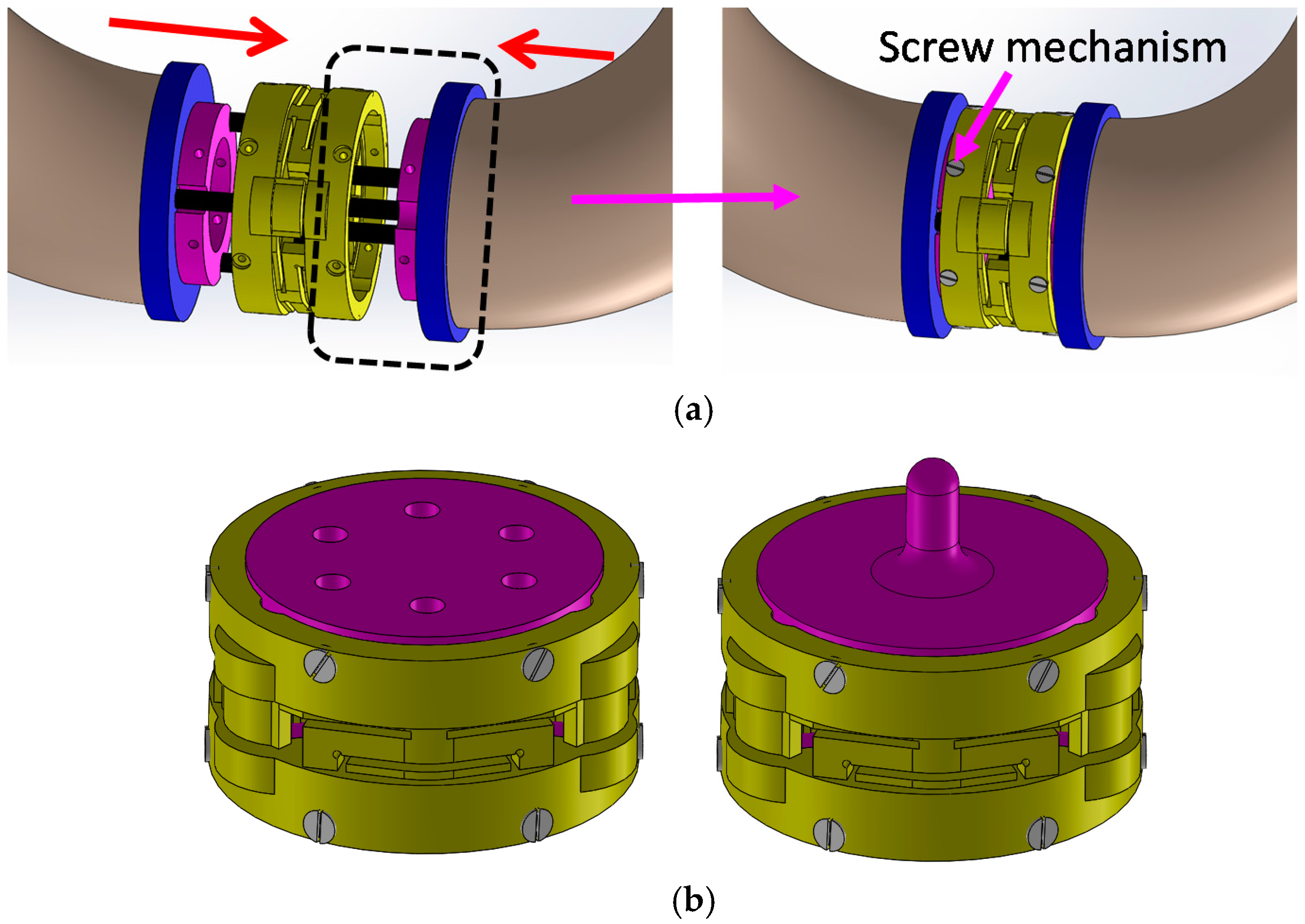
2.2. Configuration of Optoelectronic Based Force/Torque Sensor
2.3. Sensor Structure Design, Modelling, Simulation, and Sensor’s Optoelectronic Optimization
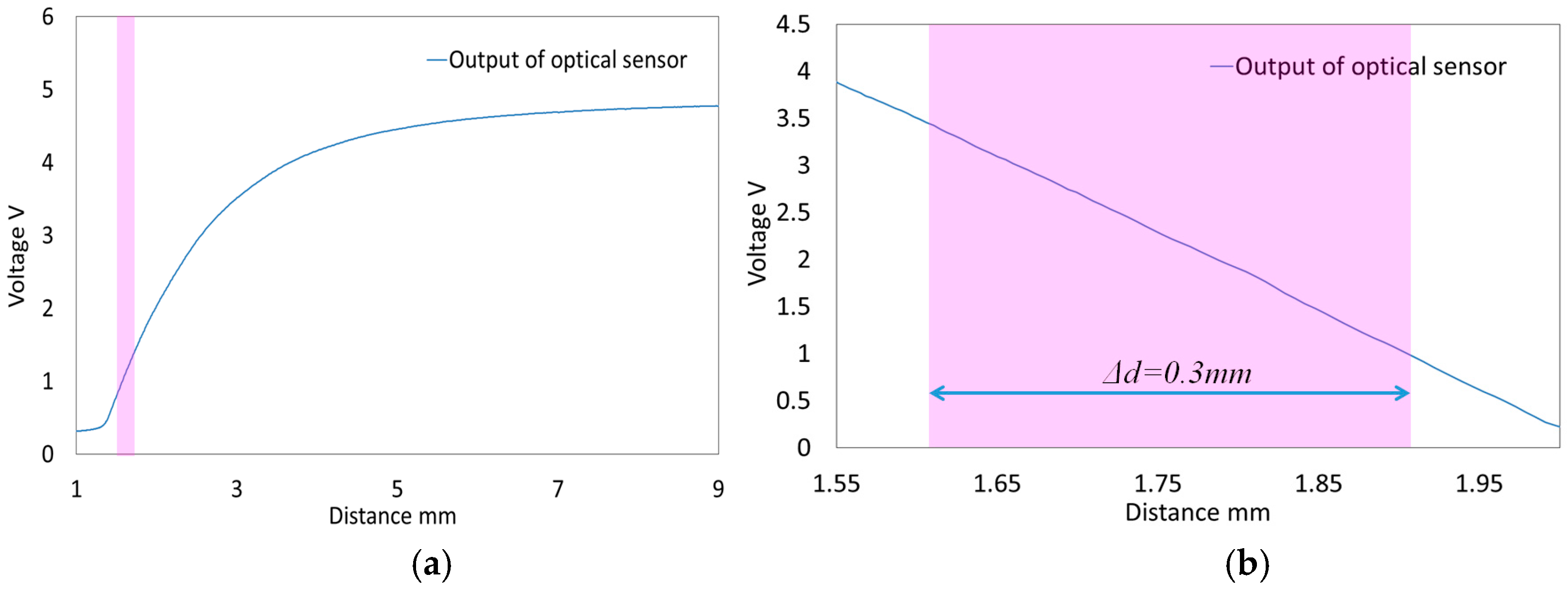
2.3.1. Optimization of Characteristic Curves on Optoelectronic Sensor
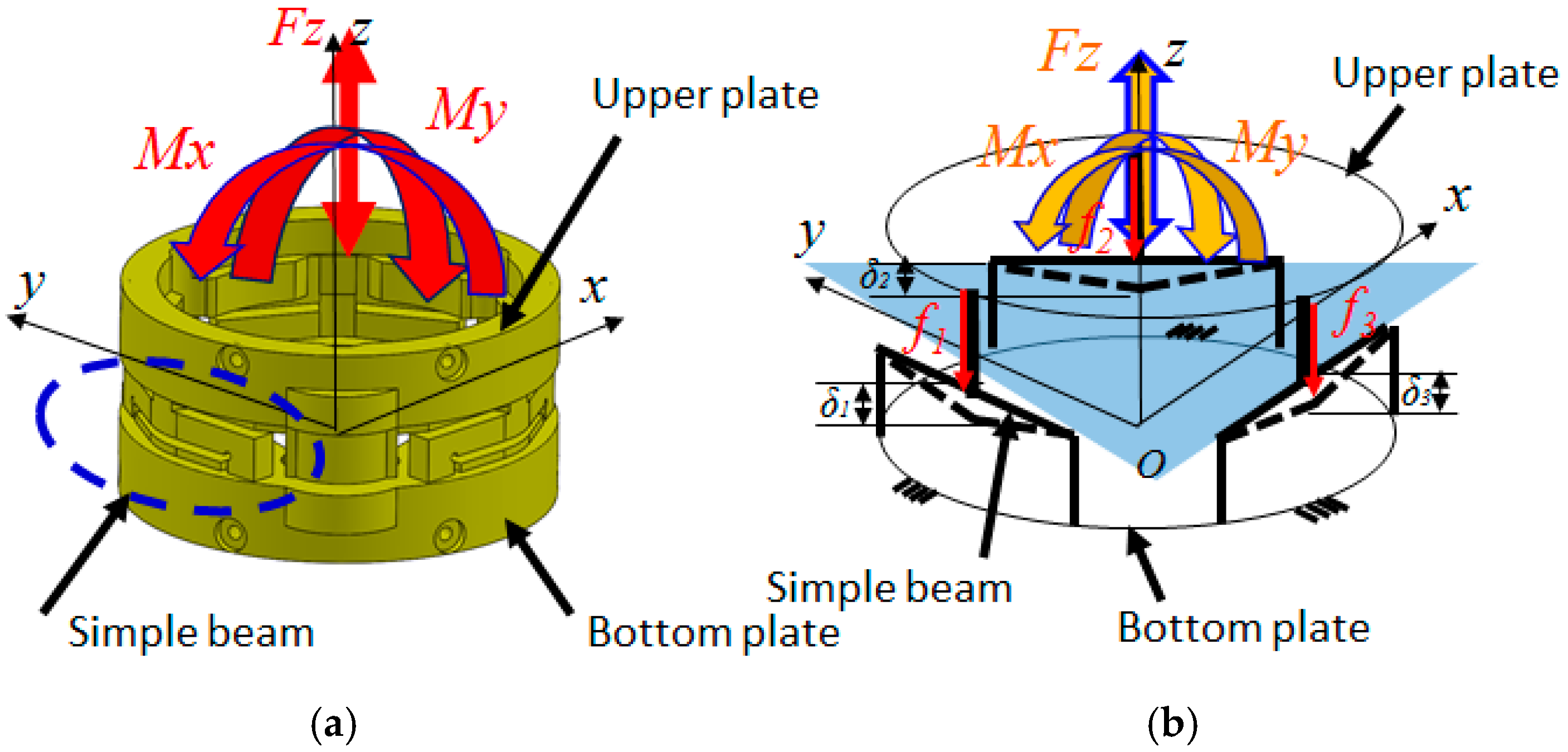
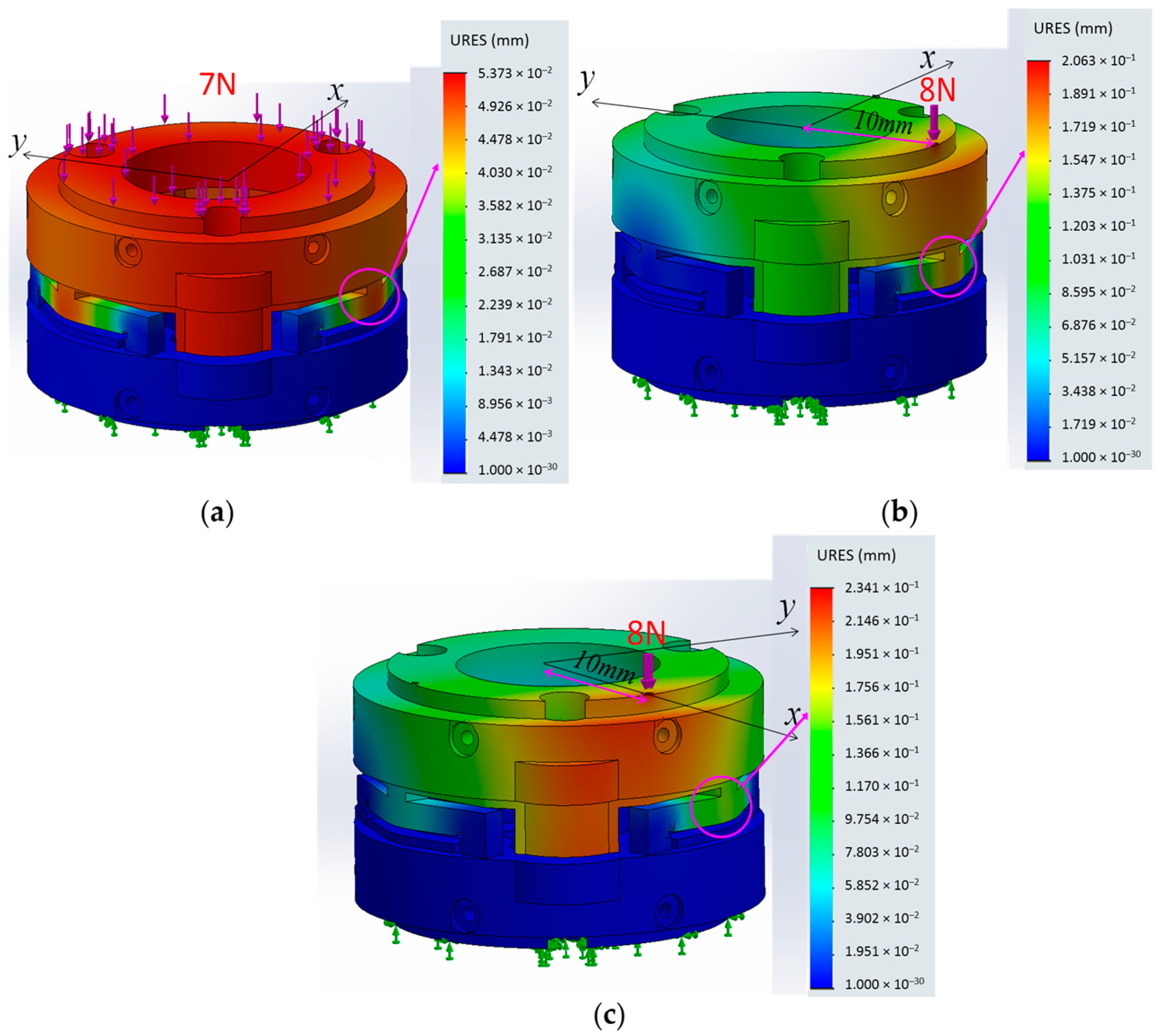
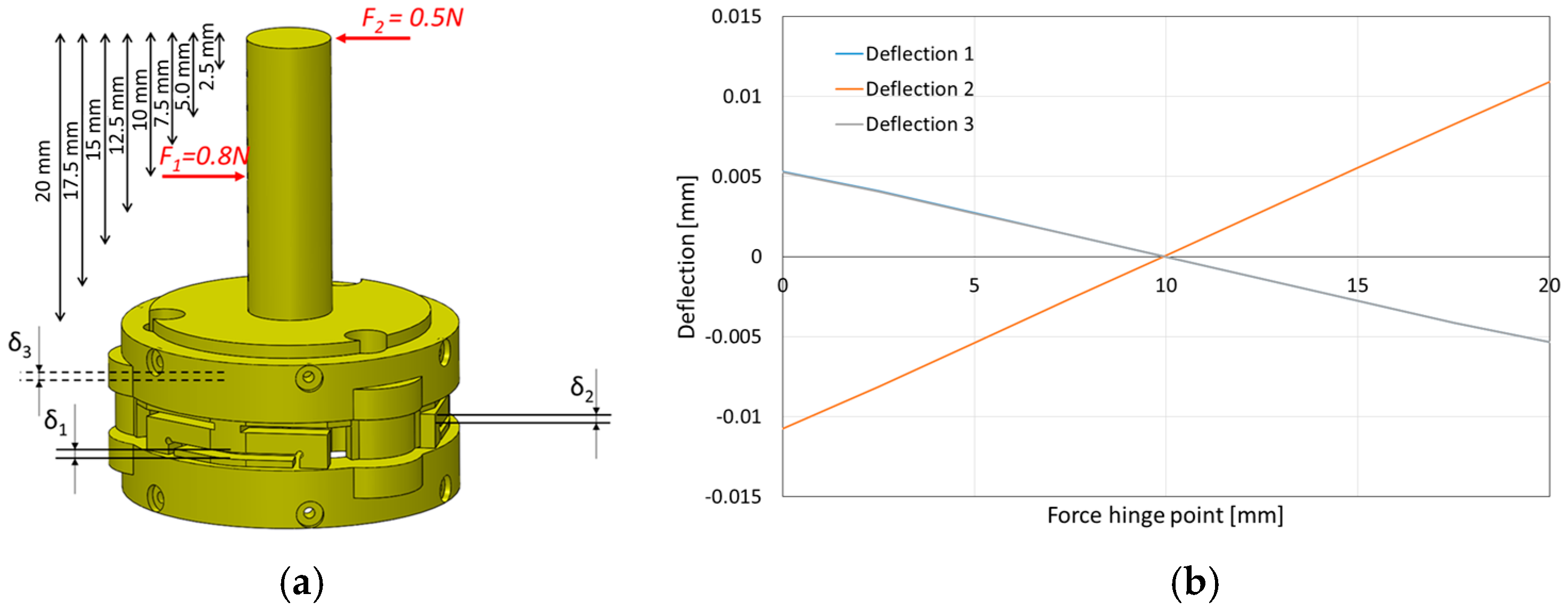
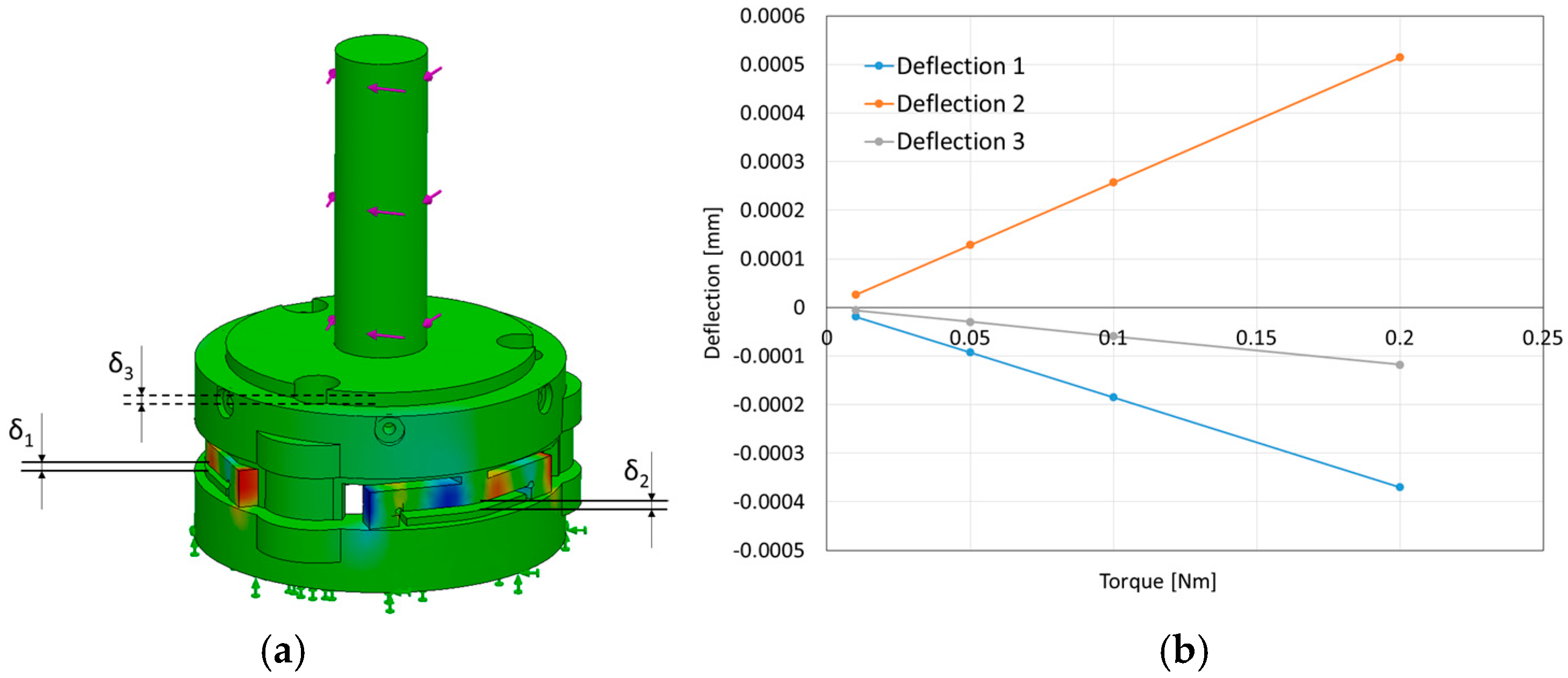
2.3.2. Model and Simulation for Sensor Structure
3. Sensor Calibration
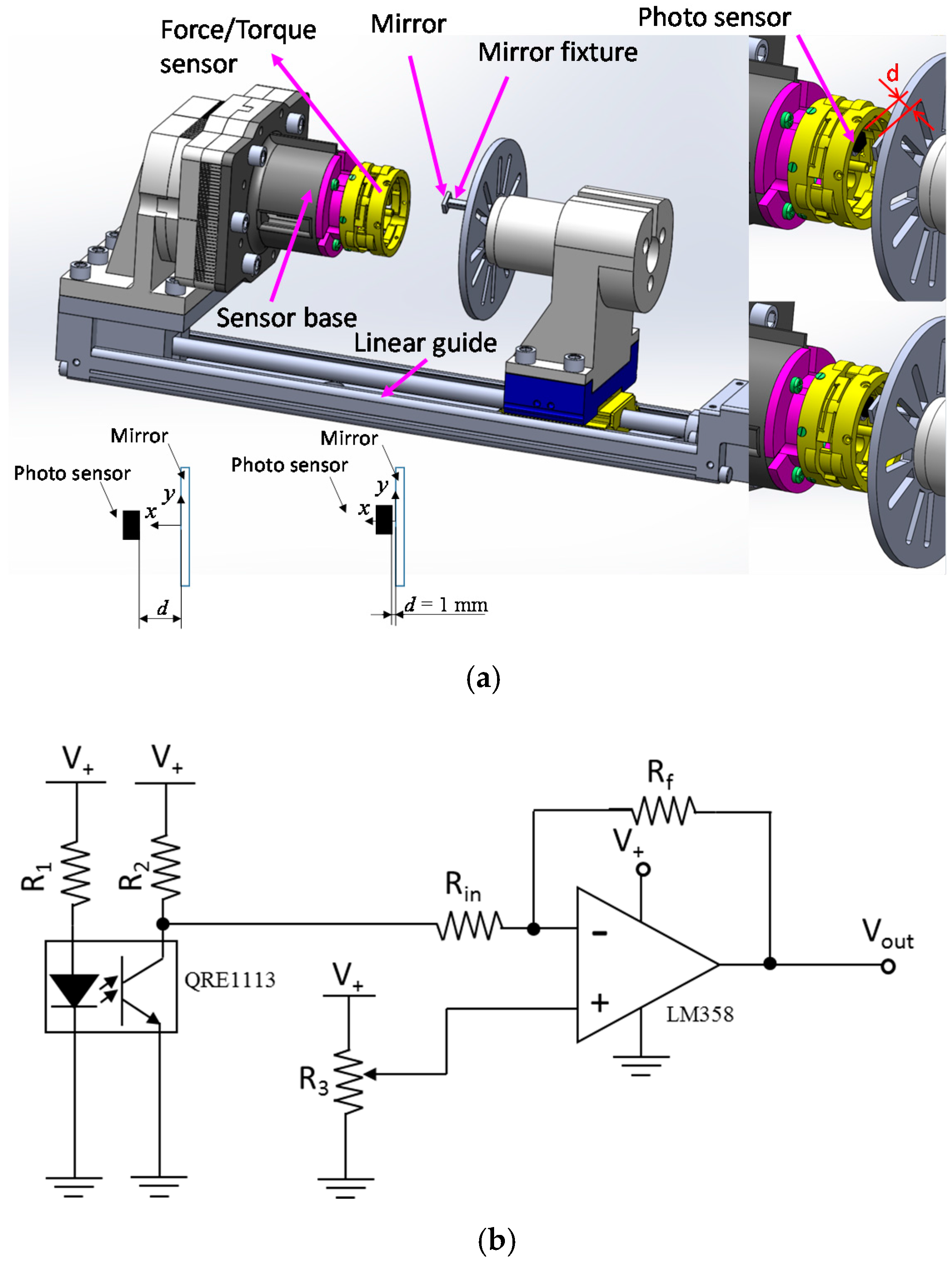
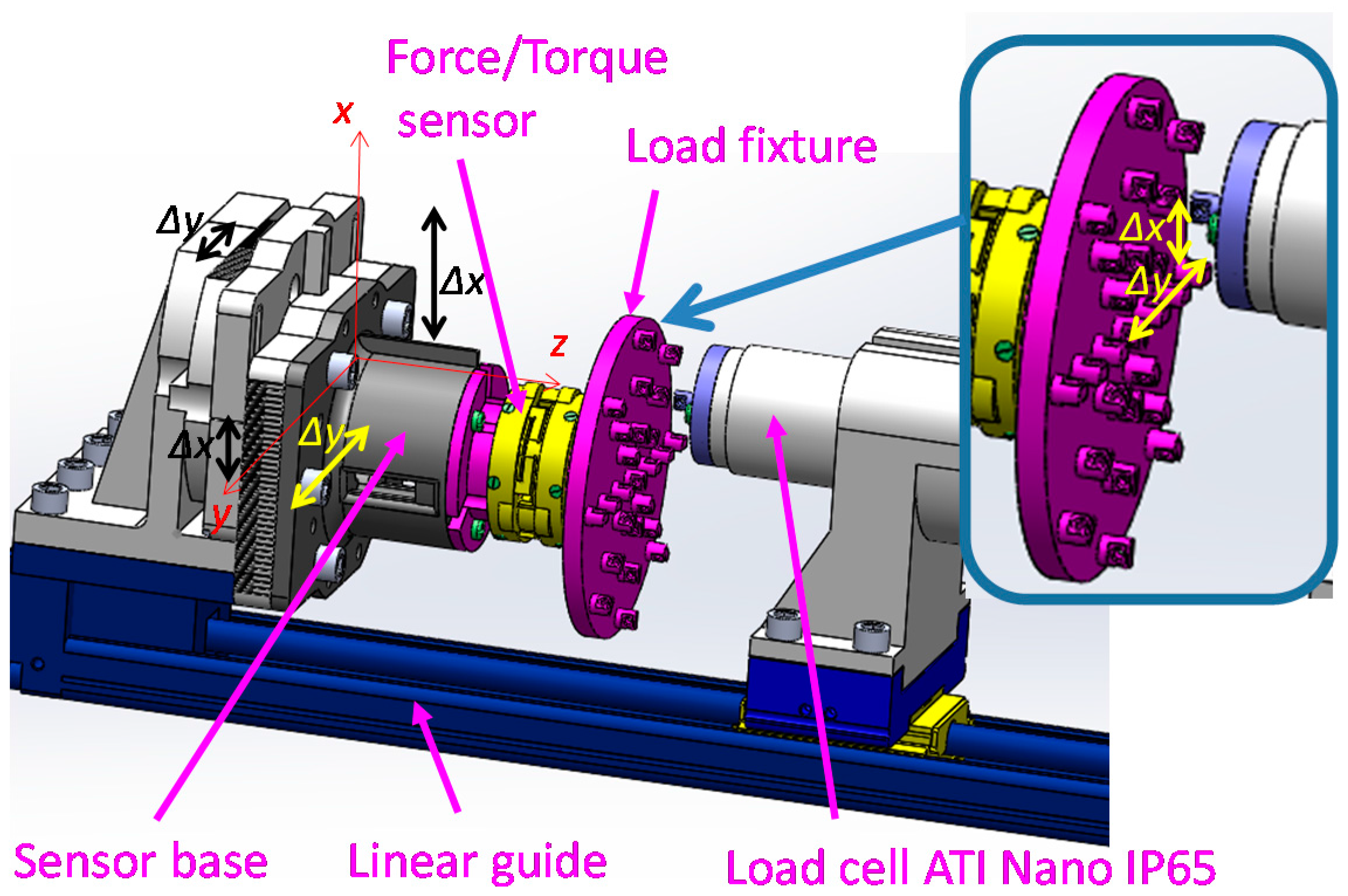
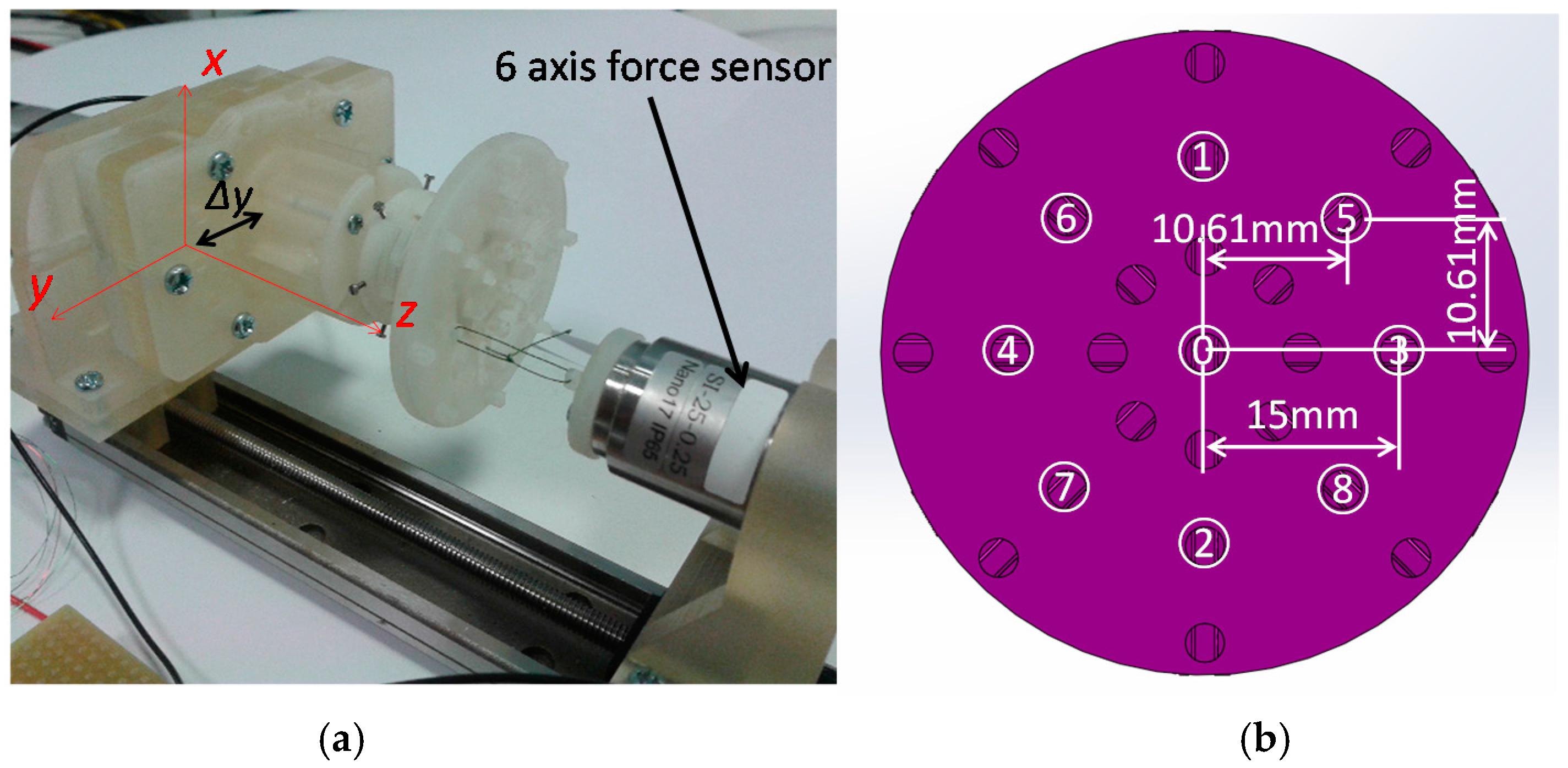
3.1. Setup for Calibration Experiments
- (1)
- (2)
- (3)
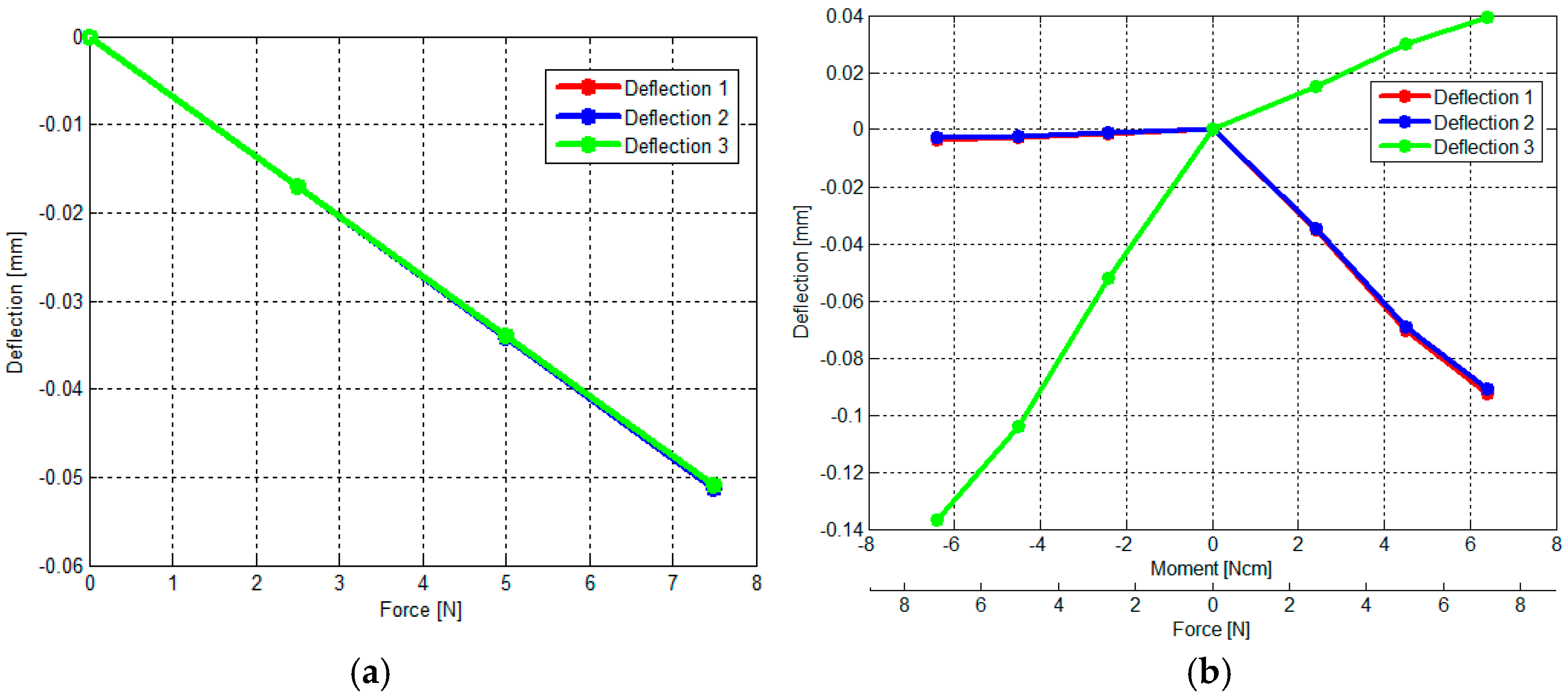
3.2. Calculation of Calibration Matrix by Analytical and Empirical Approaches
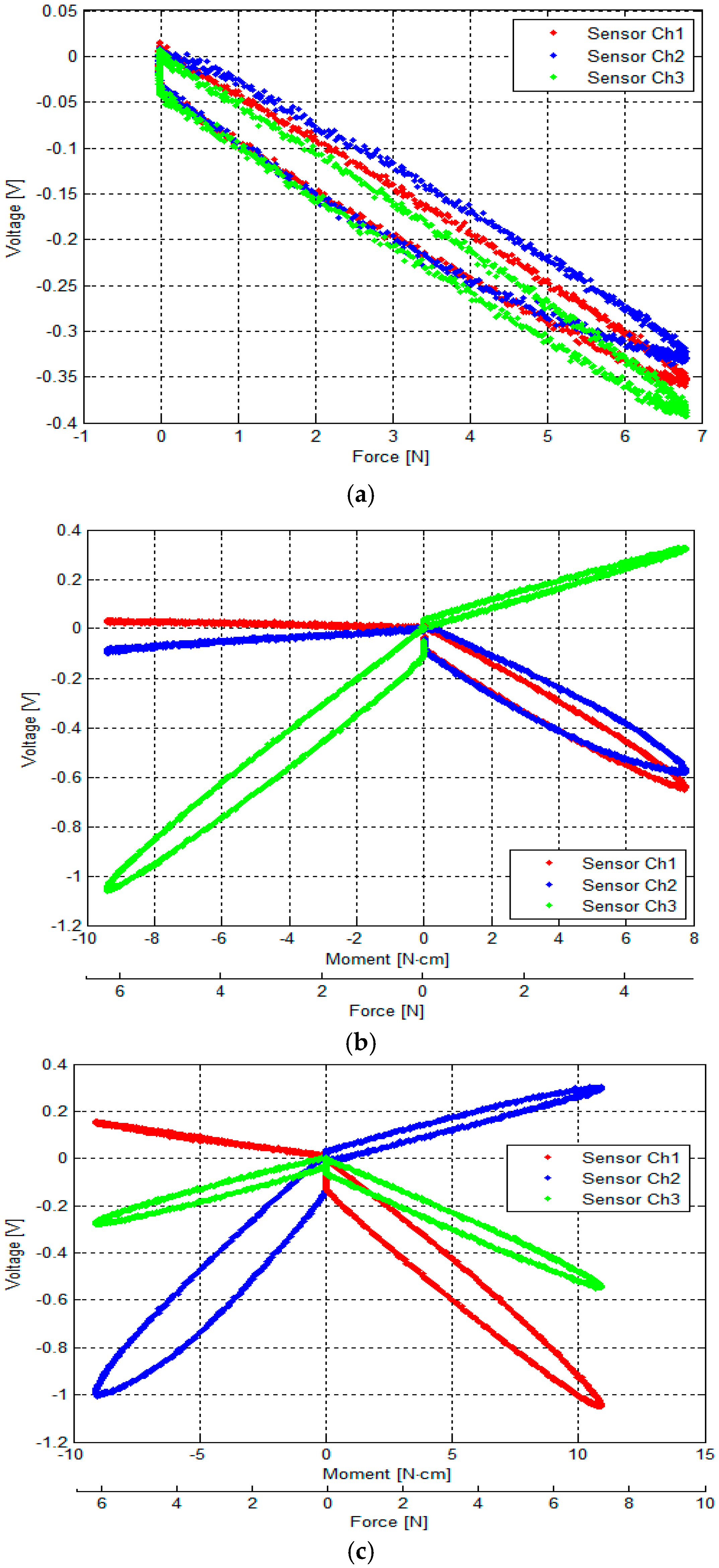
- Figure 13a shows the relationship between the output voltages of the three optoelectronic sensing elements and Fz.
- Figure 13b shows the relationship between output voltages of the three optoelectronic sensing elements and (Fz, Mx).
- Figure 13c shows the relationship between the output voltages of the three optoelectronic sensing elements and (Fz, My).
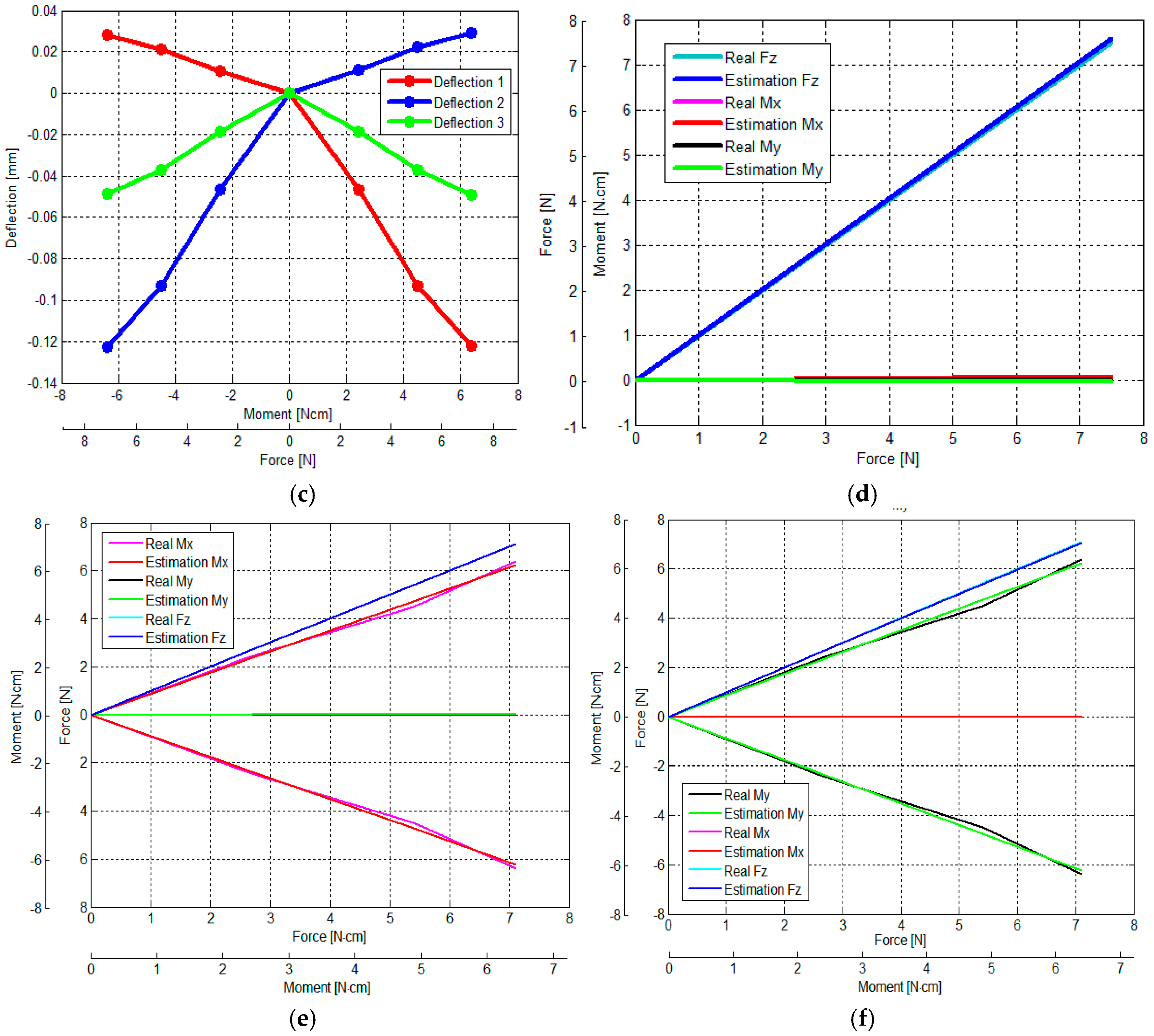
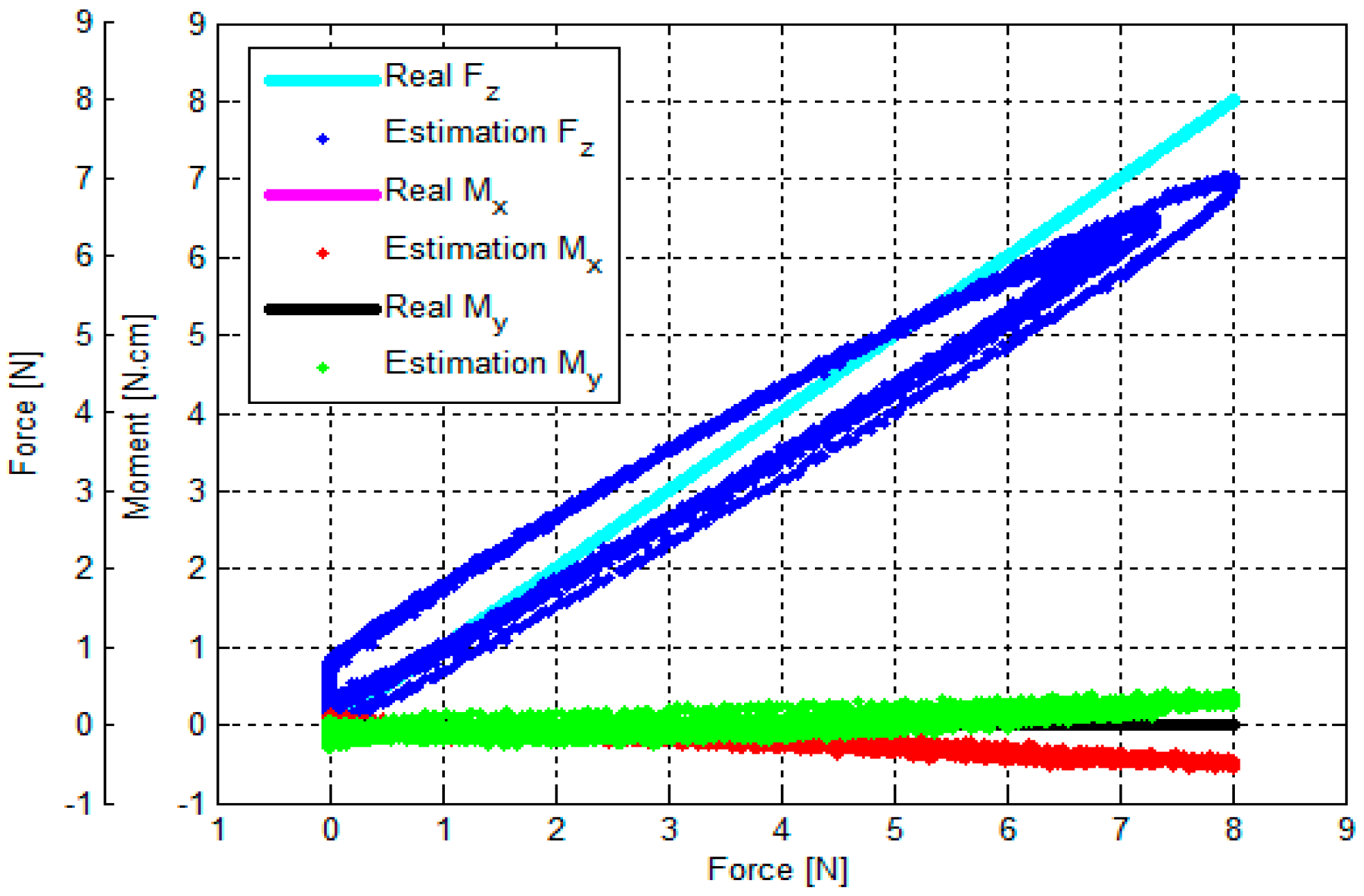
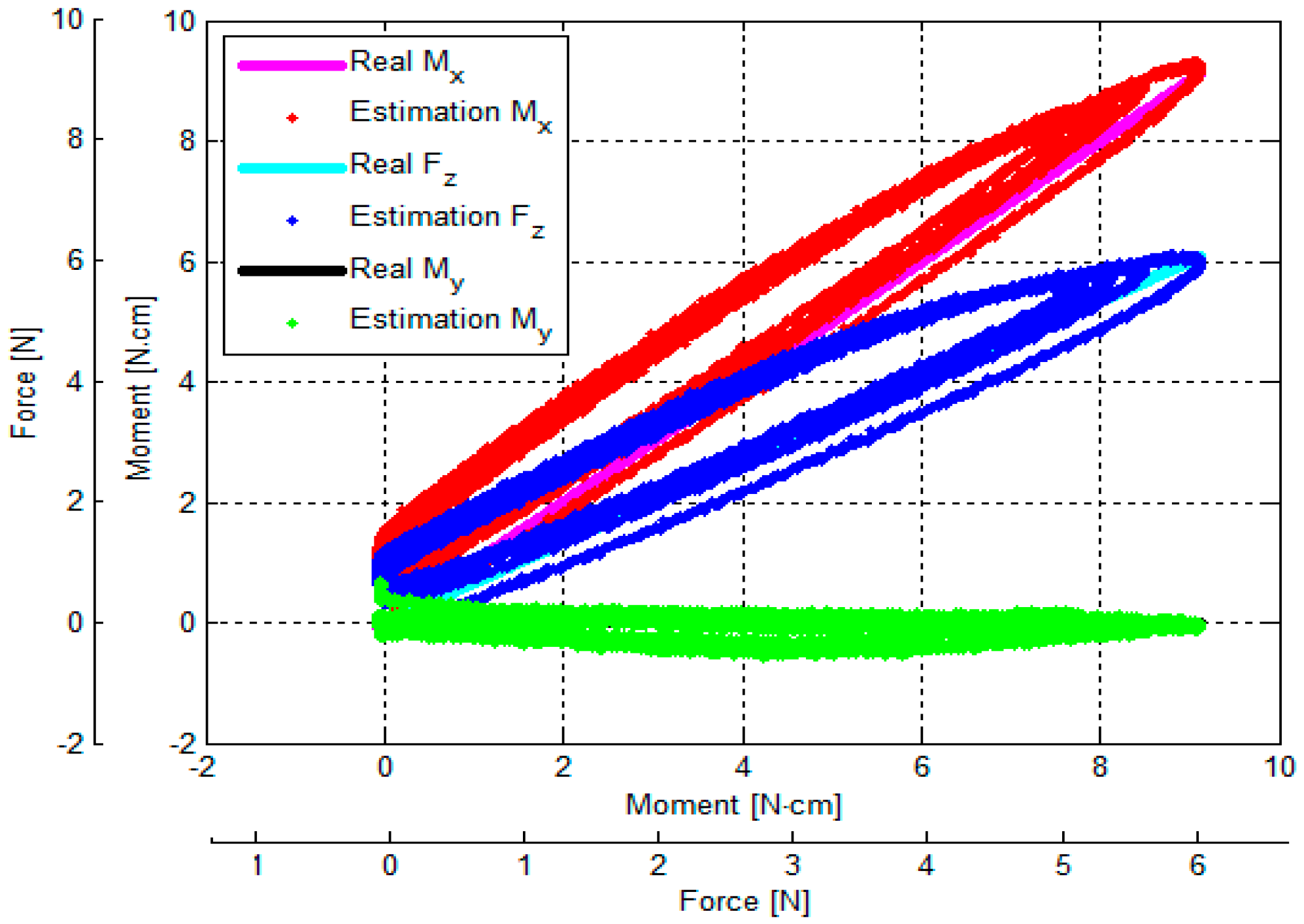
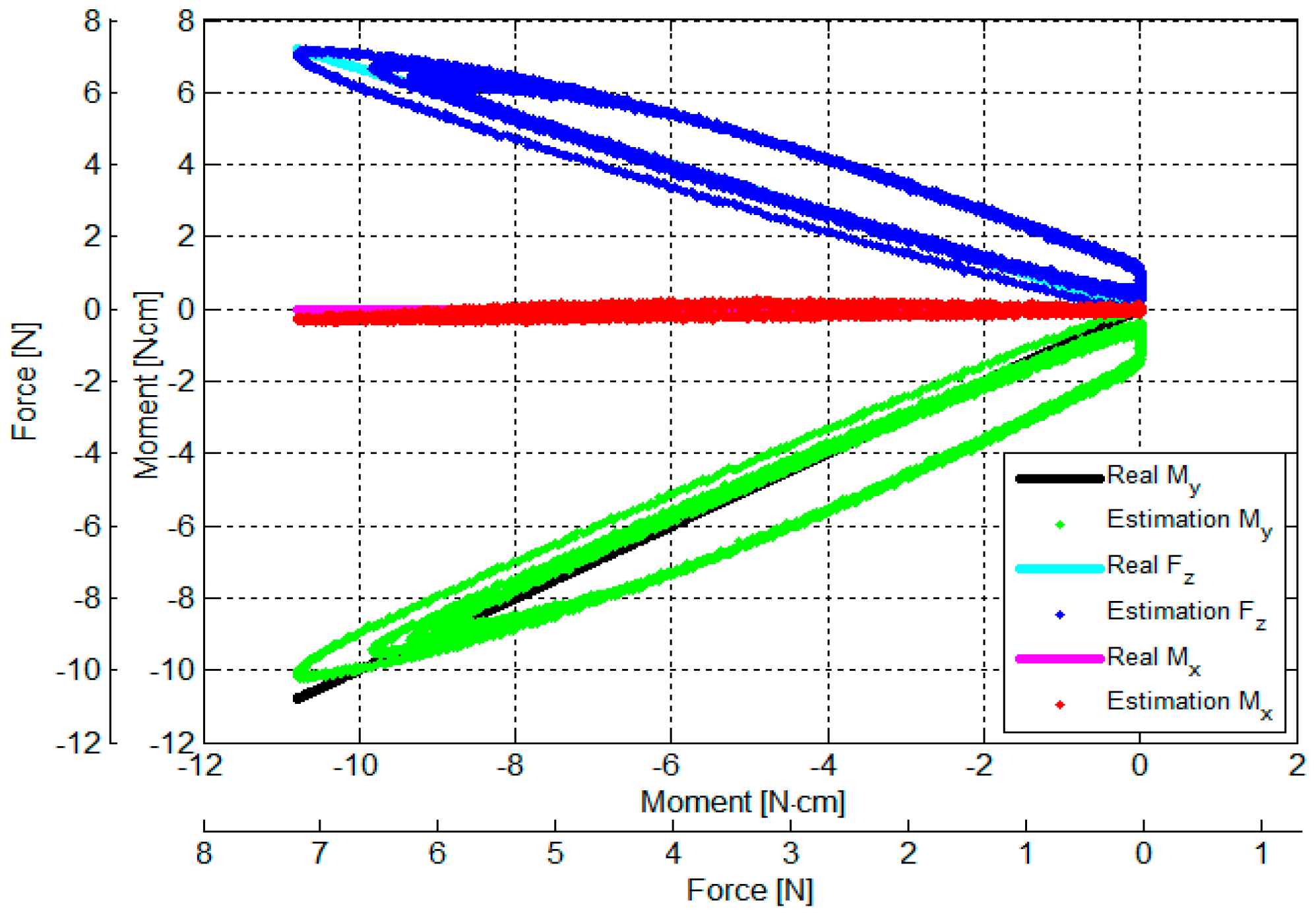
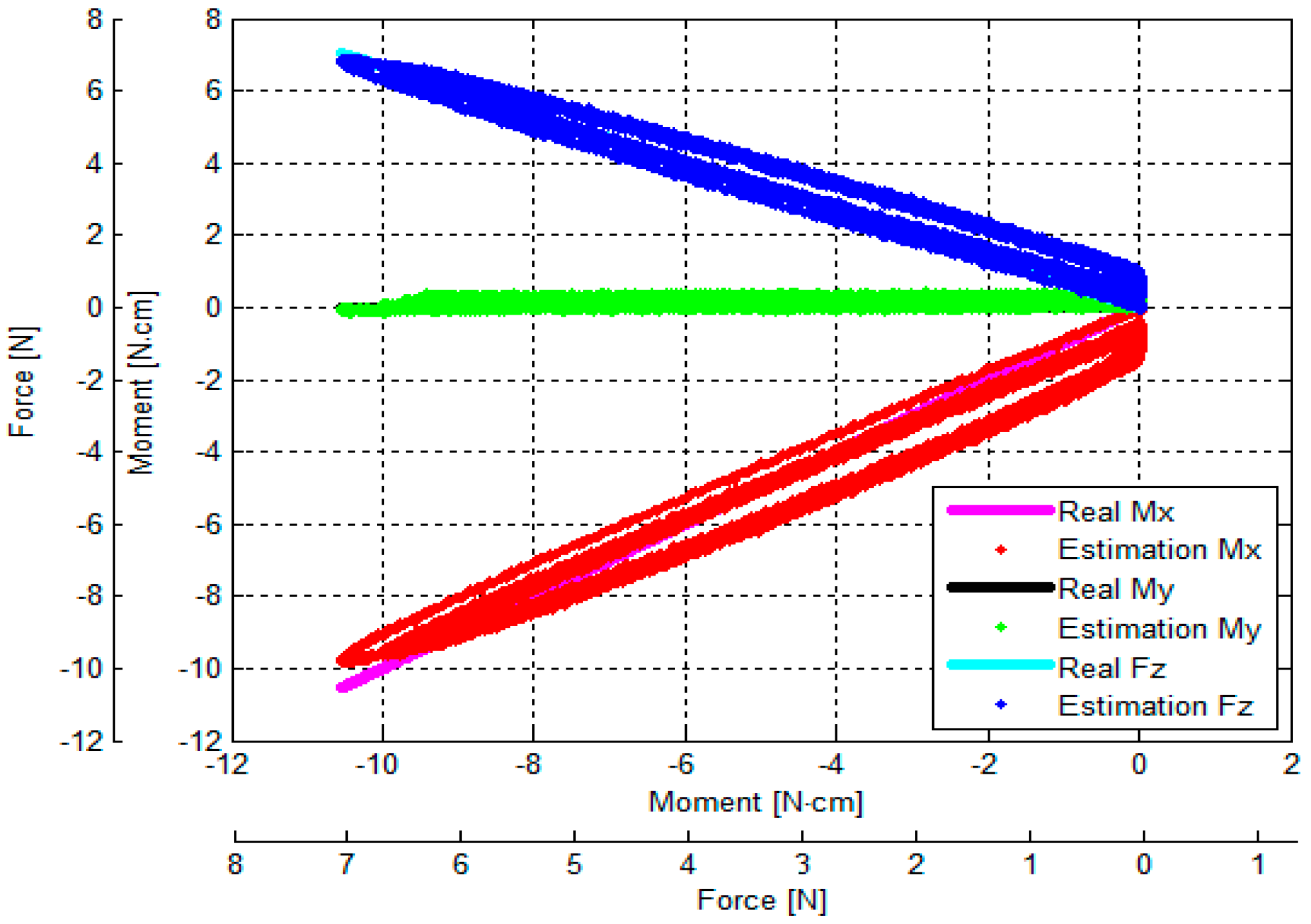
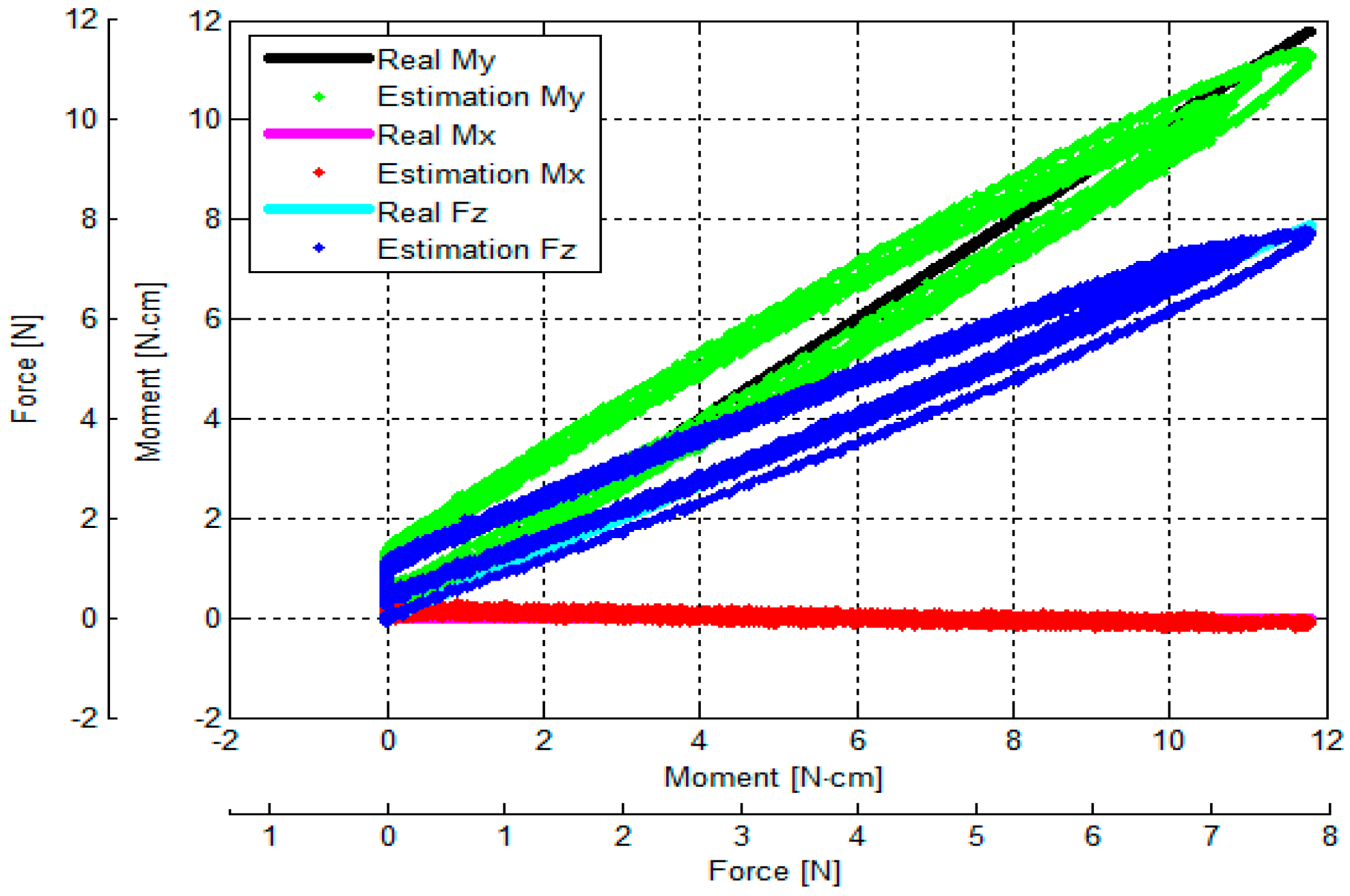
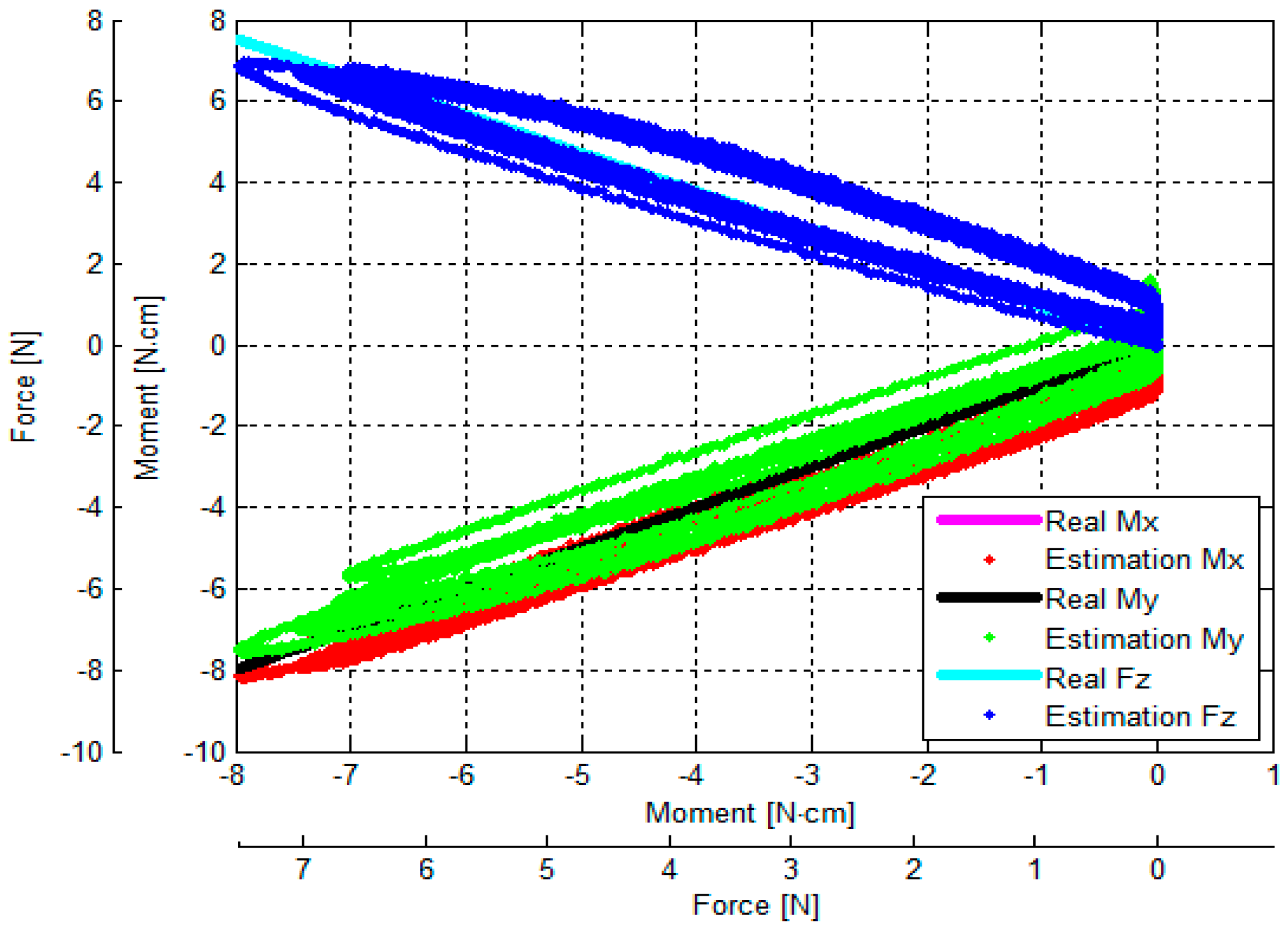
3.3. Verification of Calibration Matrix and Objective Evaluation of Our Proposed Force/Torque Sensor
- (1)
- (2)
- (3)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Works
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernandez, R.; Payo, I.; Vazquez, A.S.; Becedas, J. Micro-vibration-based slip detection in tactile force sensors. Sensors 2014, 14, 709–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannata, G.; Maggiali, M. Design of a tactile sensor for robot hands. In Sensors: Focus on Tactile Force and Stress Sensors; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Cupcic, U.; Dai, J.S. An optimization approach to teleoperation of the thumb of a humanoid robot hand: Kinematic mapping and calibration. J. Mech. Des. 2014, 136, 091005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.; Lee, D.; Yoon, W.; Hannaford, B.; Choi, H. Force sensor integrated surgical forceps for minimally invasive robotic surgery. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, U.; Choi, H. Development of multi-axial force sensing system for haptic feedback enabled minimally invasive robotic surgery. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) 2014, Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 September 2014.
- Polygerinos, P.; Ataollahi, A.; Schaeffter, T.; Seneviratne, L.D.; Althoefer, K. MRI-compatible intensity-modulated force sensor for cardiac catheterization procedures. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polygerinos, P.; Ataollahi, A.; Schaeffter, T.; Seneviratne, L.D.; Althoefer, K. Miniaturized triaxial optical fiber force sensor for MRI-guided minimally invasive surgery. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2010, Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–8 May 2010.
- Shang, J.; Noonan, D.P.; Payne, C.; Clark, J.; Sodergren, M.H.; Darzi, A.; Yang, G.Z. An articulated universal joint based flexible access robot for minimally invasive surgery. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2011, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011.
- Degani, A.; Choset, H.; Zubiate, B.; Ota, T.; Zenati, M. Highly articulated robotic probe for minimally invasive surgery. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC) 2008, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–24 August 2008.
- Li, Z.; Yu, H.; Ren, H.; Chiu, P.W.Y.; Du, R. A novel constrained tendon-driven serpentine manipulator. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) 2015, Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015.
- Xu, K.; Zhao, J.; Fu, M. Development of the SJTU unfoldable robotic system (SURS) for single port laparoscopy. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 2133–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.; Liu, H.; Sareh, S.; Chathuranga, D.; Wurdemann, H.; Rhode, K.; Althoefer, K. Image-based optical miniaturized three-axis force sensor for cardiac catheterization. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 7924–7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.; Sareh, S.; Würdemann, H.; Liu, H.; Housden, J.; Rhode, K.; Althoefer, K. Three-axis fiber-optic body force sensor for flexible manipulators. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 16, 1641–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.; Secco, E.L.; Sareh, S.; Wurdemann, H.; Faragasso, A.; Back, J.; Liu, H.; Sklar, E.; Althoefer, K. A continuum body force sensor designed for flexible surgical robotics devices. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC) 2014, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014.
- Xie, H.; Liu, H.; Noh, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Kaspar, A. A fiber-optics-based body contact sensor for a flexible manipulator. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 3543–3550. [Google Scholar]
- Vithanage, D.; Wang, Z.; Noh, Y.; Nanayakkara, T.; Hirai, S. Robust real time material classification algorithm using soft three axis tactile sensor: Evaluation of the algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) 2015, Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015.
- Assaf, T.; Roke, C.; Rossiter, J.; Pipe, T.; Melhuish, C. Seeing by touch: Evaluation of a soft biologically-inspired artificial fingertip in real-time active touch. Sensors 2014, 14, 2561–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, A.; Wu, J.; Qin, G.; Huang, W. A novel self-decoupled four degree-of-freedom wrist force/torque sensor. Measurement 2007, 40, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.; Song, A.; Xiao, J. A robust static decoupling algorithm for 3-axis force sensors based on coupling error model and Ɛ-SVR. Sensors 2012, 12, 14537–14555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibold, U.; Kubler, B.; Hirzinger, G. Prototype of instrument for minimally invasive surgery with 6-axis force sensing capability. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2005, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005.
- Haslinger, R.; Leyendecker, P.; Seibold, U. A fiberoptic force-torque-sensor for minimally invasive robotic surgery. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2013, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013.
- ATI Industrial Automation, Multi-axis Force/Torque Sensors. Available online: http://www.ati-ia.com/products/ft/sensors.aspx (accessed on 5 November 2016).
- Flavigne, D.; Perdereau, V. A learning-free method for anthropomorphic grasping. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) 2013, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013.
- Koiva, R.; Zenker, M.; Schurmann, C.; Haschke, R.; Ritter, H.J. A highly sensitive 3D-shaped tactile sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM) 2013, Wollongong, Australia, 9–12 July 2013.
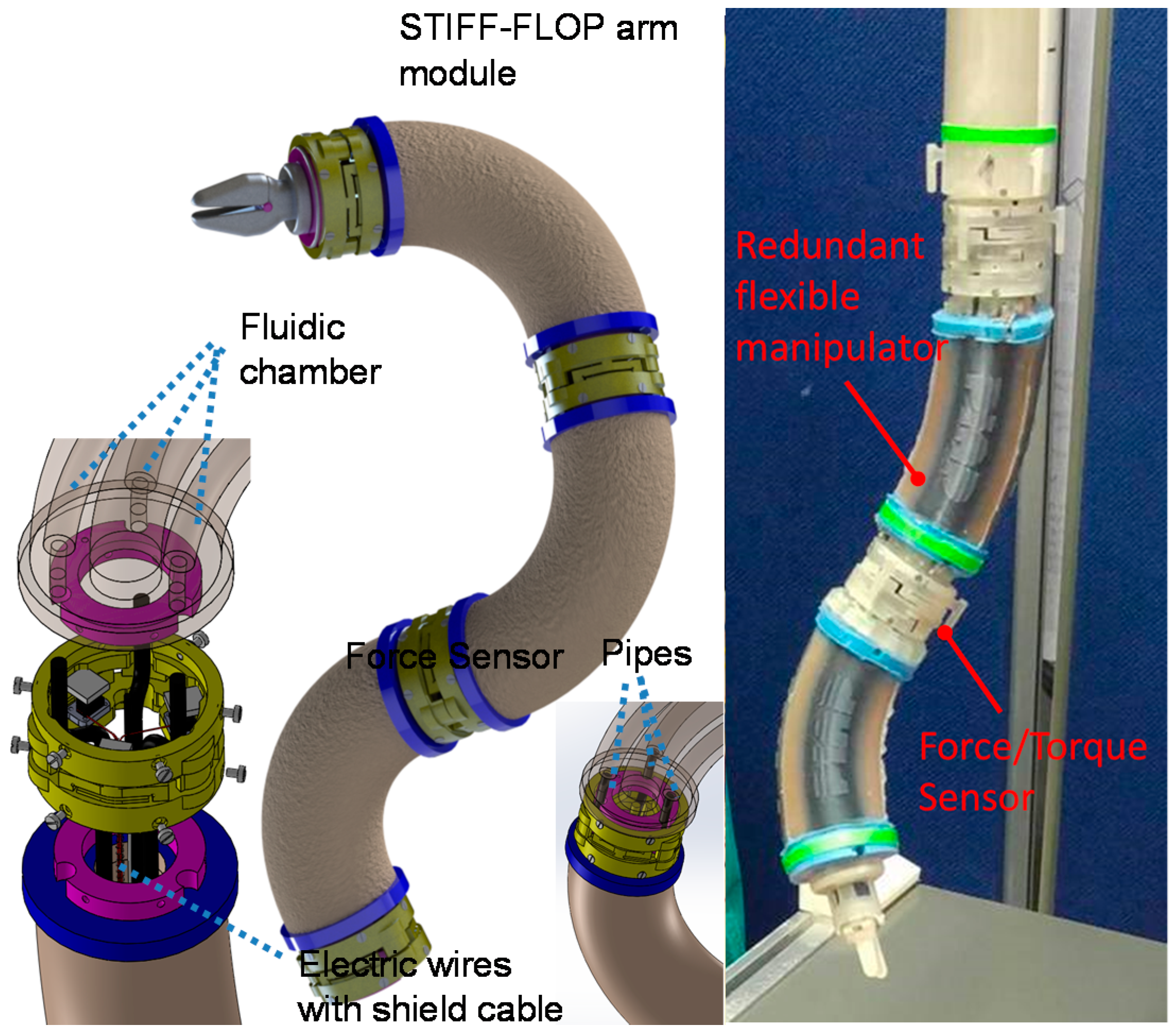
- Fraś, J.; Czarnowski, J.; Maciaś, M.; Główka, J.; Cianchetti, M.; Menciassi, A. new STIFF-FLOP module construction idea for improved actuation and sensing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2015, Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015.
- Gerboni, G.; Ranzani, T.; Diodato, A.; Ciuti, G.; Cianchetti, M.; Menciassi, A. Modular soft mechatronic manipulator for minimally invasive surgery (MIS): Overall architecture and development of a fully integrated soft module. Meccanica 2015, 50, 2865–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranzani, T.; Gerboni, G.; Cianchetti, M.; Menciassi, A. A bioinspired soft manipulator for minimally invasive surgery. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 035008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sareh, S.; Noh, Y.; Li, M.; Ranzani, T.; Liu, H.; Althoefer, K. Macro-bend optical sensing for pose measurement in soft robot arms. Smart Mater. Struct 2015, 24, 125024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sareh, S.; Noh, Y.; Ranzani, T.; Wurdemann, H.; Liu, H.; Althoefer, K. A 7.5mm Steiner chain fiber-optic system for multi-segment flex sensing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) 2015, Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015.
- Sklar, E.; Sareh, S.; Secco, E.; Faragasso, A.; Althoefer, K. A non-linear model for predicting tip position of a pliable robot arm segment using bending sensor data. Sens. Transducers 2016, 199, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, Y.; Sareh, S.; Back, J.; Wurdemann, H.A.; Ranzani, T.; Secco, E.L.; Faragasso, A.; Liu, H.; Althoefer, K. A three-axial body force sensor for flexible manipulators. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2014, Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014.
- Sareh, S.; Jiang, A.; Faragasso, A.; Noh, Y.; Nanayakkara, T.; Dasgupta, P.; Seneviratne, L.D.; Wurdemann, H.A.; Althoefer, K. Bio-inspired tactile sensor sleeve for surgical soft manipulators. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2014, Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014.
- Jia, Y.; Chen, X.; Ni, Q.; Li, L.; Ju, C. Dependence of the impact response of polyvinylidene fluoride sensors on their supporting materials’ elasticity. Sensors 2013, 13, 8669–8678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, D.V.; Toriyama, T.; Wells, J.; Sugiyama, S. Silicon piezoresistive six-degree of freedom micro force-moment sensor. Sens. Mater. 2003, 15, 113–135. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, C.J.; Bruno, A.C. A noncontact force sensor based on a fibre bragg grating and its application for corrosion measurement. Sensors 2013, 13, 11476–11489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tar, A.; Cserey, G. Development of a low cost 3d optical compliant tactile force sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM) 2011, Budapest, Hungary, 3–7 July 2011.
- De Maria, G.; Natale, C.; Pirozzi, S. Force/tactile sensor for robotic applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 175, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palli, G.; Moriello, L.; Scarcia, U.; Melchiorri, C. Development of an optoelectronic 6-axis force/torque sensor for robotic applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 220, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, F., Jr.; Johnston, E.R. Mechanics of Materials, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, G.; Shin, Y.; Son, J.; Kim, J. Design and characterization of a photo-sensor based force measurement unit (FMU). Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 182, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Kim, S. Note: A compact three-axis optical force/torque sensor using photo-interrupters. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 84, 126109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gafford, J.B.; Wood, R.J.; Walsh, C.J. Self-assembling, low-cost, and modular mm-scale force sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palli, G.; Pirozzi, S. A miniaturized optical force sensor for tendon-driven mechatronic systems: Design and experimental evaluation. Mechatronics 2012, 22, 1097–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.; Shimomura, A.; Segawa, M.; Ishii, H.; Solis, J.; Takanishi, A.; Hatake, K. Development of tension/compression detection sensor system designed to acquire quantitative force information while training the airway management task. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM) 2009, Singapore, 14–17 July 2009.
- Noh, Y.; Nagahiro, K.; Ogura, Y.; Ishii, H.; Solis, J.; Hatake, K.; Takanishi, A. Development of the Airway Management Training System WKA-1 designed to embed arrays of Sensors into a Conventional Mannequin. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) 2007, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 October 2007–2 November 2007 2007.
- Cobp Photo Reflector. Available online: http://www.njr.com/semicon/PDF/NJL5901R-2_E.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2016).
- Reiley, C.E.; Akinbiyi, T.; Burschka, D.; Chang, D.C.; Okamura, A.M.; Yuh, D.D. Effects of visual force feedback on robot-assisted surgical task performance. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2008, 135, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, C.R.; Stylopoulos, N.; Jackson, P.G.; Howe, R.D. The benefit of force feedback in surgery: Examination of blunt dissection. Presence Teleoper. Virtual Environ. 2007, 16, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, M.; Dokko, D.; Okamura, A.M.; Yuh, D.D. Effect of sensory substitution on suture-manipulation forces for robotic surgical systems. J. Thoracic Cardiovasc. Surg. 2005, 129, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QRE113 Miniature Reflective Object Sensor Datasheet. Available online: https://www.fairchild-semi.com/datasheets/QR/QRE1113.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2016).
- Nathans, L.L.; Oswald, F.L.; Nimon, K. Interpreting multiple linear regression: A guidebook of variable importance. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2012, 17, 1–19. [Google Scholar]

| Force and Moment Ranges | Sensor Structure Size, Height H and Diameter D | Sensor Structure’s Design Variables |
|---|---|---|
| Fz ±7 N | H = 12 mm D = 24 mm | L = 6 mm, L1x = 9.3 mm, L1y = 5.4 mm, L2x = 9.3 mm, L2y = 5.4 mm, L3y = 10.8 mm, h = 1.5 mm, and b = 1.5 mm |
| Mx ±8.0 N·cm | ||
| My ±8.0 N·cm |
| Force/Moment | Range | Maximum Error |
|---|---|---|
| Fz | ±8.0 N | 1.8 N (22.5%) |
| Mx | ±9.0 N·cm | 1.6 N·cm (17.7% ) |
| My | ±11.0 N·cm | 1.7 N·cm (16.0%) |
| Force/Moment | Repeatability | Hysteresis |
|---|---|---|
| Fz | 2.2% | 28.7 % |
| Mx | 3.7% | 22.6% |
| My | 2.9% | 21.1% |
| Force/Moment Applied | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fz | Fz Mx | Fz My | |||
| Force/Moment | Mx,y/Fz (N·cm/N) | My/Fz (N·cm/N) | My/Mx (%) | Mx/Fz (N·cm/N) | Mx/My (%) |
| Fz | Fz | Fz | Fz | ||
| Mx | 0.078 | Mx | 0.0656 | 4.84 | |
| My | 0.054 | 0.1284 | 9.26 | My | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noh, Y.; Bimbo, J.; Sareh, S.; Wurdemann, H.; Fraś, J.; Chathuranga, D.S.; Liu, H.; Housden, J.; Althoefer, K.; Rhode, K. Multi-Axis Force/Torque Sensor Based on Simply-Supported Beam and Optoelectronics. Sensors 2016, 16, 1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111936
Noh Y, Bimbo J, Sareh S, Wurdemann H, Fraś J, Chathuranga DS, Liu H, Housden J, Althoefer K, Rhode K. Multi-Axis Force/Torque Sensor Based on Simply-Supported Beam and Optoelectronics. Sensors. 2016; 16(11):1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111936
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoh, Yohan, Joao Bimbo, Sina Sareh, Helge Wurdemann, Jan Fraś, Damith Suresh Chathuranga, Hongbin Liu, James Housden, Kaspar Althoefer, and Kawal Rhode. 2016. "Multi-Axis Force/Torque Sensor Based on Simply-Supported Beam and Optoelectronics" Sensors 16, no. 11: 1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111936
APA StyleNoh, Y., Bimbo, J., Sareh, S., Wurdemann, H., Fraś, J., Chathuranga, D. S., Liu, H., Housden, J., Althoefer, K., & Rhode, K. (2016). Multi-Axis Force/Torque Sensor Based on Simply-Supported Beam and Optoelectronics. Sensors, 16(11), 1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111936









