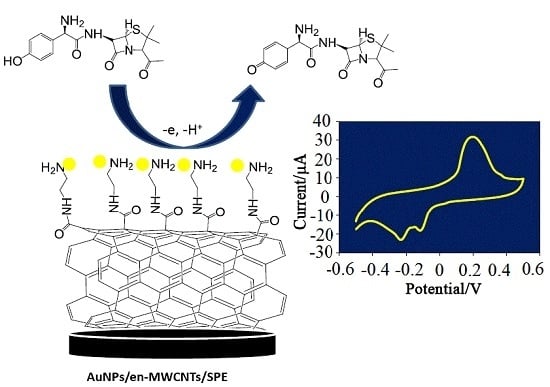
Construction of an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Carbon Nanotubes/Gold Nanoparticles for Trace Determination of Amoxicillin in Bovine Milk
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Material and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Real Sample Extraction
2.4. Preparation of AuNPs/en-MWCNTs Sensor
2.4.1. Pretreatment of MWCNTS
2.4.2. Synthesis of AuNPs/en-MWCNTs
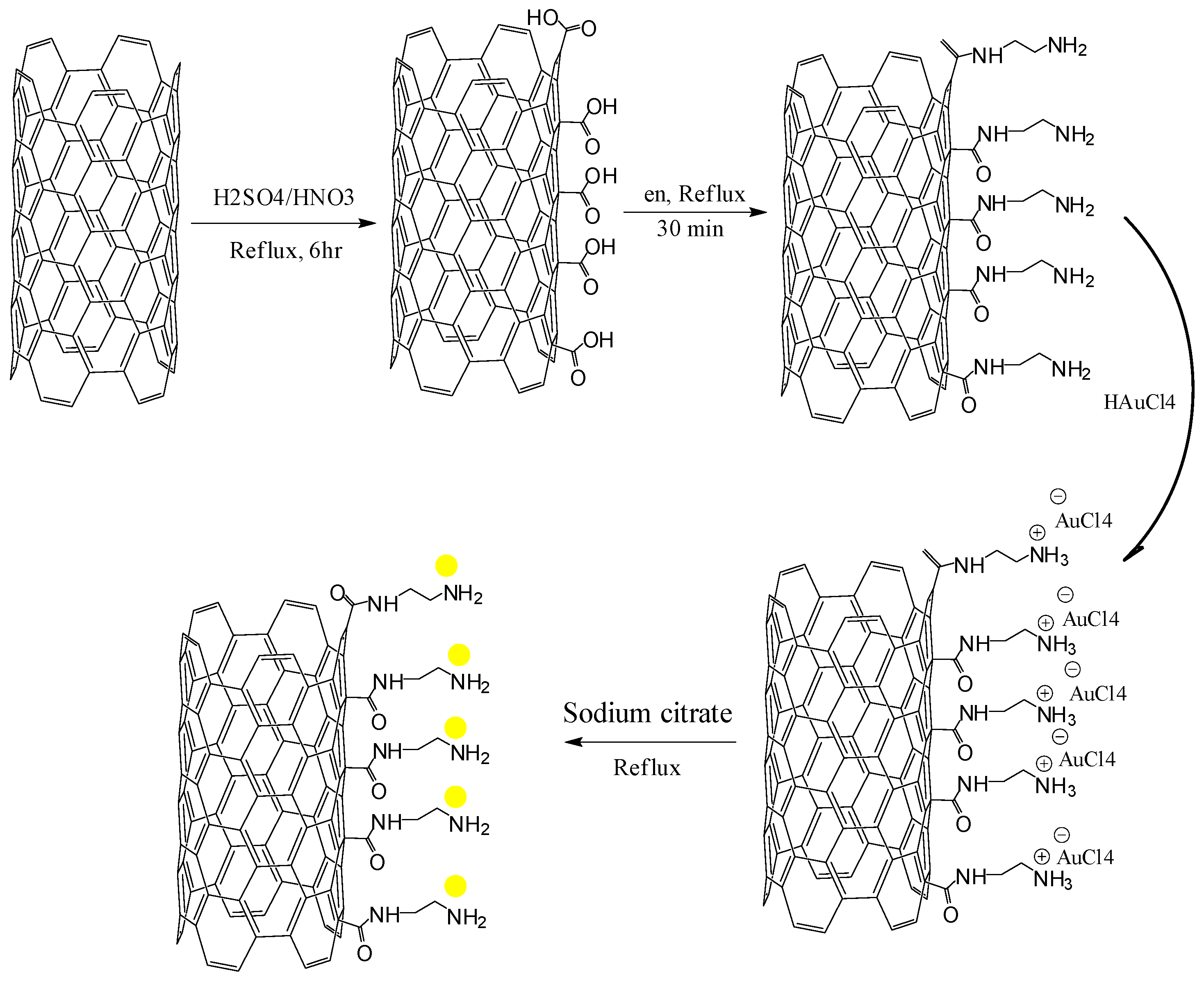
2.4.3. Fabrication of AuNPs/en-MWCNTs Based Electrode
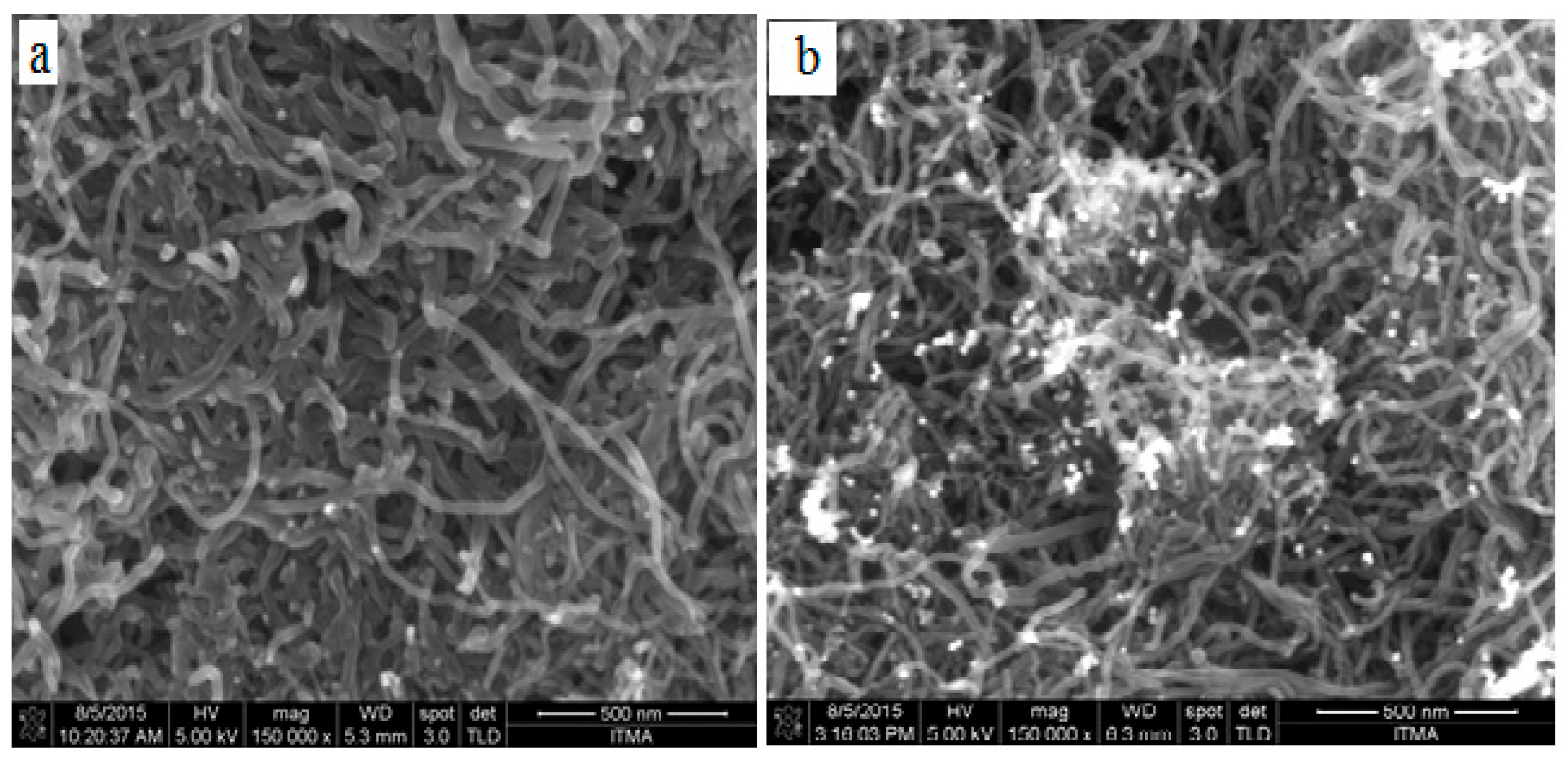
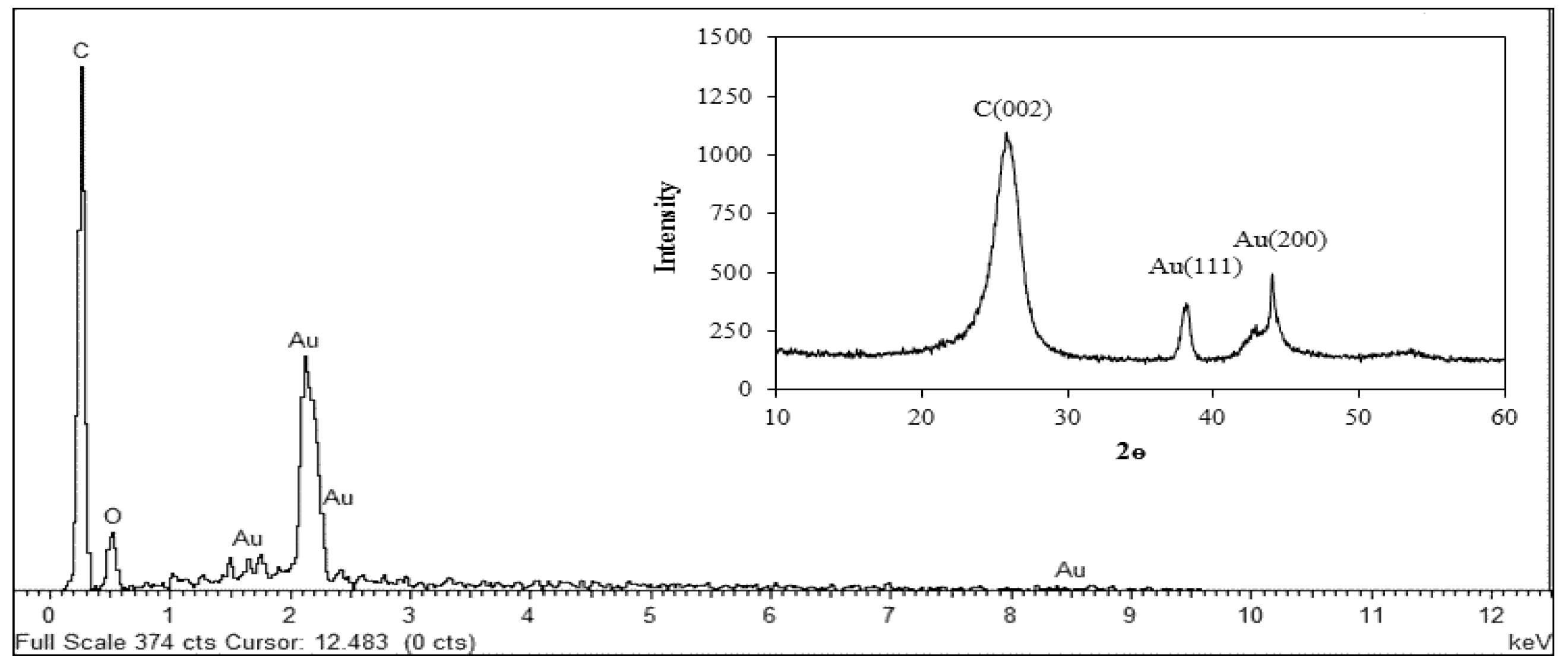
2.5. Characterizations of AuNPs/en-MWCNTs
2.6. Analytical Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrochemical Behavior of Amoxicillin
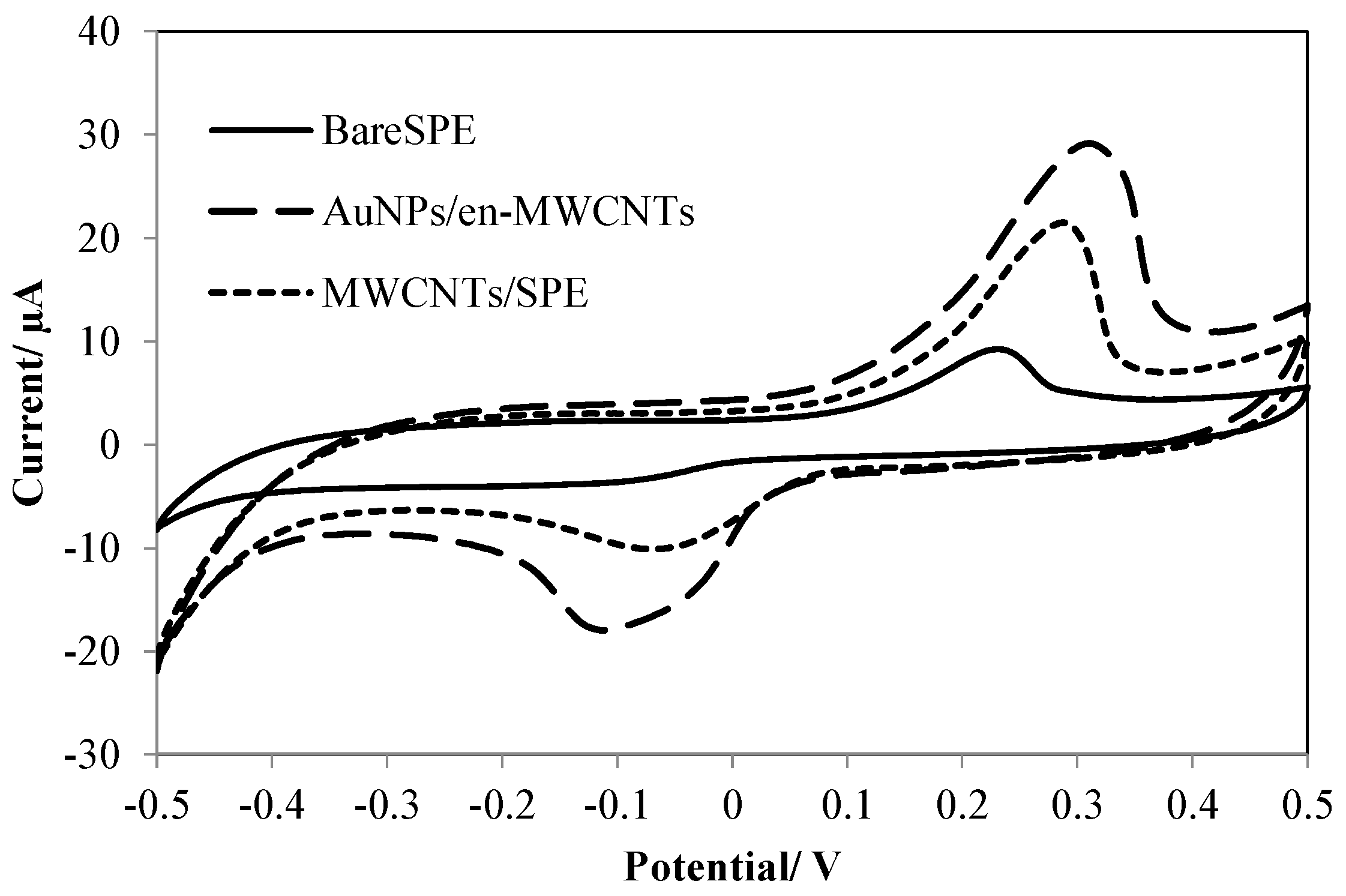
3.2. Optimization of Effective Parameters on the Sensitivity of the Electrochemical Sensor
3.2.1. Effect of Supporting Electrolyte
3.2.2. Accumulation Parameters
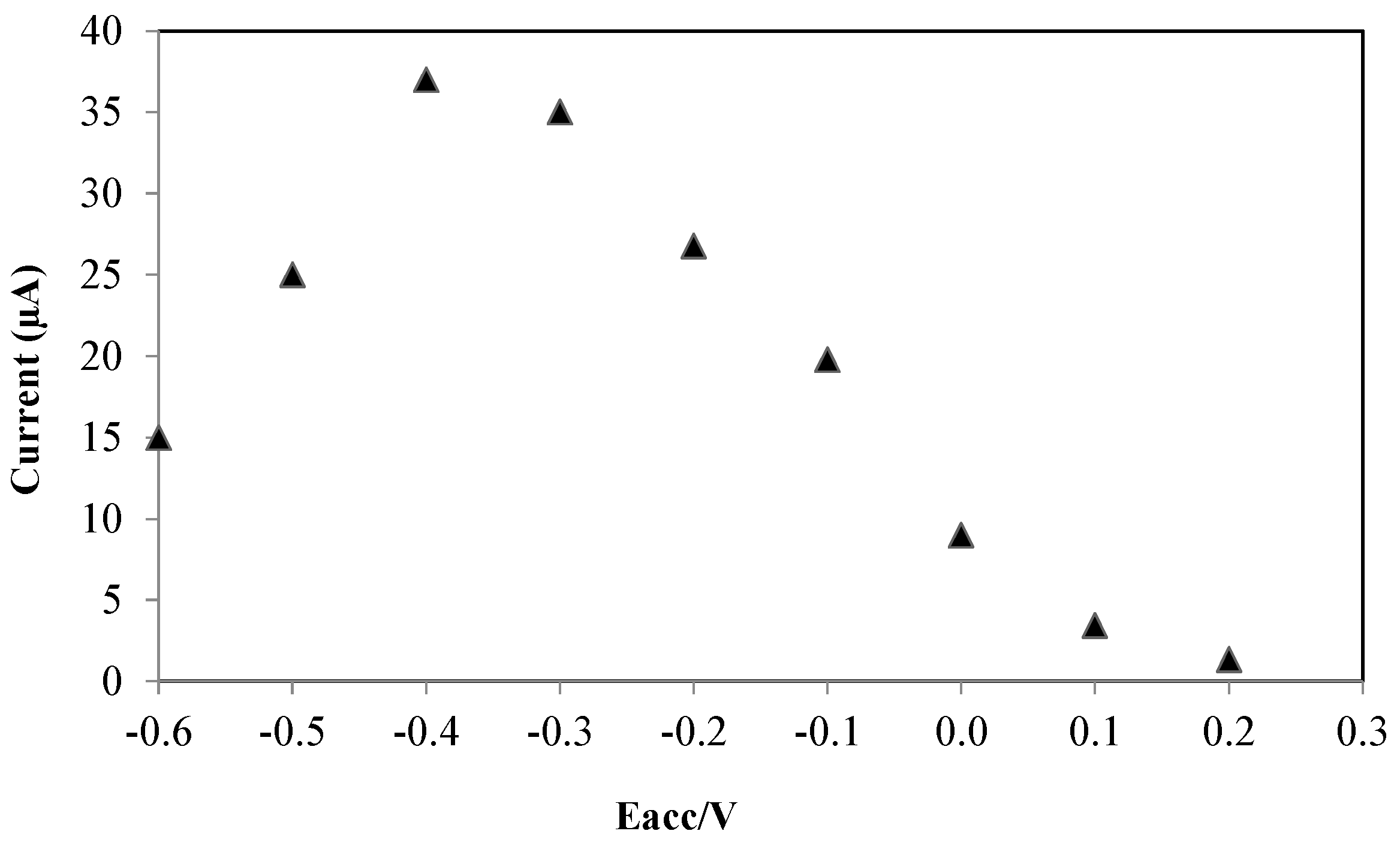
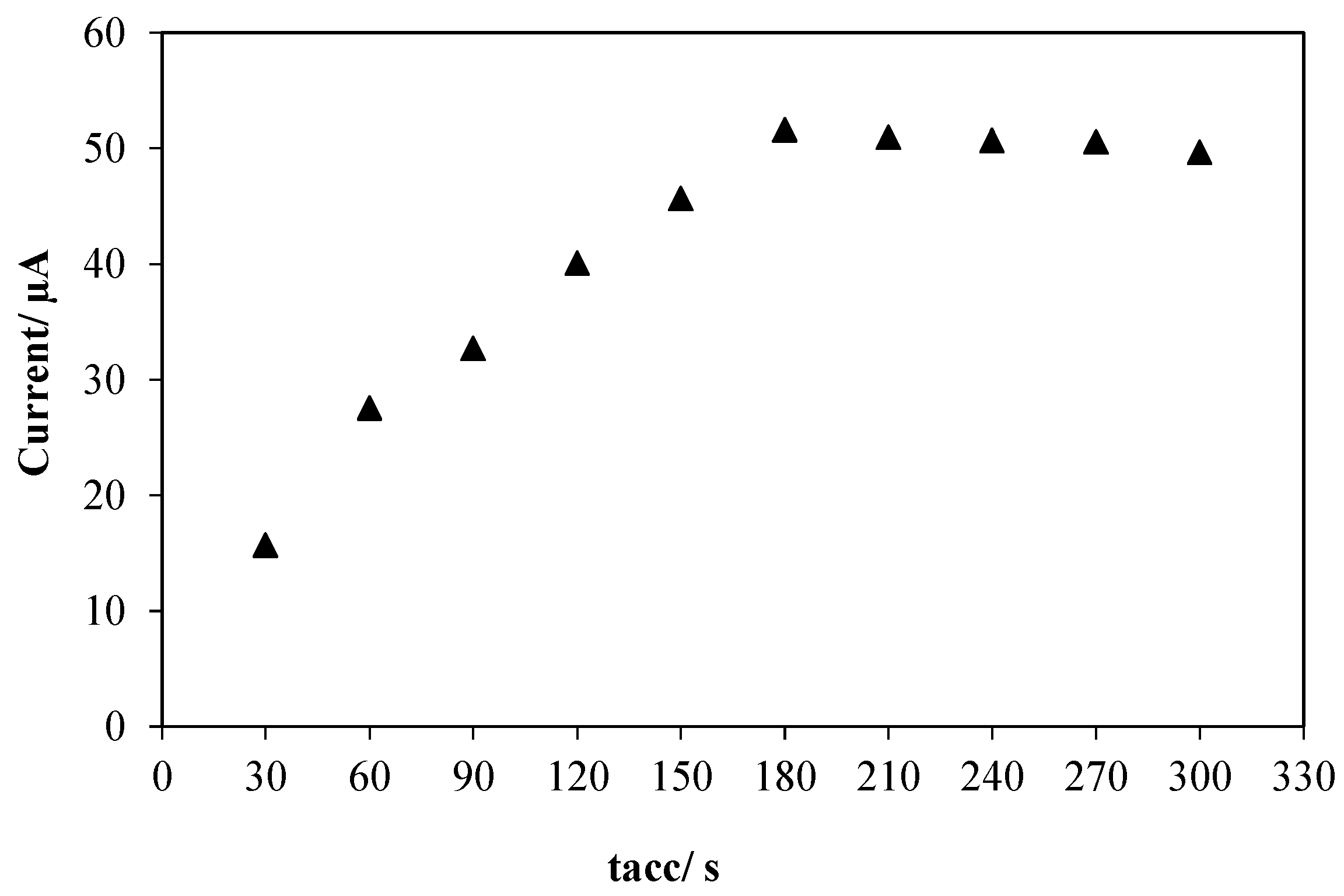
3.2.3. The Effect of Drop Casted Volume
3.2.4. Influence of HAuCl4 Concentration
3.2.5. Effect of Scan Rate
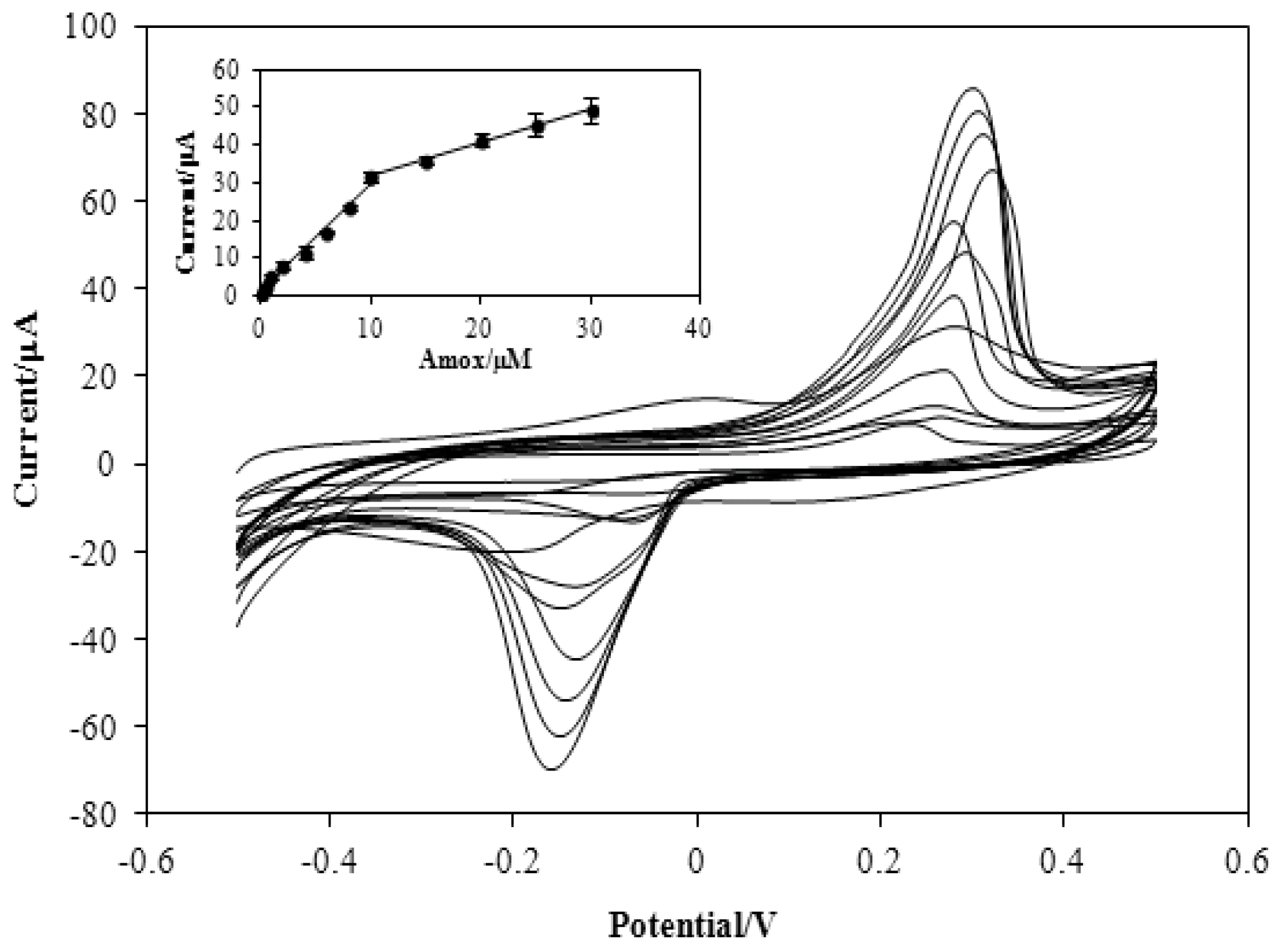
3.3. Figures of Merit
| Electrode | Technique | LDR/µM | LOD/µM | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni/Curcumin/CPE | Amp 1, CV | 8–100 | 5 | [29] |
| MWCNT/GCE | AdSV 2 | 0.6–80 | 0.2 | [30] |
| Glutaraldehyde/GA 3/GCE | SWV 4 | 2–25 | 0.92 | [31] |
| PNI 5/CPE | CV | 1–200 | 0.812 | [32] |
| AuNPs/en-MWCNTs/SPE | AdSV | 0.2–30 | 0.015 | Present work |
| Specie | Tolerance Limit (Fold) | Signal Change (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Ampicillin | 50 | −4.00 |
| Penicillin G | 50 | −4.65 |
| Thiamphenicol | 50 | −4.77 |
| Lactose | 100 | +0.79 |
| Casein protein | 100 | −4.72 |
| K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Zn2+, Na+, Mn2+, Fe2+ | 200 | <5.0 |
3.4. Application of the Proposed Method in Real Sample Analysis
| Sample | Spiked (µM) | Found (µM) | Recovery (%) | HPLC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Putra Mart Milk 1 | - | <LOD | - | ND 2 |
| 1.0 | 0.940 ± 0.011 | 94. | 0.978 ± 0.058 | |
| 2.0 | 1.91 ± 0.023 | 95.5 | 1.976 ± 0.35 | |
| Fresh Milk 3 | - | <LOD | - | ND |
| 1.0 | 0.915 ± 0.038 | 91.5 | 0.980 ± 0.15 | |
| 2.0 | 1.87 ± 0.060 | 93.5 | 1.957 ± 0.01 |
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akhond, M.; Absalan, G.; Ershadifar, H. Highly sensitive colorimetric determination of amoxicillin in pharmaceutical formulations based on induced aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 143, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Injac, R.; Ko, N.; Štrukelj, B. Optimized Method for Determination of Amoxicillin, Ampicillin, Sulfamethoxazole and Sulfacetamide in Animal Feed by Micellar Electrokinetic Capillary Chromatography and Comparison with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Chroatica CT Chem. 2009, 82, 685–694. [Google Scholar]
- Dayan, A.D. Allergy to antimicrobial residues in food: Assessment of the risk to man. Vet. Microbiol. 1993, 35, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantiani, L.; Farré, M.; Barceló, D.; Barceló, D. Analytical methodologies for the detection of β-lactam antibiotics in milk and feed samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires de Abreu, L.R.; Ortiz, R.M.; de Castro, S.C.; Pedrazzoli, J. HPLC determination of amoxicillin comparative bioavailability in healthy volunteers after a single dose administration. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 6, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dhoka, P.J.M.; Gawande, V. High Performance Liquid Chromatographic Method for Determination of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Bromhexine Hydrochloride in Oral Dosage Forms. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 2, 129–133. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, B.; Shi, A.; Li, L.; Kang, Y. Pharmacokinetics of amoxicillin in human urine using online coupled capillary electrophoresis with electrogenerated chemiluminescence detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 48, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.; Tang, W.; Han, R.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; He, P.; Fang, Y. Sensitive analysis of aminoglycoside antibiotics via hyphenation of transient moving substitution boundary with field-enhanced sample injection in capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1295, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, R.N.; Shetti, N.P.; Nandibewoor, S.T. Electro-oxidation and determination of trazodone at multi-walled carbon nanotube-modified glassy carbon electrode. Talanta 2009, 79, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Fan, X. Multiple functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with carboxyl and amino groups. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 276, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Rather, J.A. Stripping voltammetry of tinidazole in solubilized system and biological fluids. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 378, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Chen, S.; Yuan, R.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X. An ECL sensor for dopamine using reduced graphene oxide/multiwall carbon nanotubes/gold nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 191, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajian, R.; Yusof, N.A.; Faragi, T.; Shams, N. Fabrication of an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Gold Nanoparticles/Carbon Nanotubes as Nanocomposite Materials: Determination of Myricetin in Some Drinks. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Afkhami, A.; Bahiraei, A.; Madrakian, T. Gold nanoparticle/multi-walled carbon nanotube modified glassy carbon electrode as a sensitive voltammetric sensor for the determination of diclofenac sodium. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 59, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Guo, S.; Fang, Y.; Dong, S. Gold nanoparticle/carbon nanotube hybrids as an enhanced material for sensitive amperometric determination of tryptophan. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 3927–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Shan, C.; Song, J.; Han, D.; Niu, L. Preparation of gold nanoparticles/functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotube nanocomposites and its glucose biosensing application. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 1765–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajian, R.; Mehrayin, Z.; Mohagheghian, M.; Zafari, M.; Hosseini, P.; Shams, N. Fabrication of an electrochemical sensor based on carbon nanotubes modified with gold nanoparticles for determination of valrubicin as a chemotherapy drug: Valrubicin-DNA interaction. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 49, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moors, M.; Massart, D.L. Evaluation of solid-phase extraction of basic drugs from human milk. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1991, 9, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Lee, S.C.; Lee, J.K. Reinforcement of norbernene-based nanocomposites with norbernene functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 288, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukovic, G.D.; Marinkovic, M.; Colic, M.D.; Ristic, R.; Aleksic, A.A.; Peric, G.; Uskokovic, P.S. Removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions by oxidized and ethylenediamine functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 157, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzadeh, T.M.; Mohammed, T. Nitrate removal from water using functionalized carbon nanotube sheets. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2012, 9, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kucera, L.R.; Ummadisetty, S.; Nykaza, J.R.; Elabd, Y.A.; Storey, R.F.; Cavicchi, K.A.; Weiss, R.A. Supramolecular multiblock polystyrene—polyisobutylene copolymers via ionic interactions. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 4387–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, T.A.; Mattos, A.B.; Silva, B.V.M.; Dutra, R.F. Amino-functionalization of carbon nanotubes by using a factorial design: Human cardiac troponin T immunosensing application. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.R.; Bach, L.G.; Nga, T.T.; Lim, K.T. Covalent ligation of gold coated iron Fnanoparticles to the multi-walled carbon nanotubes employing click chemistry. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 561, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. Coating multiwalled carbon nanotubes with gold nanoparticles derived from gold salt precursors. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2011, 20, 1329–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, A.; Soltani-Felehgari, F.; Madrakian, T. Gold nanoparticles modified carbon paste electrode as an efficient electrochemical sensor for rapid and sensitive determination of cefixime in urine and pharmaceutical samples. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 103, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Hosseini, H. Electrochemistry of raloxifene on glassy carbon electrode and its determination in pharmaceutical formulations and human plasma. Bioelectrochemistry 2012, 88, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawal, A.T. Synthesis and utilization of carbon nanotubes for fabrication of electrochemical biosensors. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 73, 308–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojani, R.; Raoof, J.B.; Zamani, S. A novel voltammetric sensor for amoxicillin based on nickel–curcumin complex modified carbon paste electrode. Bioelectrochemistry 2012, 85, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, B.; Damiri, S. Electrochemistry and adsorptive stripping voltammetric determination of amoxicillin on a multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.P.; Bergamini, M.F.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Voltammetric sensor for amoxicillin determination in human urine using polyglutamic acid/glutaraldehyde film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 133, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslu, B.; Biryol, I. Voltammetric determination of amoxicillin using a poly (N-vinyl imidazole) modified carbon paste electrode. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999, 20, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, M.M.L.; Hogenboom, A.C.; Brinkman, U.A.T. Analytical strategies for the screening of veterinary drugs and their residues in edible products. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 1995, 667, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, N.; Varshosaz, J.; Dorkoosh, F.; Zargarzadeh, M.R. Development and validation of a simple HPLC method for simultaneous in vitro determination of amoxicillin and metronidazole at single wavelength. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muhammad, A.; Yusof, N.A.; Hajian, R.; Abdullah, J. Construction of an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Carbon Nanotubes/Gold Nanoparticles for Trace Determination of Amoxicillin in Bovine Milk. Sensors 2016, 16, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16010056
Muhammad A, Yusof NA, Hajian R, Abdullah J. Construction of an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Carbon Nanotubes/Gold Nanoparticles for Trace Determination of Amoxicillin in Bovine Milk. Sensors. 2016; 16(1):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16010056
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuhammad, Aliyu, Nor Azah Yusof, Reza Hajian, and Jaafar Abdullah. 2016. "Construction of an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Carbon Nanotubes/Gold Nanoparticles for Trace Determination of Amoxicillin in Bovine Milk" Sensors 16, no. 1: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16010056
APA StyleMuhammad, A., Yusof, N. A., Hajian, R., & Abdullah, J. (2016). Construction of an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Carbon Nanotubes/Gold Nanoparticles for Trace Determination of Amoxicillin in Bovine Milk. Sensors, 16(1), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16010056