A Kinect-Based Real-Time Compressive Tracking Prototype System for Amphibious Spherical Robots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works and Application Requirements
2.1. Amphibious Spherical Robot
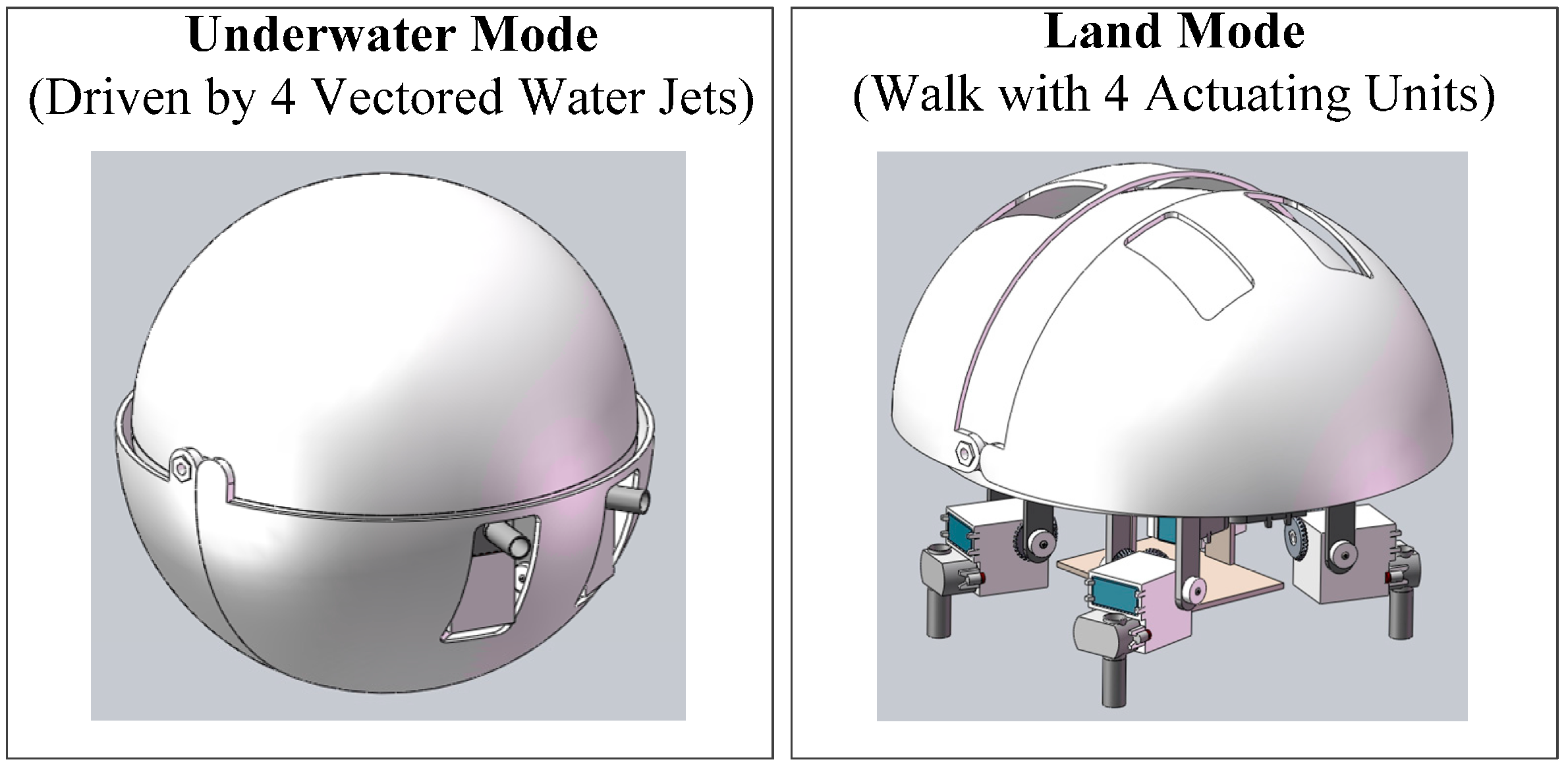
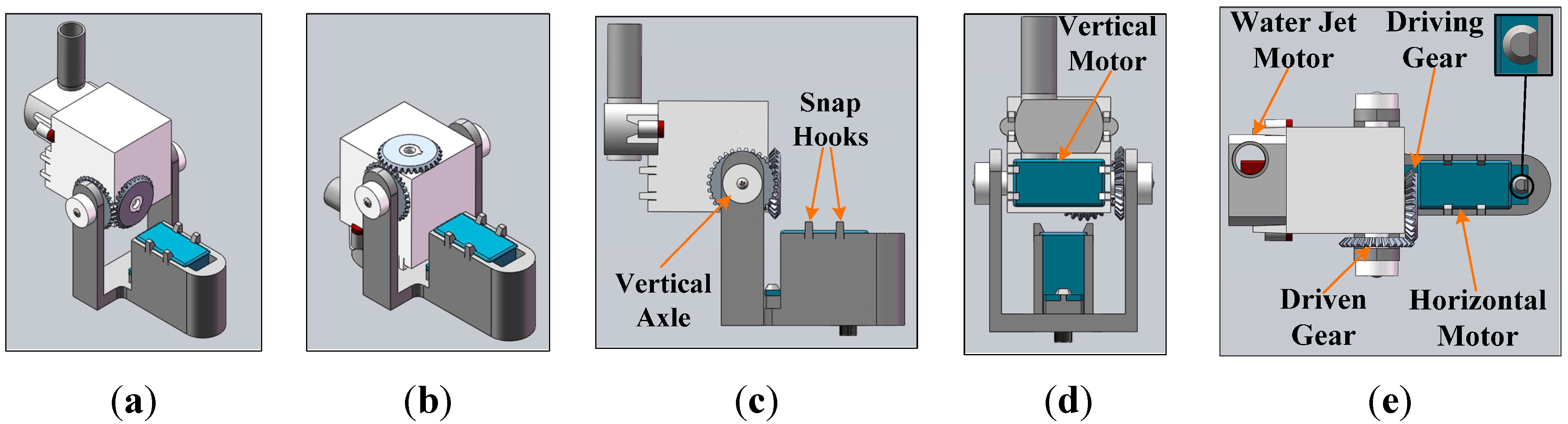
2.2. Real-Time Compressive Tracking Algorithms
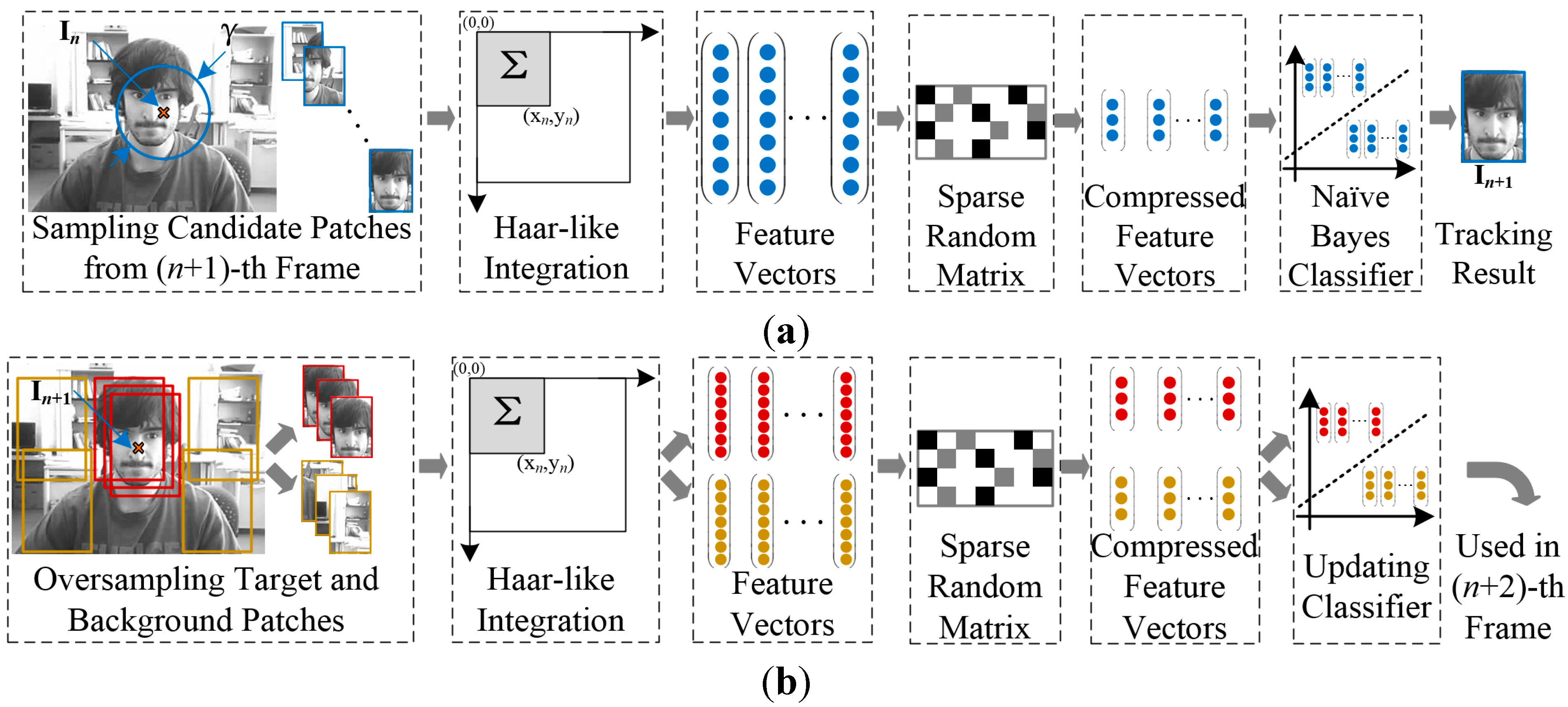
3. Proposed Algorithm
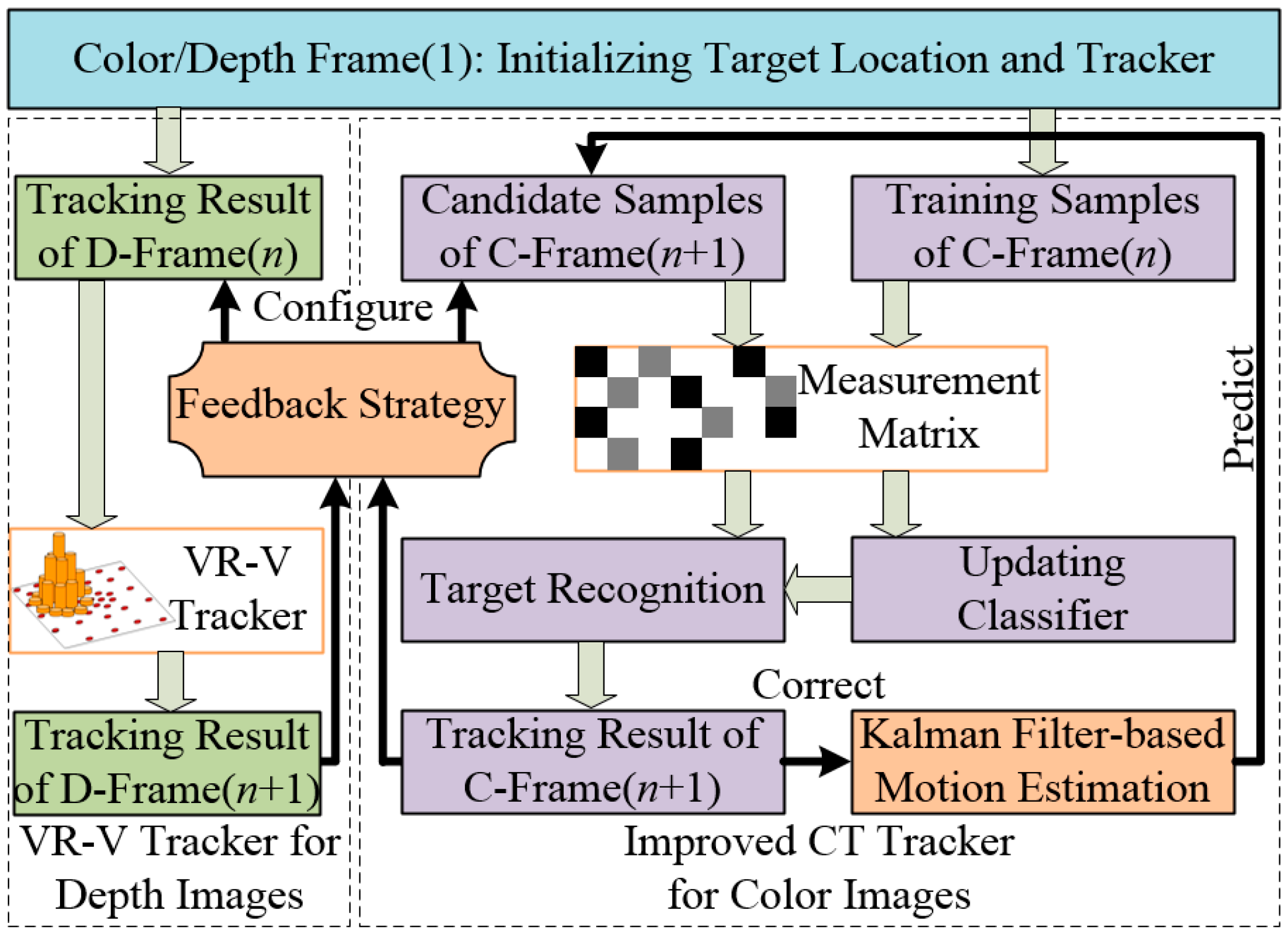
3.1. Visual Compressive Tracking with Motion Estimation

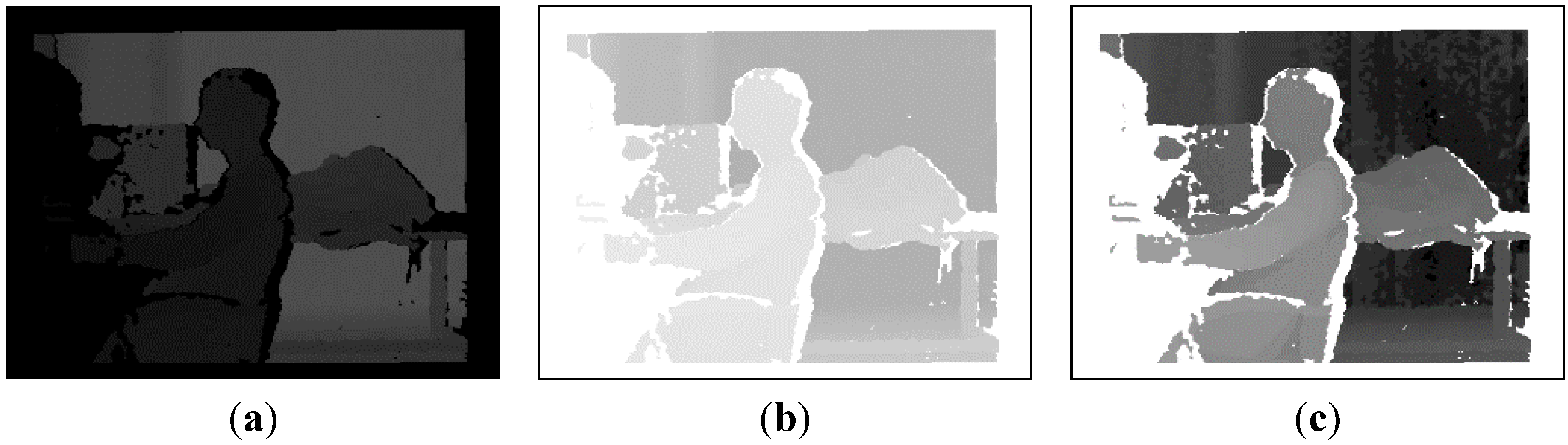
3.2. Depth Tracking Based on Improved VR-V
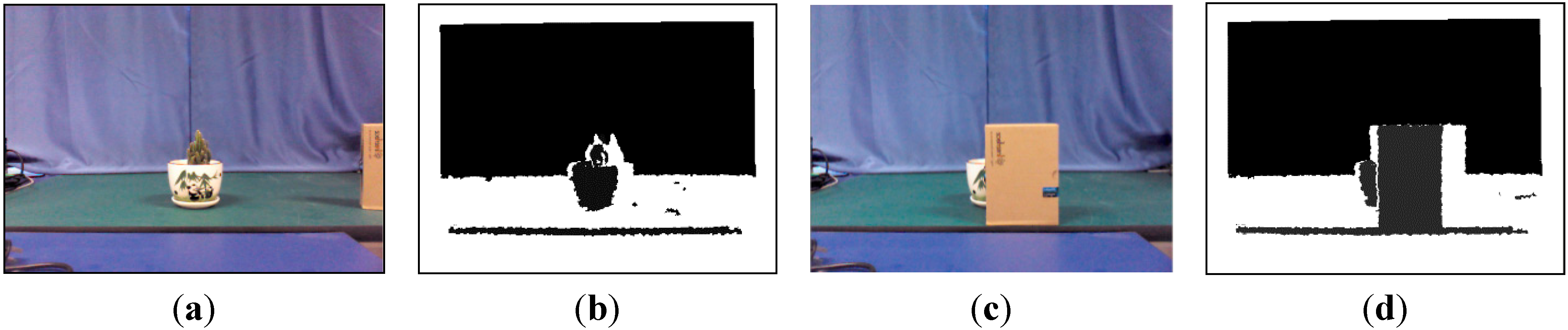

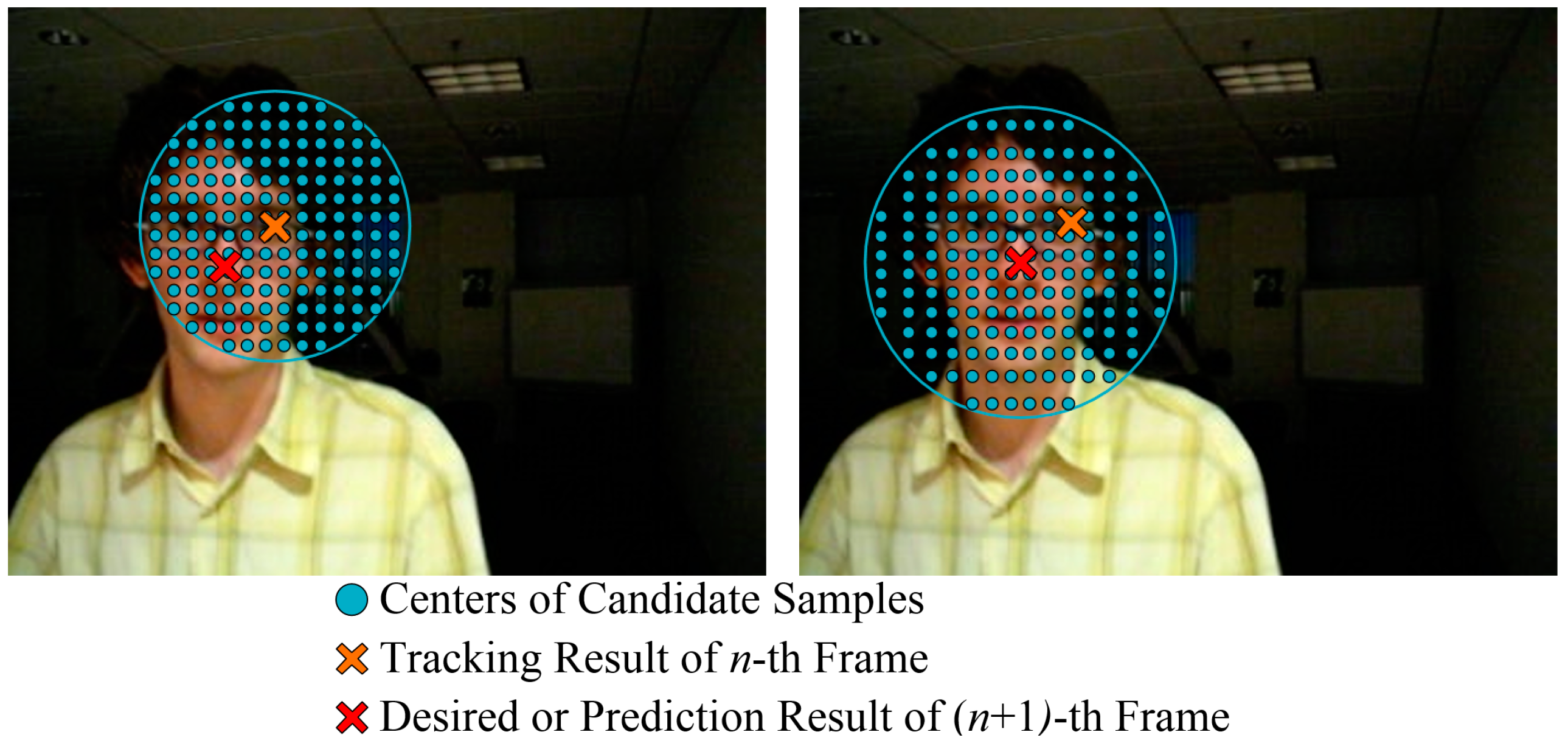
3.3. Feedback Strategy for Adaptive Online Learning
| No. | IC(n + 1) − ID(n + 1) | ID(n + 1) − ID(n) | shist | Adjust Parameter | Classifier Update |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | True | ||||
| 2 | ,, | True | |||
| 3 | False | ||||
| 4 | , Reset VR-V | True | |||
| 5 | ,, Reset VR-V | True | |||
| 6 | False | ||||
| 7 | True | ||||
| 8 | False | ||||
| 9 | False |
4. Experiment and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Environment and Tracking System Prototype
- (1)
- In the benchmark test, the improved CT algorithm, which contained a motion estimation mechanism and ran on a computer (Intel Core i7-4712MQ, 8 GB RAM), was tested on seven standard benchmark sequences compared with the original CT algorithm and the online multiple-instance learning (MIL) algorithm [41].
- (2)
- In the actual test, the proposed algorithm, running on the same computer, was deployed to process colour and depth image sequences captured by a Kinect compared with MIL algorithm, RGBD baseline algorithm and RGBDOcc algorithm [38].
- (3)
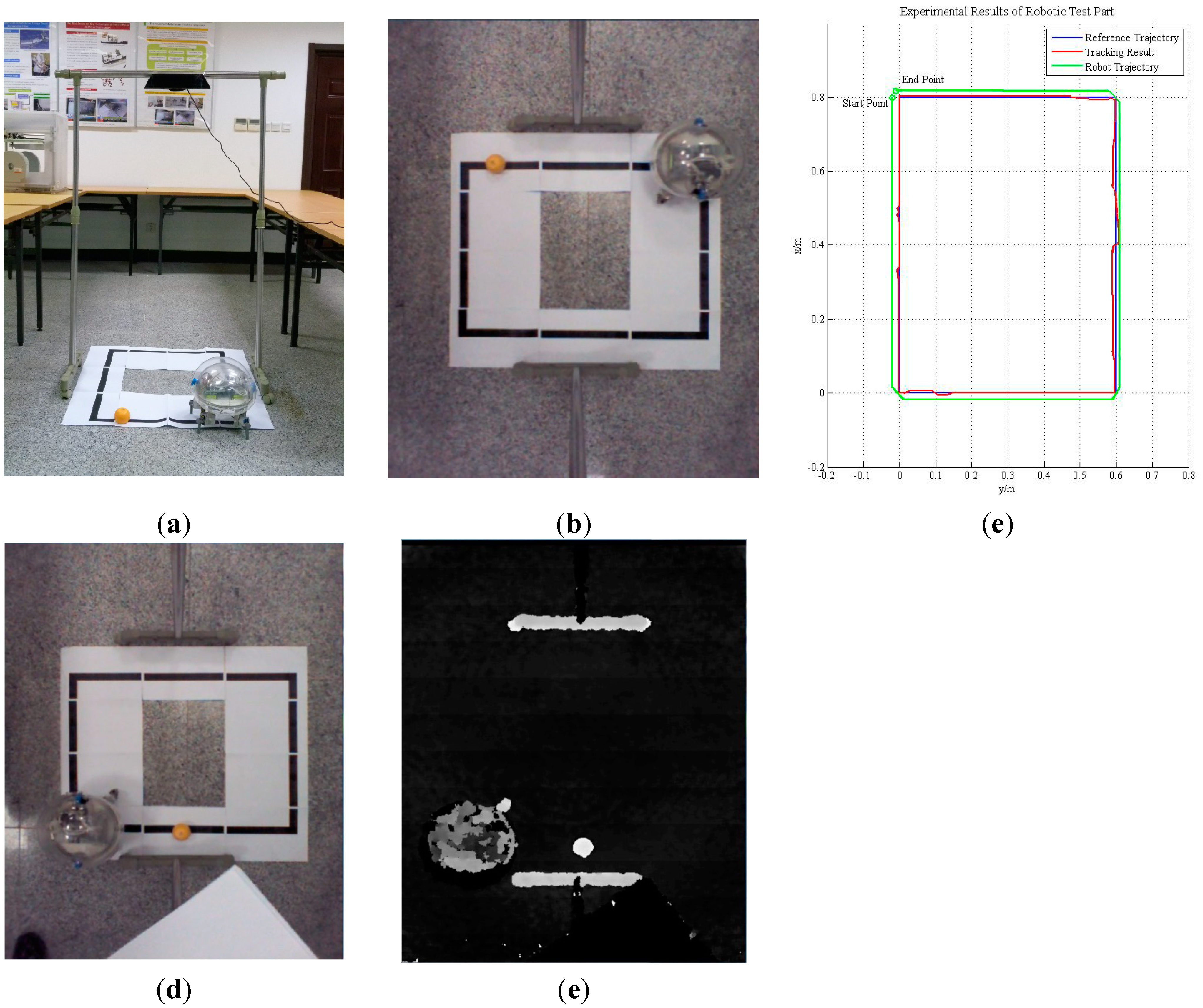
- In the robotic test, the proposed algorithm was implemented to guide the motion of our amphibious spherical robot. As shown in Figure 8, due to limitations imposed by the size of the current version of our robot, a preliminary prototype of the robotic tracking system for the algorithm evaluation was fabricated, in which a Kinect was installed in the region of activity of the robot, where it monitored the motion of the robot while the proposed algorithm, running on the same computer, tracked a specialised guiding object and controlled the robot via the wireless local network as it followed the object.

4.2. Experimental Results
| Sequences | Major Challenge | |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | Coke | Fast motion, Occlusion, Background Clutters |
| Couple | Fast Motion, Deformation, Background Clutters | |
| Liquid | Occlusion, Fast Motion, Background Clutters | |
| Suv | Occlusion, In-Plane Rotation, Out-of-View | |
| Tiger1 | Illumination Variation, Fast Motion, Occlusion | |
| Tiger2 | Illumination Variation, Fast Motion, Occlusion | |
| Fish | Out-of-View | |
| Ours | Note | Fast Motion, Occlusion |
| Book | Random Motion | |
| Glove 1 | Random Motion, Occlusion | |
| Glove 2 | Random Motion, Leave Field of View | |
| Sequences | Improved CT | Original CT | MILTrack | Number of Frames | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR | CLE | SR | CLE | SR | CLE | |||
| Standard | Coke | 19.2 | 31.2 | 15.8 | 36.1 | 9.2 | 28.8 | 291 |
| Couple | 83.6 | 8.6 | 68.6 | 35.4 | 65.7 | 35.9 | 140 | |
| Liquor | 40.1 | 141.9 | 28.1 | 168.9 | 21.0 | 131.8 | 1741 | |
| Suv | 58.5 | 39.1 | 17.9 | 79.2 | 46.2 | 59.8 | 945 | |
| Tiger1 | 49.3 | 23.6 | 46.8 | 28.0 | 8.5 | 104.6 | 354 | |
| Tiger2 | 51.7 | 24.5 | 45.2 | 28.6 | 45.7 | 28.3 | 365 | |
| Fish | 9.5 | 37.1 | 3.8 | 38.8 | 81.3 | 10.2 | 476 | |
| Frames per Second | 61.4 | 63.1 | 32.5 | |||||

| Sequences | Proposed Algorithm | Improved CT | MILTrack | RGBD Baseline | RGBDOcc | Number of Frames | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR | CLE | SR | CLE | SR | CLE | SR | CLE | SR | CLE | |||
| Ours | Note | 87.2 | 18.3 | 62.1 | 22.6 | 57.2 | 27.2 | 72.1 | 21.7 | 91.1 | 13.9 | 600 |
| Book | 88.5 | 9.7 | 36.6 | 55.3 | 46.3 | 47.9 | 76.8 | 17.9 | 86.3 | 9.1 | 600 | |
| Glove1 | 85.5 | 12.3 | 43.5 | 29.1 | 40.9 | 63.6 | 69.3 | 41.8 | 88.3 | 8.3 | 600 | |
| Glove2 | 79.2 | 17.5 | 47.2 | 23.5 | 41.6 | 42.7 | 59.4 | 49.3 | 75.1 | 16.2 | 400 | |
| Frames per Second | 39.7 | 57.3 | 31.7 | <1.0 | <1.0 | |||||||

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fabian, J.; Young, T.; Peyton Jones, J.C.; Clayton, G.M. Integrating the microsoft kinect with simulink: Real-time object tracking example. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2014, 19, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capi, G.; Toda, H.; Nagasaki, T. A vision based robot navigation and human tracking for social robotics. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Robotic and Sensors Environments (ROSE), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 15–16 October 2010; pp. 1–6.
- Wirbel, E.; Steux, B.; Bonnabel, S.; de la Fortelle, A. Humanoid robot navigation: From a visual SLAM to a visual compass. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC), Evry, France, 10–12 April 2013; pp. 678–683.
- Bischoff, B.; Duy, N.-T.; Streichert, F.; Ewert, M.; Knoll, A. Fusing vision and odometry for accurate indoor robot localization. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Control Automation Robotics & Vision (ICARCV), Guangzhou, China, 5–7 December 2012; pp. 347–352.
- Lin, R.; Li, M.; Sun, L. Image features-based mobile robot visual SLAM. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Shenzhen, China, 12–14 December 2013; pp. 2499–2504.
- Siradjuddin, I.; Behera, L.; McGinnity, T.M.; Coleman, S. A position based visual tracking system for a 7 DOF robot manipulator using a Kinect camera. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Brisbane, Australia, 10–15 June 2012; pp. 1–7.
- Wang, P.; Su, J.; Li, W.; Qiao, H. Adaptive visual tracking based on discriminative feature selection for mobile robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE 4th Annual International Conference on Cyber Technology in Automation, Control, and Intelligent Systems (CYBER), Hong Kong, China, 4–7 June 2014; pp. 55–61.
- Oonishi, S.; Yanou, A.; Minami, M. Human-face-tracking using visual servoing by patient robot. In Proceedings of the SICE Annual Conference (SICE), Nagoya, Japan, 14–17 September 2013; pp. 2266–2271.
- Gupta, M.; Behera, L.; Subramanian, V.K.; Jamshidi, M.M. A Robust visual human detection approach with UKF-based motion tracking for a mobile robot. IEEE Syst. J. 2014, PP, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Hou, Z. Survey of single-target visual tracking methods based on online learning. IEEE Trans. Comput. Vis. 2014, 8, 419–428. [Google Scholar]
- Salti, S.; Cavallaro, A.; Di Stefano, L. Adaptive appearance modeling for video tracking: Survey and evaluation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 4334–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Li, Q.; Fang, H.; Xu, H.C. Research on embedded system with implementation of a moving object tracking algorithm based on improved meanshift on DM6437. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1003, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xin, M.; Yang, J. Adaptive multi-cue based particle swarm optimization guided particle filter tracking in infrared videos. Neurocomputing 2013, 122, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D.A.; Lim, J.; Lin, R.S.; Yang, M.H. Incremental learningfor robust visual tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 77, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Subramanian, K.R.; Yoo, T.S. An optical flow approach to tracking colonoscopy video. Comput. Med. Imag. Gr. 2013, 37, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirzada, N.; Nayan, M.Y.; Hassan, F.S.M.F.; Khan, M.A. Device-free localization technique for indoor detection and tracking of human body: A survey. Proced. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 129, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avidan, S. Support vector T racking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2004, 26, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wu, J. Scalable compressive tracking based on motion. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Shenzhen, China, 12–14 December 2013; pp. 504–509.
- Qi, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Wu, H.; Chen, Q. EK-means tracker: A pixel-wise tracking algorithm using kinect. In Proceedings of the Third Chinese Conference on Intelligent Visual Surveillance (IVS), Beijing, China, 1–2 December 2011; pp. 77–80.
- Shi, Q.; Ishii, H.; Sugahara, Y.; Sugita, H.; Takanishi, A.; Huang, Q.; Fukuda, T. Design and control of a biomimetic robotic rat for interaction with laboratory rats. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2014, PP, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.; Ishii, H.; Kinoshita, S.; Konno, S.; Takanishi, A.; Okabayashi, S.; Iida, N.; Kimura, H.; Shibata, S. Modulation of rat behaviour by using a rat-like robot. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2013, 8, 46002–46012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, L. Visual servoing trajectory tracking of nonholonomic mobile robots without direct position measurement. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2014, 30, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, L. Visual servoing based trajectory tracking of underactuated water surface robots without direct position measurement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2014), Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 September 2014; pp. 767–772.
- Guo, S.; Mao, S.; Shi, L.; Li, M. Development of an Amphibious Mother Spherical Robot Used as the Carrier for Underwater Microrobots. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Complex Medical Engineering (ICME), Kobe, Japan, 1–4 July 2012; pp. 758–762.
- Shi, L.; Guo, S.; Li, M.; Yue, C.; Mao, S.; Asaka, K. Development of an amphibious turtle-inspired spherical mother robot. J. Bion. Eng. 2013, 10, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Shi, L.; Xiao, N.; Asaka, K. A Biomimetic underwater microrobot with multifunctional locomotion. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2012, 60, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Guo, S.; Shi, L.; He, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Q. A Spherical Robot based on all Programmable SoC and 3-D Printing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Tianjin, China, 3–6 August 2014; pp. 150–155.
- Wang, H.-S.; Chen, W.-D.; Wang, Z.-L. Visual tracking of robots in uncalibrated environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011; pp. 2959–2964.
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M.-H. Real-Time Compressive Tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2012), Florence, Italy, 7–13 October 2012; pp. 864–877.
- Xu, R.; Gu, X.; Wei, B. An improved real time compressive tracking. In Proceedings of the 2nd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR), Okinawa, Japan, 5–8 November 2013; pp. 692–696.
- Yan, Q.-S.; Li, L.-S. Kernel sparse tracking with compressive sensing. IET Comput. Vis. 2014, 8, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M.-H. Fast compressive tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 2002–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Shao, L.; Xu, D.; Shotton, J. Enhanced computer vision with microsoft kinect sensor: A review. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 43, 1318–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smisek, J.; Jancosek, M.; Pajdla, T. 3-D with kinect. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 1154–1160.
- Tang, S.; Wang, X.; Lv, X.; Han, T.-X.; Keller, J.; He, Z.; Skubic, Z.; Lao, S. Histogram of Oriented Normal Vectors for Object Recognition with a Depth Sensor. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV), Daejeon, Korea, 5–9 November 2012; pp. 525–538.
- Wang, P.; Ma, S.; Shen, Y. Performance study of feature descriptors for human detection on depth map. Int. J. Model. Simul. Sci. Comput. 2014, 5, 13–29. [Google Scholar]
- Spinello, L.; Arras, K. People detection in RGB-D data. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011; pp. 3838–3843.
- Song, S.; Xiao, J. Tracking revisited using RGB-D camera: Unified benchmark and baselines. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV2013), Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 233–240.
- Ren, H.-L.; Liu, W.; Lim, A. Marker-based surgical instrument tracking using dual kinect sensors. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2014, 11, 921–924. [Google Scholar]
- Collin, R.T.; Liu, Y.; Leordeanu, M. Online selection of discriminative tracking features. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 1631–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babenko, B.; Yang, M.-H.; Belongie, S. Robust object tracking with online multiple instance learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 1619–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jongwoo, Lim; Yang, M.-H. Online Object Tracking: A Benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2411–2418.
- Prats, M.; Fernandez, J.J.; Sanz, P.J. Combining template tracking and laser peak detection for 3d reconstruction and grasping in underwater environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vilamoura, Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 106–112.
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, S.; Shi, L.; Guo, S. A Kinect-Based Real-Time Compressive Tracking Prototype System for Amphibious Spherical Robots. Sensors 2015, 15, 8232-8252. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150408232
Pan S, Shi L, Guo S. A Kinect-Based Real-Time Compressive Tracking Prototype System for Amphibious Spherical Robots. Sensors. 2015; 15(4):8232-8252. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150408232
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Shaowu, Liwei Shi, and Shuxiang Guo. 2015. "A Kinect-Based Real-Time Compressive Tracking Prototype System for Amphibious Spherical Robots" Sensors 15, no. 4: 8232-8252. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150408232
APA StylePan, S., Shi, L., & Guo, S. (2015). A Kinect-Based Real-Time Compressive Tracking Prototype System for Amphibious Spherical Robots. Sensors, 15(4), 8232-8252. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150408232








