A Review on the Trophic Shifts Among Habitat Types of the Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes Linnaeus) and Insights on Its Role as Bioindicator in Mediterranean Landscapes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- -
- expand habitat-explicit dietary studies across underrepresented Mediterranean regions to address current geographical gaps;
- -
- quantify the effectiveness of seed dispersal by red foxes through integrated approaches combining faecal analysis, genetic identification of dispersed seeds, and monitoring of seedling recruitment;
- -
- link trophic networks with restoration objectives by evaluating how fox-mediated seed dispersal and predation on seed predators and small herbivores influence vegetation recovery in forest habitats and agroecosystem mosaics;
- -
- assess how management interventions—such as silvicultural practices, ecological corridor creation, hedgerow planting, and agroforestry systems—interact with disturbance regimes to enhance the reciprocal benefits of red fox conservation and ecosystem functioning across Mediterranean landscapes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sillero, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Macdonald, D. Canids: Foxes, Wolves, Jackals and Dogs. Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Cavallini, P.; Lovari, S. Home range, habitat selection and activity of the red fox in a Mediterranean coastal ecotone. Acta Theriol. 1994, 39, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, B.; La Mantia, T. Forestry, Pasture, Agriculture and Fauna Correlated to Recent Changes in Sicily. Forest@ 2007. Available online: http://www.sisef.it/forest@/ (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Bianchetto, E.; Buscemi, I.; Corona, P.; Giardina, G.; La Mantia, T.; Pasta, S. Fitting the Stocking Rate with Pastoral Resources to Manage and Preserve Mediterranean Forestlands: A Case Study. Sustainability 2015, 7, 7232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, R.S.; García, D.; Galetti, M.; La Mantia, T. Past cover modulates the intense and spatially structured natural regeneration of woody vegetation in a pastureland. Plant Ecol. 2020, 221, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosalino, L.; Santos-Reis, M. Fruit consumption by carnivores in Mediterranean Europe. Mammal Rev. 2009, 39, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soe, E.; Davison, J.; Süld, K.; Valdmann, H.; Laurimaa, L.; Saarma, U. Europe-wide biogeographical patterns in the diet of an ecologically and epidemiologically important mesopredator, the red fox Vulpes vulpes: A quantitative review. Mammal Rev. 2017, 47, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, I.; Doherty, T.S.; Fleming, P.A.; Stobo-Wilson, A.M.; Woinarski, J.C.Z.; Newsome, T.M. Variation in red fox Vulpes vulpes diet in five continents. Mammal Rev. 2022, 52, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldeschi, B.; Tomassini, O.; Bedini, G.; Petroni, G.; Giunchi, D.; Massolo, A. An attempt to evidence post-fire adaptation of red fox diet in a Mediterranean area. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 36, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampalini, B.; Lovari, S. Food habits and trophic niche overlap of the badger and the red fox in a Mediterranean coastal area. Z. Säugetierkd. 1984, 50, 226–234. [Google Scholar]
- Bassi, E.; Donaggio, E.; Marcon, A.; Scandura, M.; Apollonio, M. Trophic niche overlap and wild ungulate consumption by red fox and wolf in a mountain area in Italy. Mamm. Biol. 2012, 77, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallini, P.; Volpi, T. Variation in the diet of the red fox in a Mediterranean area. Rev. Écol. 1996, 51, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Arte, G.L.; Leonardi, G. Effects of habitat composition on the use of resources by the red fox in a semi-arid environment of North Africa. Acta Oecol. 2005, 27, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, P.; Lovari, S. Food habits and trophic niche overlap of the red fox and the stone marten in a Mediterranean rural area. Acta Theriol. 1993, 38, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padial, J.M.; Avila, E.; Sanchez, J.M. Feeding habits and overlap among red fox (Vulpes vulpes) and stone marten (Martes foina) in two Mediterranean mountain habitats. Mamm. Biol. 2002, 67, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patalano, M.; Lovari, S. Food habits and trophic niche overlap of the Wolf (Canis lupus L. 1758) and the Red fox (Vulpes vulpes L. 1758) in a Mediterranean mountain area. Rev. Écol. 1993, 48, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.; Gomes, Y. Food habits and trophic niche overlap of the red fox, European wild cat and common genet in the Peneda-Gerês National Park. Galemys 2001, 13, 41–56. [Google Scholar]
- Fais, I.; Costanzo, M.; Massa, B. First data on the feeding habits of the Red fox (Vulpes vulpes L.) in Sicily. Hystrix Ital. J. Mammal. 1991, 3, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Massa, B. Atlante Iconografico Della Fauna Vertebrata Della Riserva Naturale Orientata Dello Zingaro (Sicilia); Azienda Foreste Demaniali della Regione Siciliana: Palermo, Italy, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Siracusa, A.; Dell’Arte, G.L. Dieta della volpe (Vulpes vulpes) (Mammalia Carnivora) in agroecosistemi del Parco dell’Etna. Nat. Sicil. 2006, 30, 421–434. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, G. Il Ruolo della Volpe Nella Ricostituzione dei Sistemi Naturali (The Role of the Fox in the Restoration of Natural Systems). Tesi di Laurea, University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bullock, J.; Aronson, J.; Newton, A.; Pywell, R.; Benayas, J. Restoration of ecosystem services and biodiversity: Conflicts and opportunities. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2011, 26, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.; Harris, N. Forecasting habitat suitability across large carnivore ranges with climate and land use change. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 113815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, J.; Aronson, J. Biology and Wildlife of the Mediterranean Region; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- La Mantia, T.; Bueno, R.S. Colonization of Eurasian jay Garrulus glandarius and holm oaks Quercus ilex: The establishment of ecological interactions in urban areas. Avocetta 2016, 40, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, R.S.; García, D.; Galetti, M.; La Mantia, T. Trophic and spatial complementarity on seed dispersal services by birds, wild mammals, and cattle in a Mediterranean woodland pasture. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 27, e01880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mantia, T.; Rühl, J.; Massa, B.; Pipitone, S.; Verde, G.; Bueno Da Silveira, R. Vertebrate-mediated seed rain and artificial perches contribute to overcome seed dispersal limitation in a Mediterranean old field. Restor. Ecol. 2019, 27, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, C. Frugivory and Seed Dispersal by Carnivorous Mammals, and Associated Fruit Characteristics, in Undisturbed Mediterranean Habitats. Oikos 1989, 55, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordano, P.; García, C.; Godoy, J.A.; García-Castaño, J.L. Differential contribution of frugivores to complex seed dispersal patterns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3278–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Ruiz, F.; Delibes-Mateos, M.; García-Moreno, J.L.; López-Martín, J.M.; Ferreira, C.; Ferreira, C.; Ferreras, P. Biogeographical Patterns in the Diet of an Opportunistic Predator: The Red Fox Vulpes Vulpes in the Iberian Peninsula. Mammal Rev. 2013, 43, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MiPAAF. Strategia Forestale Nazionale per il 2022–2042; Ministero delle Politiche Agricole Alimentari e Forestali: Roma, Italia, 2022. Available online: https://www.politicheagricole.it (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Priolo, A. Distrutti i Grifoni delle Caronie? Riv. Ital. Orn. 1967, 37, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
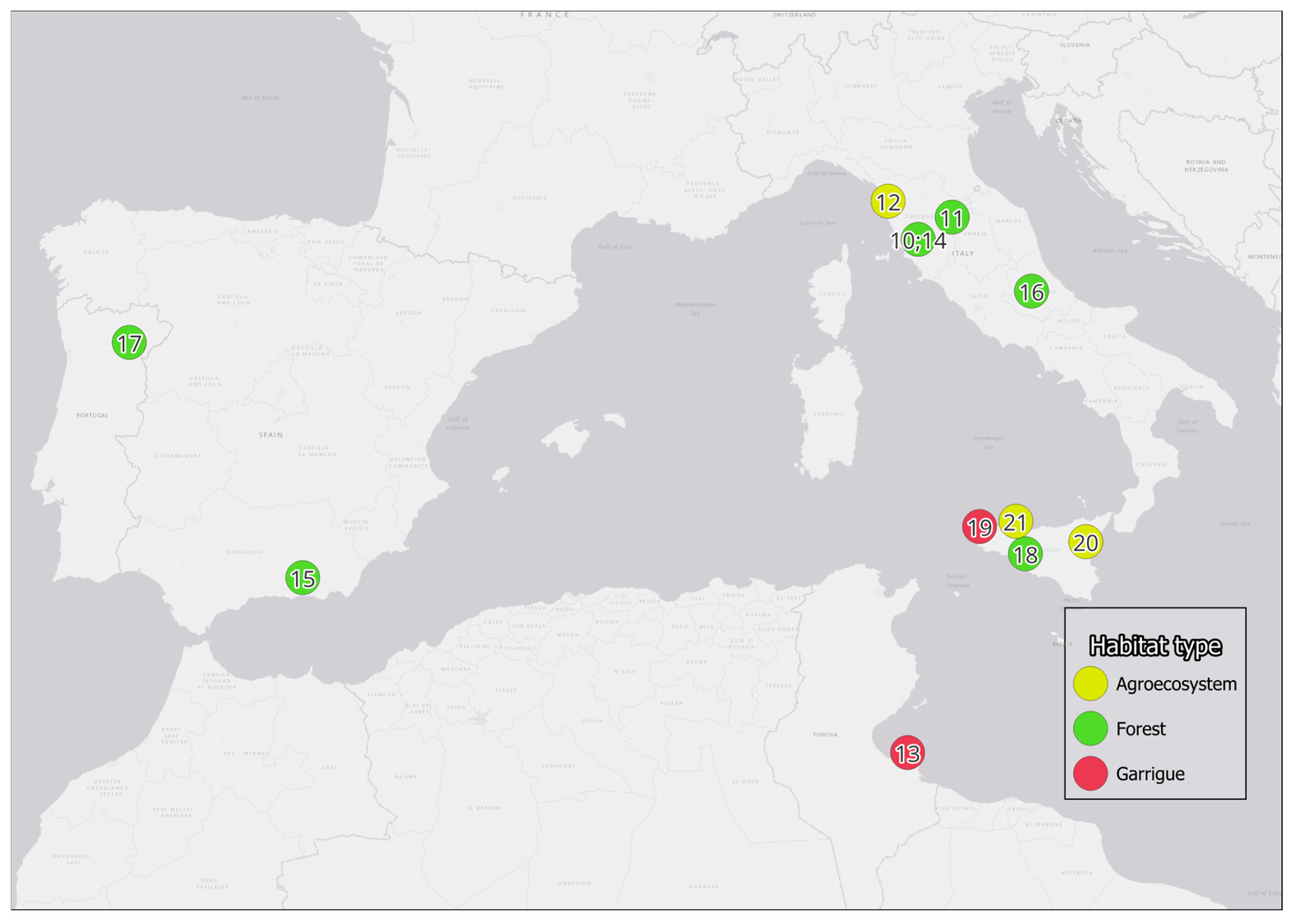

| Habitat | Country | Study Area | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forest | Italy | Siena | [10] |
| Forest | Italy | Arezzo | [11] |
| Agroecosystem | Italy | Pisa | [12] |
| Agroecosystem | Tunisia | Island of Djerba | [13] |
| Forest | Italy | Siena | [14] |
| Forest | Spain | Sierra Nevada | [15] |
| Forest | Italy | Abruzzo | [16] |
| Forest | Portugal | Geres | [17] |
| Forest | Italy | Palermo | [18] |
| Garrigue | Italy | Trapani | [19] |
| Agroecosystem | Italy | Mt. Etna | [20] |
| Agroecosystem | Italy | Palermo | [21] |
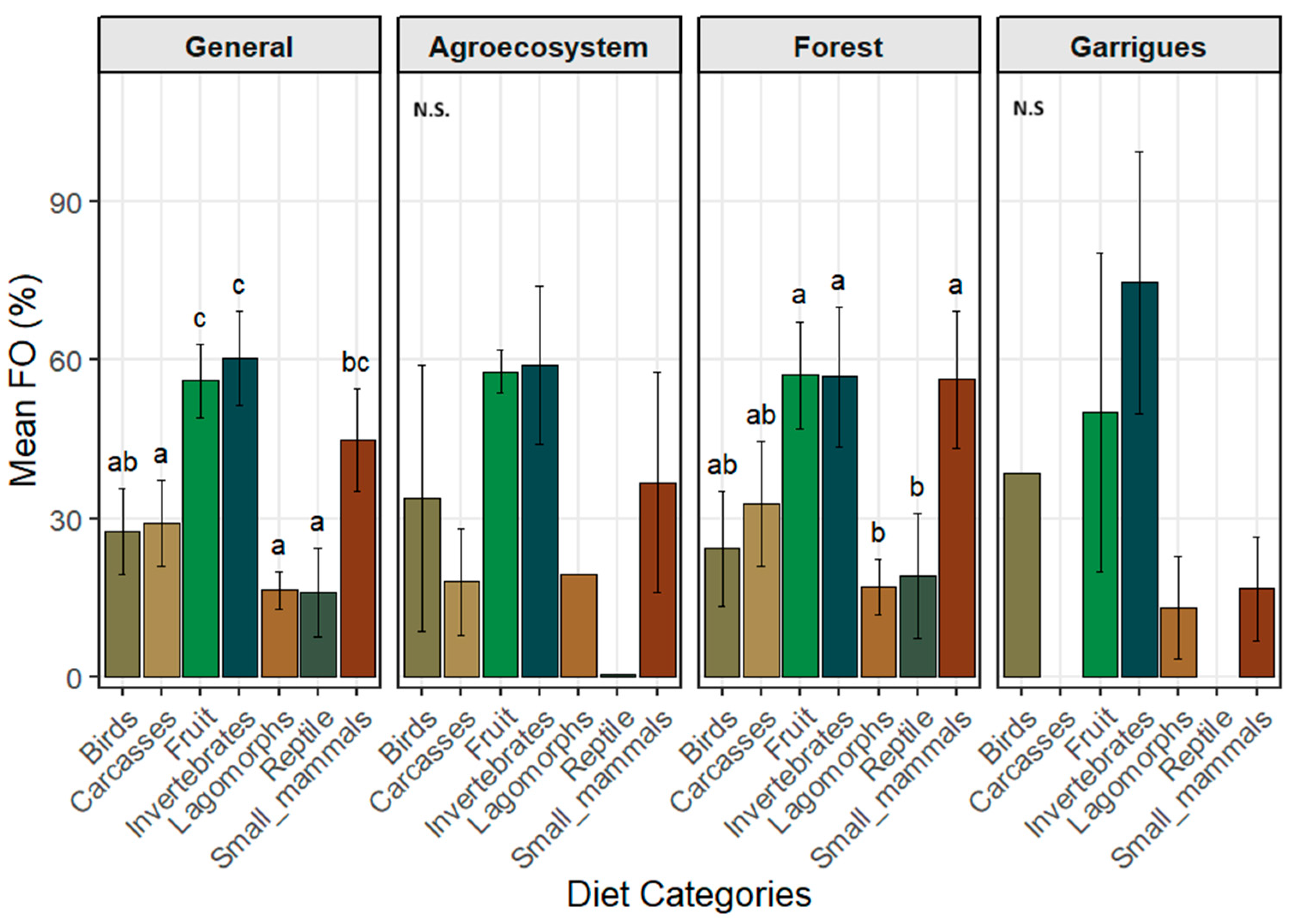
| Trophic Category | Overall | Forest | Agroecosystem | Garrigues |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Invertebrates | 61.8 ± 29.3 | 62.1 ± 32.6 | 59.0 ± 26.3 | 74.7 ± 34.9 |
| Fruits | 56.0 ± 23.7 | 56.7 ± 26.2 | 57.9 ± 6.9 | 50.2 ± 42.6 |
| Small mammals | 45.1 ± 33.1 | 56.6 ± 34.2 | 36.9 ± 32.1 | 16.7 ± 13.8 |
| Birds | 27.0 ± 28.3 | 24.9 ± 30.8 | 33.9 ± 35.2 | 38.6 ± 27.3 |
| Carcasses | 19.0 ± 18.1 | 32.3 ± 31.6 | 18.1 ± 17.4 | — |
| Lagomorphs | 16.3 ± 11.0 | 17.7 ± 11.4 | 19.4 ± 0.0 | 13.3 ± 13.8 |
| Reptiles | 10.4 ± 25.3 | 19.4 ± 30.7 | 0.7 ± 0.0 | — |
| Shannon index | 1.26 ± 0.10 | 1.22 ± 0.13 | 1.34 ± 0.17 | 1.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Rizzo, S.; Bueno, R.S.; La Mantia, T. A Review on the Trophic Shifts Among Habitat Types of the Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes Linnaeus) and Insights on Its Role as Bioindicator in Mediterranean Landscapes. Diversity 2026, 18, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/d18020062
Rizzo S, Bueno RS, La Mantia T. A Review on the Trophic Shifts Among Habitat Types of the Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes Linnaeus) and Insights on Its Role as Bioindicator in Mediterranean Landscapes. Diversity. 2026; 18(2):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/d18020062
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizzo, Salvatore, Rafael Silveira Bueno, and Tommaso La Mantia. 2026. "A Review on the Trophic Shifts Among Habitat Types of the Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes Linnaeus) and Insights on Its Role as Bioindicator in Mediterranean Landscapes" Diversity 18, no. 2: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/d18020062
APA StyleRizzo, S., Bueno, R. S., & La Mantia, T. (2026). A Review on the Trophic Shifts Among Habitat Types of the Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes Linnaeus) and Insights on Its Role as Bioindicator in Mediterranean Landscapes. Diversity, 18(2), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/d18020062






