Species Diversity of Calocybe (Agaricales, Lyophyllaceae) from Shanxi Province of Northern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Morphological Studies
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and DNA Sequencing
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
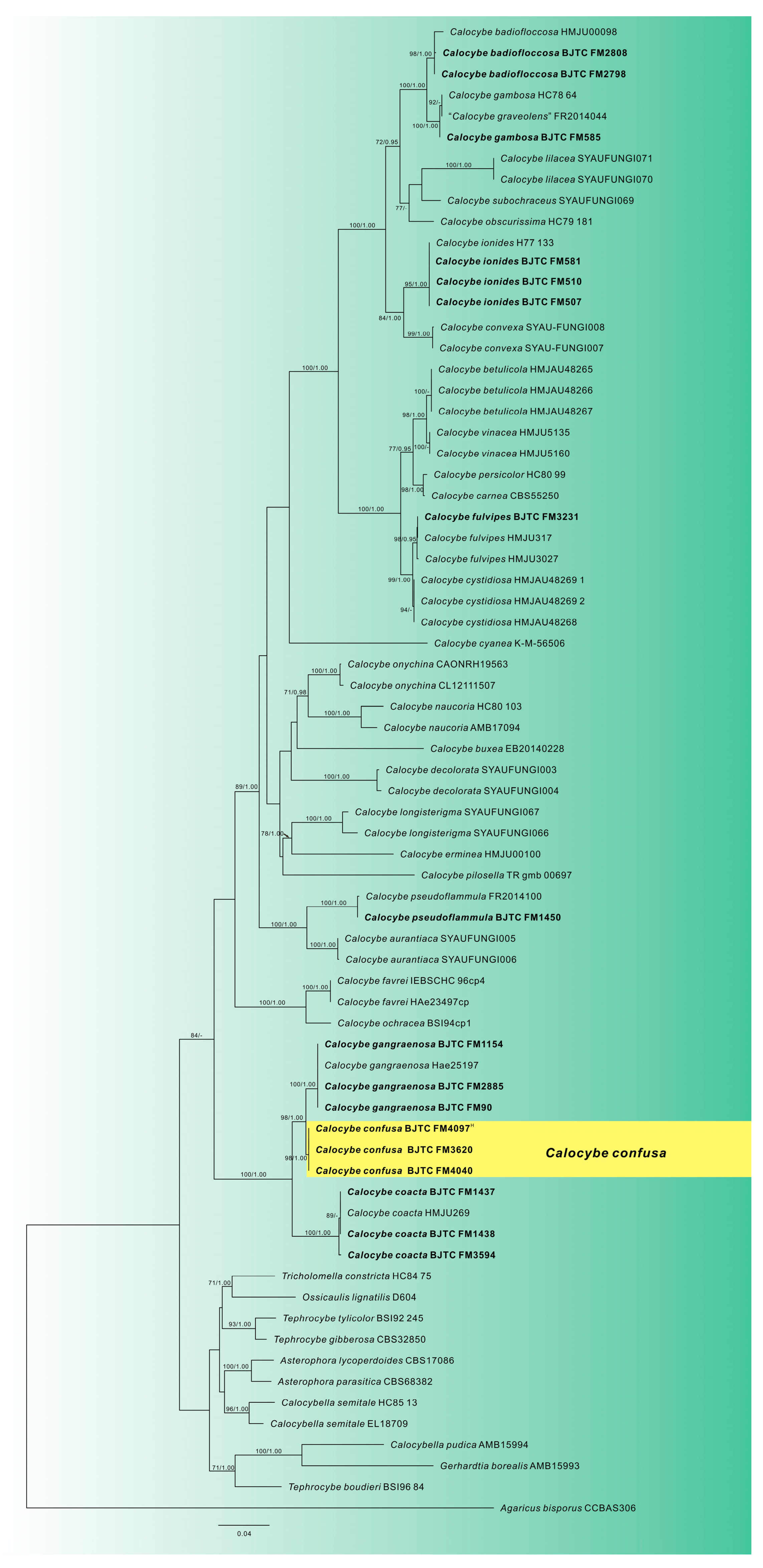
3.1. Phylogenetic Analysis
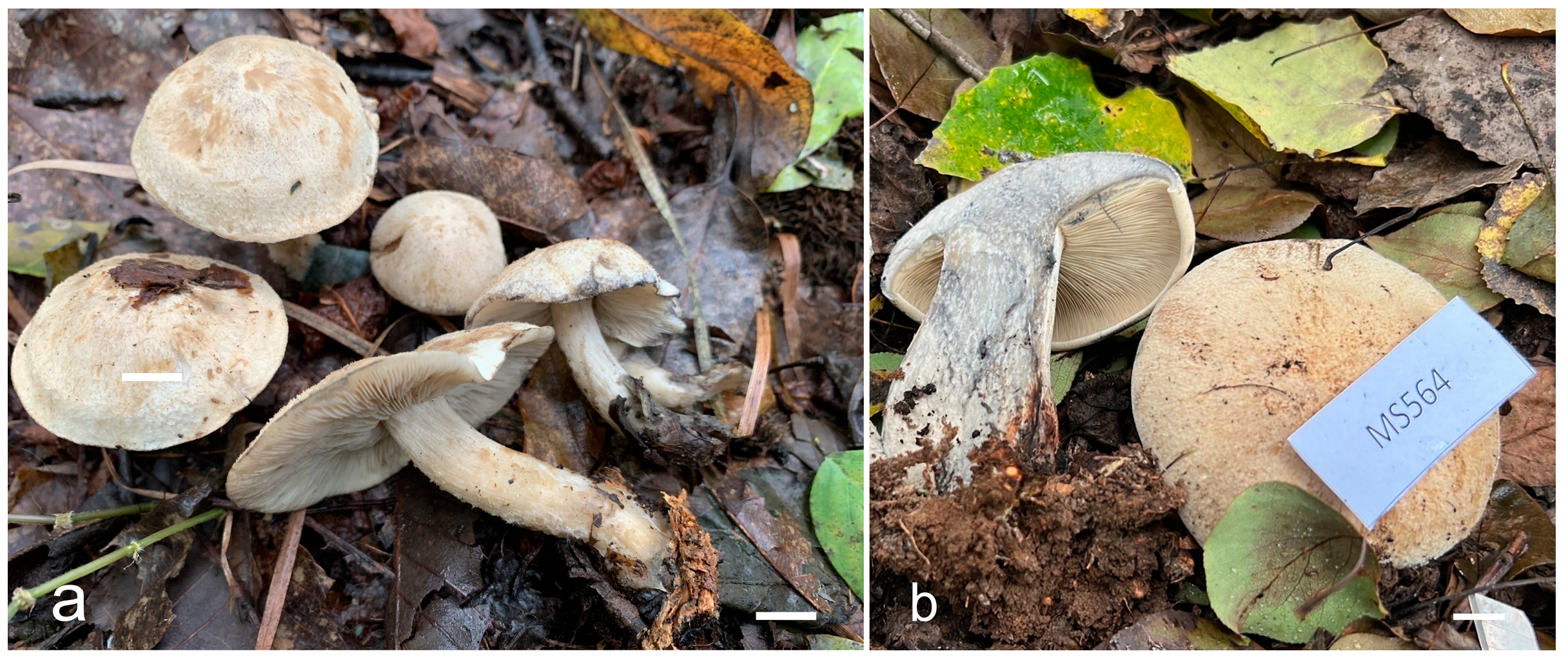
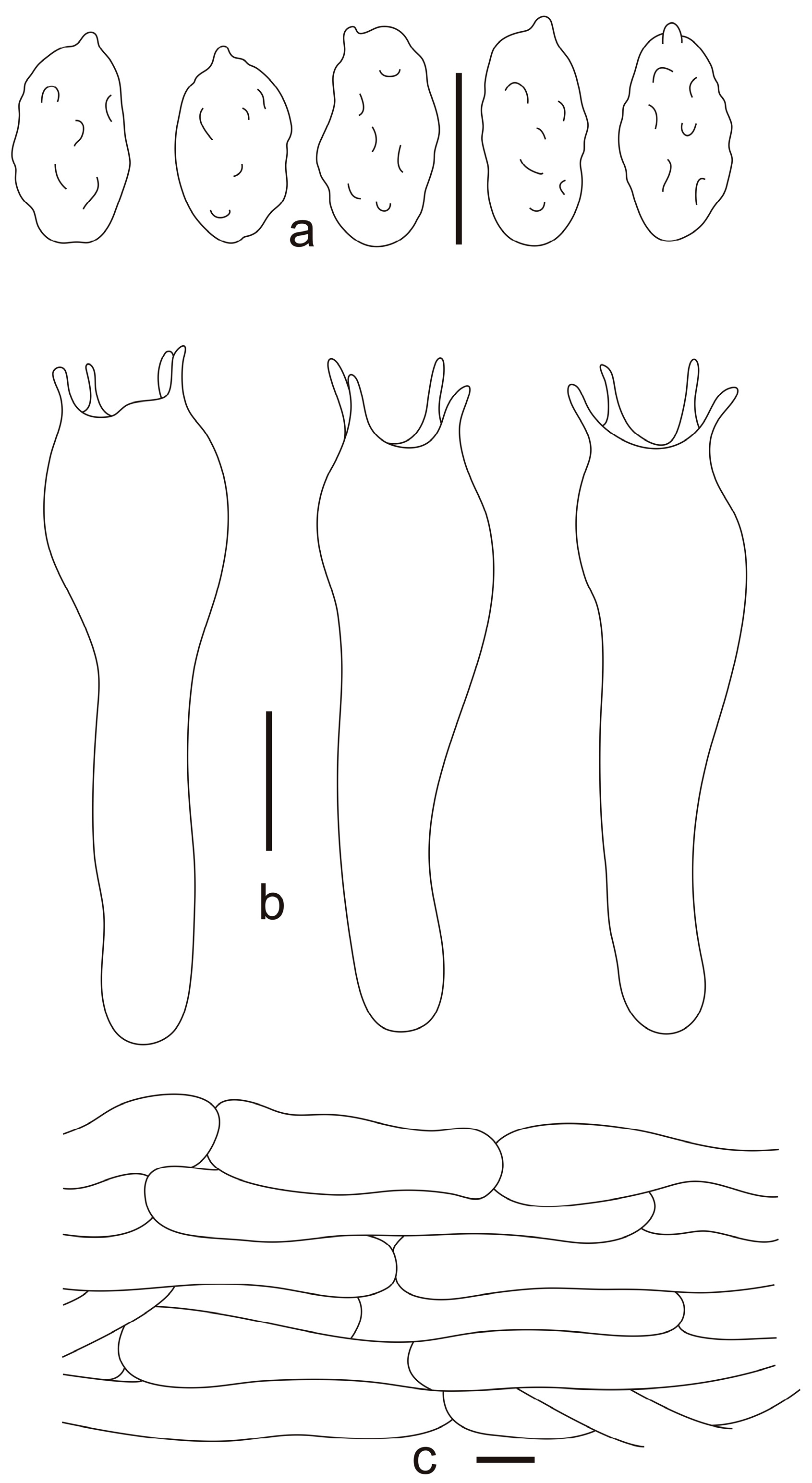
3.2. Taxonomy
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donk, M.A. The Generic Names Proposed for Agaricaceae; Beih. 5 Von Nova Hedwig; Verlag Von J. Cramer: Weinheim, Germany, 1962; ISBN 978-3-768-25405-2. [Google Scholar]
- Navathe, S.; Borkar, P.; Kadam, J. Cultivation of Calocybe indica (P & C) in Konkan Region of Maharashtra, India. World J. Agric. Res. 2014, 2, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Singer, R. The Agaricales in Modern Taxonomy; Koeltz Scientific Books: Schmitten, Germany, 1986; Volume 24. [Google Scholar]
- Kühner, R.; Romagnesi, H. Flore analytique des Champignons supérieurs (Agarics, Bolets, Chanterelles); Masson et Cie, éditeurs: Paris, France, 1953; p. 199. [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter, V.; Clémençon, H.; Vilgalys, R.; Moncalvo, J.M. Phylogenetic analyses of the Lyophylleae (Agaricales, Basidiomycota) based on nuclear and mitochondrial rDNA sequences. Mycol. Res. 2002, 106, 1043–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstetter, V.; Redhead, S.A.; Kauff, F.; Moncalvo, J.M.; Matheny, P.B.; Vilgalys, R. Taxonomic revision and examination of ecological transitions of the Lyophyllaceae (Basidiomycota, Agaricales) based on a multigene phylogeny. Cryptogam. Mycol. 2014, 35, 399–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncalvo, J.M.; Vilgalys, R.; Redhead, S.A.; Johnson, J.E.; James, T.Y.; Aime, M.C.; Hofstetter, V.; Verduin, S.; Larsen, E.; Baroni, T.J.; et al. One hundred and seventeen clades of euagarics. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2002, 23, 357–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheny, P.B.; Curtis, J.M.; Hofstetter, V.; Aime, M.C.; Moncalvo, J.-M.; Ge, Z.-W.; Yang, Z.-L.; Slot, J.C.; Ammirati, J.F.; Baroni, T.J.; et al. Major clades of Agaricales: A multi-locus phylogenetic overview. Mycologia 2006, 98, 982–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnica, S.; Weiss, M.; Walther, G.; Oberwinkler, F. Reconstructing the evolution of agarics from nuclear gene sequences and basidiospore ultrastructure. Mycol. Res. 2007, 111, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellanger, J.M.; Moreau, P.A.; Corriol, G.; Bidaud, A.; Chalange, R.; Dudova, Z.; Richard, F. Plunging hands into the mushroom jar: A phylogenetic framework for Lyophyllaceae (Agaricales, Basidiomycota). Genetica 2015, 143, 169–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.-Q.; Zhao, R.-L.; Hyde, K.D.; Begerow, D.; Kemler, M.; Yurkov, A.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Raspé, O.; Kakishima, M.; Sánchez-Ramírez, S.; et al. Notes, outline and divergence times of Basidiomycota. Fungal Divers. 2019, 99, 105–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dring, D.M. Techniques for microscopic preparation. In Methods in Microbiology; Booth, C., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1971; pp. 95–111. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, N.; Lv, J.-C.; Zhao, T.-Y.; Fan, L. Bonomyces pseudoarnoldii (Biannulariaceae, Agaricales), a new species from China revealed by morphology, and multilocus phylogenetic analysis. Phytotaxa 2022, 545, 069–078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes-Application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-J.; Wu, S.-Y.; Yu, X.-D.; Zhang, S.-B.; Cao, D.-X. Three new species of Calocybe (Agaricales, Basidiomycota) from northeastern China are supported by morphological and molecular data. Mycologia 2017, 109, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nylander, J. MrModeltest2.2. Computer software distributed by the University of Uppsala; Evolutionary Biology Centre: Uppsala, Sweden, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hillis, D.M.; Bull, J.J. An empirical test of bootstrapping as a method for assessing confidence in phylogenetic analysis. Syst. Biol. 1993, 42, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, M.E.; Zoller, S.; Lutzoni, F. Bayes or bootstrap? A simulation study comparing the performance of Bayesian Markov chain Monte Carlo sampling and bootstrapping in assessing phylogenetic confidence. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, R.D.M. TreeView; Glasgow University: Glasgow, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bon, M. Les Collybio-Marasmïoïdes et ressemblants. Flore Mycologique d’Europe 5; Documents Mycologiques, Mémoire Hors-Série n° 5; Verlag nicht ermittelbar: Amiens, France, 1999; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Consiglio, G.; Contu, M. Il genere Lyophyllum P. Karst. Emend. Kühner, in Italia. Riv. Micol. 2002, 45, 99–181. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.Z.; Yu, X.D.; Suwannarach, N.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, Y. Additions to Lyophyllaceae s.l. from China. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, A.; Hu, J.-J.; Chen, Y.-Q.; Wang, X.; Tuo, Y.-L.; Yue, L.; Li, X.-F.; Dai, D.; Wei, Y.-H.; Zhang, B.; et al. Multiple evidence reveals two new species and new distributions of Calocybe species (Lyophyllaceae) from northeastern China. MycoKeys 2024, 103, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Species | Collections | GenBank Accession Number | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | nrLSU | ||
| Agaricus bisporus | CCBAS306 | LN714517 | — |
| Asterophora lycoperdoides | CBS17086 | AF357037 | AF223190 |
| Asterophora parasitica | CBS68382 | AF357038 | AF223191 |
| Calocybe aurantiaca | SYAU-FUNGI-005 | KU528828 | KU528833 |
| Calocybe aurantiaca | SYAU-FUNGI-006 | NR_156304 | NG_058937 |
| Calocybe badiofloccosa | HMJU00098 | MN172332 | MN172334 |
| Calocybe badiofloccosa | BJTC FM2798 | PX220057 | — |
| Calocybe badiofloccosa | BJTC FM2808 | PX220058 | — |
| Calocybe betulicola | HMJAU48265 | OR771918 | OR771923 |
| Calocybe betulicola | HMJAU48266 | OR771919 | OR771924 |
| Calocybe betulicola | HMJAU48267 | OR771920 | OR771925 |
| Calocybe buxea | EB20140228 | KP885633 | KP885625 |
| Calocybe carnea | CBS55250 | AF357028 | AF223178 |
| Calocybe coacta | HMJU269 | OK649907 | OL687156 |
| Calocybe coacta | BJTC FM1437 | PX220060 | — |
| Calocybe coacta | BJTC FM1438 | PX220061 | — |
| Calocybe coacta | BJTC FM3594 | PX220062 | — |
| Calocybe confusa | BJTC FM3620 | PX220067 | PX220070 |
| Calocybe confusa | BJTC FM4040 | PX220068 | PX220071 |
| Calocybe confusa | BJTC FM4097 (Holotype) | PX220069 | PX220072 |
| Calocybe convexa | SYAU-FUNGI-007 | KU528826 | KU528830 |
| Calocybe convexa | SYAU-FUNGI-008 | NR_156303 | NG_058936 |
| Calocybe cyanea | K(M):56506 | OM905975 | — |
| Calocybe cystidiosa | HMJAU48268 | OR771915 | — |
| Calocybe cystidiosa | HMJAU48269(1) | OR771916 | — |
| Calocybe cystidiosa | HMJAU48269(2) | OR771917 | — |
| Calocybe decolorata | SYAU-FUNGI-003 | KU528824 | KU528834 |
| Calocybe decolorata | SYAU-FUNGI-004 | NR_156302 | NG_058938 |
| Calocybe erminea | HMJU00100 | MN172331 | MN172333 |
| Calocybe favrei | HAe23497cp | AF357034 | AF223183 |
| Calocybe favrei | IE-BSC-HC 96cp4 | EF421102 | AF223184 |
| Calocybe fulvipes | HMJU3027 | OK649910 | OK649880 |
| Calocybe fulvipes | HMJU317 | MT071590 | OK649878 |
| Calocybe fulvipes | BJTC FM3231 | PX220063 | — |
| Calocybe gambosa | HC78/64 | AF357027 | AF223177 |
| Calocybe gangraenosa | Hae25197 | AF357032 | AF223202 |
| Calocybe gangraenosa | BJTC FM0090 | PX220064 | — |
| Calocybe gangraenosa | BJTC FM2885 | PX220065 | — |
| Calocybe gangraenosa | BJTC FM1154 | PX220066 | — |
| Calocybe graveolens | FR2014044 | KP192590 | — |
| Calocybe graveolens | BJTC FM0585 | PX220059 | — |
| Calocybe ionides | BJTC FM0507 | — | PX220073 |
| Calocybe ionides | BJTC FM0510 | — | PX220074 |
| Calocybe ionides | BJTC FM0581 | — | PX220075 |
| Calocybe ionides | H77/133 | AF357029 | AF223179 |
| Calocybe lilacea | SYAU-FUNGI-070 | OM203538 | OM341407 |
| Calocybe lilacea | SYAU-FUNGI-071 | OM203539 | OM341409 |
| Calocybe longisterigma | SYAU-FUNGI-066 | OM203542 | OM341406 |
| Calocybe longisterigma | SYAU-FUNGI-067 | OM203543 | OM341408 |
| Calocybe naucoria | AMB17094 | KP885642 | KP885630 |
| Calocybe naucoria | HC80/103 | AF357030 | AF223180 |
| Calocybe obscurissima | HC79/181 | AF357031 | AF223181 |
| Calocybe ochracea | BSI94.cp1 | AF357033 | AF223185 |
| Calocybe onychina | CAON-RH19-563 | MW084664 | MW084704 |
| Calocybe onychina | CL121115-07 | KP885644 | KP885632 |
| Calocybe persicolor | HC80/99 | AF357026 | AF223176 |
| Calocybe pilosella | TR gmb 00697 | KJ883237 | — |
| Calocybe pseudoflammula | FR2014100 | KP192649 | — |
| Calocybe pseudoflammula | BJTC FM1450 | PX220056 | — |
| Calocybe subochraceus | SYAU-FUNGI-069 | OM203541 | — |
| Calocybe vinacea | HMJU5135 | OK649908 | OK649876 |
| Calocybe vinacea | HMJU5160 | OK649909 | OK649877 |
| Calocybella pudica | AMB15994 | KP858000 | KP858005 |
| Calocybella semitale | EL187-09 | HM572552 | — |
| Calocybella semitale | HC85/13 | AF357049 | AF042581 |
| Gerhardtia borealis | AMB15993 | KP858004 | KP858009 |
| Ossicaulis lignatilis | D604 | DQ825426 | AF261397 |
| Tephrocybe boudieri | BSI96/84 | AF357047 | DQ825430 |
| Tephrocybe gibberosa | CBS328.50 | AF357041 | AF223197 |
| Tephrocybe tylicolor | BSI92/245 | AF357040 | AF223195 |
| Tricholomella constricta | HC84/75 | DQ825429 | AF223188 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Huang, M.; Mao, N.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, L. Species Diversity of Calocybe (Agaricales, Lyophyllaceae) from Shanxi Province of Northern China. Diversity 2025, 17, 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17090619
Li T, Huang M, Mao N, Zhang Y, Fan L. Species Diversity of Calocybe (Agaricales, Lyophyllaceae) from Shanxi Province of Northern China. Diversity. 2025; 17(9):619. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17090619
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ting, Manrong Huang, Ning Mao, Yuxin Zhang, and Li Fan. 2025. "Species Diversity of Calocybe (Agaricales, Lyophyllaceae) from Shanxi Province of Northern China" Diversity 17, no. 9: 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17090619
APA StyleLi, T., Huang, M., Mao, N., Zhang, Y., & Fan, L. (2025). Species Diversity of Calocybe (Agaricales, Lyophyllaceae) from Shanxi Province of Northern China. Diversity, 17(9), 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17090619








