Recruitment and Controlled Growth of Juveniles of the Critically Endangered Fan Mussel Pinna nobilis in the Northern Adriatic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
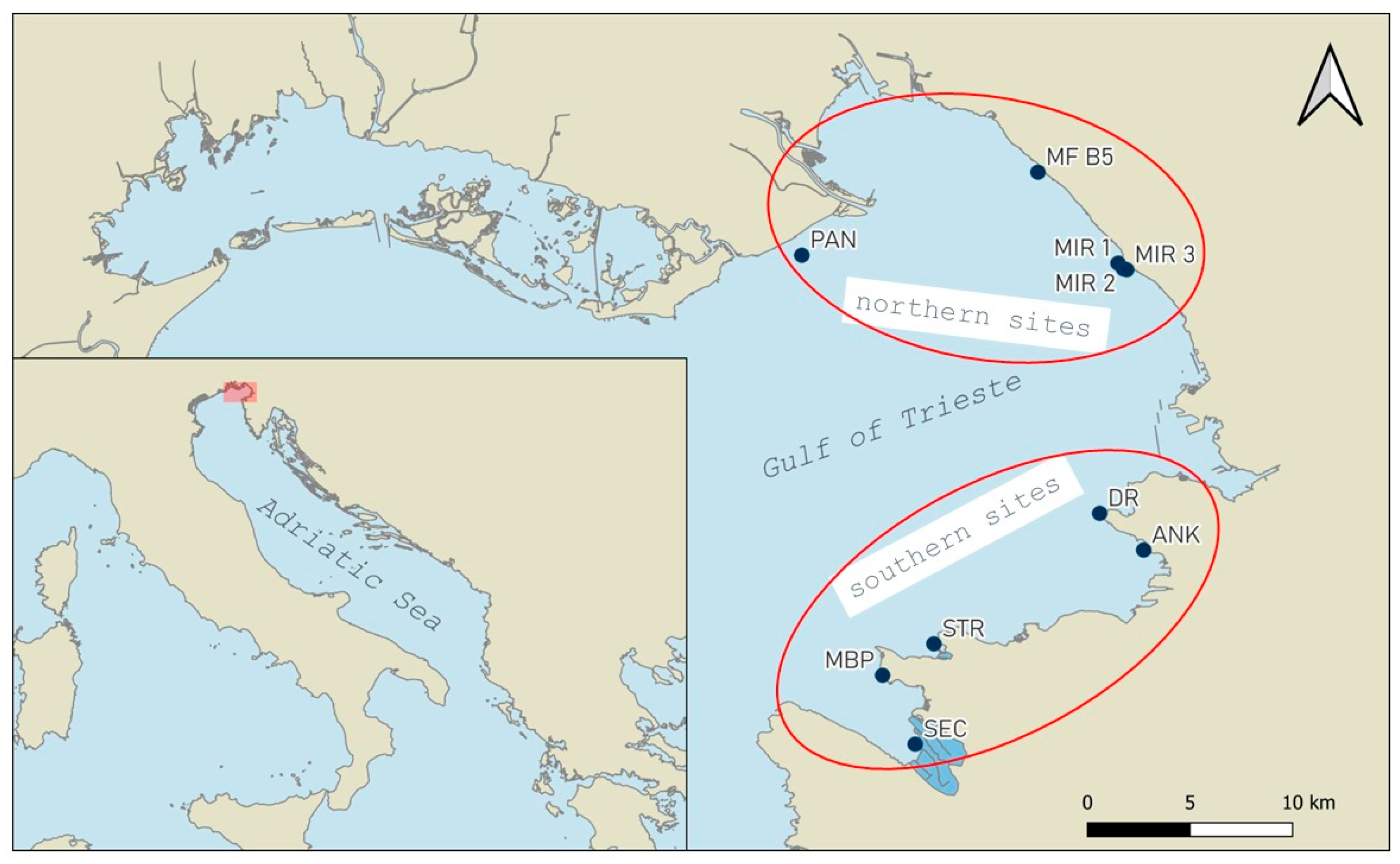
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Work
2.3. Ex Situ Controlled Maintenance
2.4. In Situ Controlled Maintenance
2.5. Taxonomic Identification of P. nobilis and Molecular Diagnostic Analyses of Pathogens of P. nobilis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
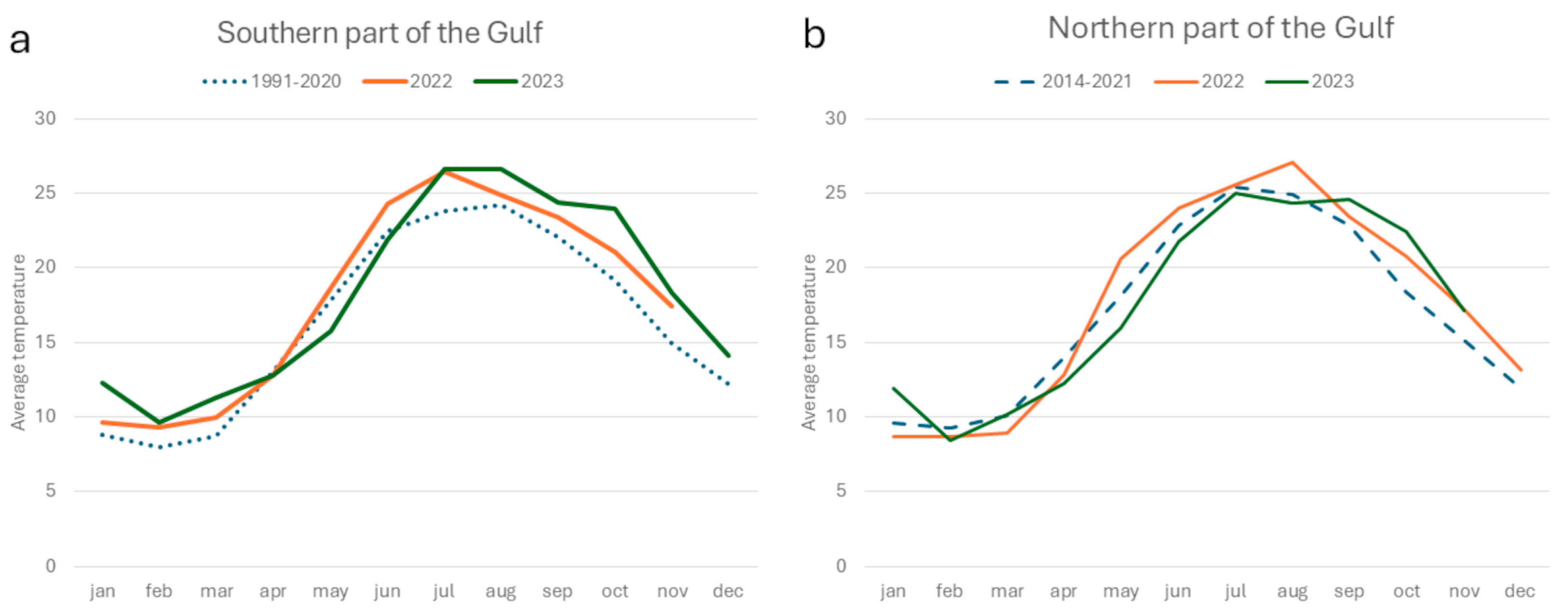
3.1. Sea Temperature
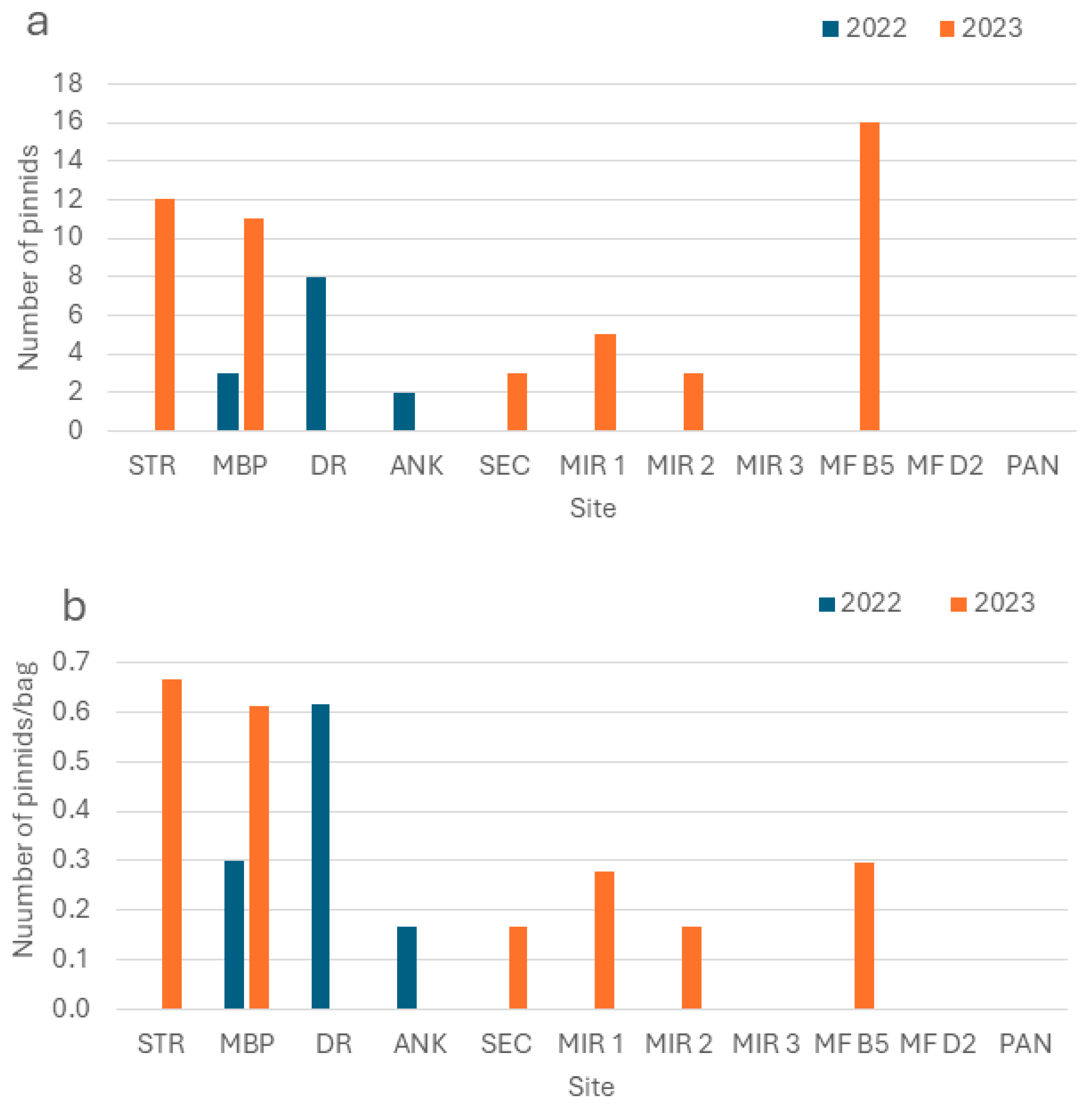
3.2. Pinna nobilis Recruitment
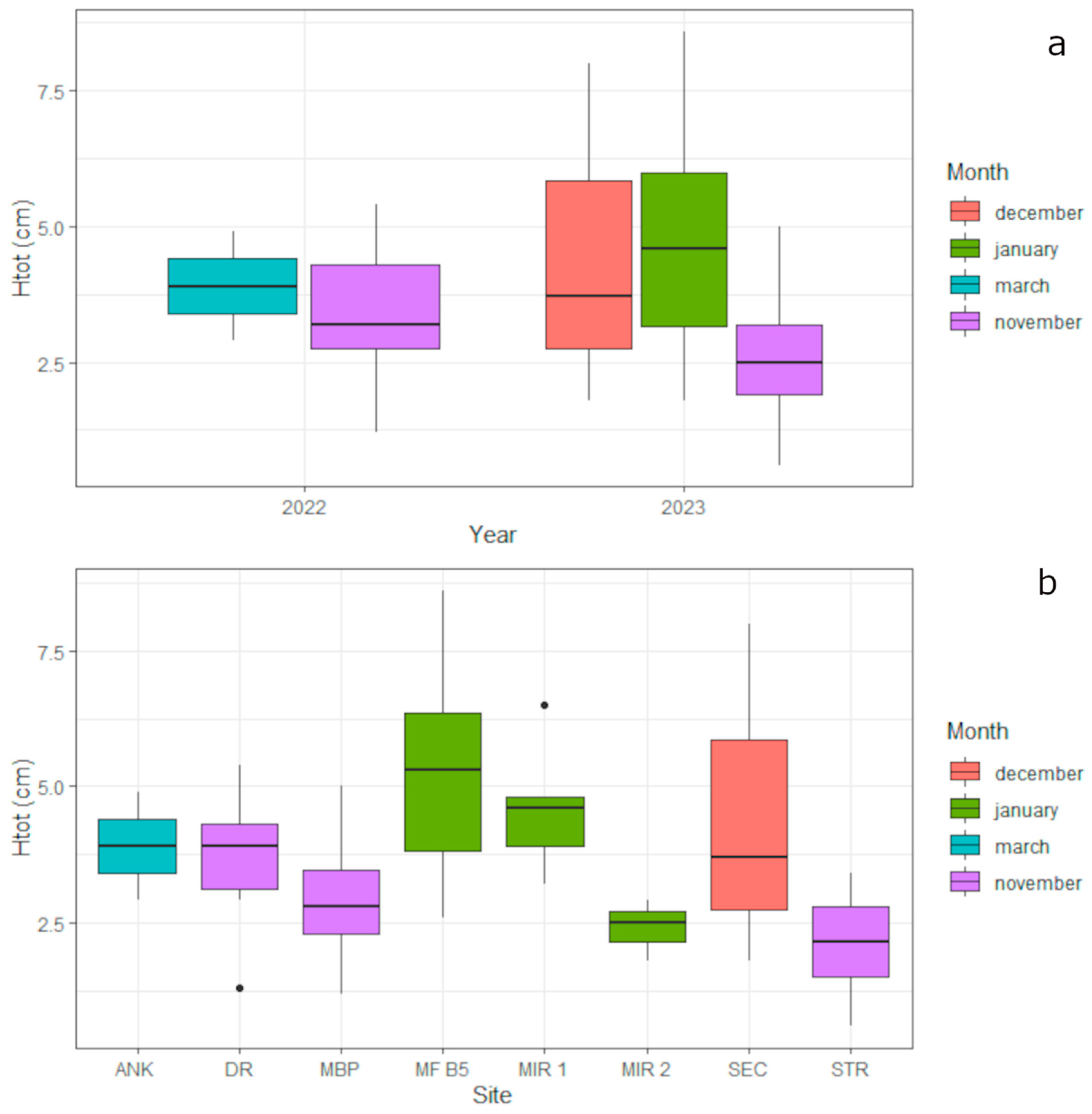
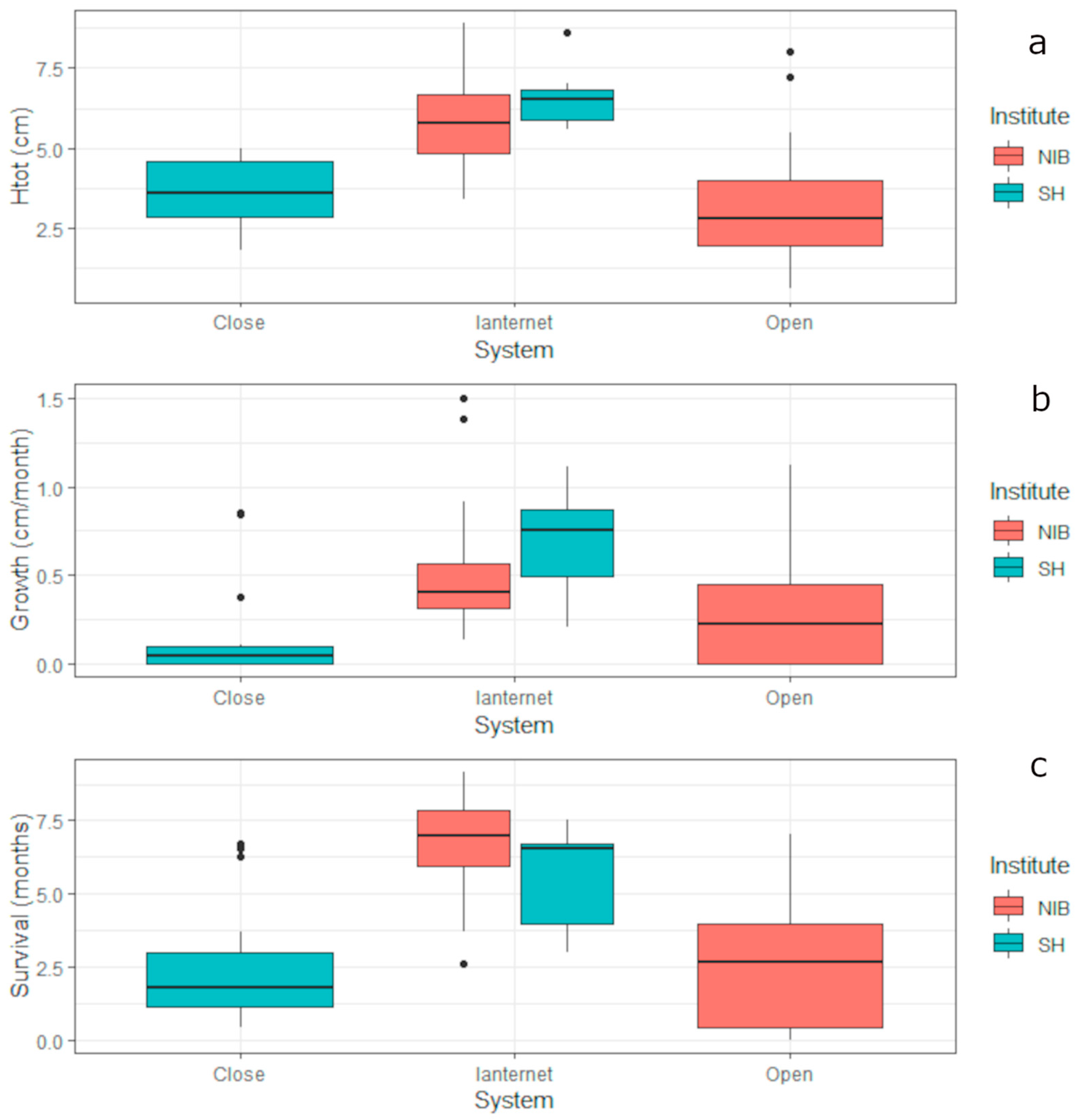
3.3. Pinna nobilis Controlled Growth
3.4. Taxonomic Identification of P. nobilis and Molecular Diagnostic Analyses of Pathogens
4. Discussion
4.1. Pinna nobilis Recruitment
4.2. Pinna nobilis Controlled Growth
4.3. Taxonomic Identification of P. nobilis and Molecular Diagnostic Analyses of Pathogens
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IUCN | International Union for Conservation of Nature |
| MMEs | Mass Mortality Events |
| MPA | Marine protected Area |
| PnPV | Pinna nobilis Picornavirus |
References
- Trigos, S.; García-March, J.; Vicente, N.; Tena, J.; Torres, J. Utilization of muddy detritus as organic matter source by the fan mussel Pinna nobilis. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2014, 15, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaoui, L.; Belgacem, W.; Ismail, D.B.; Mansour, L.; Tlig-Zouari, S. Engineering effect of Pinna nobilis shells on benthic communities. Oceanologia 2015, 57, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannucci, S.; Auriemma, R.; Davanzo, A.; Ciriaco, S.; Segarich, M.; Del Negro, P. Can the Empty Shells of Pinna nobilis Maintain the Ecological Role of the Species? A Structural and Functional Analysis of the Associated Mollusc Fauna. Diversity 2023, 15, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trkov, D.; Ivajnšič, D.; Kovačić, M.; Lipej, L. Factors influencing habitat selection of three cryptobenthic clingfish species in the shallow North Adriatic Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trkov, D.; Fortič, A.; Pitacco, V.; Lipej, L. Importance of dead fan mussel (Pinna nobilis) shells for fish community. In Proceedings of the 43rd CIESM Congress Proceedings, Palermo, Italy, 14–18 October 2024; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Trkov, D.; Mavrič, B.; Orlando-Bonaca, M.; Lipej, L. Marine cryptobenthic fish fauna of Slovenia (northern Adriatic Sea). Ann. Anal. Za Istrske Mediter. študije. Ser. Hist. Nat. 2019, 29, 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Addis, P.; Secci, M.; Brundu, G.; Manunza, A.; Corrias, S.; Cau, A. Density, size structure, shell orientation and epibiontic colonization of the fan mussel Pinna nobilis L. 1758 (Mollusca: Bivalvia) in three contrasting habitats in an estuarine area of Sardinia (W Mediterranean). Sci. Mar. 2009, 73, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipej, L.; Mavrič, B.; Orlando Bonaca, M. Opredelitev Stanja Populacij Leščurja in Morskega Datlja ter Habitatnih Tipov Morski Travniki in Podmorski Grebeni v Naravnem Rezervatu Strunjan in Priporočila za Usmerjanje Obiska Morskega dela Rezervata: Zaključno Poročilo o Projektu; Nacionalni Inštitut za Biologijo: Morska Biološka Postaja: Piran, Slovenia, 2012; 49p. [Google Scholar]
- Plećaš, D. Epibionti na Plemenitoj Periski (Pinna nobilis Linnaeus, 1758; Mollusca: Bivalvia). Master’s Thesis, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Giacobbe, S. Epibiontic mollusc communities on Pinna nobilis L.(Bivalvia, Mollusca). J. Nat. Hist. 2002, 36, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaoui, L.; Zouari, S.T.; Hassine, O.K.B. Two species of Crustacea (Decapoda) associated with the fan mussel, Pinna nobilis Linnaeus, 1758 (Mollusca, Bivalvia). Crustaceana 2008, 81, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acarli, S.; Vural, P.; Öktener, A. Association between the crab, Nepinnotheres pinnotheres (Linnaeus, 1758), and the endangered species fan mussel, Pinna nobilis (Linnaeus, 1758), from the Aegean Sea, Turkey. Alinteri J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 34, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorito, G.; Gherardi, F. Prey-handling behaviour of Octopus vulgaris (Mollusca, Cephalopoda) on bivalve preys. Behav. Processes 1999, 46, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çinar, M.E.; Bilecenoglu, M. The Predation of Pinna nobilis (Mollusca) Juveniles by the Spiny Sea Star Marthasterias glacialis (Echinodermata) in the Sea of Marmara. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Luis, M.; Álvarez, E.; Barrajón, A.; García-March, J.R.; Grau, A.; Hendriks, I.E.; Jiménez, S.; Kersting, D.; Moreno, D.; Pérez, M. SOS Pinna nobilis: A mass mortality event in western Mediterranean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, D.; Benabdi, M.; Čižmek, H.; Grau, A.; Jimenez, C.; Katsanevakis, S.; Öztürk, B.; Tuncer, S.; Tunesi, L.; Vázquez-Luis, M. Pinna nobilis. In The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 e.T160075998A160081499; 2019; p. 24. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/160075998/160081499 (accessed on 9 May 2025).
- IUCN. Pinna nobilis Mass Mortality Outbreak in the Mediterranean—Call to Action for Central and Western Mediterranean Countries. Available online: https://www.iucn.org/news/mediterranean/201805/pinna-nobilis-mass-mortality-outbreak-mediterranean-%E2%80%93-call-action-central-and-western-mediterranean-countries (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Katsanevakis, S.; Tsirintanis, K.; Tsaparis, D.; Doukas, D.; Sini, M.; Athanassopoulou, F.; Κolygas, M.N.; Tontis, D.; Koutsoubas, D.; Bakopoulos, V. The cryptogenic parasite Haplosporidium pinnae invades the Aegean Sea and causes the collapse of Pinna nobilis populations. Aquat. Invasions 2019, 14, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN. Mediterranean Noble Pen Shell Crisis (Pinna nobilis)—June 2019 Update. Available online: https://www.iucn.org/news/mediterranean/201907/mediterranean-noble-pen-shell-crisis-pinna-nobilis-june-2019-update. (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Čižmek, H.; Čolić, B.; Gračan, R.; Grau, A.; Catanese, G. An emergency situation for pen shells in the Mediterranean: The Adriatic Sea, one of the last Pinna nobilis shelters, is now affected by a mass mortality event. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2020, 173, 107388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, S. First haplosporidan parasite reported infecting a member of the Superfamily Pinnoidea (Pinna nobilis) during a mortality event in Alicante (Spain, Western Mediterranean). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 148, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanese, G.; Grau, A.; Valencia, J.M.; Garcia-March, J.R.; Vázquez-Luis, M.; Alvarez, E.; Deudero, S.; Darriba, S.; Carballal, M.J.; Villalba, A. Haplosporidium pinnae sp. nov., a haplosporidan parasite associated with mass mortalities of the fan mussel, Pinna nobilis, in the Western Mediterranean Sea. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 157, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panarese, R.; Tedesco, P.; Chimienti, G.; Latrofa, M.S.; Quaglio, F.; Passantino, G.; Buonavoglia, C.; Gustinelli, A.; Tursi, A.; Otranto, D. Haplosporidium pinnae associated with mass mortality in endangered Pinna nobilis (Linnaeus 1758) fan mussels. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2019, 164, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, F.; Sanna, D.; Azzena, I.; Mugetti, D.; Cerruti, F.; Hosseini, S.; Cossu, P.; Pinna, S.; Grech, D.; Cabana, D. Multiple non-species-specific pathogens possibly triggered the mass mortality in Pinna nobilis. Life 2020, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carella, F.; Antuofermo, E.; Farina, S.; Salati, F.; Mandas, D.; Prado, P.; Panarese, R.; Marino, F.; Fiocchi, E.; Pretto, T. Corrigendum: In the Wake of the Ongoing Mass Mortality Events: Co-occurrence of Mycobacterium, Haplosporidium and Other Pathogens in Pinna nobilis Collected in Italy and Spain (Mediterranean Sea). Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattos, A.; Bitchava, K.; Giantsis, I.A.; Theodorou, J.A.; Batargias, C.; Michaelidis, B. The implication of vibrio bacteria in the winter mortalities of the critically endangered Pinna nobilis. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattos, A.; Giantsis, I.A.; Karagiannis, D.; Theodorou, J.A.; Michaelidis, B. Gut symbiotic microbial communities in the IUCN critically endangered Pinna nobilis suffering from mass mortalities, revealed by 16S rRNA amplicon NGS. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, P.; Carrasco, N.; Catanese, G.; Grau, A.; Cabanes, P.; Carella, F.; García-March, J.R.; Tena, J.; Roque, A.; Bertomeu, E. Presence of Vibrio mediterranei associated to major mortality in stabled individuals of Pinna nobilis L. Aquaculture 2020, 519, 734899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carella, F.; Prado, P.; De Vico, G.; Palic, D.; Villari, G.; Garcia March, J.R.; Medialdea, J.T.; Cortés Melendreras, E.; Casalduero, F.G.; Sigovini, M.; et al. A widespread picornavirus affects the hemocytes of the noble pen shell (Pinna nobilis) leading to immunosuppression. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1273521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carella, F.; Prado, P.; García-March, J.R.; Tena-Medialdea, J.; Melendreras, E.C.; Porcellini, A.; Feola, A. Measuring immunocompetence in the natural population and captive individuals of noble pen shell Pinna nobilis affected by Pinna nobilis Picornavirus (PnPV). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2024, 151, 109664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempesta, M.; Del Piero, D.; Ciriaco, S. Definition of a new formula for the calculation of the total height of the fan shell Pinna nobilis in the Miramare Marine Protected Area (Trieste, Italy). Ann. Ser. Hist. Nat. 2013, 23, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lipej, L.; Mavrič, B.; Šiško, M.; Orlando Bonaca, M. Pregled Morske Biodiverzitete v Občini Ankaran; National Institute of Biology, Marine Biology Station Piran: Piran, Slovenia, 2016; p. 146. [Google Scholar]
- Manfrin, C.; Ciriaco, S.; Segarich, M.; Aiello, A.; Florian, F.; Avian, M.; Terlizzi, A.; Giulianini, P.G.; Spoto, M.; Pallavicini, A. Haplosporidium pinnae Detection from the Faeces of Pinna nobilis: A Quick and Noninvasive Tool to Monitor the Presence of Pathogen in Early-Stage or during Fan Mussel Mass Mortalities. Diversity 2023, 15, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boicourt, W.C.; Kuzmić, M.; Hopkins, T.S. The inland sea: Circulation of Chesapeake Bay and the Northern Adriatic. In Ecosystems at the Land-Sea Margin: Drainage Basin to Coastal Sea, 1st ed.; Malone, T.C., Malej, A., Harding, L.W.J., Smodlaka, N., Turner, R.E., Eds.; Coastal and Estuarine Studies, American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; Volume 55, pp. 81–129. [Google Scholar]
- Mozetič, P.; Umani, S.F.; Cataletto, B.; Malej, A. Seasonal and inter-annual plankton variability in the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1998, 55, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stravisi, F. The vertical structure annual cycle of the mass field parameters in the Gulf of Trieste. Boll Oceanol. Teor. Appl. 1983, 1, 239–250. [Google Scholar]
- ARPAFVG. Stato Oceanografico ed Ecologico del Golfo di Trieste. 2022–2023. Available online: https://arpa.fvg.it/temi/temi/acqua/sezioni-principali/acque-marino-costiere-e-di-transizione/bollettino-oceanografico/ (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- ARSO. Mesečni Bilten ARSO (Slovenian Environment Agency). 2022–2023. Available online: http://www.arso.gov.si/o%20agenciji/knji%C5%BEnica/mese%C4%8Dni%20bilten/bilten2023.htm (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Kersting, D.K.; Hendriks, I.E. Short Guidance for the Construction, Installation and Removal of Pinna nobilis Larval Collectors. IUCN 2019, 6p. Available online: https://iucn.org/sites/default/files/content/documents/2019/larval_colectors_p._nobilis_guidance_-_pinna_nobilis.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Trigos, S.; García-March, J.R.; Vicente, N.; Tena, J.; Torres, J. Respiration rates of the fan mussel Pinna nobilis at different temperatures. J. Molluscan Stud. 2015, 81, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, P.; Cabanes, P.; Catanese, G.; Carella, F.; Carrasco, N.; Grau, A.; Hernandis, S.; García-March, J.R.; Tena, J.; Caiola, N. Growth of juvenile Pinna nobilis in captivity conditions: Dietary and pathological constraints. Aquaculture 2020, 522, 735167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandis, S.; Ibarrola, I.; Tena-Medialdea, J.; Vázquez-Luis, M.; García-March, J.; Prado, P.; Albentosa, M. Scope for growth and dietary needs of Mediteranean Pinnids maintained in captivity. BMC Zool. 2022, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, D.; Cossu, P.; Dedola, G.L.; Scarpa, F.; Maltagliati, F.; Castelli, A.; Franzoi, P.; Lai, T.; Cristo, B.; Curini-Galletti, M.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA Reveals Genetic Structuring of Pinna nobilis across the Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carella, F.; Aceto, S.; Pollaro, F.; Miccio, A.; Iaria, C.; Carrasco, N.; Prado, P.; De Vico, G. A mycobacterial disease is associated with the silent mass mortality of the pen shell Pinna nobilis along the Tyrrhenian coastline of Italy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, S.C.; Fidler, A.; Renault, T. Primers for PCR-based detection of ostreid herpes virus-1 (OsHV-1): Application in a survey of New Zealand molluscs. Aquaculture 2007, 272, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Nanami, A.; Bayne, C.J.; Makino, M.; Hori, M. Changes in the potential stocks of coral reef ecosystem services following coral bleaching in Sekisei Lagoon, southern Japan: Implications for the future under global warming. Sustain. Sci. 2020, 15, 863–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, S.K.; Phelps, N.B.; Barbknecht, M.; Hoffman, M.A.; Goyal, S.M. A multiplex RT-PCR assay for the detection of fish picornaviruses. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 221, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füstös, Z.; Belák, Á.; Maráz, A. Colonization ability of Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes in the endosphere of sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum var. grossum). Acta Aliment. 2017, 46, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramilo, A.; Navas, J.I.; Villalba, A.; Abollo, E. Species-specific diagnostic assays for Bonamia ostreae and B. exitiosa in European flat oyster Ostrea edulis: Conventional, real-time and multiplex PCR. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2013, 104, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protasov, E.S.; Axenov-Gribanov, D.V.; Rebets, Y.V.; Voytsekhovskaya, I.V.; Tokovenko, B.T.; Shatilina, Z.M.; Luzhetskyy, A.N.; Timofeyev, M.A. The diversity and antibiotic properties of actinobacteria associated with endemic deepwater amphipods of Lake Baikal. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 1593–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaulot, D.; Geisen, S.; Mahé, F.; Bass, D. pr2-primers: An 18S rRNA primer database for protists. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearham, D.; Spiers, Z.; Raidal, S.; Jones, J.B.; Nicholls, P.K. Detection of Minchinia sp., in rock oysters Saccostrea cuccullata (Born, 1778) using DNA probes. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2008, 97, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spearman, C. Demonstration of formulae for true measurement of correlation. Am. J. Psychol. 1907, 18, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RDevelopmentCoreTeam. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Bakran-Petricioli, T.; Kujundžić, D.; Naranđa, M.; Petricioli, D.; Petricioli, L.; Kipson, S. Fouling Community on Pinna nobilis Larval Collectors in the Adriatic—Impact of Invasive Species. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, D.K.; Vázquez-Luis, M.; Mourre, B.; Belkhamssa, F.Z.; Álvarez, E.; Bakran-Petricioli, T.; Barberá, C.; Barrajón, A.; Cortés, E.; Deudero, S.; et al. Recruitment disruption and the role of unaffected populations for potential recovery after the Pinna nobilis mass mortality event. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 594378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, D.K.; García-March, J.R. Long-term assessment of recruitment, early stages and population dynamics of the endangered Mediterranean fan mussel Pinna nobilis in the Columbretes Islands (NW Mediterranean). Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 130, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigos, S.; Vicente, N.; Prado, P.; Espinós, F.J. Adult spawning and early larval development of the endangered bivalve Pinna nobilis. Aquaculture 2018, 483, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferranti, M.P. (Department of Earth, Environment and Llife Science—DISTAV, University of Genova, Corso Europa 26, Genova, Italy). Personal communication, 2025.
- Ferranti, M.P.; Azzena, I.; Batistini, E.; Caracciolo, D.; Casu, M.; Chiantore, M.; Ciriaco, S.; Firpo, V.; Intini, L.; Locci, C. Handling of the Bivalve Pinna nobilis, Endangered and Pathogen-Affected Species, for Controlled Reproduction: Precautions Taken. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e70565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesselmann, M.; González-Wangüemert, M.; Serrão, E.A.; Engelen, A.H.; Renault, L.; García-March, J.R.; Duarte, C.M.; Hendriks, I.E. Genetic and oceanographic tools reveal high population connectivity and diversity in the endangered pen shell Pinna nobilis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortič, A. (Marine Biology Station Piran, National Institute of Biology, Fornače 41, SI-6330 Piran, Slovenia); Trkov, D. (Marine Biology Station Piran, National Institute of Biology, Fornače 41, SI-6330 Piran, Slovenia); Lipej, L. (Marine Biology Station Piran, National Institute of Biology, Fornače 41, SI-6330 Piran, Slovenia); Mavrič, B. (Marine Biology Station Piran, National Institute of Biology, Fornače 41, SI-6330 Piran, Slovenia). Unpublished data. 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Ciriaco, S. (SHORELINE Soc. Coop, E3, Località Padriciano, 99, 34149 Area di Ricerca, Trieste, Italy); Segarich, M. (SHORELINE Soc. Coop, E3, Località Padriciano, 99, 34149 Area di Ricerca, Trieste, Italy); Batistini, E. (SHORELINE Soc. Coop, E3, Località Padriciano, 99, 34149 Area di Ricerca, Trieste, Italy). Unpublished data. 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Sigovini, M.; Sabino, A.; Manea, E.; Carella, F.; Bergamasco, A. The last stronghold in the Adriatic: Distribution and status of Pinna nobilis in the Venice lagoon. In Proceedings of the 43rd CIESM Congress Proceedings, Palermo, Italy, 14–18 October 2024; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Kožul, V.; Glavić, N.; Bolotin, J.; Antolović, N. The experimental rearing of fan mussel Pinna nobilis (Linnaeus, 1758). In Proceedings of the 46th Croatian and 6th International Symposium on Agriculture, Opatija, Croatia, 14–18 February 2011; p. 806. [Google Scholar]
- Acarli, S.; Lok, A.; Yigitkurt, S.; Palaz, M. Culture of fan mussel (Pinna nobilis, Linnaeus 1758) in relation to size on suspended culture system in Izmir Bay, Aegean Sea, Turkey. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fakültesi Derg. 2011, 17, 995–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Kožul, V.; Glavić, N.; Bolotin, J.; Antolović, N. Growth of the fan mussel Pinna nobilis (L innaeus, 1758)(Mollusca: Bivalvia) in experimental cages in the South Adriatic Sea. Aquacult. Res. 2012, 44, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitacco, V.; Fortič, A.; Trkov, D.; Mavrič, B.; Mlinar, C.; Lipej, L. Growth rates of the critically endangered fan mussel Pinna nobilis in the Slovenian Sea (Northern Adriatic). Endanger Spec. Res. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S. Growth and mortality rates of the fan mussel Pinna nobilis in Lake Vouliagmeni (Korinthiakos Gulf, Greece): A generalized additive modelling approach. Mar. Biol. 2007, 152, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-March, J.R.; García-Carrascosa, A.; Peña Cantero, A.; Wang, Y.-G. Population structure, mortality and growth of Pinna nobilis Linnaeus, 1758 (Mollusca, Bivalvia) at different depths in Moraira bay (Alicante, Western Mediterranean). Mar. Biol. 2007, 150, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvozdenović, S.; Mačić, V.; Pešić, V.; Nikolić, M.; Peraš, I.; Mandić, M. Review on Pinna rudis (Linnaeus, 1758)(Bivalvia: Pinnidae) presence in the Mediterranean. Poljopr. Sumar. 2019, 65, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petović, S. Additions to the checklist of the malacofauna of the Boka Kotorska Bay (south-east Adriatic Sea). Stud. Mar. 2018, 31, 23–36. [Google Scholar]
- Kersting, D.K.; Ballesteros, E. Is the local extinction of Pinna nobilis facilitating Pinna rudis recruitment? Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2021, 2, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprandi, A.; Aicardi, S.; Azzola, A.; Benelli, F.; Bertolino, M.; Bianchi, C.N.; Chiantore, M.; Ferranti, M.P.; Mancini, I.; Molinari, A. A tale of two sisters: The southerner Pinna rudis is getting north after the regional extinction of the congeneric P. nobilis (Mollusca: Bivalvia). Diversity 2024, 16, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotou, M.; Papadakis, O.; Catanese, G.; Stranga, Y.; Ragkousis, M.; Kampouris, T.; Aga-Spyridopoulou, R.N.; Papadimitriou, E.; Koutsoubas, D.; Katsanevakis, S. New kid in town: Pinna rudis spreads in the eastern Mediterranean. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2023, 24, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denti, G.; Fanelli, G.; Tiscar, P.G.; Paoletti, B.; Hattab, J.; Mastrototaro, F.; Carella, F.; Villari, G.; Montesanto, F.; Chimienti, G.; et al. Mass mortality of Pinna nobilis Linnaeus, 1758 (MOLLUSCA, BIVALVIA) in the Taranto and Tremiti Islands populations: Citizen Science to help scientists. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2023, 27, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
| Code | Site | Date | Htot | Species | Haplo | Sample Type | Genetic Analyses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L9 | DR | 23 November 2022 | 1.3 | Pinna nobilis ** | negative | tissue (dead specimen) | UNISS |
| L12 | ANK | 23 March 2023 | 4.9 | Pinna nobilis ** | negative | tissue (dead specimen) | UNISS |
| L13 | ANK | 23 March 2023 | 2.9 | Pinna nobilis ** | negative | tissue (dead specimen) | UNISS |
| L15 | MBP | 20 November 2023 | 2.3 | Pinna nobilis ** | negative | tissue (dead specimen) | UNISS |
| L17 | MBP | 20 November 2023 | 3.6 | Pinna nobilis ** | positive | tissue (dead specimen) | UNISS |
| L19 | MBP | 20 November 2023 | 2.6 | Pinna nobilis ** | positive | tissue (dead specimen) | UNISS |
| L32 | STR | 21 November 2023 | 0.9 | ND | negative | tissue (dead specimen) | UNISS |
| SH2 | MF B5 | 30 January 2024 | 5.9 | Pinna nobilis * | negative | feaces | UNITS |
| SH3 | MF B5 | 30 January 2024 | 6.8 | Pinna nobilis * | positive | feaces | UNITS |
| SH4 | MF B5 | 30 January 2024 | 4.6 | Pinna nobilis * | negative | feaces | UNITS |
| SH5 | MF B5 | 30 January 2024 | 6.5 | Pinna nobilis * | negative | feaces | UNITS |
| SH6 | MF B5 | 30 January 2024 | 6.3 | Pinna nobilis * | positive | mantle | UNITS |
| SH8 | MF B5 | 30 January 2024 | 5.6 | Pinna nobilis * | negative | feaces | UNITS |
| SH9 | MF B5 | 30 January 2024 | 7 | Pinna nobilis * | negative | feaces | UNITS |
| SH10 | MF B5 | 30 January 2024 | 3.6 | Pinna nobilis * | positive | gill | UNITS |
| SH16 | MIR 1 | 30 January 2024 | 4.8 | Pinna nobilis * | negative | feaces | UNITS |
| SH22 | MF B5 | 30 January 2024 | 5.9 | Pinna nobilis * | positive | mantle | UNITS |
| SH23 | MF B5 | 30 January 2024 | 8.6 | Pinna nobilis * | negative | feaces | UNITS |
| SH24 | MF B5 | 30 January 2024 | 3.9 | Pinna nobilis * | negative | feaces | UNITS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pitacco, V.; Trkov, D.; Caracciolo, D.; Ciriaco, S.; Segarich, M.; Batistini, E.; Orlando-Bonaca, M.; Lipej, L.; Mavrič, B.; Rogelja, M.; et al. Recruitment and Controlled Growth of Juveniles of the Critically Endangered Fan Mussel Pinna nobilis in the Northern Adriatic. Diversity 2025, 17, 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17100666
Pitacco V, Trkov D, Caracciolo D, Ciriaco S, Segarich M, Batistini E, Orlando-Bonaca M, Lipej L, Mavrič B, Rogelja M, et al. Recruitment and Controlled Growth of Juveniles of the Critically Endangered Fan Mussel Pinna nobilis in the Northern Adriatic. Diversity. 2025; 17(10):666. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17100666
Chicago/Turabian StylePitacco, Valentina, Domen Trkov, Daniela Caracciolo, Saul Ciriaco, Marco Segarich, Edoardo Batistini, Martina Orlando-Bonaca, Lovrenc Lipej, Borut Mavrič, Manja Rogelja, and et al. 2025. "Recruitment and Controlled Growth of Juveniles of the Critically Endangered Fan Mussel Pinna nobilis in the Northern Adriatic" Diversity 17, no. 10: 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17100666
APA StylePitacco, V., Trkov, D., Caracciolo, D., Ciriaco, S., Segarich, M., Batistini, E., Orlando-Bonaca, M., Lipej, L., Mavrič, B., Rogelja, M., Azzena, I., Locci, C., Scarpa, F., Sanna, D., Casu, M., Manfrin, C., Pallavicini, A., & Fortič, A. (2025). Recruitment and Controlled Growth of Juveniles of the Critically Endangered Fan Mussel Pinna nobilis in the Northern Adriatic. Diversity, 17(10), 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17100666














