Response Analysis of Microbial Community Structures and Functions Under Water and Sediment Changes in the Middle and Lower Yellow River
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
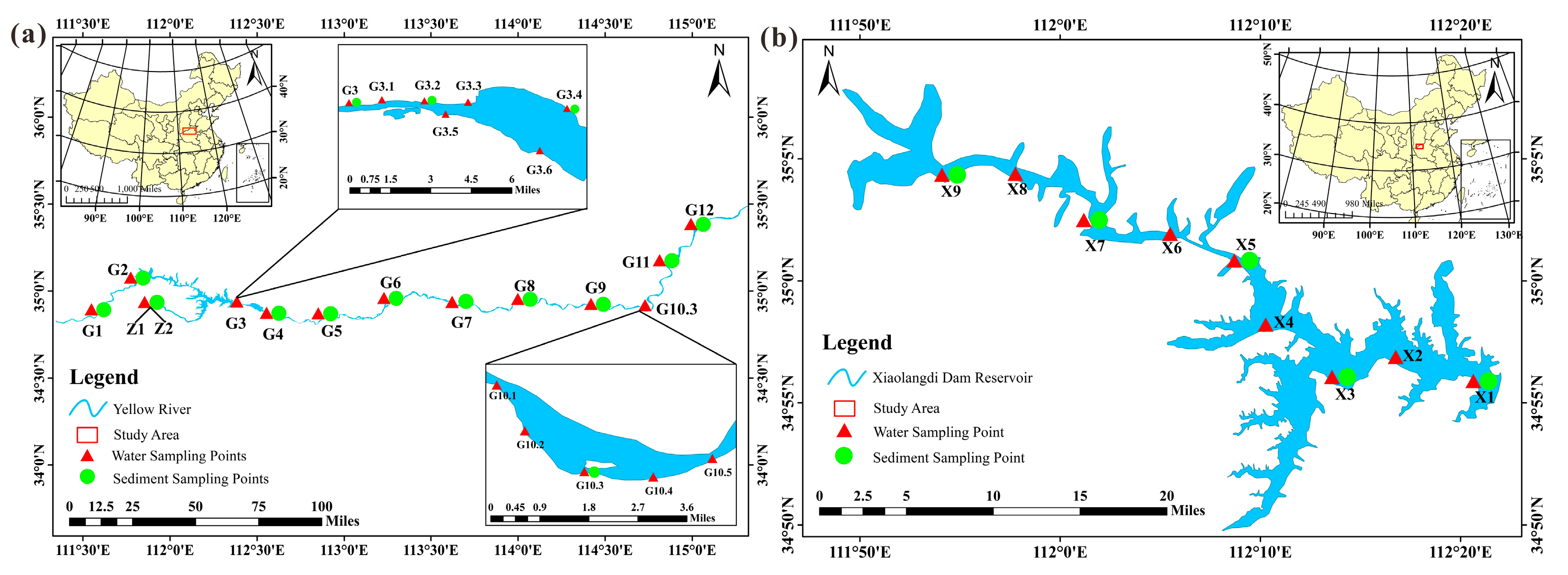
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Water Quality Physicochemical Research Methods
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR, and Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differential Changes in Physicochemical Characteristics of Environmental Factors in the Pre- and Post-WSR Periods
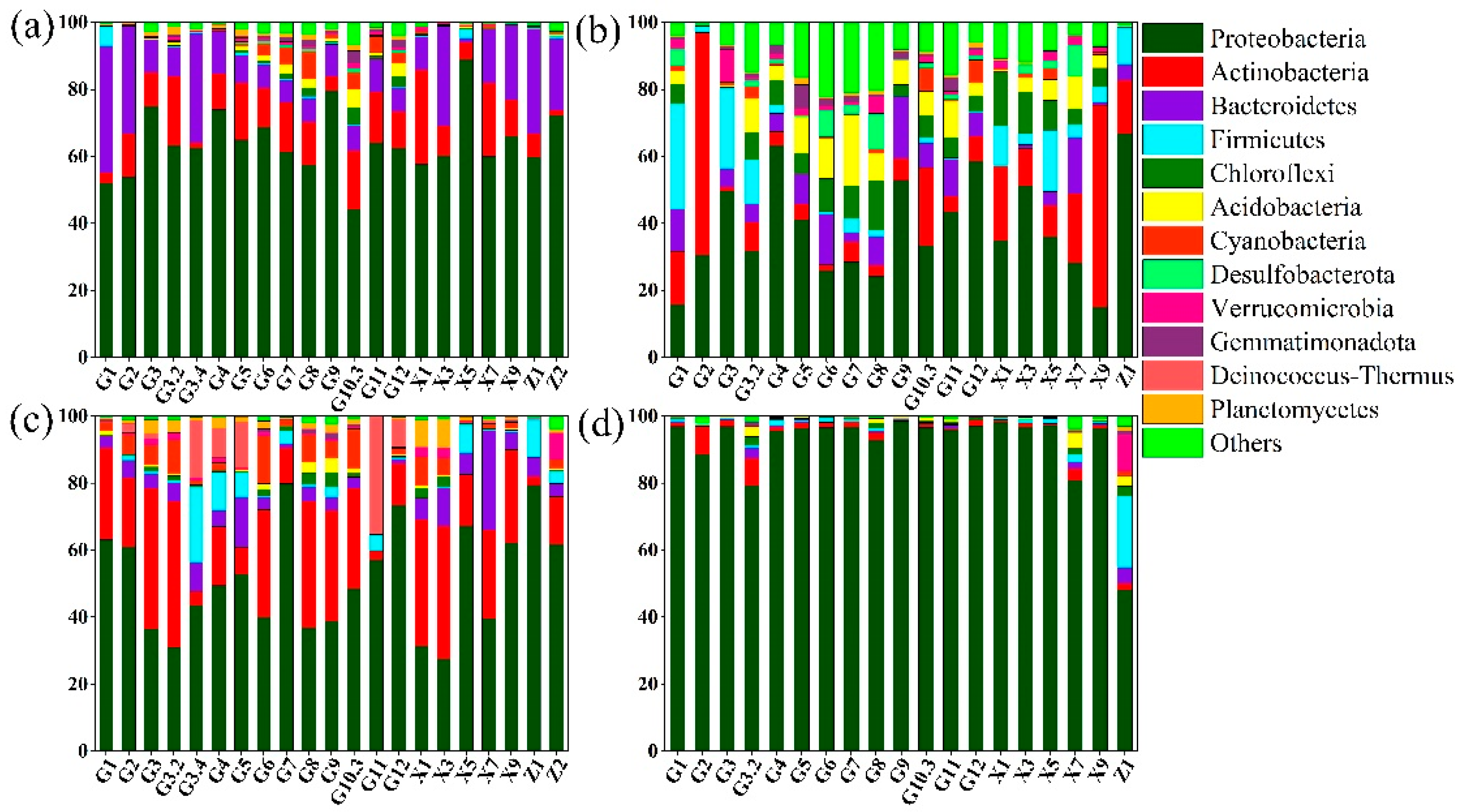
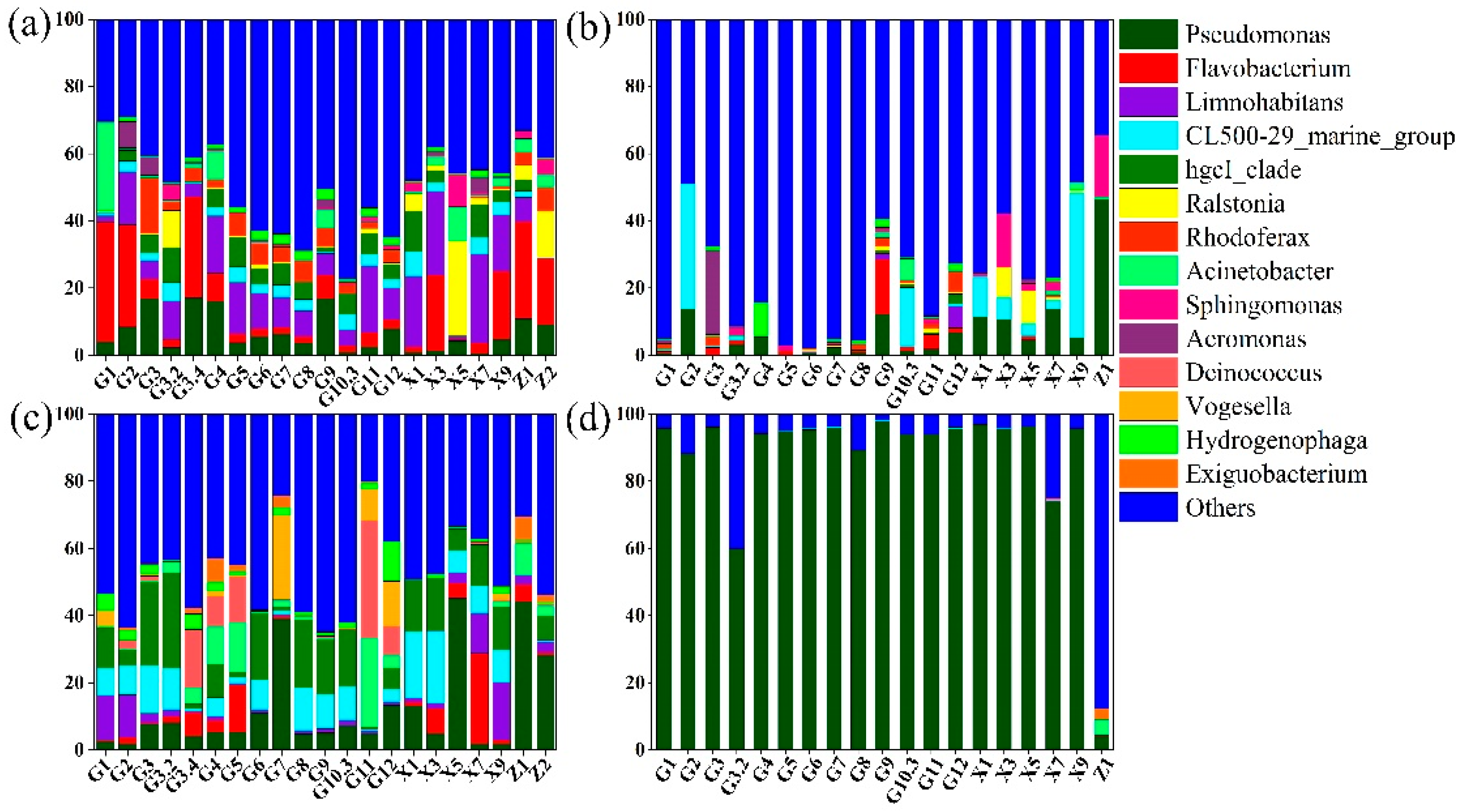
3.2. Microbial Community Structure Pre- and Post-WSR
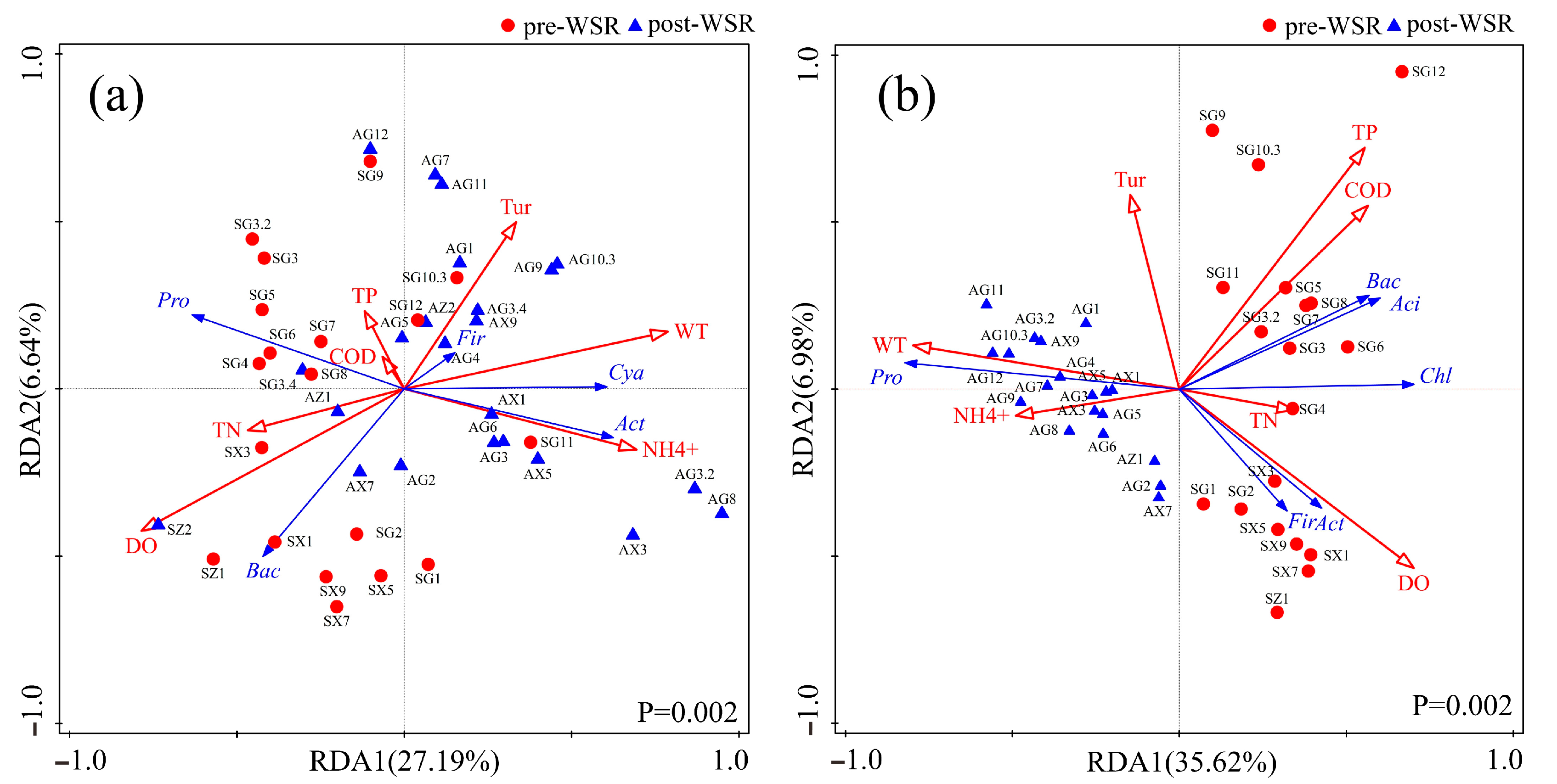
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Water Environmental Factors and Microbial Community Composition in Pre- and Post-WSR Waters
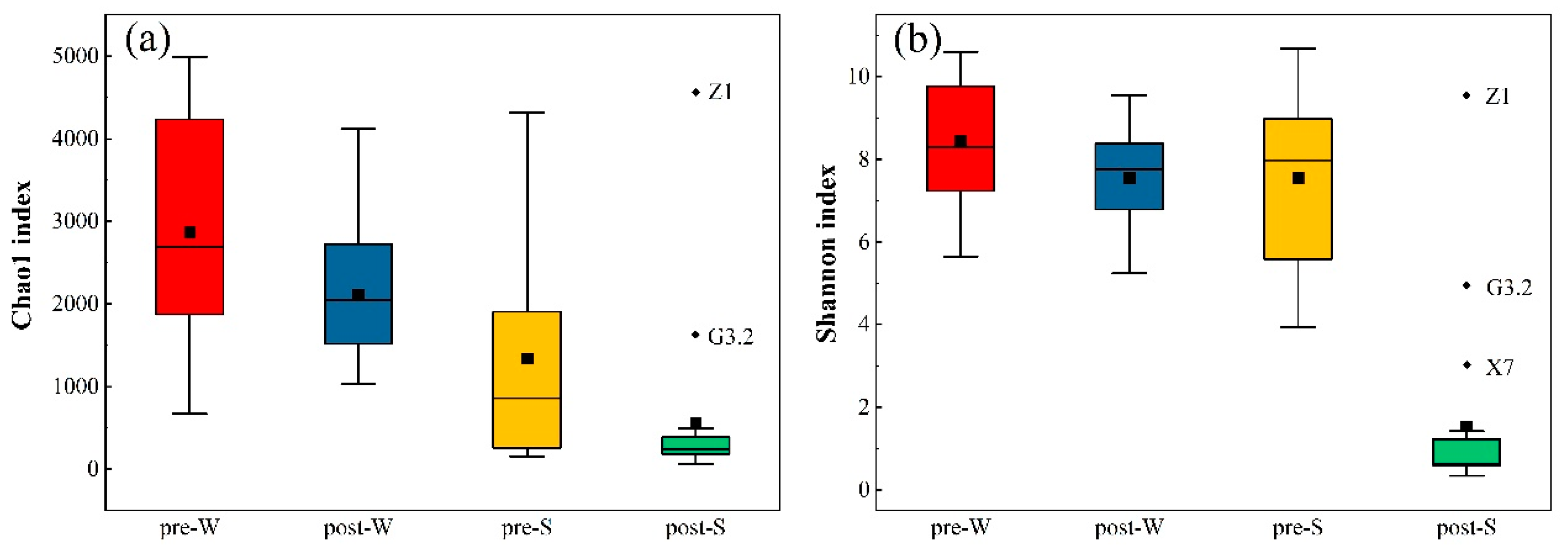
3.4. Microbial Community Diversity Analysis in Surface Water and Sediment in the Pre- and Post-WSR Periods
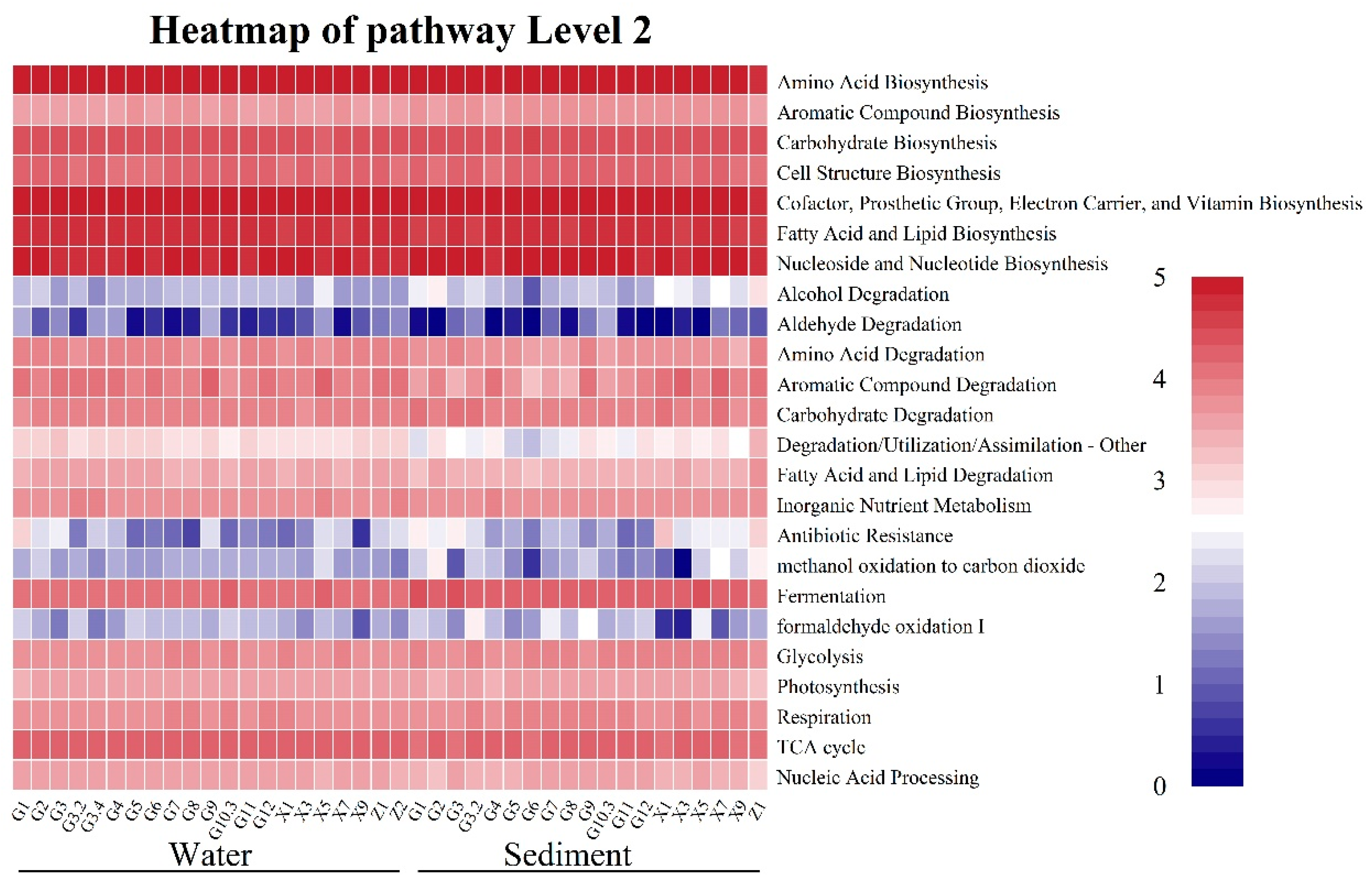
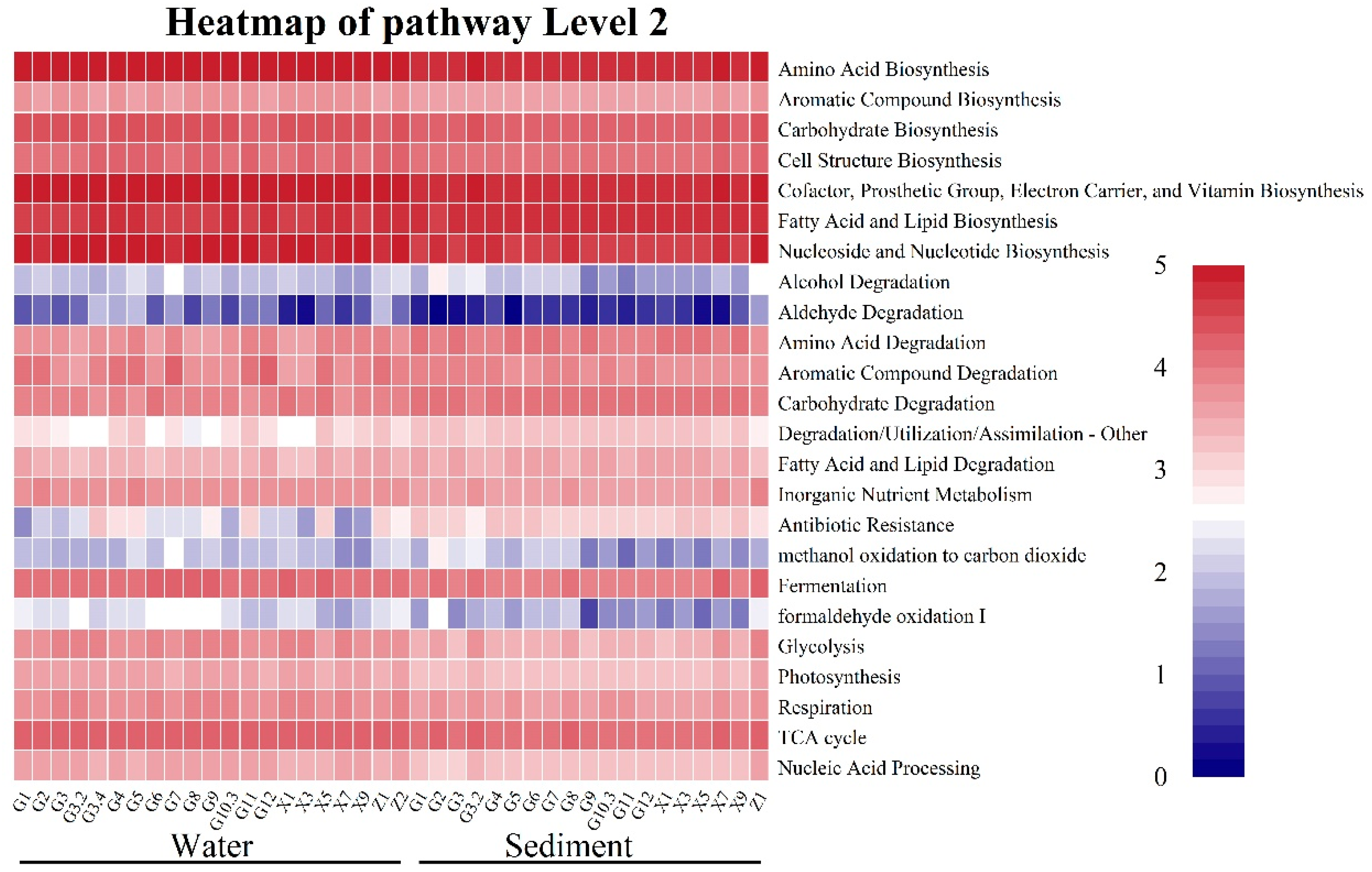
3.5. Functional Prediction of Microbial Functional Groups Under the Effects of WSR
4. Discussion
4.1. Differential Characterisation of Surface Water and Sediment Communities Under Shifting Water and Sediment Changes
4.2. Response Analysis of the Effects of Environmental Factors on Microbial Communities in the Pre- and Post-WSR Periods
4.3. Effect of WSR on the Functional Group Compositions of the Microbial Community
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, K.; Dong, Z.; Guo, L.; Boyer, E.W.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Fan, B. Coupled coordination spatiotemporal analyses inform sustainable development and environmental protection for the Yellow River Basin of China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 151, 110283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Pahl-Wostl, C. The Development of Water Allocation Management in The Yellow River Basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 3395–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, B.; Shen, G. Adjustment in the main-channel geometry of the lower Yellow River before and after the operation of the Xiaolangdi Reservoir from 1986 to 2015. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 74, 2411–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Ma, P.-P.; Kan, Y.-B.; Huang, Q. Ecological risk assessment based on IHA-RVA in the lower Xiaolangdi reservoir under changed hydrological situation. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 100, 012214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Engel, B.A.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z. Hydrological connectivity: One of the driving factors of plant communities in the Yellow River Delta. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmalal, D.; Maya, K.; Padmalal, D.; Maya, K. Rivers-structure and functions. In Sand Mining: Environmental Impacts and Selected Case Studies; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Hu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Ke, M.; Lu, T.; Penuelas, J.; Qian, H. Geographic patterns of microbial traits of river basins in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Liang, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Y. Bacterial community and eutrophic index analysis of the East Lake. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caracciolo, A.B.; Bottoni, P.; Grenni, P. Microcosm studies to evaluate microbial potential to degrade pollutants in soil and water ecosystems. Microchem. J. 2013, 107, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Yan, P.; Li, M.; Wei, G.; Li, H.; Gao, Z. Molecular Fingerprint and Dominant Environmental Factors of Nitrite-Dependent Anaerobic Methane-Oxidizing Bacteria in Sediments from the Yellow River Estuary, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e137996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Ji, F.-Y.; Xu, X.; Xu, X.-Y.; Chen, Q.-K.; Li, Q. Microbial and metabolic characterization of a denitrifying phosphorus-uptake/side stream phosphorus removal system for treating domestic sewage. Biodegradation 2014, 25, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, Z.; Sun, Q.; Ding, Y.; Ding, Z.; Sun, L. The spatial and seasonal variations of bacterial community structure and influencing factors in river sediments. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.M.; Chen, Y.-p.; Xue, L.-g.; Fan, T.T.; Emaneghemi, B. Greater health risk in wet season than in dry season in the Yellow River of the Lanzhou region. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Yang, H.; Peng, C.; Peng, Z.; Lu, L. Shift in the microbial community composition of surface water and sediment along an urban river. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.-Z.; He, L.-Y.; Hu, L.-X.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Zou, H.-Y.; He, L.-X.; Bai, H.; Liu, Y.-S.; Zhao, J.-L.; et al. Anthropogenic activities and seasonal properties jointly drive the assemblage of bacterial communities in subtropical river basins. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, T.L.; Clements, K.; Baas, J.H.; Jago, C.F.; Jones, D.L.; Malham, S.K.; McDonald, J.E. Sediment composition influences spatial variation in the abundance of human pathogen indicator bacteria within an estuarine environment. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, N.; Xia, X.; Zhu, B.; Zheng, S.; Zhuang, J. Bacterial diversity and community structure in the sediment of the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, the largest turbid river in the world. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 71, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Yi, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Q. How the flow and sediment pulse influencing the distribution and functional gene composition of bacterial communities? Case study of the lower Yellow River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Hou, C.; Liu, Q.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yi, Y. Spatial and temporal variations in the plankton community because of water and sediment regulation in the lower reaches of Yellow River. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 120972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, L.F.; Margis, R. The source of the river as a nursery for microbial diversity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Xi, W.; Ye, W.; Yang, H. Bacterial community composition of a shallow hypertrophic freshwater lake in China, revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequences. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 61, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhao, C.; Feng, Y. Influence of plants and environmental variables on the diversity of soil microbial communities in the Yellow River Delta Wetland, China. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Gao, Y.; Annandale, G.W.; Morris, G.L.; Jiang, E.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Carling, P.; Fu, K.; Guo, Q.; et al. Sustainable sediment management in reservoirs and regulated rivers: Experiences from five continents. Earth’s Future 2014, 2, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintern, A.; Webb, J.A.; Ryu, D.; Liu, S.; Bende-Michl, U.; Waters, D.; Leahy, P.; Wilson, P.; Western, A.W. Key factors influencing differences in stream water quality across space. WIREs Water 2017, 5, e1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ding, S.; Lu, X.; Liang, G.; Hong, Z.; Lu, M.; Jing, Y. Water-sediment regulation scheme of the Xiaolangdi Dam influences redistribution and accumulation of heavy metals in sediments in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River. Catena 2022, 210, 105880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zou, X.; Yang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, Z. Biogeography of eukaryotic plankton communities along the upper Yangtze River: The potential impact of cascade dams and reservoirs. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, G.; Wu, G.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Q. Microbial communities and sediment nitrogen cycle in a coastal eutrophic lake with salinity and nutrients shifted by seawater intrusion. Environ. Res 2023, 225, 115590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagova-Mareckova, M.; Boenigk, J.; Bouchez, A.; Cermakova, K.; Chonova, T.; Cordier, T.; Eisendle, U.; Elersek, T.; Fazi, S.; Fleituch, T.; et al. Expanding ecological assessment by integrating microorganisms into routine freshwater biomonitoring. Water Res. 2021, 191, 116767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Saito, Y.; Liu, J.P.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y. Stepwise decreases of the Huanghe (Yellow River) sediment load (1950–2005): Impacts of climate change and human activities. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2007, 57, 331–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Huang, L.; Zhao, H.; Cheng, W.; Chen, Y.; Fazeli, M.; Shang, Q.; Fang, H.; Huang, L.; Zhao, H. Surface Micro-morphology and Adsorption Properties of Sediment Particles. In Mechanics of Bio-Sediment Transport; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yu, K.; Liao, Z.; Yu, X.; Qin, Z.; Liang, J.; Wang, G.; Wu, Q.; Jiang, L. Microbiome community and complexity indicate environmental gradient acclimatisation and potential microbial interaction of endemic coral holobionts in the South China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruprecht, J.E.; Birrer, S.C.; Dafforn, K.A.; Mitrovic, S.M.; Crane, S.L.; Johnston, E.L.; Wemheuer, F.; Navarro, A.; Harrison, A.J.; Turner, I.L.; et al. Wastewater effluents cause microbial community shifts and change trophic status. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Dai, T.; Tang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Huang, B.; Mu, Q.; Wen, D. Sediment bacterial community structures and their predicted functions implied the impacts from natural processes and anthropogenic activities in coastal area. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruaud, P.; Vigneron, A.; Fradette, M.S.; Dorea, C.C.; Culley, A.I.; Rodriguez, M.J.; Charette, S.J. Annual bacterial community cycle in a seasonally ice-covered river reflects environmental and climatic conditions. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, S21–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, J.E.; Binnerup, S.J. Contribution of cytophaga-like bacteria to the potential of turnover of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus by bacteria in the rhizosphere of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Microb. Ecol. 2002, 43, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Lin, C.; Wang, W.; Song, J. Habitat and seasonal variations in bacterial community structure and diversity in sediments of a Shallow lake. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstrom, E.S.; Kamst-Van Agterveld, M.P.; Zwart, G. Distribution of typical freshwater bacterial groups is associated with pH, temperature, and lake water retention time. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8201–8206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.; Yi, Y.; Song, J.; Zhou, Y. Effect of water-sediment regulation operation on sediment grain size and nutrient content in the lower Yellow River. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, H.; Jiang, X.; Yu, Z.; Yao, Q. Impacts of human activities on nutrient transport in the Yellow River: The role of the Water-Sediment Regulation Scheme. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, C.J.; Beman, J.M. Microbial diversity and community structure along a lake elevation gradient in Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1782–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibekwe, A.M.; Ma, J.; Murinda, S.E. Bacterial community composition and structure in an Urban River impacted by different pollutant sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchman, D.; Dittel, A.; Findlay, S.; Fischer, D. Changes in bacterial activity and community structure in response to dissolved organic matter in the Hudson River, New York. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 35, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, C.; Hein, T.; Kavka, G.; Mach, R.L.; Farnleitner, A.H. Longitudinal changes in the bacterial community composition of the Danube River: A whole-river approach. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.; Dong, J.; Yang, A.; Wang, G.; Zhou, X. Spatiotemporal distributions and environmental drivers of diversity and community structure of nosZ-type denitrifiers and anammox bacteria in sediments of the Bohai Sea and North Yellow Sea, China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Marrs, R.; Sekar, R.; Luo, X.; Wu, N. Evaluating ecosystem functioning following river restoration: The role of hydromorphology, bacteria, and macroinvertebrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.S.; Huang, L.; White, J.R.; Wang, J.; DeLaune, R.D.; Ogram, A. Response of microbial populations regulating nutrient biogeochemical cycles to oiling of coastal saltmarshes from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Environ. Pollut 2018, 241, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Environmental Factor | WSR | F | p Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Post | |||||
| Min–Max | Median | Min–Max | Median | |||
| pH | 7.87–8.61 | 8.37 | 8.23–8.60 | 8.42 | 0.016 | 0.899 |
| WT (°C) | 10.5–22.5 | 17.1 | 20.5–25.7 | 23.9 | 20.339 | 0.000 * |
| DO (mg/L) | 7.7–11.1 | 9.5 | 6.9–10.4 | 8.0 | 0.087 | 0.769 |
| Tur (NTU) | 0.5–758.0 | 59.5 | 7.1–688.0 | 140.6 | 0.038 | 0.847 |
| EC (μs/cm) | 578–630 | 602 | 550–656 | 636.5 | 0.088 | 0.768 |
| TSS (g/L) | 0.001–2.649 | 0.166 | 0.002–3.182 | 0.147 | 0.286 | 0.595 |
| TN (mg/L) | 4.63–7.07 | 6.02 | 3.05–8.38 | 4.29 | 0.107 | 0.745 |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.25–9.59 | 1.84 | 0.01–0.80 | 0.08 | 51.128 | 0.000 * |
| NO3− (mg/L) | 3.60–4.53 | 4.01 | 1.11–3.47 | 2.99 | 3.181 | 0.081 |
| NO2− (mg/L) | 0.04–0.08 | 0.06 | 0.007–0.071 | 0.021 | 0.466 | 0.498 |
| NH4+ (mg/L) | 0.01–0.14 | 0.03 | 0.03–1.10 | 0.15 | 19.630 | 0.000 * |
| PO4− (mg/L) | 0.002–0.011 | 0.007 | 0.001–0.032 | 0.012 | 11.631 | 0.001 * |
| CODMn (mg/L) | 3.98–13.62 | 6.04 | 2.67–8.98 | 3.64 | 7.410 | 0.009 * |
| Environmental Factor | WSR | F | p Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Post | |||||
| Min–Max | Median | Min–Max | Median | |||
| pH | 8.57–8.61 | 8.60 | 8.41–8.71 | 8.65 | 4.135 | 0.059 |
| WT (°C) | 16.7–18.5 | 18.0 | 21.5–23.5 | 22.5 | 0.078 | 0.784 |
| DO (mg/L) | 10–11.1 | 10.7 | 7.8–10.3 | 8.3 | 3.947 | 0.064 |
| Tur (NTU) | 0.1–1.5 | 0.4 | 5.8–16.1 | 7.7 | 7.451 | 0.015 * |
| EC (μs/cm) | 589–631 | 607 | 596–650 | 622 | 0.655 | 0.430 |
| TSS (g/L) | 0.001–0.116 | 0.002 | 0.001–0.009 | 0.001 | 4.161 | 0.058 |
| TN (mg/L) | 4.67–5.73 | 4.97 | 2.90–3.88 | 3.31 | 0.573 | 0.460 |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.35–0.74 | 0.45 | 0.03–0.13 | 0.06 | 14.901 | 0.001 ** |
| NO3− (mg/L) | 3.30–4.36 | 3.66 | 2.65–3.23 | 3.06 | 1.394 | 0.255 |
| NO2− (mg/L) | 0.036–0.042 | 0.040 | 0.011–0.288 | 0.020 | 7.125 | 0.017 * |
| NH4+ (mg/L) | 0.03–0.16 | 0.06 | 0.06–0.83 | 0.19 | 31.832 | 0.000 ** |
| PO4− (mg/L) | 0.002–0.007 | 0.002 | 0.010–0.021 | 0.012 | 0.528 | 0.478 |
| CODMn (mg/L) | 4.17–6.51 | 5.38 | 3.11–4.09 | 3.45 | 4.084 | 0.060 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Hong, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xie, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, H.; Fan, Z. Response Analysis of Microbial Community Structures and Functions Under Water and Sediment Changes in the Middle and Lower Yellow River. Diversity 2025, 17, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17010041
Wu J, Hong Q, Zhang J, Xie C, Liu Y, Li D, Liu H, Fan Z. Response Analysis of Microbial Community Structures and Functions Under Water and Sediment Changes in the Middle and Lower Yellow River. Diversity. 2025; 17(1):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17010041
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Ji, Quan Hong, Jin Zhang, Chen Xie, Yang Liu, Dandan Li, Hao Liu, and Ziwu Fan. 2025. "Response Analysis of Microbial Community Structures and Functions Under Water and Sediment Changes in the Middle and Lower Yellow River" Diversity 17, no. 1: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17010041
APA StyleWu, J., Hong, Q., Zhang, J., Xie, C., Liu, Y., Li, D., Liu, H., & Fan, Z. (2025). Response Analysis of Microbial Community Structures and Functions Under Water and Sediment Changes in the Middle and Lower Yellow River. Diversity, 17(1), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17010041







